Abstract
Since their first documentation in 1952, plaque reduction neutralization tests (PRNTs) have become the choice of test for the measurement of neutralizing antibodies against a particular virus. However, PRNTs can be performed only against viruses that cause cytopathic effects (CPE). PRNTs also require skilled personnel and can be time-consuming depending on the time required for the virus to cause CPE. Hence, their application limits large-scale studies or epidemiological and laboratory investigations. Since 1978, many surrogate PRNTs or immunocolorimetric assay (ICA)-based focus reduction neutralization tests (FRNT) have been developed. In this article, ICAs and their utility in FRNTs for the characterization of neutralizing antibodies, homologous or heterologous cross-neutralization, and laboratory diagnosis of viruses of public health importance have been discussed. Additionally, possible advancements and automations have been described that may help in the development and validation of novel surrogate tests for emerging viruses.
1. Developments in Detection of Viral Plaques
Renato Dulbecco was the first to demonstrate the presence of ‘virus plaques’ on a monolayer of chicken embryo fibroblasts, specifically for Western Equine Encephalomyelitis and Newcastle Disease viruses [1]. These findings were followed by reports of plaque formation and isolation of pure lines for polioviruses [2]. Subsequently, newer developments were reported for plaque detection and its successful application in plaque reduction neutralization tests (PRNTs) [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Tomori et al. described a plaque assay and PRNT for the highly infectious and fatal Lassa virus and its utility in passive immunization for the treatment of Lassa fever [12]. For many decades, PRNTs have been considered ‘a gold standard test’ for the characterization of functional neutralizing antibodies (Nt-Abs) to specific viral agents [13]. Neutralization tests (NTs) utilize live viruses to assess virus-serum interactions, indirectly measuring the level of Nt-Abs [10]. NTs are mainly established for viruses that produce distinct cell cytopathic effects (CPE), for partially grown viruses in different cell lines, and for a few viruses that do not show any evident CPE. In the PRNT, the cell monolayer is stained with various stains, i.e., crystal violet, neutral red, methylene blue, amido black, and naphthalene black, and the clear zone (plaque) formed due to cell CPE is counted, recorded, and the Nt-Abs titers are deduced using a statistical formula [10]. Ultimately, the quantity of live-challenge virus neutralized by the diluted serum (Nt-Abs) is measured. Two types of PRNTs have been described, wherein the first method test serum dilutions are varied and challenged with a fixed amount of virus, and in the second method, a test serum dilution is fixed, and the amount of challenge virus is varied.
For the first time, Okuno’s group has described peroxidase-anti-peroxidase (PAP) staining-based NTs, and afterwards, immunostaining-based methods on various cell substrates have been standardized for other viruses of public health importance [14,15,16,17,18]. A human epithelial cell (Hep-2C)-based sensitive, specific, and rapid method was described for detection and identification of polioviruses in a large number of clinical specimens [19]. The majority of immunostaining-based methods [Table 1] require a specific cell fixative (formaldehyde, paraformaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, methanol, methanol-acetone, ethanol, acetone, etc.), a cell permeabilization reagent (Triton-X 100, NP-40 solution, Ethanol, Methanol, etc.), a blocking buffer (containing bovine serum albumin, skimmed milk powder, fetal bovine serum, Tween-80, etc.), a primary antibody (monoclonal or polyclonal), an alkaline phosphatase or peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody, and a particular substrate (3,3′, 5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine, Nitro blue Tetrazolium plus X Gal, 3,3′-Diaminobenzedene tetrachloride, 3-amino 9-ethylcarbazole, etc.) for the immuno-precipitation of viral foci. All of the published immuno-staining-based assays described in Table 1 were based on various cell substrates (i.e., epithelial, endothelial, fibroblast, and neuroblastoma), These assays also required various incubation periods for virus-serum interactions, primary or secondary antibody binding, and the assay completion time may vary between 12 h to 13 days after infection, depending on the appearance of visible and countable virus foci. Afterwards, for the detection of viruses directly from the clinical samples or cell culture fluids (virus isolates), many investigators utilized immunocolorimetric assay (ICA)-based methods. Detection of virus-infected cells and their quantifications were documented for the wild-type polioviruses and rubella viruses using cell passaged soup and clinical specimens [19,20]. These studies describe the utility of ICAs for their respective surveillance programs and pre- and post-vaccination studies. Subsequently, ICA has been employed for the detection of measles, mumps, and rubella viruses in the clinical specimens collected from suspected cases and cell culture-grown viral isolates [21,22].

Table 1.
Published immuno-staining-based neutralization tests for various viruses important for public health.
2. Plaque- and Focus-Based Neutralization Tests
A PRNT measures the level of virus-specific Nt-Abs in a serum or plasma sample by determining the ability of various dilutions to block the production of viral plaques on cell monolayers by a known amount of live virus [7]. A PRNT is a more sensitive quantitative assay than other serological methods, and is preferred for the accurate measurement of immune responses during vaccine trials or epidemiological studies. PRNTs have proven to be a useful tool for detecting low levels of Nt-Abs due to their high sensitivity over HI and ELISA-based serological assays that may fail to detect weak antibody responses in infants or younger children due to their immunological immaturity [10]. Despite their superior sensitivity, PRNTs have some disadvantages. They are time-consuming to perform and have incubation periods of 5–7 days or more. Therefore, testing large numbers of sera samples is labor-intensive and requires skilled operators. Like any biological assay, a PRNT is inherently variable and cumbersome to standardize, and it can be operator-dependent [10,21]. Both focus- and plaque-based methods work on the same principle and differ only in the surface area of the tissue culture plates used, the volumes of reagents added, and in the final staining and visualization steps (Figure 1). A Focus Reduction Neutralization Test (FRNT) is performed in a 96-well format; therefore, it enables the use of multichannel pipettes for dispensing cells, preparing serum dilutions, and transferring reaction mixes in micro-titer plates. This method results in greater inter- and intra-assay reproducibility than in a PRNT. The micro-titer well format allows a greater number of samples to be tested within a plate in a FRNT compared to a PRNT. FRNTs also consume less sample volume, reagents, and take up less space in CO2 incubators, reducing the overall assay cost and saving time with an increased output. The precipitation of viral foci on cell substrates by primary and secondary antibodies used in FRNTs results in a faster NT than plaque staining using crystal violet or other stains. Though both FRNTs and PRNTs showed similar sensitivity with inter-assay variation (Nt-Ab titers) of two- and three-fold, respectively, FRNTs offer the advantage of speed, reduced sample volume, and the possibility of automation using 96-well plates [21,22]. Other studies have also indicated good correlations between PRNT- and FRNT-derived Nt-Ab titers for Japanese encephalitis viruses (JEV) [29]. Thus, FRNTs offer an added advantage for studying JEV vaccine efficacy and subsequently for other Vaccine Preventable Diseases (VPDs).
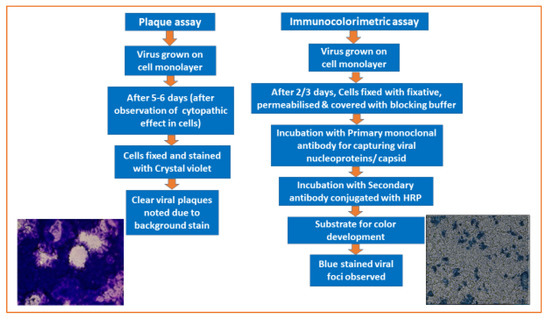
Figure 1.
Detection of the mumps virus grown on Vero cell substrates using a plaque assay (after 5 days) and an immunocolorimetric assay (after 2 days).
3. Measurement of Neutralizing Antibodies to Public Health-Important Viruses
Generally, for the characterization of the qualitative and quantitative immune responses against wild-type and vaccine strains, in-vitro NTs are the preferred methods. For various viruses, viral plaque or focus reduction-based NTs have been standardized, validated with established virus-specific IgG Enzyme Immuno-Assays (EIAs), and employed to measure the Nt-Abs response. NTs have been utilized for confirmation of recent or past infections (with known or unknown etiology). In addition, modified NTs based on the principle of fluorescence detection and pseudo-viruses or recombinant-viruses have also been explored. The level of Nt-Ab titers that protect against the acquisition of viral infection and development of clinical disease have been documented using a sensitive PRNT for mumps and measles viruses [6,65]. Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, laboratories in the USA have initiated collaborative networks to develop, validate, and improve serological methods and related technologies, and to share these advances with different institutions. Such comparative studies have demonstrated variability the in results of live-virus neutralization, pseudo-virus neutralization, and surrogate NTs. Hence, the characterization, comparison, and harmonization of serological assays and their performance is crucial in virology laboratories [66].
There are methods in place to characterize functional Nt-Ab responses to the Poliovirus and Yellow fever virus, for which well-tested and proven vaccines are available [2,11,19,49,67]. Different types of NTs based on either viral plaque or focus staining procedures have been developed for the VPDs, i.e., Measles virus (MeV), Mumps virus (MuV), Rubella (RuV) and Varicella Zoster virus [7,10,13,16,21,22,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,55,56,65,68]. Similarly, many improved versions of NTs have been described for JEV, especially for vaccine and wild-type strains [14,15,27,28,29]. The applications of various NTs have been documented for Rotaviruses that can be easily prevented by immunization [69,70]. Interestingly, rapid and reliable NTs are crucial to understanding the homologous and heterologous immune response in the vaccine recipients and are crucial to understanding the vaccine’s effectiveness and any antibody decay. In developed countries, vaccines for influenza viruses are available through routine immunizations; hence, rapid FRNTs and their usefulness for nasal wash specimens are crucial [18]. An automated FRNT was described for the characterization of immune responses to influenza viruses amongst immunized subjects [46]. For the Respiratory Syncytial virus (RSV) and the Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus (CCHFV), ICA-based NT and pseudo-PRNT has been standardized [23,62]. Interestingly, vaccines are under development for RSV, and limited use vaccines are available for CCHFV. Likewise, NTs have been developed for the measurement of immune responses to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Corona virus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants [33,35,66].
Similarly, various types of NTs, i.e., FRNTs, micro-NTs, fluorescent-FRNTs, immunostaining based PRNTs, PAP-NTs, and automated versions of FRNTs, have been established by various investigators for Hantavirus, Bourbon virus, West Nile Virus (WNV), Zika virus (ZIKV), Dengue virus (DENV), and Chikungunya virus (CHIKV), either for vaccine developments, epidemiological investigations, sero-prevalence studies, or laboratory diagnoses [8,14,17,25,26,27,30,31,32,48,51,52,53,54,63,71,72]. These viruses cause infections in the form of sporadic cases, outbreaks, or epidemics which lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Likewise, improved NTs have been described for other viruses of public health importance, i.e., Metapneumovirus, Cytomegalovirus, Adenovirus type 7, Coxsackievirus B3, BK virus, and Hepatitis C virus [24,57,58,59,64,73]. In addition, the application of NTs for Infectious anemia and Herpesvirus type-1 animal viruses has been described [60,61], indicating their utility for a one-health program. Recently, many countries are working on a ‘one health approach’ to study various infectious/zoonotic diseases.
4. Sero-Epidemiological Investigations, Vaccine Trials, and Cross-Neutralization Studies
Previously, many sero-epidemiological investigations of viruses of public health importance, i.e., DENV, CCHFV, Rift Valley fever virus, WNV, Usutu virus, CHIKV, Bourbon virus, Hantavirus, ZIKV, and SARS-CoV-2, have been carried out to confirm the presence of virus-specific IgM and IgG antibodies, and subsequently, case confirmation using gold standard PRNTs or by virus isolation [74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84]. Due to cross-reactivity amongst the arboviruses, cell culture-based NTs are the preferred serological tool for case confirmation. PRNT is a widely utilized serological reference test for assessing the performance of newly developed IgM and IgG ELISAs [83], MMRV multiplexed immunoassays [85], SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow immunoassays [86], and for assessing Rotavirus vaccine performance [87,88,89]. PRNT has also been widely used for antigenic characterization and cross-neutralization studies of poliovirus serotypes [11], Coxsackie B strains [90] and hantavirus serotypes [91]. Despite the accessibility of commercial ELISAs, the NTs are being utilized in sero-epidemiological investigations for different viruses.
The comparative dengue seroprevalence in children (n = 2996) from Philippines was studied using IgG ELISAs and FRNTs. Although high sensitivity and specificity (>90%) were documented for ELISAs, their false-negative and false-positive results limit their use for pre-vaccination screening [26]. This could be due to the type of antigen (i.e., whole/disrupted virus particles, purified target protein, or recombinant protein) utilized in the coated ELISA plates. The prevalence of CHIKV infection in suspected dengue patients was studied amongst six countries using FRNT, and the results were compared with IgM and IgG ELISAs [32]. For the confirmation of acute hantavirus infection in suspected leptospirosis cases from the Netherlands, use of FRNTs was documented successfully [54]. A subset of serum samples (n = 53) referred for MeV diagnosis were tested using FRNTs, of which 47.1% of cases showed a correlation with measles IgM antibody detection [40]. Similarly, the utility of FRNTs was studied for the laboratory diagnosis of MuV in parotitis patients (n = 80), where 58.8% of serum samples showed positivity in all three tests, i.e., IgM ELISA, IgG ELISA and FRNT [42]. Such studies would help to understand the appearance of different classes of antibodies in the symptomatic and asymptomatic cases coupled with rapid and sensitive molecular methods. The WNV-specific Nt-Abs were detected by fluorescent-FRNT in 21 of 145 wild bird serum samples, indicating WNV prevalence in the Eastern region of Russia [30]. Such studies are crucial to monitor the virus transmission pathways within and between different countries due to migratory birds.
Recently, a study investigated vaccine-induced antibody responses in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia, against live SARS-CoV-2 (WA1/2020), B.1.167.2 (Delta), and B.1.1.529 (Omicron) strains [34]. Interestingly, FRNT titers were found to be comparatively lower in the patients than in immunized healthy individuals. A FRNT-based cross-neutralization study indicated that the hybrid immunity developed by vaccination (Pfizer’s BNT162b2 or Johnson & Johnson’s Ad26.CoV2.S) and Omicron BA.1 infection offers protection against Delta and other variants of SARS-CoV-2, whereas immunity developed due to infection with Omicron BA.1 alone offers limited cross-protection [36]. A significant reduction in the FRNT titers of both vaccine-induced and vaccine-plus-infection was observed for the Omicron variant [35]. In the context of SARS-CoV-2 infections or reinfections due to different strains, such surrogate NTs play an important role in understanding the decay of vaccine-induced immunity (after one dose, two doses, or booster doses with different types of vaccines) to measure the functional Nt-Abs.
A study from Iran measured homologous and heterologous Nt-Abs to MeV A, B3, D4, and H1 genotypes among measles-immunized children, indicating sufficient levels of Nt-Abs titers against the circulating genotypes [68]. Such studies play a useful role in the context of the global measles elimination goal (and goals for elimination of other diseases) to determine the waning of vaccine-induced immunity (if any), or to determine antigenic differences between vaccine and circulating wild-type viruses. Applications of FRNTs for MeV, MuV, and RuV cross-neutralization studies between wild types and vaccine strains were studied in India, which are ultimately crucial for understanding qualitative and quantitative immune responses to VPDs [41,43,44]. A report from the Netherlands detected cross-Nt-Abs in measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine recipients by utilizing MuV genotypes A, D, and G-based FRNTs [39]. Gouma et al. showed significantly lower FRNT titers to MuV genotype A (Jeryl Lynn strain) in pre-outbreak serum samples (n = 50) obtained from symptomatic, asymptomatic, and non-infected subjects, suggesting the possibility of a strain-specific neutralization pattern. Similarly, cross-neutralization studies using MuV genotypes A, F, H, and I challenge viruses have been carried out from Korea, which revealed that post-vaccination FRNT titers in the vaccine recipients (MMR one dose) were significantly lower against wild types compared to vaccine strains [38]. Such studies are crucial because the majority of the countries (where mumps-containing vaccines are available through their national immunization programs) are experiencing outbreaks due to MuV genotype G viruses, and current vaccines (the majority) are based on the genotype A strains. This also applies to the other viruses of public health importance for which vaccines are available.
5. Recent Developments and Automations
Recently, various types of liquid handling systems have become available in the market that can be utilized for NTs. In addition, viral plaques or foci stained with various dyes or fluorescent reagents can be captured using high-resolution digital cameras, and results can be recorded using advanced instrumentation systems. In-built statistical formulas in the software can be used to obtain Nt-Ab titers, enabling results to be recorded in a digital format. An automated colorimetric micro-NT was developed for WNV which utilizes the principle of neutral red dye retention and records results on a spectrophotometer using advanced software [71]. An improved and rapid version of the NT was standardized for RSV using an automated plaque counting system, which showed a high correlation (R2 = 0.95) between manual and automated methods with Nt-Ab titer differences within two-fold [23]. A similar semi-automated ICA-based NT has been described for equine infectious anemia virus [60]. A rapid and efficient NT based on ELISA was standardized for Coxsackievirus B3 that showed good correlation (R2 = 0.94) with the CPE-based NT [24]. Similarly, blue-stained viral foci of herpes simplex virus type-1 on Human U-2 OS cells were captured using an automated analyzer that eventually resulted in a reduced assay time [50]. A study by Lin et al., demonstrated the utility of an improved micro-NT using a flatbed scanner and a well-plate reader software for measurement of Nt-Ab response against Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09, A(H3N2), and B viruses [47]. A replication-competent luciferase-secreting DENV reporter was generated by Saipin et al., and afterwards an NT was standardized and compared with FRNT on a panel of serum samples that revealed a good agreement [92]. Recently, the Viridot program showed the process for standardization of manual and Viridot plaque counting methods, and its performance was evaluated on a variety of plaque images which revealed comparable Nt-Ab titer outputs [72]. Recently, two advanced methods for evaluating the neutralization capacity of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies were described, of which one was based on immunostaining of infected cells with chromogen (FRNT), and the other was based on an infectious clone-derived SARS-CoV-2 virus expressing a fluorescent reporter (mNeonGreen based FRNT) [33]. Both protocols are useful in a high-throughput setting and large-scale vaccine studies or clinical testing. Thus, the advancements and automation of FRNTs are possible and useful for public health virology. Furthermore, the cost of FRNTs can be reduced through automation, ultimately improving the quality/quantity of scientific data.
6. Important Unresolved Issues and Way Forward
A large number of commercial companies are producing monoclonal antibodies against various viruses using different approaches; thus, the cost of such antibodies may be lowered, and ultimately, the assay expenses could be reduced. In addition, the use of secondary IgG antibodies may be excluded by conjugating virus-specific monoclonal antibodies directly with different peroxidases or other enzymes, which will ultimately help in reducing the assay time. Moreover, there is a great need for the development of ‘universal’ cell-fixative and permeabilization reagents, blocking buffer solutions, and very specific primary/secondary antibodies that can efficiently bind to target virus surface proteins. However, optimization of various steps (i.e., virus-serum incubation, cell-fixation, cell-permeabilization, blocking of cell monolayer, application of various antibodies/concentrations, and use of a particular substrate for visualization) is critical during standardization of immuno-staining protocols and ICA-based NTs. Studies on bovine herpesvirus 1, indicated virus-serum incubation (i.e., incubation period) as crucial step for accurate measurement of antibody levels [93,94]. Thus, optimization of all the steps in NTs is essential before they are included in particular studies. Large-scale sero-epidemiological studies based on gold standard NTs can be performed by utilizing automation (automated liquid handling system, plate washers, and image analyzers). Additionally, mobile BSL-2/3 laboratories with basic cell culture facilities can be equipped in countries where the population resides in difficult terrains. Such an integrated approach may be explored under the ‘One Health program’ so that various infectious diseases can be studied, and effective control measures can be implemented [95]. For the differential diagnosis of various viral infections with inconclusive clinical presentations, and for large-scale sero-epidemiological/vaccine studies, ICA-based rapid and reliable NTs can be explored.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the Director of the ICMR-National Institute of Virology, Pune (India) for providing intramural support to undertake work on the immunocolorimetric assay (ICA) and the ICA-based focus reduction neutralization tests for various public health important viruses since year 2012. The author would also like to thank Neelakshi S. Kumbhar for laboratory support and K. Alagarasu, (Scientist-E, ICMR-NIV Pune) for English language editing.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Dulbecco, R. Production of Plaques in Monolayer Tissue Cultures by Single Particles of an Animal Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1952, 38, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulbecco, R.; Vogt, M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J. Exp. Med. 1954, 99, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchin, J.E. Use of methyl cellulose gel as a substitute for agar in tissue-culture overlays. Nature 1955, 175, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, I.T.; Schlesinger, R.W. Plaque assay of dengue and other group B arthropod-borne viruses under methyl cellulose overlay media. Virology 1963, 19, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, F. Variants of herpes simplex virus: Isolation, characterization, and factors influencing plaque formation. J. Bacteriol. 1963, 86, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, F.A. Immunity to mumps in an institutional epidemic. Correlation of insusceptibility to mumps with serum plaque neutralizing and hemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies. J. Infect. Dis. 1969, 119, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, P.; Herrmann, K.; Burns, G.R. Role of virus strain in conventional and enhanced measles plaque neutralization test. J. Virol. Methods 1981, 3, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Halstead, S.B.; Repik, P.M.; Putvatana, R.; Raybourne, N. Simplified plaque reduction neutralization assay for dengue viruses by semimicro methods in BHK-21 cells: Comparison of the BHK suspension test with standard plaque reduction neutralization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 22, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosovich, M.; Matrosovich, T.; Garten, W.; Klenk, H.D. New low-viscosity overlay medium for viral plaque assays. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.J.; Audet, S.; Andrews, N.; Beeler, J.; WHO working group on measles plaque reduction neutralization test. Plaque reduction neutralization test for measles antibodies: Description of a standardised laboratory method for use in immunogenicity studies of aerosol vaccination. Vaccine 2007, 26, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, W.C.; Oberste, M.S.; Pallansch, M.A. Standardized Methods for Detection of Poliovirus Antibodies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1387, 145–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomori, O.; Johnson, K.M.; Kiley, M.P.; Elliott, L.H. Standardization of a plaque assay for Lassa virus. J. Med. Virol. 1987, 22, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauldin, J.; Carbone, K.; Hsu, H.; Yolken, R.; Rubin, S. Mumps virus-specific antibody titers from pre-vaccine era sera: Comparison of the plaque reduction neutralization assay and enzyme immunoassays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4847–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Igarashi, A.; Fukai, K. Neutralization tests for dengue and Japanese encephalitis viruses by the focus reduction method using peroxidase-anti-peroxidase staining. Biken J. 1978, 21, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Okuno, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Tadano, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Takagi, M. Rapid focus reduction neutralization test of Japanese encephalitis virus in microtiter system. Brief report. Arch. Virol. 1985, 86, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Yamanishi, K.; Lwin, S.; Takahashi, M. Micro-neutralization test for mumps virus using the 96-well tissue culture plate and PAP (peroxidase-antiperoxidase) staining technique. Microbiol. Immunol. 1985, 29, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raharjo, E.; Tadano, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Okuno, Y. Development of a micro-neutralization test for chikungunya virus. Biken J. 1986, 29, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Okuno, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Baba, K.; Maeda, A.; Kunita, N.; Ueda, S. Rapid focus reduction neutralization test of influenza A and B viruses in microtiter system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, D.; Megson, B.; Strang, M.; Appleton, H. A microtitre plate method for isolation and typing of poliovirus using a blue-cell ELISA. J. Virol. Methods 2000, 90, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Favors, S.; Xu, W.B.; Featherstone, D.A.; Icenogle, J.P. An indirect immunocolorimetric assay to detect rubella virus infected cells. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 146, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Brown, D.W.; Jin, L.; Samuel, D.; Andrews, N.; Brown, K.E. Development of a focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT) for detection of mumps virus neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Kumbhar, N.S.; Bhide, V.S. Detection of measles, mumps and rubella viruses by immuno-colorimetric assay and its application in focus reduction neutralization tests. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinska, E.; Liu, D.; Wu, H.Y.; Quiroz, J.; Rappaport, R.; Yang, D.P. Development of an improved microneutralization assay for respiratory syncytial virus by automated plaque counting using imaging analysis. Virol. J. 2005, 2, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; He, D.; Tang, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay to measure serum-neutralizing antibodies against coxsackievirus B3. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, M.C.; Bogardus, L.; Giacone, D.G.; Rubinstein, L.J.; Antonello, J.M.; Sun, D.; Daijogo, S.; Gurney, K.B. Virus Reduction Neutralization Test: A Single-Cell Imaging High-Throughput Virus Neutralization Assay for Dengue. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.L.; Adams, C.; Ylade, M.; Jadi, R.; Daag, J.V.; Molloy, C.T.; Agrupis, K.A.; Kim, D.R.; Silva, M.W.; Yoon, I.K.; et al. Determining dengue virus serostatus by indirect IgG ELISA compared with focus reduction neutralization test in children in Cebu, Philippines: A prospective population-based study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e44–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirakanjanakit, N.; Sanohsomneing, T.; Yoksan, S.; Bhamarapravati, N. The micro-focus reduction neutralization test for determining dengue and Japanese encephalitis neutralizing antibodies in volunteers vaccinated against dengue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 91, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Hirokawa, C.; Kon, M.; Tamura, T.; Nishikawa, M. Estimation of focus reduction neutralization test for measurement of neutralizing antibody titer against Japanese encephalitis virus. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, A.R.; Hwang, Y.H.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, G.T.; Yoo, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Comparison of plaque reduction and focus reduction neutralization tests for the measurement of neutralizing antibody titers against japanese encephalitis virus. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 306, 114540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, R.; Hashiguchi, K.; Yoshii, K.; Kariwa, H.; Nakajima, K.; Ivanov, L.I.; Leonova, G.N.; Takashima, I. Seroprevalence of West Nile virus in wild birds in far eastern Russia using a focus reduction neutralization test. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, B.M.; Beasley, D.W. ELISA and Neutralization Methods to Measure Anti-West Nile Virus Antibody Responses. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1435, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwe Tun, M.M.; Inoue, S.; Thant, K.Z.; Talemaitoga, N.; Aryati, A.; Dimaano, E.M.; Matias, R.R.; Buerano, C.C.; Natividad, F.F.; Abeyewickreme, W.; et al. Retrospective seroepidemiological study of chikungunya infection in South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Pacific region. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 2268–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderheiden, A.; Edara, V.V.; Floyd, K.; Kauffman, R.C.; Mantus, G.; Anderson, E.; Rouphael, N.; Edupuganti, S.; Shi, P.Y.; Menachery, V.D.; et al. Development of a Rapid Focus Reduction Neutralization Test Assay for Measuring SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2020, 131, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Akhtar, A.; Linderman, S.L.; Lai, L.; Orellana-Noia, V.M.; Valanparambil, R.; Ahmed, H.; Zarnitsyna, V.I.; McCook-Veal, A.A.; Switchenko, J.M.; et al. Humoral Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern After mRNA Vaccines in Patients With Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3020–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medigeshi, G.R.; Batra, G.; Murugesan, D.R.; Thiruvengadam, R.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Das, B.; Gosain, M.; Ayushi Singh, J.; Anbalagan, A.; Shaman, H.; et al. Sub-optimal neutralisation of omicron (B.1.1.529) variant by antibodies induced by vaccine alone or SARS-CoV-2 Infection plus vaccine (hybrid immunity) post 6-months. EBioMedicine 2022, 78, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Karim, F.; Cele, S.; Reedoy, K.; San, J.E.; Lustig, G.; Tegally, H.; Rosenberg, Y.; Bernstein, M.; Jule, Z.; et al. Omicron infection enhances Delta antibody immunity in vaccinated persons. Nature 2022, 607, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassert, M.; Geerling, E.; Stone, E.T.; Steffen, T.L.; Feldman, M.S.; Dickson, A.L.; Class, J.; Richner, J.M.; Brien, J.D.; Pinto, A.K. mRNA induced expression of human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in mice for the study of the adaptive immune response to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, J.S.; Chung, G.T.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, J.W. Cross-neutralization between vaccine and circulating wild-type mumps viruses in Korea. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouma, S.; Ten Hulscher, H.I.; Schurink-van ‘t Klooster, T.M.; de Melker, H.E.; Boland, G.J.; Kaaijk, P.; van Els, C.A.C.M.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; van Binnendijk, R.S. Mumps-specific cross-neutralization by MMR vaccine-induced antibodies predicts protection against mumps virus infection. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4166–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Kamble, M.B.; Chowdhury, D.T.; Kumbhar, N.S. Measles & rubella outbreaks in Maharashtra State, India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 143, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Dvivedi, G.M.; Jadhav, S.M. Cross-neutralization between three mumps viruses & mapping of haemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) epitopes. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 143, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Hamde, V.S.; Kumbhar, N.S.; Walimbe, A.M. Utility of neutralization test for laboratory diagnosis of suspected mumps. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Kasibhatla, S.M.; Kamble, M.B.; Munivenkatappa, A.; Kumbhar, N.S.; Jayaswamy, M.M.; Ramtirthkar, M.R.; Kale, M.M.; Kulkarni-Kale, U. Genetic and antigenic characterization of wild type rubella viruses isolated from India. Vaccine 2021, 39, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Kumbhar, N.S.; Kamble, S.S.; Walimbe, A.M.; Ashok, M. Usefulness of diverse serological tests in the laboratory diagnosis of fever with skin-rash cases in children. J. Clin. Virol. Plus 2022, 2, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terletskaia-Ladwig, E.; Enders, G.; Meier, S.; Dietz, K.; Enders, M. Development and evaluation of an automatable focus reduction neutralisation test for the detection of measles virus antibodies using imaging analysis. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 178, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terletskaia-Ladwig, E.; Meier, S.; Enders, M. Improved high-throughput virus neutralisation assay for antibody estimation against pandemic and seasonal influenza strains from 2009 to 2011. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 189, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Gu, Y.; McCauley, J.W. Optimization of a Quantitative Micro-neutralization Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 118, 54897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Hirsch, A.J. Analysis of Serum Anti-Zika Virus Antibodies by Focus Reduction Neutralization Test. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2142, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheck, M.K.; Lehmann, L.; Zaucha, M.; Schwarzlmueller, P.; Huber, K.; Pritsch, M.; Barba-Spaeth, G.; Thorn-Seshold, O.; Krug, A.B.; Endres, S.; et al. FluoRNT: A robust, efficient assay for the detection of neutralising antibodies against yellow fever virus 17D. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xiong, D.; Li, H.H.; Qiu, S.P.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, Q.; Huang, C.H.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N.S. Development of an HSV-1 neutralization test with a glycoprotein D specific antibody for measurement of neutralizing antibody titer in human sera. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundkvist, A.; Hukic, M.; Hörling, J.; Gilljam, M.; Nichol, S.; Niklasson, B. Puumala and Dobrava viruses cause hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Bosnia-Herzegovina: Evidence of highly cross-neutralizing antibody responses in early patient sera. J. Med. Virol. 1997, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundkvist, A.; Vapalahti, O.; Henttonen, H.; Vaheri, A.; Plyusnin, A. Hantavirus infections among mammalogists studied by focus reduction neutralisation test. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 19, 802–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundkvist, A.; Lindegren, G.; Brus Sjölander, K.; Mavtchoutko, V.; Vene, S.; Plyusnin, A.; Kalnina, V. Hantavirus infections in Latvia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 21, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeijenbier, M.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Reimerink, J.; Verner-Carlsson, J.; Wagenaar, J.F.; Goris, M.G.; Martina, B.E.; Lundkvist, Å.; Koopmans, M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; et al. The hanta hunting study: Underdiagnosis of Puumala hantavirus infections in symptomatic non-travelling leptospirosis-suspected patients in the Netherlands, in 2010 and April to November 2011. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 20878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerna, G.; Chambers, R.W. Varicella-zoster plaque assay and plaque reduction neutralization test by the immunoperoxidase technique. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1976, 4, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Ye, J.; Wen, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, T.; Xia, N. Development of a varicella-zoster virus neutralization assay using a glycoprotein K antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 200, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, C.; Duverlie, G.; François, C.; Schnuriger, A.; Dedeurwaerder, S.; Brochot, E.; Capron, D.; Wychowski, C.; Thibault, V.; Castelain, S. A focus reduction neutralization assay for hepatitis C virus neutralizing antibodies. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaegstad, T.; Traavik, T.; Christie, K.E.; Joergensen, J. Neutralization test for BK virus: Plaque reduction detected by immunoperoxidase staining. J. Med. Virol. 1986, 19, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.R.; Formica, M.A.; Walsh, E.E. Microneutralization assay for the measurement of neutralizing antibodies to human metapneumovirus. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigo, J.K.; Ezzelarab, C.; Montelaro, R.C. Development of a high throughput, semi-automated, infectious center cell-based ELISA for equine infectious anemia virus. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 185, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannai, H.; Nemoto, M.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T.; Matsumura, T. Development of a focus-reduction neutralizing test for detecting equine herpesvirus type-1-neutralizing antibodies. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakoglu, N.; Berber, E.; Ertek, M.; Yoruk, M.D.; Tonbak, S.; Bolat, Y.; Aktas, M.; Kalkan, A.; Ozdarendeli, A. Pseudo-plaque reduction neutralization test (PPRNT) for the measurement of neutralizing antibodies to Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamunuarachchi, G.; Harastani, H.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Dai, Y.N.; Ellebedy, A.; Fremont, D.; Whelan, S.P.J.; Wang, D.; Boon, A.C.M. Detection of Bourbon Virus-Specific Serum Neutralizing Antibodies in Human Serum in Missouri, USA. mSphere 2022, 7, e0016422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abai, A.M.; Smith, L.R.; Wloch, M.K. Novel microneutralization assay for HCMV using automated data collection and analysis. J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 322, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.T.; Markowitz, L.E.; Albrecht, P.; Stewart, J.A.; Mofenson, L.M.; Preblud, S.R.; Orenstein, W.A. Measles antibody: Reevaluation of protective titers. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 162, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, A.B.; Brien, J.D.; Christen, J.M.; Dhakal, S.; Kemp, T.J.; Klein, S.L.; Pinto, L.A.; Premkumar, L.; Roback, J.D.; Binder, R.A.; et al. The Serological Sciences Network (SeroNet) for COVID-19: Depth and Breadth of Serology Assays and Plans for Assay Harmonization. mSphere 2022, 7, e0019322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.; Camacho, L.A.; Yamamura, A.M.; Miranda, E.H.; Cajaraville, A.C.; da Silva Freire, M. Evaluation of accuracy and reliability of the plaque reduction neutralization test (micro-PRNT) in detection of yellow fever virus antibodies. Biologicals 2012, 40, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi Nasab, G.S.; Salimi, V.; Abbasi, S.; Adjami Nezhad Fard, F.; Mokhtari Azad, T. Comparison of neutralizing antibody titers against outbreak-associated measles genotypes (D4, H1 and B3) in Iran. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Shane, A.L.; Nguyen, T.; Ray, P.; Dennehy, P.; Baek, L.J.; Parashar, U.; Glass, R.I.; Jiang, B. Inhibitory effect of breast milk on infectivity of live oral rotavirus vaccines. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.S.; Groome, M.J.; Velasquez, D.E.; Parashar, U.D.; Jones, S.; Koen, A.; van Niekerk, N.; Jiang, B.; Madhi, S.A. Prevaccination Rotavirus Serum IgG and IgA Are Associated With Lower Immunogenicity of Live, Oral Human Rotavirus Vaccine in South African Infants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketa-Graham, M.; Powell Pereira, J.L.; Baylis, E.; Cossen, C.; Oceguera, L.; Patiris, P.; Chiles, R.; Hanson, C.V.; Forghani, B. High throughput quantitative colorimetric microneutralization assay for the confirmation and differentiation of West Nile Virus and St. Louis encephalitis virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzelnick, L.C.; Coello Escoto, A.; McElvany, B.D.; Chávez, C.; Salje, H.; Luo, W.; Rodriguez-Barraquer, I.; Jarman, R.; Durbin, A.P.; Diehl, S.A.; et al. Viridot: An automated virus plaque (immunofocus) counter for the measurement of serological neutralizing responses with application to dengue virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Ma, C.; Nawaz, M.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Outbreak of acute respiratory disease caused by human adenovirus type 7 in a military training camp in Shaanxi, China. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, I.C.B.; Haguinet, F.; Colares, J.K.B.; Coelho, Z.C.B.; Araújo, F.M.C.; Schwarcz, W.D.; Duarte, A.C.; Borges, B.; Minguet, C.; Guignard, A. Dengue Infection in Children in Fortaleza, Brazil: A 3-Year School-Based Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigoi, C.; Lwande, O.; Orindi, B.; Irura, Z.; Ongus, J.; Sang, R. Seroepidemiology of selected arboviruses in febrile patients visiting selected health facilities in the lake/river basin areas of Lake Baringo, Lake Naivasha, and Tana River, Kenya. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Savic, V.; Sabadi, D.; Peric, L.; Barbic, L.; Klobucar, A.; Miklausic, B.; Tabain, I.; Santini, M.; Vucelja, M.; et al. Prevalence and molecular epidemiology of West Nile and Usutu virus infections in Croatia in the ‘One health’ context, 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Moi, M.L.; Le, T.Q.M.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Vu, T.B.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Pham, T.T.H.; Le, T.H.T.; Nguyen, L.M.H.; Phu Ly, M.H.; et al. Prevalence of Zika virus neutralizing antibodies in healthy adults in Vietnam during and after the Zika virus epidemic season: A longitudinal population-based survey. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvai, E.A.C.; Kyaw, A.K.; Sabin, N.S.; Yu, F.; Hmone, S.W.; Thant, K.Z.; Inoue, S.; Morita, K.; Ngwe Tun, M.M. Evidence of Chikungunya virus seroprevalence in Myanmar among dengue-suspected patients and healthy volunteers in 2013, 2015, and 2018. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.C.; Gidlewski, T.; Root, J.J.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Lash, R.R.; Harmon, J.R.; Brault, A.C.; Panella, N.A.; Nicholson, W.L.; Komar, N. Bourbon Virus in Wild and Domestic Animals, Missouri, USA, 2012–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1752–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaduskar, O.; Gurav, Y.K.; Deshpande, K.; Desphande, G.R.; Yadav, P.; Rakhe, A.; Tilekar, B.N.; Gomade, P.; Salunke, A.; Patil, C.; et al. Understanding the dynamics of IgM & IgG antibodies in COVID-19-positive patients. Indian J. Med. Res. 2022, 155, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, A.K.M.; Hunt, D.; George, K.S.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Kramer, L.D.; Shi, P.Y.; Wong, S. Use of the immunoglobulin G avidity assay to differentiate between recent Zika and past dengue virus infections. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.T.; Clapham, H.E.; Phung, K.L.; Nguyen, T.K.; DInh, T.T.; Nguyen, T.H.Q.; Tran, V.N.; Whitehead, S.; Simmons, C.; Wolbers, M.; et al. Methods to discriminate primary from secondary dengue during acute symptomatic infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medialdea-Carrera, R.; Levy, F.; Castanha, P.; Carvalho de Sequeira, P.; Brasil, P.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Turtle, L.; Solomon, T.; Bispo de Filippis, A.M.; Brown, D.W.; et al. A Systematic Evaluation of IgM and IgG Antibody Assay Accuracy in Diagnosing Acute Zika Virus Infection in Brazil: Lessons Relevant to Emerging Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0289320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevencan, F.; Gözalan, A.; Uyar, Y.; Kavakli, I.; Türkyilmaz, B.; Ertek, M.; Lundkvist, A. Serologic Investigation of Hantavirus Infection in Patients with Previous Thrombocytopenia, and Elevated Urea and Creatinine Levels in an Epidemic Region of Turkey. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 68, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theel, E.S.; Sorenson, M.; Rahman, C.; Granger, D.; Vaughn, A.; Breeher, L. Performance Characteristics of a Multiplex Flow Immunoassay for Detection of IgG-Class Antibodies to Measles, Mumps, Rubella, and Varicella-Zoster Viruses in Presumptively Immune Health Care Workers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00136-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Nielsen, M.C.; Muruato, A.E.; Fontes-Garfias, C.R.; Ren, P. Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow assay using the plaque reduction neutralization test. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 99, 115248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.M.; Nguyen, T.V.; Azevedo, M.S.; Jeong, K.; Agarib, F.; Iosef, C.; Chang, K.; Lovgren-Bengtsson, K.; Morein, B.; Saif, L.J. Antibody responses to human rotavirus (HRV) in gnotobiotic pigs following a new prime/boost vaccine strategy using oral attenuated HRV priming and intranasal VP2/6 rotavirus-like particle (VLP) boosting with ISCOM. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 135, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Azevedo, M.S.; Wen, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Saif, L.J.; Li, G.; Yousef, A.E.; Yuan, L. Probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus enhances the immunogenicity of an oral rotavirus vaccine in gnotobiotic pigs. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3655–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.S.; Yuan, L.; Iosef, C.; Chang, K.O.; Kim, Y.; Nguyen, T.V.; Saif, L.J. Magnitude of serum and intestinal antibody responses induced by sequential replicating and nonreplicating rotavirus vaccines in gnotobiotic pigs and correlation with protection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maha, M.M.; Ali, M.A.; Abdel-Rehim, S.E.; Abu-Shady, E.A.; El-Naggar, B.M.; Maha, Y.Z. The role of coxsackieviruses infection in the children of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 2003, 78, 305–318. [Google Scholar]
- Çelebi, G.; Öztoprak, N.; Öktem, İ.M.A.; Heyman, P.; Lundkvist, Å.; Wahlström, M.; Köktürk, F.; Pişkin, N. Dynamics of Puumala hantavirus outbreak in Black Sea Region, Turkey. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saipin, K.; Thaisomboonsuk, B.; Siridechadilok, B.; Chaitaveep, N.; Ramasoota, P.; Puttikhunt, C.; Sangiambut, S.; Jones, A.; Kraivong, R.; Sriburi, R.; et al. A replication competent luciferase-secreting DENV2 reporter for sero-epidemiological surveillance of neutralizing and enhancing antibodies. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 308, 114577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramps, J.A.; Magdalena, J.; Quak, J.; Weerdmeester, K.; Kaashoek, M.J.; Maris-Veldhuis, M.A.; Rijsewijk, F.A.; Keil, G.; van Oirschot, J.T. A simple, specific, and highly sensitive blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to bovine herpesvirus 1. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramps, J.A.; Perrin, B.; Edwards, S.; van Oirschot, J.T. A European inter-laboratory trial to evaluate the reliability of serological diagnosis of bovine herpesvirus 1 infections. Vet. Microbiol. 1996, 53, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzietchueng, S.; Kitua, A.; Nyatanyi, T.; Rwego, I.B. Facilitating implementation of the one health approach: A definition of a one health intervention. One Health 2023, 16, 100491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).