Abstract
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) requires four essential virion glycoproteins—gD, gH, gL, and gB—for virus entry and cell fusion. To initiate fusion, the receptor binding protein gD interacts with one of two major cell receptors, HVEM or nectin-1. Once gD binds to a receptor, fusion is carried out by the gH/gL heterodimer and gB. A comparison of free and receptor-bound gD crystal structures revealed that receptor binding domains are located within residues in the N-terminus and core of gD. Problematically, the C-terminus lies across and occludes these binding sites. Consequentially, the C-terminus must relocate to allow for both receptor binding and the subsequent gD interaction with the regulatory complex gH/gL. We previously constructed a disulfide bonded (K190C/A277C) protein that locked the C-terminus to the gD core. Importantly, this mutant protein bound receptor but failed to trigger fusion, effectively separating receptor binding and gH/gL interaction. Here, we show that “unlocking” gD by reducing the disulfide bond restored not only gH/gL interaction but fusion activity as well, confirming the importance of C-terminal movement in triggering the fusion cascade. We characterize these changes, showing that the C-terminus region exposed by unlocking is: (1) a gH/gL binding site; (2) contains epitopes for a group (competition community) of monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) that block gH/gL binding to gD and cell–cell fusion. Here, we generated 14 mutations within the gD C-terminus to identify residues important for the interaction with gH/gL and the key conformational changes involved in fusion. As one example, we found that gD L268N was antigenically correct in that it bound most Mabs but was impaired in fusion, exhibited compromised binding of MC14 (a Mab that blocks both gD–gH/gL interaction and fusion), and failed to bind truncated gH/gL, all events that are associated with the inhibition of C-terminus movement. We conclude that, within the C-terminus, residue 268 is essential for gH/gL binding and induction of conformational changes and serves as a flexible inflection point in the critical movement of the gD C-terminus.
1. Introduction
The first essential step in HSV viral entry requires binding to a cellular receptor. The HSV receptor binding protein gD recognizes three distinct receptors: nectin-1, herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), and specific sulfate-modified forms of the glycan heparan sulfate [1]. Once gD binds to a receptor, fusion is carried out by three other viral glycoproteins: the heterodimer gH/gL (modulator of fusion) and gB (fusogen). Crystallography studies have shown that the C-terminus of the gD ectodomain (C-term) normally occludes the binding site for nectin-1 (gD is in a closed, autoregulated conformation) and prevents the formation of the N-terminal loop needed for HVEM binding [2,3,4]. For either HVEM or nectin-1 to interact with full-length gD (369 aa), the C-term residues of gD (roughly 265–316) must be displaced to expose the nectin-1 binding site, now considered to be an open conformation. As soluble proteins, gD306t represents the closed conformation (non-binding) and gD285t represents the open form (binding).
The next step in the proposed fusion pathway is the interaction of receptor-activated gD with gH/gL protein complex. Recent evidence shows that gD interacts directly with gH/gL [5,6,7]. In that study, the physical interaction between gD and gH/gL was measured by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) when gD was presented as the shorter truncation (gD285t) in which the nectin-1 binding site is fully exposed [2,8]. We found that the gD–gH/gL interaction is blocked by specific neutralizing and virus spread blocking anti-gD monoclonal antibodies (Mabs), the epitopes of which define three putative gH/gL-interacting sites on gD: site 1 (MC23, mar 213), site 2 (MC5, 54, 75–77), and site 3 (MC14, 262–272) (Figure 1a). The location of site 3 is in a region termed “profusion” [9,10], hypothesized to be required for viral membrane fusion, and appears to function by recruiting other glycoproteins, namely gH/gL, to form a complex that triggers fusion [9,11]. The formation of the gD–gH/gL complex and triggering of the fusion cascade is highly dependent on specific conformational changes that occur in gD, beginning with receptor binding [12,13,14]. To further define these conformational changes, a gD mutant was engineered to contain an additional disulfide bond (K190C-A277C) which, based on the gD crystal structure, would constrain the motion of the C-term. This mutant (referred to as cys2) was able to bind both HVEM and nectin-1 [15], but failed to trigger cell–cell fusion and did not complement a gD-null virus, effectively separating the receptor binding and gH/gL interaction functions of gD. Together, these findings suggest that gD binding to a receptor is necessary but not sufficient for gH/gL binding and subsequent fusion. This mutant also helped define two physical “faces” on gD: a receptor binding face and a gH/gL binding face. Finally, the region in the gD cys2 protein that is locked by the newly introduced disulfide bond also hosts multiple epitopes targeted by protective antibodies (Figure 1b) [6,15] that block the physical interaction between gD and gH/gL [6], reduce viral spread [16] and protect against disease following passive immunization [16,17], further supporting a critical role for this region in transmission of the virus.
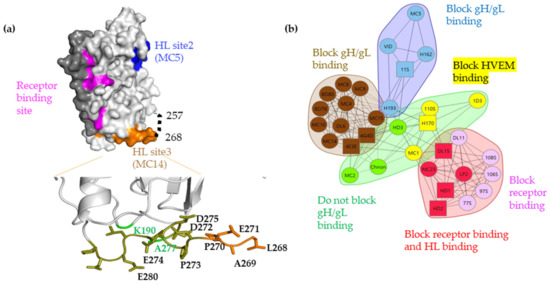
Figure 1.
(a) Surface representation of gD306 crystal structure (PDB 2c36) showing the C-term (dark gray), the nectin-1 biding site (pink), and two of the three gH/gL binding sites defined by MC5 (site 2, blue) and MC14 (site 3, brown). gH/gL binding site 1 overlaps with the nectin-1 binding site. Region 257-267 which is missing from all crystal structures is shown as a dotted line and the C-term, lying over the receptor binding site. Point mutations generated in the gH/gL binding site 3 are shown as labelled side chains. In green are the point mutations that introduced the cysteine residues (at positions 190 and 277), which allow for the formation of a disulfide bond. (b) Based on competition and biological function, gD Mabs were grouped into communities: blue, brown, green, and red. The red community is subdivided into red and pink. The green community is subdivided into green and yellow. Circles indicate that competition was measured as both a ligand and an analyte; squares indicate that competition was measured as either a ligand or an analyte only. Solid connecting lines specify that competition between the two Mabs was measured in both directions (each as a ligand and analyte). Dashed connecting lines identify that the competition between Mabs was measured in one direction only.
In this study, we address the underlying mechanism used by gD to transition from the “closed” form to the “open” conformation that (1) allow the transfer of information to gH/gL, (2) activate gH/gL, and (3) lead to induction of fusion. Specifically, we show that: (1) Binding of the nectin-1 receptor to the closed form of gD (gD306t) induces/allows the conformational changes required for gH/gL binding. (2) Unlocking of the disulfide bond in the gD mutant cys2 by reducing reagents enhances fusion due to unfettered movement of the C-term of gD, thus providing access for gH/gL to all three binding sites on gD. (3) Site directed mutagenesis of the gH/gL binding site 3 (262–282) on gD reveals epitopes of specific Mabs mapped to this region, and importantly, defines residues required for shifting from the closed to open state of gD. Together, our results delineate the conformational transitions induced in gD by the nectin-1 receptor for three key steps in fusion: (1) release of the autoregulation of gD; (2) full exposure of the nectin-1 binding site; and (3) rearrangements in gD structure that allow for the binding of gH/gL, all potential new targets for drug intervention.
2. Materials and Methods
Cells. Mouse melanoma cells B78H1 (gift from Meenhard Herlyn from the Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, PA, USA) were grown in DMEM containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 100 µg/mL penicillin-streptomycin. For B78-C10 stably expressing nectin-1 [18], medium was supplemented with 500 µg/mL geneticin (G418). 293-T cells were grown in DMEM/10% FBS/100 µg/mL penicillin-streptomycin.
Plasmids. Wild-type glycoprotein constructs pTC580 (gB2), pTC578 (gD2), pTC510 (gH2), pTC579 (gL2), and Rluc8(1–7), Rluc8(8–11) for the fusion assay have all been described previously [19,20,21,22]. Full length gD2 DNA plasmids encoding point mutations N262A, Q265A, E267A, L268N, V269D, P270R, E271V, D272A, D275A, E280N, disulfide bonded cys2 mutant (K190C-A277C), and truncated versions of wt, L268N (285t and 306t), and Cys2 (306t) were generated by GenScript (Piscataway, NJ, USA) and cloned into pcDNA3.1 plasmid.
Production and purification of soluble proteins. Soluble nectin-1 [23] and gH2/gL2 [24] were purified from baculovirus-infected insect cells (Sf9) as previously described [25,26]. 6xHis tagged wt (285t, 306t), L268N (285t, 306t) and cys2 (306t) mutant proteins were purified from mammalian cells. 293T cells were plated in 6-well plates and transfected with 2 µg/well of each plasmid. Proteins were purified using Ni-nitriliacetic acid resin column and eluted with 250 mM imidazole.
Antibodies used. The following antibodies were used in this study: 1D3 [27], DL6, DL11 [28], MC2, 5, 10, 14, 23 [29], 4E3E (a gift from R. N. Laush).
Split luciferase fusion assay. The assay is described elsewhere [30,31]. Briefly, 5 × 104 B78 cells (effector cells) were seeded on white, cell-culture treated 96-well plates. Then, 4 × 105 C10 cells (target cells) were seeded on 6-well plates. Transfection was performed the following day. Briefly, a master mix containing 125 ng each of the gB, gH, gL, and Rluc8(1–7) plasmids and 30 ng of either pCAGGS (mock), wt or mutant gD plasmid was split over three wells of effector cells. Target cells were transfected with 1 µg of Rluc8(8–11) plasmid/per well. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, effector cells were pre-incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with EnduRen substrate (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) diluted 1:1000 in 40 µL fusion medium (DMEM without phenol red supplemented with 50 mM HEPES and 5% FBS). Target cells were detached with versene and pelleted. The pellet was resuspended in fusion medium and 40 µL of cells were transferred to effector cells, making the final volume 80 µL. Luciferase production was monitored over 2 h with measurements every 5 min using a BioTek plate reader.
TCEP treatments: Effector cells transfected as described were pre-incubated with 10 mM of freshly made TCEP for 10 min. Cells were washed with fusion medium and EnduRen substrate was added [31]. Fusion was triggered by the addition of target cells. A negative control (effector cell transfected with gB, gH, gL, but no gD) was also included.
Cell-based ELISA (CELISA). B78 cells were seeded on clear 96 well plates (5 × 104 cells per well). Transfection was done as described above for effector cells. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cells were assayed for surface expression following a previously described protocol [31]. Briefly, 24 h post transfection cells were blocked with blocking solution (3% BSA in PBS++ containing Ca2+ and Mg2+) for 30 min. For detection, a 1 µg/mL of primary antibody and anti-rabbit or anti-mouse IgG HRP-linked secondary antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) were used. After addition of ABTS (2,2′-azinobis [3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid]) peroxidase substrate (Moss, Inc., Pasadena, MD, USA) absorbance at 405 nm was measured using a BioTek plate reader.
Western blotting. Here, 1 × 105 C10 cells were seeded on 24-well plates and transfected with 125 ng of pCAGGS, gD wt or mutants. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, cells were washed 3 times with PBS and lysed (100 mM TRIS pH8, 1% NP40, 0.5% deoxycholate and 1× protease inhibitor). The protein concentration was measured using the Bradford assay. Twenty µg total lysate was run on Novex 10% tris-glycine gels, under “native” conditions [32]. After the transfer, nitrocellulose blots were probed with 1 µg/mL of the indicated antibodies. Secondary anti-rabbit/mouse IgG HRP-linked antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) were used, diluted to 1:2500. The blots were developed with ECL Western Blotting substrate or SuperSignal™ West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate, both from Pierce (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Images were captured with Odyssey Imaging System (Li-Cor Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA).
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Experiments were performed using a Biacore 3000 biosensor (Cytiva, Marlborough, MA, USA), at room temperature. Filtered and degassed HBS-EP buffer (10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 3 mM EDTA, 0.005% surfactant P20) was used in all the experiments. An anti-His (Qiagen, Inc., Germantown, MD, USA) or anti-gD 1D3 antibody was covalently coupled to a CM5 sensor chip (Cytiva, Marlborough, MA, USA) following our previous protocol [33]. Then, 150–200 resonance units (RUs) of purified gD wt or mutants were captured by the antibodies. Purified IgGs and/or nectin-1 were then injected for 300 s, followed by gH/gL, also for 300 s. After each experiment, the chip surface was treated with brief pulses of 0.2 M Na2CO3 (pH 11) until the RU signal returned to baseline, and then a new cycle was started. All injections were performed at a flow rate of 5 μL/min.
3. Results
3.1. Binding of Nectin-1 Induces Conformational Changes in gD306t (Closed Conformation) That Allow for gH/gL Binding
We previously showed that the open form of gD (gD285t) can physically interact efficiently with gH/gL [5,6] and could be blocked by specific gD and gH/gL Mabs. Notably, we had previously divided these Mabs into blue, red, and brown communities based upon their ability to compete for binding (Figure 1b), thus allowing us to refine the proposed protein–protein interaction sites on both gD and gH/gL [5,6]. We hypothesized that gD306t would not physically interact with gH/gL in vitro because its conformation was locked in a closed position. However, if a conformational change in gD306t is required to initiate the cascade, then the addition of soluble receptor nectin-1 in the SPR experiment should drive the C-terminus of gD away from the core, thus altering its conformation and allowing for gH/gL binding.
To address this hypothetical model, we adapted the Biacore 3000 biosensor system (SPR) assay (Figure 2a). First, we amine-coupled anti-gD Mab 1D3 to a CM5 SPR chip. 1D3 Mab [34], which binds residues 11–21 in the N-terminus, captures both gD306t (closed) and gD285t (open), but importantly presents gD285t in a conformation that allows for interaction with gH/gL interaction [5,6].
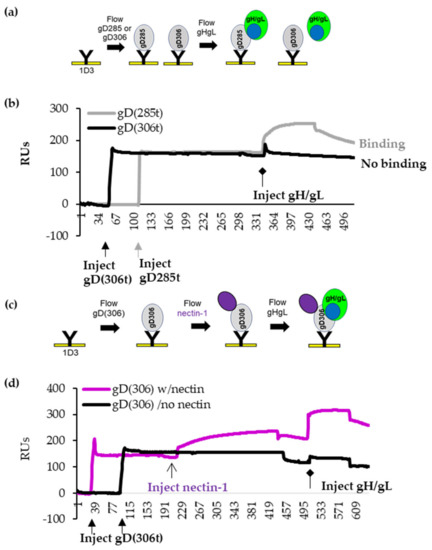
Figure 2.
Binding of gHgL to gD by SPR. (a). Diagram outlining the SPR protocol. (b). 1D3 (anti-gD Mab) was covalently coupled to a CM5 biosensor chip. An equal amount of gD285t (gray) and gD306t (black) were immobilized to different spots on the Biacore chip. Soluble gD306t or gD285t and gH/gL were sequentially injected (injection start indicated by diamond arrow). An increase in response units (RUs) after injection indicates binding. gH/gL binds to gD285t only (black curve). No gH/gL binding was observed for gD306t (gray curve). x axis, time (seconds). y axis, resonant units (RU). (c) Diagram of the SPR protocol for sequential injections of gD306t and nectin-1, followed by injection of soluble gH/gL. (d) gD306 was attached to two flow cells on the biosensor chip via 1D3 Mab. Nectin-1 was flowed over cell 1 only. Flow cell 2 did not receive nectin. gH/gL was flowed over both flow cells. In the absence of nectin-1, gD306t does not bind gH/gL (black curves). Pre-binding of nectin-1 to gD306t induced conformational changes that allow for gH/gL binding (purple). Experiments were performed a minimum of three times.
We used 1D3-coupled chips to capture equal resonance units (RUs) of gD285t (open) and gD306t (closed) (Figure 2b, thick arrows) and then flowed soluble gH/gL across the chip (Figure 2b, diamond arrowhead). gH/gL binding is indicated by the increase in RUs. As expected, gD285t efficiently bound gH/gL (gray curve in Figure 2b), whereas gD306t did not (black curve). Thus, the presence of residues 286–306 in the closed conformation of gD interferes with gH/gL binding.
Next, we captured gD306t with 1D3 Mab and sequentially flowed nectin-1 to “open” gD and then gH/gL to assess the ability of gD to interact with gH/gL. Figure 2c shows the overview of a representative experiment. Nectin-1 binding to gD306t is indicated by an increase in the number of RUs (Figure 2d, purple line). As shown in Figure 2b, the addition of gH/gL to gD306t alone did not result in binding (no increase in mass) (Figure 2d, black line). However, gH/gL was able to bind to the nectin-gD306t complex (Figure 2d, purple). This experiment shows that nectin-1 induced the necessary structural changes in gD that allow gH/gL to bind. Although displacement of the C-term of gD by receptor binding was expected to promote interaction with gH/gL based on the crystal structures of free and receptor-bound gD [2,8], this is the first time that these interactions were shown experimentally, albeit using soluble proteins.
3.2. Tethering of the C-Term by a Disulfide Bond in gD Prevents Movement Required for Fusion Function
We previously showed that cys2, a disulfide-bonded gD mutant (K190C-A277C; Figure 1a), could bind both nectin-1 and HVEM receptors but failed to trigger fusion [15]. This suggested that receptor binding was necessary but not sufficient to activate gD, and that additional changes in gD structure are needed for subsequent interaction with gH/gL (which at the time, could not be tested). As we are now capable of testing for gH/gL binding, we set out to determine whether the disulfide lock in cys2 restricted conformational changes in full length and/or soluble gD. We asked two questions: (1) what changes (if any) were induced by the presence of the disulfide bond in the putative gD–gH/gL interaction sites on gD and (2) how did the disulfide bond affect the fusion function of gD and its interaction with gH/gL?
To determine if gD conformation was altered by the presence of the disulfide bond, we used a cell-based ELISA (CELISA) to compare the antigenic structure of full length wt gD and cys2 mutant on the surface of B78 cells using Mabs MC5 (blue), MC23 (red) and MC4, MC10, MC14, DL6, and 4E3E (brown) (Figure 1b). The cys2 mutant is expressed at 40% of wt [15], as shown by a polyclonal gD antibody (R7), binding. As binding of our panel of Mabs was also at 40–60% of wt levels, the antigenic structure of the cys2 mutant appears similar to that of wt gD (Figure 3a) but is expressed at lower levels.
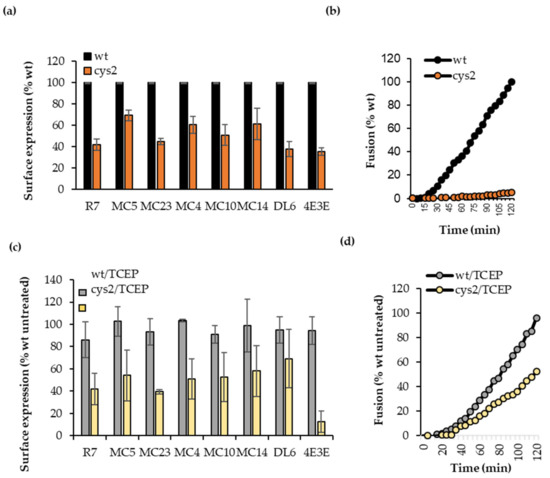
Figure 3.
Characterization of wt and cys2 proteins. (a) CELISA of B78 cells transfected with full-length wt and cys2 gD and probed with select Mabs. Expression of cys2 (brown bars) is presented as % of binding to wt with the same antibody. The average of three experiments, each done in duplicate. (b) Fusion assay. Ability of full-length gD wt (black curve) and cys2 (brown curve) to trigger fusion in a live cell fusion assay. Data are presented as percent fusion by wt gD at the 2 h time point. Representative curve from three independent experiments, each done in duplicate. (c) CELISA after TCEP treatment. Binding of sentinel Mabs from each community to B78 cells transfected with full-length wt (gray) or cys2 (yellow) gD after cells were treated with TCEP for 10 min. Average of three experiments, each done in duplicate. Data for each antibody was normalized to no treatment wt samples. (d) Fusion assay. Effector cells expressing gB, gH/gL, and wt or cys2 gD were treated for 10 min with 10 mM TCEP before fusion was triggered by the addition of donor nectin-1 expressing cells. Data are presented as percent fusion by untreated wt gD at the 2-h time point, when the rate of fusion was at its maximum. Representative curve from three independent experiments, each done in duplicate.
To test for the effect of the disulfide bond on fusion function, we used a split luciferase assay [31,35] in which effector B78 cells were transfected with the split luciferase RLuc1–7, gB, gH/gL, and gD, either as the wt or cys2 form. Donor C10 cells (constitutively expressing nectin-1) were transfected with the split luciferase RLuc8-11 plasmid. Upon co-cultivation of donor and effector cells, fusion is detected by reconstitution of the luciferase gene. As previously reported, we found that unlike wt gD (Figure 3b, black curve), cys2 was unable to trigger fusion (Ref. [15] and Figure 3b, brown curve).
3.3. Reduction of the Disulfide Bond with TCEP Restores Fusion Function of Cys2
We next set out to determine if relieving the “lock” on the movement of gD C-term restored gD fusion function. Reduction of artificially generated disulfide bonds successfully identified the residues essential for fusion triggering in measles H protein [36,37]. The bulky reducing reagent Tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP) preferentially reduces the exposed disulfide bonds [38]. Wt gD carries three disulfide bonds that are essential for stabilization of its secondary and tertiary structure: Cys66-Cys189, Cys106-Cys202, and Cys118-Cys127 [2,39,40]. Notably, the native gD disulfides appear buried in the crystal structure [2,8,41], while the engineered Cys190-Cys277 bond appears completely exposed. Thus, preferential reduction of the engineered Cys190-Cys277 bond by TCEP would potentially “open” cys2 by freeing the C-term and allowing gH/gL to bind.
Before testing for gain of function, we used CELISA to determine whether TCEP treatment affects the general folding of the proteins. For this, B78 cells were transfected with full-length wt gD or cys2. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cells were treated with 10 mM TCEP solution for 10 min. After treatment, cells were washed with PBS and CELISA was performed, as described. CELISA readings were normalized to the untreated wt samples probed with the same antibodies. TCEP treatment did not significantly change the antigenic structure of wt gD (Figure 3c, gray bars) or cys2 (yellow bars) compared to the untreated samples (Figure 3a). One exception was a loss of 4E3E epitope, which is consistent with conformational changes associated with this region of gD [6,34].
To test our hypothesis that the disulfide bond trapped gD in an intermediate conformation, we next determined if reduction of the artificial disulfide bond by TCEP led to a gain of fusion. For this, we used the cell-based fusion assay in which effector B78 cells were transfected with the split luciferase RLuc1–7, gB, gH/gL, and full-length gD, either wt or cys2. Donor C10 cells containing nectin-1 receptor were transfected with the split luciferase RLuc8–11. Twenty-four hours post-transfection effector cells were treated with 10 mM TCEP for 10 min at 37 °C. After treatment, cells were washed with fusion medium and incubated with EnduRen luciferase substrate for 1 h/37 °C. The fusion assay was carried out as described. The activity of both wt and cys2 was expressed as % of untreated wt gD. Figure 3d shows that the addition of TCEP did not affect the function of wt gD (gray curves). In contrast, TCEP treatment resulted in a gain in fusion function for full-length cys2 from 0 (Figure 3b) to 50% of wt activity, indicating that the cysteine substitutions themselves did not compromise the fusion activity of gD. We thus concluded that (1) the lack of function in cys2 was due to the disulfide lock introduced by the two new cysteine residues and (2) the reduction of the disulfide bond by TCEP treatment relieved the block, which resulted in a functional molecule.
3.4. Locking of C-Term to the Core of gD Allows for Nectin-1 Binding but Prevents the gD–gH/gL Interaction
To determine whether the inability of cys2 to function in fusion was specifically related to the inability of the locked C-term, associated with a lack of gH/gL interaction, we next determined whether the cys2 protein was capable of physically interacting with gH/gL by SPR. For this, soluble wt and cys2 gD proteins, truncated at position 306 and with 6xHis tags at the C-term, were purified by nickel column chromatography from supernatants of 293T transfected cells. Both wt and cys2 proteins were recognized by R7 anti-gD polyclonal antibody as well as by several sentinel Mabs representing different communities (Figure S1), confirming the correct folding of both proteins. Furthermore, as in our previous report using total cell lysates of cells transfected with full length constructs [15], cys2 soluble protein migrated faster on SDS-PAGE than wt (presumably due to the more compact structure adopted due to the disulfide bond).
To test for gH/gL binding, the truncated proteins were captured at their N-terminus on the surface of a CM5 chip via immobilized 1D3 antibody, as done in Figure 2. After capture, soluble gH/gL was flowed across the chip surface (Figure 4a). As expected, both gD306t and cys2 bound gH/gL poorly (Figure 4b). We then asked whether nectin-1 would induce the necessary conformational changes in gD cys2 that allowed for gH/gL binding in wt gD. Both proteins bound nectin-1 (Figure 4d and [15]), albeit with different efficiencies (cys2 bound nectin-1 ~40% of wt). As shown in Figure 2d, after gH/gL was flowed, there was a significant binding of gH/gL to wt gD306 (Figure 4e, blue curve). However, there was no increase of gH/gL binding to cys2 (cyan). We thus concluded that, despite similarities to wt gD (antigenic profile, binding to receptor), the failure of cys2 to induce fusion may be linked to its inability to interact with gH/gL and that the disulfide bond prevented conformational changes in cys2 required for this interaction.
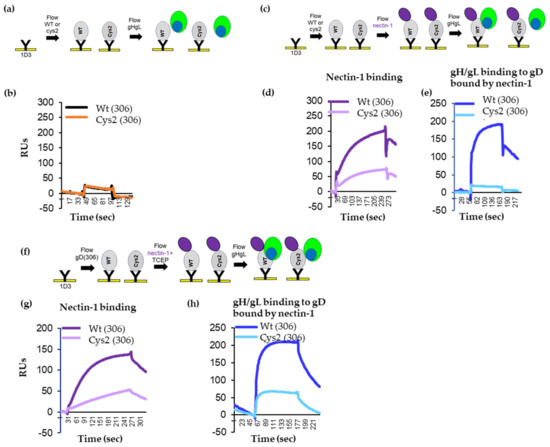
Figure 4.
Characterization of wt and cys2 proteins. (a) Diagram of the Biacore 3000 protocol for analyzing gH/gL binding to gD, wt or cys2. (b) Soluble wt306t and cys2306t proteins were attached to the biosensor chip via 1D3 Mab. Soluble gH/gL was injected across the chip surface. Only the gH/gL binding curves are shown. Black curve, binding of gH/gL to wt gD; brown curve, binding of gH/gL to cys2. (c) Diagram of the Biacore 3000 protocol for analyzing the binding of gH/gL to a gD-nectin-1 receptor complex. gD molecules were attached to the biosensor chip via 1D3 Mab. Sequential injection of nectin-1 followed by injection of soluble gH/gL. (d) Nectin-1 binds to both wt (dark purple) and cys2 (light purple) gD proteins. (e) gH/gL bound to wt gD (blue) but not to cys2 mutant gD (cyan). (f) Diagram of the Biacore 3000 protocol for analyzing gD–gH/gL binding in the presence of TCEP. gD molecules were attached to the biosensor chip via 1D3 Mab. Nectin-1 was pre-mixed with 1 mM TCEP and flowed over the captured gD molecules, followed by the injection of soluble gH/gL. (g) Nectin-1 binds to both wt (purple) and cys2 (light purple) gD proteins. (h) As expected, gH/gL bound to wt gD (blue). Due to the reduction of the disulfide bond, gH/gL is now able to bind cys2 mutant gD as well (cyan).
3.5. TCEP Treatment of Soluble Cys2 Truncated Protein Allows for the Interaction with gH/gL
To demonstrate that the gain-of-fusion function by cys2 after TCEP treatment (Figure 3d) was associated with a restored gD–gH/gL interaction, we repeated the SPR experiments in the presence of TCEP. Similar amounts of wt and cy2 gD proteins were immobilized on the 1D3-coupled chip. We then flowed soluble nectin-1 pre-mixed with 1 mM TCEP, followed by an injection of gH/gL (Figure 4f). The addition of TCEP did not affect the binding of nectin-1 to wt or mutant gD (compare Figure 3d,g). Furthermore, the nectin-1/TCEP mix did not change the ability of wt gD to bind soluble gH/gL (compare the blue lines in Figure 3e,h). In contrast, after nectin-1/TCEP treatment, gH/gL bound to cys2 (compare the cyan curves in Figure 3e,h). We propose that the soluble cys2 mutant failed to interact with gH/gL due to a locking of gD C-term and that the removal of the lock resulted in the opening of gD to a functional fusion competent molecule that could physically bind gH/gL and trigger fusion.
3.6. Site-Directed Mutagenesis in the 262–282 Region of gD Identifies Residues Important for gH/gL Binding
The engineered disulfide bond (Cys190-Cys277) links the core of gD to the postulated interaction site (262–282) with gH/gL (gH/gL site 3). This region contains multiple, critical epitopes that are recognized by Mabs from the brown community (Refs. [29,34,42] and Figure 1b) that block the physical gD–gH/gL interaction [6], inhibit fusion [7], block virus spread [16], and passively protect mice against herpes disease [16,43,44]. We hypothesized that these Mabs functions either work directly by blocking the physical gD–gH/gL interaction or indirectly by interfering with the movement of the C-term. We focused first on movement, as cys2 failed to bind gH/gL (Figure 4e) despite an intact MC14 epitope (gH/gL binding site 3) (Figure 3a and Figure S1). This suggested that MC14 might block the movement of the C-term and, in the process, affect the ability of gD to interact with gH/gL. To characterize the effect of point mutations on the movement involved in the opening of gD and its relationship to gH/gL binding, we generated 10-point mutations within the 262–282 region by site-directed mutagenesis. The expectation was that: (1) some mutants might show a defect in fusion activity; or (2) some mutations might change or inhibit the gD–gH/gL interaction. This would identify residues important for both the gD function and gH/gL interaction.
CELISA data (Figure 5a) shows that the B78 cells surface expression level for all 10 mutant gDs was equivalent as measured by gD polyclonal antibody (Pab) R7 (black bars). Mabs MC2 (green bars) or MC5 (blue bars) recognized all constructs at wt levels. Thus, proper synthesis, processing, and transport of each gD mutant to the cell surface was unaffected. Notably, three Mabs from the brown community, MC14, DL6, and 4E3E (Figure 1b), which recognized overlapping peptides [34,42], differentially recognized gD (data summarized in Table 1). Briefly, L268N, V269D, P270R, and E271V mutants failed to bind MC14, but were bound normally by DL6 and 4E3E. The E271V, D272A mutants showed lower DL6 binding, and the D275A and E280D mutants failed to bind 4E3E, effectively mapping important residues in MC14, DL6, and 4E3E epitopes, respectively.
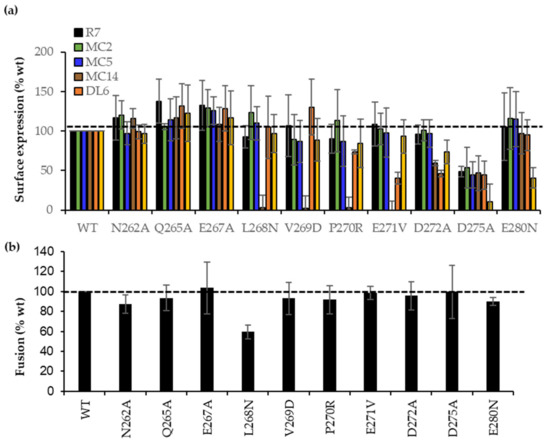
Figure 5.
Characterization of point mutations in region 262–280 of full-length gD. (a) CELISA. Detection of the surface-expressed wt and point gD mutations with sentinel Mabs from each community. Data normalized to wt with each Mab (dotted line). Average of three experiments, each done in duplicate. (b) Fusion function of full-length wt and mutant gDs when combined with gB, gH, and gL constructs. Data normalized to wt gD (dotted line). Average of three independent experiments, each in duplicate.

Table 1.
Summary of the point mutations generated in region 262–280.
Next, we asked if the mutants impacted the functional interaction with gH/gL. Given the importance of this region in the gD–gH/gL interaction [6], we hypothesized that mutants deficient in the binding of brown antibodies would have a disrupted the gD–gH/gL interface, which would block the ability of gD to trigger fusion. For this, B78 cells were transfected with RLuc1–7, full-length wt, or mutant gDs alongside gB, gH, and gL. Figure 5b shows that most mutants had wt activity. Because V269D, P270R, and E271V had wt fusion phenotypes but failed to bind MC14, they fulfilled the concept of antibody-escape mutants [45]. Similarly, E271V, D272A, and D275A were escape mutations for DL6 and D275A, and E280N for 4E3E Mab. However, the L268N mutant showed 60% activity when combined with gB and gH/gL. The functional impairment of L268N, combined with its failure to bind MC14 (Figure 5a), suggests that the fusion impairment might be due directly to the gH/gL interaction rather than binding to the nectin-1 receptor.
3.7. Characterization of Soluble gD L268N
To distinguish between defects in receptor binding and altered physical interactions between gD and gH/gL, both wt and L268N gD soluble proteins were expressed and purified from the supernatants of transfected 293t cells. Each construct was expressed in two forms: the open 285t and the closed 306t. If the L268N mutation affected the conformational changes necessary to expose the nectin-1 binding site, then the open 285t protein should readily bind nectin-1 while the closed 306t protein should not. However, if the L268N protein was unable to interact with gH/gL, then neither the 285t truncation nor the 306t form should bind gH/gL, even after opening of the molecule with nectin-1.
By western blotting analysis, we found quantitatively similar binding of wt and mutant protein with the anti-His Mab. Notably, the L268N mutant protein consistently runs faster than expected (Figure S2a), suggesting that this mutation induces gD to adopt a more compact shape, similar to that of cys2 protein (Figure S1a). Second, we used SPR to determine the possible epitope alterations of the L268N mutant compared to that of wt gD. For this, wt gD and L268N mutant proteins were each presented via an anti-His Mab covalently bound to the chip. Non-competing sentinel antibodies from each community were then flowed sequentially over the chip. Wt and L268N gD proteins were tested in both the shorter (285t) and longer (306t) configurations. Similar to our findings with full-length proteins by CELISA (Figure 5a), we saw that except for MC14, soluble wt and mutant gD proteins bound each Mab with similar kinetics (Figure S2c). This confirms that the mutant gD protein is antigenically correct and that the L268N mutation introduces local changes that affect the MC14 binding only.
3.8. gD L268N Mutant Does Not Bind gH/gL
To determine whether the L268N mutation directly affected conformational changes necessary for nectin-1 binding or instead affected the subsequent gD–gH/gL interaction, we used SPR. First, similar amounts of the wt and mutant gD proteins were immobilized on the chip surface. Then, soluble nectin-1 was added, followed by soluble gH/gL (Figure 6a). Both wt gD306t and gDL268N306t bound nectin-1 (Figure 6b) albeit with different efficiencies (L268N bound nectin-1 ~50% of wt). After soluble gH/gL was flowed over the chip, only wt gD showed an increase in RUs (indicative of gH/gL binding) (Figure 6c, blue curve); mutant L268N306t did not bind gH/gL (cyan).
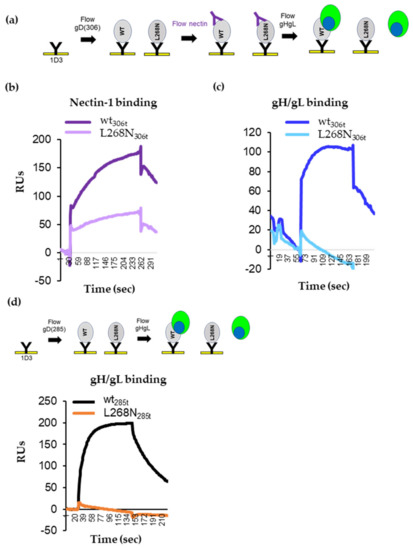
Figure 6.
Ability of gD L268N to bind gH/gL. (a) Diagram of the Biacore 3000 protocol for analyzing the binding of gH/gL to a gD-receptor complex. gD molecules, wt, or L268N, both as 306t truncations were attached to the biosensor chip via 1D3 Mab. Sequential injection of nectin-1 followed by injection of soluble gH/gL. (b) Nectin-1 binds to both wt (purple) and L268N (pink) gD proteins. (c) gH/gL was flowed over the gD-nectin-1 complexes. gH/gL bound to wt gD (blue) but not to L268N mutant gD (cyan). (d) Diagram of the SPR protocol for analyzing gH/gL binding to gD285t, wt, or the L268N mutant. Only the gH/gL binding curves are shown. gH/L binds to wt gD (black curve). No gH/gL binding was observed for the L268N mutant (orange curve).
Second, we looked at the binding of gH/gL to the open 285t truncation forms. Wt and L268N gD were captured by the 1D3 Mab anti-gD Mab that was covalently coupled to the surface of the chip. Then, soluble gH/gL was flowed over the chip. As expected from our previous studies (Figure 2b and [5,6]), wt gD285t bound efficiently to gH/gL (the black curve in Figure 6d). In contrast, gD L268N285t failed to bind gH/gL (orange curve).
Together, these results suggested that although wt and mutant gD were antigenically similar and could move the C-term to expose residues important for nectin-1 receptor binding, the conformational changes in L268N were not sufficient to allow binding to gH/gL.
We propose that the L268N mutation is essential for gD–gH/gL interactions by either directly affecting the gD–gH/gL interface or indirectly restricting the movement of the gD C-term. We hypothesize that there are multiple inflection points within the C-term of gD and that residue 268 acts as a fulcrum point that prevents specific, local conformational changes that restrict access to the gH/gL binding site 3 by introducing a rigidity in the C-term of gD (intermediate 2 in Figure 7), much like the disulfide bond in the cys2 gD mutant.
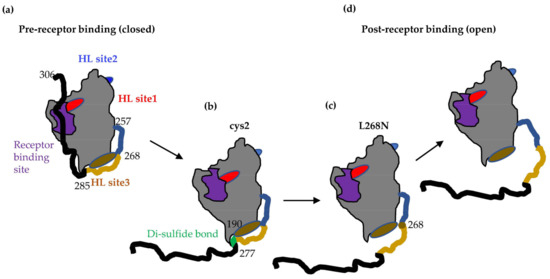
Figure 7.
Proposed intermediates for the transition of gD from a pre-receptor (closed) to post-receptor binding state (open). (a) Before binding to a receptor, gD is in a closed conformation, with the receptor binding site (purple) covered by the C-term (black). The three gH/gL binding sites are also shown in red (site 1), blue (site 2), and brown (site 3). (b) In the presence of receptor or antibodies that compete with the receptor for binding, the C-term is displaced to expose the receptor binding site. Residue 277 is one inflection point in the C-term that is sufficient for receptor binding, but not gH/gL interaction. (c) Access to gH/gL binding site 3 (brown) is controlled by a second inflection point at position 268. Mutagenesis of this residue results in a molecule that partially exposes the gH/gL site 3. (d) After opening of gD past residue 268, gD is in a fully open conformation that can bind gH/gL.
4. Discussion
HSV viral entry begins with the binding of gD to one of its cellular receptors and ends with the fusion of the two membranes mediated by the fusogen gB. While conformational changes in HSV gD were thought to be required for the initiation and execution of virus entry, supporting evidence was based on crystal structures and many presumed steps based on similarities with other viruses. In this study, we provide essential insight into the conformational changes that the HSV viral-entry glycoprotein gD undergoes following initial binding to nectin-1 that promote physical interaction with the modulator of fusion, gH/gL to promote fusion.
In the absence of its receptors, gD adopts a closed conformation (Figure 7a) in which the C-terminal region (residues 285–306) is anchored by Trp294 and contacts the N-terminal region (23–27). In this conformation, the C-term of gD covers the nectin-1 binding site and occupies the same space as the gD N-terminal residues in the gD-HVEM complex. As a result, the formation of either nectin-1-gD [41] or HVEM-gD complexes [2] requires similar conformational changes [8], with displacement of residues from the gD C-terminal region. This conformational change was hypothesized to serve as a signal to trigger the fusion cascade, as binding of gD to receptor would not only bring the viral and cellular membranes in close proximity but would also expose regions of gD that permit recruitment of gH/gL and/or gB, thus permitting fusion. The flexible, proline-rich C-terminal region of gD (260–285) was termed “the profusion domain” [9] and contains linear epitopes recognized by Mabs from the brown community (Figure 1a) that block viral spread and cell–cell fusion [7,16] and define one of the three gH/gL binding sites on gD [6].
The physical interaction between gD and gH/gL only occurs with the open form of gD (gD285t) ([5,6] and Figure 2b). As a longer gD truncation (gD306t/closed conformation), does not bind gH/gL, it suggests that the presence of a longer C-term interferes with gH/gL binding (Figure 2b). However, in the presence of nectin-1, the C-term of gD is displaced, which then allows for gH/gL to bind (Figure 2d). Thus, while the movement of gD C-term is necessary for receptor binding [2,8], it may also be required for physical interaction with gH/gL.
Notably, we find that a partial opening of gD that allows for nectin-1 binding is not sufficient to accommodate binding to gH/gL. Indeed, gD molecules that carry mutations at Trp294 or a linker insertion (∇290–299) are impaired in promoting virus entry and complement virus entry at levels of about 10% of wt, despite a more flexible C-term and an increased affinity for receptors [8,33,46,47]. The requirement for a full opening of gD is further exemplified by the gD cys2 mutant presented here. When the C-term is locked to the core of gD by the introduction of a disulfide bond (Figure 7b), gD does not complement the virus, does not trigger cell–cell fusion (Ref. [15] and Figure 3b), and does not bind gH/gL (Figure 4e), despite the ability of nectin-1 to displace the C-term and access the binding site (Ref. [15] and Figure 4d). Removal of the lock in the presence of reducing agents restores gH/gL binding and converts gD to a fully functional molecule (Figure 3d, and Figure 4h). This demonstrates that the opening of the C-term needs to be wide enough to minimally expose the region locked by the disulfide (past residue 277) and that the movement exposes a region in gD essential for the gH/gL interaction.
A portion of gD upstream of the cys2 disulfide bond is missing from all the crystal structures available, suggesting a high degree of flexibility in this region. It was hypothesized that this region (256–268) could potentially serve as a hinge that moves in response to receptor binding [15]. Mutagenesis in the 262–275 region identified residue L268 as playing an important role in the function of gD. The full-length version of the mutant gD was only impaired in fusion. However, the truncated versions resembled the cys2 mutant in that they were unable to physically bind gH/gL or trigger cell–cell fusion (Figure 5b and Figure 6c) despite displacement of C-term by nectin-1 binding (Figure 6b). However, while the open conformation of wt gD285t allows it to bind gH/gL even in the absence of a receptor [5,6], gD-L268N(285t) was surprisingly unable to bind gH/gL (Figure 6d). This suggests that substitution of Leu268, which is located in the gH/gL binding site 3, is either: (1) essential for the gD–gH/gL interaction; or (2) induces conformational changes necessary for the gH/gL binding. Preliminary data suggest that the main limitation observed with gD-L268N is a decreased mobility of the C-term that results in an occlusion of gH/gL binding site 3 (Figure 7c).
We have also shown that movement of C-term of gD306t can occur not only in the presence of nectin-1 [2,8], but can also be driven by specific Mabs. A consequence of this movement is to increase the affinity of gD306t for receptors to levels similar to those measured for the open gD285t [6,29,34], and to increase binding of gH/gL to gD306t. (Figure 7d). Preliminary data suggest that MC2 can move the C-term of gDL268N306t sufficiently to increase binding of MC14 Mab (located in gH/gL binding site 3) but does not allow for gH/gL to bind.
We propose that the high degree of flexibility of region 257–267 is related to gD function and that Leu268 serves as in inflexion point in this region. Changes at this position reduce the flexibility of gD C-term and prevent conformational changes that allow for gH/gL binding. This suggests that although gH/gL binding site 3 was defined by Mabs that block this interaction (brown community, Figure 1b), these Mabs do not block the gD–gH/gL interaction directly, but rather prevent further conformational changes that would allow access to gH/gL site 3. While Mabs from the brown community do not neutralize the virus, they do block the virus spread of the cell–cell fusion and provide significant protection against herpes disease in animal models [48], highlighting the potential physiologic requirement of gD movement in HSV disease.
We conclude that the unravelling of C-term from the core of gD, beginning with Trp294 and extending all the way to Ala277, is sufficient for receptor binding [8,15]. However, further opening of gD beyond Leu268 is necessary to trigger fusion and allow full access to the gH/gL binding site 3. This study not only brings experimental proof for the conformational changes that occur in gD and are necessary for function, but also offers new targets for vaccine design and therapies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v15040895/s1, Figure S1: Characterization of cys2 soluble protein. Figure S2: Characterization of soluble gD L268N.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A., R.J.E., G.H.C.; methodology D.A., T.M.C., W.T.S.; validation, D.A., W.T.S.; formal analysis, D.A., T.M.C., G.H.C.; data curation, D.A., W.T.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.A.; writing—review and editing, D.A., T.M.C., W.T.S., H.M.F., G.H.C.; funding acquisition, H.M.F., G.H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health grant AI-18289 (G.H.C) and AI-139618 (G.H.C., H.M.F.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the members of our laboratory, past and present, for helpful advice and generation of reagents. We thank Leslie King, School of Veterinary Medicine for editorial input.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Spear, P.G.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Three classes of cell surface receptors for alphaherpesvirus entry. Virology 2000, 275, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carfi, A.; Willis, S.H.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Wiley, D.C. Herpes simplex virus glyco-protein D bound to the human receptor HveA. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.A.; Landsburg, D.J.; Carfi, A.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Zuo, Y.; Wiley, D.C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Potential nectin-1 binding site on herpes simplex virus glycoprotein d. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.; Zago, A.; Shukla, D.; Spear, P.G. Mutations in the N termini of herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 gDs alter functional interactions with the entry/fusion receptors HVEM, nectin-2, and 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate but not with nectin-1. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9221–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, T.M.; Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Lou, H.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Ditto, N.T.; Bruun, B.; Browne, H.; Bennett, L.; Wu, C.; et al. Localization of the Interaction Site of Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein D (gD) on the Membrane Fusion Regulator, gH/gL. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00983-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, T.M.; Ditto, N.T.; Atanasiu, D.; Lou, H.; Brooks, B.D.; Saw, W.T.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Surface Plasmon Resonance Reveals Direct Binding of Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoproteins gH/gL to gD and Locates a gH/gL Binding Site on gD. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00289-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Cairns, T.M.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Using Split Luciferase Assay and anti-HSV Glycoprotein Monoclonal Antibodies to Predict a Functional Binding Site between gD and gH/gL. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00053-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenacher, C.; Supekar, V.M.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Lazear, E.; Connolly, S.A.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; Wiley, D.C.; Carfí, A. Structure of unliganded HSV gD reveals a mechanism for receptor-mediated activation of virus entry. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 4144–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchi, F.; Fusco, D.; Menotti, L.; Gianni, T.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. The soluble ectodomain of herpes simplex virus gD contains a membrane-proximal pro-fusion domain and suffices to mediate virus entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7445–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, A.; Jogger, C.R.; Spear, P.G. Use of herpes simplex virus and pseudorabies virus chimeric glycoprotein D molecules to identify regions critical for membrane fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17498–17503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Longnecker, R.; Connolly, S.A. Substitution of herpes simplex virus 1 entry glycoproteins with those of saimiriine herpesvirus 1 reveals a gD-gH/gL functional interaction and a region within the gD profusion domain that is critical for fusion. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6470–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, T.M.; Connolly, S.A. Entry of Alphaherpesviruses. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 41, 63–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. The structural basis of herpesvirus entry. Nat. Reviews. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, R.J.; Atanasiu, D.; Cairns, T.M.; Gallagher, J.R.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H. Herpes virus fusion and entry: A story with many characters. Viruses 2012, 4, 800–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, E.; Carfi, A.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Cairns, T.M.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Engineered disulfide bonds in herpes simplex virus type 1 gD separate receptor binding from fusion initiation and viral entry. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, L.M.; Cairns, T.M.; Awasthi, S.; Brooks, B.D.; Ditto, N.T.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; Friedman, H.M. Vaccine-induced antibodies to herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D epitopes involved in virus entry and cell-to-cell spread correlate with pro-tection against genital disease in guinea pigs. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, R.D.; Pereira, L.; Baringer, J.R. Use of monoclonal antibody directed against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins to protect mice against acute virus-induced neurological disease. Infect. Immun. 1981, 34, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.G.; Krummenacher, C.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; Fraser, N.W. Development of a syngenic murine B16 cell line-derived melanoma susceptible to destruction by neuroattenuated HSV-1. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertel, P.E. Human herpesvirus 8 glycoprotein B (gB), gH, and gL can mediate cell fusion. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4390–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, T.M.; Milne, R.S.; Ponce-de-Leon, M.; Tobin, D.K.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Structure-function analysis of herpes simplex virus type 1 gD and gH-gL: Clues from gDgH chimeras. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6731–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, T.M.; Friedman, L.S.; Lou, H.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Shaner, M.S.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. N-terminal mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2 gH are transported without gL but require gL for function. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5102–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Meng, F.; Kondo, N.; Iwamoto, A.; Matsuda, Z. Generation of a dual-functional split-reporter protein for moni-toring membrane fusion using self-associating split GFP. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2012, 25, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenacher, C.; Nicola, A.V.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Lou, H.; Hou, W.; Lambris, J.D.; Geraghty, R.J.; Spear, P.G.; Cohen, G.H.; Ei-senberg, R.J. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D can bind to poliovirus receptor-related protein 1 or herpesvirus entry medi-ator, two structurally unrelated mediators of virus entry. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7064–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, B.P.; Cairns, T.M.; Bender, F.C.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Lou, H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B associates with target membranes via its fusion loops. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6825–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisk, W.P.; Bradley, J.D.; Leipold, R.J.; Stoltzfus, A.M.; Ponce de Leon, M.; Hilf, M.; Peng, C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. High-level expression and purification of secreted forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gD synthesized by baculovirus-infected insect cells. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rux, A.H.; Willis, S.H.; Nicola, A.V.; Hou, W.; Peng, C.; Lou, H.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Functional region IV of glycopro-tein D from herpes simplex virus modulates glycoprotein binding to the herpesvirus entry mediator. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7091–7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, R.J.; Ponce de Leon, M.; Pereira, L.; Long, D.; Cohen, G.H. Purification of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by use of monoclonal antibody. J. Virol. 1982, 41, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, R.J.; Long, D.; Ponce de Leon, M.; Matthews, J.T.; Spear, P.G.; Gibson, M.G.; Lasky, L.A.; Berman, P.; Golub, E.; Cohen, G.H. Localization of epitopes of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. J. Virol. 1985, 53, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, E.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Ponce-de-Leon, M.; Cairns, T.M.; Willis, S.H.; Zuo, Y.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Antibody-induced conformational changes in herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gD reveal new targets for virus neutrali-zation. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Gallagher, J.R.; Hannah, B.P.; Matsuda, Z.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Dual Split Pro-tein-Based Fusion Assay Reveals that Mutations to Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Glycoprotein gB Alter the Kinetics of Cell-Cell Fusion Induced by HSV Entry Glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11332–11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, W.T.; Matsuda, Z.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; Atanasiu, D. Using a split luciferase assay (SLA) to measure the kinetics of cell-cell fusion mediated by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Methods 2015, 90, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.H.; Isola, V.J.; Kuhns, J.; Berman, P.W.; Eisenberg, R.J. Localization of discontinuous epitopes of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D: Use of a nondenaturing (“native” gel) system of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis coupled with Western blot-ting. J. Virol. 1986, 60, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krummenacher, C.; Baribaud, I.; Ponce de Leon, M.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Lou, H.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Localization of a binding site for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D on herpesvirus entry mediator C by using antireceptor monoclonal anti-bodies. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10863–10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, T.M.; Ditto, N.T.; Lou, H.; Brooks, B.D.; Atanasiu, D.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Global sensing of the antigenic struc-ture of herpes simplex virus gD using high-throughput array-based SPR imaging. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Regulation of HSV glycoprotein induced cascade of events governing cell-cell fusion. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 10535–10544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratnarajah, C.K.; Kumar, S.; Generous, A.; Apte-Sengupta, S.; Mateo, M.; Cattaneo, R. The measles virus hemagglutinin stalk: Structures and functions of the central fusion activation and membrane-proximal segments. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6158–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratnarajah, C.K.; Negi, S.; Braun, W.; Cattaneo, R. Membrane fusion triggering: Three modules with different structure and function in the upper half of the measles virus attachment protein stalk. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38543–38551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, D.J.; Redding, S.E.; Brohawn, S.G.; Psathas, J.N.; Schneider, J.P.; Thorpe, C. New water-soluble phosphines as reductants of peptide and protein disulfide bonds: Reactivity and membrane permeability. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 15195–15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Wilcox, W.C.; Abrams, W.R.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Disulfide bond structure of glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6668–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, W.C.; Long, D.; Sodora, D.L.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. The contribution of cysteine residues to antigenicity and extent of processing of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovine, P.; Settembre, E.C.; Bhargava, A.K.; Luftig, M.A.; Lou, H.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Krummenacher, C.; Carfi, A. Structure of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D bound to the human receptor nectin-1. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, V.J.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Siebert, G.R.; Heilman, C.J.; Wilcox, W.C.; Cohen, G.H. Fine mapping of antigenic site II of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, R.J.; Cerini, C.P.; Heilman, C.J.; Joseph, A.D.; Dietzschold, B.; Golub, E.; Long, D.; Ponce de Leon, M.; Cohen, G.H. Synthetic glycoprotein D-related peptides protect mice against herpes simplex virus challenge. J. Virol. 1985, 56, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heber-Katz, E.; Dietzschold, B. Immune response to synthetic herpes simplex virus peptides: The feasibility of a synthetic vac-cine. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1986, 130, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Lazear, E.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Cairns, T.M.; Lou, H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Using Antibodies and Mutants To Localize the Presumptive gH/gL Binding Site on Herpes Simplex Virus gD. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01694-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.Y.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Identification of functional regions of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gD by using linker-insertion mutagenesis. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 2529–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, R.S.; Hanna, S.L.; Rux, A.H.; Willis, S.H.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Function of herpes simplex virus type 1 gD mutants with different receptor-binding affinities in virus entry and fusion. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8962–8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, S.T.; Piacente, P.; Silva, J.; Mishkin, E.M. IgG subtype is correlated with efficiency of passive protection and effector function of anti-herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D monoclonal antibodies. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).