Virtual Screening-Based Peptides Targeting Spike Protein to Inhibit Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Biological Materials
2.3. Analysis of the S1-CTD Amino Acid Sequence of PEDV
2.4. Molecular Docking Virtual Screening
2.5. ELISA Assay for Affinity and Specificity
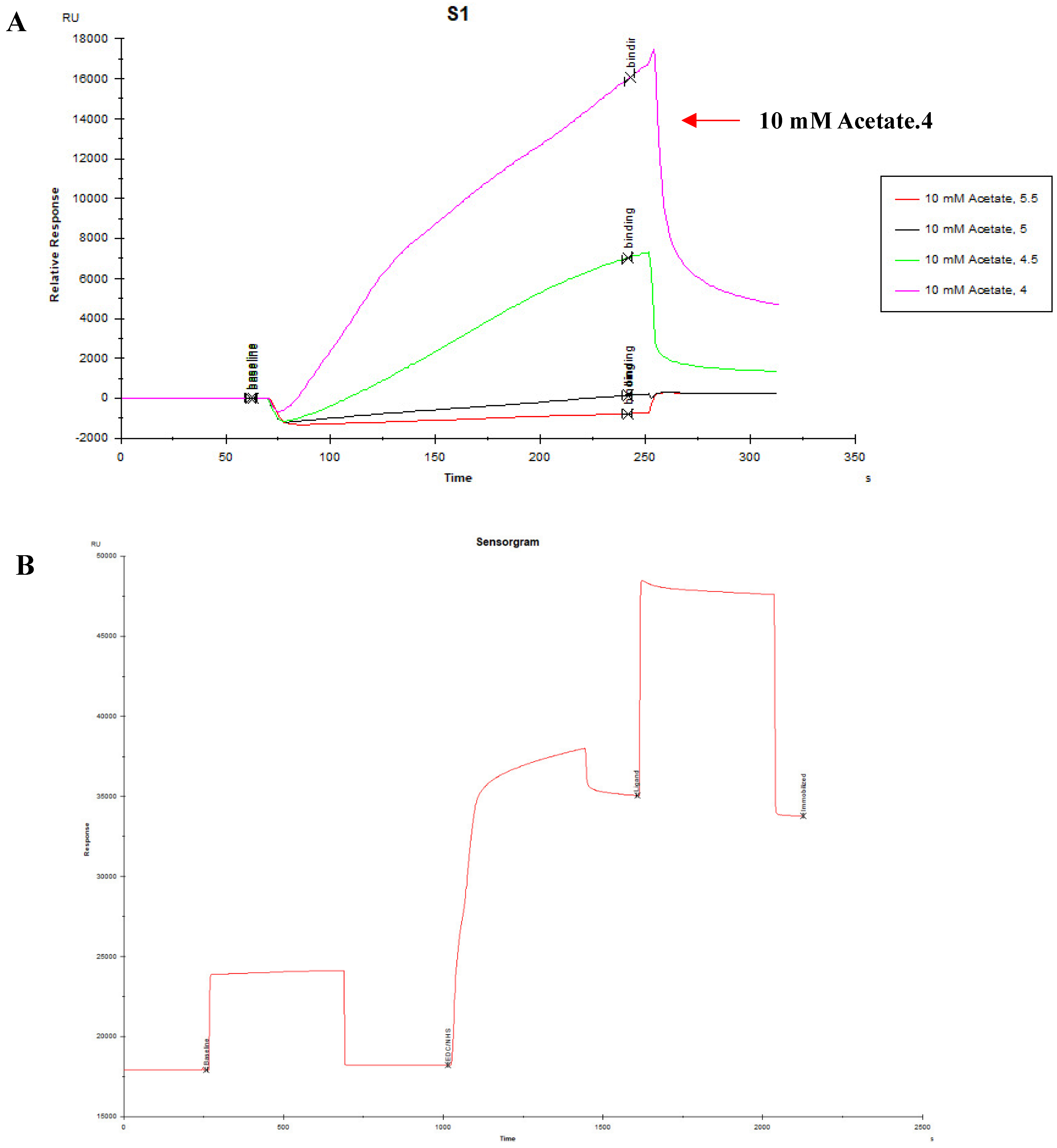
2.6. Kinetic Dissociation Measurements
2.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. Absolute Quantification Real-Time PCR Assay
2.9. Western Blot Assay
2.10. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Design and Synthesis of Peptides
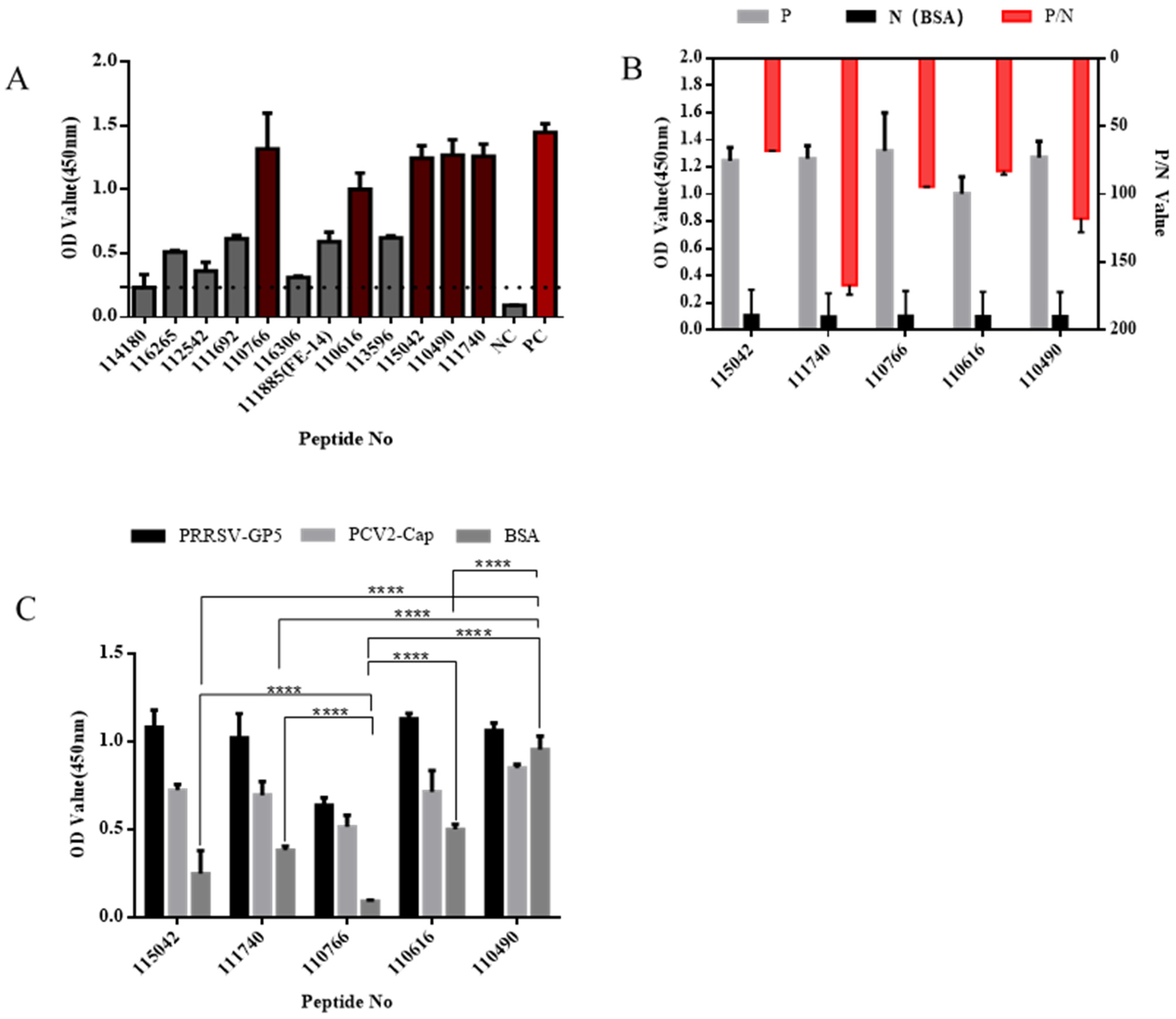
3.2. Affinity and Specificity Analysis of Peptides by ELISA
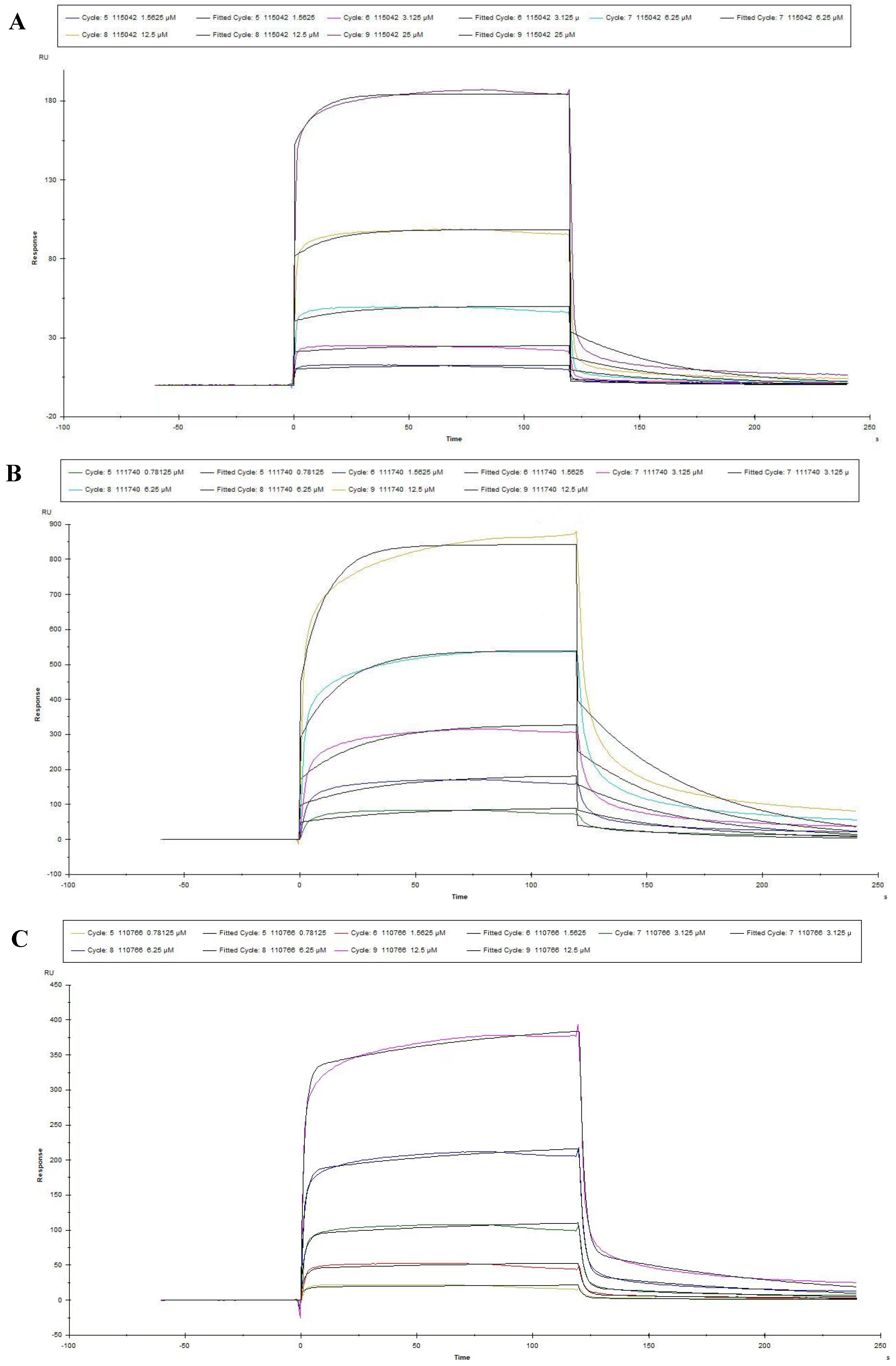
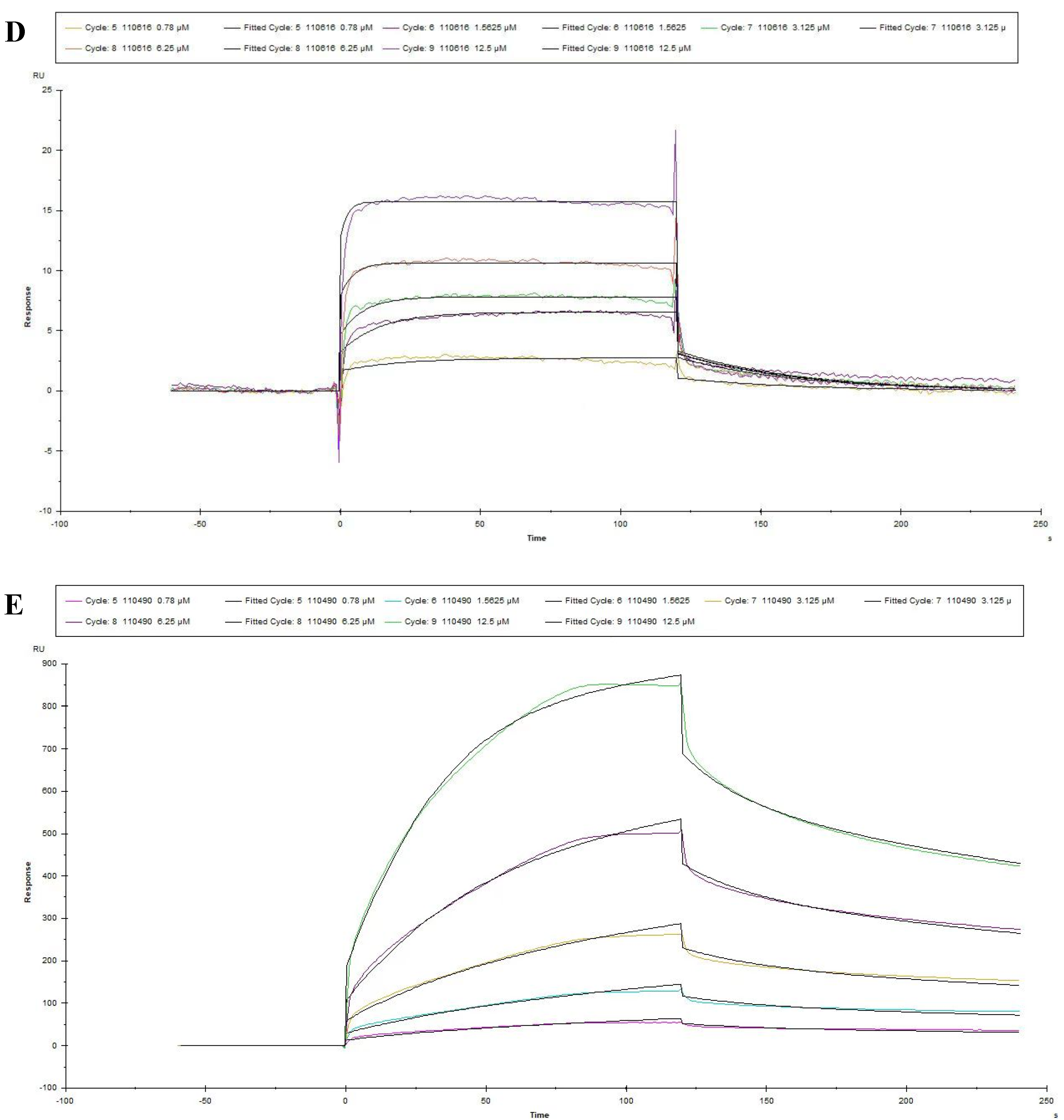
3.3. Measures for the KD Values of Peptides by SPR
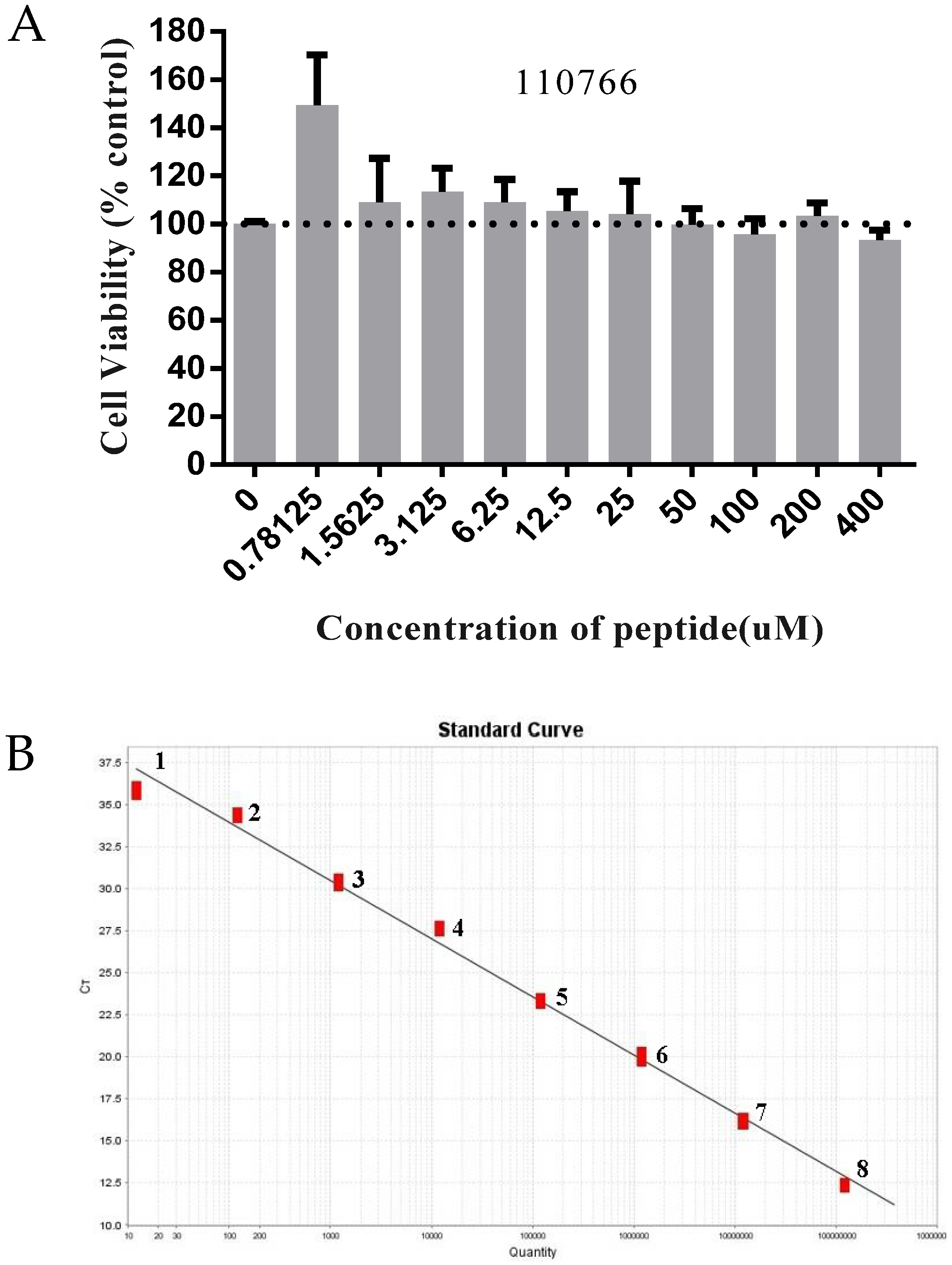
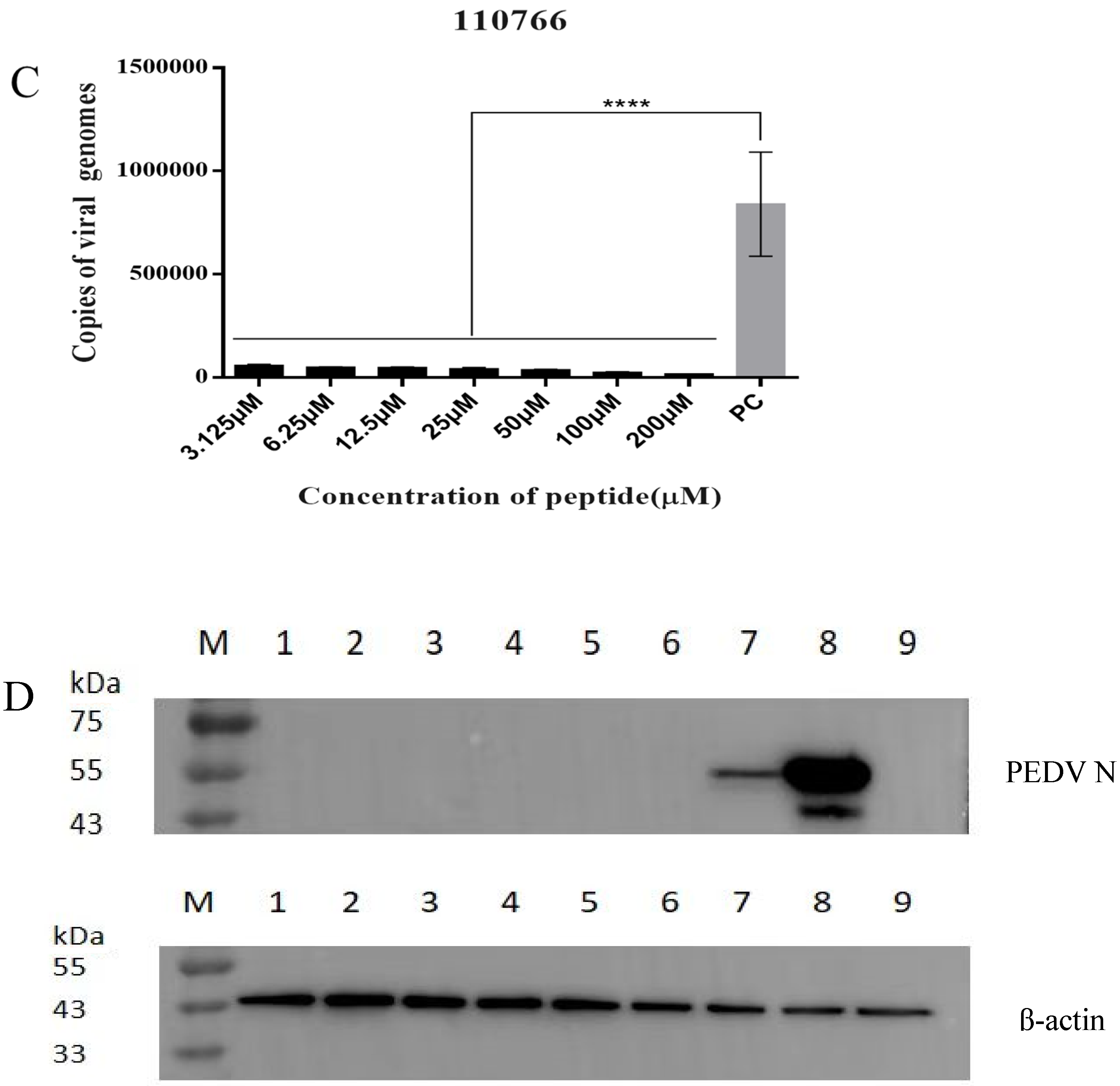
3.4. The Inhibitory Effect of 110766 against HB-PEDV Strain
3.4.1. Cytotoxicity Test
3.4.2. Absolute Quantification Real-Time PCR
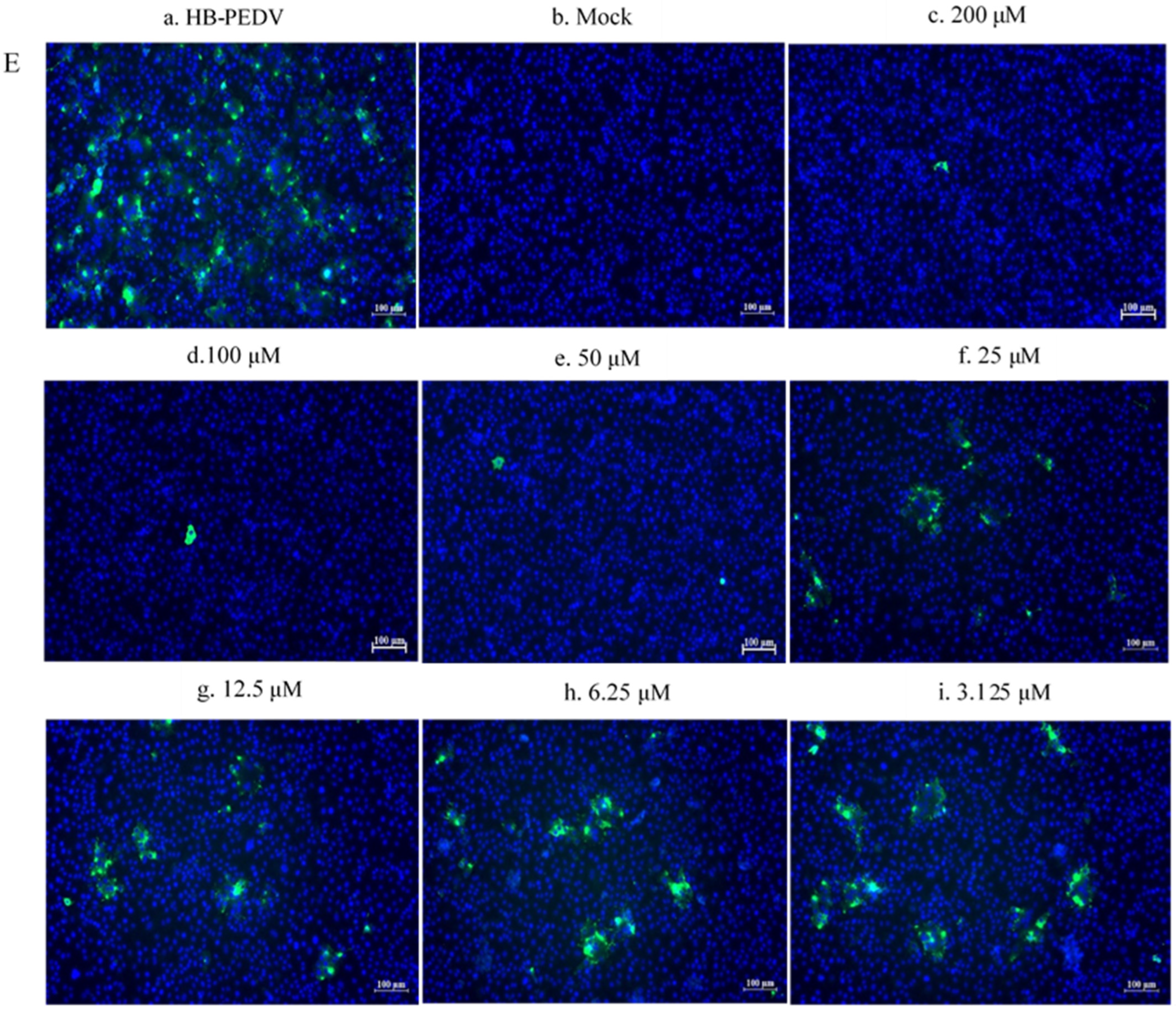
3.4.3. Western Blot and Immunofluorescence Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pensaert, M.B.; de Bouck, P. A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch. Virol. 1978, 58, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Qiu, H.J.; Liu, S.; Shi, D.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L. Complete genome sequence of a Chinese virulent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11538–11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhu, J.P.; Tong, W.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Y.F.; Tong, G.Z. Complete genome sequence of a virulent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.W.; Dickerman, A.W.; Pineyro, P.; Li, L.; Fang, L.; Kiehne, R.; Opriessnig, T.; Meng, X.J. Origin, evolution, and genotyping of emergent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains in the United States. MBio 2013, 4, e00737-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojkic, D.; Hazlett, M.; Fairles, J.; Marom, A.; Slavic, D.; Maxie, G.; Alexandersen, S.; Pasick, J.; Alsop, J.; Burlatschenko, S. The first case of porcine epidemic diarrhea in Canada. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 2015, 56, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Dastjerdi, A.; Carr, J.; Ellis, R.J.; Steinbach, F.; Williamson, S. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus among Farmed Pigs, Ukraine. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2235–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, J.R.; Hakze-van der Honing, R.; Almeida, A.; Lourenco, M.; van der Poel, W.H.; Nascimento, M.S. Outbreak of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in Portugal, 2015. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Park, B. Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus: A comprehensive review of molecular epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccines. Virus Genes 2012, 44, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor. Science 2005, 309, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, R.; He, Q.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Bosch, B.J. Aminopeptidase N is not required for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus cell entry. Virus Res. 2017, 235, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewska, A.; Zarebski, M.; Nowak, P.; Stozek, K.; Potempa, J.; Pyrc, K. Human coronavirus NL63 utilizes heparan sulfate proteoglycans for attachment to target cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13221–13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Shi, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Tong, P.; Guo, D.; Fu, L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Structure of MERS-CoV spike receptor-binding domain complexed with human receptor DPP4. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Li, W.; Peng, G.; Li, F. Crystal structure of NL63 respiratory coronavirus receptor-binding domain complexed with its human receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19970–19974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.F.N.; Amaral, J.L.; Bezerra, L.P.; Lopes, F.E.S.; Freire, V.N.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Freitas, C.D.T. ACE2-derived peptides interact with the RBD domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, disrupting the interaction with the human ACE2 receptor. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 5493–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boohaker, R.J.; Lee, M.W.; Vishnubhotla, P.; Perez, J.M.; Khaled, A.R. The use of therapeutic peptides to target and to kill cancer cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3794–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, P.E.; Song, E.W. Phage display screening of therapeutic peptide for cancer targeting and therapy. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 787–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, F.; Li, N.; Xing, G.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S.; Cui, N.; Zhang, G. An antigen display system of GEM nanoparticles based on affinity peptide ligands. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193 Pt A, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuriev, E.; Ramsland, P.A. Latest developments in molecular docking: 2010-2011 in review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinberg, C.E.; Khare, S.D.; Dou, J.; Doyle, L.; Nelson, J.W.; Schena, A.; Jankowski, W.; Kalodimos, C.G.; Johnsson, K.; Stoddard, B.L.; et al. Computational design of ligand-binding proteins with high affinity and selectivity. Nature 2013, 501, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammond, D.W.; Bosch, D.E.; Butterfoss, G.L.; Purbeck, C.; Machius, M.; Siderovski, D.P.; Kuhlman, B. Computational design of the sequence and structure of a protein-binding peptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4190–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hao, J.; Li, N.; Xing, G.; Hu, M.; Zhang, G. Integrated System for Purification and Assembly of PCV Cap Nano Vaccine Based on Targeting Peptide Ligand. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8507–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yu, Q.; Hu, M.; Xing, G.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, G. Purification of Classical Swine Fever Virus E2 Subunit Vaccines Based on High Affinity Peptide Ligand. Protein Pept. Lett. 2021, 28, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrapp, D.; McLellan, J.A.-O.X. The 3.1-Angstrom Cryo-electron Microscopy Structure of the Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Spike Protein in the Prefusion Conformation. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00923-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Wang, F.; Xing, G.; Liu, Y.; Deng, R.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, A.; Zhang, G. Design and preliminary application of affinity peptide based on the structure of the porcine circovirus type II Capsid (PCV2 Cap). PeerJ 2019, 7, e8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Song, D.S.; Park, B.K. Differential detection of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus by duplex RT-PCR. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2001, 13, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qi, J.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Bao, J.; et al. Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26. Nature 2013, 500, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.S.; Mou, H.; Smits, S.L.; Dekkers, D.H.; Muller, M.A.; Dijkman, R.; Muth, D.; Demmers, J.A.; Zaki, A.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013, 495, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.H.M.; Tomlinson, A.C.A.; Zhou, D.; Satkunarajah, M.; Chen, K.; Sharon, C.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J.; Rini, J.M. Receptor-binding loops in alphacoronavirus adaptation and evolution. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, C.L.; Ashmun, R.A.; Williams, R.K.; Cardellichio, C.B.; Shapiro, L.H.; Look, A.T.; Holmes, K.V. Human aminopeptidase N is a receptor for human coronavirus 229E. Nature 1992, 357, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, B.; Gelfi, J.; L’Haridon, R.; Vogel, L.K.; Sjöström, H.; Norén, O.; Laude, H. Aminopeptidase N is a major receptor for the entero-pathogenic coronavirus TGEV. Nature 1992, 357, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, J.; Santiago, C.; Mudgal, G.; Ordoño, D.; Enjuanes, L.; Casasnovas, J.M. Structural bases of coronavirus attachment to host aminopeptidase N and its inhibition by neutralizing antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Ye, G.; Liu, Q.; Navid, M.T.; Zhong, X.; Li, Y.; Wan, C.; Xiao, S.; He, Q.; Fu, Z.F.; et al. Identification and Comparison of Receptor Binding Characteristics of the Spike Protein of Two Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Strains. Viruses 2016, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirato, K.; Maejima, M.; Islam, M.T.; Miyazaki, A.; Kawase, M.; Matsuyama, S.; Taguchi, F. Porcine aminopeptidase N is not a cellular receptor of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, but promotes its infectivity via aminopeptidase activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2528–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Xiang, R.; Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z.; Tian, S.; Liang, R.; Li, Y.; Ying, T.; Jiang, S. Receptor-binding domain-specific human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marqus, S.; Pirogova, E.; Piva, T.J. Evaluation of the use of therapeutic peptides for cancer treatment. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thundimadathil, J. Cancer treatment using peptides: Current therapies and future prospects. J. Amino Acids 2012, 2012, 967347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiao, F.; Lu, L.; Xia, S.; Jiang, S. Pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors to combat COVID-19 and other emerging coronavirus infectious diseases. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2022, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, B.; Ji, C.M.; Cong, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.W. Identification of a peptide derived from the heptad repeat 2 region of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) spike glycoprotein that is capable of suppressing PEDV entry and inducing neutralizing antibodies. Antivir. Res. 2018, 150, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
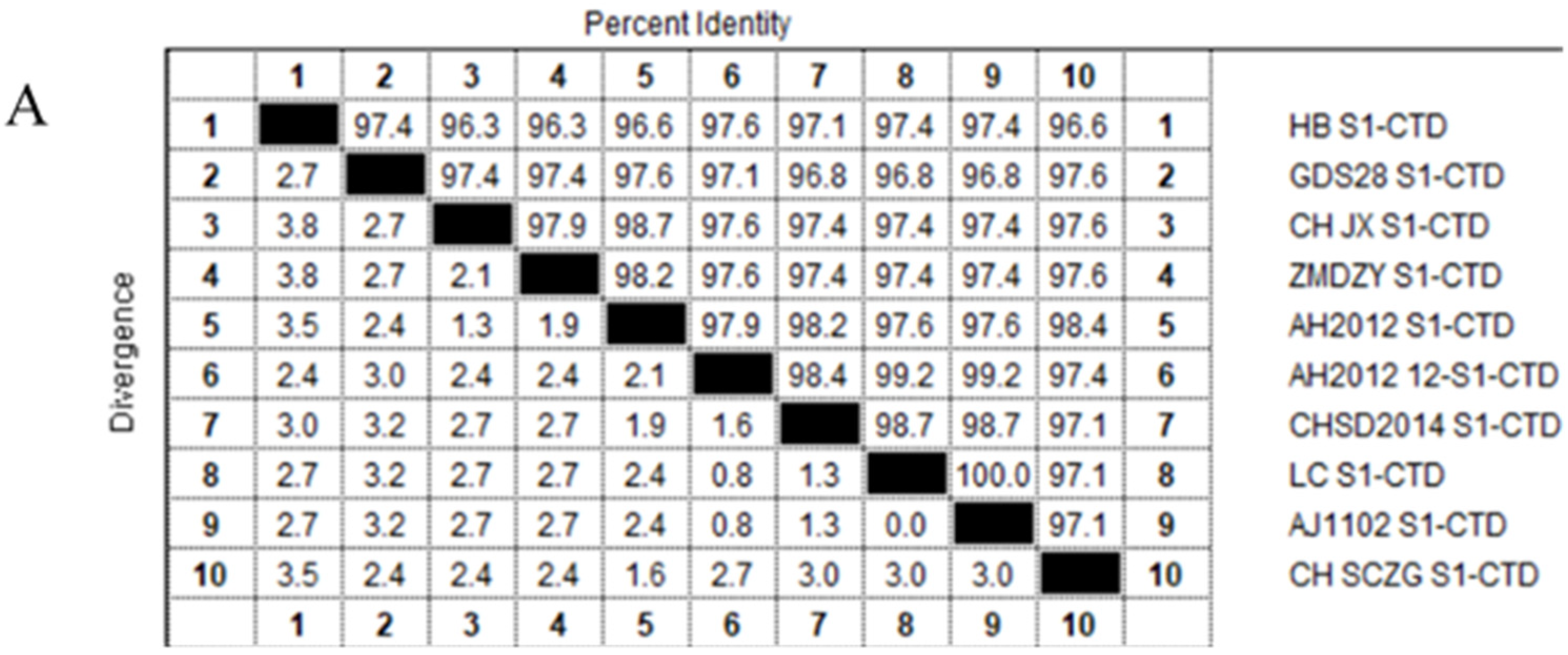

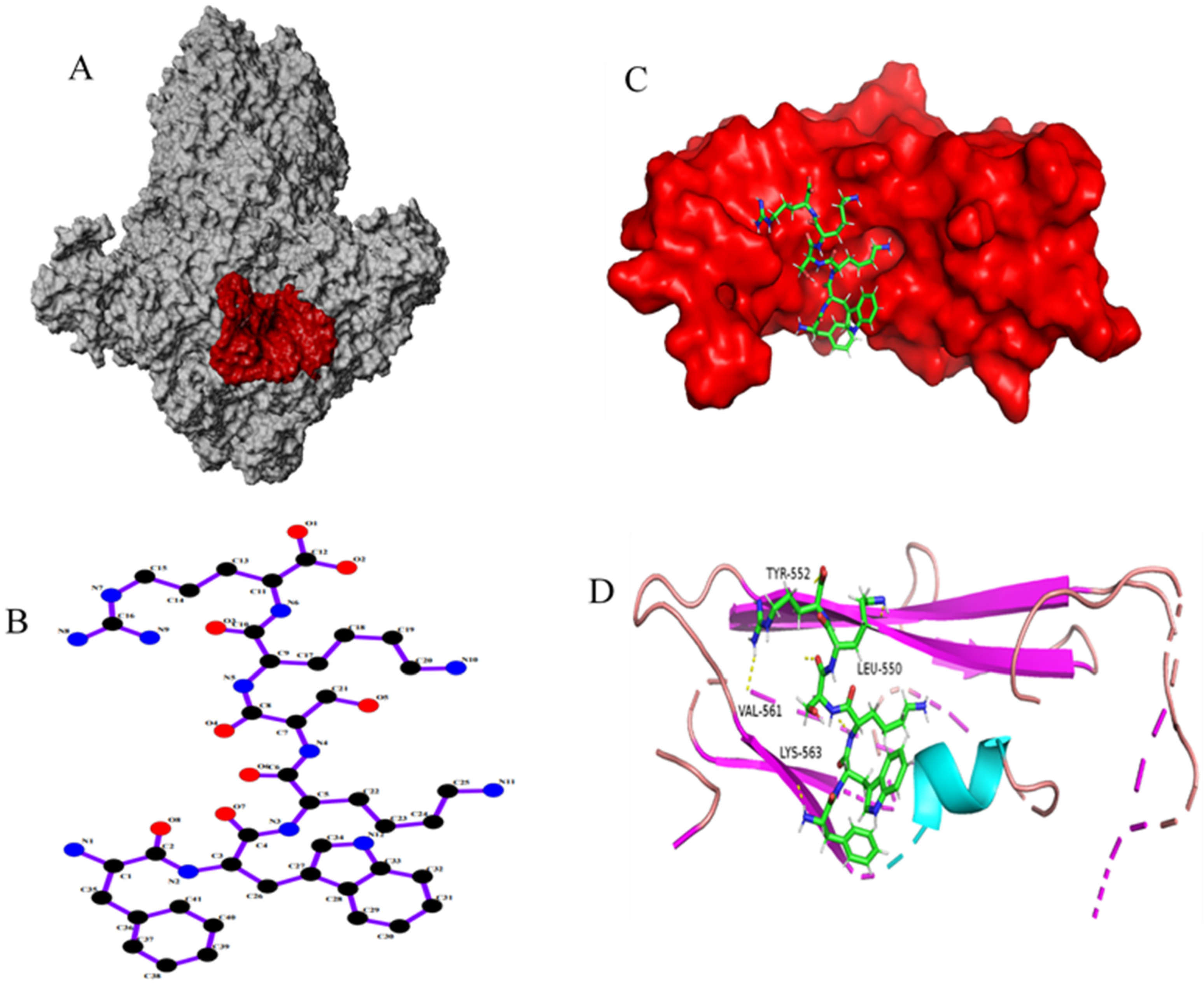
| Strain Name | Countries | Time | Type | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB | China | 2016 | G2b | KY928065.1 |
| GDS28 | China | None | G2a | MH726372.1 |
| CH JX | China | 2015 | G2a | KJ526096.1 |
| ZMDZY | China | 2011 | G2a | KC196276.1 |
| AH2012 | China | 2012 | G2a | KC210145 |
| AH2012-12 | China | 2012 | G2b | KU646831.1 |
| CHSD2014 | China | 2014 | G2b | KX791060.1 |
| LC | China | 2012 | G2b | JX489155.1 |
| AJ1102 | China | 2011 | G2b | JX188454.1 |
| CH SGZG | China | 2017 | G2b | MH061337 |
| Peptide NO | Amino Acid Sequence | CScore | Crash | Polar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 114180 | FWKPKR | 11.4180 | −3.2727 | 6.5323 |
| 116265 | FWKPDQ | 11.6265 | −3.0837 | 10.3922 |
| 112542 | FWKHEK | 11.2542 | −3.1835 | 10.0943 |
| 111692 | KHQKRC | 11.1692 | −3.1609 | 8.7458 |
| 110766 | FWKSKR | 11.0766 | −2.8652 | 5.9879 |
| 116306 | RKQFDK | 11.6036 | −2.4966 | 12.7206 |
| 111885 | FWKYAW | 11.1885 | −3.5336 | 6.9276 |
| 110616 | FWKEAK | 11.0616 | −2.8072 | 7.1044 |
| 113596 | FWKCDV | 11.3596 | −3.8652 | 9.0346 |
| 115042 | WHFNRP | 11.5042 | −3.0164 | 8.1665 |
| 110490 | FWKQNKFLFWKQNKCL | 11.0490 | −4.2913 | 11.9966 |
| 111740 | FWKHRIFWKHRI | 11.1740 | −3.9744 | 9.8984 |
| Peptide No. | Ka (1/Ms) | Kd (1/s) | KD (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 115042 | 3454 | 0.02252 | 6.518 × 10−6 |
| 111740 | 5482 | 0.01975 | 3.603 × 10−6 |
| 110766 | 7.055 × 104 | 0.01523 | 2.159 × 10−7 |
| 110616 | 3.050 × 104 | 0.02355 | 7.721 × 10−7 |
| 110490 | 5743 | 0.03522 | 1.495 × 10−6 |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| N-F | CGCAAAGACTGAACCCACTAAC |
| N-R | TTGCCTCTGTTGTTACTTGGAGAT |
| PEDV N probe | TGTTGCCATTACCACGACTCCTGC 5′fam-3′BHQ3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Wang, F.; Jiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Xing, G.; Feng, H.; Sun, X.; Hu, M.; Zhang, G. Virtual Screening-Based Peptides Targeting Spike Protein to Inhibit Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020381
Xu Q, Wang F, Jiao W, Zhang M, Xing G, Feng H, Sun X, Hu M, Zhang G. Virtual Screening-Based Peptides Targeting Spike Protein to Inhibit Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) Infection. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020381
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qian, Fangyu Wang, Wenqiang Jiao, Mengting Zhang, Guangxu Xing, Hua Feng, Xuefeng Sun, Man Hu, and Gaiping Zhang. 2023. "Virtual Screening-Based Peptides Targeting Spike Protein to Inhibit Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) Infection" Viruses 15, no. 2: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020381
APA StyleXu, Q., Wang, F., Jiao, W., Zhang, M., Xing, G., Feng, H., Sun, X., Hu, M., & Zhang, G. (2023). Virtual Screening-Based Peptides Targeting Spike Protein to Inhibit Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) Infection. Viruses, 15(2), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020381





