Isopeptide Bonding In Planta Allows Functionalization of Elongated Flexuous Proteinaceous Viral Nanoparticles, including Non-Viable Constructs by Other Means
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning in Expression Vectors and Agroinfiltration
2.2. Protein Extraction and Monitoring of GFP Formation
2.3. VLPs Characterization
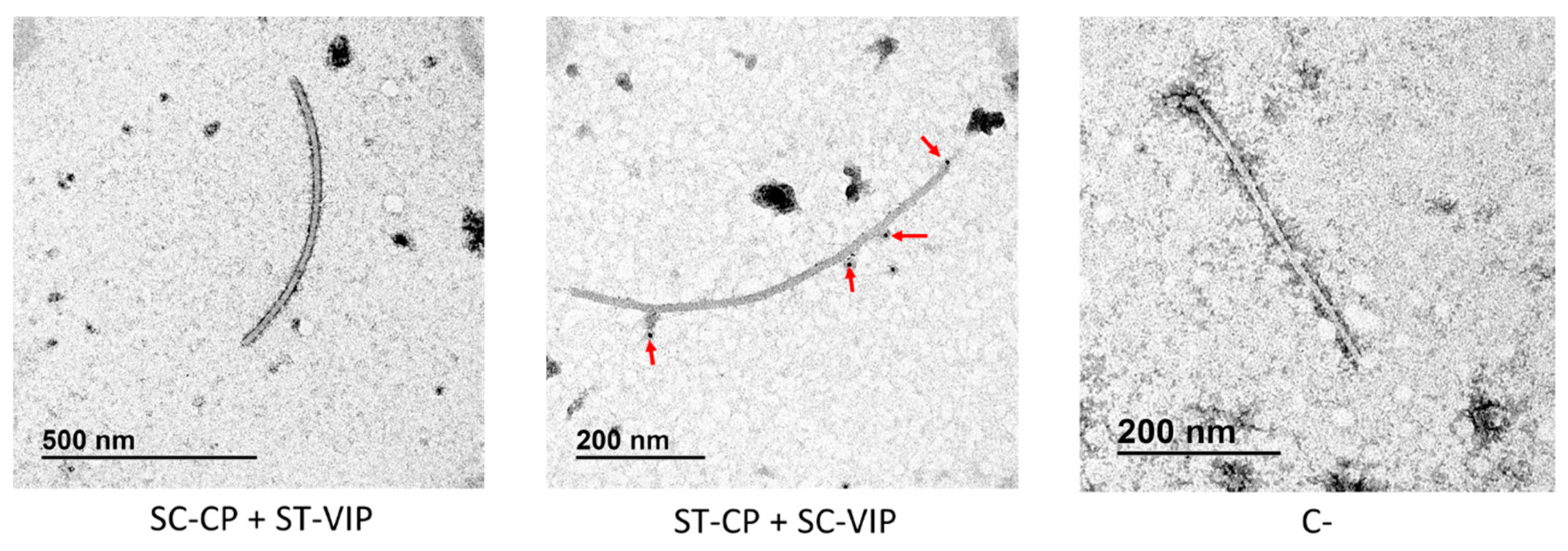
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Fusion
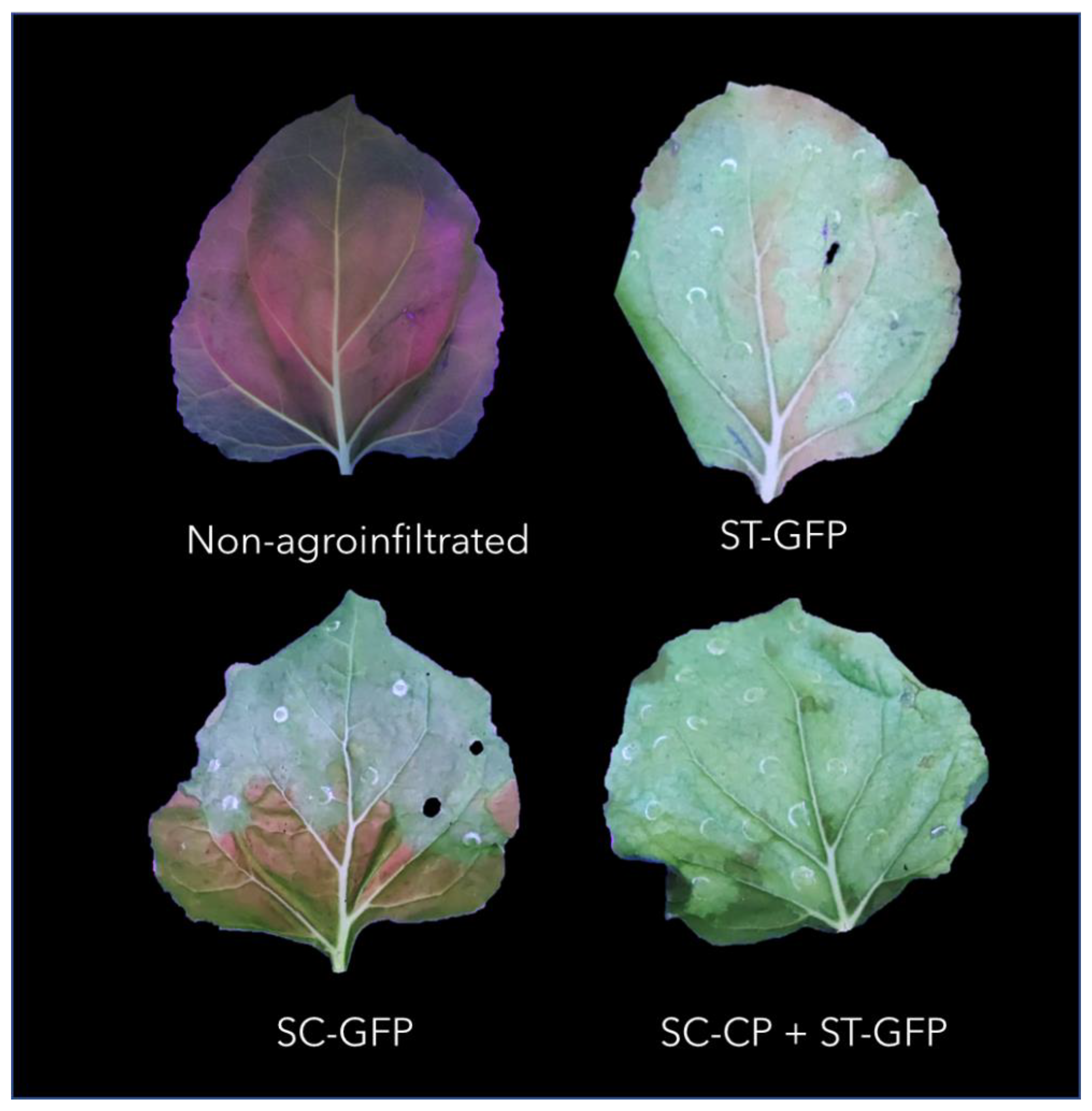
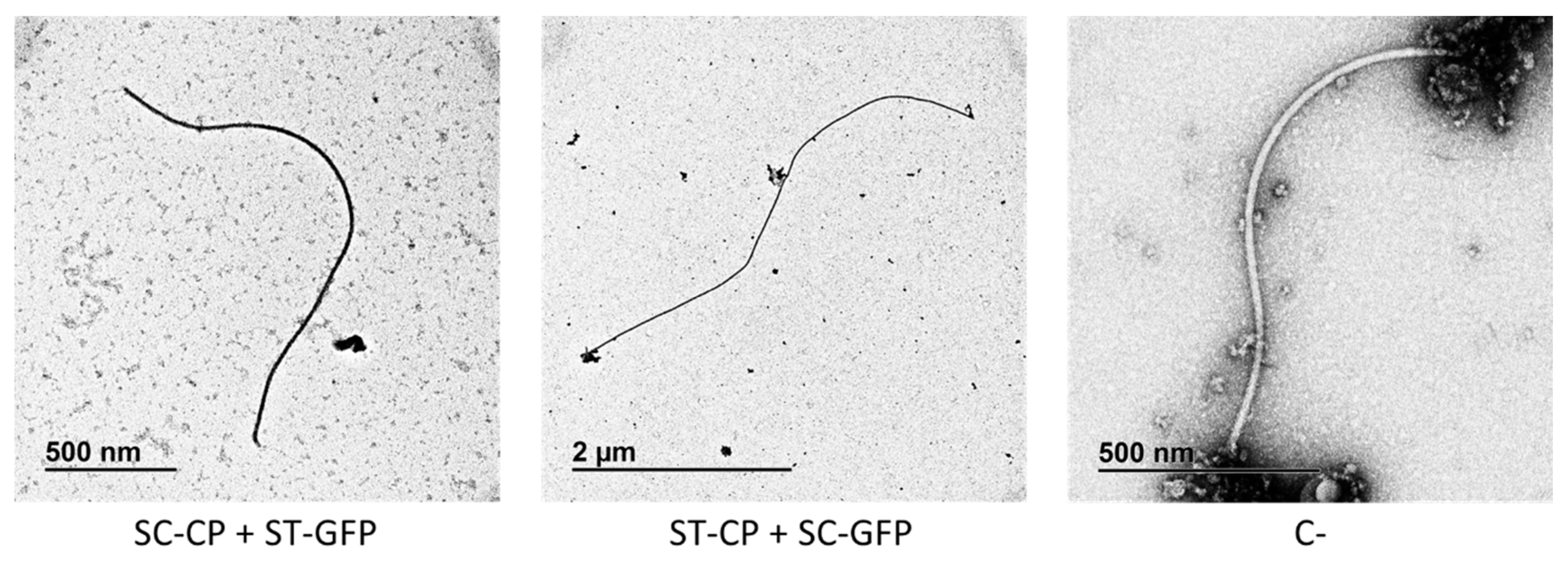
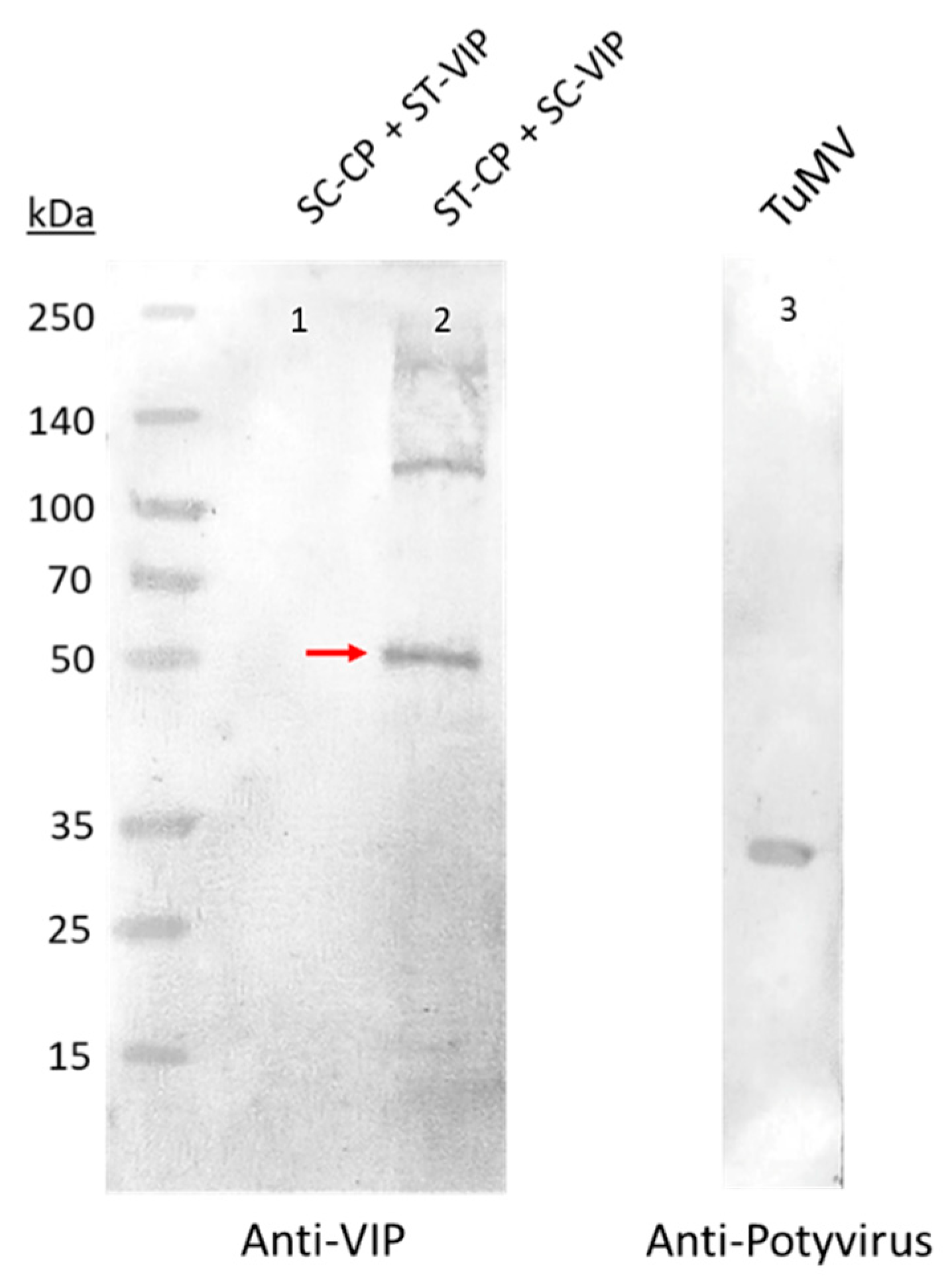
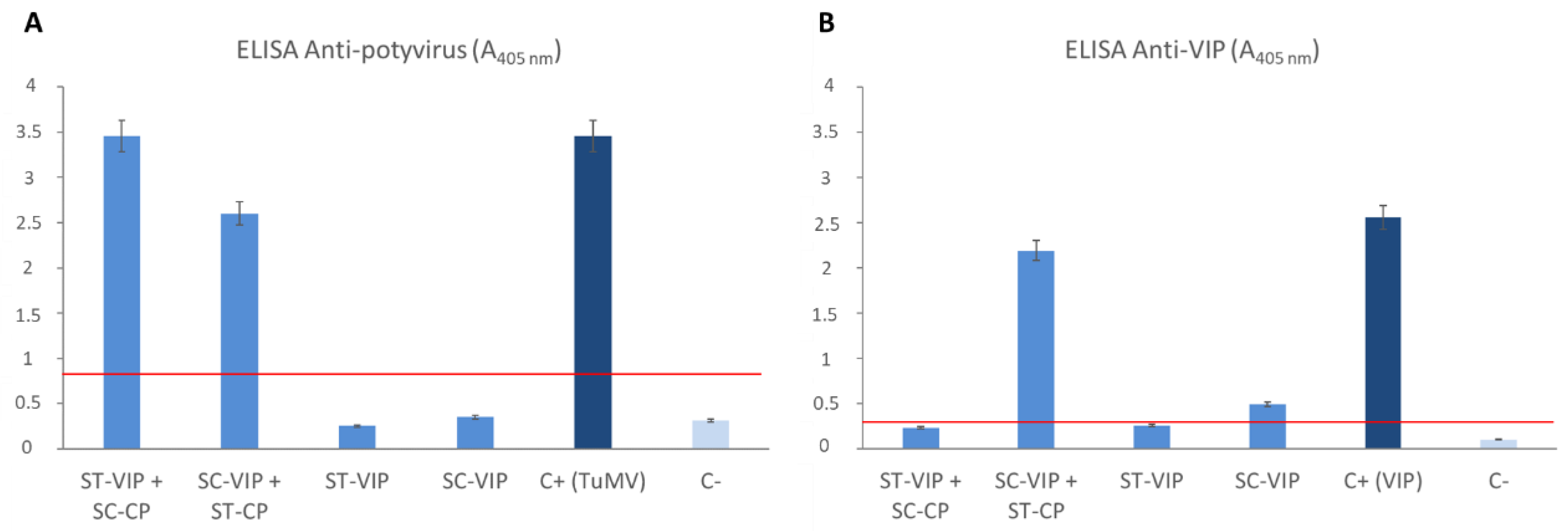
3.2. SpyTag/SpyCatcher
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Koudelka, K.J.; Pitek, A.S.; Manchester, M.; Steinmetz, N.F. Virus-Based Nanoparticles as Versatile Nanomachines. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2015, 2, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.F.C.; Peyret, H.; Saunders, K.; Castells-Graells, R.; Marsian, J.; Meshcheriakova, Y.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Synthetic Plant Virology for Nanobiotechnology and Nanomedicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S.; Hefferon, K. Application of Plant Viruses in Biotechnology, Medicine, and Human Health. Viruses 2021, 13, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, A.J.; Solomon, K.V. Surface Functionalization of Rod-Shaped Viral Particles for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, F.; Sáez, M.; Lunello, P.; Ponz, F. Plant Viral Elongated Nanoparticles Modified for Log-Increases of Foreign Peptide Immunogenicity and Specific Antibody Detection. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, S.; Mansilla, C.; Aguado, M.; Yuste-Calvo, C.; Sánchez, F.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Ponz, F. Nanonets Derived from Turnip Mosaic Virus as Scaffolds for Increased Enzymatic Activity of Immobilized Candida Antarctica Lipase B. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchado, D.A.; Rincón, S.; Zurita, L.; Ponz, F. Turnip Mosaic Virus Nanoparticles: A Versatile Tool in Biotechnology. In Plant Molecular Farming; 2023; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez-Lam, E.; Imperial, J.; Ponz, F. Polyphenol-Functionalized Plant Viral-Derived Nanoparticles Exhibit Strong Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Formation Activities. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Lam, E.; Tome-Amat, J.; Segrelles, C.; Yuste-Calvo, C.; Asensio, S.; Peral, J.; Ponz, F.; Lorz, C. Antitumor Applications of Polyphenol-Conjugated Turnip Mosaic Virus-Derived Nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gamboa, I.; Velázquez-Lam, E.; Lobo-Zegers, M.J.; Frías-Sánchez, A.I.; Tavares-Negrete, J.A.; Monroy-Borrego, A.; Menchaca-Arrendondo, J.L.; Williams, L.; Lunello, P.; Ponz, F.; et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels Containing Turnip Mosaic Virus for Fabrication of Nanostructured Materials for Tissue Engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 907601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos-Castro, D.; Margain, C.; Gonzalez-Klein, Z.; Yuste-Calvo, C.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; Zurita, L.; Esteban, V.; Tome-Amat, J.; Diaz-Perales, A.; Ponz, F. Suitability of Potyviral Recombinant Virus-like Particles Bearing a Complete Food Allergen for Immunotherapy Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 986823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F. Presenting Peptides at the Surface of Potyviruses In Planta. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1776, pp. 471–485. [Google Scholar]
- González-Gamboa, I.; Manrique, P.; Manrique, P.; Ponz, F. Plant-Made Potyvirus-like Particles Used for Log-Increasing Antibody Sensing Capacity. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 254, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuste-Calvo, C.; López-Santalla, M.; Zurita, L.; Cruz-Fernández, C.F.; Sánchez, F.; Garín, M.I.; Ponz, F. Elongated Flexuous Plant Virus-Derived Nanoparticles Functionalized for Autoantibody Detection. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías-Sánchez, A.I.; Quevedo-Moreno, D.A.; Samandari, M.; Tavares-Negrete, J.A.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, V.H.; González-Gamboa, I.; Ponz, F.; Alvarez, M.M.; Trujillo-De Santiago, G. Biofabrication of Muscle Fibers Enhanced with Plant Viral Nanoparticles Using Surface Chaotic Flows. Biofabrication 2021, 13, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, R.; Yuste-Calvo, C.; Gil-Cartón, D.; Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F.; Valle, M. Structure of Turnip Mosaic Virus and Its Viral-like Particles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röder, J.; Fischer, R.; Commandeur, U. Adoption of the 2A Ribosomal Skip Principle to Tobacco Mosaic Virus for Peptide Display. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddington, S.C.; Howarth, M. Secrets of a Covalent Interaction for Biomaterials and Biotechnology: SpyTag and SpyCatcher. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 29, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, B.; Fierer, J.O.; Celik, E.; Chittock, E.C.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Moy, V.T.; Howarth, M. Peptide Tag Forming a Rapid Covalent Bond to a Protein, through Engineering a Bacterial Adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E690–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyret, H.; Ponndorf, D.; Meshcheriakova, Y.; Richardson, J.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Covalent Protein Display on Hepatitis B Core-like Particles in Plants through the in Vivo Use of the SpyTag/SpyCatcher System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuphan, J.; Commandeur, U. Analysis of Engineered Tobacco Mosaic Virus and Potato Virus X Nanoparticles as Carriers for Biocatalysts. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 710869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.I.; Kim, K.H. Display of Streptococcus Iniae α-Enolase on the Surface of Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) of Nervous Necrosis Virus (NNV) Using SpyTag/SpyCatcher. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinimäki, S.; Lampinen, V.; Tamminen, K.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Malm, M.; Hytönen, V.P.; Blazevic, V. Antigenicity and Immunogenicity of HA2 and M2e Influenza Virus Antigens Conjugated to Norovirus-like, VP1 Capsid-Based Particles by the SpyTag/SpyCatcher Technology. Virology 2022, 566, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvie, N.C.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Rodriguez-Aponte, S.A.; Kaur, K.; Bajoria, S.; Kumru, O.S.; Martinot, A.J.; Chandrashekar, A.; McMahan, K.; Mercado, N.B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Displayed on HBsAg Virus-like Particles Elicits Protective Immunity in Macaques. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stander, J.; Chabeda, A.; Rybicki, E.P.; Meyers, A.E. A Plant-Produced Virus-like Particle Displaying Envelope Protein Domain III Elicits an Immune Response against West Nile Virus in Mice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 738619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Juarranz, Y.; Gutiérrez-Cañas, I.; Carrión, M.; Pérez-García, S.; Villanueva-Romero, R.; Castro, D.; Lamana, A.; Mellado, M.; González-álvaro, I.; et al. A Clinical Approach for the Use of VIP Axis in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessillier, S.; Adams, G.; Montero-Melendez, T.; Jones, R.; Seed, M.; Perretti, M.; Chernajovsky, Y. Molecular Engineering of Short Half-Life Small Peptides (VIP, AMSH and γ 3MSH) Fused to Latency-Associated Peptide Results in Improved Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutics. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuste-Calvo, C.; González-Gamboa, I.; Pacios, L.F.; Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F. Structure-Based Multifunctionalization of Flexuous Elongated Viral Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 5019–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuenemann, E.C.; Meyers, A.E.; Verwey, J.; Rybicki, E.P.; Lomonossoff, G.P. A Method for Rapid Production of Heteromultimeric Protein Complexes in Plants: Assembly of Protective Bluetongue Virus-like Particles. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 11, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mínguez-Toral, M.; Pacios, L.F.; Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F. Structural intrinsic disorder in a functionalized potyviral coat protein as a main viability determinant of their assembled nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Keeble, A.H.; Howarth, M. Power to the Protein: Enhancing and Combining Activities Using the Spy Toolbox. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7281–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, V.R.; Manea, F.; Borys, N.J.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M.; Cohen, B.E. Controlled and Stable Patterning of Diverse Inorganic Nanocrystals on Crystalline Two-Dimensional Protein Arrays. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Abad, C.; Martinez, C.; Juarranz, M.; Arranz, A.; Gomariz, R.; Leceta, J. Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide in the Immune System: Potential Therapeutic Role in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 80, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, K.D.; Leneghan, D.B.; Brian, I.J.; Ishizuka, A.S.; Bachmann, M.F.; Draper, S.J.; Biswas, S.; Howarth, M. Plug-and-Display: Decoration of Virus-Like Particles via Isopeptide Bonds for Modular Immunization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrane, S.; Janitzek, C.M.; Matondo, S.; Resende, M.; Gustavsson, T.; Jongh, W.A.; Clemmensen, S.; Roeffen, W.; Vegte-Bolmer, M.; Gemert, G.J.; et al. Bacterial Superglue Enables Easy Development of Efficient Virus-like Particle Based Vaccines. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janitzek, C.M.; Matondo, S.; Thrane, S.; Nielsen, M.A.; Kavishe, R.; Mwakalinga, S.B.; Theander, T.G.; Salanti, A.; Sander, A.F. Bacterial Superglue Generates a Full-Length Circumsporozoite Protein Virus-like Particle Vaccine Capable of Inducing High and Durable Antibody Responses. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, M.; Fukushima, M.; Kameyama, K.I.; Kokuho, T.; Nakahira, Y.; Takeuchi, K. Novel Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV) Virus-like Particle Vaccine Candidates Presenting the E2 Protein Using the SpyTag/SpyCatcher System Induce a Robust Neutralizing Antibody Response in Mice. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röder, J.; Fischer, R.; Commandeur, U. Engineering Potato Virus X Particles for a Covalent Protein Based Attachment of Enzymes. Small 2017, 13, 1702151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Truchado, D.A.; Rincón, S.; Zurita, L.; Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F. Isopeptide Bonding In Planta Allows Functionalization of Elongated Flexuous Proteinaceous Viral Nanoparticles, including Non-Viable Constructs by Other Means. Viruses 2023, 15, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020375
Truchado DA, Rincón S, Zurita L, Sánchez F, Ponz F. Isopeptide Bonding In Planta Allows Functionalization of Elongated Flexuous Proteinaceous Viral Nanoparticles, including Non-Viable Constructs by Other Means. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020375
Chicago/Turabian StyleTruchado, Daniel A., Sara Rincón, Lucía Zurita, Flora Sánchez, and Fernando Ponz. 2023. "Isopeptide Bonding In Planta Allows Functionalization of Elongated Flexuous Proteinaceous Viral Nanoparticles, including Non-Viable Constructs by Other Means" Viruses 15, no. 2: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020375
APA StyleTruchado, D. A., Rincón, S., Zurita, L., Sánchez, F., & Ponz, F. (2023). Isopeptide Bonding In Planta Allows Functionalization of Elongated Flexuous Proteinaceous Viral Nanoparticles, including Non-Viable Constructs by Other Means. Viruses, 15(2), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020375






