HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Stimulate the Glutamine Pathway Maintaining Cell Proliferation in a SNAT1-Dependent Fashion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Proliferation Assays
2.3. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Metabolic Measurements
2.6. HPV16 E6/E7 and SNAT1 siRNA Knock Down
2.7. Immunofluorescence and Cell Imaging
2.8. Cervical Samples
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
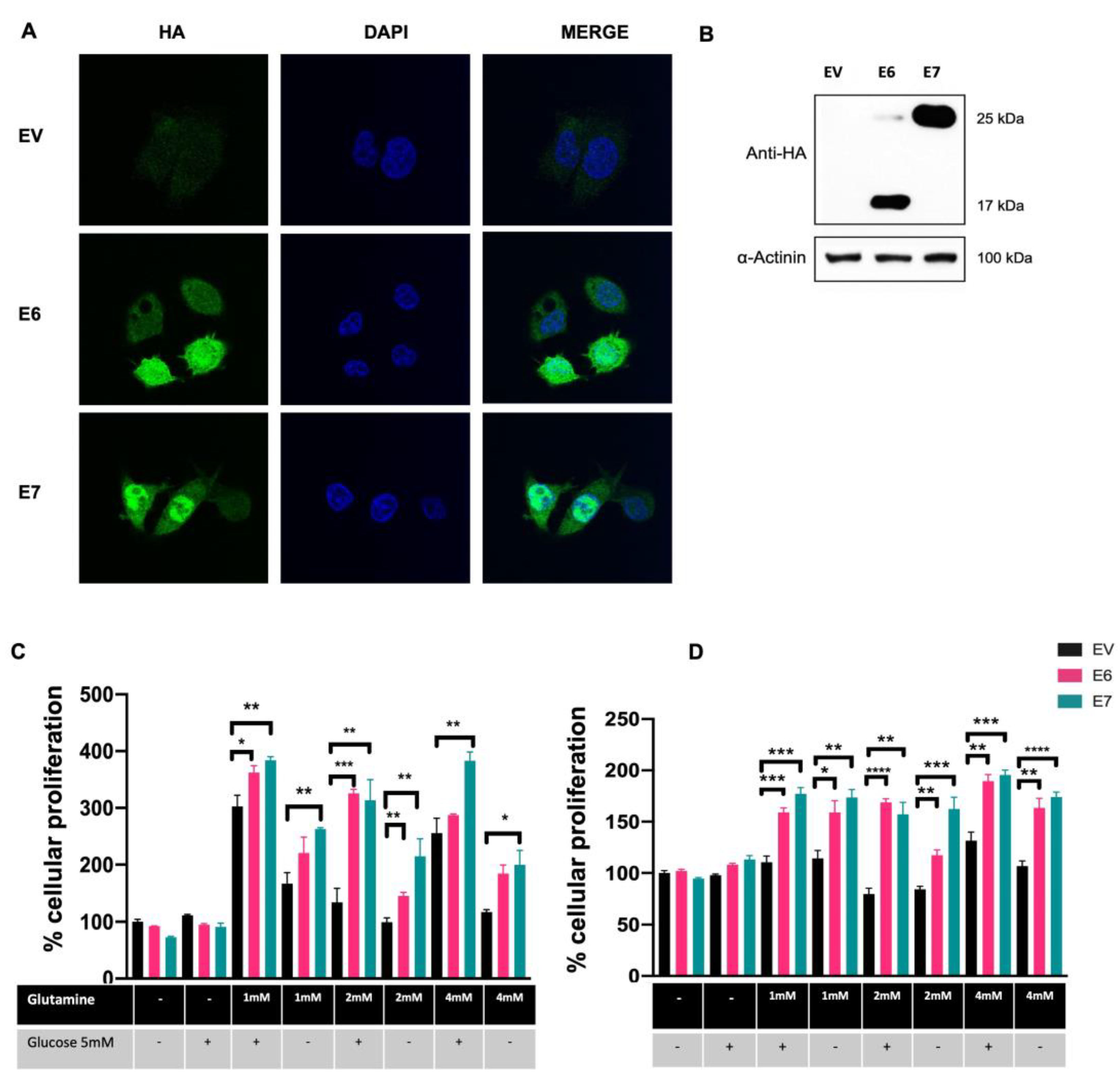
3.1. HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Promote Glutamine-Dependent Proliferation
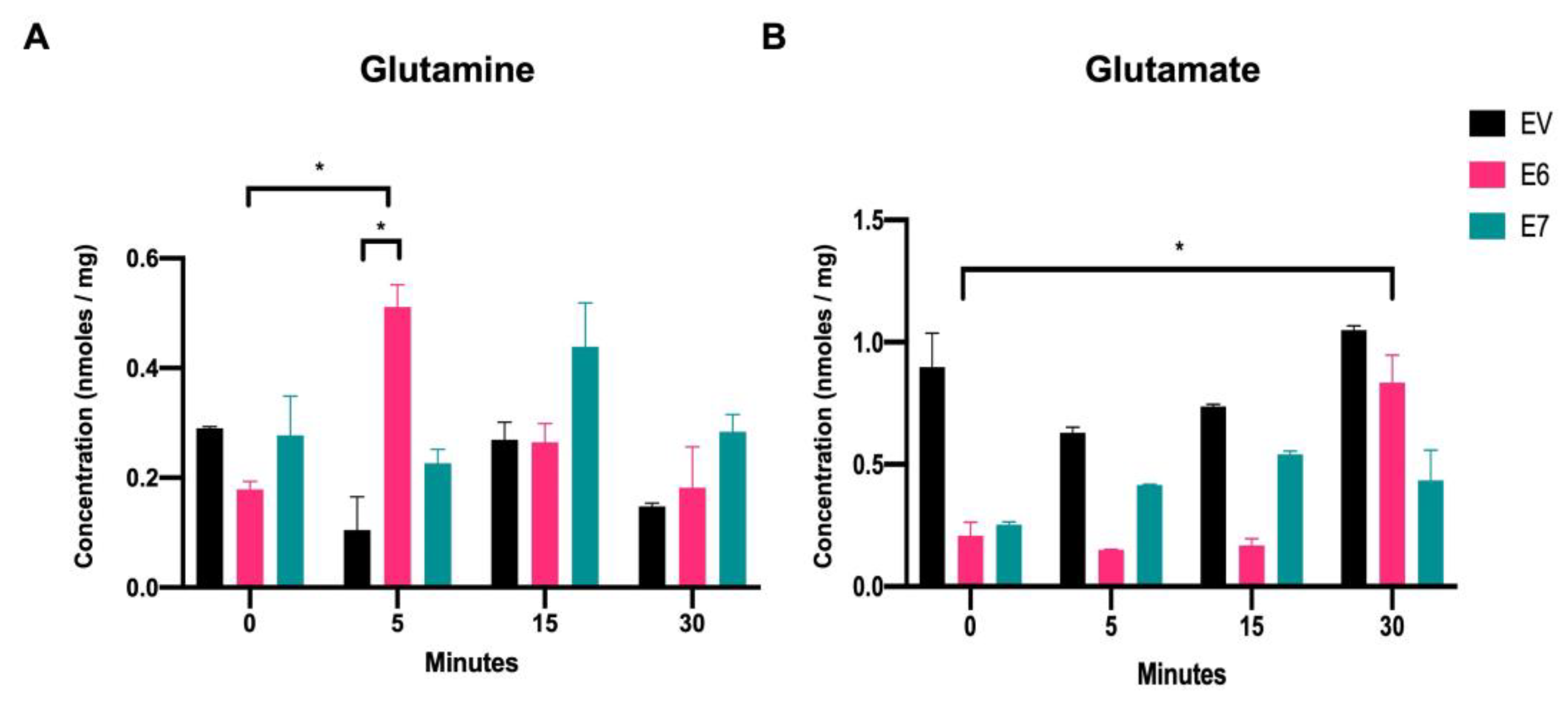
3.2. Intracellular Glutamine and Glutamate Increase in the Presence of HPV16 E6 Oncoprotein
3.3. SNAT1 Glutamine Transporter Expression and Protein Levels Increase in the Presence of HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins
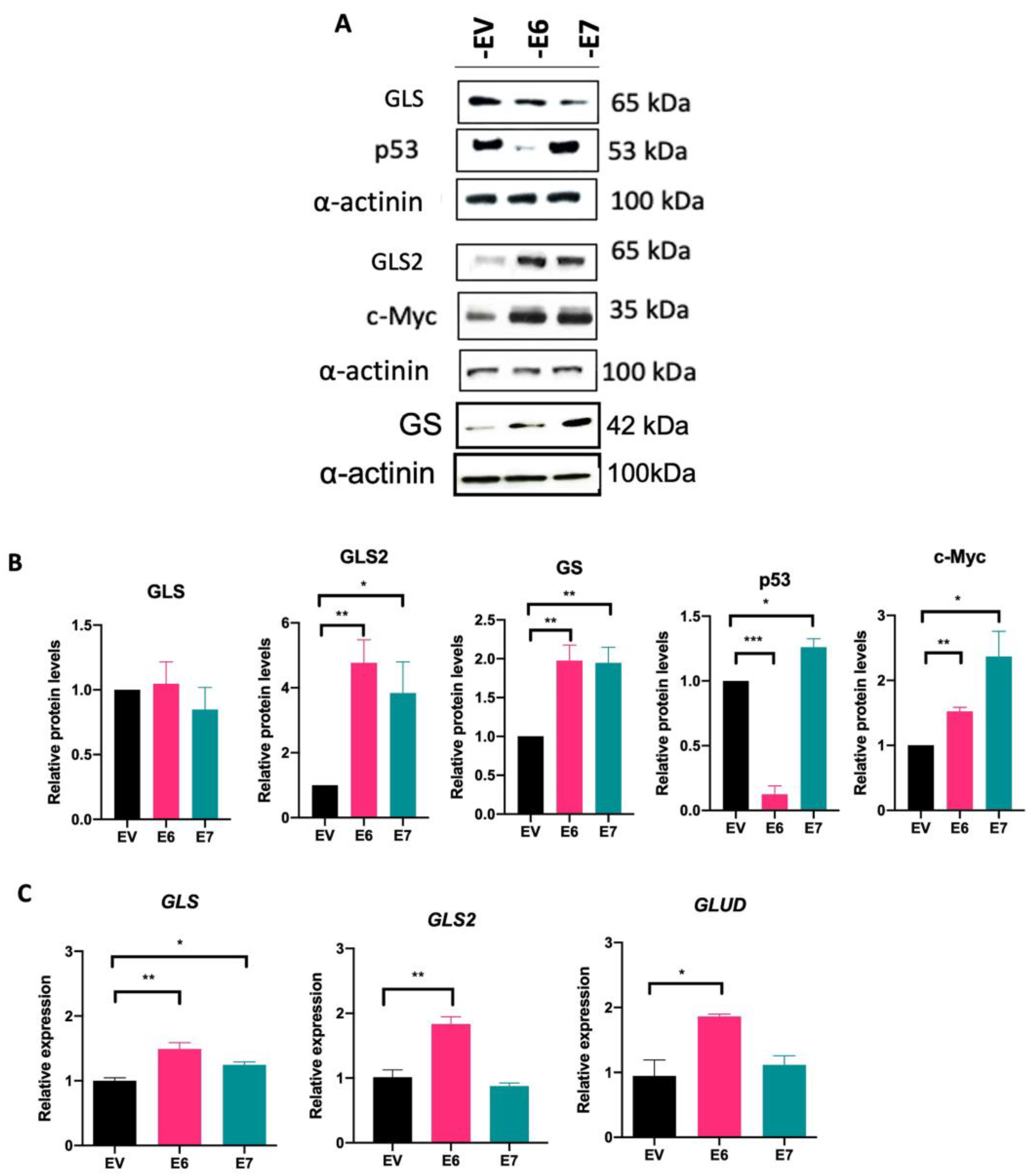
3.4. HPV16 E6 and E7 Modify Glutaminolysis-Related Components
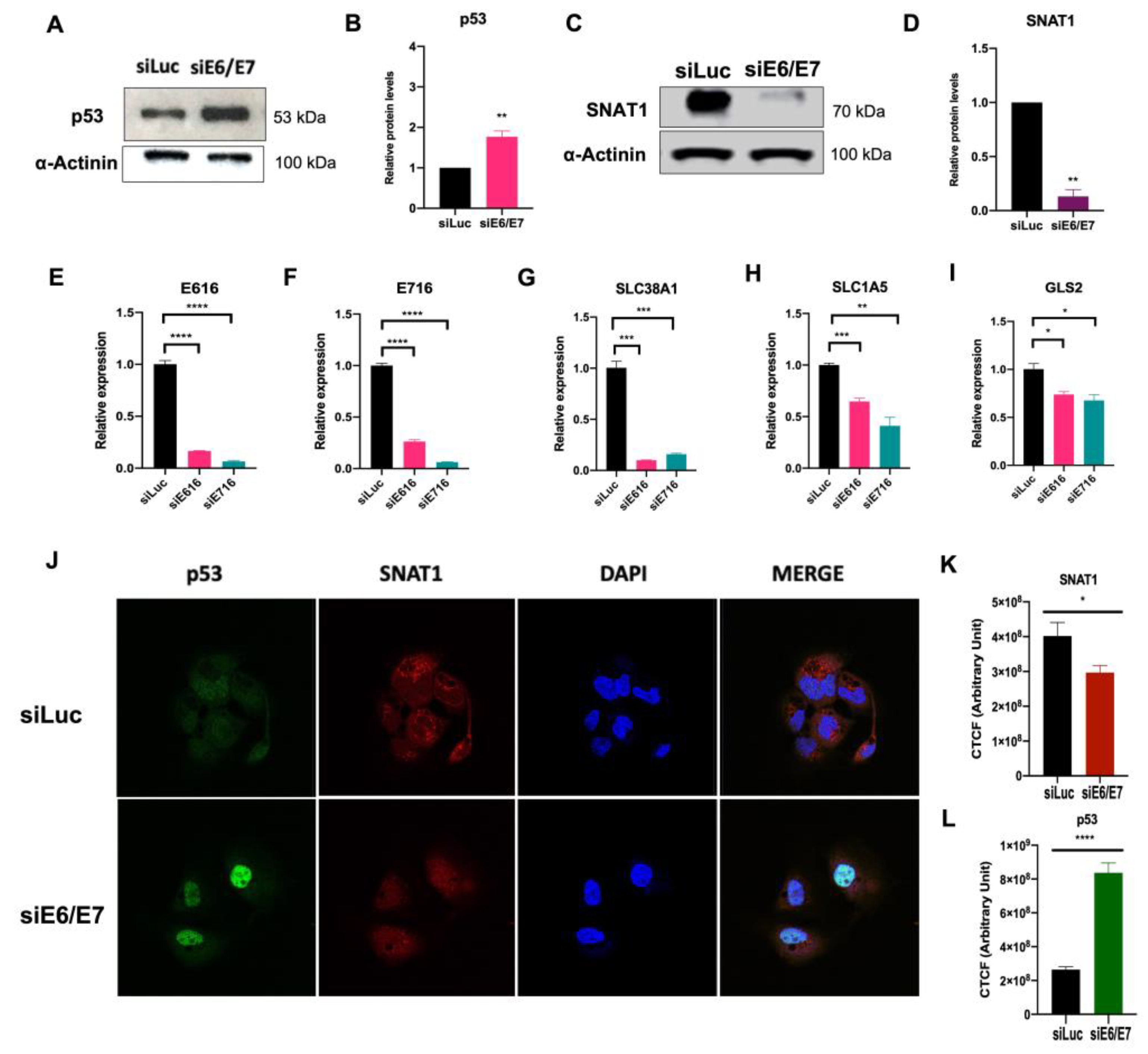
3.5. SNAT1 Transporter Expression and Protein Levels Are Reduced in Ca Ski E6/E7-Silenced Cells
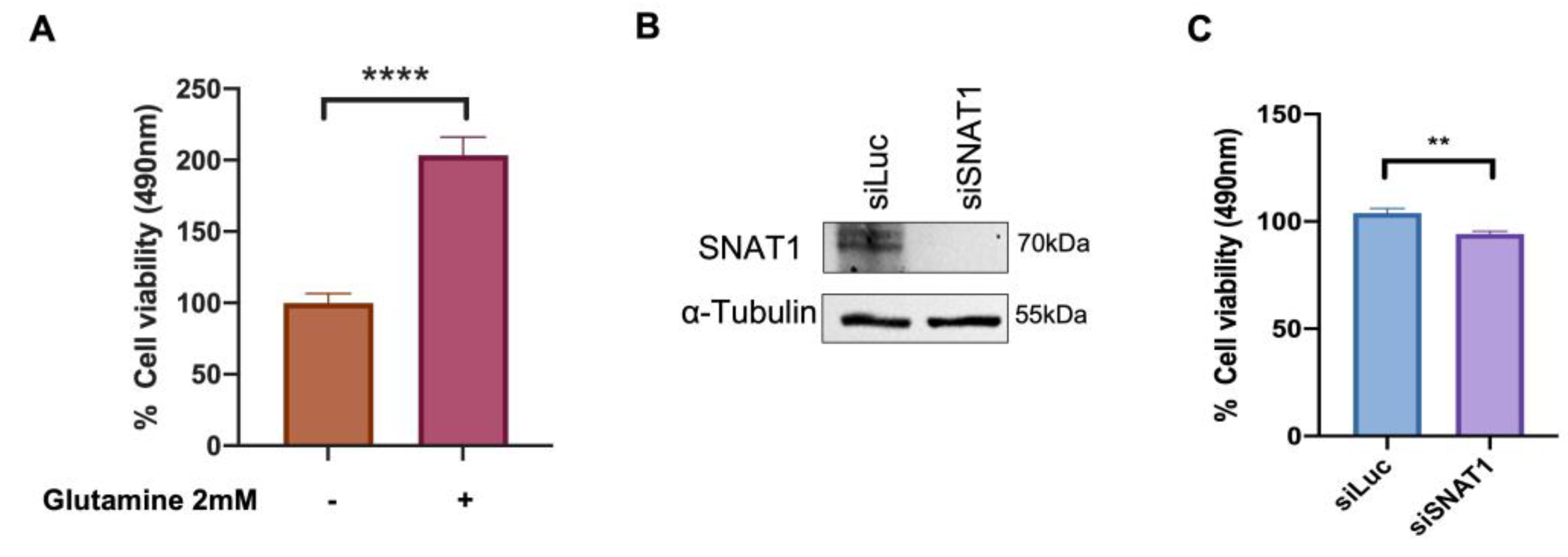
3.6. SNAT1 Transporter Partially Contributes to Ca Ski Cell Proliferation
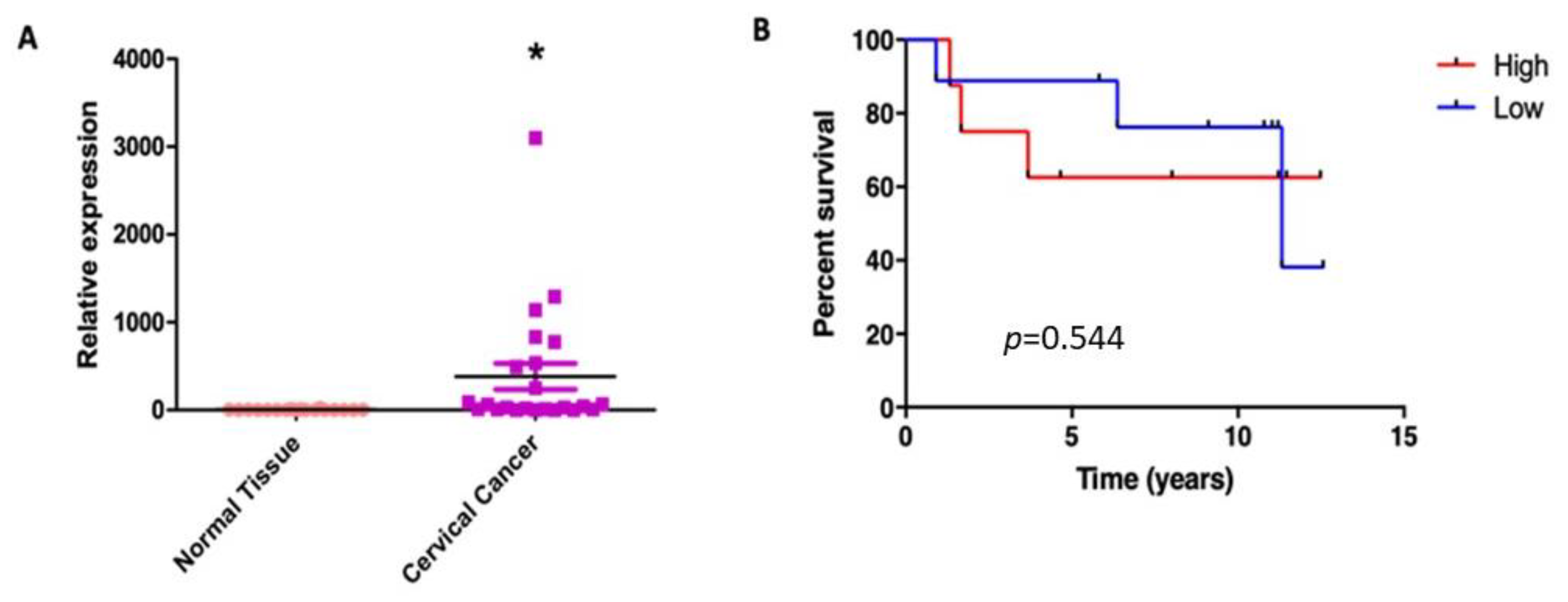
3.7. SNAT1 Expression Is Increased in Cervical Cancer Samples and Its High Expression Is Associated with a Poorer Prognosis in Cervical Cancer Patients
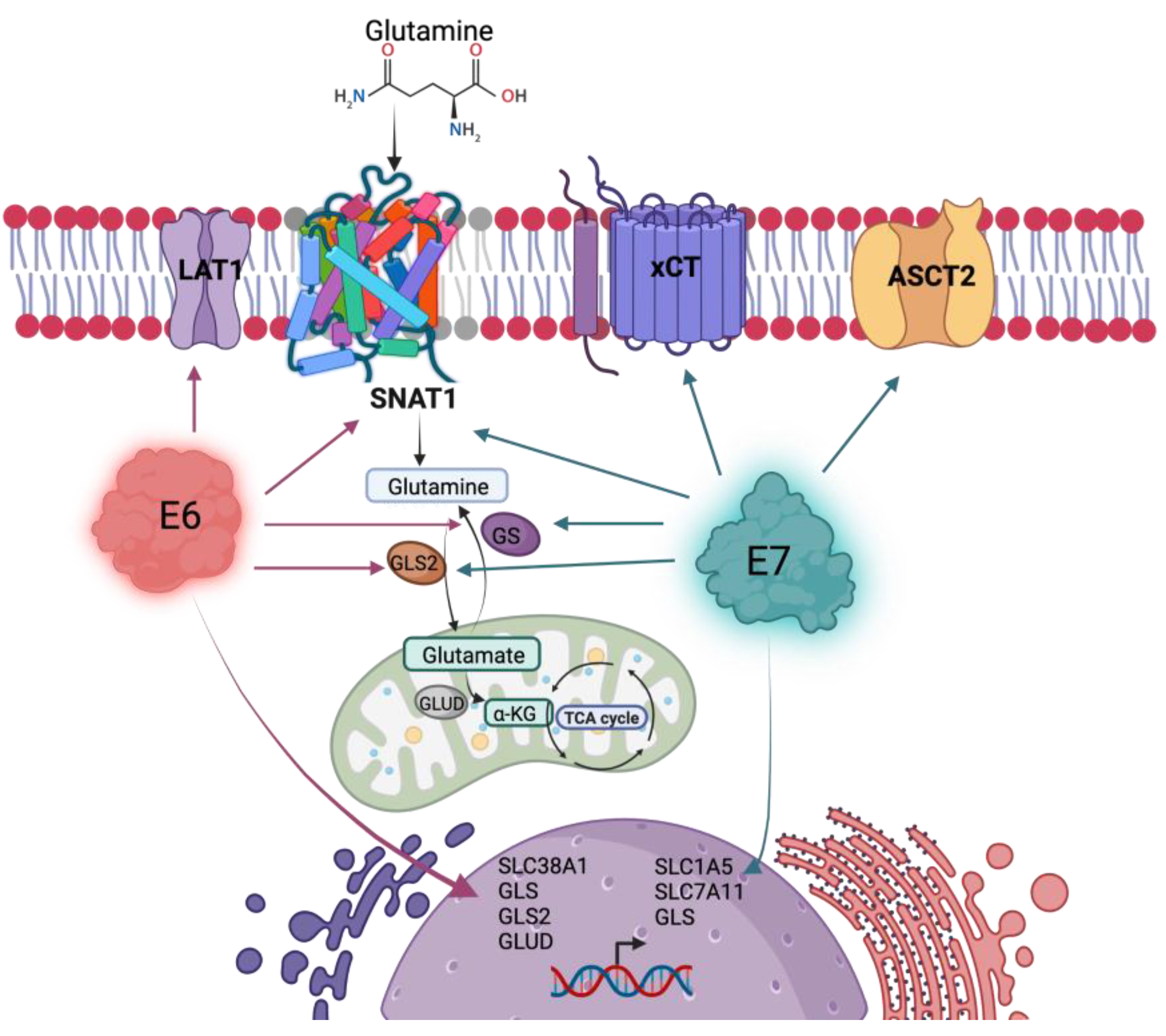
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- HPV Information Centre. Available online: https://hpvcentre.net/ (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Sabatini, M.E.; Chiocca, S. Human Papillomavirus as a Driver of Head and Neck Cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbyn, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Bruni, L.; de Sanjosé, S.; Saraiya, M.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F. Estimates of Incidence and Mortality of Cervical Cancer in 2018: A Worldwide Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e191–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Banks, L. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 Oncoprotein-Induced Cell Transformation. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 772, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kumar, P.; Das, B.C. HPV: Molecular Pathways and Targets. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2018, 42, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; David, P.; Banks, L. The Role of the E6-P53 Interaction in the Molecular Pathogenesis of HPV. Oncogene 1999, 18, 7690–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, S.N.; Wazer, D.E.; Band2, V. E7 Protein of Human Papilloma Virus-16 Induces Degradation of Retinoblastoma Protein through the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway’. Cancer 1996, 56, 4620–4624. [Google Scholar]
- Vats, A.; Trejo-Cerro, O.; Thomas, M.; Banks, L. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7: What Remains? Tumour Virus Res. 2021, 11, 200213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ramírez, I.; Carrillo-García, A.; Contreras-Paredes, A.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E.; Cruz-Gregorio, A.; Lizano, M. Regulation of Cellular Metabolism by High-Risk Human Papillomaviruses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaszadeh, Z.; Çeşmeli, S.; Biray Avcı, Ç. Crucial Players in Glycolysis: Cancer Progress. Gene 2020, 726, 144158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Venneti, S.; Nagrath, D. Glutaminolysis: A Hallmark of Cancer Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Du, K.; Li, S.; Lu, L.; Mei, J.; Lin, W.; Deng, M.; Wei, W.; Guo, R. Glutamine Metabolism Regulators Associated with Cancer Development and the Tumor Microenvironment: A Pan-Cancer Multi-Omics Analysis. Genes 2021, 12, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deberardinis, R.J.; Cheng, T. Q’s next: The Diverse Functions of Glutamine in Metabolism, Cell Biology and Cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Oshikawa, K.; Shimizu, H.; Yoshioka, S.; Takahashi, M.; Izumi, Y.; Bamba, T.; Tateishi, C.; Tomonaga, T.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. A Shift in Glutamine Nitrogen Metabolism Contributes to the Malignant Progression of Cancer. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bott, A.J.; Maimouni, S.; Zong, W.X. The Pleiotropic Effects of Glutamine Metabolism in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, J.W.; Cerione, R.A. Glutaminase: A Hot Spot for Regulation of Cancer Cell Metabolism? Oncotarget 2010, 1, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, H. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors Regulate Glutamine Metabolism in Cancer Cells. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 18, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.C.; Yu, Y.C.; Sung, Y.; Han, J.M. Glutamine Reliance in Cell Metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1496–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröer, A.; Gauthier-Coles, G.; Rahimi, F.; van Geldermalsen, M.; Dorsch, D.; Wegener, A.; Holst, J.; Bröer, S. Ablation of the ASCT2 (SLC1A5) Gene Encoding a Neutral Amino Acid Transporter Reveals Transporter Plasticity and Redundancy in Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4012–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Johnson, R.L.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, S.B.; Shim, J.J.; Mangala, L.S.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, J.E.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; et al. Yes-Associated Protein 1 and Transcriptional Coactivator with PDZ-Binding Motif Activate the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Pathway by Regulating Amino Acid Transporters in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2016, 63, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormerais, Y.; Massard, P.A.; Vucetic, M.; Giuliano, S.; Tambutté, E.; Durivault, J.; Vial, V.; Endou, H.; Wempe, M.F.; Parks, S.K.; et al. The Glutamine Transporter ASCT2 (SLC1A5) Promotes Tumor Growth Independently of the Amino Acid Transporter LAT1 (SLC7A5). J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leke, R.; Schousboe, A. The Glutamine Transporters and Their Role in the Glutamate/GABA-Glutamine Cycle. Adv. Neurobiol. 2016, 13, 223–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutia, Y.D.; Ganapathy, V. Glutamine Transporters in Mammalian Cells and Their Functions in Physiology and Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López de la Oliva, A.R.; Campos-Sandoval, J.A.; Gómez-García, M.C.; Cardona, C.; Martín-Rufián, M.; Sialana, F.J.; Castilla, L.; Bae, N.; Lobo, C.; Peñalver, A.; et al. Nuclear Translocation of Glutaminase GLS2 in Human Cancer Cells Associates with Proliferation Arrest and Differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Pedraza, Y.; Muñoz-Bello, J.O.; Olmedo-Nieva, L.; Contreras-Paredes, A.; Martínez-Ramírez, I.; Langley, E.; Lizano, M. Non-Coding RNAs as Key Regulators of Glutaminolysis in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, S.; Zwerschke, W.; Jansen-Dürr, P.; Eigenbrodt, E. Effects of the Human Papilloma Virus HPV-16 E7 Oncoprotein on Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis: Role of Pyruvate Kinase Type M2 and the Glycolytic-Enzyme Complex. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwerschke, W.; Mazurek, S.; Massimi, P.; Banks, L.; Eigenbrodt, E.; Jansen-Dürr, P. Modulation of Type M2 Pyruvate Kinase Activity by the Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Oncoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.L.; Nagy, E.; Zietkowski, D.; Payne, G.S.; Phillips, D.H.; DeSouza, N.M. Molecular and Metabolic Consequences Following E6 Transfection in an Isogenic Ovarian Cell Line (A2780) Pair. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hémon, A.; Louandre, C.; Lailler, C.; Godin, C.; Bottelin, M.; Morel, V.; François, C.; Galmiche, A.; Saidak, Z. SLC7A11 as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in HPV-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo-Nieva, L.; Muñoz-Bello, J.O.; Martínez-Ramírez, I.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, A.D.; Ortiz-Pedraza, Y.; González-Espinosa, C.; Madrid-Marina, V.; Torres-Poveda, K.; Bahena-Roman, M.; Lizano, M. RIPOR2 Expression Decreased by HPV-16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins: An Opportunity in the Search for Prognostic Biomarkers in Cervical Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seavey, S.E.; Holubar, M.; Saucedo, L.J.; Perry, M.E. The E7 Oncoprotein of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Stabilizes P53 through a Mechanism Independent of P19(ARF). J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7590–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Chernock, R.D.; Kuhs, K.A.L.; Lewis, J.S.; Luo, J.; Gay, H.A.; Thorstad, W.L.; Wang, X. A Prognostic Gene Expression Signature for Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Ma, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Liang, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; et al. Reprogramming of Glutamine Metabolism and Its Impact on Immune Response in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Commun. Signal 2022, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, F.; Cherukuri, M.K.; Choyke, P.L. Metabolic Reprogramming in Prostate Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The Emerging Hallmarks of Cancer Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Q. The Role of Ubiquitination and Deubiquitination in Cancer Metabolism. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, S.; Zaal, E.A.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Bosma, A.; Jochems, F.; Isima, N.; Jin, G.; Lieftink, C.; et al. A Powerful Drug Combination Strategy Targeting Glutamine Addiction for the Treatment of Human Liver Cancer. Elife 2020, 9, e56749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, S.; Risk, B.B.; Neill, S.G.; Shu, H.K.; Fleischer, C.C. Characterization of Dysregulated Glutamine Metabolism in Human Glioma Tissue with 1H NMR. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, K.; Derveaux, E.; Graulus, G.J.; Mesotten, L.; Thomeer, M.; Noben, J.P.; Guedens, W.; Adriaensens, P. Glutamine Addiction and Therapeutic Strategies in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demas, D.M.; Demo, S.; Fallah, Y.; Clarke, R.; Nephew, K.P.; Althouse, S.; Sandusky, G.; He, W.; Shajahan-Haq, A.N. Glutamine Metabolism Drives Growth in Advanced Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Front Oncol. 2019, 9, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Sheng, X.; Willson, A.K.; Roque, D.R.; Stine, J.E.; Guo, H.; Jones, H.M.; Zhou, C.; Bae-Jump, V.L. Glutamine Promotes Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation through the MTOR/S6 Pathway. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arizmendi-Izazaga, A.; Navarro-Tito, N.; Jiménez-Wences, H.; Mendoza-Catalán, M.A.; Martínez-Carrillo, D.N.; Zacapala-Gómez, A.E.; Olea-Flores, M.; Dircio-Maldonado, R.; Torres-Rojas, F.I.; Soto-Flores, D.G.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer: Role of HPV 16 Variants. Pathogens 2021, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, R.V.; Oppliger, W.; Robitaille, A.M.; Heiserich, L.; Skendaj, R.; Gottlieb, E.; Hall, M.N. Glutaminolysis Activates Rag-MTORC1 Signaling. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, G.J. The Harmonious Interplay of Amino Acid and Monocarboxylate Transporters Induces the Robustness of Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2021, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwangwa, M.V.; Joubert, A.M.; Visagie, M.H. Effects of Glutamine Deprivation on Oxidative Stress and Cell Survival in Breast Cell Lines. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janpipatkul, K.; Suksen, K.; Borwornpinyo, S.; Jearawiriyapaisarn, N.; Hongeng, S.; Piyachaturawat, P.; Chairoungdua, A. Downregulation of LAT1 Expression Suppresses Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Invasion and Migration. Cell Signal 2014, 26, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, N.; Zhao, F.; Ge, C.; Liang, L.; Jia, D.; Chen, T.; Yao, M.; et al. Disruption of XCT Inhibits Cell Growth via the ROS/Autophagy Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2011, 312, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bothwell, P.J.; Kron, C.D.; Wittke, E.F.; Czerniak, B.N.; Bode, B.P. Targeted Suppression and Knockout of ASCT2 or LAT1 in Epithelial and Mesenchymal Human Liver Cancer Cells Fail to Inhibit Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Fang, W.; Liu, K.; Jiao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zang, Y.S. Increased SNAT1 Is a Marker of Human Osteosarcoma and Potential Therapeutic Target. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 78930–78939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröer, A.; Rahimi, F.; Bröer, S. Deletion of Amino Acid Transporter ASCT2 (SLC1A5) Reveals an Essential Role for Transporters SNAT1 (SLC38A1) and SNAT2 (SLC38A2) to Sustain Glutaminolysis in Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13194–13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.K.; Riazul Islam, S.M.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Islam, S.; Ali, F.; Park, K.S. Multiomics Analysis Reveals That GLS and GLS2 Differentially Modulate the Clinical Outcomes of Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.M.; Adamoski, D.; dos Reis, L.M.; Ascenção, C.F.R.; de Oliveira, K.R.S.; Mafra, A.C.P.; da Silva Bastos, A.C.; Quintero, M.; Cassago, C.D.G.; Ferreira, I.M.; et al. GLS2 Is Protumorigenic in Breast Cancers. Oncogene 2020, 39, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukey, M.J.; Cluntun, A.A.; Katt, W.P.; Lin, M.; Chong, J.; Druso, J.E.; Ramachandran, S.; Erickson, J.W.; Le, H.H.; Wang, Z.E.; et al. Liver-Type Glutaminase GLS2 Is a Druggable Metabolic Node in Luminal-Subtype Breast Cancer. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, C.; Wu, R.; Sun, Y.; Levine, A.; Feng, Z. Glutaminase 2, a Novel P53 Target Gene Regulating Energy Metabolism and Antioxidant Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7455–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Blanco, F.; Li, S.; Bhanot, G.; et al. Glutaminase 2 Is a Novel Negative Regulator of Small GTPase Rac1 and Mediates P53 Function in Suppressing Metastasis. Elife 2016, 5, e10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, T.; Poyurovsky, M.V.; Nagano, H.; Mayama, T.; Ohkubo, S.; Lokshin, M.; Hosokawa, H.; Nakayama, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Phosphate-Activated Glutaminase (GLS2), a P53-Inducible Regulator of Glutamine Metabolism and Reactive Oxygen Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7461–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobbe, A.; Bongiorno-Borbone, L.; Bernassola, F.; Terrinoni, A.; Markert, E.K.; Levine, A.J.; Feng, Z.; Agostini, M.; Zolla, L.; Agrò, A.F.; et al. P63 Regulates Glutaminase 2 Expression. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cai, B.; Ding, M.; Su, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L. C-Myc Overexpression Promotes Oral Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration by Enhancing Glutaminase and Glutamine Synthetase Activity. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 358, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme-Schäfer, I.; Lörentz, S.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Role of Amino Acid Transporter SNAT1/SLC38A1 in Human Melanoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, P.; Gao, H.F.; Qian, J.X.; Yuan, L.Y.; Wang, J.J. Overexpression of SLC38A1 Is Associated with Poorer Prognosis in Chinese Patients with Gastric Cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cao, F.; Fang, W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, H.; Yu, G. Activation of SNAT1/SLC38A1 in Human Breast Cancer: Correlation with p-Akt Overexpression. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-Pedraza, Y.; Muñoz-Bello, J.O.; Ramos-Chávez, L.A.; Martínez-Ramírez, I.; Olmedo-Nieva, L.; Manzo-Merino, J.; López-Saavedra, A.; Pérez-de la Cruz, V.; Lizano, M. HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Stimulate the Glutamine Pathway Maintaining Cell Proliferation in a SNAT1-Dependent Fashion. Viruses 2023, 15, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020324
Ortiz-Pedraza Y, Muñoz-Bello JO, Ramos-Chávez LA, Martínez-Ramírez I, Olmedo-Nieva L, Manzo-Merino J, López-Saavedra A, Pérez-de la Cruz V, Lizano M. HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Stimulate the Glutamine Pathway Maintaining Cell Proliferation in a SNAT1-Dependent Fashion. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020324
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-Pedraza, Yunuen, J. Omar Muñoz-Bello, Lucio Antonio Ramos-Chávez, Imelda Martínez-Ramírez, Leslie Olmedo-Nieva, Joaquín Manzo-Merino, Alejandro López-Saavedra, Verónica Pérez-de la Cruz, and Marcela Lizano. 2023. "HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Stimulate the Glutamine Pathway Maintaining Cell Proliferation in a SNAT1-Dependent Fashion" Viruses 15, no. 2: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020324
APA StyleOrtiz-Pedraza, Y., Muñoz-Bello, J. O., Ramos-Chávez, L. A., Martínez-Ramírez, I., Olmedo-Nieva, L., Manzo-Merino, J., López-Saavedra, A., Pérez-de la Cruz, V., & Lizano, M. (2023). HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Stimulate the Glutamine Pathway Maintaining Cell Proliferation in a SNAT1-Dependent Fashion. Viruses, 15(2), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020324






