Immunostimulatory Profile of Cancer Cell Death by the AdV-Lumc007-Derived Oncolytic Virus ‘GoraVir’ in Cultured Pancreatic Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Buffers
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Adenoviruses
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Adenovirus Genome Copies
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
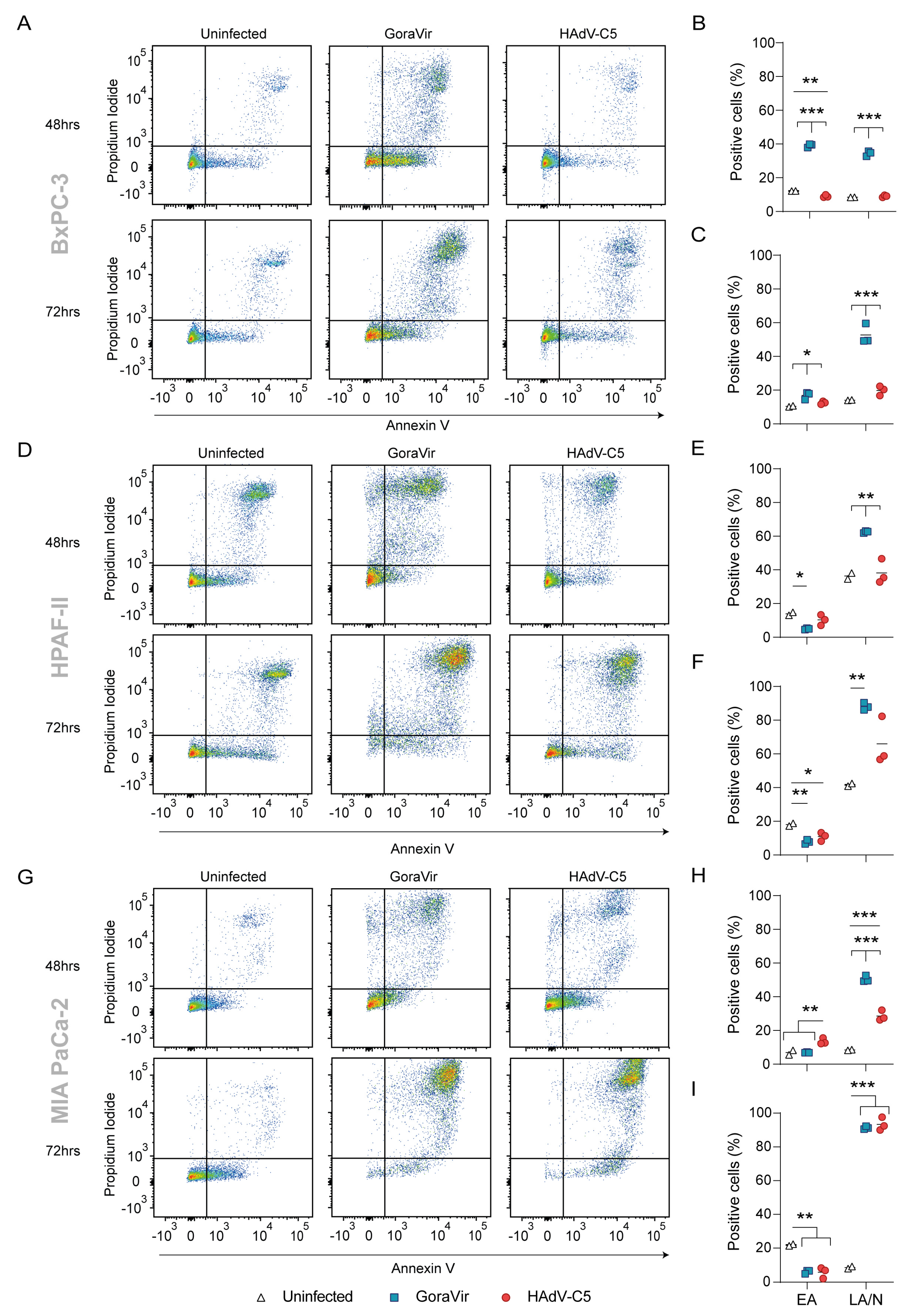
3.1. GoraVir Rapidly Induces Late Apoptotic/Necrotic Cell Death
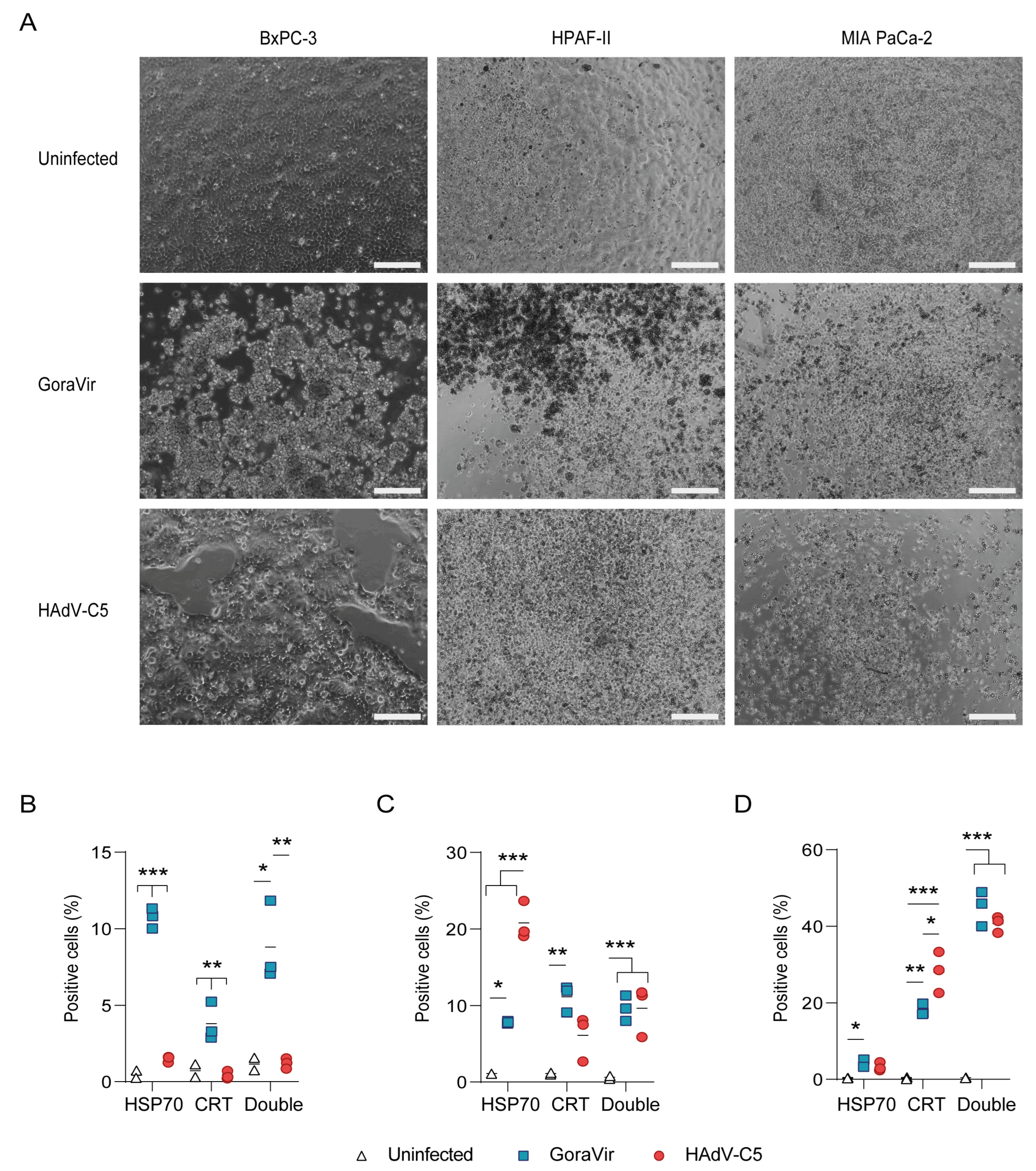
3.2. Infection with GoraVir Leads to Immunogenic Cell Death
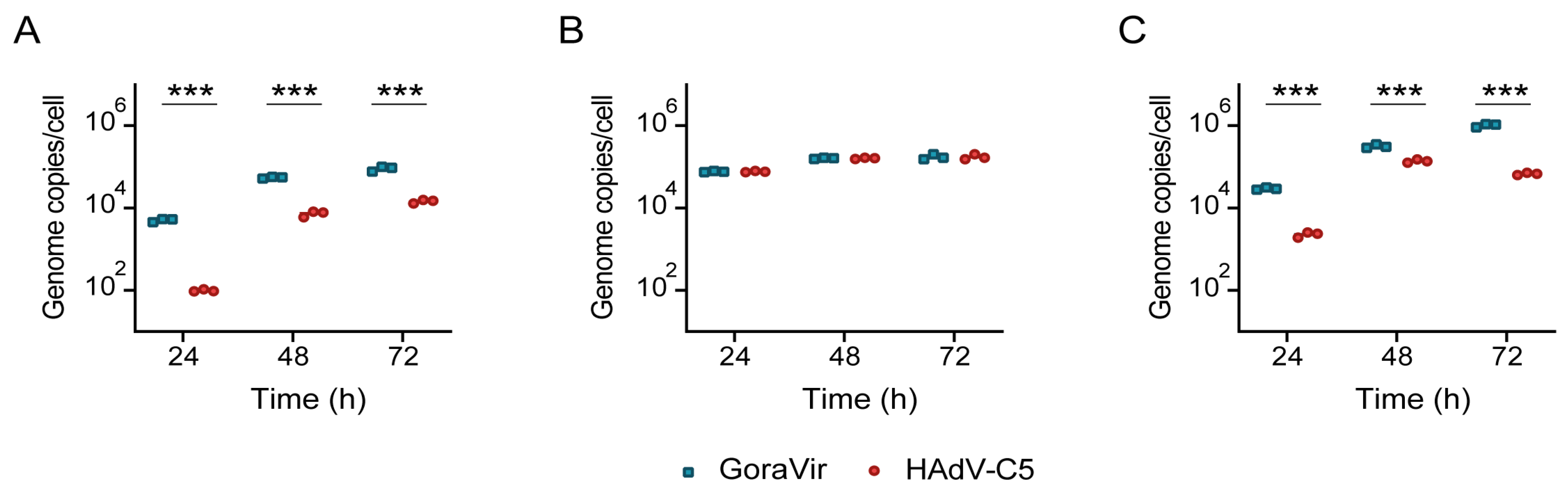
3.3. GoraVir Replicates Efficiently in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
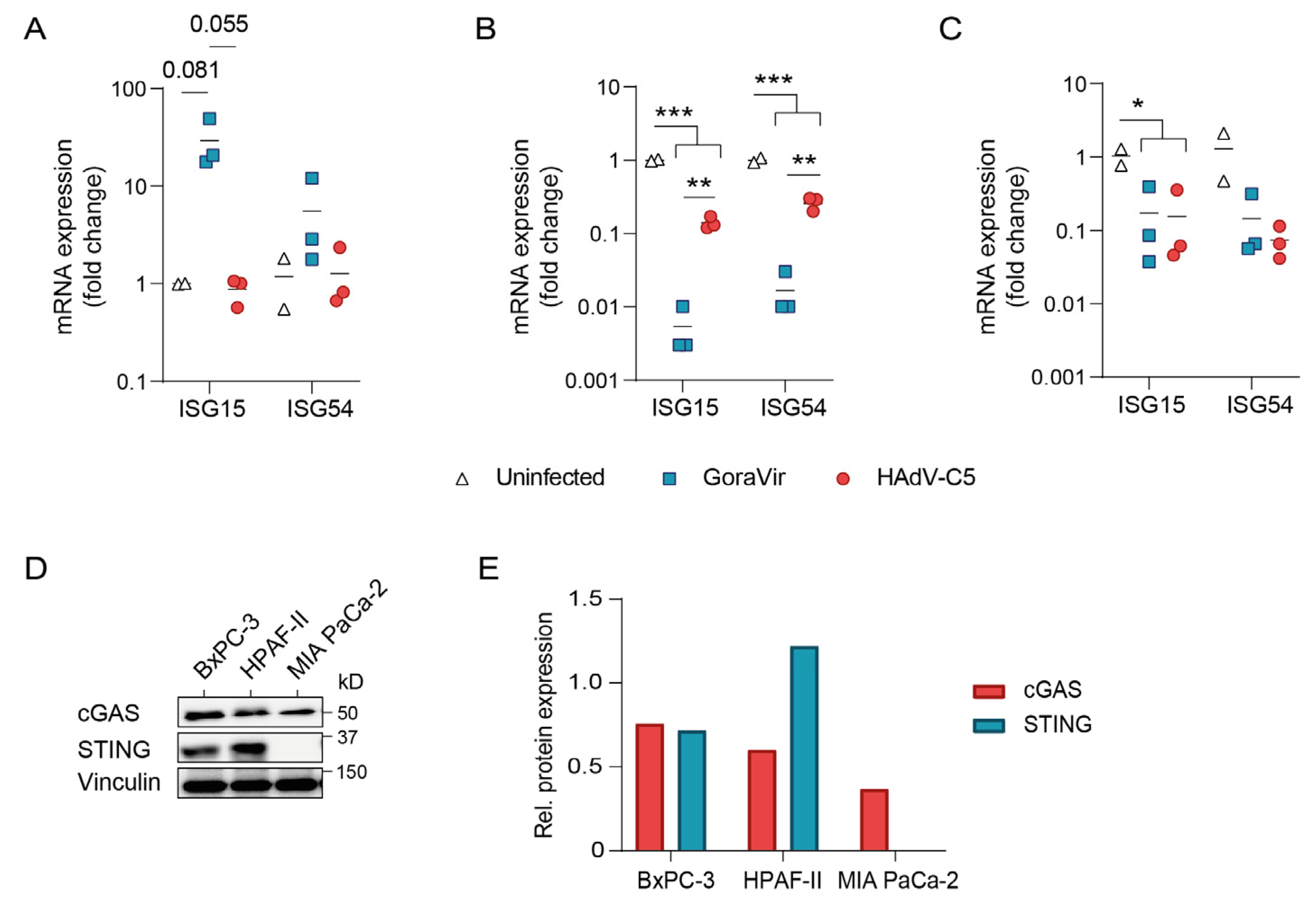
3.4. GoraVir Is a Strong Modulator of Antiviral Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns, A.C.; Wei, L.; Grogan, M.; Hoyd, R.; Bridges, J.F.P.; Patel, S.H.; Li, M.; Husain, M.; Kendra, K.L.; Otterson, G.A.; et al. Checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy toxicity and overall survival among older adults with advanced cancer. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2021, 12, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, M.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and survival outcomes in brain metastasis: A time series-based meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 564382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin-Acevedo, J.A.; Kimbrough, E.M.O.; Lou, Y. Next generation of immune checkpoint inhibitors and beyond. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmer, F.E.F.; Geboers, B.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Dijkstra, M.; Schouten, E.A.C.; Puijk, R.S.; de Vries, J.J.J.; van den Tol, P.M.; Bruynzeel, A.M.E.; Streppel, M.M.; et al. Pancreatic cancer and immunotherapy: A clinical overview. Cancers 2021, 13, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Yang, Z.H.; Guo, Q.Q. Immune checkpoint inhibition for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Limitations and prospects: A systematic review. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteran, L.; Erez, N. The dark side of fibroblasts: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as mediators of immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.Z.; Wang, X.P. Immunogenic cell death-based cancer vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Tait, S.W.G. Targeting immunogenic cell death in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2994–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, K.P.; Wolfson, B.; Hodge, J.W. From immunogenic cell death to immunogenic modulation: Select chemotherapy regimens induce a spectrum of immune-enhancing activities in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 728018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzeibak, R.; Mishchenko, T.A.; Shilyagina, N.Y.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Vedunova, M.V.; Krysko, D.V. Targeting immunogenic cancer cell death by photodynamic therapy: Past, present and future. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Hua, Y.; Cai, Z. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy: Present and emerging inducers. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4854–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Ramachandran, M.; Jin, C.; Quijano-Rubio, C.; Martikainen, M.; Yu, D.; Essand, M. Characterization of virus-mediated immunogenic cancer cell death and the consequences for oncolytic virus-based immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujar, S.; Pol, J.G.; Kroemer, G. Heating it up: Oncolytic viruses make tumors “hot” and suitable for checkpoint blockade immunotherapies. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1442169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, S.T.F.; Kemp, V.; Cramer, S.J.; van den Wollenberg, D.J.M.; Hornsveld, M.; Lamfers, M.L.M.; van der Pluijm, G.; Hoeben, R.C. Nonhuman primate adenoviruses of the Human Adenovirus B species are potent and broadly acting oncolytic vector candidates. Hum. Gene Ther. 2022, 33, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bots, S.T.F.; Harryvan, T.; Groeneveldt, C.; Kinderman, P.; Kemp, V.; van Montfoort, N.; Hoeben, R.C. Preclinical evaluation of the gorilla-derived oncolytic adenovirus AdV-lumc007 “GoraVir” for the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2022; under review. [Google Scholar]
- Davola, M.E.; Mossman, K.L. Oncolytic viruses: How “lytic” must they be for therapeutic efficacy? Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1581528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos de Matos, A.; Franco, L.S.; McFadden, G. Oncolytic viruses and the immune system: The dynamic duo. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matveeva, O.V.; Chumakov, P.M. Defects in interferon pathways as potential biomarkers of sensitivity to oncolytic viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2018, 28, e2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froechlich, G.; Caiazza, C.; Gentile, C.; D’Alise, A.M.; De Lucia, M.; Langone, F.; Leoni, G.; Cotugno, G.; Scisciola, V.; Nicosia, A.; et al. Integrity of the antiviral STING-mediated DNA sensing in tumor cells is required to sustain the immunotherapeutic efficacy of herpes simplex oncolytic virus. Cancers 2020, 12, 3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buqué, A.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesniere, A.; Panaretakis, T.; Kepp, O.; Apetoh, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Molecular characteristics of immunogenic cancer cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhu, B.; Chen, D. Type I interferon-mediated tumor immunity and its role in immunotherapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcıa-Sastre, A. Ten strategies of interferon evasion by viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, E.; Stein, S.; Falck-Pedersen, E. Adenovirus detection by the cGAS/STING/TBK1 DNA sensing cascade. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, D.; Matsumura, S.; Bustos-Villalobos, I.; Sibal, P.A.; Ichinose, T.; Naoe, Y.; Eissa, I.R.; Abdelmoneim, M.; Mukoyama, N.; Miyajima, N.; et al. C-rev retains high infectivity regardless of the expression levels of cGAS and STING in cultured pancreatic cancer cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, V.K.; Ornelles, D.A.; Gooding, L.R.; Wilms, H.T.; Huang, W.; Tollefson, A.E.; Wold, W.S.M.; Garnett-Benson, C. Adenovirus Death Protein (ADP) is required for lytic infection of human lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, P.; Narayan, L.; Kajon, A.E. Human mastadenovirus-B (HAdV-B)-specific E3-CR1β and E3-CR1γ glycoproteins interact with each other and localize at the plasma membrane of non-polarized airway epithelial cells. Virology 2020, 546, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windheim, M.; Höning, S.; Leppard, K.N.; Butler, L.; Seed, C.; Ponnambalam, S.; Burgert, H.-G. Sorting motifs in the cytoplasmic tail of the immunomodulatory E3/49K protein of species D adenoviruses modulate cell surface expression and ectodomain shedding. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 6796–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frietze, K.M.; Campos, S.K.; Kajon, A.E. No evidence of a death-like function for species B1 human adenovirus type 3 E3-9K during A549 cell line infection. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, S.T.F.; Hoeben, R.C. Non-human primate-derived adenoviruses for future use as oncolytic agents? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, S.; Iannuzzi, C.A.; Passaro, C.; Forte, I.M.; Iannone, R.; Gigantino, V.; Indovina, P.; Botti, G.; Giordano, A.; Formisano, P.; et al. The oncolytic virus dl922-947 triggers immunogenic cell death in mesothelioma and reduces xenograft growth. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy, P.K.; Zloza, A.; Rabkin, S.D.; Kaufman, H.L. Oncolytic virus immunotherapy induces immunogenic cell death and overcomes STING deficiency in melanoma. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1591875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.J.; Wang, J.D.; Xu, J.Q.; Lei, X.X.; Liu, Q. cGAS/STING cross-talks with cell cycle and potentiates cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, E.; Falck-Pedersen, E. Unabated adenovirus replication following activation of the cGAS/STING-dependent antiviral response in human cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 14426–14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Persson, J.; Beyer, I.; Möller, T.; Koyuncu, D.; Drescher, M.R.; Strauss, R.; Zhang, Z.B.; et al. Desmoglein 2 is a receptor for adenovirus serotypes 3, 7, 11 and 14. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.; Gray, E.E.; Brunette, R.L.; Stetson, D.B. DNA tumor virus oncogenes antagonize the cGAS-STING DNA-sensing pathway. Science 2015, 350, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Ghonime, M.G.; Wang, R.; Cassady, K.A. The antiviral apparatus: STING and oncolytic virus restriction. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 13, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, M.A.; Tan, N.Y.; Thaim, C.H.; Khatoo, M.; MacAry, P.A.; Angeli, V.; Gasser, S.; Zhang, Y.L. cGAS–STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway is suppressed by JAK2-STAT3 in tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufer, S.; Coffey, C.M.; Parker, J.S.L. The cellular chaperone Hsc70 is specifically recruited to reovirus viral factories independently of its chaperone function. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbanes, S.L.; Blomen, V.A.; Lam, E.; Heissel, S.; Luna, J.M.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Falck-Pedersen, E.; Hoffman, H.H.; Rice, C.M. E3 ubiquitin ligase Mindbomb 1 facilitates nuclear delivery of adenovirus genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 118, e2015794118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, V.; Dautzenberg, I.J.C.; Limpens, R.W.; van den Wollenberg, D.J.M.; Hoeben, R.C. Oncolytic reovirus infection is facilitated by the autophagic machinery. Viruses 2017, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guan, W. STING signaling promotes apoptosis, necrosis, and cell death: An overview and update. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1202797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulen, M.F.; Koch, U.; Haag, S.M.; Schuler, F.; Apetoh, L.; Villunger, A.; Radtke, F.; Ablasser, A. Signalling strength determines proapoptotic functions of STING. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arwert, E.N.; Milford, E.L.; Rullan, A.; Derzsi, S.; Hooper, S.; Kato, T.; Mansfield, D.; Melcher, A.; Harrington, K.J.; Sahai, E. STING and IRF3 in stromal fibroblasts enable sensing of genomic stress in cancer cells to undermine oncolytic viral therapy. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bots, S.T.F.; Landman, S.L.; Rabelink, M.J.W.E.; van den Wollenberg, D.J.M.; Hoeben, R.C. Immunostimulatory Profile of Cancer Cell Death by the AdV-Lumc007-Derived Oncolytic Virus ‘GoraVir’ in Cultured Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Viruses 2023, 15, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020283
Bots STF, Landman SL, Rabelink MJWE, van den Wollenberg DJM, Hoeben RC. Immunostimulatory Profile of Cancer Cell Death by the AdV-Lumc007-Derived Oncolytic Virus ‘GoraVir’ in Cultured Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020283
Chicago/Turabian StyleBots, Selas T. F., Sanne L. Landman, Martijn J. W. E. Rabelink, Diana J. M. van den Wollenberg, and Rob C. Hoeben. 2023. "Immunostimulatory Profile of Cancer Cell Death by the AdV-Lumc007-Derived Oncolytic Virus ‘GoraVir’ in Cultured Pancreatic Cancer Cells" Viruses 15, no. 2: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020283
APA StyleBots, S. T. F., Landman, S. L., Rabelink, M. J. W. E., van den Wollenberg, D. J. M., & Hoeben, R. C. (2023). Immunostimulatory Profile of Cancer Cell Death by the AdV-Lumc007-Derived Oncolytic Virus ‘GoraVir’ in Cultured Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Viruses, 15(2), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020283





