Effects of Deformed Wing Virus-Targeting dsRNA on Viral Loads in Bees Parasitised and Non-Parasitised by Varroa destructor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
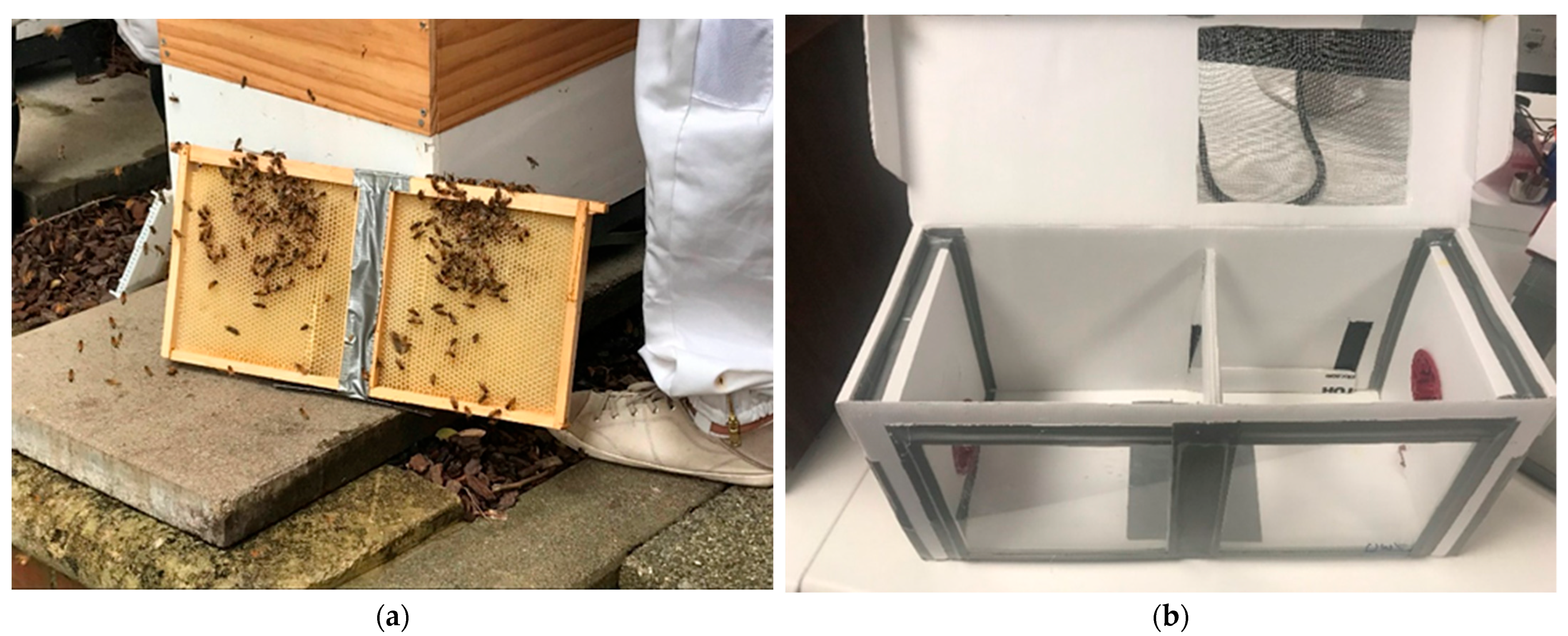
2.1. Mini-Hive and Mini-Frame Design
2.2. Maintaining Laboratory Mini-Hives
2.3. Double-Stranded RNA Treatments
2.4. Experiment Sampling
2.5. Prevalence of Wing Deformities in Uncapped Bees
2.6. Relative Quantification of Deformed Wing Virus in Uncapped Bees
2.7. RNA-Sequencing of Brood-Parasitising Varroa Mites
2.8. Differential Gene Expression
2.9. Viral Community Analysis in Varroa Mites
3. Results
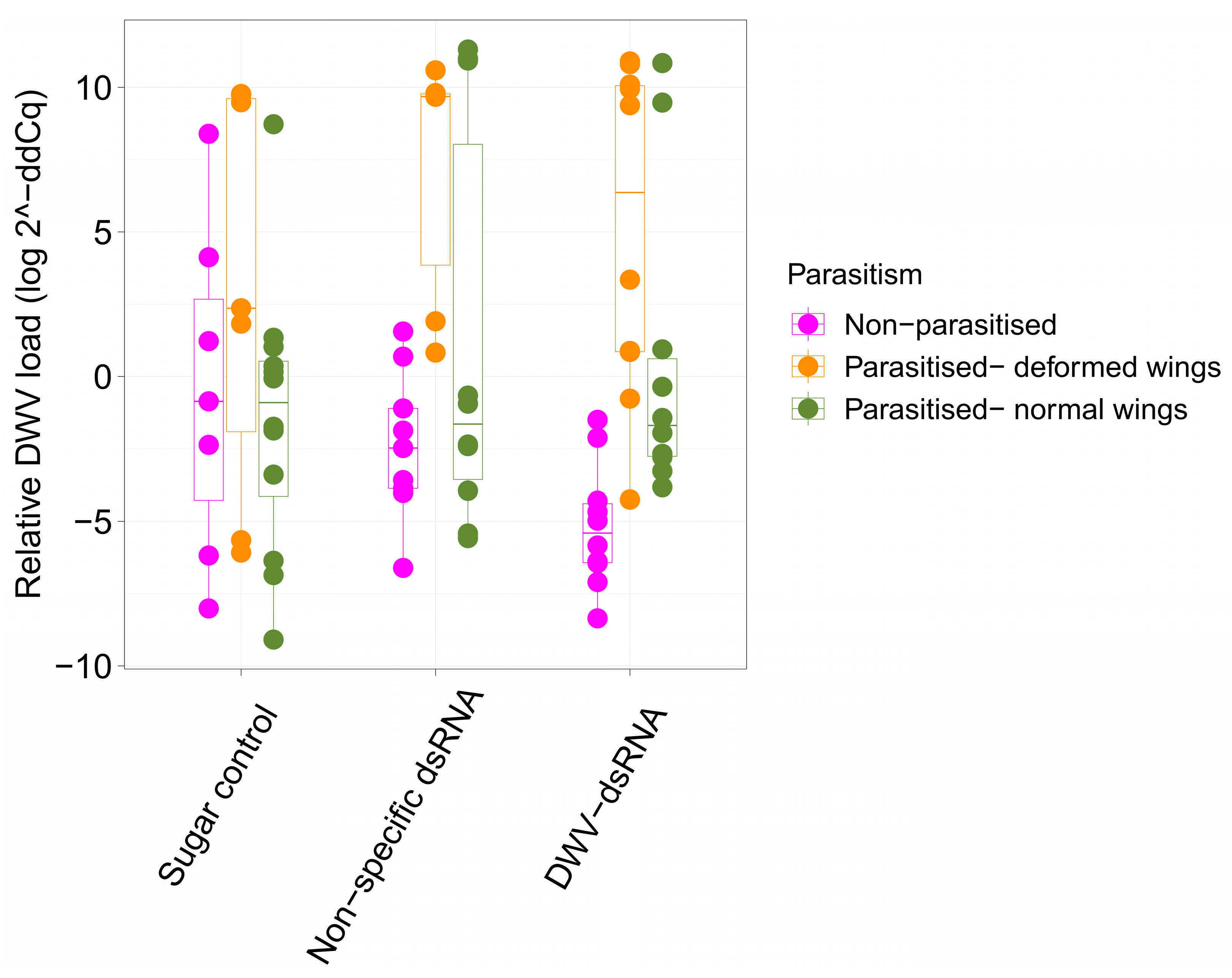
3.1. Deformed Wing Virus Loads in Uncapped Bees
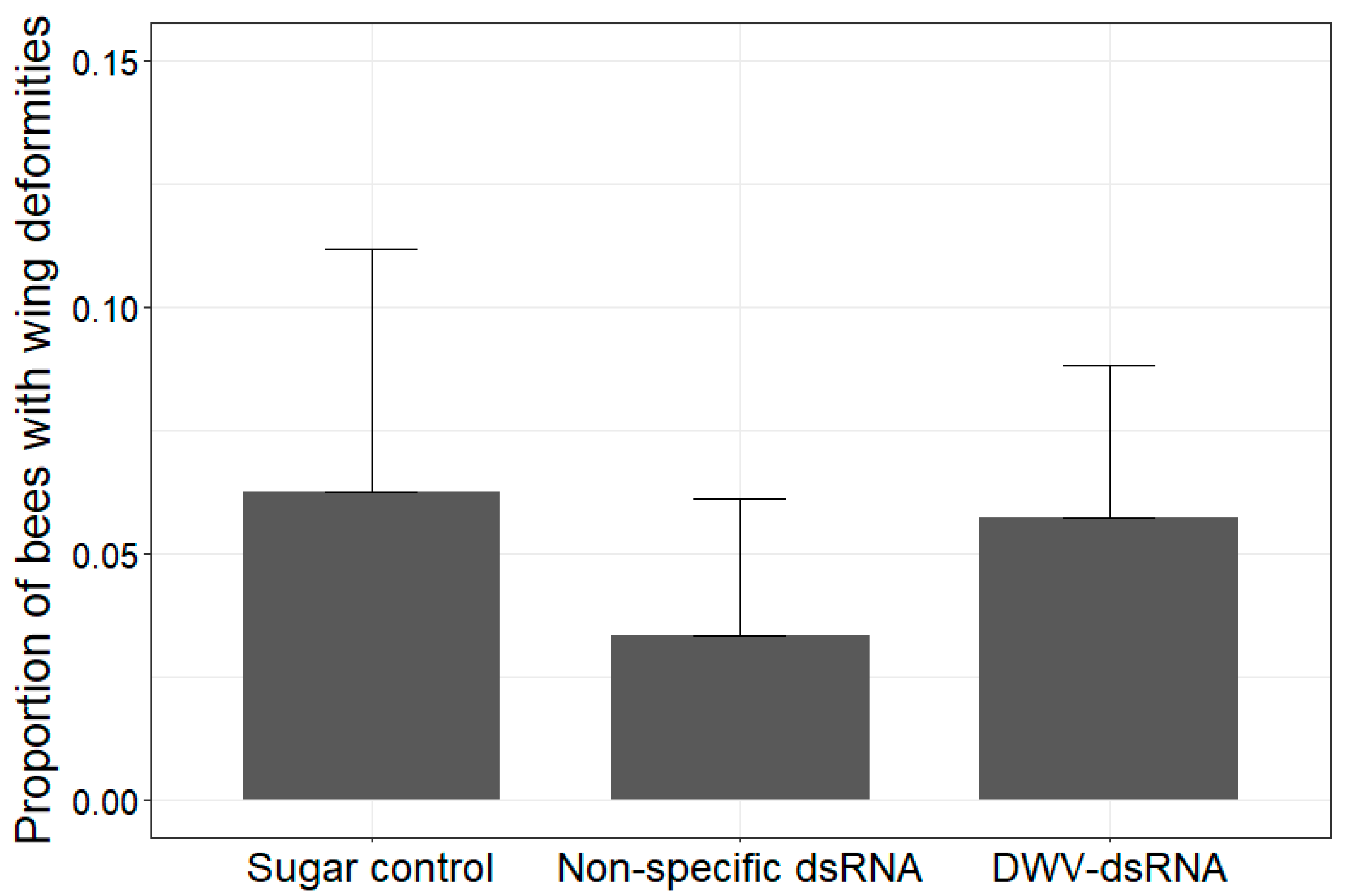
3.2. Instance of Wing Deformities in Uncapped Bees
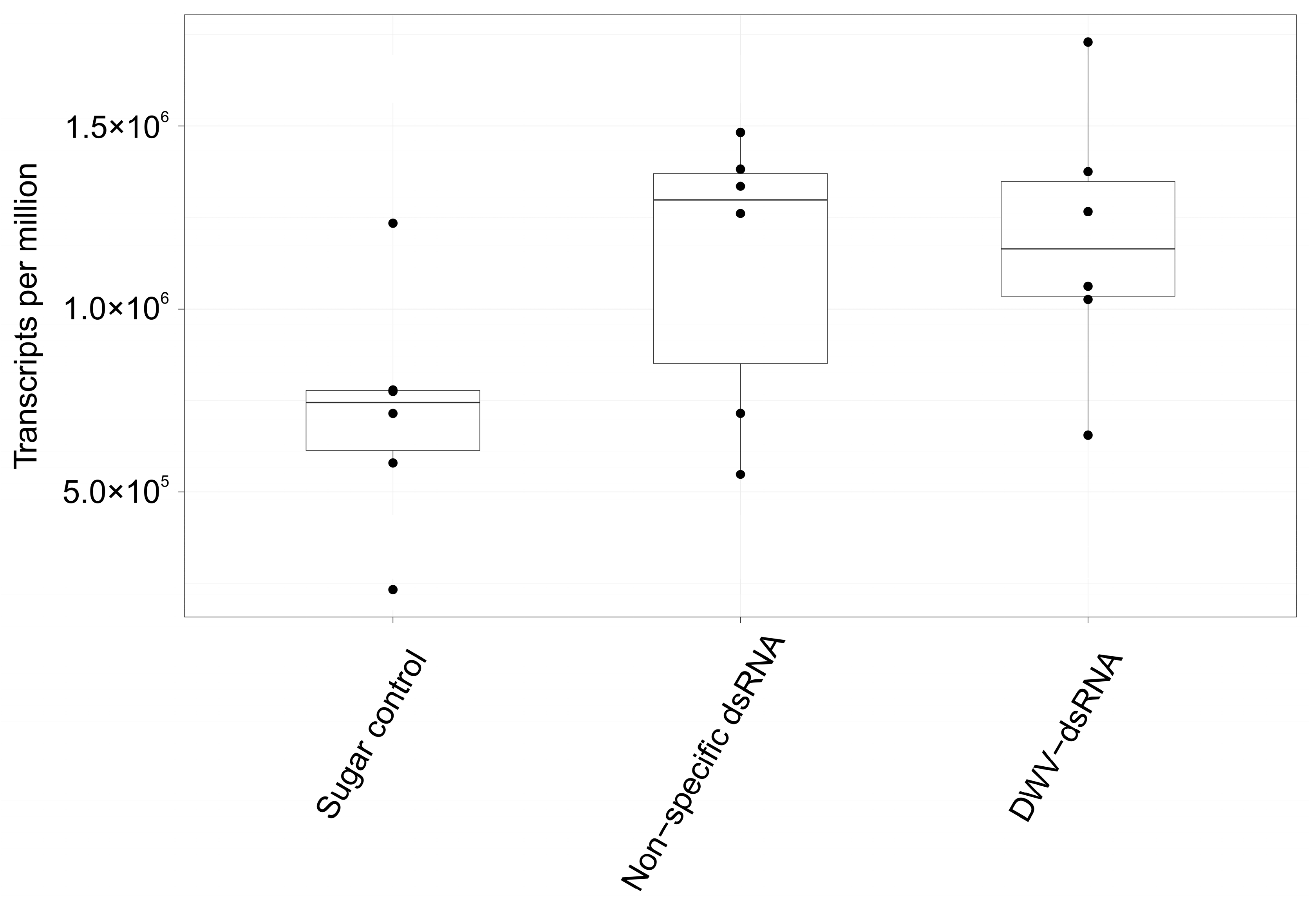
3.3. Differential Gene Expression in Varroa Mites
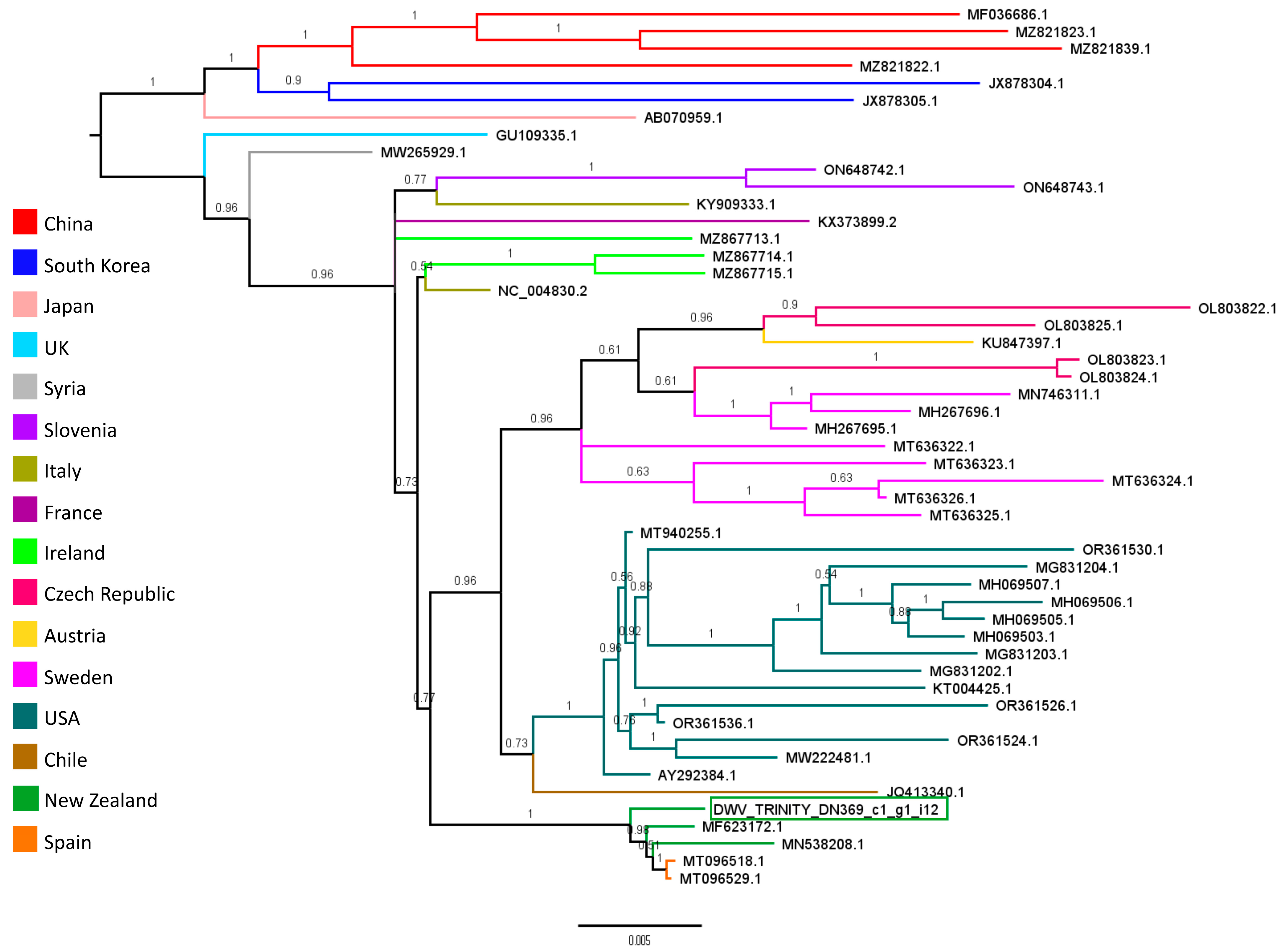
3.4. Viral Community and Abundances in Varroa RNA-Seq Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowen-Walker, P.L.; Martin, S.J.; Gunn, A. The transmission of Deformed wing virus between honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) by the ectoparasitic mite Varroa jacobsoni Oud. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1999, 73, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Pettis, J.S.; Evans, J.D.; Kramer, M.; Feldlaufer, M.F. Transmission of Kashmir bee virus by the ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor. Apidologie 2004, 35, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prisco, G.; Pennacchio, F.; Caprio, E.; Boncristiani, H.F.; Evans, J.D.; Chen, Y. Varroa destructor is an effective vector of Israeli acute paralysis virus in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 92, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, S.D.; Ochoa, R.; Bauchan, G.; Gulbronson, C.; Mowery, J.D.; Cohen, A.; Lim, D.; Joklik, J.; Cicero, J.M.; Ellis, J.D.; et al. Varroa destructor feeds primarily on honey bee fat body tissue and not hemolymph. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillán-Galicia, M.T.; Ball, B.V.; Clark, S.J.; Alderson, P.G. Slow bee paralysis virus and its transmission in honey bee pupae by Varroa destructor. J. Apic. Res. 2014, 53, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Yang, X.; Cox-Foster, D.; Cui, L. The role of varroa mites in infections of Kashmir bee virus (KBV) and deformed wing virus (DWV) in honey bees. Virology 2005, 342, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Arévalo, S.; Fernández-Carrión, E.; Goyache, J.; Molero, F.; Puerta, F.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. High load of Deformed wing wirus and Varroa destructor infestation are related to weakness of honey bee colonies in southern Spain. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreck, N.L.; Ball, B.V.; Martin, S.J. Honey bee colony collapse and changes in viral prevalence associated with Varroa destructor. J. Apic. Res. 2010, 49, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainat, B.; Neumann, P. Clinical signs of deformed wing virus infection are predictive markers for honey bee colony losses. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 112, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhanek, K.; Steinhauer, N.; Rennich, K.; Caron, D.M.; Sagili, R.R.; Pettis, J.S.; Ellis, J.D.; Wilson, M.E.; Wilkes, J.T.; Tarpy, D.R.; et al. A national survey of managed honey bee 2015–2016 annual colony losses in the USA. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, K.S.; Mondet, F.; de Miranda, J.R.; Techer, M.; Kowallik, V.; Oddie, M.A.; Chantawannakul, P.; McAfee, A. Varroa destructor: A complex parasite, crippling honey bees worldwide. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cox-Foster, D. Effects of parasitization by Varroa destructor on survivorship and physiological traits of Apis mellifera in correlation with viral incidence and microbial challenge. Parasitology 2006, 134 Pt 3, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfert, L.; Long, G.; Leggett, H.C.; Schmid-Hempel, P.; Butlin, R.; Martin, S.J.M.; Boots, M. Deformed wing virus is a recent global epidemic in honeybees driven by Varroa mites. Science 2016, 351, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.J.; Highfield, A.C.; Brettell, L.; Villalobos, E.M.; Budge, G.E.; Powell, M.; Nikaido, S.; Schroeder, D.C. Global Honey Bee Viral Landscape Altered by a Parasitic Mite. Science 2012, 336, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondet, F.; de Miranda, J.R.; Kretzschmar, A.; Le Conte, Y.; Mercer, A.R. On the Front Line: Quantitative Virus Dynamics in Honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) Colonies along a New Expansion Front of the Parasite Varroa destructor. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettell, L.E.; Mordecai, G.J.; Schroeder, D.C.; Jones, I.M.; Da Silva, J.R.; Vicente-Rubiano, M.; Martin, S.J. A Comparison of Deformed Wing Virus in Deformed and Asymptomatic Honey Bees. Insects 2017, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzi, G.; de Miranda, J.R.; Boniotti, M.B.; Cameron, C.E.; Lavazza, A.; Capucci, L.; Camazine, S.M.; Rossi, C. Molecular and Biological Characterization of Deformed Wing Virus of Honeybees (Apis mellifera L.). J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4998–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Mueller, U. Virus infection causes specific learning deficits in honeybee foragers. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaets, K.; Van Geystelen, A.; Cardoen, D.; De Smet, L.; De Graaf, D.C.; Schoofs, L.; Larmuseau, M.H.D.; Brettell, L.E.; Martin, S.J.; Wenseleers, T. Covert deformed wing virus infections have long-term deleterious effects on honeybee foraging and survival. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20162149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traniello, I.M.; Bukhari, S.A.; Kevill, J.; Ahmed, A.C.; Hamilton, A.R.; Naeger, N.L.; Schroeder, D.C.; Robinson, G.E. Meta-analysis of honey bee neurogenomic response links Deformed wing virus type A to precocious behavioral maturation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, B.; Forsgren, E.; Fries, I.; de Miranda, J.R. Acaricide Treatment Affects Viral Dynamics in Varroa destructor-Infested Honey Bee Colonies via both Host Physiology and Mite Control. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.J.; Ball, B.V.; Carreck, N.L. Prevalence and persistence of Deformed wing virus (DWV) in untreated or acari-cide-treated Varroa destructor infested honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies. J. Apic. Res. 2010, 49, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkevich, F.D. Detection of amitraz resistance and reduced treatment efficacy in the Varroa Mite, Varroa destructor, within commercial beekeeping operations. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stara, J.; Pekar, S.; Nesvorna, M.; Erban, T.; Vinsova, H.; Kopecky, J.; Doskocil, I.; Kamler, M.; Hubert, J. Detection of tau-fluvalinate resistance in the mite Varroa destructor based on the comparison of vial test and PCR–RFLP of kdr mutation in sodium channel gene. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 77, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlogiannitis, S.; Jonckheere, W.; Laget, D.; de Graaf, D.C.; Vontas, J.; Van Leeuwen, T. Pyrethroid target-site resistance mutations in populations of the honey bee parasite Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae) from Flanders, Belgium. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 85, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.B.; Monteiro, T.R.; Cabral, G.B.; Aragão, F.J.L. RNAi-mediated resistance to whitefly (Bemisia tabaci) in genetically engineered lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Transgenic Res. 2017, 26, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, S.; Reidy-Crofts, J.; Sperschneider, J.; Kamphuis, L.G.; Gao, L.-L.; Edwards, O.R.; Singh, K.B. An RNAi supplemented diet as a reverse genetics tool to control bluegreen aphid, a major pest of legumes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Chen, M.; Sun, J.; Van Leeuwen, T.; He, L. Comparing the efficiency of RNAi after feeding and injection of dsRNA in spider mites. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 179, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Fang, M.; Lee, D.; Park, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Shin, C. Double-stranded RNA confers resistance to pepper mottle virus in Nicotiana benthamiana. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.B.; Dhandapani, R.K.; Duan, J.J.; Palli, S.R. RNA interference in the Asian longhorned beetle: Identification of key RNAi genes and reference genes for RT-qPCR. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gonzales, M.A.A.; Poland, T.M.; Mittapalli, O. Core RNAi machinery and gene knockdown in the emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis). J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 72, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.C.; Doudna, J.A. Molecular Mechanisms of RNA Interference. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.M.; Budge, G.E.; Bowman, A.S. Gene-knockdown in the honey bee mite Varroa destructor by a non-invasive approach: Studies on a glutathione S-transferase. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbian, Y.; Maori, E.; Kalev, H.; Shafir, S.; Sela, I. Bidirectional Transfer of RNAi between Honey Bee and Varroa destructor: Varroa Gene Silencing Reduces Varroa Population. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.P.; Powell, J.E.; Perutka, J.; Geng, P.; Heckmann, L.C.; Horak, R.D.; Davies, B.W.; Ellington, A.D.; Barrick, J.E.; Moran, N.A. Engineered symbionts activate honey bee immunity and limit pathogens. Science 2020, 367, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Neumann, P.; Li, W.; Evans, J.D. Effective Silencing of Dicer Decreases Spore Load of the Honey Bee Parasite Nosema ceranae. Fungal Genom. Biol. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paldi, N.; Glick, E.; Oliva, M.; Zilberberg, Y.; Aubin, L.; Pettis, J.; Chen, Y.; Evans, J.D. Effective Gene Silencing in a Microsporidian Parasite Associated with Honeybee (Apis mellifera) Colony Declines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5960–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, W.; Ellis, J.; Vanengelsdorp, D.; Hayes, J.; Westervelt, D.; Glick, E.; Williams, M.; Sela, I.; Maori, E.; Pettis, J.; et al. Large-scale field application of RNAi technology reducing Israeli acute paralysis virus disease in honey bees (Apis mellifera, Hymenoptera: Apidae). PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maori, E.; Paldi, N.; Shafir, S.; Kalev, H.; Tsur, E.; Glick, E.; Sela, I. IAPV, a bee-affecting virus associated with Colony Collapse Disorder can be silenced by dsRNA ingestion. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, X.; Han, R. Prevention of Chinese Sacbrood Virus Infection in Apis cerana using RNA Interference. Curr. Microbiol. 2010, 61, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, R. The high-throughput production of dsRNA against sacbrood virus for use in the honey bee Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Virus Genes 2016, 52, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.E.; Bradish, H.M.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Fitches, E.C. Systemic RNAi in the small hive beetle Aethina tumida Murray (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae), a serious pest of the European honey bee Apis mellifera. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Eu, Y.J.; Whyard, S.; Currie, R.W. Reduction in Deformed wing virus infection in larval and adult honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) by double-stranded RNA ingestion. Insect Mol. Biol. 2012, 21, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.-S.; Truong, A.-T.; Jeong, H.; Hahn, D.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Yoon, S.-S.; Youn, S.-Y.; Cho, Y.-S. Large-Scale Application of Double-Stranded RNA Shows Potential for Reduction of Sacbrood Virus Disease in Apis cerana Apiaries. Viruses 2023, 15, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maori, E.; Garbian, Y.; Kunik, V.; Mozes-Koch, R.; Malka, O.; Kalev, H.; Sabath, N.; Sela, I.; Shafir, S. A Transmissible RNA Pathway in Honey Bees. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1949–1959.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Alaux, C.; Costa, C.; Csaki, T.; Doublet, V.; Eisenhardt, D.; Fries, I.; Kuhn, R.; McMahon, D.P.; Medrzycki, P.; et al. Standard methods for maintaining adult Apis mellifera in cages under in vitro laboratory conditions. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Neto, M.; Soares, M.P.M.; Bitondi, M.M.G. Changes in integument structure during the imaginal molt of the honey bee. Apidologie 2008, 40, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, R.C.; Duncan, E.J.; Dearden, P.K. Stable reference genes for the measurement of transcript abundance during larval caste development in the honeybee. Apidologie 2013, 44, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Wakem, M.; Dijkman, G.; Alsarraj, M.; Nguyen, M. A practical approach to RT-qPCR—Publishing data that conform to the MIQE guidelines. Methods 2010, 50, S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J. Vegan: Ecological diversity. R Proj. 2013, 368, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondet, F.; Rau, A.; Klopp, C.; Rohmer, M.; Severac, D.; Le Conte, Y.; Alaux, C. Transcriptome profiling of the honeybee parasite Varroa destructor provides new biological insights into the mite adult life cycle. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nganso, B.T.; Sela, N.; Soroker, V. A genome-wide screening for RNAi pathway proteins in Acari. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.D.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Reuter, K.; Drost, H.-G. Sensitive protein alignments at tree-of-life scale using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kans, J. Entrez Direct: E-Utilities on the UNIX Command Line, in Entrez Programming Utilities; National Center for Bio-Technology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogeny. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnberg, L.; Temmam, S.; Aranda, C.; Correa-Fiz, F.; Talavera, S.; Bigot, T.; Eloit, M.; Busquets, N. Viromics on Honey-Baited FTA Cards as a New Tool for the Detection of Circulating Viruses in Mosquitoes. Viruses 2020, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möckel, N.; Gisder, S.; Genersch, E. Horizontal transmission of deformed wing virus: Pathological consequences in adult bees (Apis mellifera) depend on the transmission route. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Genersch, E. RT-PCR analysis of Deformed wing virus in honeybees (Apis mellifera) and mites (Varroa destructor). J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 3419–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabov, E.V.; Childers, A.K.; Lopez, D.; Grubbs, K.; Posada-Florez, F.; Weaver, D.; Girten, W.; Vanengelsdorp, D.; Chen, Y.; Evans, J.D. Dynamic evolution in the key honey bee pathogen deformed wing virus: Novel insights into virulence and competition using reverse genetics. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobelmann, J.; Felden, A.; Lester, P.J. Genetic strain diversity of multi-host RNA viruses that infect a wide range of polli-nators and associated is shaped by geographic origins. Viruses 2020, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, P.J.; Felden, A.; Baty, J.W.; Bulgarella, M.; Haywood, J.; Mortensen, A.N.; Remnant, E.J.; Smeele, Z.E. Viral communities in the parasite Varroa destructor and in colonies of their honey bee host (Apis mellifera) in New Zealand. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, S.; Millán-Leiva, A.; Coll, S.; González-Martínez, R.M.; Parenti, S.; González-Cabrera, J. Identification of new viral variants specific to the honey bee mite Varroa destructor. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 79, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, S.; Sela, N.; Chejanovsky, N. Two novel viruses associated with the Apis mellifera pathogenic mite Varroa destructor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, S.; Sela, N.; Erez, T.; Nestel, D.; Pettis, J.; Neumann, P.; Chejanovsky, N. New Viruses from the Ectoparasite Mite Varroa destructor Infesting Apis mellifera and Apis cerana. Viruses 2019, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisder, S.; Aumeier, P.; Genersch, E. Deformed wing virus: Replication and viral load in mites (Varroa destructor). J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, Z.S.; Solmaz, S.; Ryabov, E.V.; Mowery, J.; Heermann, M.; Sonenshine, D.; Evans, J.D.; Hawthorne, D.J. Promiscuous feeding on multiple adult honey bee hosts amplifies the vectorial capacity of Varroa destructor. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, N.; Hall, M.J.; Hellmich, R.L.; Coats, J.R.; Bradbury, S.P. Evaluating toxicity of Varroa mite (Varroa destructor)-active dsRNA to monarch butterfly (Danaus plex-ippus) larvae. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taning, C.N.T.; Mezzetti, B.; Kleter, G.; Smagghe, G.; Baraldi, E. Does RNAi-based technology fit within EU sustainability goals? Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, C.; Evans, J.D.; Li, W.; Branchiccela, B.; Li, J.H.; Heerman, M.C.; Banmeke, O.; Zhao, Y.; Hamilton, M.; Higes, M.; et al. Nosemosis control in European honey bees, Apis mellifera, by silencing the gene encoding Nosema ceranae polar tube protein 3. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221 Pt 19, jeb184606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Mercer, A.; Mitchell, A.; de Miranda, J.R.; Ward, V.; Mondet, F.; Bostina, M. Viral infections alter antennal epithelium ultrastructure in honey bees. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 168, 107252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annoscia, D.; Brown, S.P.; Di Prisco, G.; De Paoli, E.; Del Fabbro, S.; Frizzera, D.; Zanni, V.; Galbraith, D.A.; Caprio, E.; Grozinger, C.M.; et al. Haemolymph removal by Varroa mite destabilizes the dynamical interaction between immune effectors and virus in bees, as predicted by Volterra’s model. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20190331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erban, T.; Sopko, B.; Kadlikova, K.; Talacko, P.; Harant, K. Varroa destructor parasitism has a greater effect on proteome changes than the Deformed wing virus and ac-tivates TGF-β signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smeele, Z.E.; Baty, J.W.; Lester, P.J. Effects of Deformed Wing Virus-Targeting dsRNA on Viral Loads in Bees Parasitised and Non-Parasitised by Varroa destructor. Viruses 2023, 15, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112259
Smeele ZE, Baty JW, Lester PJ. Effects of Deformed Wing Virus-Targeting dsRNA on Viral Loads in Bees Parasitised and Non-Parasitised by Varroa destructor. Viruses. 2023; 15(11):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112259
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmeele, Zoe E., James W. Baty, and Philip J. Lester. 2023. "Effects of Deformed Wing Virus-Targeting dsRNA on Viral Loads in Bees Parasitised and Non-Parasitised by Varroa destructor" Viruses 15, no. 11: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112259
APA StyleSmeele, Z. E., Baty, J. W., & Lester, P. J. (2023). Effects of Deformed Wing Virus-Targeting dsRNA on Viral Loads in Bees Parasitised and Non-Parasitised by Varroa destructor. Viruses, 15(11), 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112259




