Molecular Epidemiology of Rotavirus A in Calves: Evolutionary Analysis of a Bovine G8P[11] Strain and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of G6 Lineages in the Americas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Farms, Calves, and Sample Collection
2.2. RVA Reference Strains and Antigen Detection
2.3. RNA Extraction and G/P Genotyping
2.4. Sequencing of VP7 and VP8*
2.5. Sequencing of RVA Gene Segments
2.6. Sequence Analysis, Genotype Assignment, and Percentage Identity
2.7. Substitution Models and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.8. Determination of G8 Lineages
2.9. Phylodynamic and Phylogeographic Analyses of G6 RVA Strains
2.10. GenBank Accession Numbers
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Frequency of RVA Infections
3.2. Genotyping of RVA Field Strains
3.3. Genome Analysis of the G8P[11] RVA Strain
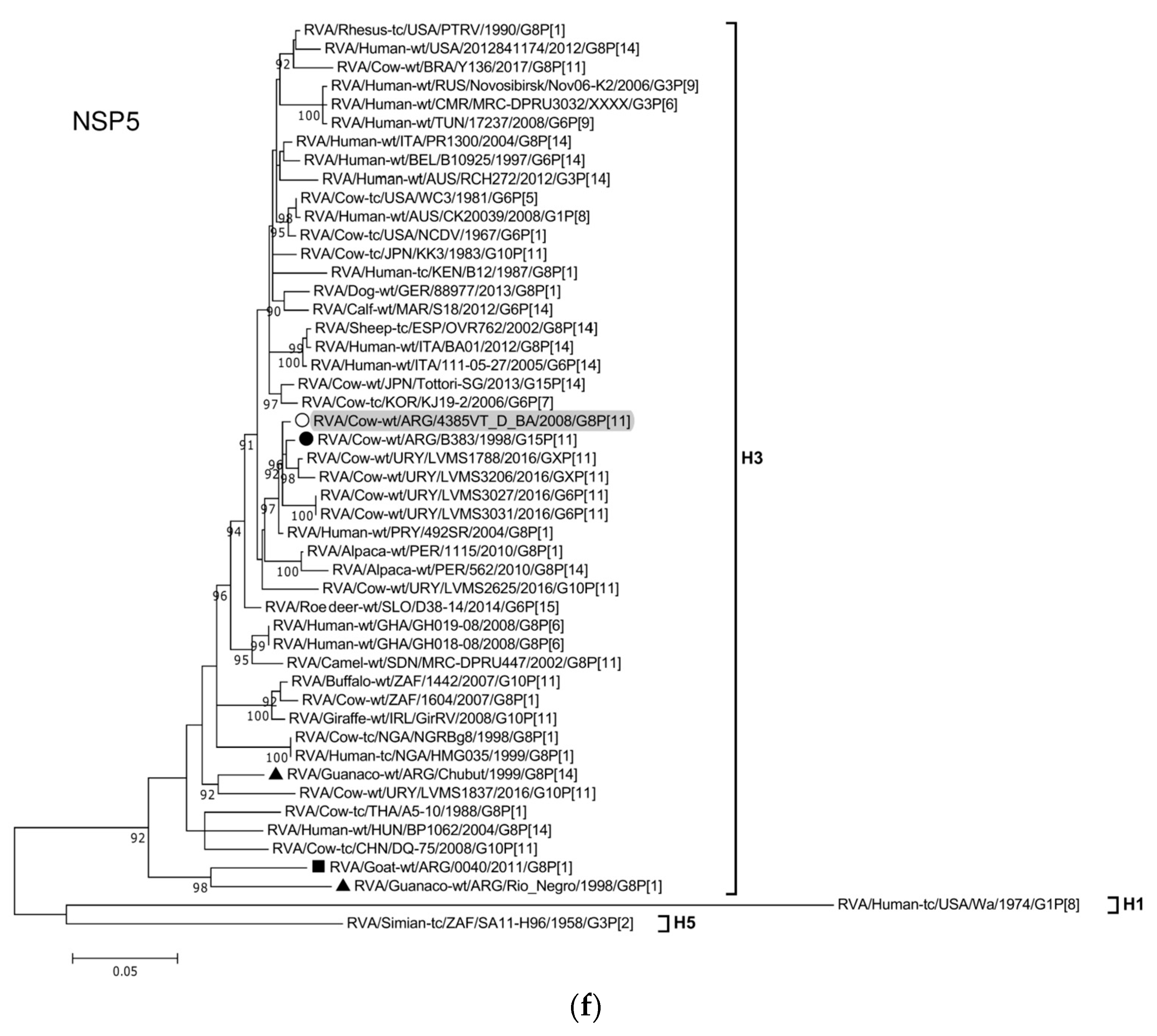
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of the G8P[11] RVA Strain
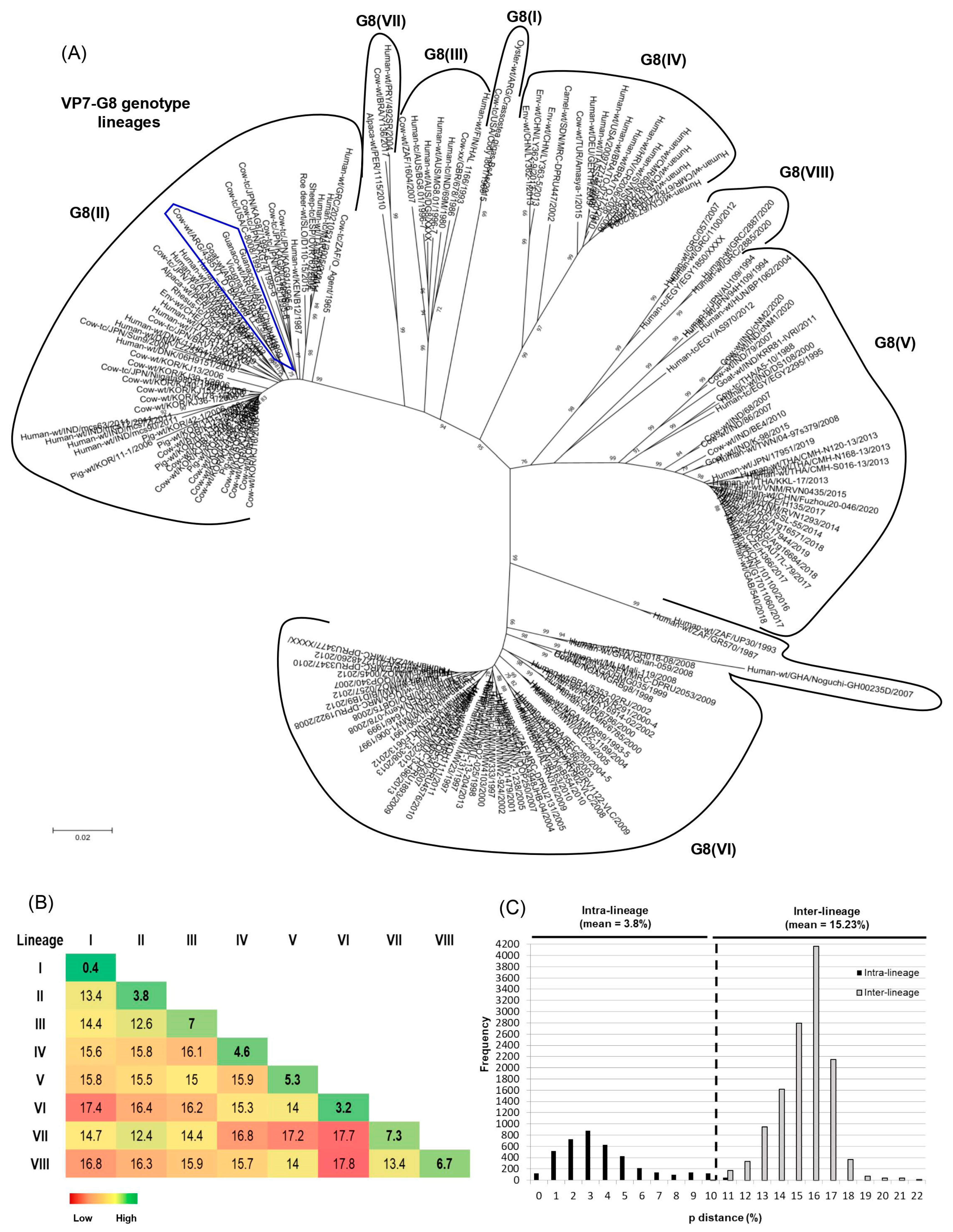
3.5. G8 Lineages and Genetic Distance Analysis
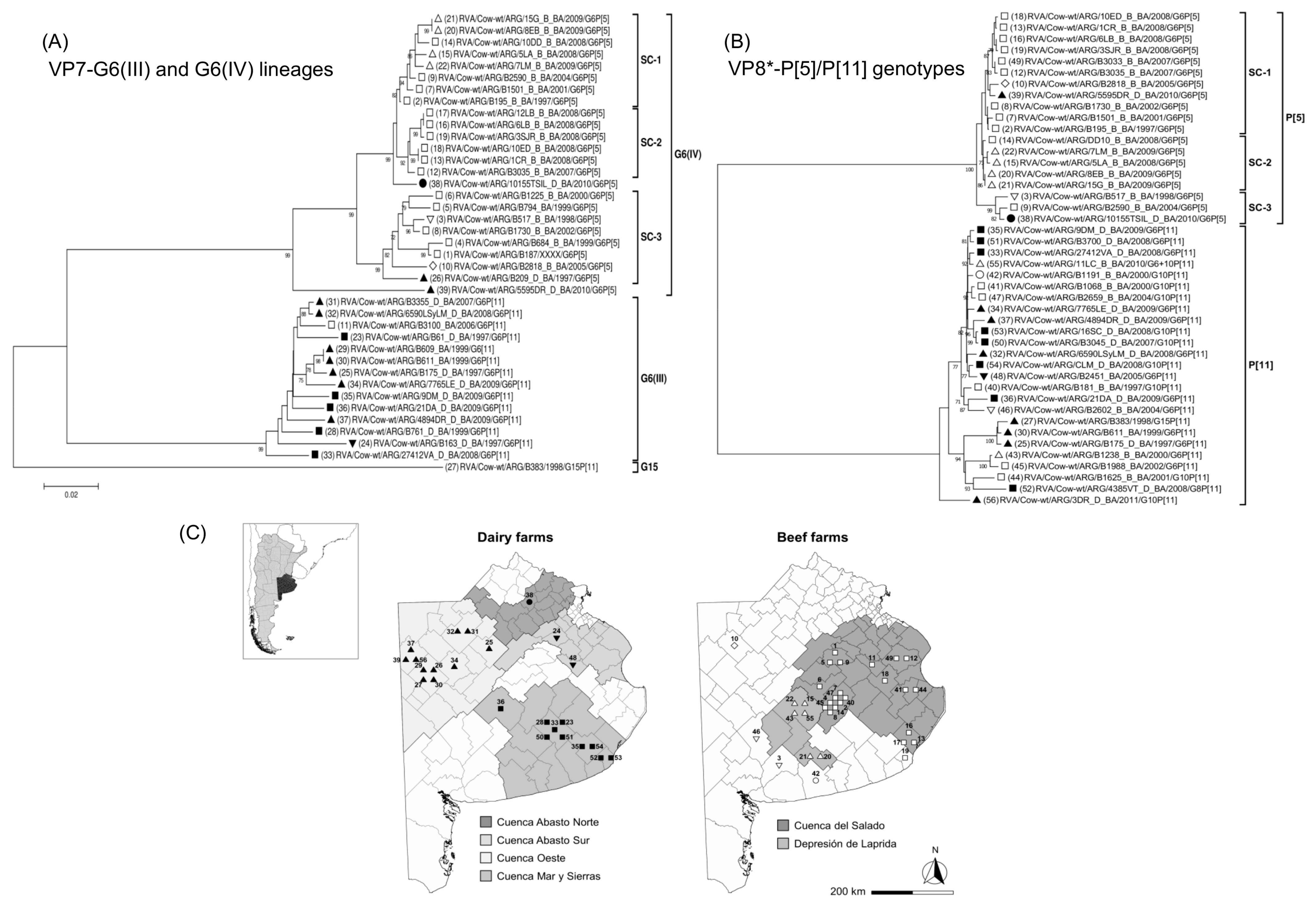
3.6. Phylogenetic Analyses of VP7 and VP8* among G6 and G10 Strains
3.7. Phylogeny of G6 RVA Strains According to Production Systems and Farm Location
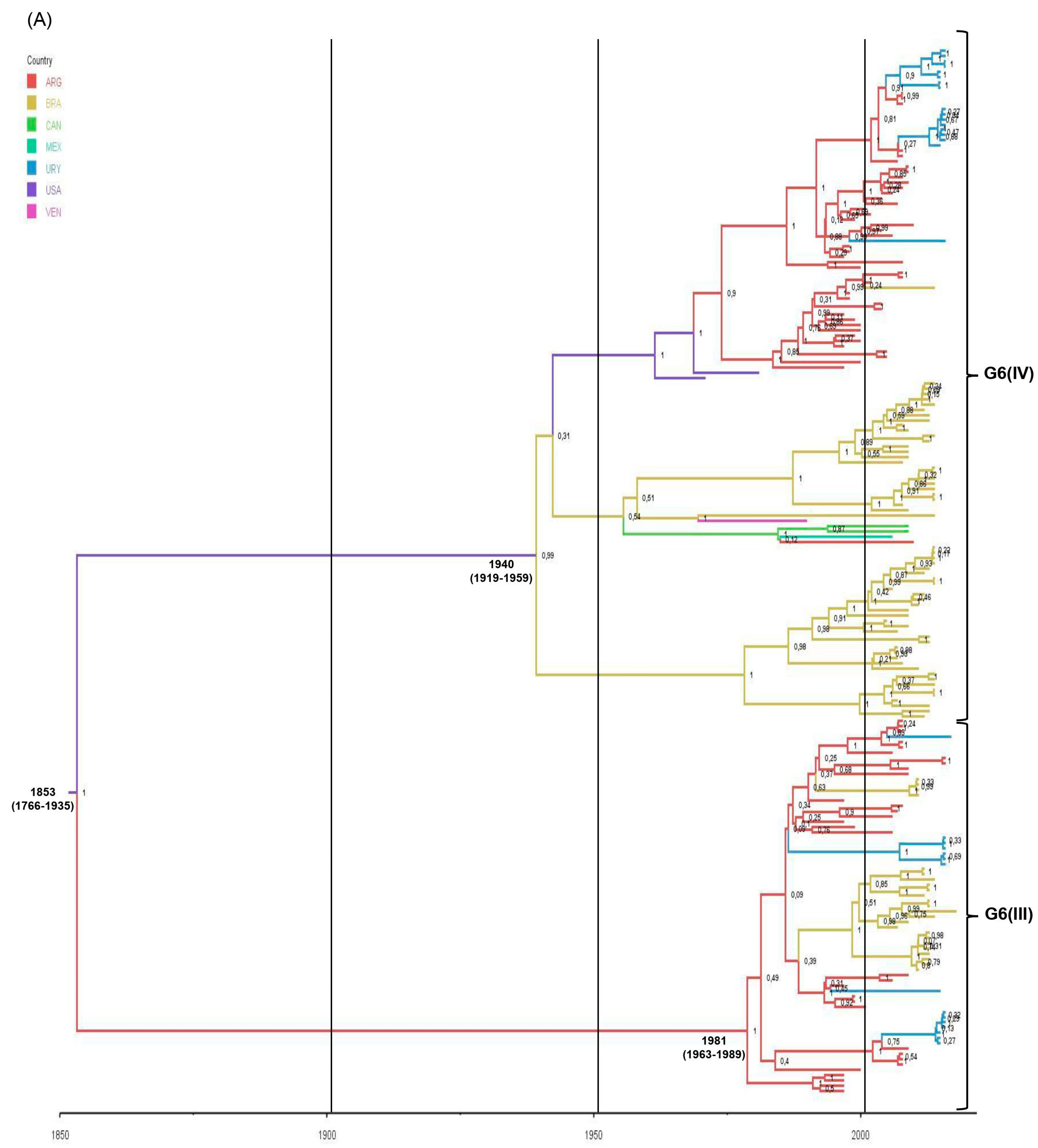
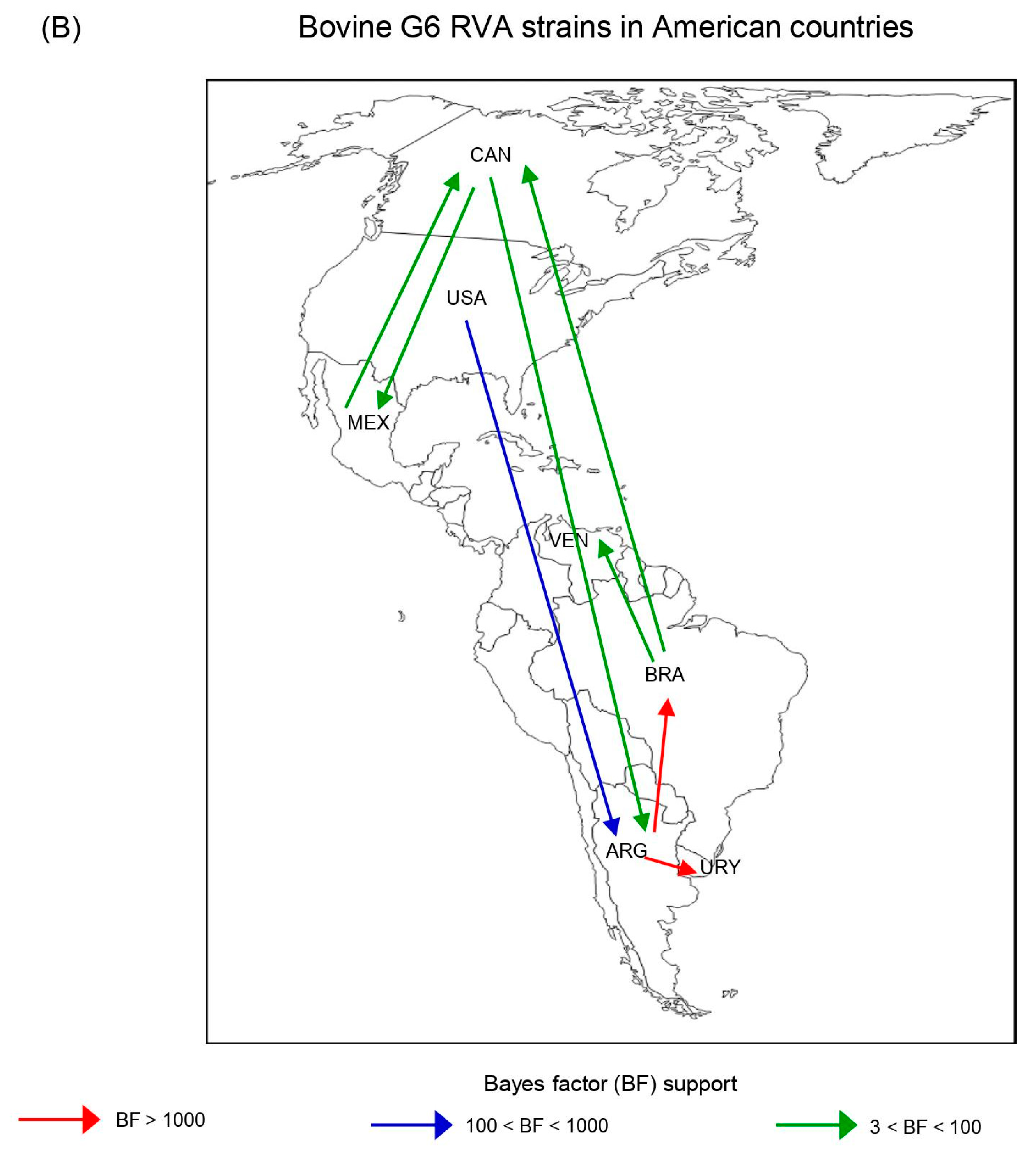
3.8. Phylodynamic and Phylogeographic Analyses of G6(III) and G6(IV) Lineages
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, D.R. Field disease diagnostic investigation of neonatal calf diarrhea. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2012, 28, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.I.; Yoon, K.J. An overview of calf diarrhea-infectious etiology, diagnosis, and intervention. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Deol, P.; Sircar, S.; Ghosh, S.; Jakab, S.; Bányai, K.; Dhama, K.; Amimo, J.O.; Saif, L.J.; Malik, Y.S. Animal Rotaviruses. In Animal-Origin Viral Zoonoses. Livestock Diseases and Management, 1st ed.; Malik, Y.S., Singh, R.K., Dhama, K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020; pp. 163–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, E.; Barragán, A.A.; Bok, M.; Vega, C.; Martínez, M.; Gil, J.F.; Cimino, R.O.; Parreño, V. Assessment of Influential Factors for Scours Associated with Cryptosporidium sp., Rotavirus and Coronavirus in Calves from Argentinean Dairy Farms. Animals 2021, 11, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV): 2022 Release. Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Matthijnssens, J.; Otto, P.H.; Ciarlet, M.; Desselberger, U.; Van Ranst, M.; Johne, R. VP6-sequence-based cutoff values as a criterion for rotavirus species demarcation. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desselberger, U. Rotaviruses. Virus Res. 2014, 190, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.J.; Morgan, J.H.; Chanter, N.; Jones, P.W.; Bridger, J.C.; Debney, T.G.; Bunch, K.J. Microbiology of calf diarrhoea in southern Britain. Vet. Rec. 1986, 119, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz Uhde, F.L.; Kaufmann, T.; Sager, H.; Albini, S.; Zanoni, R.; Schelling, E.; Meylan, M. Prevalence of four enteropathogens in the faeces of young diarrhoeic dairy calves in Switzerland. Vet. Rec. 2008, 163, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, M.M.; Kirkland, P.D.; Mohler, V.L.; Perkins, N.R.; Gunn, A.A.; House, J.K. Prevalence of major enteric pathogens in Australian dairy calves with diarrhoea. Aust. Vet. J. 2011, 89, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaracco, A.; Garaicoechea, L.; Rodríguez, D.; Louge Uriarte, E.L.; Odeón, A.; Bilbao, G.; Galarza, R.; Abdala, A.; Fernández, F.; Parreño, V. Bovine rotavirus strains circulating in beef and dairy herds in Argentina from 2004 to 2010. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 158, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.I.; Han, J.I.; Wang, C.; Cooper, V.; Schwartz, K.; Engelken, T.; Yoon, K.J. Case–control study of microbiological etiology associated with calf diarrhea. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, A.A.; Monteagudo, L.V.; Arnal, J.L.; Baselga, C.; Quílez, J. Occurrence and genetic diversity of rotavirus A in faeces of diarrheic calves submitted to a veterinary laboratory in Spain. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 185, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells, M.; Caffarena, R.D.; Casaux, M.L.; Schild, C.; Miño, S.; Castells, F.; Castells, D.; Victoria, M.; Riet-Correa, F.; Giannitti, F.; et al. Phylogenetic Analyses of Rotavirus A from Cattle in Uruguay Reveal the Circulation of Common and Uncommon Genotypes and Suggest Interspecies Transmission. Pathogens 2020, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, M.K.; Greenberg, H.B. Rotaviruses. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Cohen, J.I., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Racaniello, V.R., Roizman, B., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 1347–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, H.; László, B.; Jakab, F.; Ganesh, B.; De Grazia, S.; Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K. Review of group A rotavirus strains reported in swine and cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Verdier Klingenberg, K.; Nilsson, M.; Svensson, L. Rotavirus G-type restriction, persistence, and herd type specificity in Swedish cattle herds. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1999, 6, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A.; Barreiros, M.A.B.; Leite, J.P.G.; Richtzenhain, L.J. G and P genotypes of group A rotavirus strains circulating in calves in Brazil, 1996–1999. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 99, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Limas, W.A.; Flores-Samaniego, B.; de la Mora, G.; Ramírez, O.T.; Palomares, L.A. Genotypification of bovine group A rotavirus in Mexico. Vaccine 2009, 27, 6411–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, F.; Ozkul, A.; Oguzoglu, T.C.; Timurkan, M.O.; Caliskan, E.; Martella, V.; Burgu, I. Distribution of G (VP7) and P (VP4) genotypes of group A bovine rotaviruses from Turkish calves with diarrhea, 1997–2008. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 141, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, O.; Lennon, G.; Sleator, R.D.; Power, E.; Fanning, S.; O’Shea, H. Changing profile of the bovine rotavirus G6 population in the south of Ireland from 2002 to 2009. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 146, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatek, D.L.; Palombo, E.A.; Lee, A.; Coventry, M.J.; Britz, M.L.; Kirkwood, C.D. Detection and analysis of bovine rotavirus strains circulating in Australian calves during 2004 and 2005. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplon, J.; Fremy, C.; Bernard, S.; Rehby, L.; Aho, S.; Pothier, P.; Ambert-Balay, K. Impact of rotavirus vaccine on rotavirus genotypes and caliciviruses circulating in French cattle. Vaccine 2013, 31, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.J.; Mulherin, E.; Cashman, O.; Lennon, G.; Gunn, L.; O’Shea, H.; Fanning, S. Detection and characterisation of bovine rotavirus in Ireland from 2006–2008. Ir. Vet. J. 2014, 67, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Medeiros, T.N.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. G and P genotype profiles of rotavirus A field strains circulating in beef and dairy cattle herds in Brazil, 2006–2015. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 64, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinzoni, R.C.; Blackhall, J.; Baro, N.; Auza, N.; Mattion, N.; Casaro, A.; La Torre, J.L.; Scodeller, E.A. Efficacy of an inactivated oil-adjuvanted rotavirus vaccine in the control of calf diarrhoea in beef herds in Argentina. Vaccine 1989, 7, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Rahman, M.; Attoui, H.; Bányai, K.; Estes, M.K.; Gentsch, J.R.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Martella, V.; et al. Recommendations for the classification of group A rotaviruses using all 11 genomic RNA segments. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Heiman, E.; Arijs, I.; Delbeke, T.; McDonald, S.M.; Palombo, E.A.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Maes, P.; Patton, J.T.; et al. Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-Like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3204–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jere, K.C.; Mlera, L.; O’Neill, H.G.; Peenze, I.; van Dijk, A.A. Whole genome sequence analyses of three African bovine rotaviruses reveal that they emerged through multiple reassortment events between rotaviruses from different mammalian species. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jere, K.C.; Esona, M.D.; Ali, Y.H.; Peenze, I.; Roy, S.; Bowen, M.D.; Saeed, I.K.; Khalafalla, A.I.; Nyaga, M.M.; Mphahlele, J.; et al. Novel NSP1 genotype characterised in an African camel G8P [11] rotavirus strain. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bányai, K.; Bogdán, Á.; Domonkos, G.; Kisfali, P.; Molnár, P.; Tóth, A.; Melegh, B.; Martella, V.; Gentsch, J.R.; Szűcs, G. Genetic diversity and zoonotic potential of human rotavirus strains, 2003–2006, Hungary. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Gatheru, Z.; Nyangao, J.; Adachi, N.; Urushibara, N.; Kobayashi, N. Full genomic analysis of a G8P[1] rotavirus strain isolated from an asymptomatic infant in Kenya provides evidence for an artiodactyl-to-human interspecies transmission event. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoto, S.; Adah, M.I.; Ide, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Taniguchi, K. Whole genomic analysis of human and bovine G8P[1] rotavirus strains isolated in Nigeria provides evidence for direct bovine-to-human interspecies transmission. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 43, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esona, M.D.; Geyer, A.; Page, N.; Trabelsi, A.; Fodha, I.; Aminu, M.; Agbaya, V.A.; Tsion, B.; Kerin, T.K.; Armah, G.E.; et al. Genomic characterization of human rotavirus G8 strains from the African rotavirus network: Relationship to animal rotaviruses. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Ciarlet, M.; Lawrence, J.; Steele, D.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J. Comparative analysis of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine strains and G8 rotaviruses identified during vaccine trial in Africa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutelíková, R.; Sauer, P.; Dvořáková Heroldová, M.; Holá, V.; Prodělalová, J. Emergence of Rare Bovine-Human Reassortant DS-1-Like Rotavirus A Strains with G8P[8] Genotype in Human Patients in the Czech Republic. Viruses 2019, 11, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebus, C.A.; Underdahl, N.R.; Rhodes, M.B.; Twiehaus, M.J. Calf diarrhea (Scours): Reproduced with a virus from a field outbreak. Univ. Nebraska Res. Bull. 1969, 233, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Komoto, S.; Pongsuwanna, Y.; Tacharoenmuang, R.; Guntapong, R.; Ide, T.; Higo-Moriguchi, K.; Tsuji, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Taniguchi, K. Whole genomic analysis of bovine group A rotavirus strains A5-10 and A5-13 provides evidence for close evolutionary relationship with human rotaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 195, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzen, J.T.T.; Oliveira, M.V.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Genotype constellation of a rotavirus A field strain with an uncommon G8P[11] genotype combination in a rotavirus-vaccinated dairy cattle herd. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchs, A.; Timenetsky, M.C. G8P[6] rotaviruses isolated from Amerindian children in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, during 2009: Close relationship of the G and P genes with those of bovine and bat strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaracco, A.; Garaicoechea, L.; Matthijnssens, J.; Louge Uriarte, E.L.; Odeón, A.; Bilbao, G.; Fernández, F.; Parra, G.; Parreño, V. Phylogenetic analyses of typical bovine rotavirus genotypes G6, G10, P[5] and P[11] circulating in Argentinean beef and dairy herds. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 18, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.C.; Kim, E.M.; Shin, S.U.; Park, J.; Choi, K.S. Molecular surveillance of rotavirus A associated with diarrheic calves from the Republic of Korea and full genomic characterization of bovine-porcine reassortant G5P[7] strain. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 100, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heide, R.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Shekary, N.; Houwers, D.J.; Van Duynhoven, Y.T.H.P.; Van der Poel, W.H.M. Molecular characterizations of human and animal group A rotaviruses in the Netherlands. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaicoechea, L.; Bok, K.; Jones, L.R.; Combessies, G.; Odeón, A.; Fernández, F.; Parreño, V. Molecular characterization of bovine rotavirus circulating in beef and dairy herds in Argentina during a 10-year period (1994–2003). Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 118, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebus, C.A.; Kono, M.; Underdahl, N.R.; Twiehaus, M.J. Cell culture propagation of neonatal calf diarrhea (scours) virus. Can. Vet. J. 1971, 12, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thrusfield, M. (Ed.) Surveys. In Veterinary Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Padstow, UK, 2005; pp. 228–246. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos (INDEC). En Censo Nacional Agropecuario 2018: Resultados Definitivos, 1st ed.; Libro Digital (PDF); Ganadería, V., Dirección Nacional de Estadísticas y Precios de la Producción y el Comercio, Dirección de Estadísticas del Sector Primario, Eds.; Publicaciones del INDEC: Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2021; pp. 604–682. ISBN 978-950-896-607-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio of Agroindustria. En Caracterización de la Producción Bovina. Sistema de Monitoreo del Sector de la Carne Bovina; Serie 1; Ministerio de Agricultura Ganadería y Pesca, Subsecretaría de Ganadería, Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria y Servicio Nacional de Sanidad Animal, Eds.; Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015; pp. 5–54. Available online: https://www.produccion-animal.com.ar/informacion_tecnica/origenes_evolucion_y_estadisticas_de_la_ganaderia/177-caracterizacion_de_la_produccion_bovina.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2023). (In Spanish)
- Carrillo, J. La Explotación de Cría Bovina. In En Manejo de un Rodeo de Cría, 2nd ed.; Carrillo, J., Ed.; Editorial Centro Regional Buenos Aires Sur: Balcarce, Argentina, 2001; pp. 1–19. ISBN 950-9853-79-8. [Google Scholar]
- Buelink, D.; Schaller, A.; Labriola, S. En Principales Cuencas Lecheras Argentinas, 2nd ed.; Secretaría de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación, Subsecretaría de Alimentación, Departamento de Lechería, Eds.; Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1996; pp. 23–32. Available online: https://alimentosargentinos.magyp.gob.ar/contenido/sectores/lacteos/miscelaneas/Cuencas_Lacteas/CuencasLecherasArgentinas.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2023). (In Spanish)
- Graham, A.N.; Renaud, D.L.; Duffield, T.F.; Kelton, D.F. Calf cleanliness does not predict diarrhea upon arrival at a veal calf facility. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3363–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midgley, S.E.; Bányai, K.; Buesa, J.; Halaihel, N.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Jakab, F.; Kaplon, J.; Larsen, L.E.; Monini, M.; Poljšak-Prijatelj, M.; et al. Diversity and zoonotic potential of rotaviruses in swine and cattle across Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaracco, A.; Matthijnssens, J.; Romero, S.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Garaicoechea, L.; Van Ranst, M.; Parreño, V. Discovery and molecular characterization of a group A rotavirus strain detected in an Argentinean vicuña (Vicugna vicugna). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 161, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louge Uriarte, E.L.; Badaracco, A.; Matthijnssens, J.; Zeller, M.; Heylen, E.; Manazza, J.; Miño, S.; Van Ranst, M.; Odeón, A.; Parreño, V. The first caprine rotavirus detected in Argentina displays genomic features resembling virus strains infecting members of the Bovidae and Camelidae. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; McDonald, S.M.; Attoui, H.; Bányai, K.; Brister, J.R.; Buesa, J.; Esona, M.D.; Estes, M.K.; Gentsch, J.R.; et al. Uniformity of rotavirus strain nomenclature proposed by the Rotavirus Classification Working Group (RCWG). Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1397–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, B.E.; Sadat, E.L.; Zhang, Y.; Noronha, J.M.; Squires, R.B.; Hunt, V.; Liu, M.; Kumar, S.; Zaremba, S.; Gu, Z.; et al. ViPR: An open bioinformatics database and analysis resource for virology research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D593–D598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, A.; Donato, C.; Peenze, I.; Potgieter, A.C.; Seheri, M.; O’Neill, H.G. Genetic characterisation of novel G29P[14] and G10P[11] rotavirus strains from African buffalo. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE7: New and improved tools for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemey, P.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A. Bayesian phylogeography finds its roots. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielejec, F.; Baele, G.; Vrancken, B.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Lemey, P. SpreaD3: Interactive visualization of spatiotemporal history and trait evolutionary processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2167–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in bayesian phylogenetics using tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumley, T. Analysis of complex survey samples. J. Stat. Softw. 2004, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, T. svyVGAM: Design-Based Inference in Vector Generalised Linear Models. R Package Version 1.2. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=svyVGAM (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Kosmidis, I.; Firth, D. Jeffreys-prior penalty, finiteness and shrinkage in binomial-response generalized linear models. Biometrika 2021, 108, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westreich, D.; Cole, S.R. Invited commentary: Positivity in practice. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Potgieter, A.C.; Ciarlet, M.; Parreño, V.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K.; Garaicoechea, L.; Palombo, E.A.; Novo, L.; Zeller, M.; et al. Are Human P[14] Rotavirus Strains the Result of Interspecies Transmissions from Sheep or Other Ungulates That Belong to the Mammalian Order Artiodactyla? J. Virol. 2009, 86, 2917–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miño, S.O.; Badaracco, A.; Louge Uriarte, E.; Ciarlet, M.; Parreño, V. Evolution of Animal South American RVA Told by the NSP4 Gene E12 Genotype. Viruses 2022, 14, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaracco, A.; Cordero, A.; Vega, C.; Bok, M.; Zeller, M.; Heylen, E.; Fernández, G.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P.; Guevara, H.; et al. Molecular characterization of group A rotavirus strains detected in alpacas (Vicugna pacos) from Peru. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Phan, T.G.; Galeano, M.E.; Russomando, G.; Parreño, V.; Delwart, E.; Parra, G.I. Genomic characterization of a rotavirus G8P[1] detected in a child with diarrhea reveal direct animal-to-human transmission. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinzoni, R.C.; Blackhall, J.; Terzolo, H.R.; Moreira, A.R.; Auza, N.; Mattion, N.; Micheo, G.L.; La Torre, J.L.; Scodeller, E.A. Microbiology of diarrhoea in young beef and dairy calves in Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 1990, 22, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass, D.R.; Terzolo, H.R.; Sherwood, D.; Campbell, I.; Menzies, J.D.; Synge, B.A. Aetiology of diarrhoea in young calves. Vet. Rec. 1986, 119, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woode, G.N. Epizootiology of bovine rotavirus infection. Vet. Rec. 1978, 103, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parreño, V.; Bejar, C.; Vagnozzi, A.; Barrandeguy, M.; Costantini, V.; Craig, M.I.; Yuan, L.; Hodgins, D.; Saif, L.; Fernández, F. Modulation by colostrum-acquired maternal antibodies of systemic and mucosal antibody responses to rotavirus in calves experimentally challenged with bovine rotavirus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 100, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendali, F.; Bichet, H.; Schelcher, F.; Sanaa, M. Risk factors associated with diarrhoea in newborn calves. Vet. Res. 1999, 30, 509–522. [Google Scholar]
- Falcone, E.; Tarantino, M.; Di Trani, L.; Cordioli, P.; Lavazza, A.; Tollis, M. Determination of bovine rotavirus G and P serotypes in Italy by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3879–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, A.A.; Parazzi, M.E.; Takiuchi, E.; Médici, K.C.; Alfieri, A.F. Frequency of group A rotavirus in diarrhoeic calves in Brazilian cattle herds, 1998–2002. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2006, 38, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.L.; Tyler, J.W. Reducing calf losses in beef herds. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. 2005, 21, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffarena, R.D.; Casaux, M.L.; Schild, C.O.; Fraga, M.; Castells, M.; Colina, R.; Maya, L.; Corbellini, L.G.; Riet-Correa, F.; Giannitti, F. Causes of neonatal calf diarrhea and mortality in pasture-based dairy herds in Uruguay: A farm-matched case-control study. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, R.K.; Grooms, D.L.; Wise, A.G.; Han, C.; Ciesicki, V.; Hanson, L.; Vickers, M.L.; Kanitz, C.; Holland, R. Evaluation of a human group a rotavirus assay for on-site detection of bovine rotavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monini, M.; Cappuccini, F.; Battista, P.; Falcone, E.; Lavazza, A.; Ruggeri, F.M. Molecular characterization of bovine rotavirus strains circulating in northern Italy, 2003–2005. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 129, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Alarcón, R.G.; Liotta, D.J.; Miño, S. Zoonotic RVA: State of the Art and Distribution in the Animal World. Viruses 2022, 14, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, T.G.; Silva, F.D.; Gregori, F.; Alfieri, A.A.; Buzinaro, M.D.; Fagliari, J.J. Longitudinal study of bovine rotavirus group A in newborn calves from vaccinated and unvaccinated dairy herds. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchelli, A.; Kang, S.Y.; Jayasekera, M.K.; Parwani, A.V.; Zeman, D.H.; Saif, L.J. A survey of G6 and G10 serotypes of group A bovine rotaviruses from diarrheic beef and dairy calves using monoclonal antibodies in ELISA. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1994, 6, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godden, S. Colostrum management for dairy calves. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2008, 24, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiros, M.A.; Alfieri, A.F.; Médici, K.C.; Leite, J.P.; Alfieri, A.A. G and P genotypes of group A rotavirus from diarrhoeic calves born to cows vaccinated against the NCDV (P[1],G6) rotavirus strain. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2004, 51, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreño, V.; Rodriguez, D.; Izuel, M.; Filippi, J.; Marangunich, L.; López, V.; Fernández, F.; Bellinzoni, R.; Vena, M.M. Bovine rotavirus vaccines: Immunogenicity of two strains of bovine rotavirus in cattle and guinea pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, E.; Aduriz, M.; Bok, M.; Vega, C.; Saif, L.; Aguirre, D.; Cimino, R.O.; Miño, S.; Parreño, V. First report of group A rotavirus and bovine coronavirus associated with neonatal calf diarrhea in the northwest of Argentina. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bányai, K.; Papp, H.; Dandár, E.; Molnár, P.; Mihály, I.; Van Ranst, M.; Martella, V.; Matthijnssens, J. Whole genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of a zoonotic human G8P[14] rotavirus strain. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, M.C.; Tummolo, F.; Bonica, M.B.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Calderaro, A.; Matthijnssens, J. Genetic diversity in three bovine-like human G8P[14] and G10P[14] rotaviruses suggests independent interspecies transmission events. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Van Ranst, M. Genotype constellation and evolution of group A rotaviruses infecting humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; Bridger, J.; Kendall, K.; Gomara, M.I.; El-Attar, L.; Gray, J. The zoonotic potential of rotavirus. J. Infect. 2004, 48, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamnikar-Ciglenecki, U.; Kuhar, U.; Sturm, S.; Kirbis, A.; Racki, N.; Steyer, A. The first detection and whole genome characterization of the G6P[15] group A rotavirus strain from roe deer. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 191, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircar, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Kumar, P.; Ansari, M.I.; Bhat, S.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Kattoor, J.J.; Vinodhkumar, O.R.; Rishi, N.; Touil, N.; et al. Genomic Analysis of an Indian G8P[1] Caprine Rotavirus-A Strain Revealing Artiodactyl and DS-1-Like Human Multispecies Reassortment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 27, 606661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Medeiros, T.N.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Phylogenetic analysis of a G6P[5] bovine rotavirus strain isolated in a neonatal diarrhea outbreak in a beef cattle herd vaccinated with G6P[1] and G10P[11] genotypes. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, D.; Donato, C.M.; Roczo-Farkas, S.; Kirkwood, C.D. Novel G10P[14] rotavirus strain, northern territory, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, O.V.; Alekseeva, A.E.; Sashina, T.A.; Brusnigina, N.F.; Epifanova, N.V.; Kashnikov, A.U.; Zverev, V.V.; Novikova, N.A. Phylodynamics of G4P[8] and G2P[4] strains of rotavirus A isolated in Russia in 2017 based on full-genome analyses. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G.M.; Rambaut, A.; Pybus, O.G.; Holmes, E.C. Rates of molecular evolution in RNA viruses: A quantitative phylogenetic analysis. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.; Shackelton, L.A.; Holmes, E.C. Rates of evolutionary change in viruses: Patterns and determinants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Rahman, M.; Lemey, P.; Van Ranst, M. Phylodynamic analyses of rotavirus genotypes G9 and G12 underscore their potential for swift global spread. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, T.N.S.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Severe diarrhea outbreak in beef calves (Bos indicus) caused by G6P [11], an emergent genotype of bovine rotavirus group A. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2014, 34, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M.; Giannitti, F.; Caffarena, R.D.; Casaux, M.L.; Schild, C.; Castells, D.; Riet-Correa, F.; Victoria, M.; Parreño, V.; Colina, R. Bovine coronavirus in Uruguay: Genetic diversity, risk factors and transboundary introductions from neighboring countries. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavian, M.; Marini, S.; Prosperi, M.; Salemi, M. A Snapshot of SARS-CoV-2 genome availability up to April 2020 and its implications: Data analysis. JMIR Public. Health Surveill. 2020, 1, e19170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, H.; Brinkmann, H.; Lavrov, D.V.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Manuel, M.; WÖrheide, G.; Baurain, D. Resolving difficult phylogenetic questions: Why more sequences are not enough. PLoS Biology. 2011, 9, e1000602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K. The effect of recombination on the accuracy of phylogeny estimation. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.A.; Strimmer, K.; Vingron, M.; Von Haeseler, A. TREE-PUZZLE: Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimmer, K.; Von Haeseler, A. Likelihood-mapping: A simple method to visualize phylogenetic content of a sequence alignment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6815–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z.; Salemi, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. An index of substitution saturation and its application. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
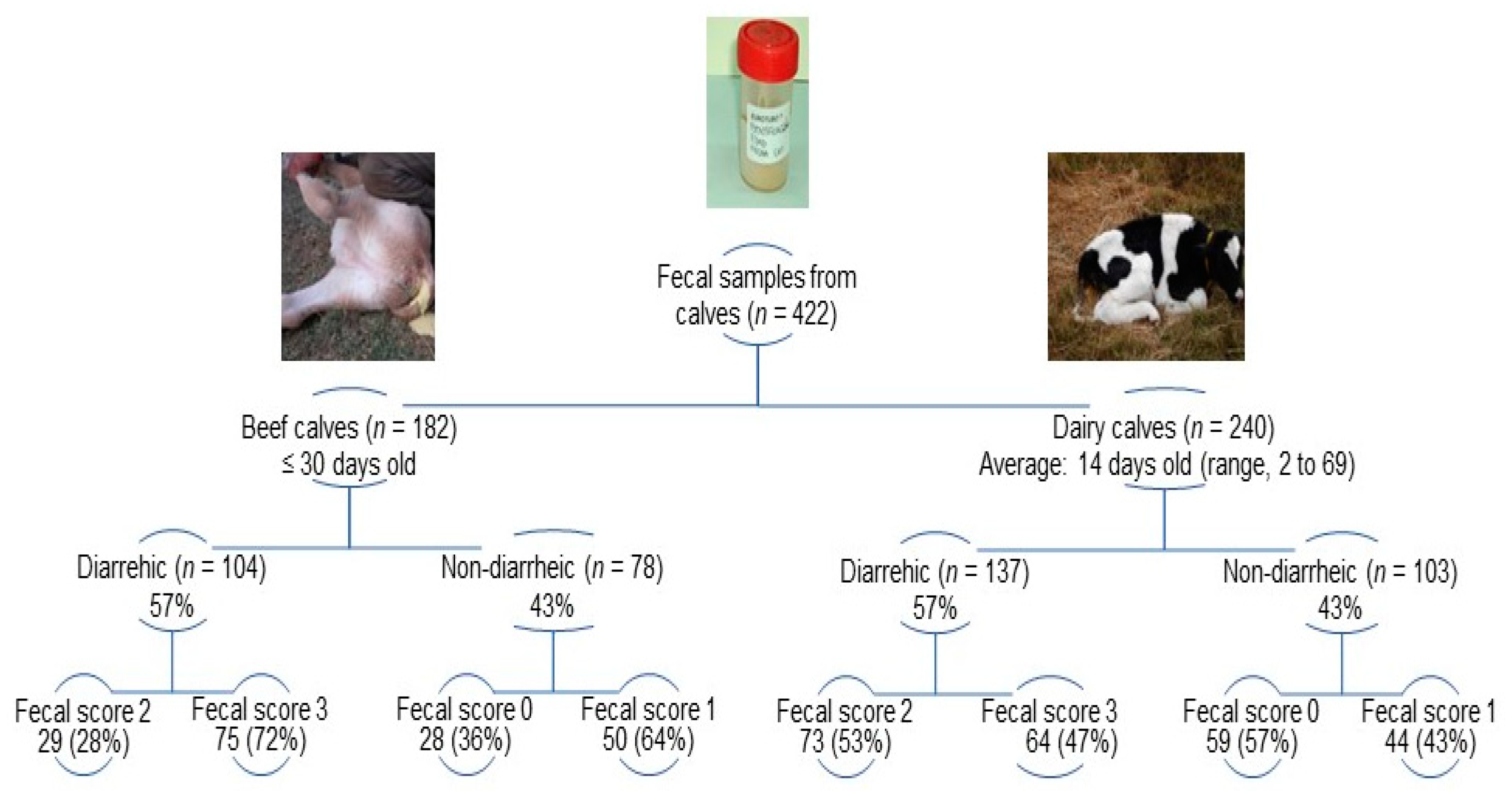


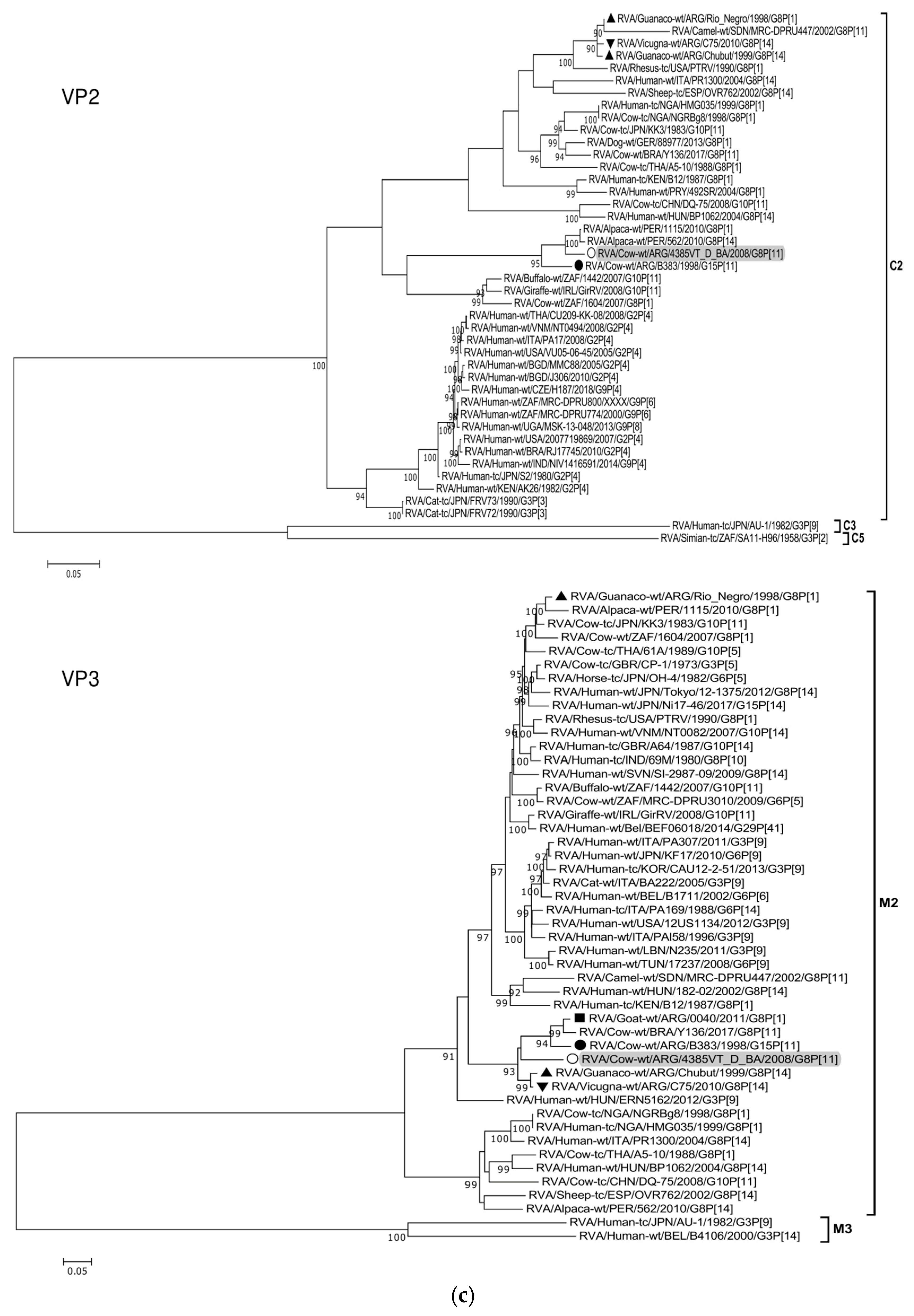
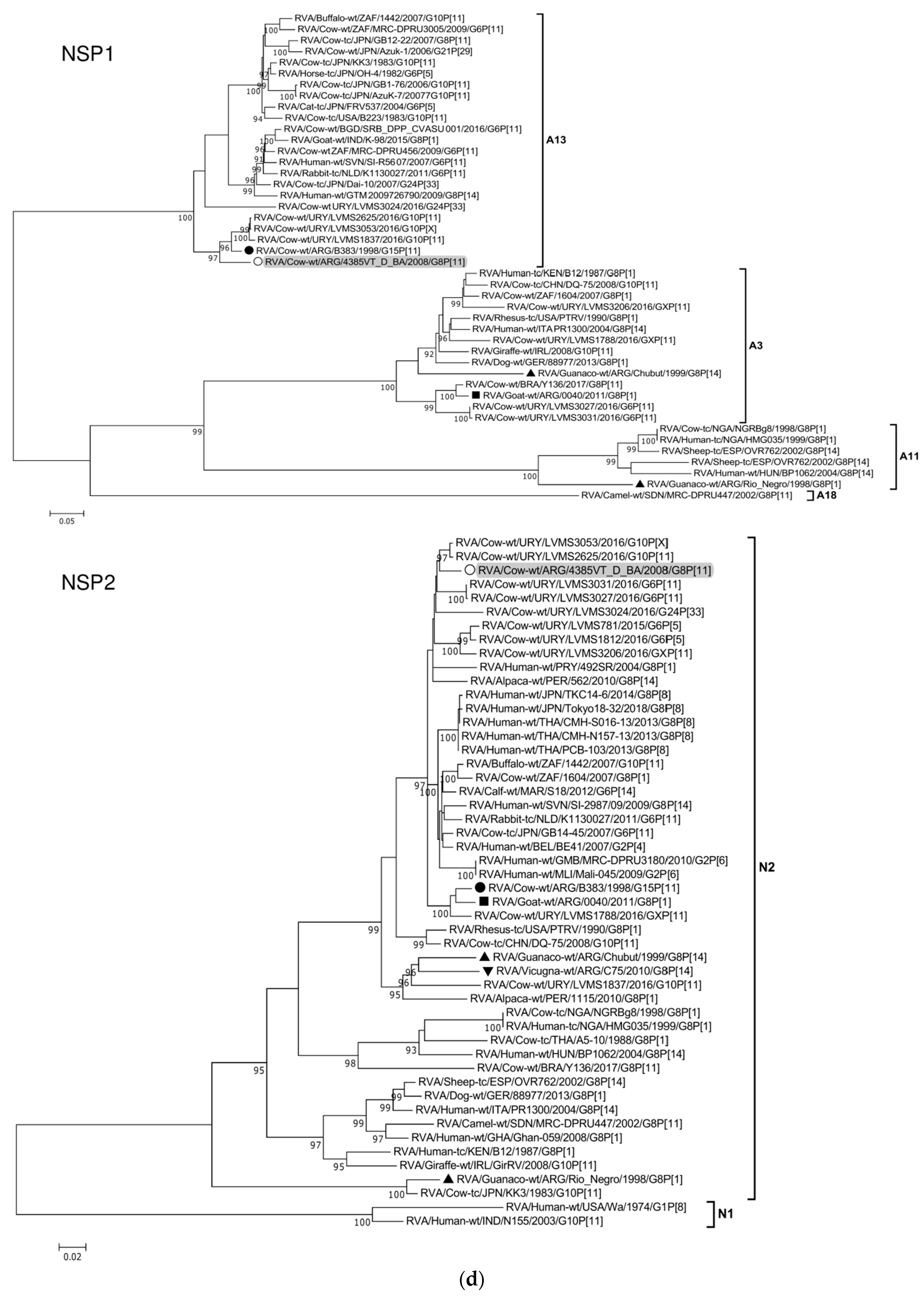
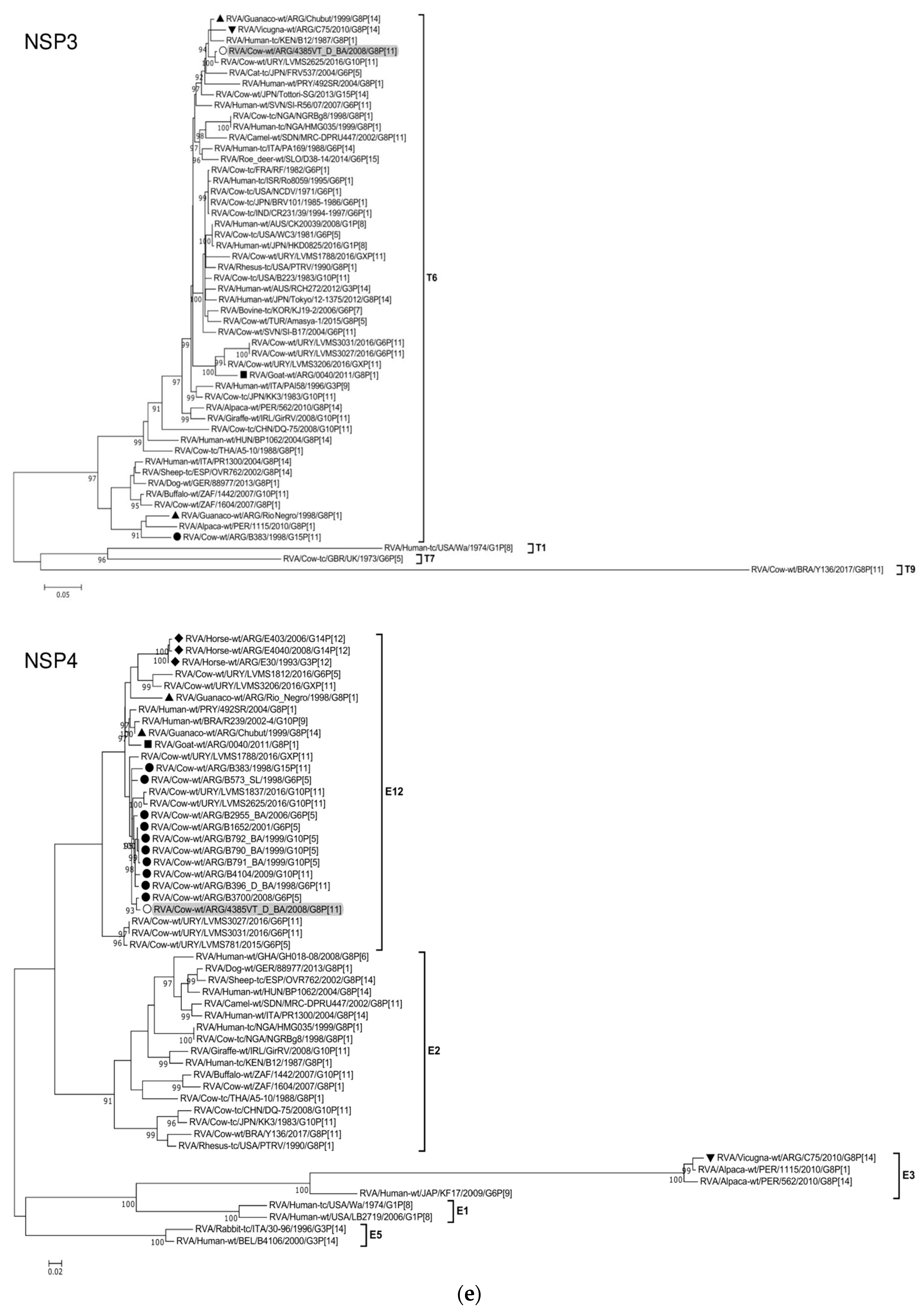

| Genotypes and G/P Combinations | Beef (n = 33) | Dairy (n = 34) | Dairy Farm DR * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | ||||
| No. (%) | p-Value FDR & | No. | ||||
| G6(III) | 0 (0.0) | 15 (44.1) | <0.0001 | |||
| G6(IV) | 30 (90.9) | 4 (11.8) | <0.0001 | |||
| G8 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.9) | 0.1734 | |||
| G10 | 0 (0.0) | 3 (8.8) | 0.0016 | |||
| P[5] | 32 (97.0) | 7 (20.6) | <0.0001 | |||
| P[11] | 1 (3.0) | 24 (70.6) | <0.0001 | |||
| G6(III)P[5] | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.9) | 0.2033 | |||
| G6(IV)P[5] | 30 (90.9) | 3 (8.8) | <0.0001 | 7 | ||
| G6(III)P[11] | 0 (0.0) | 14 (41.2) | <0.0001 | 5 | ||
| G8P[11] | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.9) | 0.2049 | |||
| G10P[11] | 0 (0.0) | 3 (8.8) | 0.0057 | 2 | ||
| GXP[5] | 2 (6.1) | 2 (5.9) | 0.9731 | |||
| GXP[11] | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.9) | 0.0639 | 2 | ||
| G6(IV) + G10P[11] | 1 (3.0) | 2 (5.9) | 0.6841 | |||
| G6(IV) + G10P[5] | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.9) | 0.2033 | |||
| G6(III) + G10P[11] | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.9) | 0.0553 | |||
| G6(IV) + P[5 + 11] | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.9) | 0.2049 | |||
| G6(IV) + G10P[5 + 11] | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.9) | 0.0553 | |||
| Mixed genotypes (total) | 1 (3.0) | 8 (23.5) | 0.0553 | |||
| Genome Segment (Protein) | Sequenced Fragment † (bp) | Position * | ORF Coverage (%) | Genotype # | Most Similar Strains after Nucleotide BLAST Search | Highest Identity (%) & | Host of Origin | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (VP1) | 3215 | 46-3260 | 98 | R5 | RVA/Cow-wt/ARG/B383/1998/G15P[11] | 98 | Cattle | Argentina |
| 2 (VP2) | 2643 | 17-2659 | 100 | C2 | RVA/Alpaca-wt/PER/1115/2010/G8P[1] | 96 | Alpaca | Peru |
| 3 (VP3) | 1518 | 50-1567 | 61 | M2 | RVA/Guanaco-wt/ARG/Chubut/1999/G8P[14] | 91 | Guanaco | Argentina |
| 4 (VP4) | 2142 | 163-2304 | 92 | P[11] | RVA/Cow-wt/ARG/B1625_B_BA/2001/G10P[11] | 95 | Cattle | Argentina |
| 5 (NSP1) | 1427 | 83-1509 | 95 | A13 | RVA/Cow-wt/ARG/B383/1998/G15P[11] | 94 | Cattle | Argentina |
| 6 (VP6) | 1167 | 51-1217 | 98 | I2 | RVA/Cow-wt/URY/LVMS3206/2016/GXP[11] | 93 | Cattle | Uruguay |
| 7 (VP7) | 898 | 49-946 | 92 | G8 | RVA/Goat-wt/ARG/0040/2011/G8P[1] | 97 | Goat | Argentina |
| 8 (NSP2) | 954 | 47-1000 | 100 | N2 | RVA/Cow-wt/URY/LVMS3053/2016/G10P[X] | 98 | Cattle | Uruguay |
| 9 (NSP3) | 933 | 35-967 | 100 | T6 | RVA/Cow-wt/URY/LVMS2625/2016/G10P[11] | 99 | Cattle | Uruguay |
| 10 (NSP4) | 528 | 42-569 | 100 | E12 | RVA/Cow-wt/ARG/B3700/2008/G6P[5] | 99 | Cattle | Argentina |
| 11 (NSP5) | 597 | 22-618 | 100 | H3 | RVA/Cow-wt/ARG/B383/1998/G15P[11] | 99 | Cattle | Argentina |
| Strains | Genotype Constellation | VP7 (%) * | VP4 (%) | VP6 (%) | VP1 (%) | VP2 (%) | VP3 (%) | NSP1 (%) | NSP2 (%) | NSP3 (%) | NSP4 (%) | NSP5 (%) | Shared Genotypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVA/Cow-wt/ARG/4385VT_D_BA/2008/G8P[11] | G8 | P[11] | I2 | R5 | C2 | M2 | A13 | N2 | T6 | E12 | H3 | ||
| RVA/Cow-wt/ARG/B383/1998/G15P[11] | Bovine | G15 | P[11] (94/94) | I2 (84/97) | R5 (98/100) | C2 (93/99) | M2 (88/95) | A13 (94/94) | N2 (95/98) | T6 (88/96) | E12 (97/99) | H3 (99/100) | 10 |
| RVA/Guanaco-wt/ARG/Rio_Negro/1998/G8P[1] | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (97/99) | P[1] | I2 (91/99) | R5 (96/99) | C2 (85/98) | M2 (84/92) | A11 | N2 (87/95) | T6 (89/97) | E12 (94/97) | H3 (93/94) | 9 |
| RVA/Goat-wt/ARG/0040/2011/G8P[1] | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (97/98) | P[1] | I2 (87/97) | R5 (98/99) | C2 (96/100) | M2 (88/94) | A3 | N2 (95/98) | T6 (94/98) | E12 (96/99) | H3 (93/94) | 9 |
| RVA/Guanaco-wt/ARG/Chubut/1999/G8P[14] | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (97/97) | P[14] | I2 (91/99) | R5 (93/99) | C2 (85/98) | M2 (91/95) | A3 | N2 (91/97) | T6 (98/99) | E12 (96/100) | H3 (96/97) | 9 |
| RVA/Rhesus-tc/USA/PTRV/1990 | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (96/98) | P[1] | I2 (91/99) | R2 | C2 (85/98) | M2 (85/92) | A3 | N2 (94/99) | T6 (95/98) | E2 | H3 (97/99) | 9 |
| RVA/Human-tc/KEN/B12/1987/G8P[1] | Human bovine-like | G8 (96/99) | P[1] | I2 (90/99) | R2 | C2 (86/98) | M2 (84/92) | A3 | N2 (88/96) | T6 (97/98) | E2 | H3 (96/98) | 9 |
| RVA/Alpaca-wt/PER/562/2010/G8P[14] | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (95/98) | P[14] | I2 (90/99) | R5 (91/98) | C2 (96/100) | M2 (80/88) | A17 | N2 (96/97) | T6 (94/98) | E3 | H3 (97/99) | 8 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/BRA/Y136/2017/G8P[11] | Bovine | G8 (87/94) | P[11] (71/71) | I2 (88/98) | R5 (89/99) | C2 (84/96) | M2 (89/93) | A3 | N2 (87/98) | T9 | E2 | H3 (96/98) | 8 |
| RVA/Alpaca-wt/PER/1115/2010/G8P[1] | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (88/93) | P[1] | I2 (91/100) | R2 | C2 (96/99) | M2 (84/92) | A17 | N2 (92/98) | T6 (87/96) | E3 | H3 (97/100) | 7 |
| RVA/Cow-wt/ZAF/1604/2007/G8P[1] | Bovine | G8 (87/98) | P[1] | I2 (91/99) | R2 | C2 (85/98) | M2 (85/91) | A3 | N2 (94/97) | T6 (89/97) | E2 | H3 (95/97) | 7 |
| RVA/Cow–tc/NGA/NGRBg8/1998/G8P[1] | Bovine | G8 (85/96) | P[1] | I2 (87/99) | R2 | C2 (85/98) | M2 (81/91) | A11 | N2 (88/97) | T6 (94/98) | E2 | H3 (95/98) | 7 |
| RVA/Cow-tc/THA/A5-10/1988/G8P[1] | Bovine | G8 (85/96) | P[1] | I2 (92/99) | R2 | C2 (84/98) | M2 (82/91) | A11 | N2 (87/96) | T6 (92/98) | E2 | H3 (95/97) | 7 |
| RVA/Cow-tc/CHN/DQ-75/2008/G10P[11] | Bovine | G10 | P[11] (72/72) | I2 (91/99) | R2 | C2 (84/98) | M2 (82/90) | A3 | N2 (94/98) | T6 (92/97) | E2 | H3 (95/97) | 7 |
| RVA/Human–tc/NGA/HMG035/1999/G8P[1] | Human bovine-like | G8 (85/96) | P[1] | I2 (87/99) | R2 | C2 (85/98) | M2 (81/91) | A11 | N2 (88/97) | T6 (94/98) | E2 | H3 (95/98) | 7 |
| RVA/Human-wt/PRY/492SR/2004/G8P[1] | Human bovine-like | G8 (87/94) | P[1] | I2 (87/97) | R2 | C2 (85/98) | M1 | -- | N2 (95/96) | T6 (95/97) | E12 (96/99) | H3 (99/99) | 7 |
| RVA/Human-wt/ITA/PR1300/2004/G8P[14] | Human bovine-like | G8 (96/98) | P[14] | I2 (87/99) | R2 | C2 (84/98) | M2 (82/90) | A3 | N2 (88/97) | T6 (90/98) | E2 | H3 (97/100) | 7 |
| RVA/Human-wt/HUN/BP1062/2004/G8P[14] | Human bovine-like | G8 (83/95) | P[14] | I2 (91/99) | R2 | C2 (84/97) | M2 (81/91) | A11 | N2 (87/97) | T6 (91/98) | E2 | H3 (95/97) | 7 |
| RVA/Sheep-tc/ESP/OVR762/2002/G8P[14] | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (94/98) | P[14] | I2 (90/99) | R2 | C2 (84/98) | M2 (81/90) | A11 | N2 (88/96) | T6 (91/98) | E2 | H3 (97/98) | 7 |
| RVA/Vicugna-wt/ARG/C75/2010/G8P[14] | Artiodactyl bovine-like | G8 (97/99) | P[14] | I2 (90/99) | R2 | C2 (85/96) | M2 (92/96) | -- | N2 (92/97) | T6 (97/98) | E3 | -- | 6 |
| RVA/Human-wt/GHA/GH018-08/2008/G8P[6] | Human bovine-like | G8 (85/96) | P[6] | I2 (91/99) | R2 | C2 (85/98) | M2 (84/92) | A2 | N2 (89/97) | T2 | E2 | H3 (97/99) | 6 |
| RVA/Dog-wt/GER/88977/2013/G8P[1] | Dog bovine-like | G8 (95/98) | P[1] | I2 (92/99) | -- & | C2 (85/99) | -- | A3 | N2 (88/97) | T6 (90/98) | E2 | H3 (97/99) | 6 |
| VP7 ORF Sequence Datasets | |||
| Parameter | RVA-G6 | RVA-G6(III) | RVA-G6(IV) |
| n | 198 | 71 | 127 |
| Sampling time interval | 1971–2018 | 1997–2018 | 1971–2016 |
| Evolutionary rate (Mean s/s/y) & * | 1.24 × 10−3 (9.97 × 10−4–1.52 × 10−3) | 1.17 × 10−3 (6.49 × 10−4–1.72 × 10−3) | 1.26 × 10−3 (9.44 × 10−4–1.58 × 10−3) |
| Mean TMRCA # * for G6 strains | 1853 (1766–1935) | NA | NA |
| Mean TMRCA # * for G6(III) lineage | 1981 (1963–1989) | 1982 (1971–1992) | NA |
| Mean TMRCA # * for G6(IV) lineage | 1940 (1919–1959) | NA | 1945 (1926–1962) |
| Country † (probability) | USA (0.57) ARG (0.23) | ARG (0.99) | USA (0.55) BRA (0.29) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Louge Uriarte, E.L.; Badaracco, A.; Spetter, M.J.; Miño, S.; Armendano, J.I.; Zeller, M.; Heylen, E.; Späth, E.; Leunda, M.R.; Moreira, A.R.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Rotavirus A in Calves: Evolutionary Analysis of a Bovine G8P[11] Strain and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of G6 Lineages in the Americas. Viruses 2023, 15, 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102115
Louge Uriarte EL, Badaracco A, Spetter MJ, Miño S, Armendano JI, Zeller M, Heylen E, Späth E, Leunda MR, Moreira AR, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Rotavirus A in Calves: Evolutionary Analysis of a Bovine G8P[11] Strain and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of G6 Lineages in the Americas. Viruses. 2023; 15(10):2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102115
Chicago/Turabian StyleLouge Uriarte, Enrique L., Alejandra Badaracco, Maximiliano J. Spetter, Samuel Miño, Joaquín I. Armendano, Mark Zeller, Elisabeth Heylen, Ernesto Späth, María Rosa Leunda, Ana Rita Moreira, and et al. 2023. "Molecular Epidemiology of Rotavirus A in Calves: Evolutionary Analysis of a Bovine G8P[11] Strain and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of G6 Lineages in the Americas" Viruses 15, no. 10: 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102115
APA StyleLouge Uriarte, E. L., Badaracco, A., Spetter, M. J., Miño, S., Armendano, J. I., Zeller, M., Heylen, E., Späth, E., Leunda, M. R., Moreira, A. R., Matthijnssens, J., Parreño, V., & Odeón, A. C. (2023). Molecular Epidemiology of Rotavirus A in Calves: Evolutionary Analysis of a Bovine G8P[11] Strain and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of G6 Lineages in the Americas. Viruses, 15(10), 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102115






