Four-Year Follow-Up of the Maternal Immunological, Virological and Clinical Settings of a 36-Year-Old Woman Experiencing Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection Leading to Intrauterine Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Direct and Indirect Diagnostic Procedures and HIG Therapy
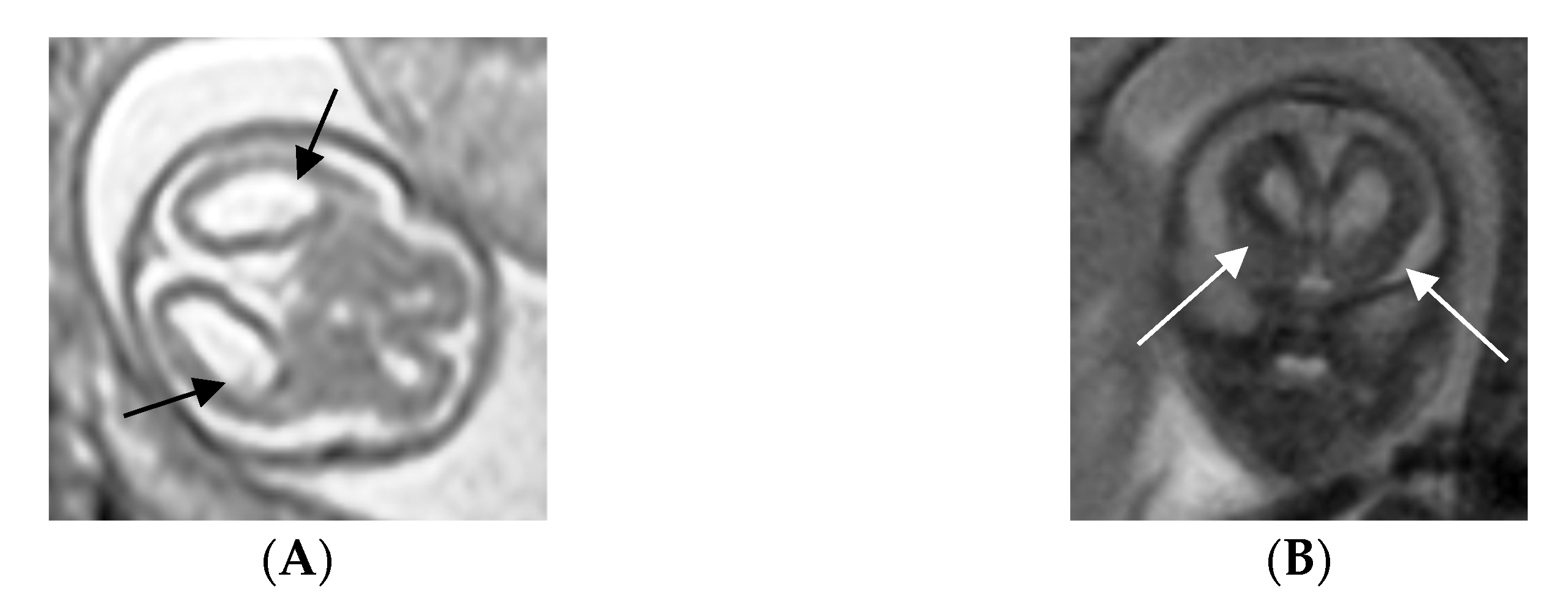
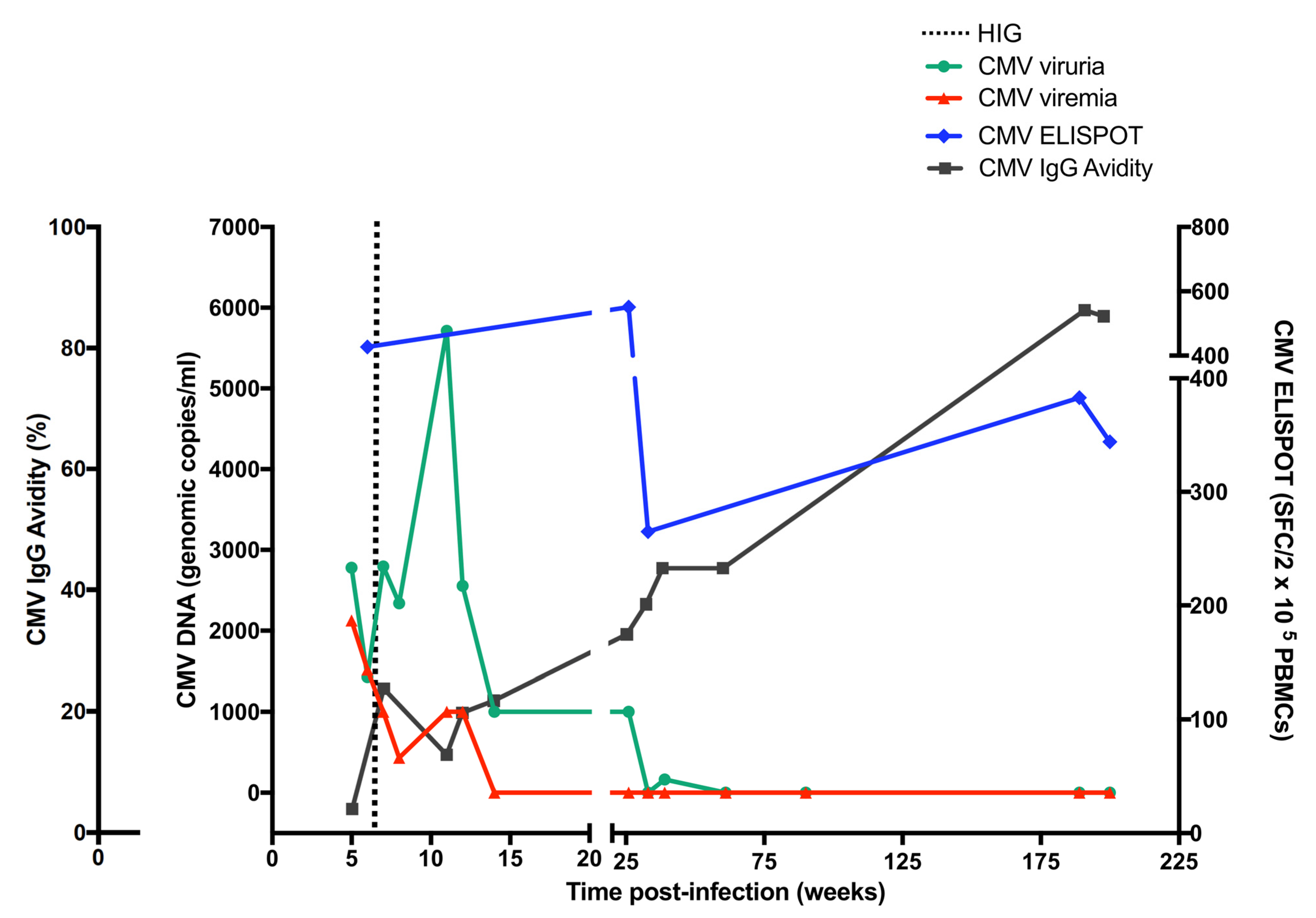
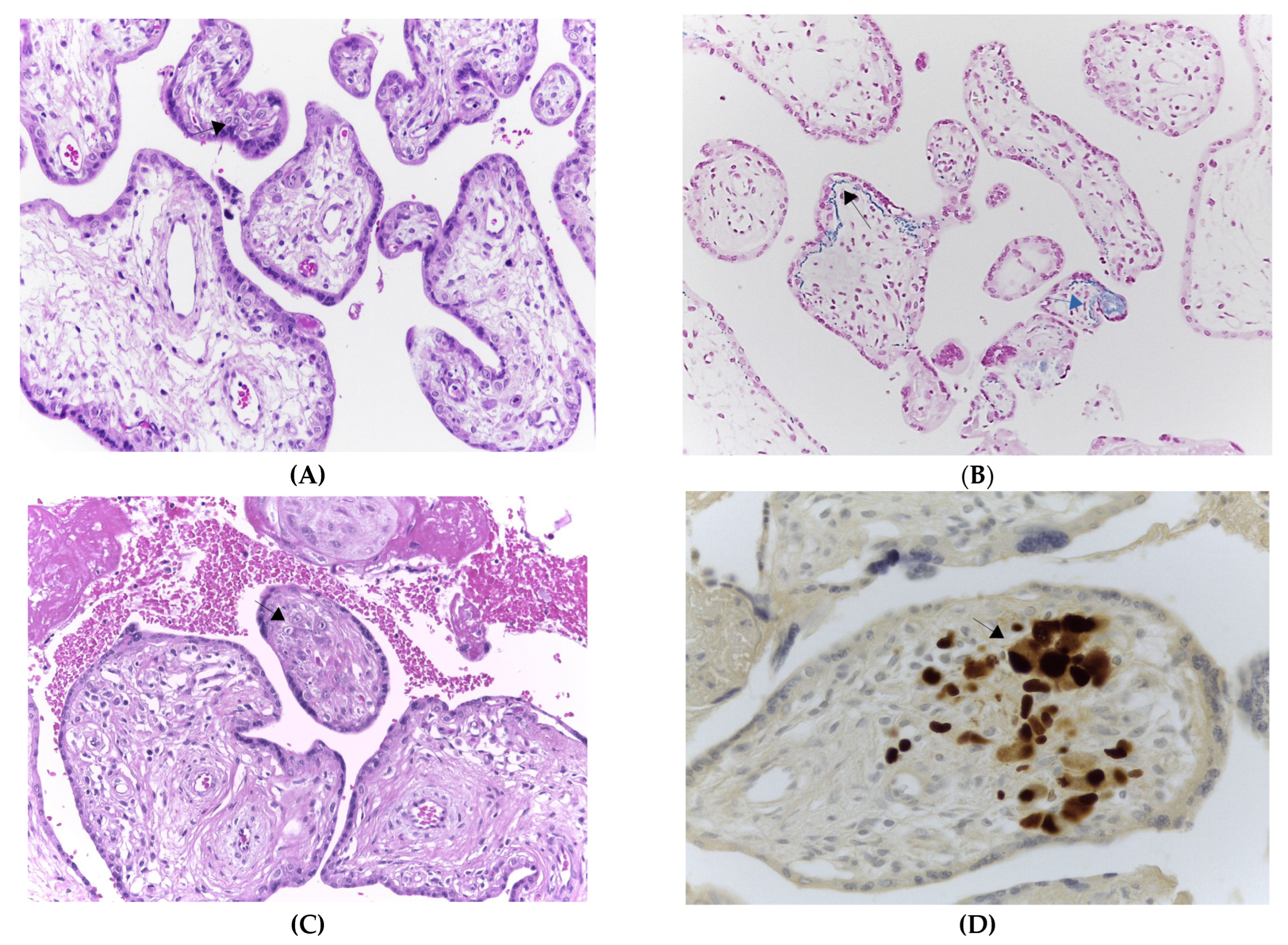
2.2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Pass, R.F.; Fowler, K.B.; Boppana, S.B.; Britt, W.J.; Stagno, S. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection following first trimester maternal infection: Symptoms at birth and outcome. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 35, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppana, S.B.; Ross, S.A.; Fowler, K.B. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Clinical Outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, S178–S181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, C.A.; Stagno, S.; Pass, R.F.; Britt, W.J. Congenital and perinatal cytomegalovirus infections. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12 (Suppl. 7), S745–S753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.P.; Nigro, G.; Pereira, L. Screening for cytomegalovirus during pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rosenthal, L.S.; Fowler, K.B.; Boppana, S.B.; Britt, W.J.; Pass, R.F.; Schmid, S.D.; Stagno, S.; Cannon, M.J. Cytomegalovirus shedding and delayed sensorineural hearing loss: Results from longitudinal follow-up of children with congenital infection. Pediatr Infect. Dis. J. 2009, 28, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldan, A.; Forner, G.; Mengoli, C.; Gussetti, N.; Palù, G.; Abate, D. Testing for Cytomegalovirus in Pregnancy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boppana, S.B.; Fowler, K.B.; Britt, W.J.; Stagno, S.; Pass, R.F. Symptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection in Infants Born to Mothers with Preexisting Immunity to Cytomegalovirus. Pediatrics 1999, 104, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldan, A.; Forner, G.; Mengoli, C.; Gussetti, N.; Palù, G.; Abate, D. Strong Cell-Mediated Immune Response to Human Cytomegalovirus Is Associated with Increased Risk of Fetal Infection in Primarily Infected Pregnant Women. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, J.J.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Wolthers, K.C.; Rusman, L.G.; Pas, S.D.; Molenkamp, R.; Claas, E.C.; Kroes, A.; Vossen, A. Real-time PCR versus viral culture on urine as a gold standard in the diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, D.; Saldan, A.; Forner, G.; Tinto, D.; Bianchin, A.; Palù, G. Optimization of interferon gamma ELISPOT assay to detect human cytomegalovirus specific T-cell responses in solid organ transplants. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 196, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldan, A.; Forner, G.; Mengoli, C.; Tinto, D.; Fallico, L.; Peracchi, M.; Gussetti, N.; Palù, G.; Abate, D. Comparison of the Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Spot and CMV QuantiFERON Cell-Mediated Immune Assays in CMV-Seropositive and -Seronegative Pregnant and Nonpregnant Women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1352–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, G.; Saldan, A.; Mengoli, C.; Gussetti, N.; Palù, G.; Abate, D. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Spot Assay but Not CMV QuantiFERON Assay Is a Novel Biomarker to Determine Risk of Congenital CMV Infection in Pregnant Women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, D.; Cesaro, S.; Cofano, S.; Fiscon, M.; Saldan, A.; Varotto, S.; Mengoli, C.; Pillon, M.; Calore, E.; Biasolo, M.A.; et al. Diagnostic Utility of Human Cytomegalovirus-Specific T-Cell Response Monitoring in Predicting Viremia in Pediatric Allogeneic Stem-Cell Transplant Patients. Transplantation 2012, 93, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, D.; Saldan, A.; Fiscon, M.; Cofano, S.; Paciolla, A.; Furian, L.; Ekser, B.; Biasolo, M.A.; Cusinato, R.; Mengoli, C.; et al. Evaluation of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific T cell immune reconstitution revealed that baseline antiviral immunity, prophylaxis, or preemptive therapy but not antithymocyte globulin treatment contribute to CMV-specific T cell reconstitution in kidney transplant recipients. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abate, D.; Fiscon, M.; Saldan, A.; Cofano, S.; Mengoli, C.; Sgarabotto, D.; D’Agostino, C.; Barzon, L.; Cusinato, R.; Toscano, G.; et al. Human Cytomegalovirus-Specific T-Cell Immune Reconstitution in Preemptively Treated Heart Transplant Recipients Identifies Subjects at Critical Risk for Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abate, D.; Saldan, A.; Mengoli, C.; Fiscon, M.; Silvestre, C.; Fallico, L.; Peracchi, M.; Furian, L.; Cusinato, R.; Bonfante, L.; et al. Comparison of cytomegalovirus (CMV) enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot and CMV quantiferon gamma interferon-releasing assays in assessing risk of CMV infection in kidney transplant recipients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forner, G.; Saldan, A.; Mengoli, C.; Pizzi, S.; Fedrigo, M.; Gussetti, N.; Visentin, S.; Angelini, A.; Cosmi, E.; Barzon, L.; et al. Four-Year Follow-Up of the Maternal Immunological, Virological and Clinical Settings of a 36-Year-Old Woman Experiencing Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection Leading to Intrauterine Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010112
Forner G, Saldan A, Mengoli C, Pizzi S, Fedrigo M, Gussetti N, Visentin S, Angelini A, Cosmi E, Barzon L, et al. Four-Year Follow-Up of the Maternal Immunological, Virological and Clinical Settings of a 36-Year-Old Woman Experiencing Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection Leading to Intrauterine Infection. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010112
Chicago/Turabian StyleForner, Gabriella, Alda Saldan, Carlo Mengoli, Sara Pizzi, Marny Fedrigo, Nadia Gussetti, Silvia Visentin, Annalisa Angelini, Erich Cosmi, Luisa Barzon, and et al. 2023. "Four-Year Follow-Up of the Maternal Immunological, Virological and Clinical Settings of a 36-Year-Old Woman Experiencing Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection Leading to Intrauterine Infection" Viruses 15, no. 1: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010112
APA StyleForner, G., Saldan, A., Mengoli, C., Pizzi, S., Fedrigo, M., Gussetti, N., Visentin, S., Angelini, A., Cosmi, E., Barzon, L., & Abate, D. A. (2023). Four-Year Follow-Up of the Maternal Immunological, Virological and Clinical Settings of a 36-Year-Old Woman Experiencing Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection Leading to Intrauterine Infection. Viruses, 15(1), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010112






