RNA Interference Approach Is a Good Strategy against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses, Cell Line, and Cell Culture
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. shRNA Construction
2.4. Cellular Viability Assay
2.5. Detection of Viral Load with Real-Time PCR
2.6. Detection of Viral Load with Plaque Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
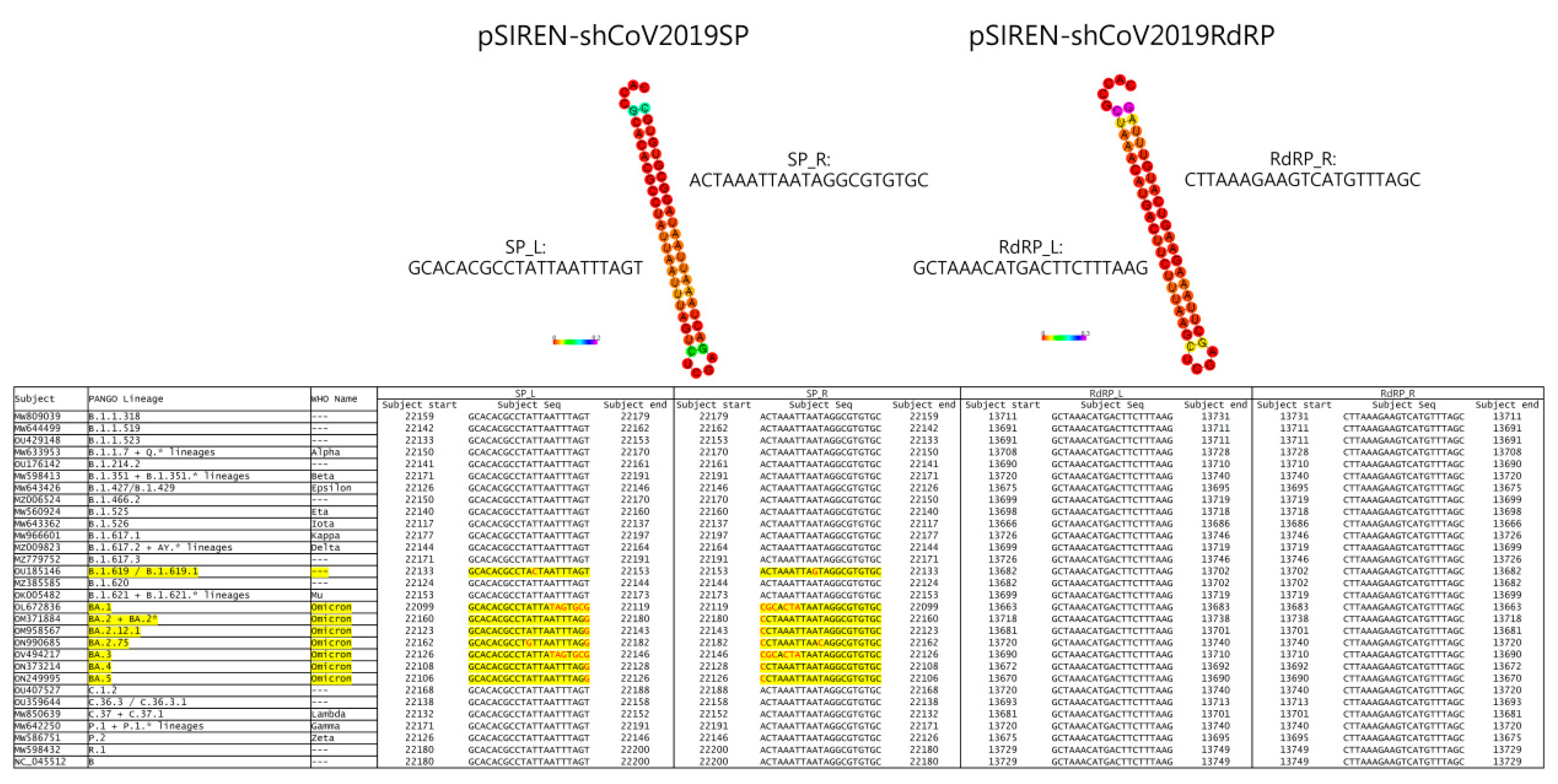
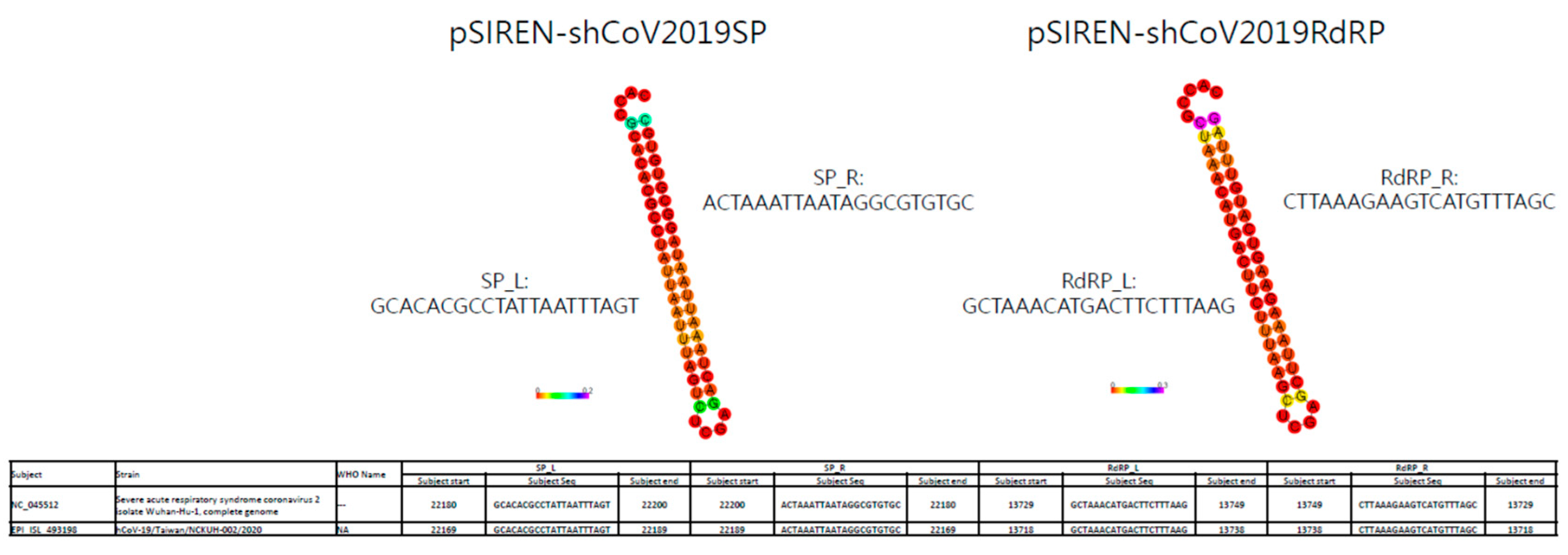
3.1. ShRNA against SARS-CoV-2 Was Designed to Target Conserved Regions of SP and RdRp Genes
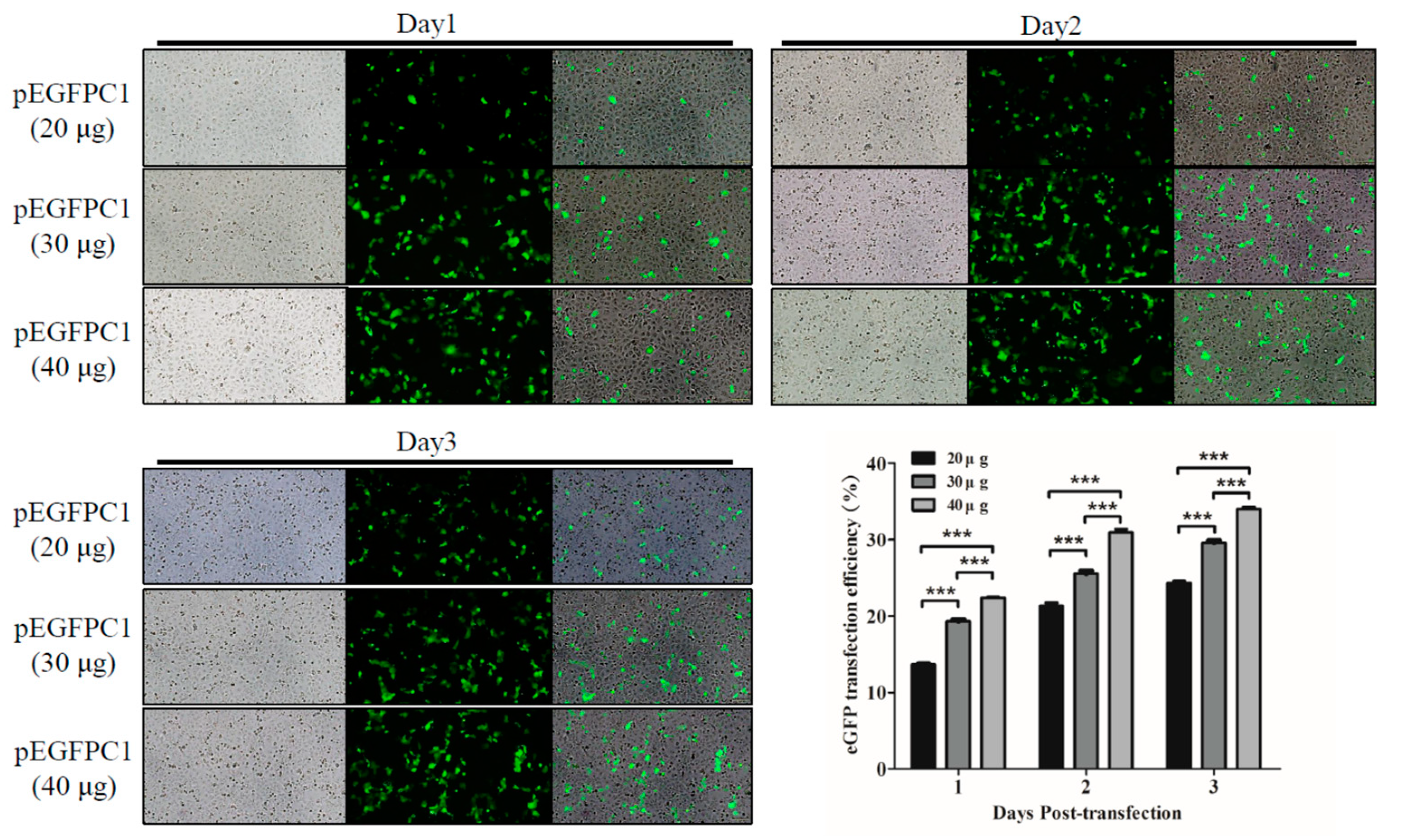
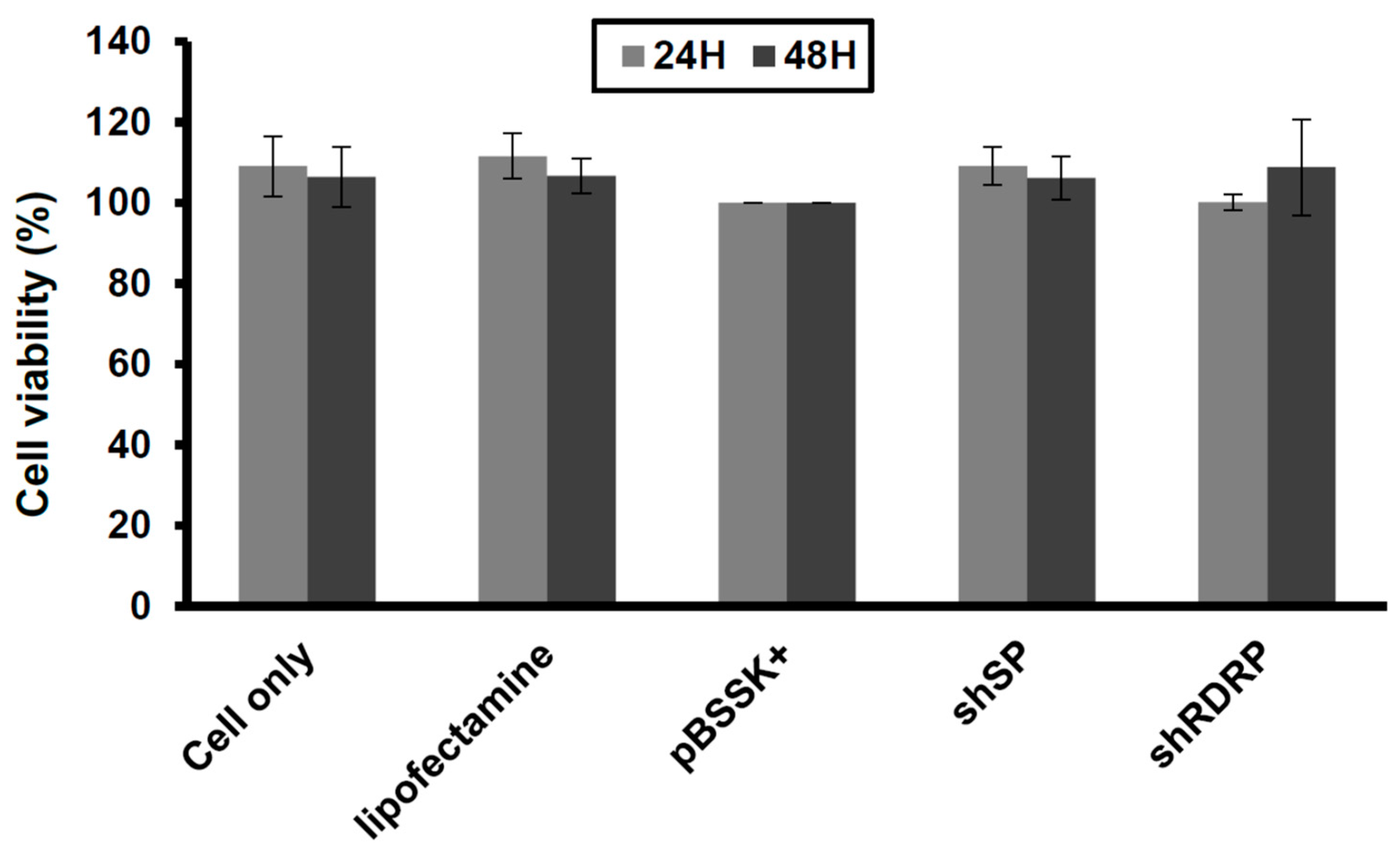
3.2. ShRNA against SARS-CoV-2 Is Nontoxic in Vero-E6 Cells
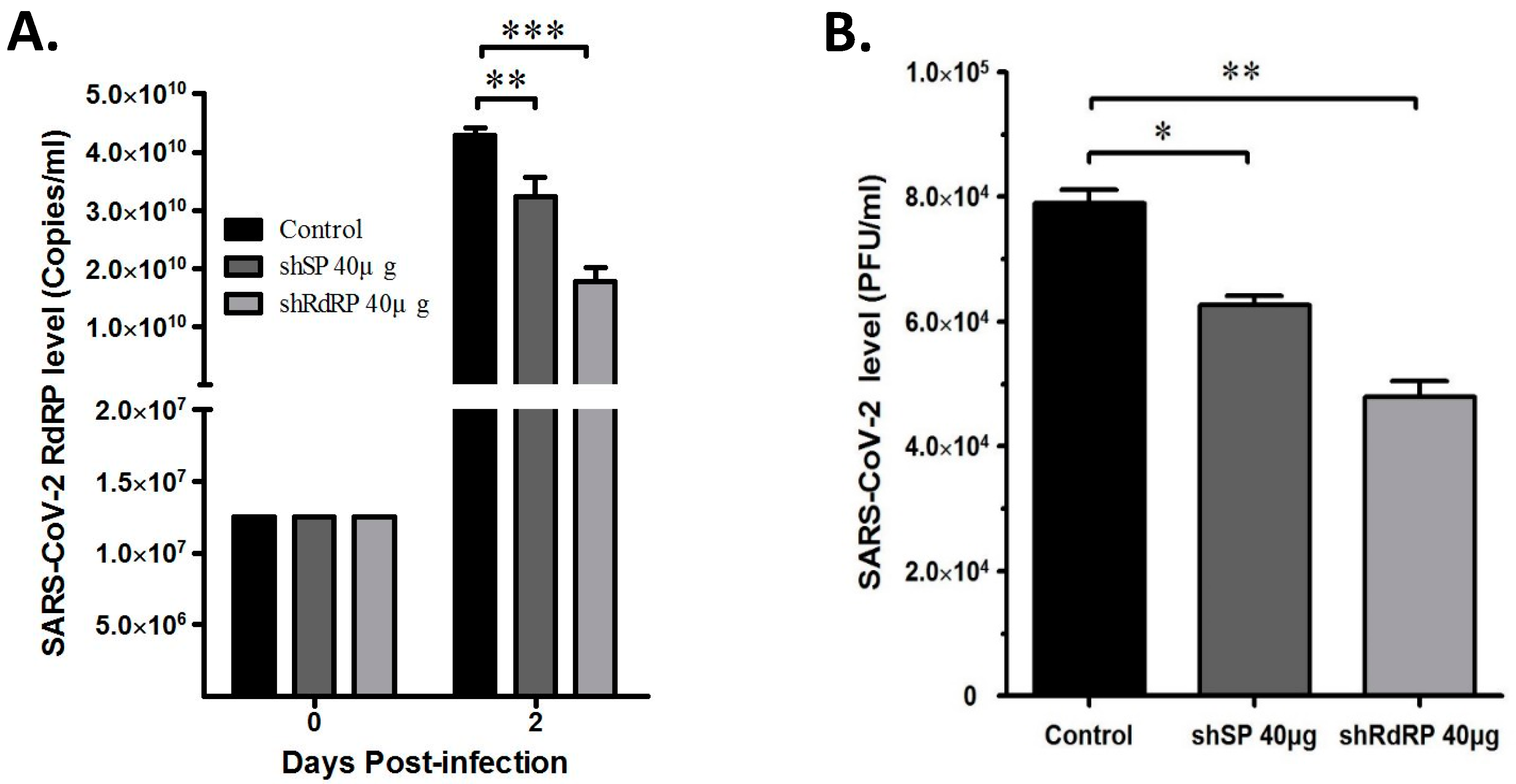
3.3. ShRNAs Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Exert Antiviral Replication Activity in Vero-E6 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupferschmidt, K.; Cohen, J. Race to find COVID-19 treatments accelerates. Science 2020, 367, 1412–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Almazi, J.G.; Ong, H.X.; Johansen, M.D.; Ledger, S.; Traini, D.; Hansbro, P.M.; Kelleher, A.D.; Ahlenstiel, C.L. Nanoparticle Delivery Platforms for RNAi Therapeutics Targeting COVID-19 Disease in the Respiratory Tract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, Q.; Inchakalody, V.P.; Merhi, M.; Mestiri, S.; Taib, N.; Moustafa Abo El-Ella, D.; Bedhiafi, T.; Raza, A.; Al-Zaidan, L.; Mohsen, M.O.; et al. Emerging COVID-19 variants and their impact on SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, therapeutics and vaccines. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor. Science 2005, 309, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, P.C.; Cupac, D.; Berkhout, B. Inhibition of virus replication by RNA interference. J. Biomed. Sci. 2003, 10, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Guo, Z.; Lu, J.; Meng, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhan, X.; Huang, B.; Yu, X.; Huang, M.; Pan, X.; et al. Inhibiting severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus by small interfering RNA. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2003, 116, 1262–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Corman, V.M.; Lienau, J.; Witzenrath, M. Coronaviruses as the cause of respiratory infections. Internist 2019, 60, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araf, Y.; Faruqui, N.A.; Anwar, S.; Hosen, M.J. SARS-CoV-2: A new dimension to our understanding of coronaviruses. Int. Microbiol. 2021, 24, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.J.; Tang, Q.; Cheng, D.; Qin, C.; Xie, F.Y.; Wei, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, B.J.; Woodle, M.C.; et al. Using siRNA in prophylactic and therapeutic regimens against SARS coronavirus in Rhesus macaque. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liu, G.H.; Chao, W.Y.; Shi, C.S.; Lin, C.Y.; Lim, Y.P.; Lu, C.H.; Lai, P.Y.; Chen, H.R.; Lee, Y.R. Piperlongumine Suppresses Proliferation of Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Yeh, S.F.; Ruan, X.M.; Zhang, H.; Hsu, S.D.; Huang, H.D.; Hsieh, C.C.; Lin, Y.S.; Yeh, T.M.; Liu, H.S.; et al. Honeysuckle aqueous extract and induced let-7a suppress dengue virus type 2 replication and pathogenesis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro. Surveill 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, J.B.; Bailey, A.L.; Kim, A.S.; Chen, R.E.; Diamond, M.S. Growth, detection, quantification, and inactivation of SARS-CoV-2. Virology 2020, 548, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayk Bernal, A.; Gomes da Silva, M.M.; Musungaie, D.B.; Kovalchuk, E.; Gonzalez, A.; Delos Reyes, V.; Martin-Quiros, A.; Caraco, Y.; Williams-Diaz, A.; Brown, M.L.; et al. Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of COVID-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.; Peacock, T.P.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; Wright, D.W.; Consortium, C.-G.U.; Willett, B.J.; Thomson, E.; Gupta, R.K.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo Arevalo, S.; Zapata Sifuentes, D.; Huallpa, J.C.; Landa Bianchi, G.; Castillo Chavez, A.; Garavito-Salini Casas, R.; Uribe Calampa, C.S.; Uceda-Campos, G.; Pineda Chavarria, R. Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 mutations reveals regional-specificity and similar trends of N501 and high-frequency mutation N501Y in different levels of control measures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntronwong, N.; Kanokudom, S.; Auphimai, C.; Assawakosri, S.; Thongmee, T.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Duangchinda, T.; Chantima, W.; Pakchotanon, P.; Chansaenroj, J.; et al. Effects of boosted mRNA and adenoviral-vectored vaccines on immune responses to omicron BA.1 and BA.2 following the heterologous CoronaVac/AZD1222 vaccination. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5713–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Consortium, C.-G.U.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Guo, Y.; Chan, J.F.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Chu, H.; Huang, Y.; Nair, M.S.; et al. Striking antibody evasion manifested by the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2022, 602, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setten, R.L.; Rossi, J.J.; Han, S.P. The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, A.A.; Adiba, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Nabi, A.N. Prediction of putative potential siRNAs for inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 strains, including variants of concern and interest. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawan, M.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Mallik, B.; Akhter, F.; Shakil, M.S.; Hossain, M.M.; Banik, S.; Lee, S.S.; Hasan, M.A.; et al. Designing an effective therapeutic siRNA to silence RdRp gene of SARS-CoV-2. Infect Genet. Evol. 2021, 93, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Davis, A.; Supramaniam, A.; Acharya, D.; Kelly, G.; Tayyar, Y.; West, N.; Zhang, P.; McMillan, C.L.D.; Soemardy, C.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 targeted siRNA-nanoparticle therapy for COVID-19. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2219–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogev, O.; Weissbrod, O.; Battistoni, G.; Bressan, D.; Naamti, A.; Falciatori, I.; Berkyurek, A.C.; Rasnic, R.; Hosmillo, M.; Ilan, S.; et al. Genome wide screen of RNAi molecules against SARS-CoV-2 creates a broadly potent prophylaxis. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casseb, S.M.M.; Khayat, A.S.; de Souza, J.E.S.; de Oliveira, E.H.C.; Dos Santos, S.E.B.; da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F.; de Assumpcao, P.P. Anticipating the Next Chess Move: Blocking SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Simultaneously Disarming Viral Escape Mechanisms. Genes 2022, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-R.; Tsai, H.-P.; Yeh, C.-S.; Fang, C.-Y.; Chan, M.W.Y.; Wu, T.-Y.; Shen, C.-H. RNA Interference Approach Is a Good Strategy against SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2023, 15, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010100
Lee Y-R, Tsai H-P, Yeh C-S, Fang C-Y, Chan MWY, Wu T-Y, Shen C-H. RNA Interference Approach Is a Good Strategy against SARS-CoV-2. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ying-Ray, Huey-Pin Tsai, Chun-Sheng Yeh, Chiung-Yao Fang, Michael W. Y. Chan, Tzu-Yun Wu, and Cheng-Huang Shen. 2023. "RNA Interference Approach Is a Good Strategy against SARS-CoV-2" Viruses 15, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010100
APA StyleLee, Y.-R., Tsai, H.-P., Yeh, C.-S., Fang, C.-Y., Chan, M. W. Y., Wu, T.-Y., & Shen, C.-H. (2023). RNA Interference Approach Is a Good Strategy against SARS-CoV-2. Viruses, 15(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010100





