Chronic Hepatitis B Viral Activity Enough to Take Antiviral Drug Could Predict the Survival Rate in Malignant Lymphoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design (Population)
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chronic Hepatitis B as a Risk Factor for Malignant Lymphoma
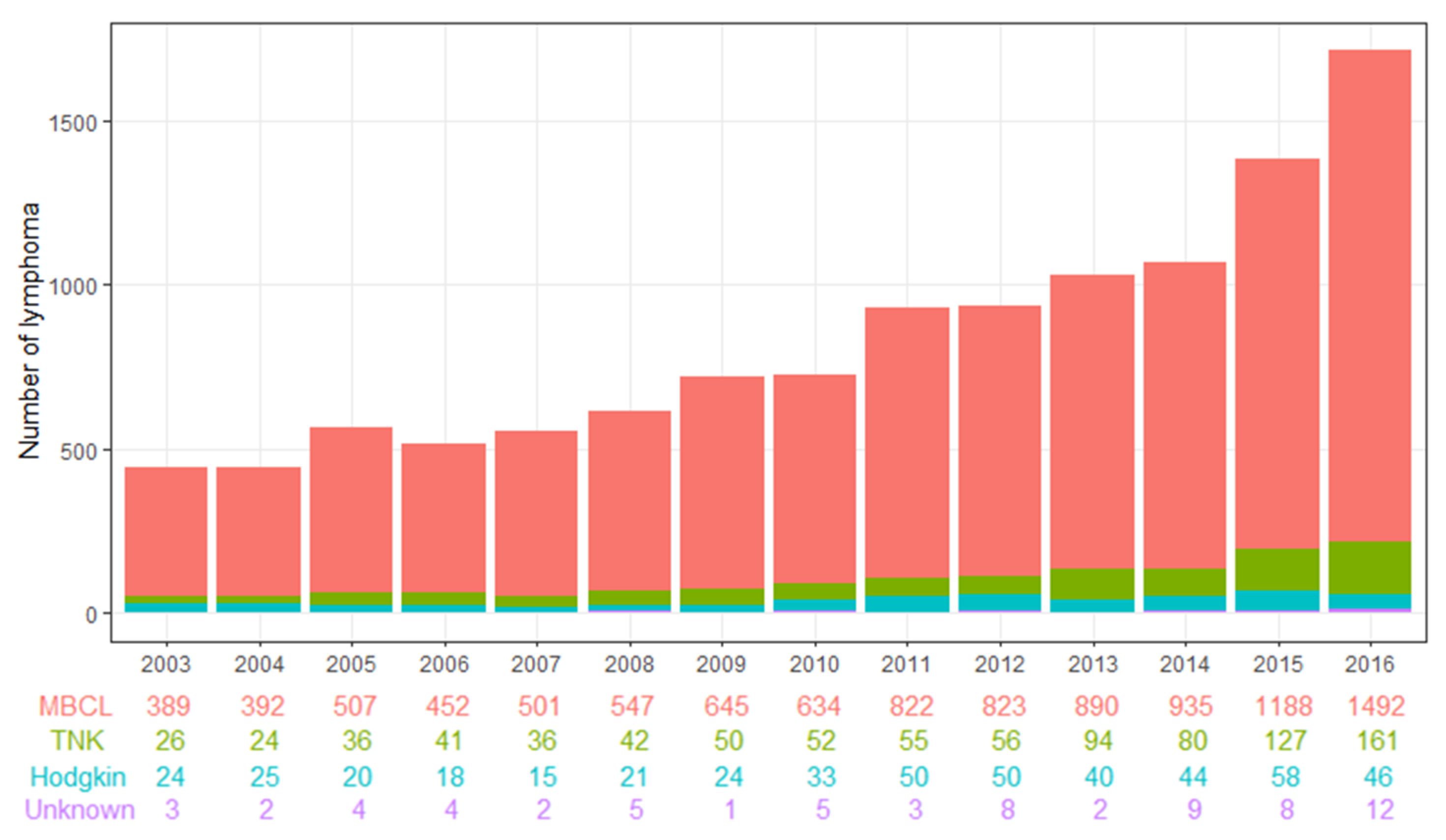
3.1.1. Crude Incidence of Malignant Lymphoma in HBV Patients in Korea (2003–2016)
3.1.2. Association between Malignant Lymphoma Development and Specific Antiviral Agents
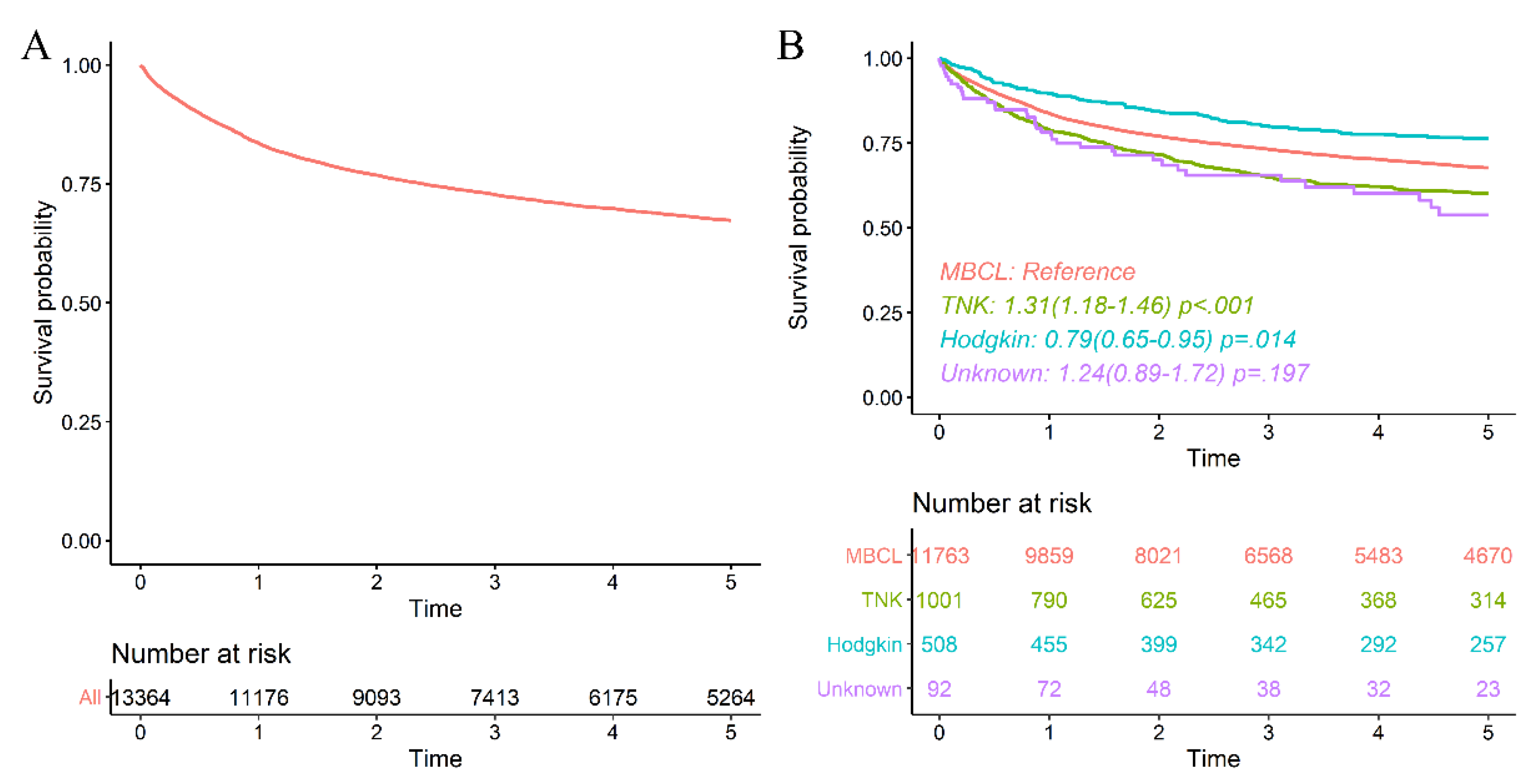
3.2. Chronic Hepatitis B as a Prognostic Factor of Malignant Lymphoma
3.2.1. Survival Rate of Malignant Lymphoma with Chronic Hepatitis B
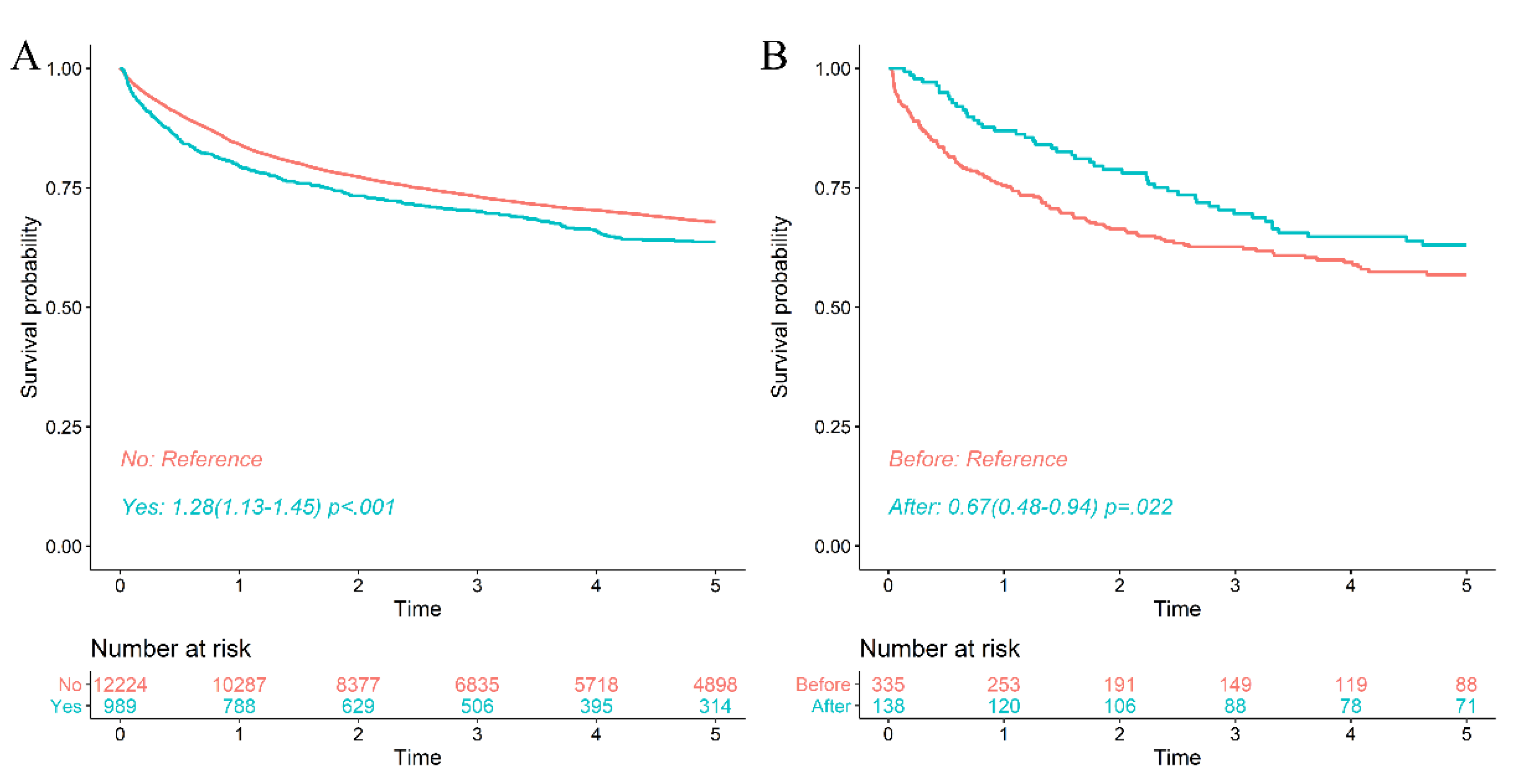
3.2.2. Prognosis of Malignant Lymphoma According to Chronic Hepatitis B Viral Activity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schweitzer, A.; Horn, J.; Mikolajczyk, R.T.; Krause, G.; Ott, J.J. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber-Stiehl, I. The silent epidemic killing more people than HIV, malaria or TB. Nature 2018, 564, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 93–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Lim, J.K.; Burak Ozbay, A.; Fraysse, J.; Liou, I.; Meyer, N.; Dusheiko, G.; Gordon, S.C. Advancing Age and Comorbidity in a US Insured Population-Based Cohort of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2019, 69, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.Y.; Sinn, D.H.; Kang, D.; Paik, S.W.; Guallar, E.; Cho, J.; Gwak, G.Y. Incidence of extrahepatic cancers among individuals with chronic hepatitis B or C virus infection: A nationwide cohort study. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiza, A.B.; Su, F.H.; Wang, W.C.; Sung, F.C.; Chang, S.N.; Yeh, C.C. Chronic hepatitis infection is associated with extrahepatic cancer development: A nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engels, E.A.; Cho, E.R.; Jee, S.H. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in South Korea: A cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Plank, L.D.; Suk, K.T.; Park, Y.E.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.H.; Heo, N.Y.; Park, J.; Kim, T.O.; Moon, Y.S.; et al. Trends in the prevalence of chronic liver disease in the Korean adult population, 1998–2017. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulcickas Yood, M.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Guo, D.; Caldwell, C.; Wells, K.; Shan, J.; Sanders, L.; Skovron, M.L.; Iloeje, U.; Manos, M.M. Incidence of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma among individuals with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2007, 46, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Young, K.H.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xi, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, O. Identification of hepatitis B virus aetiologic antigens, HBx and Pre-S2, in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Fan, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Cong, H.; et al. Characterization of hepatitis B virus infection and viral DNA integration in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.C.; Joshi, S.S.; Gao, S.; Giles, E.; Swidinsky, K.; van Marle, G.; Bathe, O.F.; Urbanski, S.J.; Terrault, N.A.; Burak, K.W.; et al. Oncogenic HBV variants and integration are present in hepatic and lymphoid cells derived from chronic HBV patients. Cancer Lett. 2020, 480, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Paik, Y.H.; Sohn, W.; Cho, H.C.; Gwak, G.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; Paik, S.W.; Yoo, B.C. Patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with oral antiviral therapy retain a higher risk for HCC compared with patients with inactive stage disease. Gut 2014, 63, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Bai, L.; Han, C.; Qi, X. Clinical Analysis and Prognostic Significance of Hepatitis B Virus Infections with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 2839–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Huang, S.C.; Chen, J.H.; Wei, C.H.; Fang, W.Q.; Su, T.H.; Yuan, C.T.; Liu, J.H.; Chuang, M.K.; Tien, H.F. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Positivity Is an Independent Unfavorable Prognostic Factor in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the Rituximab Era. Oncologist 2020, 25, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Ye, X.; Su, H.; Li, W.; Liu, D.; Pirmoradian, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Genetic landscape of hepatitis B virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2670–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.; Cho, S.; Ko, M.J.; Lim, Y.S. Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients Treated with Entecavir vs. Tenofovir for Chronic Hepatitis B: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Seo, Y.S.; Lee, H.A.; Kim, M.N.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, H.W.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.H.; et al. A multicenter study of entecavir vs. tenofovir on prognosis of treatment-naive chronic hepatitis B in South Korea. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Group | No Lymphoma (n = 13,942) | Lymphoma (n = 13,942) | OR | 95%CI | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||||||
| Sex | Male | 8173 | 58.6% | 8173 | 58.6% | ||||
| Female | 5769 | 41.4% | 5769 | 41.4% | 1.000 | 0.953 | 1.049 | 1.000 | |
| Age | <40 | 2500 | 17.9% | 2500 | 17.9% | ||||
| 40–49 | 2783 | 20.0% | 2783 | 20.0% | 1.000 | 0.926 | 1.079 | 1.000 | |
| 50–59 | 3513 | 25.2% | 3513 | 25.2% | |||||
| >60 | 5146 | 36.9% | 5146 | 36.9% | |||||
| Disease | Cirrhosis | 1025 | 7.4% | 939 | 6.7% | 0.910 | 0.830 | 0.998 | 0.044 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5937 | 42.6% | 6070 | 43.5% | 1.040 | 0.992 | 1.090 | 0.108 | |
| Hypertension | 4097 | 29.4% | 4119 | 29.5% | 1.008 | 0.957 | 1.061 | 0.773 | |
| CKD | 396 | 2.8% | 434 | 3.1% | 1.099 | 0.957 | 1.262 | 0.181 | |
| Drugs | Spironolactone | 477 | 3.4% | 421 | 3.0% | 0.879 | 0.769 | 1.004 | 0.058 |
| Terlipressin | 177 | 1.3% | 76 | 0.5% | 0.426 | 0.324 | 0.556 | 0.000 | |
| Somatostatin | 70 | 0.5% | 45 | 0.3% | 0.642 | 0.438 | 0.930 | 0.020 | |
| Propranolol | 1821 | 13.1% | 1731 | 12.4% | 0.944 | 0.879 | 1.012 | 0.106 | |
| Antiviral agents | No | 12,747 | 91.4% | 12,793 | 91.8% | ||||
| Yes | 1195 | 8.6% | 1149 | 8.2% | 0.958 | 0.880 | 1.043 | 0.321 | |
| Year | Malignant Lymphoma | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBCL | TNK | Hodgkin | Unknown | ||
| 2003 | 389 | 26 | 24 | 3 | 442 |
| 2004 | 392 | 24 | 25 | 2 | 443 |
| 2005 | 507 | 36 | 20 | 4 | 567 |
| 2006 | 452 | 41 | 18 | 4 | 515 |
| 2007 | 501 | 36 | 15 | 2 | 554 |
| 2008 | 547 | 42 | 21 | 5 | 615 |
| 2009 | 645 | 50 | 24 | 1 | 720 |
| 2010 | 634 | 52 | 33 | 5 | 724 |
| 2011 | 822 | 55 | 50 | 3 | 930 |
| 2012 | 823 | 56 | 50 | 8 | 937 |
| 2013 | 890 | 94 | 40 | 2 | 1026 |
| 2014 | 935 | 80 | 44 | 9 | 1068 |
| 2015 | 1188 | 127 | 58 | 8 | 1381 |
| 2016 | 1492 | 161 | 46 | 12 | 1711 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, K.-I.; Jo, J.-C.; Kim, D.-J.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.-S. Chronic Hepatitis B Viral Activity Enough to Take Antiviral Drug Could Predict the Survival Rate in Malignant Lymphoma. Viruses 2022, 14, 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091943
Seo K-I, Jo J-C, Kim D-J, Jeong J-Y, Lee S, Lee H-S. Chronic Hepatitis B Viral Activity Enough to Take Antiviral Drug Could Predict the Survival Rate in Malignant Lymphoma. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091943
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Kwang-Il, Jae-Cheol Jo, Da-Jung Kim, Jee-Yeong Jeong, Sangjin Lee, and Ho-Sup Lee. 2022. "Chronic Hepatitis B Viral Activity Enough to Take Antiviral Drug Could Predict the Survival Rate in Malignant Lymphoma" Viruses 14, no. 9: 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091943
APA StyleSeo, K.-I., Jo, J.-C., Kim, D.-J., Jeong, J.-Y., Lee, S., & Lee, H.-S. (2022). Chronic Hepatitis B Viral Activity Enough to Take Antiviral Drug Could Predict the Survival Rate in Malignant Lymphoma. Viruses, 14(9), 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091943






