B-Cell-Epitope-Based Fluorescent Quantum Dot Biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 Enable Highly Sensitive COVID-19 Antibody Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Serum Samples
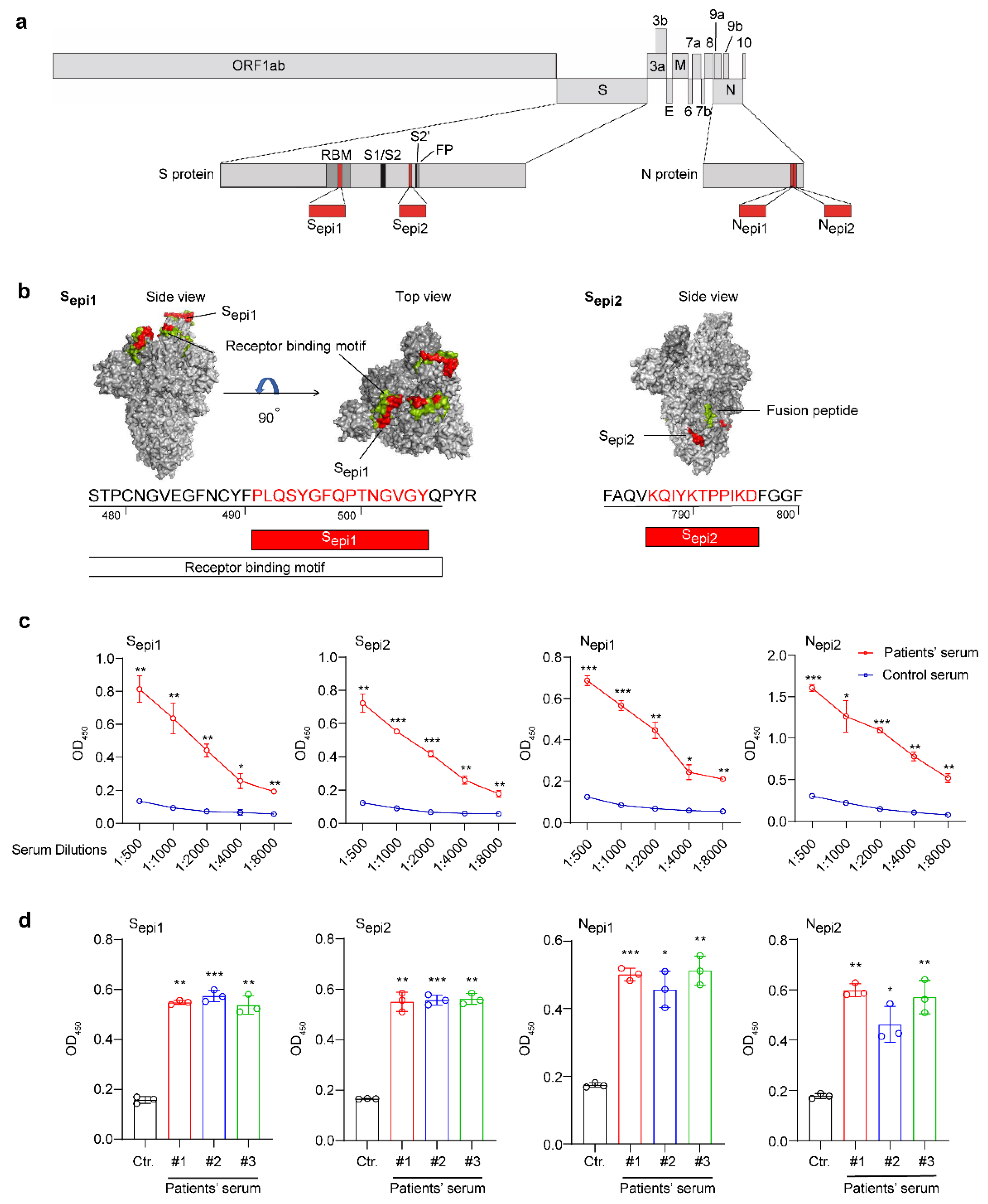
2.3. Epitope Prediction and Polypeptide Synthesis
2.4. Homologous Analysis and Proteins Model
2.5. ELISA
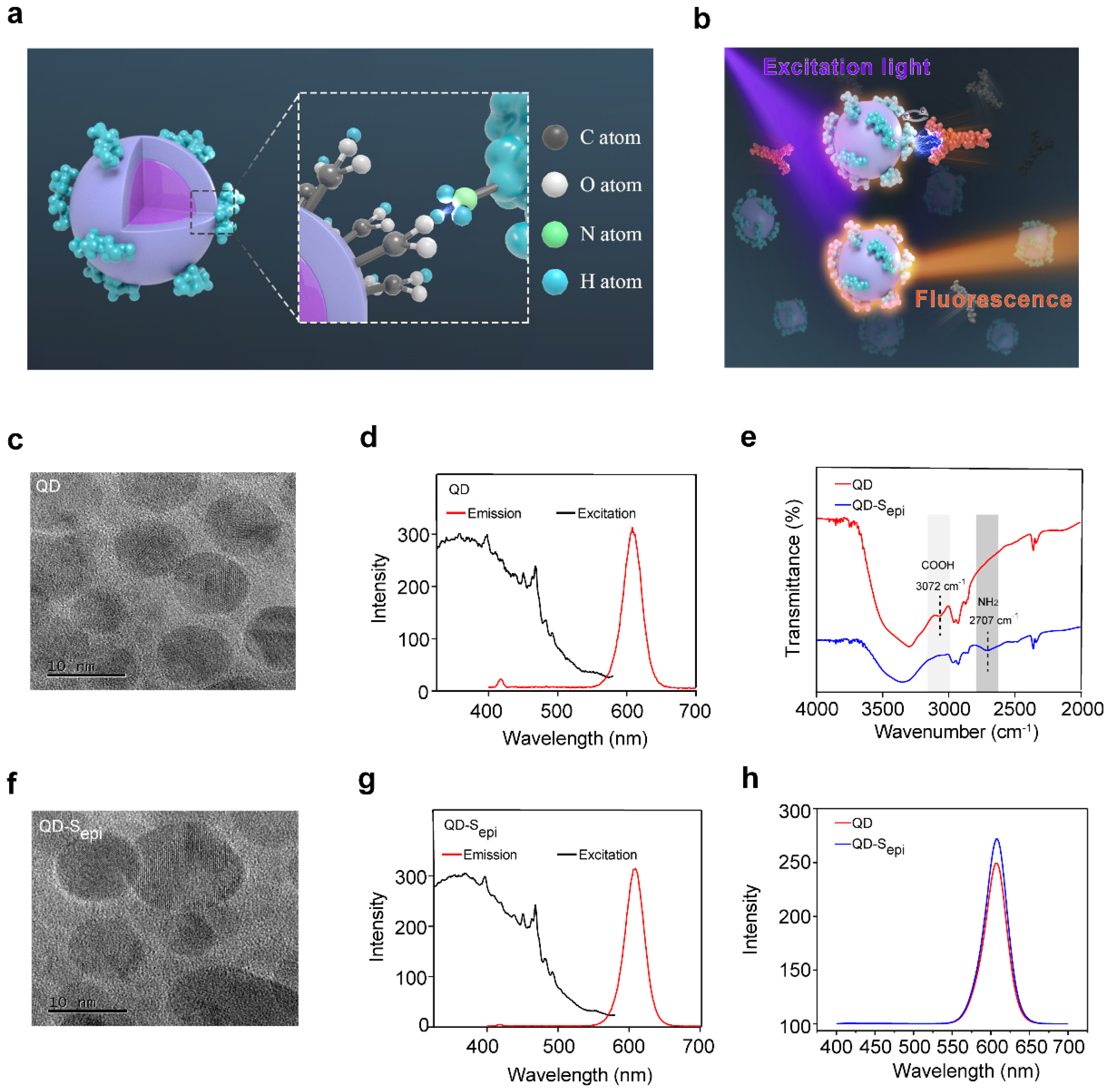
2.6. Preparation of QDs Fluorescence Probes
2.7. TEM
2.8. Absorption Spectrum Measurement
2.9. FTIR
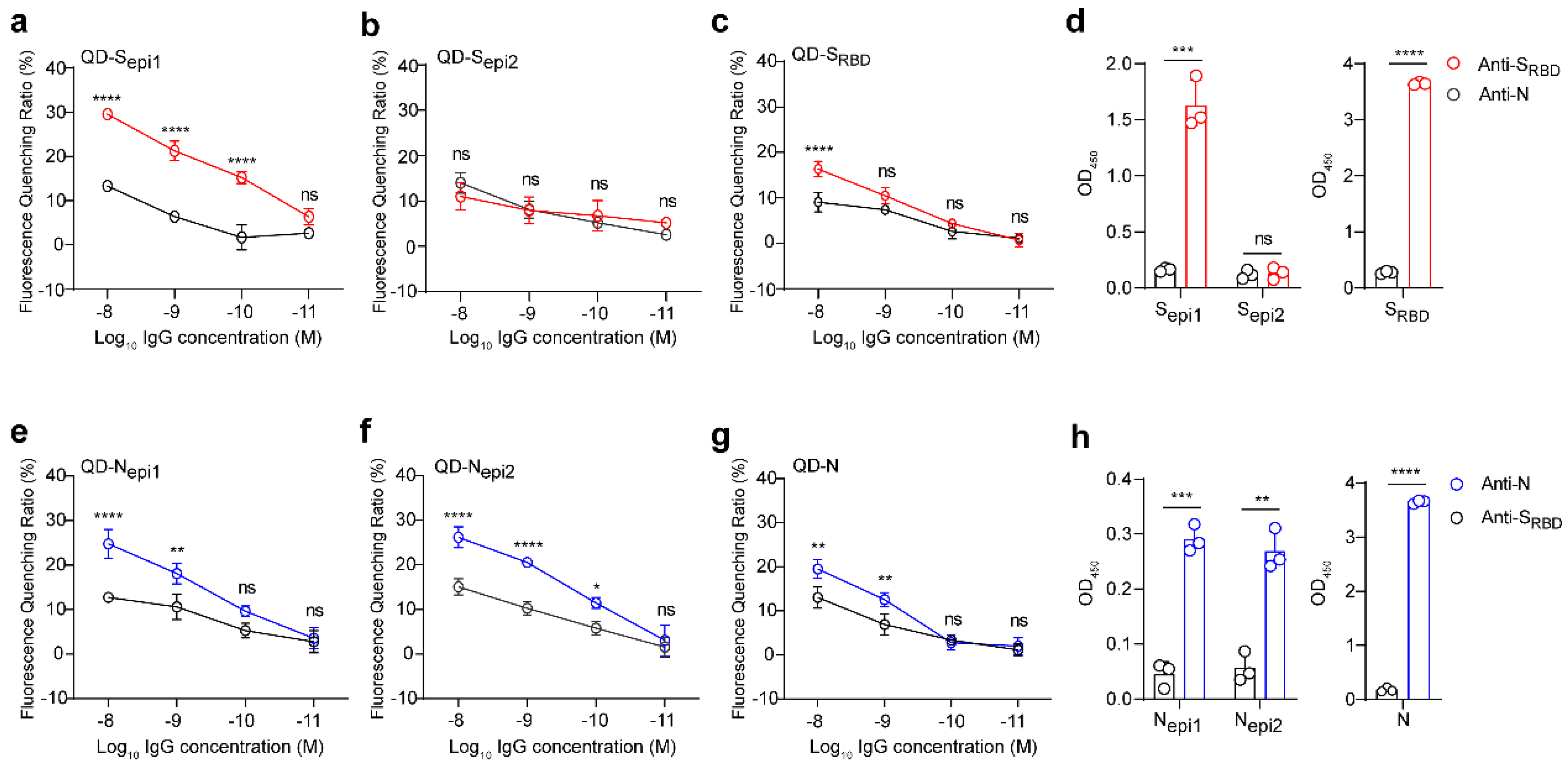
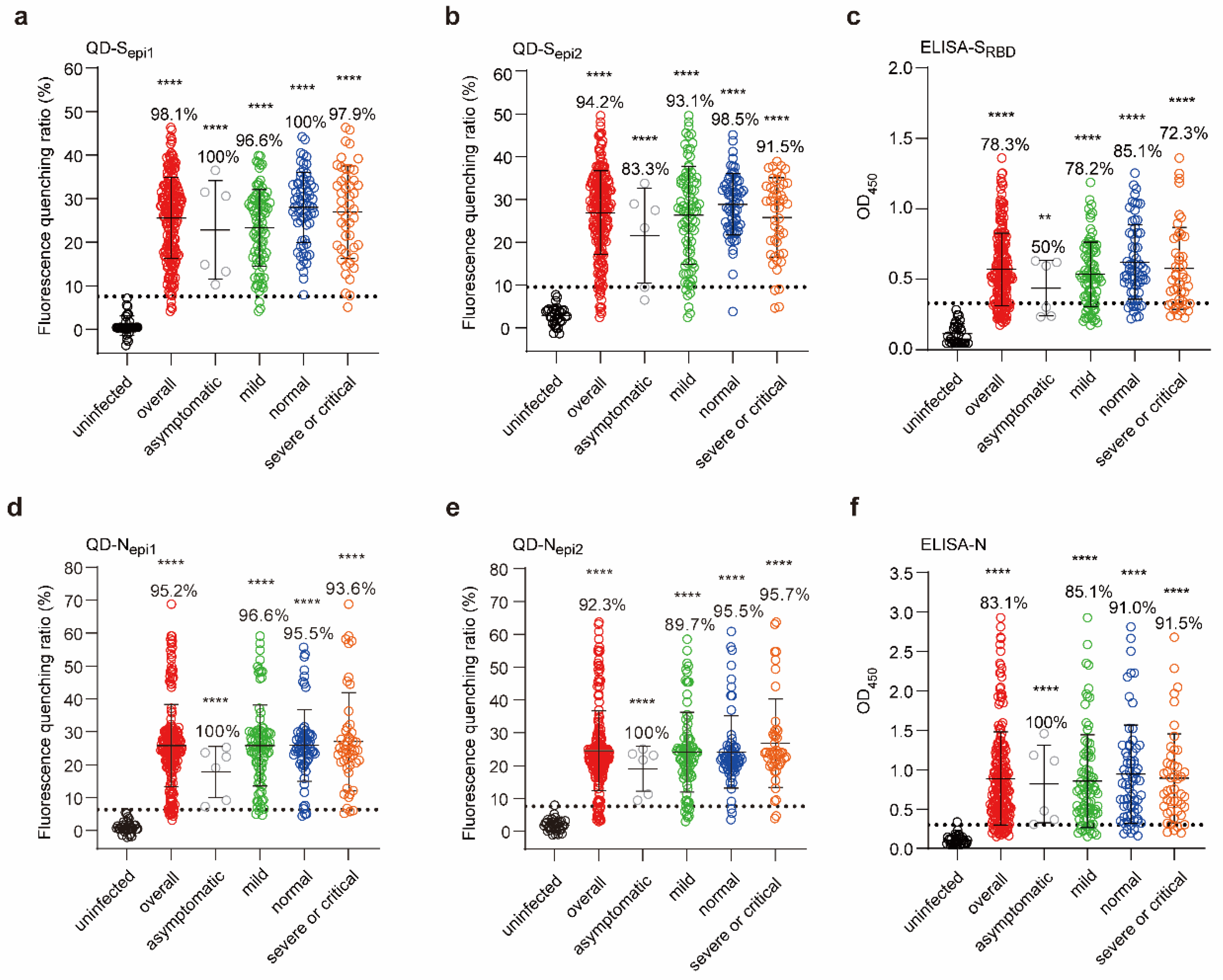
2.10. Detection of the Serum or Antibodies by Specific QDs
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Fluorescent QD-Peptides Biosensor
3.2. QD-SARS-CoV-2 Peptides React with the Corresponding Antibody
3.3. Identification of Four Highly Sensitive B Cell Epitopes of SARS-CoV-2
3.4. QDs Coupled with Four Highly Sensitive SARS-CoV-2 Peptides Efficiently Respond to the Corresponding Antibody
3.5. Fluorescent QD-Peptides Biosensors Exhibit Excellent Clinical Sensitivity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardian, Y.; Kosasih, H.; Karyana, M.; Neal, A.; Lau, C.Y. Review of Current COVID-19 Diagnostics and Opportunities for Further Development. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 615099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, R.; Lu, R.; Han, K.; Wu, G.; Tan, W. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Different Types of Clinical Specimens. JAMA 2020, 323, 1843–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalaf, K.; Papp, N.; Chou, J.T.; Hana, D.; Mackiewicz, A.; Kaczmarek, M. SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenesis, and Advancements in Diagnostics and Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 570927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa Bastos, M.; Tavaziva, G.; Abidi, S.K.; Campbell, J.R.; Haraoui, L.P.; Johnston, J.C.; Lan, Z.; Law, S.; MacLean, E.; Trajman, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of serological tests for covid-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, m2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaguer, A.G.; Mendoza-Flores, L.; Sánchez-López, L.A.; Palau-Dávila, L.A.; Padilla-Orozco, M.; Camacho-Ortiz, A. Correlation between rapid HIV testing and fourth-generation ELISA results for HIV detection among pregnant patients in the delivery room. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2017, 137, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Okba, N.M.A.; Igloi, Z.; Bogers, S.; Embregts, C.W.E.; Laksono, B.M.; Leijten, L.; Rokx, C.; Rijnders, B.; Rahamat-Langendoen, J.; et al. An evaluation of COVID-19 serological assays informs future diagnostics and exposure assessment. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, G.; Özdemir, H.; Omar, D.; Akdoğan, G. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Biophysical and biochemical aspects of SARS-CoV-2 and general characteristics. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2021, 164, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, J. Immunologic Testing for SARS-CoV-2 Infection from the Antigen Perspective. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02160-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.; Klumpp-Thomas, C.; Kalish, H.; Shunmugavel, A.; Mehalko, J.; Denson, J.P.; Snead, K.R.; Drew, M.; Corbett, K.S.; Graham, B.S.; et al. Serologic Cross-Reactivity of SARS-CoV-2 with Endemic and Seasonal Betacoronaviruses. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petherick, A. Developing antibody tests for SARS-CoV-2. Lancet 2020, 395, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lai, D.Y.; Lei, Q.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, F.; Hou, H.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Ren, Y.; Ma, M.L.; et al. Systematic evaluation of IgG responses to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-derived peptides for monitoring COVID-19 patients. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyun, J.C.; Cheong, M.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, J.S. Modification of short peptides using epsilon-aminocaproic acid for improved coating efficiency in indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). J. Immunol. Methods. 1997, 208, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Yang, M. Quantum dots: From fluorescence to chemiluminescence, bioluminescence, electrochemiluminescence, and electrochemistry. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13364–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, B.R.; Jepsen, M.L.; Ho, Y.P. Quantum dot-based nanosensors for diagnosis via enzyme activity measurement. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 13, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Park, J.C.; Nam, Y.S. Protein-quantum dot nanohybrids for bioanalytical applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghmandfard, A.; Sedighi, O.; Tabatabaei Rezaei, N.; Abedini, A.A.; Malek Khachatourian, A.; Toprak, M.S.; Seifalian, A. Recent advances in the modification of carbon-based quantum dots for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. A fluorescent nanoprobe based on cell-penetrating peptides and quantum dots for ratiometric monitoring of pH fluctuation in lysosomes. Talanta 2021, 227, 122208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Sarkes, D.A.; Stratis-Cullum, D.N.; Hurley, M.M. Direct conjugation of fluorescent quantum dots with E. coli via surface-displayed histidine-containing peptides. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Kim, T.E.; Jung, Y.K. Glutathione-decorated fluorescent carbon quantum dots for sensitive and selective detection of levodopa. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1165, 338513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portefaix, J.M.; Fanutti, C.; Granier, C.; Crapez, E.; Perham, R.; Grenier, J.; Pau, B.; Del Rio, M. Detection of anti-p53 antibodies by ELISA using p53 synthetic or phage-displayed peptides. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 259, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yan, X.P. Doped quantum dots for chemo/biosensing and bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5489–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medintz, I.L.; Uyeda, H.T.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleskova, S.; Mikheeva, E.; Gornostaeva, E. Using of Quantum Dots in Biology and Medicine. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1048, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, J.R.; Nocera, D.G.; Yocom, K.M.; Bordignon, E.; Gray, H.B. Electron-transfer kinetics of pentaammineruthenium(III) (histidine-33)-ferricytochrome c. Measurement of the rate of intramolecular electron transfer between redox centers separated by 15.ANG. in a protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 5798–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xiong, Q.; Mei, F.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, B.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhan, F.; Zhou, S.; et al. Antibody neutralization to SARS-CoV-2 and variants after 1 year in Wuhan, China. Innovation 2022, 3, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.F.F.; Pereira, M.I.A.; Assis, L.G.; Cabral Filho, P.E.; Santos, B.S.; Pereira, G.A.L.; Chaves, C.R.; Campos, G.S.; Sardi, S.I.; Pereira, G.; et al. Quantum dots-based fluoroimmunoassay for anti-Zika virus IgG antibodies detection. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 194, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, F.; Chowdhury, A.D.; Takemura, K.; Kozaki, I.; Honda, H.; Adegoke, O.; Park, E.Y. Fluorometric virus detection platform using quantum dots-gold nanocomposites optimizing the linker length variation. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2020, 1109, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.H. Quantum dot enabled molecular sensing and diagnostics. Theranostics 2012, 2, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapingidza, A.B.; Kowal, K.; Chruszcz, M. Antigen-Antibody Complexes. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2020, 94, 465–497. [Google Scholar]
- Lew, T.T.S.; Aung, K.M.M.; Ow, S.Y.; Amrun, S.N.; Sutarlie, L.; Ng, L.F.P.; Su, X. Epitope-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Rapid and Selective Detection of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12286–12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Bu, G.; Sun, Y.; Ren, C.; Qu, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of serum IgM and IgG antibodies in COVID-19 patients by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2857–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Kou, G.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q.; Tan, L.; Wu, W.; Tang, S.; et al. Evaluation of Nucleocapsid and Spike Protein-Based Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Detecting Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00461-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rongqing, Z.; Li, M.; Song, H.; Chen, J.; Ren, W.; Feng, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Song, J.; Peng, Y.; Su, B.; et al. Early Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Antibodies as a Serologic Marker of Infection in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, F.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Peng, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ye, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Antibody Detection and Dynamic Characteristics in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlbold, T.J.; Chromikova, V.; Tan, G.S.; Meade, P.; Amanat, F.; Comella, P.; Hirsh, A.; Krammer, F. Hemagglutinin Stalk- and Neuraminidase-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies Protect against Lethal H10N8 Influenza Virus Infection in Mice. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lin, R.T.P.; Renia, L.; Ng, L.F.P. Serological Approaches for COVID-19: Epidemiologic Perspective on Surveillance and Control. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Severity of Illness | ELISA-SRBD | QD-Sepi1 | QD-Sepi2 | ELISA-N | QD-Nepi1 | QD-Nepi2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic (6) | 45.08% | 49.47% | 51.36% | 60.35% | 55.19% | 62.25% |
| Mild (87) | 42.68% | 37.97% | 43.46% | 69.12% | 47.76% | 50.63% |
| Normal (67) | 42.34% | 28.86% | 24.92% | 66.34% | 42.00% | 45.49% |
| Severe or critical (47) | 50.35% | 39.51% | 35.95% | 63.42% | 55.21% | 50.30% |
| Overall (207) | 45.24% | 36.32% | 36.42% | 66.44% | 48.28% | 49.49% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Song, K.; Cai, K.; Liu, L.; Tang, D.; Long, W.; Zhai, B.; Chen, J.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. B-Cell-Epitope-Based Fluorescent Quantum Dot Biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 Enable Highly Sensitive COVID-19 Antibody Detection. Viruses 2022, 14, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051031
Zheng Y, Song K, Cai K, Liu L, Tang D, Long W, Zhai B, Chen J, Tao Y, Zhao Y, et al. B-Cell-Epitope-Based Fluorescent Quantum Dot Biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 Enable Highly Sensitive COVID-19 Antibody Detection. Viruses. 2022; 14(5):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051031
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yucheng, Kun Song, Kun Cai, Linlin Liu, Dixiao Tang, Wenbo Long, Bohui Zhai, Jianjun Chen, Yanbing Tao, Yunong Zhao, and et al. 2022. "B-Cell-Epitope-Based Fluorescent Quantum Dot Biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 Enable Highly Sensitive COVID-19 Antibody Detection" Viruses 14, no. 5: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051031
APA StyleZheng, Y., Song, K., Cai, K., Liu, L., Tang, D., Long, W., Zhai, B., Chen, J., Tao, Y., Zhao, Y., Liang, S., Huang, Q., Liu, Q., Zhang, Q., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Li, H., Wang, P., Lan, K., ... Xu, K. (2022). B-Cell-Epitope-Based Fluorescent Quantum Dot Biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 Enable Highly Sensitive COVID-19 Antibody Detection. Viruses, 14(5), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051031











