RNA Viruses in Aquatic Ecosystems through the Lens of Ecological Genomics and Transcriptomics
Abstract
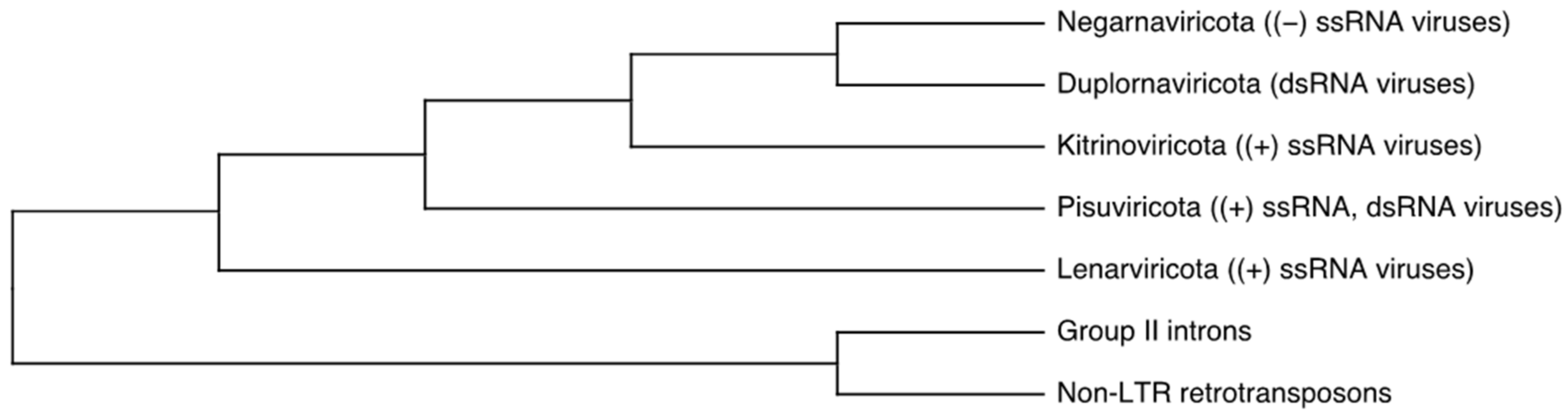
:1. Introduction
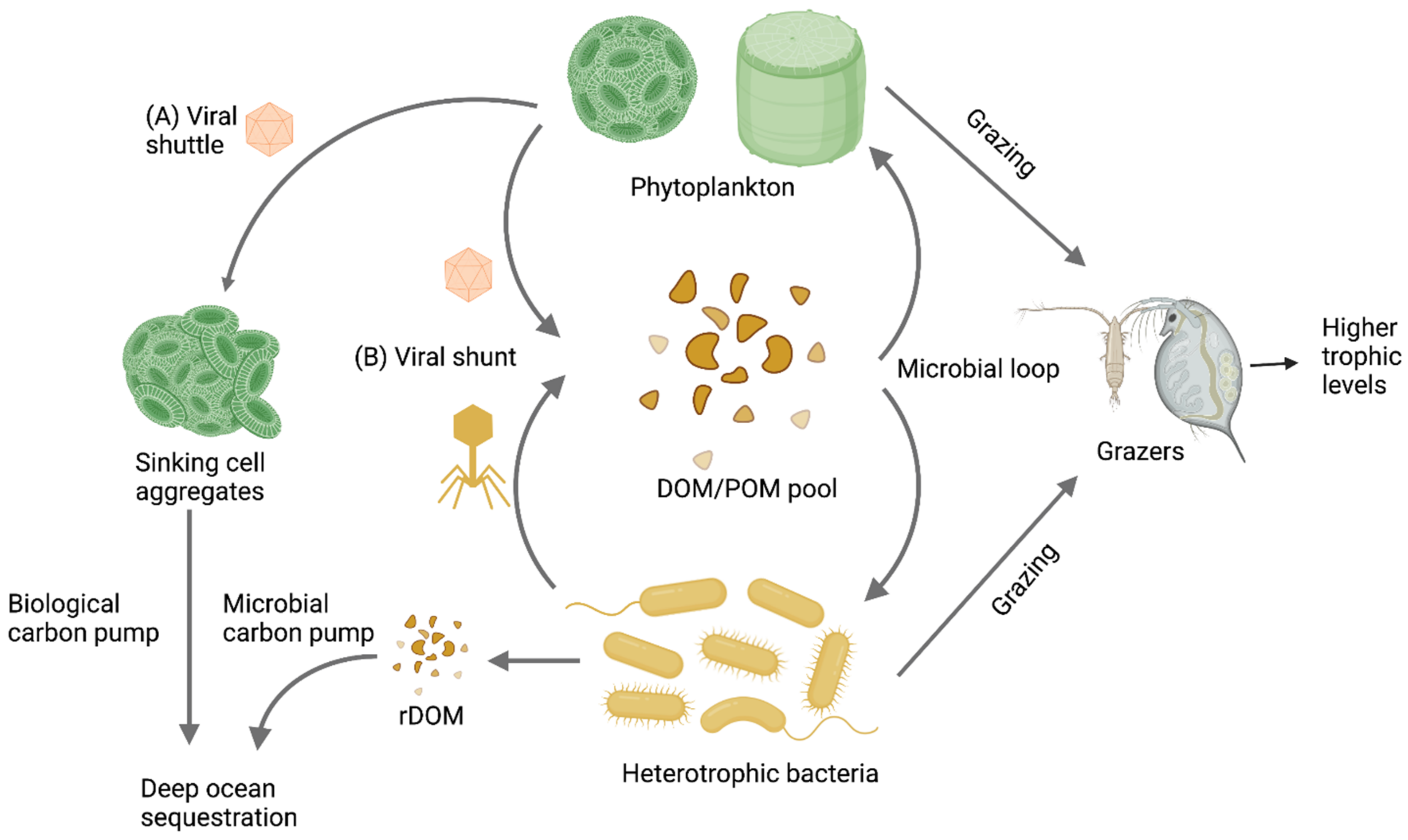
2. Methodological Challenges in the Study of Aquatic RNA Viral Communities
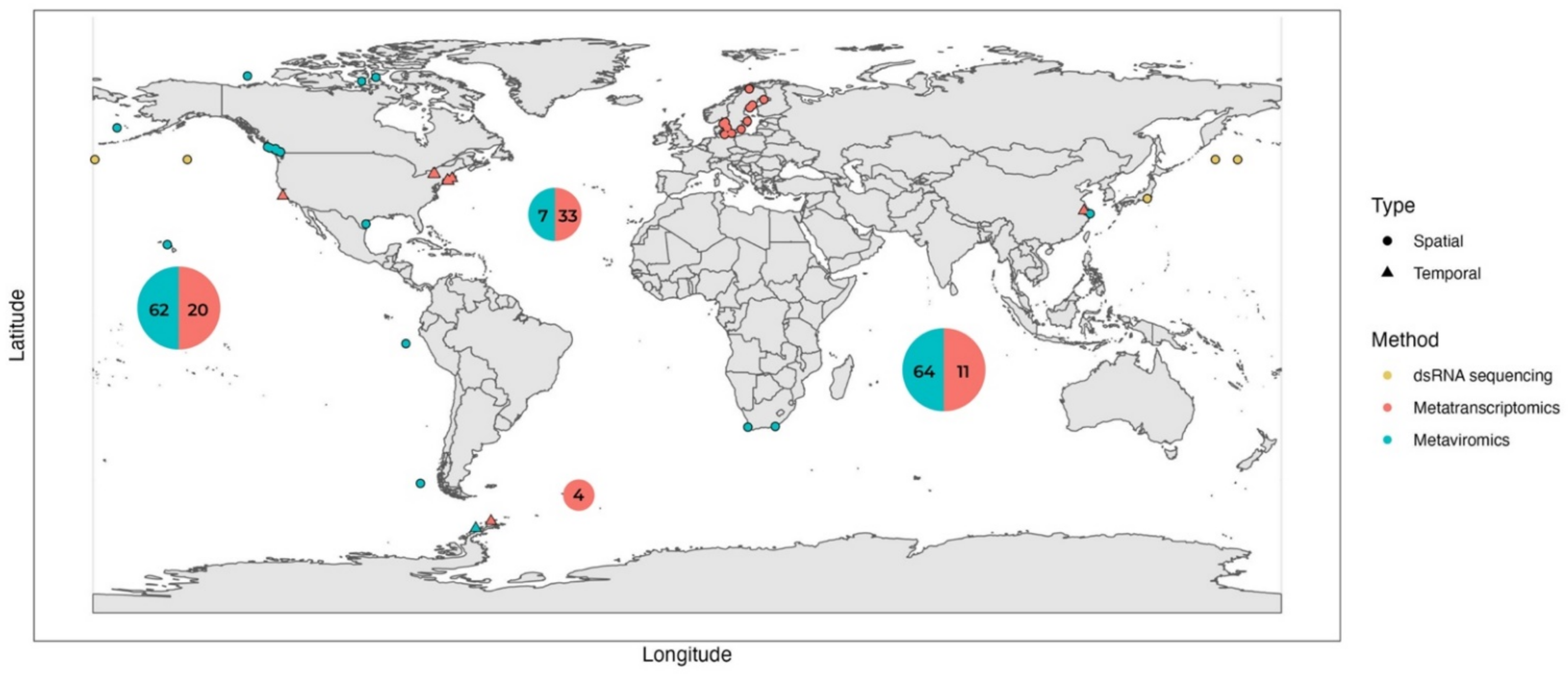
3. Environmental RNA Metaviromics: Lytic Positive-Sense ssRNA Viruses Dominate Pelagic but Not Benthic RNA Viral Assemblages
4. Environmental (Viral) Metatranscriptomics: Sampling with Size Fractionation Improves Metatranscriptome Resolution and Uncovers the Role of ssRNA Viruses
5. Environmental dsRNA Sequencing: The Enrichment of dsRNA from Marine Samples Greatly Expands the Diversity of dsRNA Viruses
6. Holobiont Metatranscriptomics: Marine Macroalgae and Cultured Marine Protists Reveal the Broad Distribution of Non-Lytic Strategies in Marine RNA Viruses
7. Recommendations for Future Studies
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses—Major players in the global ecosystem. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrman, J. Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects. Nature 1999, 399, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, J.S.; Wilhelm, S.W. Ocean viruses and their effects on microbial communities and biogeochemical cycles. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2012, 4, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, A.E.; Howard-Varona, C.; Needham, D.M.; John, S.G.; Worden, A.Z.; Waldbauer, J.R.; Coleman, M.L. Metabolic and biogeochemical consequences of viral infection in aquatic ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, F.; Roger, A.J.; Brown, M.W.; Simpson, A.G. The New Tree of Eukaryotes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coy, S.R.; Gann, E.R.; Pound, H.L.; Short, S.M.; Wilhelm, W.S. Viruses of eukaryotic algae: Diversity, methods for detection, and future directions. Viruses 2018, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Short, S.M.; Staniewski, M.A.; Chaban, Y.V.; Long, A.M.; Wang, D. Diversity of viruses infecting eukaryotic algae. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2020, 39, 29–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasir, A.; Forterre, P.; Kim, K.M.; Caetano-Anollés, G. The distribution and impact of viral lineages in domains of life. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callanan, J.; Stockdale, S.R.; Shkoporov, A.; Draper, L.A.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Expansion of known ssRNA phage genomes: From tens to over a thousand. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labonté, J.M.; Suttle, C.A. Previously unknown and highly divergent ssDNA viruses populate the oceans. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.I.; Silas, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Bocek, M.; Kazlauskas, D.; Krupovic, M.; Fire, A.; Dolja, V.V.; Koonin, E.V. Doubling of the known set of RNA viruses by metagenomic analysis of an aquatic virome. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, S.; Krupovic, M.; Poulet, A.; Debroas, D.; Enault, F. Evolution and diversity of the Microviridae viral family through a collection of 81 new complete genomes assembled from virome reads. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roux, S.; Krupovic, M.; Daly, R.A.; Borges, A.L.; Nayfach, S.; Schulz, F.; Sharrar, A.; Matheus Carnevali, P.B.; Cheng, J.F.; Ivanova, N.N.; et al. Cryptic inoviruses revealed as pervasive in bacteria and archaea across Earth’s biomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Krupovic, M.; Varsani, A.; Wolf, Y.I.; Yutin, N.; Zerbini, F.M.; Kuhn, J.H. Global Organization and Proposed Megataxonomy of the Virus World. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, e00061-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Krupovic, M.; Agol, V.I. The Baltimore Classification of Viruses 50 Years Later: How Does It Stand in the Light of Virus Evolution? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e0005321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.I.; Kazlauskas, D.; Iranzo, J.; Lucía-Sanz, A.; Kuhn, J.H.; Krupovic, M.; Dolja, V.V.; Koonin, E.V. Origins and evolution of the global RNA virome. MBio 2018, 9, e02329-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, S.; Rise, M.L.; Culley, A.I.; Steward, G.F. RNA viruses in the sea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 295–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, H.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Endo, H.; Chaffron, S.; Delmont, T.O.; Gaia, M.; Henry, N.; Hernández-Velázquez, R.; Nguyen, C.H.; Mamitsuka, H.; et al. Eukaryotic virus composition can predict the efficiency of carbon export in the global ocean. iScience 2021, 24, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbauer, M.G. Ecology of prokaryotic viruses. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 127–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, M.; Tomaru, Y.; Ahola, T. RNA Viruses in Aquatic Unicellular Eukaryotes. Viruses 2021, 13, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaru, Y.; Nagasaki, K. Flow cytometric detection and enumeration of DNA and RNA viruses infecting marine eukaryotic microalgae. J. Oceanogr. 2007, 63, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Noble, R.T.; Steele, J.A.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Hewson, I.; Fuhrman, J.A. Virus and prokaryote enumeration from planktonic aquatic environments by epifluorescence microscopy with SYBR Green I. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steward, G.F.; Culley, A.I.; Mueller, J.A.; Wood-Charlson, E.M.; Belcaid, M.; Poisson, G. Are we missing half of the viruses in the ocean? ISME J. 2013, 7, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miranda, J.A.; Culley, A.I.; Schvarcz, C.R.; Steward, G.F. RNA viruses as major contributors to Antarctic virioplankton. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 3714–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, A. New insight into the RNA aquatic virosphere via viromics. Virus Res. 2017, 244, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, E.P.; Nuccio, E.E.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Banfield, J.F.; Firestone, M.K. Metatranscriptomic reconstruction reveals RNA viruses with the potential to shape carbon cycling in soil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25900–25908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roossinck, M.J.; Martin, D.P.; Roumagnac, P. Plant virus metagenomics: Advances in virus discovery. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roossinck, M.J. Evolutionary and ecological links between plant and fungal viruses. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roux, S.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; Koonin, E.V.; Kropinski, A.M.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Lavigne, R.; Brister, J.R.; Varsani, A.; et al. Minimum information about an uncultivated virus genome (MIUVIG). Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A.; Chan, A.M.; Cottrell, M.T. Use of ultrafiltration to isolate viruses from seawater which are pathogens of marine phytoplankton. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, S.G.; Mendez, C.B.; Deng, L.; Poulos, B.; Kauffman, A.K.M.; Kern, S.; Brum, J.; Polz, M.F.; Boyle, E.A.; Sullivan, M.B. A simple and efficient method for concentration of ocean viruses by chemical flocculation. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurwitz, B.L.; Deng, L.; Poulos, B.T.; Sullivan, M.B. Evaluation of methods to concentrate and purify ocean virus communities through comparative, replicated metagenomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thurber, R.V.; Haynes, M.; Breitbart, M.; Wegley, L.; Rohwer, F. Laboratory procedures to generate viral metagenomes. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, S.; Krupovic, M.; Debroas, D.; Forterre, P.; Enault, F. Assessment of viral community functional potential from viral metagenomes may be hampered by contamination with cellular sequences. Open Biol. 2013, 3, 130160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prangishvili, D.; Bamford, D.H.; Forterre, P.; Iranzo, J.; Koonin, E.V.; Krupovic, M. The enigmatic archaeal virosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, B.I.; Cai, G. The Family Narnaviridae. Simplest of RNA Viruses, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Chapter 6; pp. 149–176. [Google Scholar]
- Valverde, R.A.; Khalifa, M.E.; Okada, R.; Fukuhara, T.; Sabanadzovic, S. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Endornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1024–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Kim, K.H.; Pearson, M.; Marzano, S.Y.L.; Yaegashi, H.; Xie, J.; Guo, L.; Kondo, H.; Koloniuk, I.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Hypoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, H.; Delwart, E.; Díaz-Muñoz, S.L. Next-generation sequencing of dsRNA is greatly improved by treatment with the inexpensive denaturing reagent DMSO. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Li, Y.; Salazar, G.; Henry, N.; Labadie, K.; de Vargas, C.; Sullivan, M.B.; Bowler, C.; Wincker, P.; et al. Biogeography of marine giant viruses reveals their interplay with eukaryotes and ecological functions. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieradzki, E.T.; Ignacio-Espinoza, J.C.; Needham, D.M.; Fichot, E.B.; Fuhrman, J.A. Dynamic marine viral infections and major contribution to photosynthetic processes shown by spatiotemporal picoplankton metatranscriptomes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Aylward, F.O. High Transcriptional Activity and Diverse Functional Repertoires of Hundreds of Giant Viruses in a Coastal Marine System. mSystems 2021, 6, e00293-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Wurch, L.L.; Alexander, H.; Dyhrman, S.T.; Gobler, C.J.; Wilhelm, S.W. Virus-host relationships of marine single-celled eukaryotes resolved from metatranscriptomics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hewson, I.; Bistolas, K.S.; Button, J.B.; Jackson, E.W. Occurrence and seasonal dynamics of RNA viral genotypes in three contrasting temperate lakes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pound, H.L.; Gann, E.R.; Tang, X.; Krausfeldt, L.E.; Huff, M.; Staton, M.E.; Talmy, D.; Wilhelm, S.W. The ‘Neglected Viruses’ of Taihu: Abundant Transcripts for Viruses Infecting Eukaryotes and Their Potential Role in Phytoplankton Succession. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gann, E.R.; Kang, Y.; Dyhrman, S.T.; Gobler, C.J.; Wilhelm, S.W. Metatranscriptome Library Preparation Influences Analyses of Viral Community Activity During a Brown Tide Bloom. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 664189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Schumacher, T.; Guajardo-Leiva, S.; Antón, J.; Llewellyn, C.A. Elucidating Viral Communities During a Phytoplankton Bloom on the West Antarctic Peninsula. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolody, B.C.; McCrow, J.P.; Allen, L.Z.; Aylward, F.O.; Fontanez, K.M.; Moustafa, A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Scholin, C.A.; Allen, E.E.; et al. Diel transcriptional response of a California Current plankton microbiome to light, low iron, and enduring viral infection. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2817–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeigler Allen, L.; McCrow, J.P.; Ininbergs, K.; Dupont, C.L.; Badger, J.H.; Hoffman, J.M.; Ekman, M.; Allen, A.E.; Bergman, B.; Venter, J.C. The Baltic Sea Virome: Diversity and Transcriptional Activity of DNA and RNA Viruses. mSystems 2017, 2, e00125-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carradec, Q.; Pelletier, E.; Da Silva, C.; Alberti, A.; Seeleuthner, Y.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Lima-Mendez, G.; Rocha, F.; Tirichine, L.; Labadie, K.; et al. A global ocean atlas of eukaryotic genes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depledge, D.P.; Mohr, I.; Wilson, A.C. Going the Distance: Optimizing RNA-Seq Strategies for Transcriptomic Analysis of Complex Viral Genomes. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01342-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Qin, X.C.; Holmes, E.C. Expanding the RNA Virosphere by Unbiased Metagenomics. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosani, U.; Shapiro, M.; Venier, P.; Allam, B. A needle in a haystack: Tracing bivalve-associated viruses in high-throughput transcriptomic data. Viruses 2019, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charon, J.; Marcelino, V.R.; Wetherbee, R.; Verbruggen, H.; Holmes, E.C. Metatranscriptomic identification of diverse and divergent RNA viruses in green and chlorarachniophyte algae cultures. Viruses 2020, 12, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urayama, S.I.; Takaki, Y.; Nishi, S.; Yoshida-Takashima, Y.; Deguchi, S.; Takai, K.; Nunoura, T. Unveiling the RNA virosphere associated with marine microorganisms. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Environmental viromes reveal global virosphere of deep-sea RNA viruses. Res. Sq. 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Vlok, M.; Lang, A.S.; Suttle, C.A. Marine RNA Virus Quasispecies Are Distributed throughout the Oceans. mSphere 2019, 4, e00157-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culley, I.; Lang, A.S.; Suttle, C.A. Metagenomic analysis of coastal RNA virus communities. Science 2006, 312, 1795–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culley, I.; Mueller, J.A.; Belcaid, M.; Wood-Charlson, M.E.; Poisson, G.; Steward, G.F. The Characterization of RNA Viruses in Tropical Seawater Using Targeted PCR and Metagenomics. mBio 2014, 5, e01210-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Holmes, E.C. Meta-transcriptomics and the evolutionary biology of RNA viruses. Virus Res. 2018, 243, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Wagner, V.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Hartmann, R.; Paludan, S.R. Double-Stranded RNA Is Produced by Positive-Strand RNA Viruses and DNA Viruses but Not in Detectable Amounts by Negative-Strand RNA Viruses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5059–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blouin, G.; Ross, H.A.; Hobson-Peters, J.; O’Brien, C.A.; Warren, B.; MacDiarmid, R. A new virus discovered by immunocapture of double-stranded RNA, a rapid method for virus enrichment in metagenomic studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marais, A.; Faure, C.; Bergey, B.; Candresse, T. Viral Double-Stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) from Plants: Alternative Nucleic Acid Substrates for High-Throughput Sequencing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1746, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovaro, R.; Corinaldesi, C.; Rastelli, E.; Dell’Anno, A. Towards a better quantitative assessment of the relevance of deep-sea viruses, Bacteria and Archaea in the functioning of the ocean seafloor. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danovaro, R.; Dell’Anno, A.; Corinaldesi, C.; Rastelli, E.; Cavicchioli, R.; Krupovic, M.; Noble, R.T.; Nunoura, T.; Prangishvili, D. Virus-mediated archaeal hecatomb in the deep seafloor. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Takaki, Y.; Eitoku, M.; Nunoura, T.; Takai, K. Metagenomic Analysis of Viral Communities in (Hado)Pelagic Sediments. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corte, D.; Martínez, J.M.; Cretoiu, M.S.; Takaki, Y.; Nunoura, T.; Sintes, E.; Herndl, G.J.; Yokokawa, T. Viral communities in the global deep ocean conveyor belt assessed by targeted viromics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, D.; Wei, G.; Pi, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.H.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hubert, C.R.; et al. Deep sea sediments associated with cold seeps are a subsurface reservoir of viral diversity. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Tangherlini, M.; Dell’Anno, A. From virus isolation to metagenome generation for investigating viral diversity in deep-sea sediments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Mochizuki, T.; Urayama, S.I.; Yoshida-Takashima, Y.; Nishi, S.; Hirai, M.; Nomaki, H.; Takaki, Y.; Nunoura, T.; Takai, K. Quantitative viral community DNA analysis reveals the dominance of single-stranded DNA viruses in offshore upper bathyal sediment from Tohoku, Japan. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, E.; Belák, S.; Granberg, F. The effect of preprocessing by sequence-independent, single-primer amplification (SISPA) on metagenomic detection of viruses. Biosecur. Bioterror. 2013, 11, S227–S234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, S.; Allgaier, M.; Hugenholtz, P. Multiple displacement amplification compromises quantitative analysis of metagenomes. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 943–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marine, R.; McCarren, C.; Vorrasane, V.; Nasko, D.; Crowgey, E.; Polson, S.W.; Wommack, K.E. Caught in the middle with multiple displacement amplification: The myth of pooling for avoiding multiple displacement amplification bias in a metagenome. Microbiome 2014, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urayama, S.I.; Takaki, Y.; Nunoura, T. FLDS: A comprehensive DSRNA sequencing method for intracellular RNA virus surveillance. Microbes Environ. 2016, 31, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Attoui, H.; Jaafar, F.M.; Belhouchet, M.; de Micco, P.; de Lamballerie, X.; Brussaard, C.P.D. Micromonas pusilla reovirus: A new member of the family Reoviridae assigned to a novel proposed genus (Mimoreovirus). J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charon, J.; Murray, S.; Holmes, E.C. Revealing RNA virus diversity and evolution in unicellular algae transcriptomes. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, Y.; Tomaru, Y.; Shimabukuro, H.; Kimura, K.; Hirai, M.; Takaki, Y.; Hagiwara, D.; Nunoura, T.; Urayama, S.I. Viral RNA genomes identified from marine macroalgae and a diatom. Microbes Environ. 2020, 35, ME20016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, S.L.; Su, S.; Dong, X.; Zappia, L.; Ritchie, M.E.; Gouil, Q. Opportunities and challenges in long-read sequencing data analysis. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overholt, W.A.; Hölzer, M.; Geesink, P.; Diezel, C.; Marz, M.; Küsel, K. Inclusion of Oxford Nanopore long reads improves all microbial and viral metagenome-assembled genomes from a complex aquifer system. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 4000–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick-Dugdale, J.; Solonenko, N.; Moore, K.; Chittick, L.; Gregory, A.C.; Allen, M.J.; Sullivan, M.B.; Temperton, B. Long-read viral metagenomics captures abundant and microdiverse viral populations and their niche-defining genomic islands. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaulaurier, J.; Luo, E.; Eppley, J.M.; Den Uyl, P.; Dai, X.; Burger, A.; Turner, D.J.; Pendelton, M.; Juul, S.; Harrington, E.; et al. Assembly-free single-molecule sequencing recovers complete virus genomes from natural microbial communities. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozarewa, I.; Ning, Z.; Quail, M.A.; Sanders, M.J.; Berriman, M.; Turner, D.J. Amplification-free Illumina sequencing-library preparation facilitates improved mapping and assembly of (G+C)-biased genomes. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danovaro, R.; Corinaldesi, C.; Dell’Anno, A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; Noble, R.T.; Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses and global climate change. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 993–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmsø, M.H.; Hellmér, M.; Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Timoneda, N.; Lukjancenko, O.; Seidel, M.; Elsässer, D.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Löfström, C.; Bofill-Mas, S.; et al. Evaluation of methods for the concentration and extraction of viruses from sewage in the context of metagenomic sequencing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conceição-Neto, N.; Zeller, M.; Lefrère, H.; De Bruyn, P.; Beller, L.; Deboutte, W.; Yinda, C.K.; Lavigne, R.; Maes, P.; Ranst, M.V.; et al. Modular approach to customise sample preparation procedures for viral metagenomics: A reproducible protocol for virome analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohl, C.; Brinkmann, A.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Radonić, A.; Nitsche, A.; Kurth, A. Protocol for metagenomic virus detection in clinical specimens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseel, T.; Ozhelvaci, O.; Freimanis, G.; Van Borm, S. Evaluation of convenient pretreatment protocols for RNA virus metagenomics in serum and tissue samples. J. Virol. Meth. 2015, 222, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
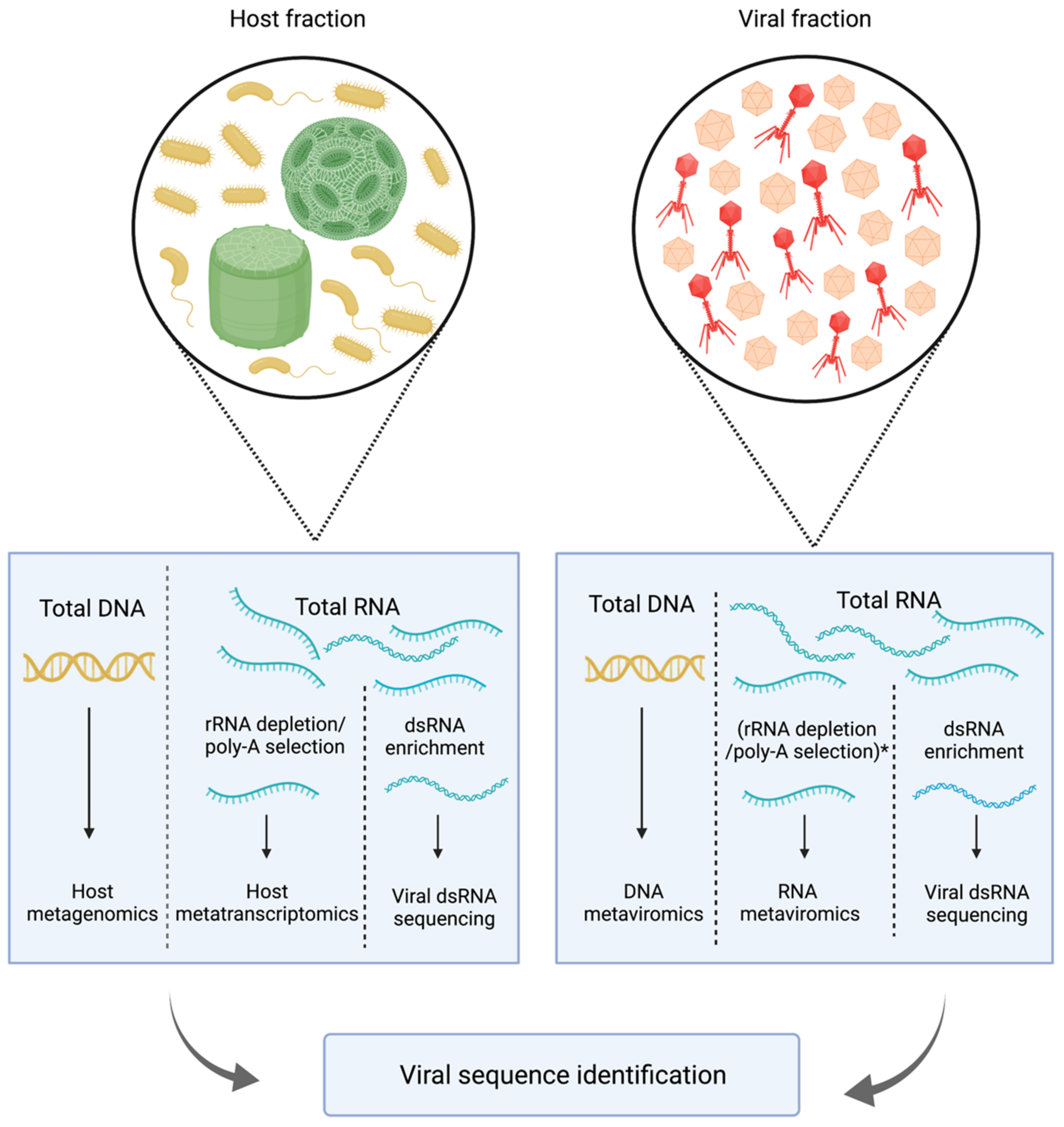
| Method | Virus Nucleic Acid Detected | Shortcomings | Advantages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metaviromics or viral metagenomics | RNA or DNA viral genomes in the extracellular stage | RNA viruses targeted separately than DNA viruses Needs special enrichment for dsRNA and ssDNA Large DNA viruses are filtered out High-burst-size viruses can be overrepresented | Enriched for viral sequences, better assembly | |
| Metatranscriptomics | Transcripts of (+) and (−) ssRNA, dsRNA, ssDNA, dsDNA | High background of nonviral sequences Potentially fragmented assemblies Misses low-titre viruses Does not distinguish between (+) ssRNA viral genome and transcripts | Captures all types of DNA and RNA viruses simultaneously Captures active infection (for DNA viruses) Can capture RNA viruses without capsids | |
| dsRNA sequencing | ssRNA as replicative intermediate dsRNA genomes | Not as effective for (−) ssRNA and DNA viruses Cellular metatranscriptomes are removed in the enrichment process | Enriched for RNA viruses Can be used for detection of both extracellular (<0.22 µm fractions) and intracellular RNA viruses |
| Region | Sampling Location | Site Characteristics | Sampling Scheme | Temporal/ Spatial | Host or Viral Fractions Collected (Host-Fractionated/Unfractionated) | Relative Abundance of Viral Reads in the Metatranscriptome | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | Multiple locations | Deep sea | 133 locations | Spatial | Only viral fraction (RNA) | - | [57] | |
| Polar | West Antarctic Peninsula | Highly productive coastal area | 1 location | Temporal | Only viral fraction (RNA) | - | [24] | |
| Polar and temperate | Multiple locations | Multiple site characteristics | 11 locations | Spatial | Only viral fraction (RNA) | - | [58] | |
| Temperate | Jericho Pier, Georgia Strait, Canada | Highly productive coastal area | 2 locations | Spatial | Only viral fraction (RNA) | - | [59] | |
| Temperate | Yangshan Harbour, Shanghai, China | Brackish coastal area | 1 location | Spatial | Only viral fraction (RNA and DNA) | - | [11] | |
| Subtropical | Kane’ohe Bay, Hawai’i | Coastal area | 1 location | Spatial | Only viral fraction (RNA) | - | [60] | |
| Subpolar | Honshu, Japan Jamstec cruise | Coastal and pelagic | 5 locations | Spatial | Host: Unfractionated >0.22 µm dsRNA + ssRNA metatranscriptomes Viral fraction (RNA) dsRNA + ssRNA viromes | 0.1% of ssRNA metatranscriptomes 1.3–36.6% of dsRNA metatranscriptomes | [56] | |
| Polar | Chile Bay, Antarctica | Highly productive coastal area | 1 location 2 samples, 3 weeks apart | Temporal | Host: Fractionated 8 µm–0.22 µm fraction | 0.04–0.05% (rRNA depletion) | [48] | |
| Temperate | Baltic sea Lake Torneträsk | Eutrophic, mostly brackish | 11 location (2 depths) | Spatial | Host: Fractionated 200–3.0 µm 3.0–0.8 µm 0.8–0.1 µm + viral fraction (DNA) | 3.2% (separate rRNA depletion and poly-A selection libraries) | [50] | |
| Temperate | Narragansett Bay (NB) Quantuck Bay (QB), USA | Eutrophic (bloom) coastal | 2 locations NB - 5 samples during 4 weeks QB - 3 samples within a week | Temporal * | Host: Fractionated QB 5–0.22 µm NB >5 µm | 0.043–2.4% (poly-A selection) | [44] | |
| Temperate | Lake Tai, China | Hypereutrophic (bloom) lake | 9 locations 1 × monthly for 5 months | Temporal * | Host: Unfractionated >0.22 µm | 0.02% (rRNA depletion) | [46] | |
| Temperate | Owasco Lake Seneca Lake Cayuga Lake, USA | Mezotrophic to eutrophic lakes | 3 locations 1 × monthly for 10 months | Temporal * | Host: Fractionated 5–0.22 µm | 0.6% (rRNA depletion) | [45] | |
| Temperate | California Current, USA | Oligotrophic, with upwelling | 1 location Every 4 h for 60 h | Temporal | Host: Fractionated >5 µm 5–0.22 µm | Not reported | [49] | |
| Temperate | Quantuck Bay (QB) Tiana Beach (TB), USA | Eutrophic (bloom) coastal | 2 locations QB 1× weekly for 10 weeks TB—1× weekly for 8 weeks | Temporal * | Host: Unfractionated >0.22 µm (for rRNA reduction) >1 µm (for poly-A selection) | 0.33–0.53% in rRNA depleted libraries 0.02–0.023% in poly-A selected libraries | [47] | |
| Global | Multiple locations | Multiple site characteristics | 68 locations 2 depths | Spatial | Host: Fractionated 2000–180 µm 180–20 µm 20–5 µm 5–0.8 µm | 0.0006% to 0.4% (poly-A selection) | [18,51] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolundžija, S.; Cheng, D.-Q.; Lauro, F.M. RNA Viruses in Aquatic Ecosystems through the Lens of Ecological Genomics and Transcriptomics. Viruses 2022, 14, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040702
Kolundžija S, Cheng D-Q, Lauro FM. RNA Viruses in Aquatic Ecosystems through the Lens of Ecological Genomics and Transcriptomics. Viruses. 2022; 14(4):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040702
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolundžija, Sandra, Dong-Qiang Cheng, and Federico M. Lauro. 2022. "RNA Viruses in Aquatic Ecosystems through the Lens of Ecological Genomics and Transcriptomics" Viruses 14, no. 4: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040702
APA StyleKolundžija, S., Cheng, D.-Q., & Lauro, F. M. (2022). RNA Viruses in Aquatic Ecosystems through the Lens of Ecological Genomics and Transcriptomics. Viruses, 14(4), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040702







