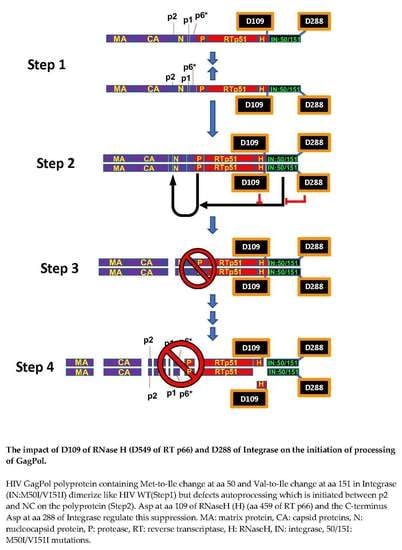
The C-Terminal Domain of RNase H and the C-Terminus Amino Acid Residue Regulate Virus Release and Autoprocessing of a Defective HIV-1 Possessing M50I and V151I Changes in Integrase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cells
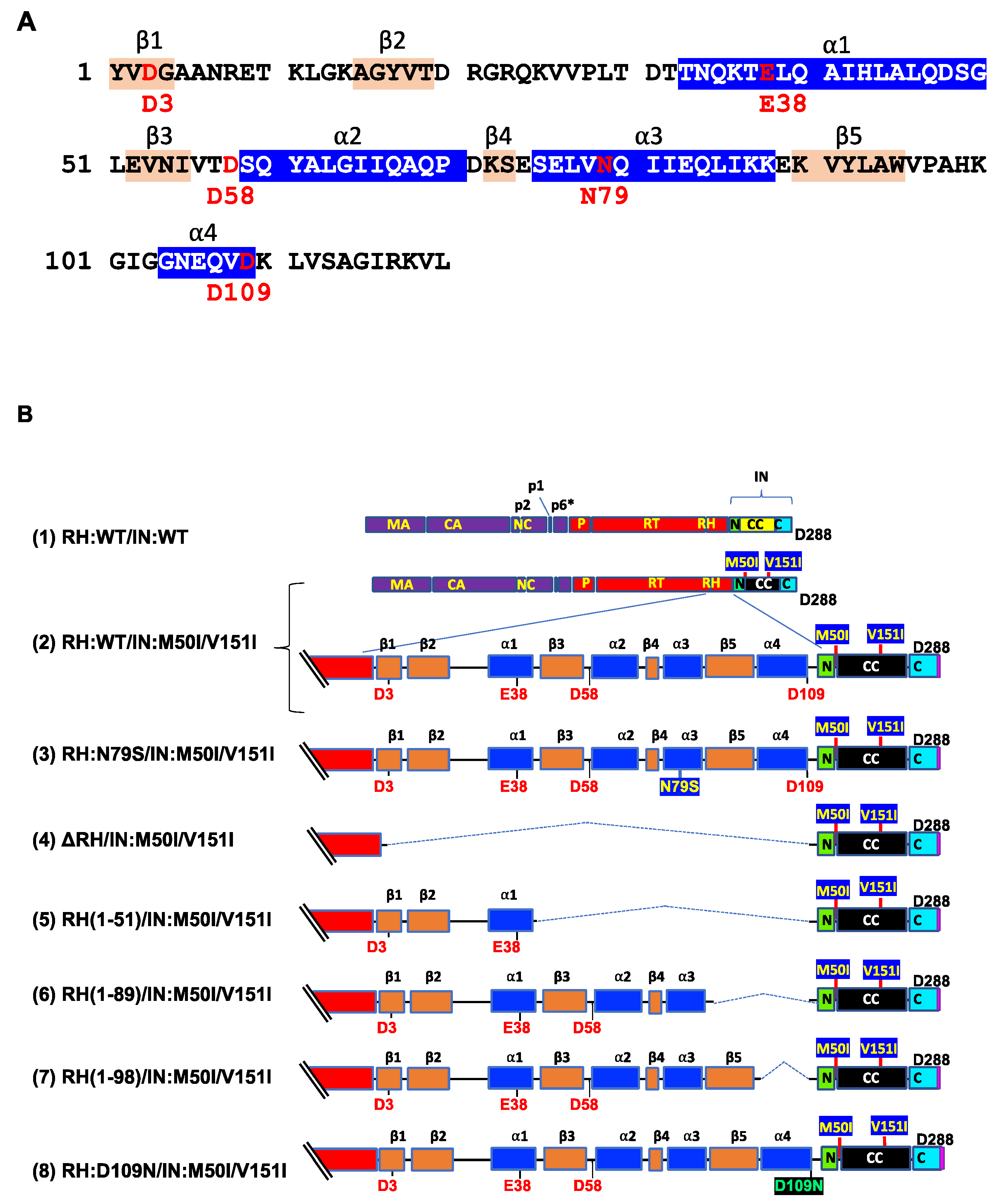
2.3. Construction of Plasmids Encoding HIV Variants
2.4. Recombinant HIV-1 Viruses
2.5. HIV Replication Assay
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Structure Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
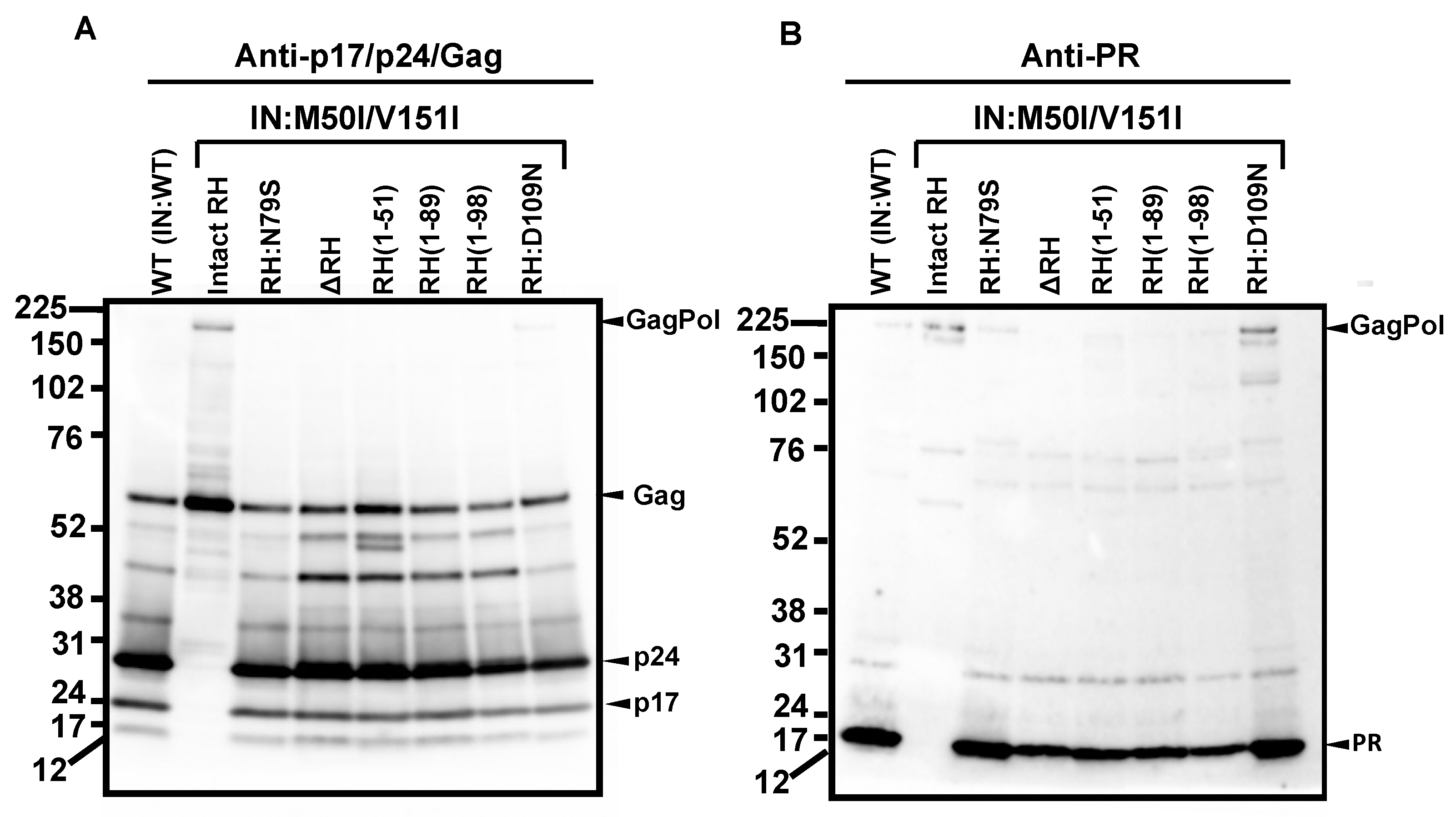
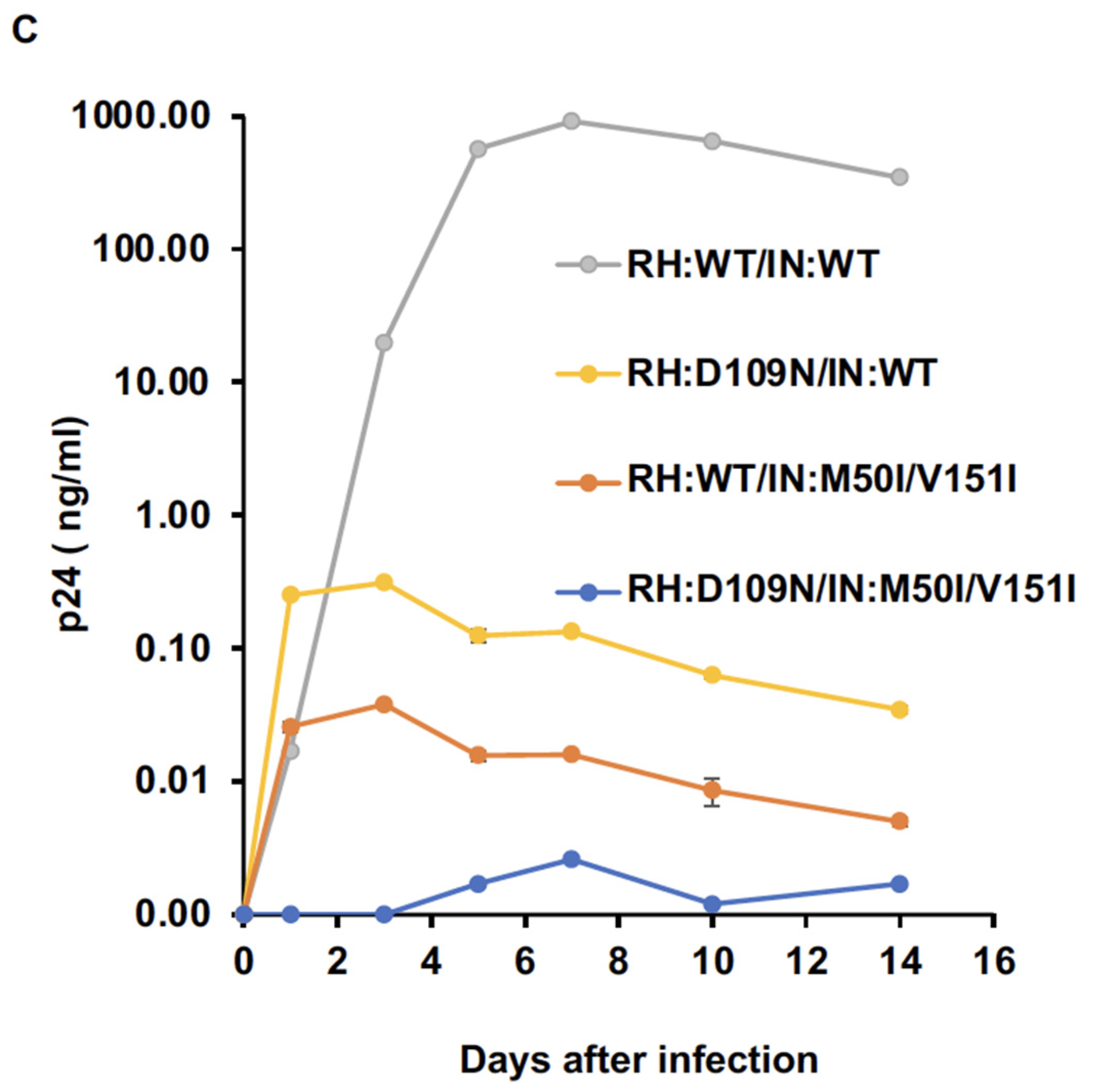
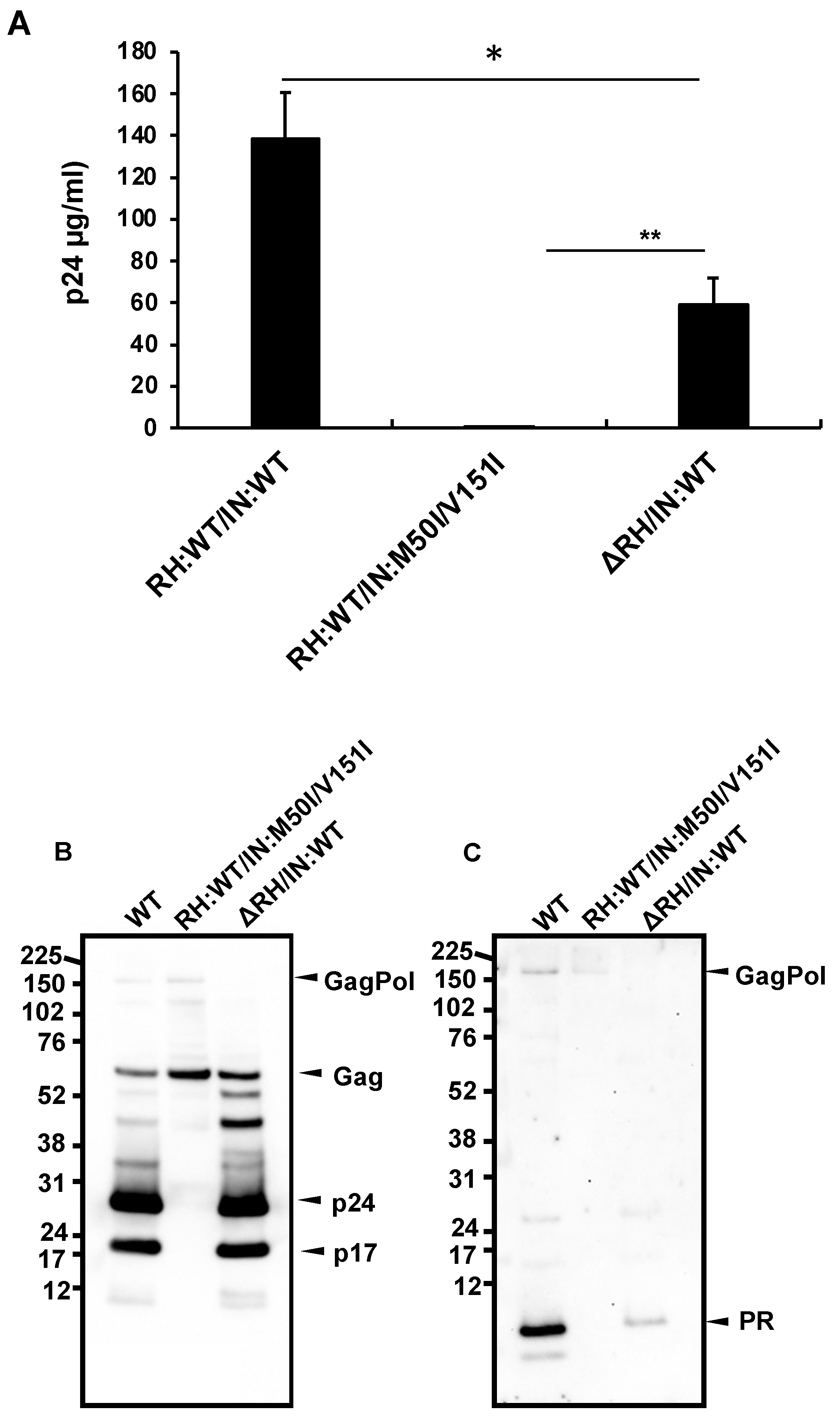
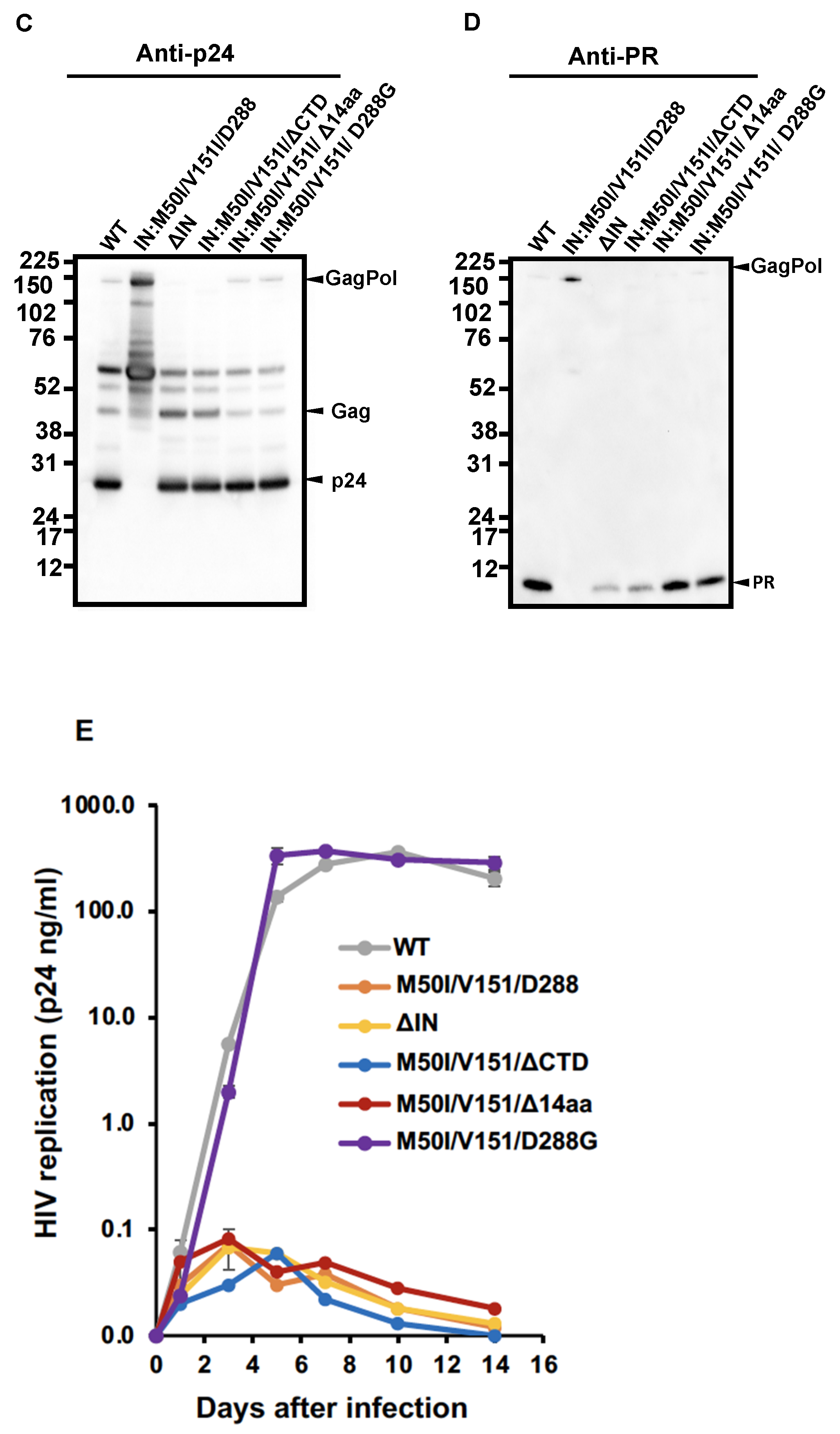
3.1. The C-Terminal Domain of RNase H in the GagPol Polyprotein Regulates the Virus Release and Autoprocessing Defects in HIV(IN:M50I/V151I)
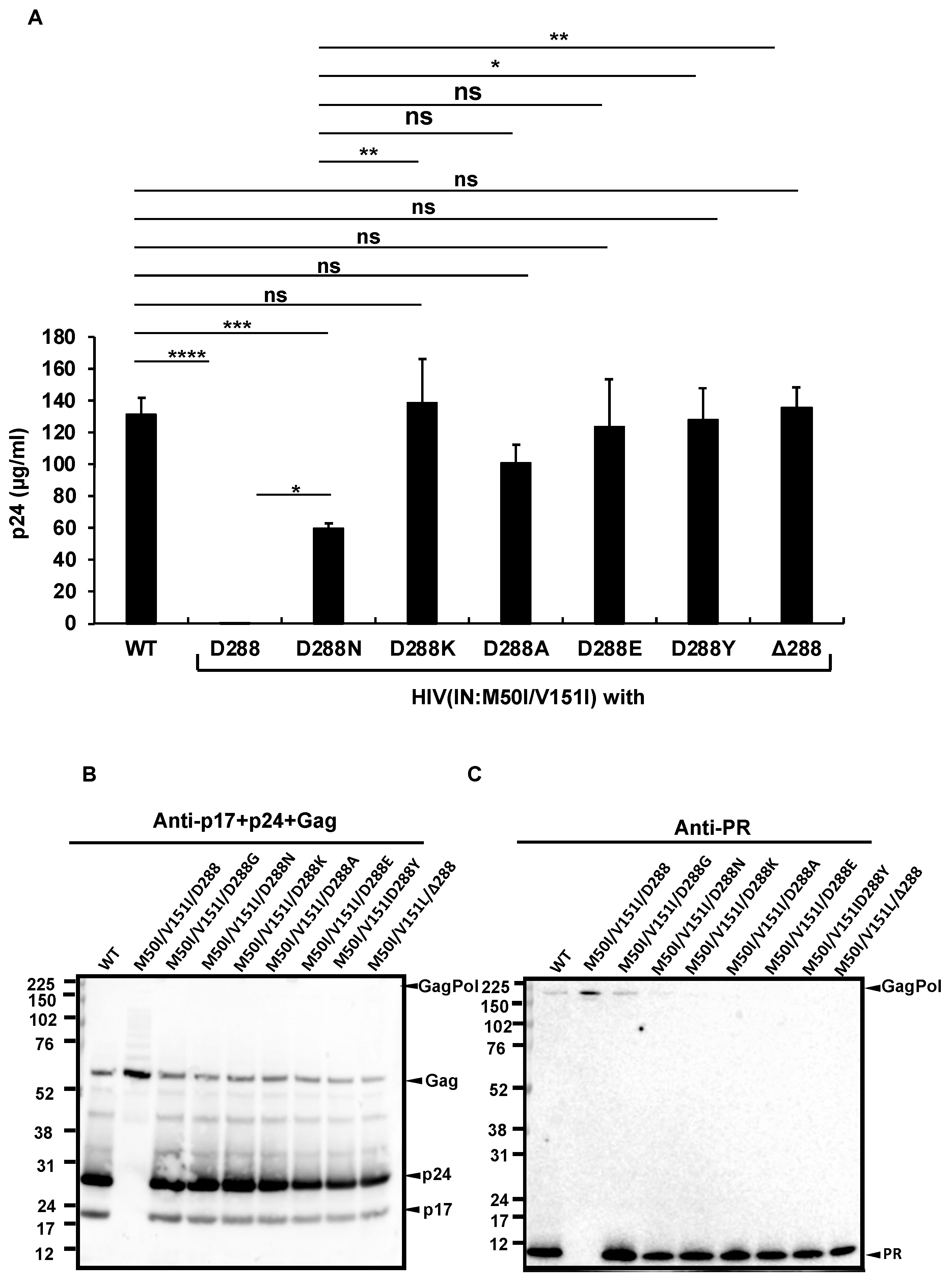
3.2. Asp 288 at the C-Terminal of Integrase (IN) Is a Key Player in the M50I/V151I Defects in Autoprocessing and Virus Release
3.3. Population Analysis of the C-Terminal Amino Acid of the Combination of IN:M50I/V151I in the HIV Sequence Database
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swanstrom, R.; Wills, J.W. Synthesis, Assembly, and Processing of Viral Proteins. In Retroviruses; Coffin, J.M., Hughes, S.H., Varmus, H.E., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Kräusslich, H.G. HIV-1 assembly, budding, and maturation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornillos, O.; Ganser-Pornillos, B.K. Maturation of retroviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 36, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, D.E. Cellular proteins detected in HIV-1. Rev. Med. Virol. 2008, 18, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacks, T.; Power, M.D.; Masiarz, F.R.; Luciw, P.A.; Barr, P.J.; Varmus, H.E. Characterization of ribosomal frameshifting in HIV-1 gag-pol expression. Nature 1988, 331, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacks, T.; Varmus, H.E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science 1985, 230, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu-Xhilaga, M.; Crowe, S.M.; Mak, J. Maintenance of the Gag/Gag-Pol ratio is important for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA dimerization and viral infectivity. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinpeter, A.B.; Freed, E.O. HIV-1 Maturation: Lessons Learned from Inhibitors. Viruses 2020, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Freed, E.O.; van Engelenburg, S.B. A Consensus View of ESCRT-Mediated Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Abscission. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2017, 4, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirov, D.G.; Freed, E.O. Retrovirus budding. Virus Res. 2004, 106, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votteler, J.; Sundquist, W.I. Virus budding and the ESCRT pathway. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, S.C.; Everitt, L.E.; Choudhury, S.; Dunn, B.M.; Kaplan, A.H. Initial cleavage of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 GagPol precursor by its activated protease occurs by an intramolecular mechanism. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8477–8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, S.C.; Clemente, J.C.; Jeung, J.A.; Dunn, B.M.; Kaplan, A.H. Ordered processing of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 GagPol precursor is influenced by the context of the embedded viral protease. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10601–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Könnyű, B.; Sadiq, S.K.; Turányi, T.; Hírmondó, R.; Müller, B.; Kräusslich, H.G.; Coveney, P.V.; Müller, V. Gag-Pol processing during HIV-1 virion maturation: A systems biology approach. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.A.; Soule, E.E.; Davidoff, K.S.; Daniels, S.I.; Naiman, N.E.; Yarchoan, R. Activity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease inhibitors against the initial autocleavage in Gag-Pol polyprotein processing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3620–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabler, C.O.; Wegman, S.J.; Chen, J.; Shroff, H.; Alhusaini, N.; Tilton, J.C. The HIV-1 Viral Protease Is Activated during Assembly and Budding Prior to Particle Release. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0219821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukovsky, A.; Göttlinger, H. Lack of integrase can markedly affect human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particle production in the presence of an active viral protease. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6820–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.G.; Taddeo, B.; Haseltine, W.A.; Farnet, C.M. Genetic analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase protein. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, A.; Englund, G.; Orenstein, J.M.; Martin, M.A.; Craigie, R. Multiple effects of mutations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase on viral replication. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, K.D.; Topper, M.B.; Muesing, M.A. Sequential deletion of the integrase (Gag-Pol) carboxyl terminus reveals distinct phenotypic classes of defective HIV-1. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4654–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyte, A.C.; Jamin, A.V.; Koneru, P.C.; Kobe, M.J.; Larue, R.C.; Fuchs, J.R.; Engelman, A.N.; Kvaratskhelia, M. Resistance to pyridine-based inhibitor KF116 reveals an unexpected role of integrase in HIV-1 Gag-Pol polyprotein proteolytic processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 19814–19825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamichi, T.; Bernbaum, J.G.; Laverdure, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q.; Highbarger, H.; Hao, M.; Sui, H.; Dewar, R.; Chang, W.; et al. Natural Occurring Polymorphisms in HIV-1 Integrase and RNase H Regulate Viral Release and Autoprocessing. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01323-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielaite, M.; Zucco, A.G.; Bennedbaek, M.; Ekenberg, C.; Kan, V.L.; Touloumi, G.; Vandekerckhove, L.; Turner, D.; Neaton, J.; Lane, H.C.; et al. Association of HIV and host genetic variants in antiretroviral therapy-naive persons. In Proceedings of the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2020, Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 March 2020; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Hao, M.; Khan, M.A.; Rehman, M.T.; Highbarger, H.C.; Chen, Q.; Goswami, S.; Sherman, B.T.; Rehm, C.A.; Dewar, R.L.; et al. A Combination of M50I and V151I Polymorphic Mutations in HIV-1 Subtype B Integrase Results in Defects in Autoprocessing. Viruses 2021, 13, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Magen, T.; Donahue, D.A.; McDonough, E.I.; Kuhl, B.D.; Faltenbacher, V.H.; Xu, H.; Michaud, V.; Sloan, R.D.; Wainberg, M.A. HIV-1 subtype B and C integrase enzymes exhibit differential patterns of resistance to integrase inhibitors in biochemical assays. AIDS 2010, 24, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofstra, L.M.; Nijhuis, M.; Mudrikova, T.; Fun, A.; Schipper, P.; Schneider, M.; Wensing, A. Use of dolutegravir in two INI-experienced patients with multiclass resistance resulted in excellent virological and immunological responses. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2014, 17, 19755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, A.; Lapovok, I.; Baryshev, P.; van de Vijver, D.; van Kampen, J.J.A.; Boucher, C.A.B.; Paraskevis, D.; Kireev, D. Genetic Features of HIV-1 Integrase Sub-Subtype A6 Predominant in Russia and Predicted Susceptibility to INSTIs. Viruses 2020, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iamarino, A.; de Melo, F.L.; Braconi, C.T.; Zanotto, P.M. BF integrase genes of HIV-1 circulating in São Paulo, Brazil, with a recurrent recombination region. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefic, K.; Salmona, M.; Capitao, M.; Splittgerber, M.; Maakaroun-Vermesse, Z.; Néré, M.L.; Bernard, L.; Chaix, M.L.; Barin, F.; Delaugerre, C. Unravelling the dynamics of selection of multiresistant variants to integrase inhibitors in an HIV-1-infected child using ultra-deep sequencing. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndashimye, E.; Li, Y.; Reyes, P.S.; Avino, M.; Olabode, A.S.; Kityo, C.M.; Kyeyune, F.; Nankya, I.; Quiñones-Mateu, M.E.; Barr, S.D.; et al. High-level resistance to bictegravir and cabotegravir in subtype A- and D-infected HIV-1 patients failing raltegravir with multiple resistance mutations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wares, M.; Mesplède, T.; Quashie, P.K.; Osman, N.; Han, Y.; Wainberg, M.A. The M50I polymorphic substitution in association with the R263K mutation in HIV-1 subtype B integrase increases drug resistance but does not restore viral replicative fitness. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakruddin, J.M.; Lempicki, R.A.; Gorelick, R.J.; Yang, J.; Adelsberger, J.W.; Garcia-Pineres, A.J.; Pinto, L.A.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T. Noninfectious papilloma virus-like particles inhibit HIV-1 replication: Implications for immune control of HIV-1 infection by IL-27. Blood 2007, 109, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, A.; Gendelman, H.E.; Koenig, S.; Folks, T.; Willey, R.; Rabson, A.; Martin, M.A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J. Virol. 1986, 59, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brann, T.W.; Dewar, R.L.; Jiang, M.K.; Shah, A.; Nagashima, K.; Metcalf, J.A.; Falloon, J.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T. Functional correlation between a novel amino acid insertion at codon 19 in the protease of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and polymorphism in the p1/p6 Gag cleavage site in drug resistance and replication fitness. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6136–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.; Passos, D.O.; Bruhn, J.F.; Bauman, J.D.; Tuberty, L.; DeStefano, J.J.; Ruiz, F.X.; Lyumkis, D.; Arnold, E. Cryo-EM structure of the HIV-1 Pol polyprotein provides insights into virion maturation. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn9874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beilhartz, G.L.; Götte, M. HIV-1 Ribonuclease H: Structure, Catalytic Mechanism and Inhibitors. Viruses 2010, 2, 900–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotny, M.; Yang, W. Stepwise analyses of metal ions in RNase H catalysis from substrate destabilization to product release. Embo J. 2006, 25, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, G.N.; Engelman, A.N.; Cherepanov, P. Structure and function of retroviral integrase. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, Y.; Johnson, A.A.; Marchand, C. Integrase inhibitors to treat HIV/AIDS. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, C.; Gouet, P.; Parissi, V.; Fiorini, F. The C-Terminal Domain of HIV-1 Integrase: A Swiss Army Knife for the Virus? Viruses 2022, 14, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, M.J.; Monel, B.; Krishnan, L.; Shun, M.C.; Di Nunzio, F.; Helland, D.E.; Engelman, A. Biochemical and virological analysis of the 18-residue C-terminal tail of HIV-1 integrase. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.-H.; Krucinski, J.; Miercke, L.J.W.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Tang, A.H.; Leavitt, A.D.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal structure of the HIV-1 integrase catalytic core and C-terminal domains: A model for viral DNA binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8233–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, A.N.; Kvaratskhelia, M. Multimodal Functionalities of HIV-1 Integrase. Viruses 2022, 14, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Jurado, K.A.; Engelman, A.N.; Craigie, R. A Peptide Derived from Lens Epithelium-Derived Growth Factor Stimulates HIV-1 DNA Integration and Facilitates Intasome Structural Studies. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.L.; Eschbach, J.E.; Koneru, P.C.; Li, W.; Puray-Chavez, M.; Townsend, D.; Lawson, D.Q.; Engelman, A.N.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Kutluay, S.B. Integrase-RNA interactions underscore the critical role of integrase in HIV-1 virion morphogenesis. eLife 2020, 9, e54311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, A. In vivo analysis of retroviral integrase structure and function. Adv. Virus Res. 1999, 52, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessl, J.J.; Kutluay, S.B.; Townsend, D.; Rebensburg, S.; Slaughter, A.; Larue, R.C.; Shkriabai, N.; Bakouche, N.; Fuchs, J.R.; Bieniasz, P.D.; et al. HIV-1 Integrase Binds the Viral RNA Genome and Is Essential during Virion Morphogenesis. Cell 2016, 166, 1257–1268.e1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urano, E.; Timilsina, U.; Kaplan, J.A.; Ablan, S.; Ghimire, D.; Pham, P.; Kuruppu, N.; Mandt, R.; Durell, S.R.; Nitz, T.J.; et al. Resistance to Second-Generation HIV-1 Maturation Inhibitors. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02017-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, U.; Ghimire, D.; Timalsina, B.; Nitz, T.J.; Wild, C.T.; Freed, E.O.; Gaur, R. Identification of potent maturation inhibitors against HIV-1 clade C. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Obukhov, Y.; Nekhai, S.; Bukrinsky, M.; Iordanskiy, S. Virus-producing cells determine the host protein profiles of HIV-1 virion cores. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, A.A.; Bruel, T.; Porrot, F.; Mallet, A.; Sachse, M.; Euvrard, M.; Liang, C.; Casartelli, N.; Schwartz, O. IFITM proteins incorporated into HIV-1 virions impair viral fusion and spread. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartour, K.; Appourchaux, R.; Gaillard, J.; Nguyen, X.N.; Durand, S.; Turpin, J.; Beaumont, E.; Roch, E.; Berger, G.; Mahieux, R.; et al. IFITM proteins are incorporated onto HIV-1 virion particles and negatively imprint their infectivity. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillat, C.; Macheboeuf, P.; Wu, Y.; McCarthy, A.A.; Boeri-Erba, E.; Effantin, G.; Göttlinger, H.G.; Weissenhorn, W.; Renesto, P. Asymmetric ring structure of Vps4 required for ESCRT-III disassembly. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Ono, A. Roles of Virion-Incorporated CD162 (PSGL-1), CD43, and CD44 in HIV-1 Infection of T Cells. Viruses 2021, 13, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dordor, A.; Poudevigne, E.; Göttlinger, H.; Weissenhorn, W. Essential and supporting host cell factors for HIV-1 budding. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, H.K.; Fernandez, M.V.; Groves, N.S.; Freed, E.O.; van Engelenburg, S.B. Genomic tagging of endogenous human ESCRT-I complex preserves ESCRT-mediated membrane-remodeling functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 16266–16281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A. HIV-1 Assembly at the Plasma Membrane: Gag Trafficking and Localization. Future Virol. 2009, 4, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietri, M.; Radulovic, M.; Stenmark, H. The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Caillat, C.; Miguet, N.; Sulbaran, G.; Effantin, G.; Schoehn, G.; Roos, W.H.; Weissenhorn, W. VPS4 triggers constriction and cleavage of ESCRT-III helical filaments. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, J.; Pelchen-Matthews, A.; Novak, P.; Burden, J.J.; Summers, P.A.; Kuimova, M.K.; Korchev, Y.; Marsh, M.; Shevchuk, A. Rapid formation of human immunodeficiency virus-like particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21637–21646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, E.O. HIV-1 assembly, release and maturation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Muesing, M.A. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic approaches for discovery of HIV-host interactions. Future Virol. 2014, 9, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobard, C.W.; Briones, M.S.; Chow, S.A. Molecular mechanisms by which human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase stimulates the early steps of reverse transcription. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10037–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobbi, L.; Octobre, G.; Dias, J.; Comisso, M.; Mirande, M. Association of mitochondrial Lysyl-tRNA synthetase with HIV-1 GagPol involves catalytic domain of the synthetase and transframe and integrase domains of Pol. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 410, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winans, S.; Goff, S.P. Mutations altering acetylated residues in the CTD of HIV-1 integrase cause defects in proviral transcription at early times after integration of viral DNA. PLoS Pathogens. 2020, 16, e1009147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shema Mugisha, C.; Dinh, T.; Kumar, A.; Tenneti, K.; Eschbach, J.E.; Davis, K.; Gifford, R.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Kutluay, S.B. Emergence of Compensatory Mutations Reveals the Importance of Electrostatic Interactions between HIV-1 Integrase and Genomic RNA. mBio 2022, 13, e0043122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imamichi, T.; Chen, Q.; Hao, M.; Chang, W.; Yang, J. The C-Terminal Domain of RNase H and the C-Terminus Amino Acid Residue Regulate Virus Release and Autoprocessing of a Defective HIV-1 Possessing M50I and V151I Changes in Integrase. Viruses 2022, 14, 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122687
Imamichi T, Chen Q, Hao M, Chang W, Yang J. The C-Terminal Domain of RNase H and the C-Terminus Amino Acid Residue Regulate Virus Release and Autoprocessing of a Defective HIV-1 Possessing M50I and V151I Changes in Integrase. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122687
Chicago/Turabian StyleImamichi, Tomozumi, Qian Chen, Ming Hao, Weizhong Chang, and Jun Yang. 2022. "The C-Terminal Domain of RNase H and the C-Terminus Amino Acid Residue Regulate Virus Release and Autoprocessing of a Defective HIV-1 Possessing M50I and V151I Changes in Integrase" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122687
APA StyleImamichi, T., Chen, Q., Hao, M., Chang, W., & Yang, J. (2022). The C-Terminal Domain of RNase H and the C-Terminus Amino Acid Residue Regulate Virus Release and Autoprocessing of a Defective HIV-1 Possessing M50I and V151I Changes in Integrase. Viruses, 14(12), 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122687