HBcrAg Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Chronic B Hepatitis Related Liver Cirrhosis Patients Undergoing Long-Term Effective Anti-Viral
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
Statistical Analysis
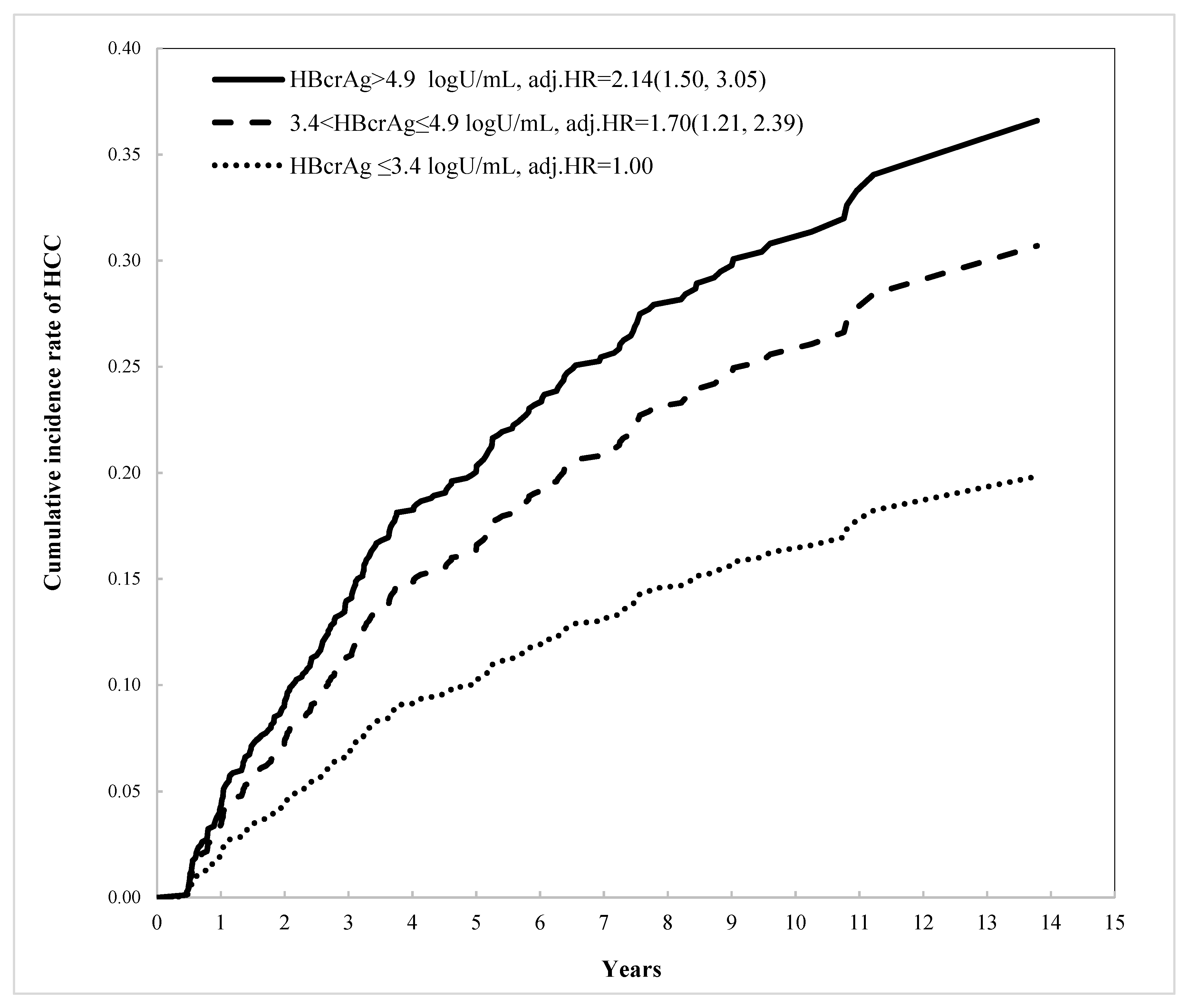
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | α-fetoprotein |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| RT-PCR | reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction |
| HBsAg-HQ | highly sensitive lumipulse HBs-HQ assay |
References
- Venook, A.P.; Papandreou, C.; Furuse, J.; de Guevara, L.L. The Incidence and Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Global and Regional Perspective. Oncologist 2010, 15, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattovich, G. Natural History and Prognosis of Hepatitis B. Semin. Liver Dis. 2003, 23, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El–Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Epidemiology and Molecular Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Bzowej, N.H.; Chang, K.-M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Murad, M.H. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2015, 63, 261–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, Y.F. Impact of therapy on the outcome of chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.-H.; Chiu, S.Y.-H.; Tseng, P.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Lu, S.-N.; Wang, J.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Kee, K.-M.; Lin, M.-T.; Chang, K.-C.; et al. Five-year comparative risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development under entecavir or tenofovir treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B-related compensated cirrhosis in Taiwan. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 52, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Idilman, R.; Dalekos, G.N.; Buti, M.; Chi, H.; Van Boemmel, F.; Calleja-Panero, J.L.; Sypsa, V.; Goulis, J.; Manolakopoulos, S.; et al. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma decreases after the first 5 years of entecavir or tenofovir in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-H.; Hu, T.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chuang, W.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Su, W.-W.; Chen, M.-Y.; Peng, C.-Y.; et al. Four-year entecavir therapy reduces hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhotic events and mortality in chronic hepatitis B patients. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Zoulim, F.; Dusheiko, G.; Ghany, M.G. Hepatitis B cure: From discovery to regulatory approval. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Rokuhara, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yagi, S.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Maki, N. Sensitive Enzyme Immunoassay for Hepatitis B Virus Core-Related Antigens and Their Correlation to Virus Load. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K.-H.; Seto, W.-K.; Cheung, K.-S.; Chong, C.-K.; Huang, F.-Y.; Fung, J.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigen as a surrogate marker for covalently closed circular DNA. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.F.; Seto, W.K.; Wong, D.; Cheung, K.S.; Fung, J.; Mak, L.Y.; Yuen, J.; Chong, C.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Sev-en-Year Treatment Outcome of Entecavir in a Real-World Cohort: Effects on Clinical Parameters, HBsAg and HBcrAg Levels. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.-K.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.-Y.; Liu, K.S.-H.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Linearized hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core-related antigen in the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, L.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Cheung, K.-S.; Seto, W.-K.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Review article: Hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg): An emerging marker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Kitabatake, S.; Yama, T.; Tanaka, J. HBcrAg predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating charac-teristics. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W.; Mak, L.; Wong, D.K.; Fung, J.; Liu, F.; Seto, W.; Lai, C.; Yuen, M. Hepatitis B core-related antigen levels after HBeAg seroconversion is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.-S.; Seto, W.-K.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Relationship between HBsAg, HBcrAg and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with undetectable HBV DNA under nucleos(t)ide therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-H.; Lu, S.-N.; Wang, J.-H.; Lee, C.-M.; Chen, T.-M.; Tung, H.-D.; Chen, C.-H.; Huang, W.-S.; Changchien, C.-S. Correlation between ultrasonographic and pathologic diagnoses of hepatitis B and C virus-related cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, V.J.; Gerber, M.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Manns, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Classification of chronic hepatitis: Diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology 1994, 19, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Ishigami, M.; Ishizu, Y.; Kuzuya, T.; Honda, T.; Hayashi, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakano, I.; Hirooka, Y.; Goto, H. Cumulative incidence and risk factors for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B who achieved sustained disappearance of viremia by nucleos(t)ide analog treatment. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, E240–E251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wursthorn, K.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Dandri, M.; Volz, T.; Buggisch, P.; Zollner, B.; Longerich, T.; Schirmacher, P.; Metzler, F.; Zankel, M.; et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b plus adefovir induce strong cccDNA decline and HBsAg reduction in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2006, 44, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werle-Lapostolle, B.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S.; Wursthorn, K.; Petersen, J.; Lau, G.; Trepo, C.; Marcellin, P.; Goodman, Z.; Delaney, W.E., IV; et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Yang, J.; Yan, L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Lu, W.; Wang, Y.-B.; Weng, Q.-C.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Feng, Y.-L. Measurement of the hepatitis B core-related antigen is valuable for predicting the pathological status of liver tissues in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 235, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Akita, T.; Tanaka, J. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigen levels predict progression to liver cirrhosis in hepatitis B carriers. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasoumy, B.; Wiegand, S.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Bremer, B.; Lehmann, P.; Deterding, K.; Taranta, A.; Manns, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Glebe, D.; et al. Hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection in a large European cohort predominantly infected with genotypes A and D. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 606.e1–606.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Yatsuji, H.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; et al. HBcrAg is a predictor of post-treatment recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma during anti-viral anti-viral therapy. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Niinomi, T.; Yasuda, S.; Andou, Y.; et al. Effect of nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy on hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B pa-tients: A propensity score analysis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Yang, H.-C.; Su, T.-H.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Kuo, S.F.; Liu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Chen, D.-S.; et al. High Levels of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Increase Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Low HBV Load. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1140–1149.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Komatsu, N.; Sato, M.; Tatsumi, A.; Miura, M.; Matsuda, S.; Muraoka, M.; Nakakuki, N.; Shindo, H.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected patients with low hepatitis B surface antigen and high hepatitis B core-related antigen titers have a high risk of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 49, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.Y.; Wong, V.W.; Toyoda, H.; Tse, Y.K.; Yip, T.C.; Yuen, B.W.; Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Lee, H.W.; Lui, G.C.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen predicts hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, S.; Kurosaki, M.; Inada, K.; Kirino, S.; Hayakawa, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Osawa, L.; Sekiguchi, S.; Higuchi, M.; Takaura, K.; et al. Hepatitis B core-related antigen predicts disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; et al. Ultrasensitive Assay for Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidences During Entecavir. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollicino, T.; Amaddeo, G.; Restuccia, A.; Raffa, G.; Alibrandi, A.; Cutroneo, G.; Favaloro, A.; Maimone, S.; Squadrito, G.; Raimondo, G. Impact of hepatitis B virus (HBV) preS/S genomic variability on HBV surface antigen and HBV DNA serum levels. Hepatology 2012, 56, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollicino, T.; Cacciola, I.; Saffioti, F.; Raimondo, G. Hepatitis B virus PreS/S gene variants: Pathobiology and clinical im-plications. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Non-HCC | Incident HCC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 889 | n = 219 | |||
| No. (%)/Mean (±SD) | No. (%)/Mean (±SD) | |||
| Age (years) | (continuous) | 60.2 ± 11.5 | 64.5 ± 10.5 | <0.0001 |
| Gender | Male | 661 (79.4%) | 172 (20.6%) | 0.1990 |
| Female | 228 (82.9%) | 47 (17.1%) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.0 ± 4.0 | 25.0 ± 3.9 | 0.9921 | |
| AST (IU/mL) | 156.9 ± 319.0 | 114.8 ± 194.8 | 0.0135 | |
| ALT (IU/mL) | 202.5 ± 451.3 | 122.0 ± 223.6 | 0.0002 | |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 2.6 ± 4.5 | 3.6 ± 25.8 | 0.5551 | |
| Platelets (×109/L) | <150 | 373 (85.4%) | 64 (14.6%) | 0.0006 |
| ≥150 | 516 (76.9%) | 155 (23.1%) | ||
| AFP (ng/mL) | <20 | 729 (82.1%) | 159 (17.9%) | 0.0018 |
| ≥20 | 160 (72.7%) | 60 (27.3%) | ||
| HBeAg | - | 712 (80.5%) | 172 (19.5%) | 0.6087 |
| + | 177 (79.0%) | 47 (21.0%) | ||
| HBV DNA (IU/mL) | <105 | 174 (80.9%) | 41 (19.1%) | 0.7754 |
| ≥105 | 715 (80.1%) | 178 (19.9%) | ||
| Creatinine | 2.0 ± 23.7 | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 0.1854 | |
| EGFR | 86.7 ± 28.7 | 88.4 ± 28.2 | 0.4288 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | No | 696 (82.1%) | 152 (17.9%) | 0.0055 |
| Yes | 193 (74.2%) | 67 (25.8%) | ||
| FIB-4 | <4.1 | 374 (87.8%) | 52 (12.2%) | <0.0001 |
| ≥4.1 | 515 (75.5%) | 167 (24.5%) | ||
| APRI | <0.9 | 249 (83.6%) | 49 (16.4%) | 0.0921 |
| ≥0.9 | 640 (79.0%) | 170 (21.0%) | ||
| HBsAg-HQ (×107 mIU/mL) | ≤3 | 711 (78.7%) | 192 (21.3%) | 0.0086 |
| >3 | 178 (86.8%) | 27 (13.2%) | ||
| HBcrAg (logU/mL) | ≤3.4 | 313 (84.4%) | 58 (15.6%) | 0.0485 |
| 3.41–4.9 | 288 (78.5%) | 79 (21.5%) | ||
| >4.9 | 288 (77.8%) | 82 (22.2%) |
| Variable | Group | HBcrAg (log U/mL) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤3.4 | 3.41–4.9 | >4.9 | |||
| n = 371 | n = 367 | n = 370 | |||
| Age (years) | 63.6 ± 11.1 | 61.1 ± 10.7 | 58.5 ± 11.8 | <0.0001 | |
| Gender | Male | 272 (32.6%) | 273 (32.8%) | 288 (34.6%) | 0.3303 |
| Female | 99 (36.0%) | 94 (34.2%) | |||
| Platelets (×109/L) | <150 | 140 (32.0%) | 142 (32.5%) | 155 (35.5%) | 0.4799 |
| ≥150 | 231 (34.4%) | 225 (33.5%) | 215 (32.1%) | ||
| AFP (ng/mL) | <20 | 312 (35.1%) | 299 (33.7%) | 277 (31.2%) | 0.0052 |
| ≥20 | 59 (26.8%) | 68 (30.9%) | 93 (42.3%) | ||
| HBeAg | - | 358 (40.5%) | 321 (36.3%) | 205 (23.2%) | <0.0001 |
| + | 13 (5.8%) | 46 (20.5%) | 165 (73.7%) | ||
| HBV DNA (IU/mL) | <105 | 121 (56.3%) | 73 (33.9%) | 21 (9.8%) | <0.0001 |
| ≥105 | 250 (28.0%) | 294 (32.9%) | 349 (39.1%) | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | No | 270 (31.8%) | 284 (33.5%) | 294 (34.7%) | 0.0895 |
| Yes | 101 (38.9%) | 83 (31.9%) | 76 (29.2%) | ||
| FIB-4 | <4.1 | 111 (29.1%) | 146 (34.3%) | 169 (39.7%) | <0.0001 |
| ≥4.1 | 260 (38.1%) | 221 (32.4%) | 201 (29.5%) | ||
| APRI | <0.9 | 111 (37.3%) | 77 (25.8%) | 110 (36.9%) | 0.0076 |
| ≥0.9 | 260 (32.1%) | 290 (35.8%) | 260 (32.1%) | ||
| HBsAg-HQ | ≤3 | 354 (39.2%) | 322 (35.7%) | 227 (25.1%) | <0.0001 |
| (×107 mIU/mL) | >3 | 17 (8.3%) | 45 (21.9%) | 143 (69.8%) | |
| Variable | Classification | Univariate | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | p-Value | adjHR (95%CI) | p-Value | ||
| Age(years) | (continuous) | 1.03 (1.02, 1.04) | <0.0001 | 1.02 (1.00, 1.03) | 0.0085 |
| Gender | M vs. F | 1.24 (0.90, 1.71) | 0.1919 | 1.44 (1.04, 2.00) | 0.0298 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | <150 vs. ≥150 | 1.74 (1.30, 2.33) | 0.0002 | --- | |
| AFP (ng/mL) | ≥20 vs. <20 | 1.55 (1.15, 2.08) | 0.0041 | --- | |
| FIB-4 | ≥4.1 vs. <4.1 | 2.33 (1.71, 3.18) | <0.0001 | 2.12 (1.52, 2.97) | <0.0001 |
| DM | Yes. Vs. No | 1.51 (1.13, 2.01) | 0.0051 | 1.51 (1.13, 2.03) | 0.0052 |
| HBsAg-HQ (×107 mIU/mL) | >3 vs. ≤3 | 0.58 (0.39, 0.87) | 0.0083 | 0.58 (0.38, 0.89) | 0.0131 |
| HBcrAg (logU/mL) | 3.4–4.9 vs. ≤3.4 | 1.41 (1.00, 1.98) | 0.0465 | 1.70 (1.21, 2.39) | 0.0001 |
| >4.9 vs. ≤3.4 | 1.50 (1.07, 2.10) | 2.14 (1.50, 3.05) | |||
| Variable | Classification | HBsAg-HQ ≤ 3 (×107 mIU/mL) | HBsAg-HQ > 3 (×107 mIU/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| adjHR (95%CI) | p-Value | adjHR (95%CI) | p-Value | ||
| Age(years) | (continuous) | 1.01 (1.00, 1.03) | 0.0459 | 1.06 (1.02, 1.11) | 0.0054 |
| Gender | Male vs. Female | 1.54 (1.07, 2.20) | 0.0194 | 0.97 (0.41, 2.29) | 0.9411 |
| FIB-4 | ≥4.1 vs. <4.1 | 2.26 (1.57, 3.26) | <0.0001 | 1.11 (0.45, 2.74) | 0.8221 |
| DM | Yes. Vs. No | 1.55 (1.13, 2.11) | 0.0058 | 1.23 (0.50, 3.05) | 0.6568 |
| HBcrAg (logU/mL) | 3.4–4.9 vs. ≤3.4 | 1.85 (1.30, 2.64) | <0.0001 | 0.22 (0.06, 0.84) | 0.0706 |
| >4.9 vs. ≤3.4 | 2.35 (1.63, 3.40) | 0.40 (0.15, 1.09) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, K.-C.; Lin, M.-T.; Wang, J.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Chiu, S.Y.-H.; Hu, T.-H. HBcrAg Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Chronic B Hepatitis Related Liver Cirrhosis Patients Undergoing Long-Term Effective Anti-Viral. Viruses 2022, 14, 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122671
Chang K-C, Lin M-T, Wang J-H, Hung C-H, Chen C-H, Chiu SY-H, Hu T-H. HBcrAg Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Chronic B Hepatitis Related Liver Cirrhosis Patients Undergoing Long-Term Effective Anti-Viral. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122671
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Kuo-Chin, Ming-Tsung Lin, Jing-Houng Wang, Chao-Hung Hung, Chien-Hung Chen, Sherry Yueh-Hsia Chiu, and Tsung-Hui Hu. 2022. "HBcrAg Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Chronic B Hepatitis Related Liver Cirrhosis Patients Undergoing Long-Term Effective Anti-Viral" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122671
APA StyleChang, K.-C., Lin, M.-T., Wang, J.-H., Hung, C.-H., Chen, C.-H., Chiu, S. Y.-H., & Hu, T.-H. (2022). HBcrAg Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Chronic B Hepatitis Related Liver Cirrhosis Patients Undergoing Long-Term Effective Anti-Viral. Viruses, 14(12), 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122671







