CoreGenes5.0: An Updated User-Friendly Webserver for the Determination of Core Genes from Sets of Viral and Bacterial Genomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability and Requirements
References
- Tettelin, H.; Masignani, V.; Cieslewicz, M.J.; Donati, C.; Medini, D.; Ward, N.L.; Angiuoli, S.V.; Crabtree, J.; Jones, A.L.; Durkin, A.S.; et al. Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: Implications for the microbial “pan-genome”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13950–13955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, C.A., 3rd; Chuang, R.Y.; Noskov, V.N.; Assad-Garcia, N.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Gill, J.; Kannan, K.; Karas, B.J.; Ma, L.; et al. Design and synthesis of a minimal bacterial genome. Science 2016, 351, aad6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, A.; Yang, F.; Williams, R.J.; Meyer, F.; Hofmockel, K.S. Identification of the Core Set of Carbon-Associated Genes in a Bioenergy Grassland Soil. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Friis, C.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Ussery, D.W. Genomic variation in Salmonella enterica core genes for epidemiological typing. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Koonin, E.V. Hidden evolutionary complexity of Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Large DNA viruses of eukaryotes. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, N.; Mazumder, R.; Seto, D. CoreGenes: A computational tool for identifying and cataloging “core” genes in a set of small genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2002, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Reynolds, D.; Seto, D.; Mahadevan, P. CoreGenes3. 5: A webserver for the determination of core genes from sets of viral and small bacterial genomes. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, R.; Seto, D.; Mahadevan, P.; Ackermann, H.W.; Kropinski, A.M. Unifying classical and molecular taxonomic classification: Analysis of the Podoviridae using BLASTP-based tools. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, R.; Darius, P.; Summer, E.J.; Seto, D.; Mahadevan, P.; Nilsson, A.S.; Ackermann, H.W.; Kropinski, A.M. Classification of Myoviridae bacteriophages using protein sequence similarity. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.M.; Edwards, R.; Nash, J.H.; Mahadevan, P.; Seto, D.; Ackermann, H.-W.; Lavigne, R.; Kropinski, A.M. Integration of genomic and proteomic analyses in the classification of the Siphoviridae family. Virology 2015, 477, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Feng, Y.; Zong, Z. Two New Lytic Bacteriophages of the Myoviridae Family Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin Jang, H.; Bolduc, B.; Zablocki, O.; Kuhn, J.H.; Roux, S.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Brister, J.R.; Kropinski, A.M.; Krupovic, M.; Lavigne, R.; et al. Taxonomic assignment of uncultivated prokaryotic virus genomes is enabled by gene-sharing networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, P.; King, J.F.; Seto, D. Data mining pathogen genomes using GeneOrder and CoreGenes and CGUG: Gene order, synteny and in silico proteomes. Int. J. Comput. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 2, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. MMseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive data sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Moreira, B.; Vinuesa, P. GET_HOMOLOGUES, a versatile software package for scalable and robust microbial pangenome analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7696–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, P.; Contreras-Moreira, B. Robust Identification of Orthologues and Paralogues for Microbial Pan-Genomics Using GET_HOMOLOGUES: A Case Study of pIncA/C Plasmids. In Bacterial Pangenomics, Methods in Molecular Biology; Mengoni, A., Galardini, M., Fondi, M., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1231, pp. 203–232. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl. Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Stoeckert, C.J.; Roos, D.S. OrthoMCL: Identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, D.M.; Kannan, L.; Coleman, M.K.; Wolf, Y.I.; Sorokin, A.; Koonin, E.V.; Mushegian, A. A low-polynomial algorithm for assembling clusters of orthologous groups from intergenomic symmetric best matches. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Lingohr, E.J.; Ackermann, H.W. The genome sequence of enterobacterial phage 7–11, which possesses an unusually elongated head. Arch Virol. 2011, 156, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, R.; Kolaskar, A.; Seto, D. GeneOrder: Comparing the order of genes in small genomes. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

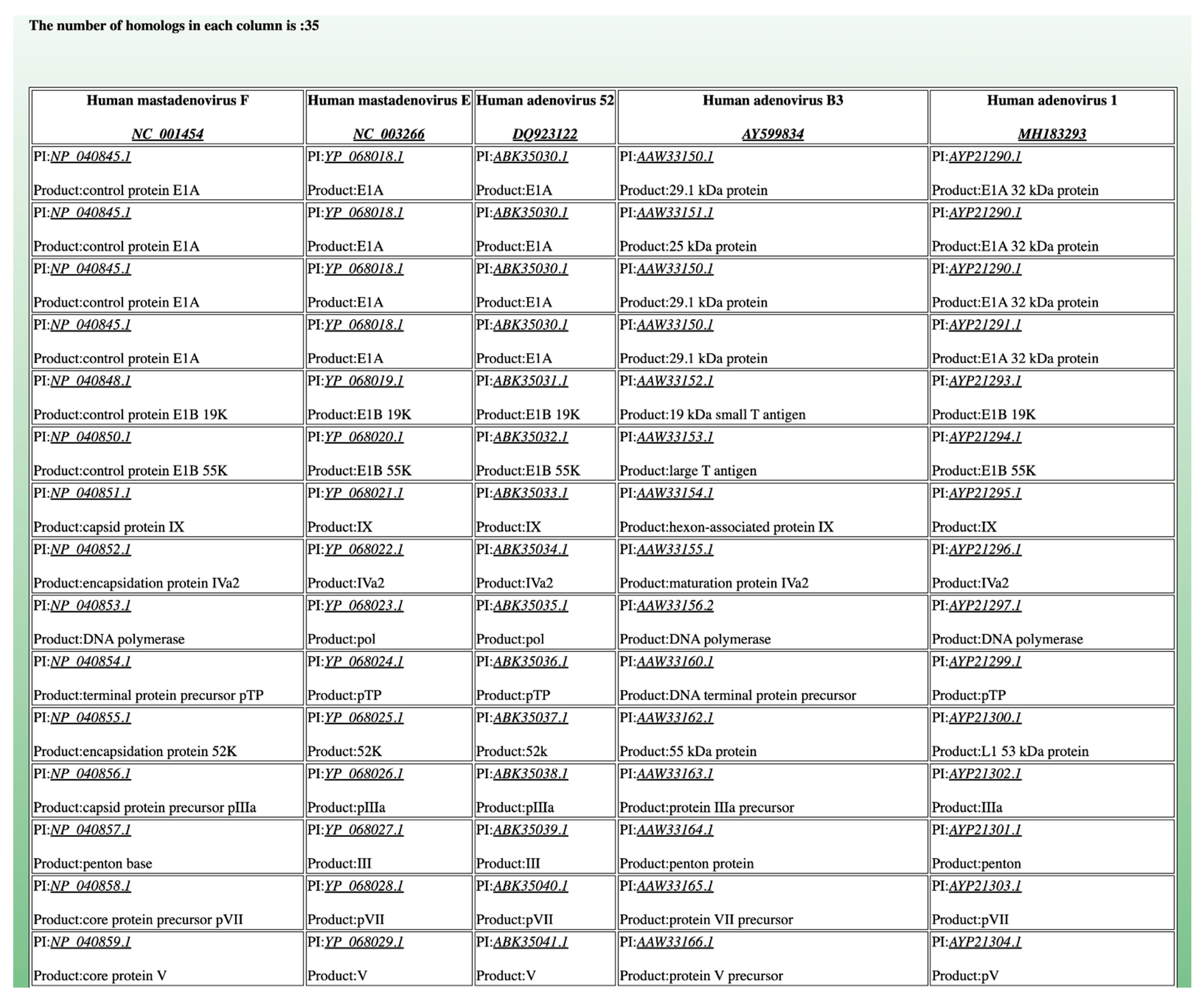
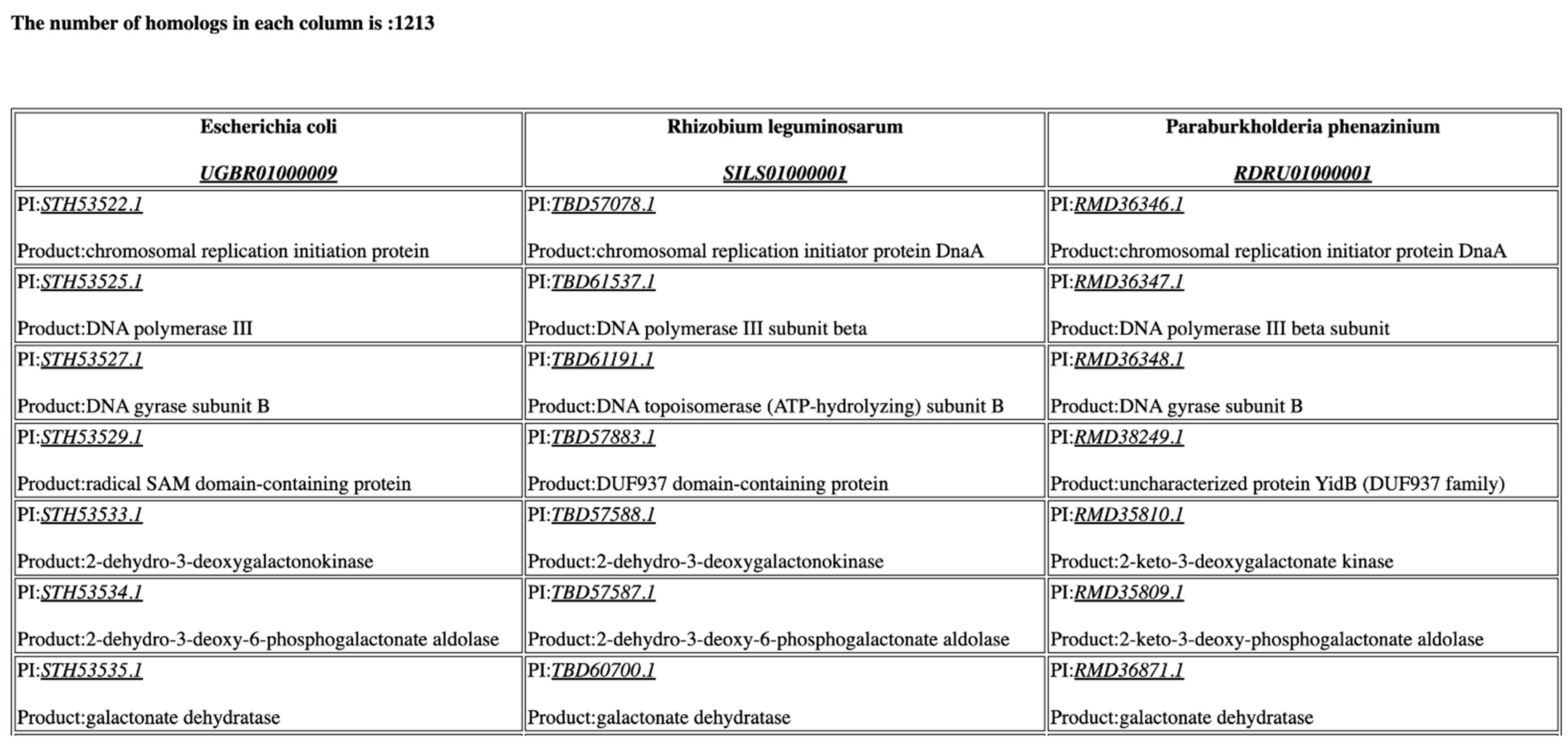
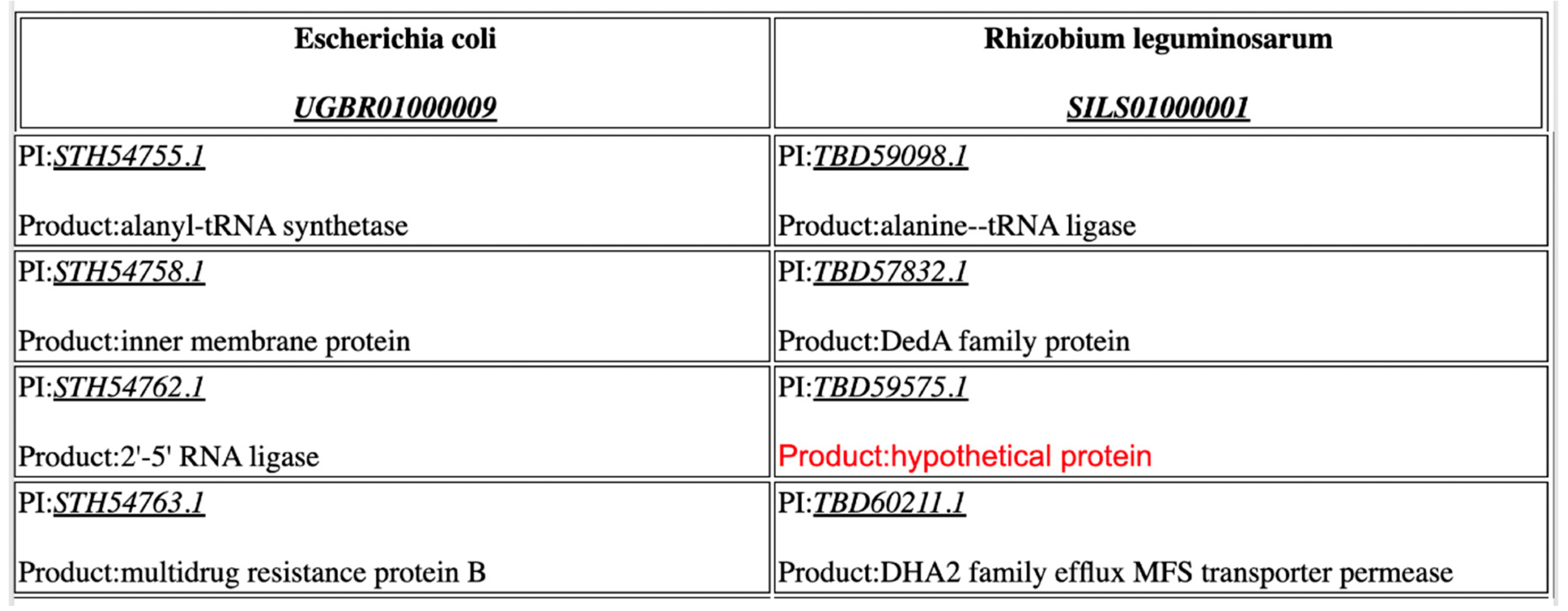
| Functionality | CoreGenes4.0 | CoreGenes5.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Additional clustering algorithms such as Bidirectional best hit, OrthoMCL and COGtriangles made available through the GET_HOMOLOGUES package | X | ✓ |
| Faster protein searches using MMseqs2 in the Iterative Comparison Algorithm | X | ✓ |
| Email results to user | X | ✓ |
| Easy CDS retrieval from GenBank | X | ✓ |
| More robust custom data input | X | ✓ |
| Genome Size | 1 Mb | 2 Mb | 3 Mb | 4 Mb | 5 Mb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession #s | NUHQ01000006.1 CAIT01000004.1 ASWA01000004.1 | MTBP01000002.1 CP033822.1 UHGI01000001.1 | UGNN01000001.1 CP035563.1 UKAD01000001.1 | CP021892.1 CP012872.1 UGNN01000001.1 | UGBR01000009.1 SILS01000001.1 RDRU01000001.1 |
| Run Time | 00 h:01 m:10 s | 00 h:02 m:22 s | 00 h:05 m:00 s | 00 h:05 m:54 s | 00 h:09 m:56 s |
| Number of Homologues | 41 | 372 | 499 | 732 | 1213 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, P.; Seto, D.; Mahadevan, P. CoreGenes5.0: An Updated User-Friendly Webserver for the Determination of Core Genes from Sets of Viral and Bacterial Genomes. Viruses 2022, 14, 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112534
Davis P, Seto D, Mahadevan P. CoreGenes5.0: An Updated User-Friendly Webserver for the Determination of Core Genes from Sets of Viral and Bacterial Genomes. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112534
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Patrick, Donald Seto, and Padmanabhan Mahadevan. 2022. "CoreGenes5.0: An Updated User-Friendly Webserver for the Determination of Core Genes from Sets of Viral and Bacterial Genomes" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112534
APA StyleDavis, P., Seto, D., & Mahadevan, P. (2022). CoreGenes5.0: An Updated User-Friendly Webserver for the Determination of Core Genes from Sets of Viral and Bacterial Genomes. Viruses, 14(11), 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112534







