Impact of Hypertension on COVID-19 Burden in Kidney Transplant Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Demographic Data
2.3. Laboratory Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romero, S.K.; Reissig, D.; Petereit-Haack, G.; Schmauder, S.; Nienhaus, A.; Seidler, A. The isolated effect of age on the risk of COVID-19 severe outcomes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejaz, H.; Alsrhani, A.; Zafar, A.; Javed, H.; Junaid, K.; Abdalla, A.E.; Abosalif, K.O.A.; Ahmed, Z.; Younas, S. COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.H.; Tipih, T.; Makoah, N.A.; Vermeulen, J.G.; Goedhals, D.; Sempa, J.B.; Burt, F.J.; Taylor, A.; Mahalingam, S. Comorbidities in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. mBio 2021, 12, e03647-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udomkarnjananun, S.; Kerr, S.J.; Townamchai, N.; Susantitaphong, P.; Tulvatana, W.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Avihingsanon, Y. Mortality risk factors of COVID-19 infection in kidney transplantation recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohorts and clinical registries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiga, M.; Wang, D.W.; Han, Y.; Lewis, D.B.; Wu, J.C. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: From basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Q.; He, H.; Ji, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z. Effects of hypertension on the outcomes of COVID-19: A multicentre retrospective cohort study. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.W.; Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.L.; Jering, K.S.; Bhatt, A.S.; Rosenthal, N.; Solomon, S.D. Clinical Outcomes in Young US Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 81, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, E.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas, V.M.; Chiloff, D.M.; Bosso, G.G.; Teixeira, J.O.P.; Hernandes, I.C.G.; Padilha, M.D.P.; Moura, G.C.; de Andrade, L.G.M.; Mancuso, F.; Finamor, F.E.; et al. A Machine Learning Model for Predicting Hospitalization in Patients with Respiratory Symptoms during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, J.C.; Adibi, S.; Wickramasinghe, N.; Nguyen, L.; Angelova, M.; Islam, S.M.S. Smartphone as a Disease Screening Tool: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravedi, P.; Mothi, S.S.; Azzi, Y.; Haverly, M.; Farouk, S.S.; Perez-Saez, M.J.; Redondo-Pachon, M.D.; Murphy, B.; Florman, S.; Cyrino, L.G.; et al. COVID-19 and kidney transplantation: Results from the TANGO International Transplant Consortium. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 3140–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillard, S.; Chavarot, N.; Francois, H.; Matignon, M.; Greze, C.; Kamar, N.; Gatault, P.; Thaunat, O.; Legris, T.; Frimat, L.; et al. Is COVID-19 infection more severe in kidney transplant recipients? Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, M.Z.; Bhalla, A.; Azhar, A.; Tsujita, M.; Talwar, M.; Balaraman, V.; Sodhi, A.; Kadaria, D.; Eason, J.D.; Hayek, S.S.; et al. Outcomes of critically ill solid organ transplant patients with COVID-19 in the United States. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarot, N.; Gueguen, J.; Bonnet, G.; Jdidou, M.; Trimaille, A.; Burger, C.; Amrouche, L.; Weizman, O.; Pommier, T.; Aubert, O.; et al. COVID-19 severity in kidney transplant recipients is similar to nontransplant patients with similar comorbidities. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Bussini, L.; Bonazzetti, C.; Pascale, R.; Pasquini, Z.; Fani, F.; Pinho Guedes, M.N.; Azzini, A.M.; Carrara, E.; et al. Clinical outcome in solid organ transplant recipients affected by COVID-19 compared to general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinson, A.J.; Agarwal, G.; Dai, R.; Anzalone, A.J.; Lee, S.B.; French, E.; Olex, A.; Madhira, V.; Mannon, R.B. COVID-19 in Solid Organ Transplantation: Results of the National COVID Cohort Collaborative. Transplant. Direct. 2021, 7, e775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcolino, M.S.; Ziegelmann, P.K.; Souza-Silva, M.V.R.; Nascimento, I.J.B.; Oliveira, L.M.; Monteiro, L.S.; Sales, T.L.S.; Ruschel, K.B.; Martins, K.P.M.P.; Etges, A.P.B.S.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Brazil: Results from the Brazilian COVID-19 registry. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 107, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, I.R.; Sanchez, M.N.; Frio, G.S.; Alves, L.C.; Pereira, C.C.A.; Lima, R.T.S.; Machado, C.; Santos, L.M.P.; Silva, E.N.D. Trends in COVID-19 case-fatality rates in Brazilian public hospitals: A longitudinal cohort of 398,063 hospital admissions from 1st March to 3rd October 2020. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranata, R.; Lim, M.A.; Huang, I.; Raharjo, S.B.; Lukito, A.A. Hypertension is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. J. Renin. Angiotensin. Aldosterone Syst. 2020, 21, 1470320320926899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.E.; McDonagh, S.T.J.; McManus, R.J.; Martin, U. COVID-19 and hypertension: Risks and management. A scientific statement on behalf of the British and Irish Hypertension Society. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 35, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, K.J.; Kramer, A.; Chesnaye, N.C.; Couchoud, C.; Sanchez-Alvarez, J.E.; Garneata, L.; Collart, F.; Hemmelder, M.H.; Ambuhl, P.; Kerschbaum, J.; et al. Results from the ERA-EDTA Registry indicate a high mortality due to COVID-19 in dialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients across Europe. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillard, S.; Chavarot, N.; Francois, H.; Matignon, M.; Snanoudj, R.; Tourret, J.; Greze, C.; Thaunat, O.; Frimat, L.; Westeel, P.F.; et al. Clinical Utility of Biochemical Markers for the Prediction of COVID-19-Related Mortality in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2689–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.L.; Perazzio, S.F.; Azzi, J.; Cravedi, P.; Riella, L.V. Remodeling of the Immune Response with Aging: Immunosenescence and Its Potential Impact on COVID-19 Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, Y.; Payab, M.; Mohammadi-Vajari, E.; Aghili, S.M.M.; Sharifi, F.; Mehrdad, N.; Kashani, E.; Shadman, Z.; Larijani, B.; Ebrahimpur, M. Association between cardiometabolic risk factors and COVID-19 susceptibility, severity and mortality: A review. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021, 20, 1743–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Hu, W.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L.; Lu, Z.; Ye, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Chronic Cardio-Metabolic Disease Increases the Risk of Worse Outcomes Among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter, Retrospective, and Real-World Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornhammar, P.; Jernberg, T.; Bergstrom, G.; Blomberg, A.; Engstrom, G.; Engvall, J.; Fall, T.; Gisslen, M.; Janson, C.; Lind, L.; et al. Association of cardiometabolic risk factors with hospitalisation or death due to COVID-19: Population-based cohort study in Sweden (SCAPIS). BMJ Open 2021, 11, e051359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Agwu, J.C.; Barlow, N.; Lee, B. Hypertension is the major predictor of poor outcomes among inpatients with COVID-19 infection in the UK: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiterer, M.; Rajan, M.; Gomez-Banoy, N.; Lau, J.D.; Gomez-Escobar, L.G.; Ma, L.; Gilani, A.; Alvarez-Mulett, S.; Sholle, E.T.; Chandar, V.; et al. Hyperglycemia in acute COVID-19 is characterized by insulin resistance and adipose tissue infectivity by SARS-CoV-2. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2174–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, E.B.; de Lucena, D.D.; Aguiar-Brito, I.; de Andrade, L.G.M.; Veronese-Araujo, A.; Cristelli, M.P.; Tedesco-Silva, H.; Medina-Pestana, J.O. COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Transpl. Int. 2022, 35, 10375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; Sehgal, K.; Nair, N.; Mahajan, S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Bikdeli, B.; Ahluwalia, N.; Ausiello, J.C.; Wan, E.Y.; et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.; Pickkers, P.; Derde, L.; Leavis, H.; van Crevel, R.; Engel, J.J.; Wiersinga, W.J.; Vlaar, A.P.J.; Shankar-Hari, M.; et al. A guide to immunotherapy for COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puelles, V.G.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Sperhake, J.P.; Wong, M.N.; Allweiss, L.; Chilla, S.; Heinemann, A.; Wanner, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Multiorgan and Renal Tropism of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, B.G.G.; Oliveira, A.E.R.; Singh, Y.; Jimenez, L.; Goncalves, A.N.A.; Ogava, R.L.T.; Creighton, R.; Schatzmann Peron, J.P.; Nakaya, H.I. ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients with Comorbidities Associated with Severe COVID-19. J Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoloni, E.; Perricone, C.; Cafaro, G.; Gerli, R. Hypertension and SARS-CoV-2 infection: Is inflammation the missing link? Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, e193–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhong, R.; Wang, W.; Chen, O.; Zou, Y. COVID-19 and Smoking: What Evidence Needs Our Attention? Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 603850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Renteria, H.; Travieso, A.; Sagir, A.; Martinez-Gomez, E.; Carrascosa-Granada, A.; Toya, T.; Nunez-Gil, I.J.; Estrada, V.; Lerman, A.; Escaned, J. In-vivo evidence of systemic endothelial vascular dysfunction in COVID-19. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 345, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffke, M.; Freitag, H.; Rudolf, G.; Seifert, M.; Doehner, W.; Scherbakov, N.; Hanitsch, L.; Wittke, K.; Bauer, S.; Konietschke, F.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction and altered endothelial biomarkers in patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.T.; Nakayama, T.; Wu, C.T.; Goltsev, Y.; Jiang, S.; Gall, P.A.; Liao, C.K.; Shih, L.C.; Schurch, C.M.; McIlwain, D.R.; et al. ACE2 localizes to the respiratory cilia and is not increased by ACE inhibitors or ARBs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Rea, F.; Ludergnani, M.; Apolone, G.; Corrao, G. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, H.R.; Adhikari, S.; Pulgarin, C.; Troxel, A.B.; Iturrate, E.; Johnson, S.B.; Hausvater, A.; Newman, J.D.; Berger, J.S.; Bangalore, S.; et al. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of COVID-19. N. Engl. J Med. 2020, 382, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abajo, F.J.; Rodriguez-Martin, S.; Lerma, V.; Mejia-Abril, G.; Aguilar, M.; Garcia-Luque, A.; Laredo, L.; Laosa, O.; Centeno-Soto, G.A.; Angeles, G.M.; et al. Use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital: A case-population study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, J.P.; Nicholson, B.D.; Lee, J.; McGagh, D.; Sherlock, J.; Koshiaris, C.; Oke, J.; Jones, N.R.; Hinton, W.; Armitage, L.; et al. Association Between Blood Pressure Control and Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outcomes in 45,418 Symptomatic Patients with Hypertension: An Observational Cohort Study. Hypertension 2021, 77, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentner, J.; Adams, T.; Knutson, V.; Zeien, S.; Abbas, H.; Moosavi, R.; Manuel, C.; Wallace, T.; Harmon, A.; Waters, R.; et al. C-reactive protein levels associated with COVID-19 outcomes in the United States. J. Osteopath. Med. 2021, 121, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.M.; Aggarwal, G.; Wong, J.; Benoit, S.; Vikse, J.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, I.; Pranata, R. Lymphopenia in severe coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.H.; Hirsch, J.S.; Hazzan, A.; Wanchoo, R.; Shah, H.H.; Malieckal, D.A.; Ross, D.W.; Sharma, P.; Sakhiya, V.; Fishbane, S.; et al. Outcomes among Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, B.; Cai, M.; Xie, Y.; Gibson, A.K.; Maddukuri, G.; Al-Aly, Z. Acute Kidney Injury in a National Cohort of Hospitalized US Veterans with COVID-19. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, Y.; Parides, M.; Alani, O.; Loarte-Campos, P.; Bartash, R.; Forest, S.; Colovai, A.; Ajaimy, M.; Liriano-Ward, L.; Pynadath, C.; et al. COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients at the epicenter of pandemics. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.G.; Malhotra, D.; Simonov, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Arora, T.; Subair, L.; Alausa, J.; Moledina, D.G.; Greenberg, J.H.; Wilson, F.P.; et al. A Comparison Study of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outcomes in Hospitalized Kidney Transplant Recipients. Kidney360 2021, 2, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HTN (+) (n = 225, 75%) | HTN (−) (n = 75, 25%) | Total (N = 300, 100%) | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data | |||||
| Age (years) | 53.2 ± 11.4 | 50.4 ± 14.1 | 52.5 ± 12.2 | 1.02 (0.997–1.042, p = 0.085) | 1.00 (0.979–1.026, p = 0.862) |
| Male (n, %) | 136 (60.4) | 36 (48.0) | 172 (57.3) | 1.66 (0.978–2.801, p = 0.060) | 1.76 (1.018–3.041, p = 0.043) |
| Race (n, %) | 0.74 (0.425–1.275, p = 0.274) | ||||
| White | 134 (59.6) | 50 (66.7) | 184 (61.3) | ||
| Black/brown | 85 (37.8) | 25 (33.3) | 110 (36.7) | ||
| Transplant time (months) | 68 (33.0;142.0) | 101 (39.5;142.5) | 81.5 (33.8;142.3) | 1.00 (0.995–1.002, p = 0.436) | |
| Donor type (n, %) | 1.62 (0.927–2.830, p = 0.090) | 1.47 (0.820–2.635, p = 0.196) | |||
| Living | 58 (25.8) | 27 (36.0) | 85 (28.3) | ||
| Deceased | 167 (74.2) | 48 (64.0) | 215 (71.7) | ||
| BMI (kg/m²) | 27.2 ± 4.7 | 26.1 ± 5.3 | 26.9 ± 4.9 | 1.05 (0.991–1.113, p = 0.100) | |
| BMI ≥ 25 (n, %) | 93 (41.3) | 27 (36.0) | 120 (40.0) | 1.19 (0.682–2.063, p = 0.546) | |
| BMI ≥ 30 (n, %) | 52 (23.1) | 13 (17.3) | 65 (21.7) | 1.40 (0.710–2.757, p = 0.332) | |
| DM (n, %) | 100 (44.4) | 17 (22.7) | 117 (39.0) | 2.73 (1.496–4.979, p = 0.001) | 2.38 (1.250–4.510, p = 0.008) |
| COPD (n, %) | 7 (3.1) | 2 (2.7) | 9 (3.0) | 1.17 (0.238–5.768, p = 0.845) | |
| Heart disease (n, %) | 30 (13.3) | 2 (2.7) | 32 (10.7) | 5.62 (1.309–24.903, p = 0.020) | 4.24 (0.952–18.897; p = 0.058) |
| Neoplasia (n, %) | 15 (6.7) | 6 (8.0) | 21 (7.0) | 0.82 (0.307–2.200, p = 0.696) | |
| Liver disease (n, %) | 9 (4.0) | 0 (0) | 9 (3.0) | - (-, p = 0.999) | |
| Autoimmune disease (n, %) | 4 (1.8) | 2 (2.7) | 6 (2.0) | 0.66 (0.119–3.681, p = 0.636) | |
| Smoking (n, %) | 48 (21.3) | 14 (18.7) | 62 (20.7) | 1.24 (0.626–2.444, p = 0.540) | |
| Laboratory data | |||||
| Basal eGFR | 47 (30;64) | 48 (32;65) | 46.8 (30.8;64.2) | 1.00 (0.990–1.011, p = 0.936) | |
| Admission eGFR | 34 (19;49) | 35 (22;52) | 34 (20;50) | 1.00 (0.985–1.009, p = 0.633) | |
| Previous glycemia (mg/dL) | 97 (86.3;136) | 94 (82;108) | 96 (84;121) | 1.00 (0.999–1.009, p = 0.158) | |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 6.3 (2.1;13.2) | 5.2 (1.2;10.6) | 5.7 (2.0;12.6) | 1.03 (0.988–1.063, p = 0.187) | |
| LDH (U/L) | 288.5 (227;405.5) | 273 (191;354) | 287 (220;395) | 1.00 (1.000–1.003, p = 0.103) | |
| Lymphocytes (mm³) | 695(461.8;1195.3) | 852 (520;1122) | 738 (468;1174.5) | 1.00 (1.000–1.000, p = 0.795) | |
| D-dimer (μg/L) | 1.2 (0.6;2.3) | 1.2 (0.5;1.8) | 1.2 (0.6;2.3) | 1.11 (0.987–1.258, p = 0.080) | |
| AST (U/L) | 28 (20;40) | 32 (24;43) | 28 (21;41) | 1.00 (0.991–1.006, p = 0.663) | |
| ALT (U/L) | 21 (14;32.5) | 20 (16;28) | 21 (15;32) | 1.00 (0.990–1.014, p = 0.768) | |
| Outcomes | |||||
| Mortality (n, %) | 74 (32.9) | 15 (20.0) | 89 (29.7) | 1.96 (1.044–3.682, p = 0.036) | 1.67 (0.572–4.850, p = 0.349) |
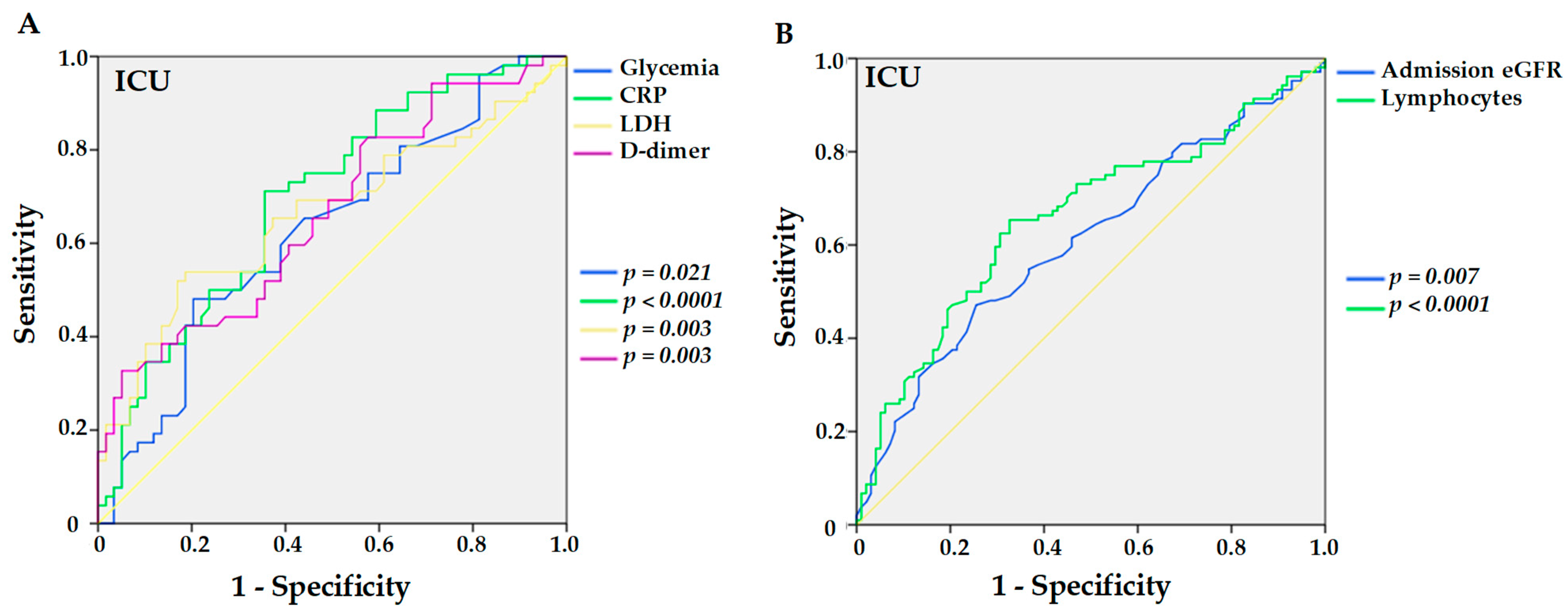
| ICU (n, %) | 114 (50.7) | 26 (34.7) | 140 (46.7) | 1.94 (1.125–3.330, p = 0.017) | 1.83 (0.724–4.646, p = 0.201) |
| O2 (n, %) | 122 (54.2) | 41 (54.7) | 163 (54.3) | 0.98 (0.581–1.660, p = 0.947) | |
| IMV (n, %) | 83 (36.9) | 19 (25.3) | 102 (34.0) | 1.72 (0.958–3.097, p = 0.069) | 0.47 (0.124–1.781, p = 0.267) |
| AKI (n, %) | 134 (59.6) | 40 (53.3) | 174 (58.0) | 1.29 (0.761–2.180, p = 0.345) | |
| Stage 1 | 25 (11.1) | 13 (17.3) | 38 (12.7) | 0.60 (0.288–1.235, p = 0.164) | |
| Stage 2 | 9 (4.0) | 7 (9.3) | 16 (5.3) | 0.41 (0.145–1.128, p = 0.084) | 0.44 (0.146–1.340; p = 0.149) |
| Stage 3 | 100 (44.4) | 20 (26.7) | 120 (40.0) | 2.20 (1.237–3.911, p = 0.007) | 1.54 (0.383–6.211; p = 0.542) |
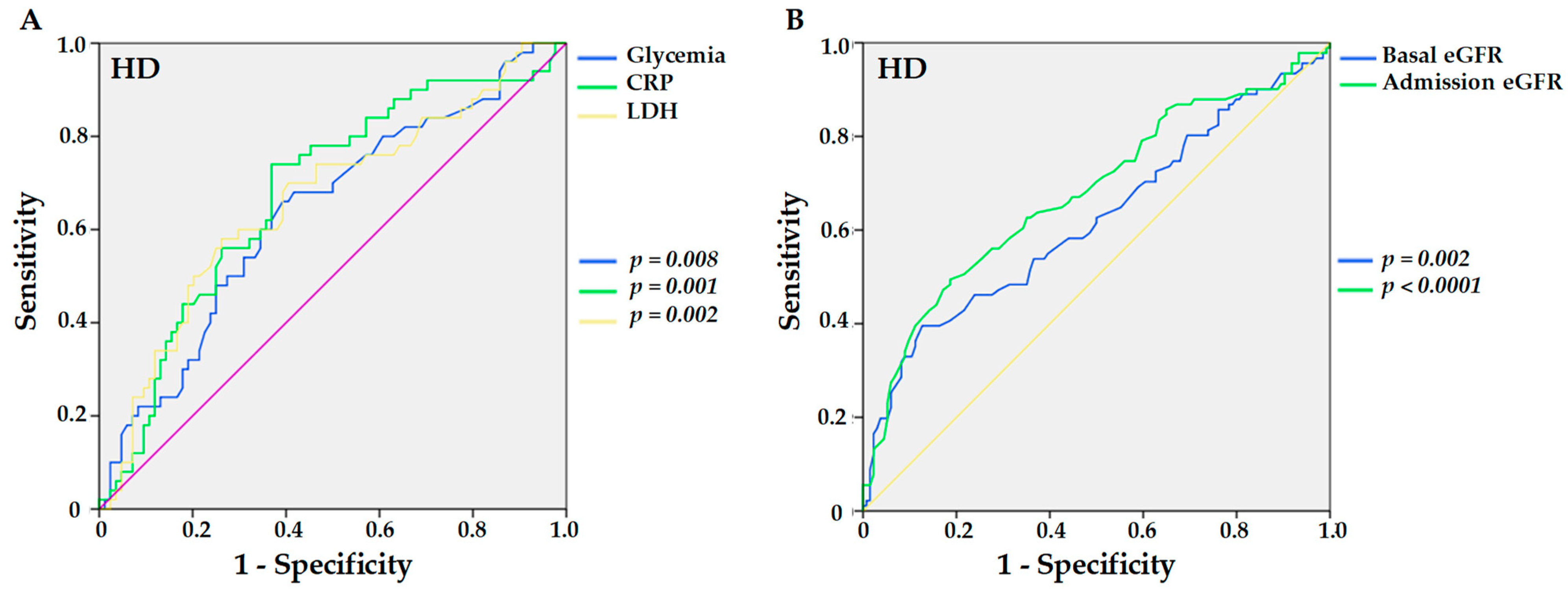
| HD (n, %) | 91 (40.4) | 18 (24.0) | 109 (36.3) | 2.15 (1.188–3.891, p = 0.011) | 1.12 (0.221–5.637, p = 0.895) |
| Not Alive (n = 74, 32.9%) | Alive (n = 151, 67.1%) | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Data | ||||
| Age (years) | 58.6 ± 10.5 | 50.5 ± 11.0 | 1.07 (1.041–1.104, p < 0.0001) | 1.06 (1.026–1.100, p = 0.001) |
| Male (n, %) | 44 (59.5) | 92 (60.9) | 0.94 (0.533–1.659, p = 0.832) | |
| Race (n, %) | 1.18 (0.665–2.081, p = 0.577) | |||
| White | 46 (62.2) | 88 (58.3) | ||
| Black/brown | 24 (32.4) | 61 (40.4) | ||
| Transplant time (months) | 78 (41;125.8) | 65 (30;143.5) | 1.00 (0.997–1.005, p = 0.654) | |
| Donor type (n, %) | 1.76 (0.893–3.477, p = 0.102) | |||
| Living | 14 (18.9) | 44 (29.1) | ||
| Deceased | 60 (81.1) | 107 (70.9) | ||
| BMI (kg/m²) | 27.2 ± 4.4 | 27.1 ± 4.9 | 1.00 (0.945–1.067, p = 0.894) | |
| BMI ≥ 25 (n, %) | 32 (43.2) | 61 (40.4) | 1.21 (0.677–2.144, p = 0.526) | |
| BMI ≥ 30 (n, %) | 17 (23.0) | 35 (23.2) | 1.04 (0.532–2.019, p = 0.915) | |
| DM (n, %) | 40 (54.1) | 60 (39.7) | 1.78 (1.018–3.128, p = 0.043) | 0.96 (0.461–1.994, p = 0.911) |
| COPD (n, %) | 2 (2.7) | 5 (3.3) | 0.81 (0.154–4.283, p = 0.805) | |
| Heart disease (n, %) | 17 (23.0) | 13 (8.6) | 3.17 (1.444–6.943, p = 0.004) | 3.70 (1.302–10.526, p = 0.014) |
| Neoplasia (n, %) | 7 (9.5) | 8 (5.3) | 1.87 (0.650–5.364, p = 0.246) | |
| Liver disease (n, %) | 5 (6.8) | 4 (2.6) | 2.66 (0.693–10.227, p = 0.154) | |
| Autoimmune disease (n, %) | 1 (1.4) | 3 (2.0) | 0.68 (0.069–6.610, p = 0.736) | |
| Smoking (n, %) | 22 (29.7) | 26 (17.2) | 2.12 (1.071–4.180, p = 0.031) | 2.20 (1.051–4.616, p = 0.036) |
| Laboratory Data | ||||
| Basal eGFR | 49 (25;63) | 46 (32;63) | 1.00 (0.988–1.010, p = 0.870) | |
| Admission eGFR | 30 (17;46) | 35 (22;50) | 1.00 (0.982–1.008, p = 0.434) | |
| Previous glycemia (mg/dL) | 115 (93;191) | 92 (83;114) | 1.01 (1.006–1.017, p < 0.0001) | 1.02 (1.007–1.029, p = 0.002) |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 13.2 (5.5;19,0) | 4.4 (1.7;10.3) | 1.08 (1.038–1.119, p < 0.0001) | 1.03 (0.964–1.095, p = 0.410) |
| LDH (U/L) | 360 (271.5;474.5) | 270 (224;356) | 1.00 (1.000–1.003, p = 0.049) | 1.00 (0.999–1.004, p = 0.193) |
| Lymphocytes (mm³) | 524 (348;789) | 819 (570;1230) | 1.00 (0.999–1.000, p = 0.039) | 1.00 (0.997–1.000, p = 0.043) |
| D-dimer (μg/L) | 1.5 (0.7;2.8) | 1.1 (0.6;2.1) | 1.10 (1.020–1.194, p = 0.014) | 1.19 (0.988–1.426, p = 0.067) |
| AST (U/L) | 29 (20;41.5) | 27 (21;39) | 1.00 (0.992–1.009, p = 0.889) | |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.5 (13.8;32.3) | 21 (15;33) | 1.00 (0.990–1.013, p = 0.836) | |
| ICU (n = 114, 50.7%) | No ICU (n = 111, 49.3%) | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Data | ||||
| Age (years) | 56.9 ± 11.1 | 49.3 ± 10.5 | 1.07 (1.039–1.096, p < 0.0001) | 1.05 (1.018–1.081, p = 0.002) |
| Male (n, %) | 65 (57.0) | 71 (64.0) | 0.75 (0.437–1.278, p = 0.287) | |
| Race (n, %) | 1.17 (0.686–1.991, p = 0.567) | |||
| White | 70 (61.4) | 64 (57.7) | ||
| Black/brown | 39 (34.2) | 46 (41.4) | ||
| Transplant time (months) | 84 (37.5;137) | 61 (29;142.5) | 1.00 (0.997–1.005, p = 0.549) | |
| Donor type (n, %) | 1.04 (0.570–1.884, p = 0.906) | |||
| Living | 29 (25.4) | 29 (26.1) | ||
| Deceased | 85 (74.6) | 82 (73.9) | ||
| BMI (kg/m²) | 27.4 ± 4.6 | 26.9 ± 4.8 | 1.02 (0.967–1.084, p = 0.422) | |
| BMI ≥ 25 (n, %) | 48 (42.1) | 45 (40.5) | 1.07 (0.622–1.830, p = 0.815) | |
| BMI ≥ 30 (n, %) | 29 (25.4) | 23 (20.7) | 1.31 (0.698–2.450, p = 0.401) | |
| DM (n, %) | 53 (46.5) | 47 (42.3) | 1.18 (0.699–2.003, p = 0.531) | |
| COPD (n, %) | 5 (4.4) | 2 (1.8) | 2.50 (0.475–13.164, p = 0.280) | |
| Heart disease (n, %) | 23 (20.2) | 7 (6.3) | 3.76 (1.540–9.159, p = 0.004) | 4.84 (1.316–17.829, p = 0.018) |
| Neoplasia (n, %) | 11 (9.6) | 4 (3.6) | 2.86 (0.881–9.259, p = 0.080) | 4.99 (0.547–45.405, p = 0.154) |
| Liver disease (n, %) | 6 (5.3) | 3 (2.7) | 2.00 (0.488–8.203, p = 0.336) | |
| Autoimmune disease (n, %) | 3 (2.6) | 1 (0.9) | 2.97 (0.305–29.022, p = 0.349) | |
| Smoking (n, %) | 31 (27.2) | 17 (15.3) | 1.97 (0.994–3.890, p = 0.052) | 2.10 (1.010–4.360, p = 0.047) |
| Laboratory Data | ||||
| Basal eGFR | 44 (27;60) | 48 (33;64.7) | 1.00 (0.985–1.005, p = 0.327) | |
| Admission eGFR | 29 (17;45) | 39 (26;52) | 0.99 (0.973–0.997, p = 0.018) | 0.98 (0.956–1.004, p = 0.094) |
| Previous glycemia (mg/dL) | 108.5 (89;163.8) | 92 (83;107.5) | 1.01 (1.006–1.018, p < 0.0001) | 1.01 (1.001–1.022, p = 0.026) |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 10.1 (3.7;17.3) | 3.7 (1.4;9.6) | 1.08 (1.038–1.124, p < 0.0001) | 1.01 (0.947–1.079, p = 0.739) |
| LDH (U/L) | 351.5 (241;483.5) | 250.5 (219.8;317.8) | 1.00 (1.002–1.007, p = 0.001) | 1.00 (1.001–1.008, p = 0.024) |
| Lymphocytes (mm³) | 585 (373.8;903.8) | 861 (578.5;1289.8) | 1.00 (0.999–1.000, p = 0.095) | 1.00 (0.998–1.000, p = 0.025) |
| D-dimer (μg/L) | 1.6 (0.8;2.9) | 0.9 (0.5;1.7) | 1.17 (1.041–1.303, p = 0.008) | 1.70 (1.102–2.626, p = 0.016) |
| AST (U/L) | 29 (20;42) | 27 (21;37) | 1.01 (0.997–1.020, p = 0.146) | |
| ALT (U/L) | 22 (14;31) | 21 (15;33.5) | 1.00 (0.990–1.013, p = 0.798) | |
| HD (n = 91, 40.4%) | No HD (n = 134, 59.6%) | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Data | ||||
| Age (years) | 56.4 ± 11.0 | 50.9 ± 11.3 | 1.05 (1.019–1.072, p = 0.001) | 1.05 (1.015–1.077, p = 0.003) |
| Male (n, %) | 56 (61.5) | 80 (59.7) | 1.08 (0.626–1.863, p = 0.782) | |
| Race (n, %) | 1.24 (0.719–2.142, p = 0.438) | |||
| White | 57 (62.6) | 77 (57.5) | ||
| Black/brown | 30 (33.0) | 55 (41.0) | ||
| Transplant time (months) | 85 (41;130) | 62 (29;143.8) | 1.00 (0.997–1.004, p = 0.683) | |
| Donor type (n, %) | 1.92 (1.009–3.649, p = 0.047) | 1.15 (0.503–2.643, p = 0.737) | ||
| Living | 17 (18.7) | 41 (30.6) | ||
| Deceased | 74 (81.3) | 93 (69.4) | ||
| BMI (kg/m²) | 27.3 ± 4.5 | 27.1 ± 4.9 | 1.01 (0.950–1.067, p = 0.815) | |
| BMI ≥ 25 (n, %) | 37 (40.7) | 56 (41.8) | 0.95 (0.549–1.649, p = 0.859) | |
| BMI ≥ 30 (n, %) | 23 (25.3) | 29 (21.6) | 1.23 (0.653–2.306, p = 0.526) | |
| DM (n, %) | 45 (49.5) | 55 (41.0) | 1.41 (0.822–2.402, p = 0.214) | |
| COPD (n, %) | 4 (4.4) | 3 (2.2) | 2.01 (0.439–9.191, p = 0.369) | |
| Heart disease (n, %) | 17 (18.7) | 13 (9.7) | 2.14 (0.982–4.655, p = 0.056) | 2.11 (0.772–5.756, p = 0.146) |
| Neoplasia (n, %) | 8 (8.8) | 7 (5.2) | 1.75 (0.611–5.004, p = 0.298) | |
| Liver disease (n, %) | 7 (7.7) | 2 (1.5) | 5.50 (1.116–27.109, p = 0.036) | 2.41 (0.445–13.048, p = 0.307) |
| Autoimmune disease (n, %) | 2 (2.2) | 3 (2.2) | 1.48 (0.205–10.724, p = 0.696) | |
| Smoking (n, %) | 26 (28.6) | 22 (16.4) | 1.78 (0.917–3.470, p = 0.088) | 1.69 (0.835–3.407, p = 0.145) |
| Laboratory Data | ||||
| Basal eGFR | 41 (21;58) | 50 (35;68) | 0.99 (0.974–0.996, p = 0.009) | 1.00 (0.977–1.017, p = 0.753) |
| Admission eGFR | 25 (13;43) | 40 (26;53) | 0.97 (0.960–0.988, p < 0.0001) | 0.98 (0.951–1.002, p = 0.075) |
| Previous glycemia (mg/dL) | 108.5 (90;164.5) | 92.5 (83;112.8) | 1.01 (1.005–1.015, p < 0.0001) | 1.01 (0.999–1.017, p = 0.075) |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 10.1 (4.5;17.1) | 3.9 (1.7;10.5) | 1.05 (1.016–1.088, p = 0.004) | 1.03 (0.975–1.084, p = 0.306) |
| LDH (U/L) | 357.5 (247.3;488.3) | 268 (221;347) | 1.00 (1.000–1.004, p = 0.041) | 1.00 (0.999–1.003, p = 0.498) |
| Lymphocytes (mm³) | 534.5 (371;834) | 847 (584.3;1260.8) | 1.00 (0.999–1.000, p = 0.161) | |
| D-dimer (μg/L) | 1.5 (0.7;2.7) | 1.1 (0.6;2.1) | 1.07 (0.990–1.153, p = 0.087) | 1.17 (0.986–1.385, p = 0.073) |
| AST (U/L) | 29 (20;42) | 27 (21;38) | 1.00 (0.993–1.009, p = 0.880) | |
| ALT (U/L) | 23 (14;32) | 21 (15;32.8) | 1.00 (0.988–1.011, p = 0.941) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguiar-Brito, I.; de Lucena, D.D.; Veronese-Araújo, A.; Cristelli, M.P.; Tedesco-Silva, H.; Medina-Pestana, J.O.; Rangel, É.B. Impact of Hypertension on COVID-19 Burden in Kidney Transplant Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study. Viruses 2022, 14, 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112409
Aguiar-Brito I, de Lucena DD, Veronese-Araújo A, Cristelli MP, Tedesco-Silva H, Medina-Pestana JO, Rangel ÉB. Impact of Hypertension on COVID-19 Burden in Kidney Transplant Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112409
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguiar-Brito, Isabella, Débora D. de Lucena, Alexandre Veronese-Araújo, Marina P. Cristelli, Hélio Tedesco-Silva, José O. Medina-Pestana, and Érika B. Rangel. 2022. "Impact of Hypertension on COVID-19 Burden in Kidney Transplant Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112409
APA StyleAguiar-Brito, I., de Lucena, D. D., Veronese-Araújo, A., Cristelli, M. P., Tedesco-Silva, H., Medina-Pestana, J. O., & Rangel, É. B. (2022). Impact of Hypertension on COVID-19 Burden in Kidney Transplant Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study. Viruses, 14(11), 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112409






