Strategies to Optimise Oncolytic Viral Therapies: The Role of Natural Killer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Oncolytic Viruses (OV) as an Emerging Class of Immunotherapy
1.2. The Potential of Natural Killer (NK) Cells to Enhance OV Efficacy
2. Natural Killer (NK) Cell Responses in the Context of OV
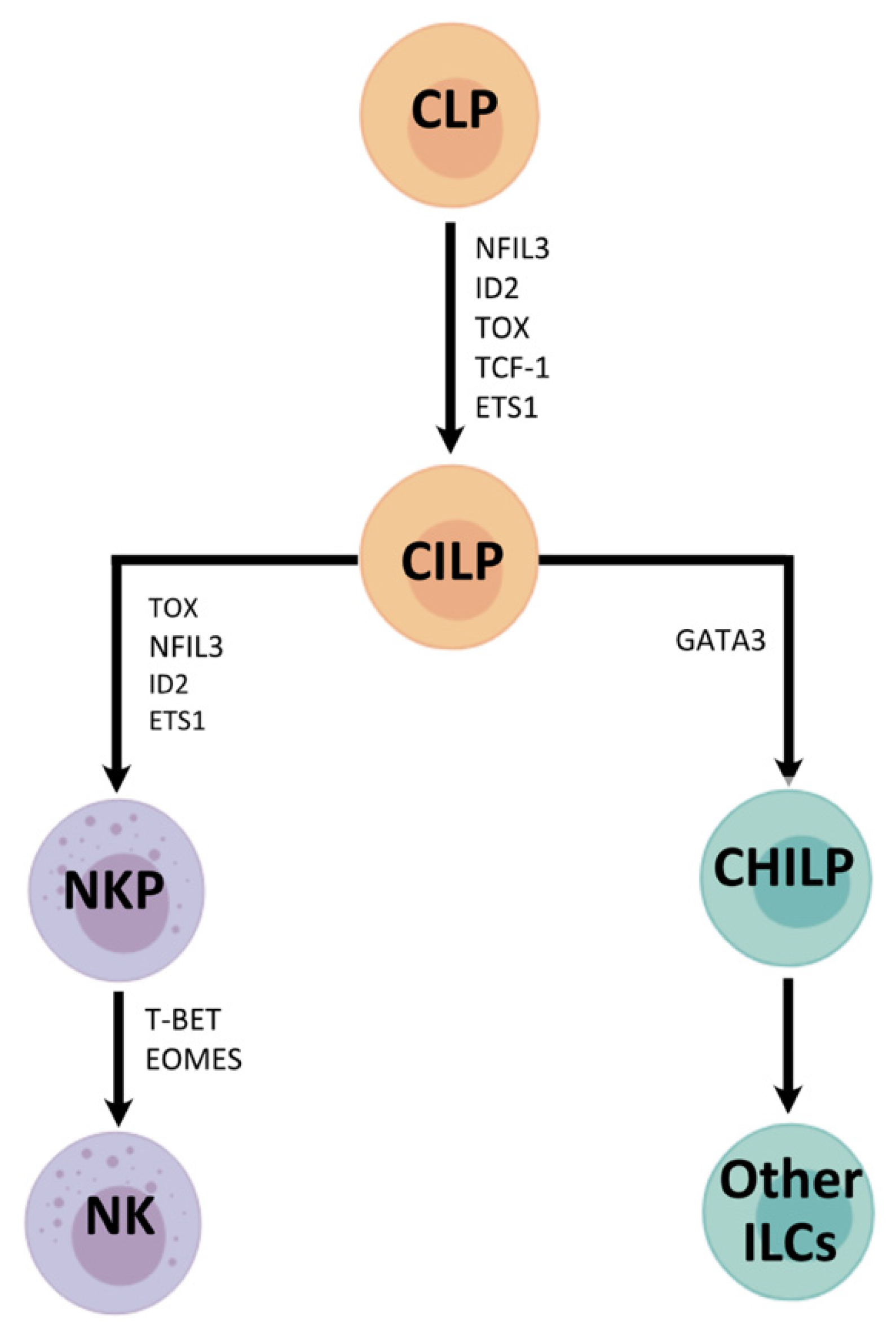
2.1. NK Cell—A Member of the Innate Lymphoid Cell Family
2.2. The Importance of NK Cells in Anti-Viral and Anti-Tumoural Defence
2.3. Determinants of NK Cell Response in the Context of OV
3. Strategies That Exploit NK Cell Response to Improve OV Efficacies
3.1. Pharmacological Modulation of NK Response
3.2. Manipulation of OV to Augment NK Activities
3.3. Adoptive Transfer of NK Cells
3.4. Other Strategies
3.5. Considerations for Future Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heo, J.; Reid, T.; Ruo, L.; Breitbach, C.J.; Rose, S.; Bloomston, M.; Cho, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Chung, H.C.; Kim, C.W.; et al. Randomized dose-finding clinical trial of oncolytic immunotherapeutic vaccinia JX-594 in liver cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Kaufman, H.L.; Collichio, F.; Amatruda, T.; Senzer, N.; Chesney, J.; Delman, K.A.; Spitler, L.E.; Puzanov, I.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec improves durable response rate in patients with advanced melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Q. Efficacy and Safety of Oncolytic Viruses in Randomized Controlled Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, S.E.; Speranza, M.C.; Cho, C.F.; Chiocca, E.A. Oncolytic Viruses in Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, N.T.; Bell, J.C. Oncolytic Virus Combination Therapy: Killing One Bird with Two Stones. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2018, 26, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemos de Matos, A.; Franco, L.S.; McFadden, G. Oncolytic Viruses and the Immune System: The Dynamic Duo. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, E.; Russell, S.J. History of Oncolytic Viruses: Genesis to Genetic Engineering. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.D.; Nakamura, T.; Russell, S.J.; Peng, K.-W. High CD46 receptor density determines preferential killing of tumor cells by oncolytic measles virus. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4919–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coffey, M.C.; Strong, J.E.; Forsyth, P.A.; Lee, P.W.K. Reovirus Therapy of Tumors with Activated Ras Pathway. Science 1998, 282, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghi, M.; Visted, T.; DePinho, R.A.; Chiocca, E.A. Oncolytic herpes virus with defective ICP6 specifically replicates in quiescent cells with homozygous genetic mutations in p16. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4249–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uusi-Kerttula, H.; Davies, J.A.; Thompson, J.M.; Wongthida, P.; Evgin, L.; Shim, K.G.; Bradshaw, A.; Baker, A.T.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Jones, R.; et al. Ad5NULL-A20: A Tropism-Modified, alphavbeta6 Integrin-Selective Oncolytic Adenovirus for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Therapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4215–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taipale, K.; Liikanen, I.; Juhila, J.; Turkki, R.; Tahtinen, S.; Kankainen, M.; Vassilev, L.; Ristimaki, A.; Koski, A.; Kanerva, A.; et al. Chronic activation of innate immunity correlates with poor prognosis in cancer patients treated with oncolytic adenovirus. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2016, 24, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerullo, V.; Koski, A.; Vähä-Koskela, M.; Hemminki, A. Chapter Eight—Oncolytic adenoviruses for cancer immunotherapy: Data from mice, hamsters, and humans. In Advances in Cancer Research; David, T.C., Paul, B.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 115, pp. 265–318. [Google Scholar]
- Greig, S.L. Talimogene Laherparepvec: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, M.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D. Tumor growth inhibition by intratumoral inoculation of defective herpes simplex virus vectors expressing granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2000, 2, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.L.; Robinson, M.; Han, Z.Q.; Branston, R.H.; English, C.; Reay, P.; McGrath, Y.; Thomas, S.K.; Thornton, M.; Bullock, P.; et al. ICP34.5 deleted herpes simplex virus with enhanced oncolytic, immune stimulating, and anti-tumour properties. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Collichio, F.; Harrington, K.J.; Middleton, M.R.; Downey, G.; Öhrling, K.; Kaufman, H.L. Final analyses of OPTiM: A randomized phase III trial of talimogene laherparepvec versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in unresectable stage III–IV melanoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Errington, F.; Steele, L.; Prestwich, R.; Harrington, K.J.; Pandha, H.S.; Vidal, L.; de Bono, J.; Selby, P.; Coffey, M.; Vile, R.; et al. Reovirus Activates Human Dendritic Cells to Promote Innate Antitumor Immunity. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6018–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prestwich, R.J.; Errington, F.; Steele, L.P.; Ilett, E.J.; Morgan, R.S.; Harrington, K.J.; Pandha, H.S.; Selby, P.J.; Vile, R.G.; Melcher, A.A. Reciprocal human dendritic cell-natural killer cell interactions induce antitumor activity following tumor cell infection by oncolytic reovirus. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4312–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottke, T.; Diaz, R.M.; Kaluza, K.; Pulido, J.; Galivo, F.; Wongthida, P.; Thompson, J.; Willmon, C.; Barber, G.N.; Chester, J.; et al. Use of biological therapy to enhance both virotherapy and adoptive T-cell therapy for cancer. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2008, 16, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottke, T.; Thompson, J.; Diaz, R.M.; Pulido, J.; Willmon, C.; Coffey, M.; Selby, P.; Melcher, A.; Harrington, K.; Vile, R.G. Improved systemic delivery of oncolytic reovirus to established tumors using preconditioning with cyclophosphamide-mediated Treg modulation and interleukin-2. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altomonte, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, L.; Meseck, M.; Ebert, O.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Fallon, J.; Woo, S.L. Exponential enhancement of oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus potency by vector-mediated suppression of inflammatory responses in vivo. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2008, 16, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Yu, J.; Price, R.; Wojton, J.; Pradarelli, J.; Mao, H.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Hardcastle, J.; et al. NK cells impede glioblastoma virotherapy through NKp30 and NKp46 natural cytotoxicity receptors. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Chen, X.; Chu, J.; Xu, B.; Meisen, W.H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Wang, Q.-E.; et al. TGFβ Treatment Enhances Glioblastoma Virotherapy by Inhibiting the Innate Immune Response. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5273–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vivier, E.; Raulet, D.H.; Moretta, A.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Zitvogel, L.; Lanier, L.L.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Ugolini, S. Innate or Adaptive Immunity? The Example of Natural Killer Cells. Science 2011, 331, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernink, J.; Mjösberg, J.; Spits, H. Th1- and Th2-like subsets of innate lymphoid cells. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 252, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artis, D.; Spits, H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature 2015, 517, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Artis, D.; Colonna, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Eberl, G.; Koyasu, S.; Locksley, R.M.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Mebius, R.E.; et al. Innate Lymphoid Cells: 10 Years On. Cell 2018, 174, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiossone, L.; Dumas, P.-Y.; Vienne, M.; Vivier, E. Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, E.M.; Orange, J.S. Emerging insights into human health and NK cell biology from the study of NK cell deficiencies. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 287, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, J.S. Natural killer cell deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smyth, M.J.; Thia, K.Y.T.; Street, S.E.A.; Cretney, E.; Trapani, J.A.; Taniguchi, M.; Kawano, T.; Pelikan, S.B.; Crowe, N.Y.; Godfrey, D.I. Differential Tumor Surveillance by Natural Killer (Nk) and Nkt Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smyth, M.J.; Crowe, N.Y.; Godfrey, D.I. NK cells and NKT cells collaborate in host protection from methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halfteck, G.G.; Elboim, M.; Gur, C.; Achdout, H.; Ghadially, H.; Mandelboim, O. Enhanced In Vivo Growth of Lymphoma Tumors in the Absence of the NK-Activating Receptor NKp46/NCR1. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2221–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasner, A.; Ghadially, H.; Gur, C.; Stanietsky, N.; Tsukerman, P.; Enk, J.; Mandelboim, O. Recognition and Prevention of Tumor Metastasis by the NK Receptor NKp46/NCR1. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, T.; Mizushima, N.; Nakamura, J.; Kanai, K. Surface markers of NK cells in peripheral blood of patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunol. Lett. 1986, 13, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schantz, S.P.; Shillitoe, E.J.; Brown, B.; Campbell, B. Natural killer cell activity and head and neck cancer: A clinical assessment. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1986, 77, 869–875. [Google Scholar]
- Strayer, D.R.; Carter, W.A.; Brodsky, I. Familial occurrence of breast cancer is associated with reduced natural killer cytotoxicity. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1986, 7, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzetti, G.G.; Cignitti, M.; Ciavattini, A.; Fabris, N.; Romanini, C. Natural killer cell activity and progression-free survival in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1993, 35, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittenden, J.; Heys, S.D.; Ross, J.; Eremin, O. Natural killer cells and cancer. Cancer 1996, 77, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Iglesias, T.; del Toro-Arreola, A.; Albarran-Somoza, B.; del Toro-Arreola, S.; Sanchez-Hernandez, P.E.; Ramirez-Dueñas, M.G.; Balderas-Peña, L.M.A.; Bravo-Cuellar, A.; Ortiz-Lazareno, P.C.; Daneri-Navarro, A. Low NKp30, NKp46 and NKG2D expression and reduced cytotoxic activity on NK cells in cervical cancer and precursor lesions. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlsten, M.; Malmberg, K.J.; Ljunggren, H.G. Natural killer cell-mediated lysis of freshly isolated human tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Matsuyama, S.; Miyake, S.; Suga, K.; Nakachi, K. Natural cytotoxic activity of peripheral-blood lymphocytes and cancer incidence: An 11-year follow-up study of a general population. Lancet 2000, 356, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca, S.; Perez-Piqueras, J.; Martinez, D.; Colmenarejo, A.; Saez, M.A.; Vallejo, C.; Martos, J.A.; Moreno, M. The prognostic significance of intratumoral natural killer cells in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 1997, 79, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, S.; Natsugoe, S.; Tokuda, K.; Nakajo, A.; Che, X.; Iwashige, H.; Aridome, K.; Hokita, S.; Aikou, T. Prognostic value of intratumoral natural killer cells in gastric carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 88, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy, P.K.; Peters, C.; Saha, D.; Rabkin, S.D.; Kaufman, H.L. Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Viruses as a Paradigm for the Treatment of Cancer. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2018, 2, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Berkeley, R.; Barr, T.; Ilett, E.; Errington-Mais, F. Past, Present and Future of Oncolytic Reovirus. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromeier, M.; Nair, S.K. Recombinant Poliovirus for Cancer Immunotherapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2018, 69, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, A.; Kavishwar, G.; Salvato, I.; Marchini, A. A Roadmap for the Success of Oncolytic Parvovirus-Based Anticancer Therapies. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020, 7, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.S.; Lu, B.; Guo, Z.; Giehl, E.; Feist, M.; Dai, E.; Liu, W.; Storkus, W.J.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Vaccinia virus-mediated cancer immunotherapy: Cancer vaccines and oncolytics. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripodi, L.; Vitale, M.; Cerullo, V.; Pastore, L. Oncolytic Adenoviruses for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J.; Peng, K.-W.; Bell, J.C. Oncolytic virotherapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, N.K.; Hale, A.; Cawood, R.; Illingworth, S.; Herbert, C.; Hermiston, T.; Subr, V.; Ulbrich, K.; van Rooijen, N.; Seymour, L.W.; et al. Tropism ablation and stealthing of oncolytic adenovirus enhances systemic delivery to tumors and improves virotherapy of cancer. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, S.; Altfeld, M. Control of human viral infections by natural killer cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pende, D.; Falco, M.; Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Munari, E.; Bertaina, A.; Moretta, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Pietra, G.; et al. Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIRs): Their Role in NK Cell Modulation and Developments Leading to Their Clinical Exploitation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivori, S.; Della Chiesa, M.; Carlomagno, S.; Quatrini, L.; Munari, E.; Vacca, P.; Tumino, N.; Mariotti, F.R.; Mingari, M.C.; Pende, D.; et al. Inhibitory Receptors and Checkpoints in Human NK Cells, Implications for the Immunotherapy of Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunia-Kubik, K.; Łacina, P. Non-KIR NK cell receptors: Role in transplantation of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cells. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2021, 48, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Leonard, J.P. Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, J.; Woller, N.; Brooks, J.; Fleischmann-Mundt, B.; Martin, N.T.; Kloos, A.; Knocke, S.; Ernst, A.M.; Manns, M.P.; Kubicka, S.; et al. Molecular retargeting of antibodies converts immune defense against oncolytic viruses into cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jegaskanda, S.; Vanderven Hillary, A.; Tan, H.-X.; Alcantara, S.; Wragg Kathleen, M.; Parsons Matthew, S.; Chung Amy, W.; Juno Jennifer, A.; Kent Stephen, J.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Influenza Virus Infection Enhances Antibody-Mediated NK Cell Functions via Type I Interferon-Dependent Pathways. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02090-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Böttcher, J.P.; Bonavita, E.; Chakravarty, P.; Blees, H.; Cabeza-Cabrerizo, M.; Sammicheli, S.; Rogers, N.C.; Sahai, E.; Zelenay, S.; Reis e Sousa, C. NK Cells Stimulate Recruitment of cDC1 into the Tumor Microenvironment Promoting Cancer Immune Control. Cell 2018, 172, 1022–1037.e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferlazzo, G.; Tsang, M.L.; Moretta, L.; Melioli, G.; Steinman, R.M.; Münz, C. Human Dendritic Cells Activate Resting Natural Killer (NK) Cells and Are Recognized via the NKp30 Receptor by Activated NK Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Chiesa, M.D.; Carlomagno, S.; Pende, D.; Aricò, M.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A. NK-dependent DC maturation is mediated by TNFα and IFNγ released upon engagement of the NKp30 triggering receptor. Blood 2005, 106, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandstadter, J.D.; Yang, Y. Natural Killer cell responses to viral infection. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muntasell, A.; Ochoa, M.C.; Cordeiro, L.; Berraondo, P.; López-Díaz de Cerio, A.; Cabo, M.; López-Botet, M.; Melero, I. Targeting NK-cell checkpoints for cancer immunotherapy. Cur. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 45, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkayyal, A.A.; Tai, L.-H.; Kennedy, M.A.; de Souza, C.T.; Zhang, J.; Lefebvre, C.; Sahi, S.; Ananth, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Makrigiannis, A.P.; et al. NK-Cell Recruitment Is Necessary for Eradication of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis with an IL12-Expressing Maraba Virus Cellular Vaccine. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, E.Y.L.; Ennis, D.P.; Kennedy, P.R.; Hansell, C.; Dowson, S.; Farquharson, M.; Spiliopoulou, P.; Nautiyal, J.; McNamara, S.; Carlin, L.M.; et al. NK Cells Augment Oncolytic Adenovirus Cytotoxicity in Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2020, 16, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prestwich, R.J.; Errington, F.; Diaz, R.M.; Pandha, H.S.; Harrington, K.J.; Melcher, A.A.; Vile, R.G. The case of oncolytic viruses versus the immune system: Waiting on the judgment of Solomon. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Jaime-Ramirez, A.C.; Bolyard, C.; Dai, H.; Nallanagulagari, T.; Wojton, J.; Hurwitz, B.S.; Relation, T.; Lee, T.J.; Lotze, M.T.; et al. Bortezomib treatment sensitizes oncolytic HSV-1–treated tumors to NK cell immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5265–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altomonte, J.; Marozin, S.; Schmid, R.M.; Ebert, O. Engineered Newcastle Disease Virus as an Improved Oncolytic Agent Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Yu, J.; Kaur, B.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Chiocca, E.A. Deciphering the multifaceted relationship between oncolytic viruses and Natural Killer cells. Adv. Virol. 2012, 2012, 702839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvinen, M.; Heiskanen, R.; Oksanen, M.; Pesonen, S.; Liikanen, I.; Joensuu, T.; Kanerva, A.; Cerullo, V.; Hemminki, A. Fc-gamma receptor polymorphisms as predictive and prognostic factors in patients receiving oncolytic adenovirus treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louie, R.J.; Perez, M.C.; Jajja, M.R.; Sun, J.; Collichio, F.; Delman, K.A.; Lowe, M.; Sarnaik, A.A.; Zager, J.S.; Ollila, D.W. Real-World Outcomes of Talimogene Laherparepvec Therapy: A Multi-Institutional Experience. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2019, 228, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Bi, J.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Peng, H.; Wei, H.; et al. Blockade of the checkpoint receptor TIGIT prevents NK cell exhaustion and elicits potent anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Wei, J. Combining Oncolytic Viruses With Cancer Immunotherapy: Establishing a New Generation of Cancer Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galivo, F.; Diaz, R.M.; Thanarajasingam, U.; Jevremovic, D.; Wongthida, P.; Thompson, J.; Kottke, T.; Barber, G.N.; Melcher, A.; Vile, R.G. Interference of CD40L-Mediated Tumor Immunotherapy by Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jennings, V.A.; Scott, G.B.; Rose, A.M.S.; Scott, K.J.; Migneco, G.; Keller, B.; Reilly, K.; Donnelly, O.; Peach, H.; Dewar, D.; et al. Potentiating Oncolytic Virus-Induced Immune-Mediated Tumor Cell Killing Using Histone Deacetylase Inhibition. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Ma, R.; Russell, L.; Yoo, J.Y.; Han, J.; Cui, H.; Yi, P.; Zhang, J.; Nakashima, H.; Dai, H.; et al. An oncolytic herpesvirus expressing E-cadherin improves survival in mouse models of glioblastoma. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Tao, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X. Arming HSV-Based Oncolytic Viruses with the Ability to Redirect the Host’s Innate Antiviral Immunity to Attack Tumor Cells. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2020, 19, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Wei, M.; He, B.; Chen, A.; Wang, S.; Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, G.; Xu, T.; Wu, J.; et al. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of a novel oncolytic vaccinia virus encoding a fully monoclonal antibody against T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT). EBioMedicine 2021, 64, 103240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, M.; Mou, T.; Shi, T.; Ma, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Wei, J. Recombinant Adenovirus Expressing a Soluble Fusion Protein PD-1/CD137L Subverts the Suppression of CD8+ T Cells in HCC. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1906–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, D.C.; Odom, C.I.; Li, L.; Markert, J.M.; Roth, J.C.; Cassady, K.A.; Whitley, R.J.; Parker, J.N. Production of Bioactive Soluble Interleukin-15 in Complex with Interleukin-15 Receptor Alpha from a Conditionally-Replicating Oncolytic HSV-1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalsky, S.J.; Liu, Z.; Feist, M.; Berkey, S.E.; Ma, C.; Ravindranathan, R.; Dai, E.; Roy, E.J.; Guo, Z.S.; Bartlett, D.L. Superagonist IL-15-Armed Oncolytic Virus Elicits Potent Antitumor Immunity and Therapy That Are Enhanced with PD-1 Blockade. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chouljenko, D.V.; Ding, J.; Lee, I.F.; Murad, Y.M.; Bu, X.; Liu, G.; Delwar, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yu, S.; Samudio, I.; et al. Induction of Durable Antitumor Response by a Novel Oncolytic Herpesvirus Expressing Multiple Immunomodulatory Transgenes. Biomedicines 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Sheng, Y.; Hou, W.; Sampath, P.; Byrd, D.; Thorne, S.; Zhang, Y. CCL5-armed oncolytic virus augments CCR5-engineered NK cell infiltration and antitumor efficiency. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myers, J.A.; Miller, J.S. Exploring the NK cell platform for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarazona, R.; Lopez-Sejas, N.; Guerrero, B.; Hassouneh, F.; Valhondo, I.; Pera, A.; Sanchez-Correa, B.; Pastor, N.; Duran, E.; Alonso, C.; et al. Current progress in NK cell biology and NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 879–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, G.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, M.; Xia, M.; Jiang, A.; Wu, J.; Beltinger, C.; et al. Oncolytic measles virus enhances antitumour responses of adoptive CD8+NKG2D+ cells in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Han, J.; Chu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yi, L.; et al. A combinational therapy of EGFR-CAR NK cells and oncolytic herpes simplex virus 1 for breast cancer brain metastases. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klose, C.; Berchtold, S.; Schmidt, M.; Beil, J.; Smirnow, I.; Venturelli, S.; Burkard, M.; Handgretinger, R.; Lauer, U.M. Biological treatment of pediatric sarcomas by combined virotherapy and NK cell therapy. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heidbuechel, J.P.W.; Engeland, C.E. Oncolytic viruses encoding bispecific T cell engagers: A blueprint for emerging immunovirotherapies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlabé, P.; Sostoa, J.d.; Fajardo, C.A.; Alemany, R.; Moreno, R. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of an oncolytic adenovirus armed with an EGFR-targeted BiTE using menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells as carriers. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, L.; Morel, A.; Anceriz, N.; Rossi, B.; Blanchard-Alvarez, A.; Grondin, G.; Trichard, S.; Cesari, C.; Sapet, M.; Bosco, F.; et al. Multifunctional Natural Killer Cell Engagers Targeting NKp46 Trigger Protective Tumor Immunity. Cell 2019, 177, 1701–1713.e1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, N.M.; Ward, S.J.; Kefalas, P.; Hyllner, J. Cell-based therapy technology classifications and translational challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20150017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomer, R.; Mondejar, R.; Romero-Laorden, N.; Alfranca, A.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Quintela-Fandino, M. When should we order a next generation sequencing test in a patient with cancer? EClinicalMedicine 2020, 25, 100487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Activating | Inhibitory | Cytokine |
|---|---|---|
| Activating KIRs NKp46 NKp44 (human only) NKp30 (human only) NKG2C NKG2D NKG2E CD16 2B4 DNAM1 Ly49D, H, L (mouse only) | Inhibitory KIRs TIGIT CD96 LAG3 TIM3 PD1 KLRG1 CD161 NKG2A NKG2B Ly49A, B, C, E, G, Q (mouse only) | IL-2R IL-4R IL-10R IL-12R IL-15R IL-18R IL-21R TGF-β |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leung, E.Y.L.; McNeish, I.A. Strategies to Optimise Oncolytic Viral Therapies: The Role of Natural Killer Cells. Viruses 2021, 13, 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081450
Leung EYL, McNeish IA. Strategies to Optimise Oncolytic Viral Therapies: The Role of Natural Killer Cells. Viruses. 2021; 13(8):1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081450
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeung, Elaine Y. L., and Iain A. McNeish. 2021. "Strategies to Optimise Oncolytic Viral Therapies: The Role of Natural Killer Cells" Viruses 13, no. 8: 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081450
APA StyleLeung, E. Y. L., & McNeish, I. A. (2021). Strategies to Optimise Oncolytic Viral Therapies: The Role of Natural Killer Cells. Viruses, 13(8), 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081450






