Effects of Pegylated Interferon Alpha and Ribavirin (pegIFN-α/RBV) Therapeutic Approach on Regulatory T Cells in HCV-Monoinfected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) Isolation
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
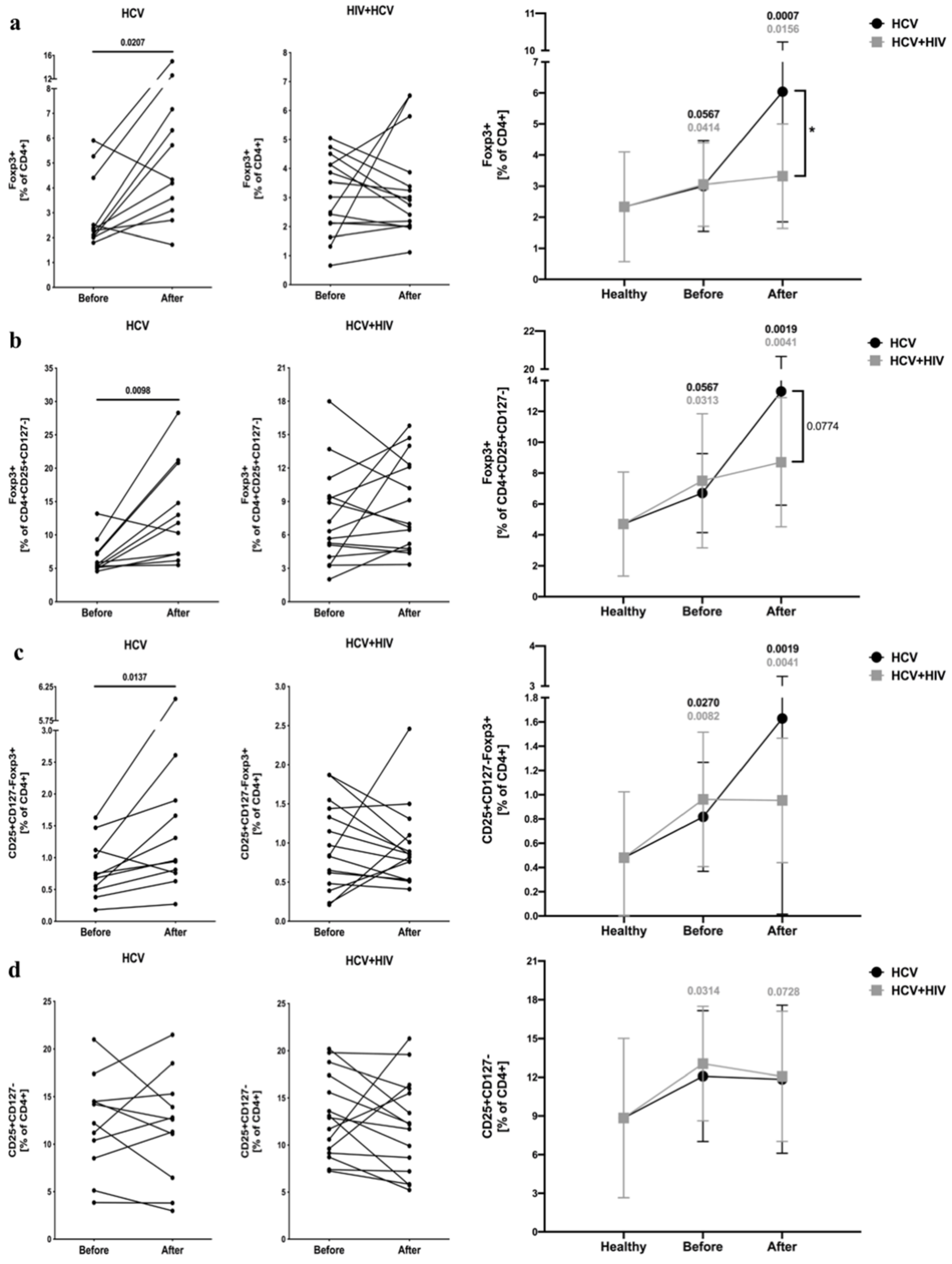
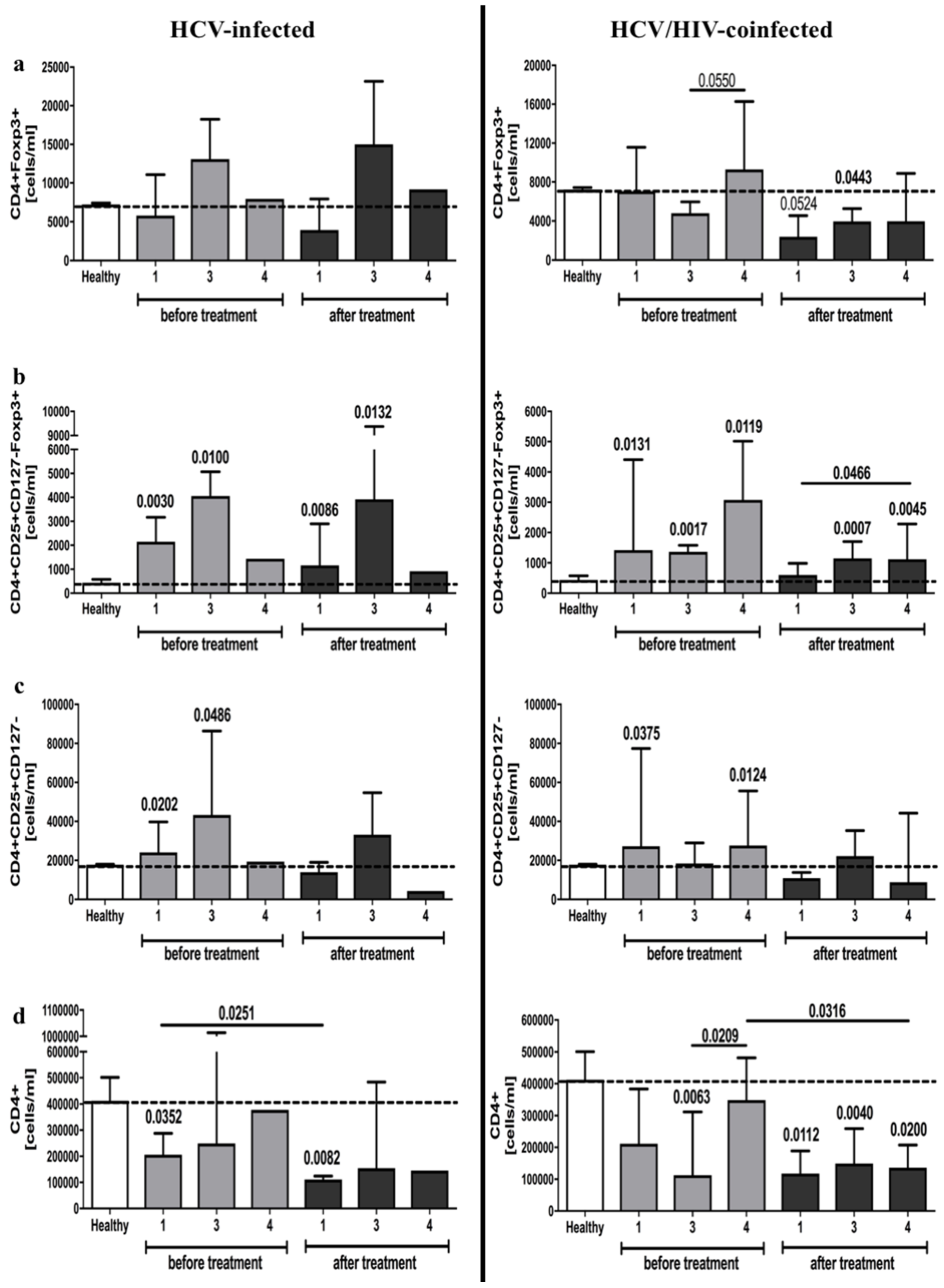
3.1. Alterations in Frequencies and Absolute Numbers of Regulatory T Cells in HCV-Infected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients in the Course of Anti-Retroviral Therapy
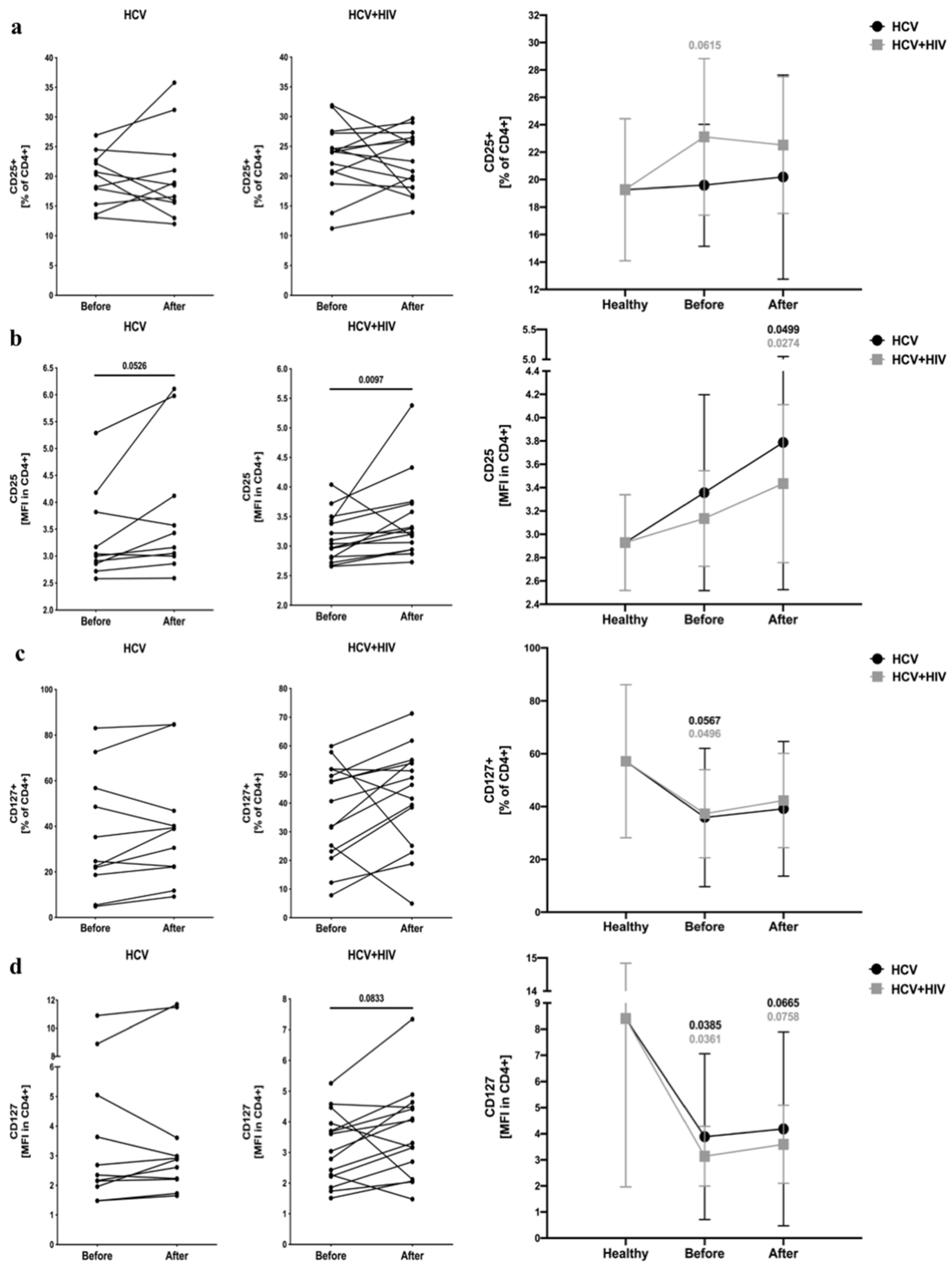
3.2. Effects of Anti-Viral Therapy on T Cell Activation- (CD25) and Development-Associated Protein (CD127) in HCV-Infected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients
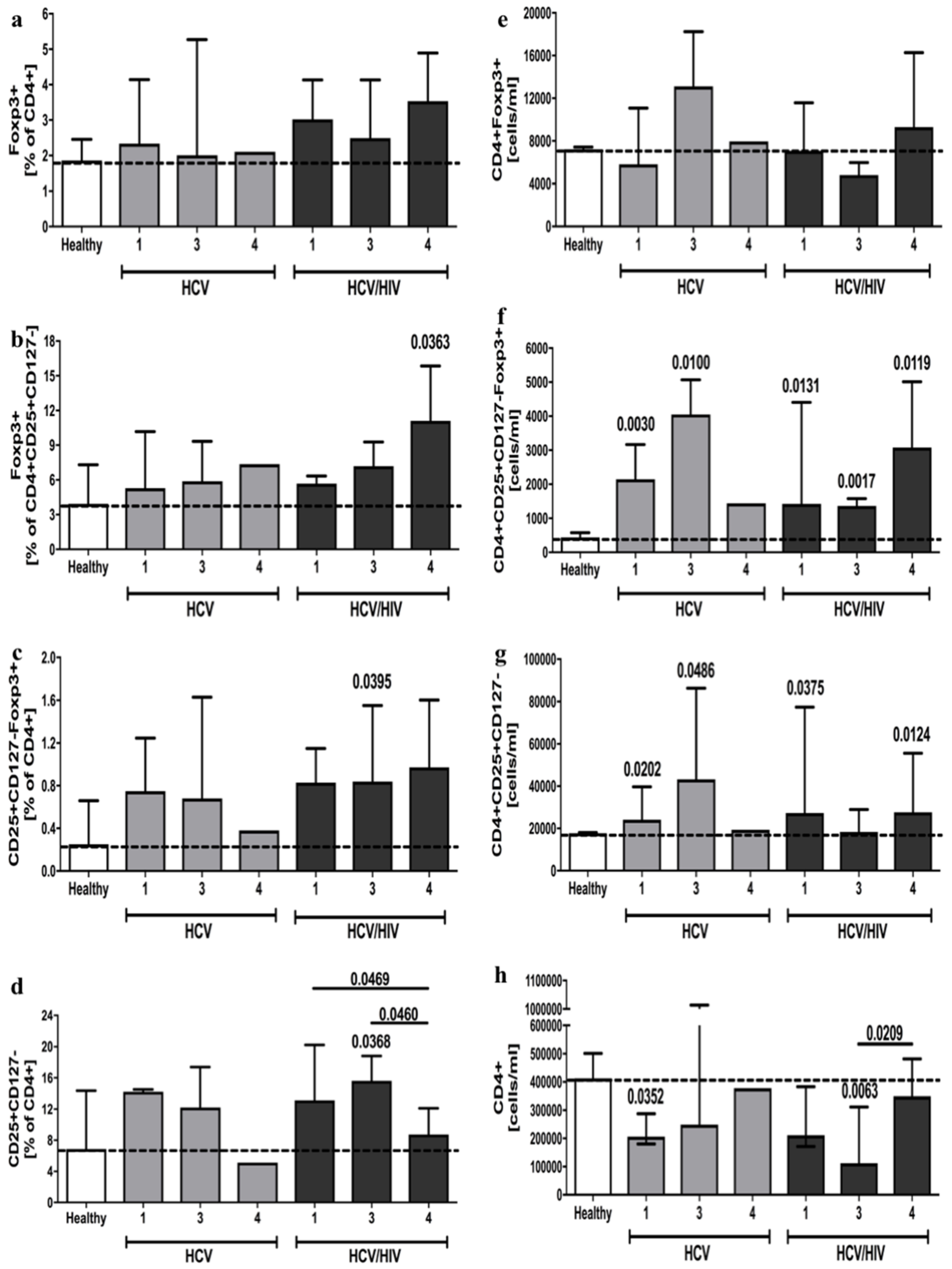
3.3. Variations in Regulatory T Cells Frequencies and Absolute Numbers among HCV-Infected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients Considering Genotype of Hepatitis C Virus
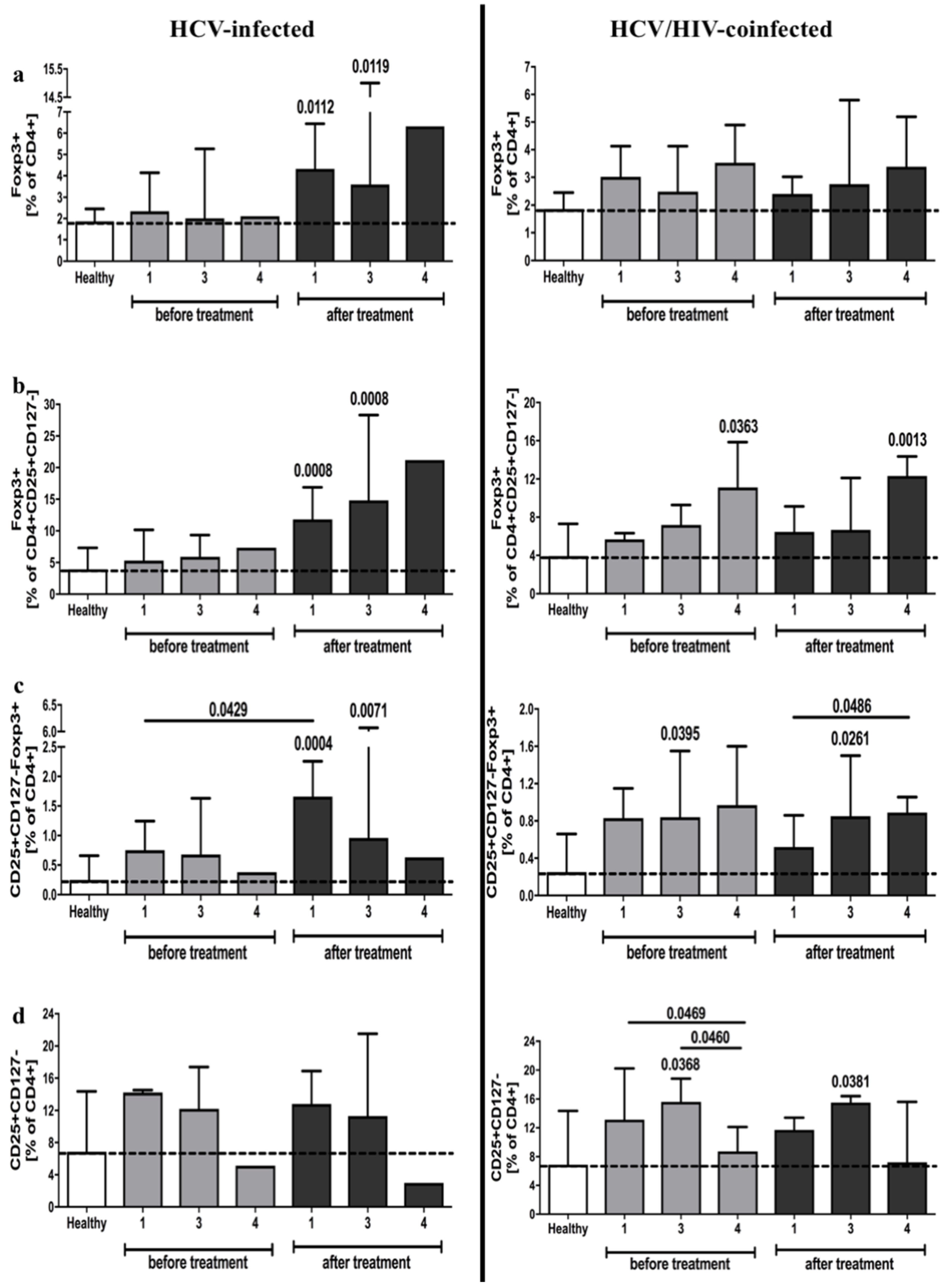
3.4. Hepatitis C Virus Genotype Influence on Differential Response of Regulatory T Cells to Anti-Viral Treatment of HCV-Infected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients
3.5. Association between Regulatory T Cells and Immunological, Biochemical and Virological Laboratory Parameters, in HCV-Infected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soriano, V.; Vispo, E.; Labarga, P.; Medrano, J.; Barreiro, P. Viral hepatitis and HIV co-infection. Antivir. Res. 2010, 85, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daar, E.S.; Lynn, H.; Donfield, S.; Gomperts, E.; Hilgartner, M.W.; Hoots, W.K.; Chernoff, D.; Arkin, S.; Wong, W.Y.; Winkler, C.A. Relation between HIV-1 and hepatitis C viral load in patients with hemophilia. J. Acquir Immune Defic. Syndr. 2001, 26, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sierra, C.; Arizcorreta, A.; Díaz, F.; Roldán, R.; Martín-Herrera, L.; Pérez-Guzmán, E.; Girón-González, J.A. Progression of chronic hepatitis C to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients coinfected with hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchante, N.; Girón-González, J.A.; González-Serrano, M.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; García-García, J.A.; Arizcorreta, A.; Ruiz-Morales, J.; Cano-Lliteras, P.; Lozano, F.; Martínez-Sierra, C.; et al. Survival and prognostic factors of HIV-infected patients with HCV-related end-stage liver disease. Aids 2006, 20, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arminio Monforte, A.; Cozzi-Lepri, A.; Castagna, A.; Antinori, A.; De Luca, A.; Mussini, C.; Caputo, S.L.; Arlotti, M.; Magnani, G.; Pellizzer, G.; et al. Risk of developing specific AIDS-defining illnesses in patients coinfected with HIV and hepatitis C virus with or without liver cirrhosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hyrcza, M.D.; Kovacs, C.; Loutfy, M.; Halpenny, R.; Heisler, L.; Yang, S.; Wilkins, O.; Ostrowski, M.; Der, S.D. Distinct transcriptional profiles in ex vivo CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are established early in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and are characterized by a chronic interferon response as well as extensive transcriptional changes in CD8+ T cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, A.; Al-Harthi, L.; Christensen, S.; Mack, W.; Cohen, M.; Landay, A. CD8(+) T cell activation in women coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and hepatitis C virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, A.; Groopman, J.; Ganju, R. Underlying pathophysiology of HCV infection in HIV-positive drug users. J. Addict. Dis. 2008, 27, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billerbeck, E.; Thimme, R. CD8+regulatory T cells in persistent human viral infections. Hum. Immunol. 2008, 69, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecher-Allan, C.; Viglietta, V.; Hafler, D. Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmer, U.; He, H.; Messer, R.J.; Schimmer, S.; Olbrich, A.R.; Ohlen, C.; Greenberg, P.D.; Stromnes, I.M.; Iwashiro, M.; Sakaguchi, S.; et al. Functional impairment of CD8(+) T cells by regulatory T cells during persistent retroviral infection. Immunity 2004, 20, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boasso, A.; Vaccari, M.; Hryniewicz, A.; Fuchs, D.; Nacsa, J.; Cecchinato, V.; Andersson, J.; Franchini, G.; Shearer, G.M.; Chougnet, C. Regulatory T-cell markers, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, and virus levels in spleen and gut during progressive simian immunodeficiency virus infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11593–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Kang, W.; Sun, Y. HCV coinfection does not alter the frequency of regulatory T cells or CD8+ T cell immune activation in chronically infected HIV+ Chinese subjects. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartling, H.J.; Gaardbo, J.C.; Ronit, A.; Knudsen, L.S.; Ullum, H.; Vainer, B.; Clausen, M.R.; Skogstrand, K.; Gerstoft, J.; Nielsen, S.D. CD4⁺ and CD8⁺ regulatory T cells (Tregs) are elevated and display an active phenotype in patients with chronic HCV mono-infection and HIV/HCV co-infection. Scand. J. Immunol. 2012, 76, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Li, Y.; Nakamoto, N.; Amorosa, V.K.; Valiga, M.E.; Chang, K.M. Induction of Multiple Immune Regulatory Pathways with Differential Impact in HCV/HIV Coinfection. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, C.; Krämer, B.; Schulte, D.; Coenen, M.; Mauss, S.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Oldenburg, J.; Nattermann, J.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Spengler, U. Effects of HCV co-infection on apoptosis of CD4+ T-cells in HIV-positive patients. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, M.; Odueyungbo, A.; Yang, H.; Saeed, S.; Klein, M. Study CC-iC. Impact of hepatitis C viral replication on CD4(+) T-lymphocyte progression in HIV-HCV coinfection before and after antiretroviral therapy. Aids 2010, 24, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.; Donkova-Petrini, V.; Caccavelli, L.; Balbo, M.; Carbonneil, C.; Levy, Y. Human immunodeficiency virus-driven expansion of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells, which suppress HIV-specific CD4 T-cell responses in HIV-infected patients. Blood 2004, 104, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ikeda, F.; Stadanlick, J.; Nunes, F.; Alter, H.; Chang, K. Suppression of HCV-specific T cells without differential hierarchy demonstrated ex vivo in persistent HCV infection. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatrakchi, N.; Graham, C.; van der Vliet, H.; Sherman, K.; Exley, M.; Koziel, M. Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific CD8(+) cells produce transforming growth factor beta that can suppress HCV-specific T-cell responses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5882–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunoya, J.; Washburn, M.; Kovalev, G.; Su, L. Regulatory T Cells Prevent Liver Fibrosis during HIV Type 1 Infection in a Humanized Mouse Model. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Putnam, A.L.; Xu-Yu, Z.; Szot, G.L.; Lee, M.R.; Zhu, S.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Kapranov, P.; Gingeras, T.R.; Fazekas de St Groth, B.; et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevyrev, D.; Tereshchenko, V. Treg Heterogeneity, Function, and Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, Z.A.; Nouraie, M.; Begum, R.; Afsari, A.; Shokrani, B.; Lee, E.; Laiyemo, A.O.; Brim, H.; Ashktorab, H. Factors influencing treatment outcome in hepatitis C virus minority patients at an inner-city hospital: A STROBE-complaint article. Medicine 2020, 99, e19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Gupta, P.; Irshad, K. Molecular targeting of antiviral drugs used against hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatoma Res. 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hesamizadeh, K.; Tavakoli, A.; Nikbin, M. Peg-interferon Plus Ribavirin Combination Therapy in HCV Mono-infected and HCV/HIV Co-infected Patients in Iran. Med. J. Islam Repub. Iran 2019, 33, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghany, M.; Strader, D.; Thomas, D.; Seeff, L. Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment of Hepatitis C: An Update. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1335–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallón, N.I.; López, M.; Soriano, V.; García-Samaniego, J.; Romero, M.; Labarga, P.; García-Gasco, P.; González-Lahoz, J.; Benito, J.M. Level, phenotype and activation status of CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus and/or hepatitis C virus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 155, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, D.; Paroli, M.; Francavilla, V.; Videtta, M.; Morrone, S.; Labbadia, G.; Cerino, A.; Mondelli, M.U.; Barnaba, V. PD-L1 negatively regulates CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs by limiting STAT-5 phosphorylation in patients chronically infected with HCV. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, R.; Tu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Firpi, R.J.; Rosen, H.R.; Liu, C.; Nelson, D.R. An immunomodulatory role for CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T lymphocytes in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebinuma, H.; Nakamoto, N.; Li, Y.; Price, D.A.; Gostick, E.; Levine, B.L.; Tobias, J.; Kwok, W.W.; Chang, K.M. Identification and in vitro expansion of functional antigen-specific CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5043–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.K.; Donaldson, E.; Van der Kleij, T.; Dixon, L.; Fisher, M.; Tibble, J.; Gilleece, Y.; Klenerman, P.; Banham, A.H.; Howard, M.; et al. Quantification of hepatic Foxp3+ T-lymphocytes in HIV/hepatitis C coinfection. J. Viral. Hepat. 2014, 21, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettler, T.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Panther, E.; Urbani, S.; Ferrari, C.; Blum, H.E.; von Weizsäcker, F.; Thimme, R. T cells with a CD4+CD25+ regulatory phenotype suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7860–7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinter, A.L.; Hennessey, M.; Bell, A.; Kern, S.; Lin, Y.; Daucher, M.; Planta, M.; McGlaughlin, M.; Jackson, R.; Ziegler, S.F.; et al. CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells from the peripheral blood of asymptomatic HIV-infected individuals regulate CD4(+) and CD8(+) HIV-specific T cell immune responses in vitro and are associated with favorable clinical markers of disease status. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietze, K.; Zelinskyy, G.; Liu, J.; Kretzmer, F.; Schimmer, S.; Dittmer, U. Combining Regulatory T Cell Depletion and Inhibitory Receptor Blockade Improves Reactivation of Exhausted Virus-Specific CD8(+) T Cells and Efficiently Reduces Chronic Retroviral Loads. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.K.; Abdel-Mohsen, M.; Guatelli, J.; Skasko, M.; Monto, A.; Fujimoto, K.; Yukl, S.; Greene, W.C.; Kovari, H.; Rauch, A.; et al. Role of retroviral restriction factors in the interferon-α-mediated suppression of HIV-1 in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunemi, S.; Iwasaki, T.; Imado, T.; Higasa, S.; Kakishita, E.; Shirasaka, T.; Sano, H. Relationship of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells to immune status in HIV-infected patients. Aids 2005, 19, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, K.; Abe, H.; Kubo, Y.; Kitahara, T.; Aizawa, R.; Matsuoka, M.; Aizawa, Y. Expansion of CD4(+)CD25(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells in hepatitis C virus-related chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, B.; Jones, R.B.; Sakhdari, A.; Sheth, P.M.; Clayton, K.; Yue, F.Y.; Gyenes, G.; Wong, D.; Klein, M.B.; Saeed, S.; et al. HCV-specific T cells in HCV/HIV co-infection show elevated frequencies of dual Tim-3/PD-1 expression that correlate with liver disease progression. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2493–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Yokosuka, O.; Imazeki, F.; Tanaka, M.; Shino, Y.; Shimada, H.; Tomonaga, T.; Nomura, F.; Nagao, K.; Ochiai, T.; et al. Inhibition of subgenomic hepatitis C virus RNA in Huh-7 cells: Ribavirin induces mutagenesis in HCV RNA. J. Viral. Hepat. 2004, 11, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolacchi, F.; Sinistro, A.; Ciaprini, C.; Demin, F.; Capozzi, M.; Carducci, F.C.; Drapeau, C.M.; Rocchi, G.; Bergamini, A. Increased hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific CD4+CD25+ regulatory T lymphocytes and reduced HCV-specific CD4+ T cell response in HCV-infected patients with normal versus abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 144, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, R.; Meyer, K.; Moriyama, M.; Kato, N.; Yokosuka, O.; Ray, R.B.; Aurora, R.; Ray, R.; Kanda, T. Rapid hepatitis C virus clearance by antivirals correlates with immune status of infected patients. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.; Rubio, R.; Lazzarin, A.; Romanova, S.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Conway, B.; Molina, J.M.; Xu, D.; Srinivasan, S.; Portsmouth, S. Safety and Efficacy of Pegylated Interferon Lambda, Ribavirin, and Daclatasvir in HCV and HIV-Coinfected Patients. J. Interferon. Cytokine Res. 2017, 37, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgard, O.; Bjøro, K.; Hellum, K.B.; Myrvang, B.; Ritland, S.; Skaug, K.; Raknerud, N.; Bell, H. Treatment with pegylated interferon and ribavarin in HCV infection with genotype 2 or 3 for 14 weeks: A pilot study. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, R.; Kanda, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Haga, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Yasui, S.; Jiang, X.; Wu, S.; Arai, M.; Yokosuka, O. Natural interferon-beta treatment for patients with chronic hepatitis C in Japan. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grubczak, K.; Grzeszczuk, A.; Groth, M.; Hryniewicz, A.; Kretowska-Grunwald, A.; Flisiak, R.; Moniuszko, M. Effects of Pegylated Interferon Alpha and Ribavirin (pegIFN-α/RBV) Therapeutic Approach on Regulatory T Cells in HCV-Monoinfected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients. Viruses 2021, 13, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081448
Grubczak K, Grzeszczuk A, Groth M, Hryniewicz A, Kretowska-Grunwald A, Flisiak R, Moniuszko M. Effects of Pegylated Interferon Alpha and Ribavirin (pegIFN-α/RBV) Therapeutic Approach on Regulatory T Cells in HCV-Monoinfected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients. Viruses. 2021; 13(8):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081448
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrubczak, Kamil, Anna Grzeszczuk, Monika Groth, Anna Hryniewicz, Anna Kretowska-Grunwald, Robert Flisiak, and Marcin Moniuszko. 2021. "Effects of Pegylated Interferon Alpha and Ribavirin (pegIFN-α/RBV) Therapeutic Approach on Regulatory T Cells in HCV-Monoinfected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients" Viruses 13, no. 8: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081448
APA StyleGrubczak, K., Grzeszczuk, A., Groth, M., Hryniewicz, A., Kretowska-Grunwald, A., Flisiak, R., & Moniuszko, M. (2021). Effects of Pegylated Interferon Alpha and Ribavirin (pegIFN-α/RBV) Therapeutic Approach on Regulatory T Cells in HCV-Monoinfected and HCV/HIV-Coinfected Patients. Viruses, 13(8), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081448






