Prevalence of Orthohantavirus-Reactive Antibodies in Humans and Peri-Domestic Rodents in Northern Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
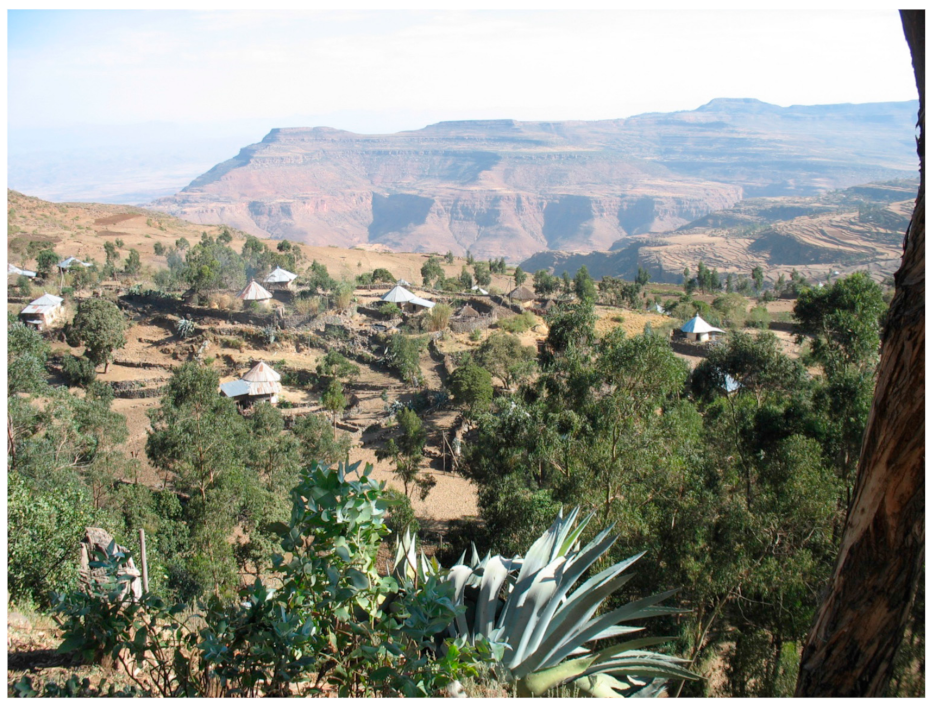
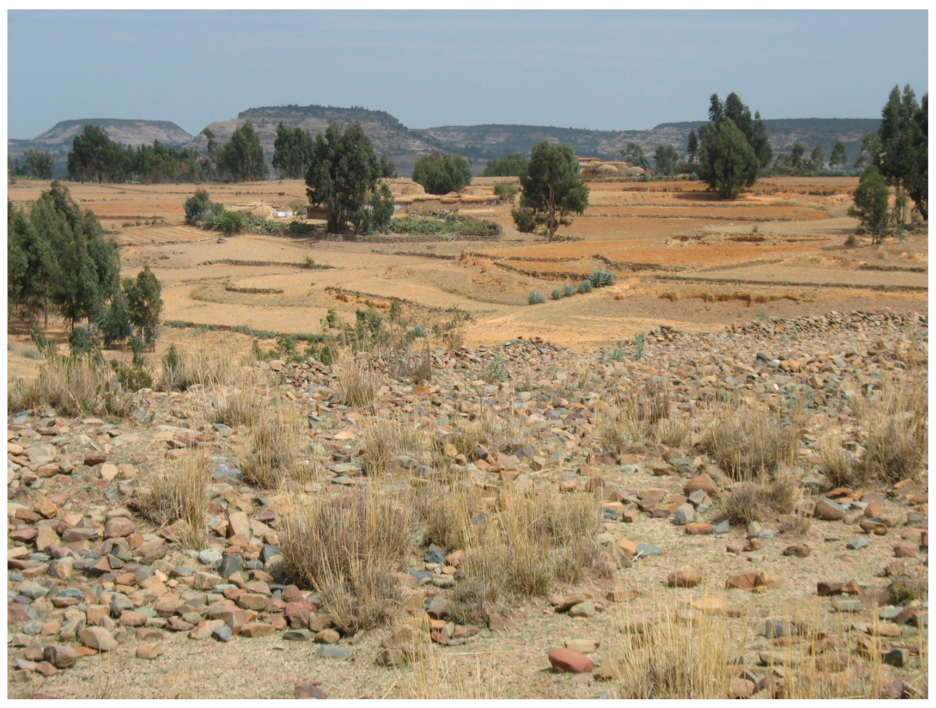
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Small Mammals Sampling
2.3. Human Blood Sampling and Questionnaire
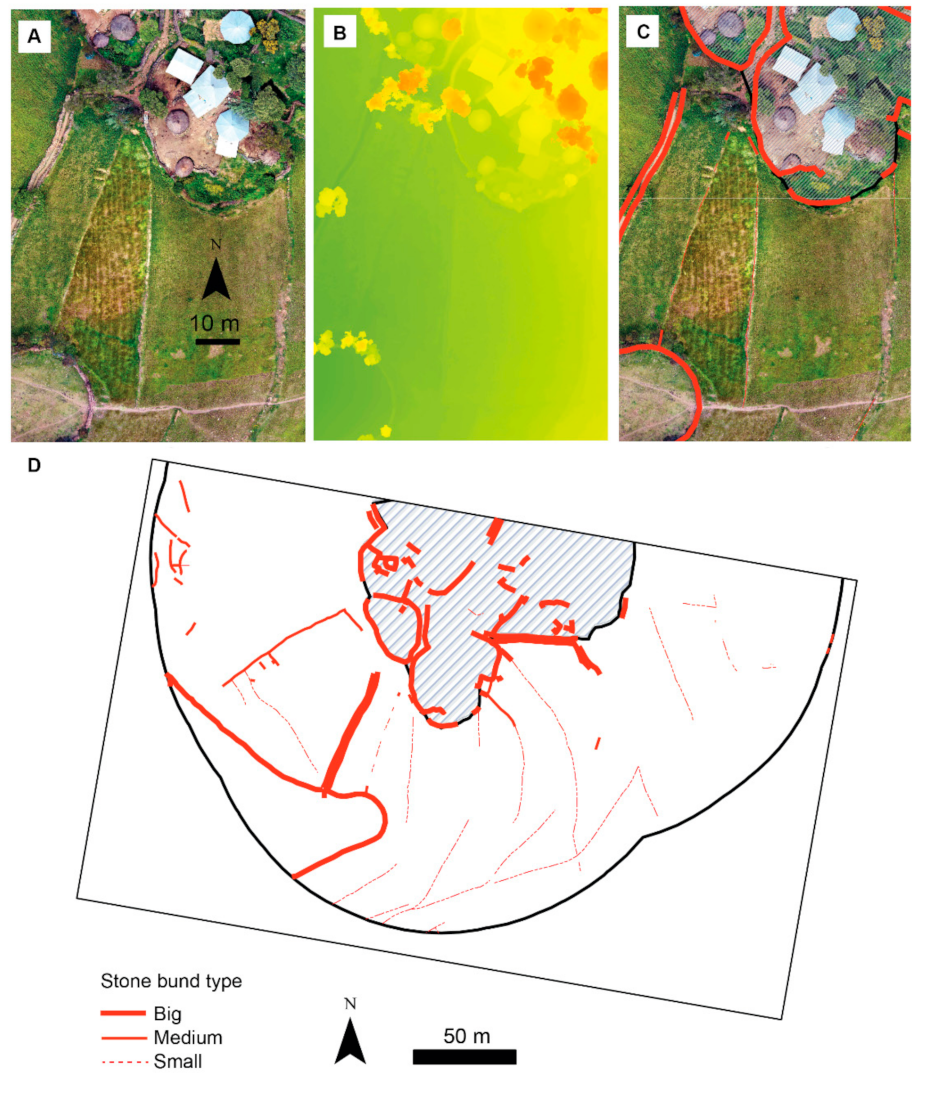
2.4. Assessment of Variability in Stone Bund Density
2.5. Viral Screening
2.5.1. Detection of Human IgG Antibodies
2.5.2. Detection of Rodent IgG Antibodies
2.5.3. Viral RNA Analyses
2.5.4. Risk Factors for Human Infection
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Small Mammals
3.2. Prevalence of TIGV in Small Mammals
3.3. Seroprevalence in Humans
3.4. Risk Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Small Mammal Abundance and Diversity
4.2. Tigray Orthohantavirus: Seroprevalence and Risk Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmaljohn, C.; Hjelle, B. Hantaviruses: A global disease problem. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmuson, J.; Andersson, C.; Norrman, E.; Haney, M.; Evander, M.; Ahlm, C. Time to revise the paradigm of hantavirus syndromes? Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome caused by European hantavirus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 30, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, J.; Maes, P.; Van Ranst, M. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in the new, and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in the old world: Paradi(se)gm lost or regained? Virus Res. 2014, 187, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, J.; LeDuc, J.W.; Lloyd, G.; Reynes, J.M.; McElhinney, L.; Van Ranst, M.; Lee, H.W. Wild rats, laboratory rats, pet rats: Global Seoul hantavirus disease revisited. Viruses 2019, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempa, B.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Auste, B.; Aniskin, V.; Meisel, H.; Denys, C.; Koivogui, L.; ter Meulen, J.; Krüger, D.H. Comments to Author. Hantavirus in African Wood Mouse, Guinea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, M.M.; Dieng, I.; Granjon, L.; Lucaccioni, H.; Sow, A.; Ndiaye, O.; Faye, M.; Bâ, K.; Bâ, Y.; Diallo, M.; et al. Seoul Orthohantavirus in Wild Black Rats, Senegal, 2012–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 10, 2460–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meheretu, Y.; Čížková, D.; Tĕšíková, J.; Welegerima, K.; Tomas, Z.; Kidane, D.; Girmay, K.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Bryja, J.; Günther, S.; et al. High Diversity of RNA Viruses in Rodents, Ethiopia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2047–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempa, B.; Koivogui, L.; Sylla, O.; Koulemou, K.; Auste, B.; Krüger, D.H.; ter Meulen, J. Serological Evidence of Human Hantavirus Infections in Guinea, West Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempa, B.; Koulemou, K.; Auste, B.; Emmerich, P.; Thomé-Bolduan, C.; Günther, S.; Koivogui, L.; Krüger, D.H.; Fichet-Calvet, E. Seroepidemiological study reveals regional co-occurrence of Lassa- and Hantavirus antibodies in Upper Guinea, West Africa. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2013, 18, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, P.T.; Klempa, B.; Ithete, N.L.; Auste, B.; Mfune, J.K.E.; Hoveka, J.; Matthee, S.; Preiser, W.; Krugera, D.H. Hantaviruses in Africa. Virus Res. 2014, 187, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffinger, D.M.; Nofchissey, R.; Jacobson, M.; Goade, D. Serological survey of hantavirus in adult humans living in Tanzania. Investig. Med. 2006, 54, S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, P.; Tia, M.; Alabi, A.; Anon, J.C.; Auste, B.; Essbauer, S.; Gnionsahe, A.; Kigninlman, H.; Klempa, B.; Kraef, C.; et al. Human Infections by Non-Rodent Associated Hantaviruses in Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.N.; Gu, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Arai, S.; Yanagihara, R. Reconstructing the evolutionary origins and phylogeography of hantaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Těšíková, J.; Bryjová, A.; Bryja, J.; Lavrenchenko, L.A.; Goüy de Bellocq, J. Hantavirus Strains in East Africa Related to Western African Hantaviruses. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meheretu, Y.; Stanley, W.T.; Craig, E.W.; Goüy de Bellocq, J.; Bryja, J.; Leirs, L.; Pahlmann, M.; Günther, S. Tigray Orthohantavirus Infects Two Related Rodent Species Adapted to Different Elevations in Ethiopia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, D.H.; Ulrich, R.; Lundkvist, Å. Hantavirus infections and their prevention. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.O.; Pérez-Sautu, U.; Bellomo, C.M.; Prieto, K.; Iglesias, A.; Coelho, R.; Periolo, N.; Domenech, I.; Talmon, G.; Hansen, R.; et al. Person-to-person transmission of andes virus in hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, Argentina, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; George, D.; Pepin, K.M.; Pitzer, V.E.; Pulliam, J.R.C.; Dobson, A.P.; Hudson, P.J.; Grenfell, B.T. Epidemic Dynamics at the Human-Animal Interface. Science 2009, 326, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Hörnfeldt, B.; Evander, M.; Magnusson, M.; Olsson, G.; Ecke, F. Dynamics and Drivers of Hantavirus Prevalence in Rodent Populations. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Ecke, F.; Evander, M.; Magnusson, M.; Hörnfeldt, B. Declining ecosystem health and the dilution effect. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeijenbier, M.; Wagenaar, J.; Goris, M.; Martina, B.; Henttonen, H.; Vaheri, A.; Reusken, C.; Hartskeerl, R.; Osterhaus, A.; Van Gorp, E. Rodent-borne hemorrhagic fevers: Under recognized; widely spread and preventable epidemiology, diagnostics and treatment. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 39, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meheretu, Y.; Leirs, H.; Welegerima, K.; Breno, M.; Tomas, Z.; Kidane, D.; Girmay, K.; Goüy de Bellocq, J. Bartonella Prevalence and Genetic Diversity in Small Mammals from Ethiopia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welegerima, K.; Meheretu, Y.; Haileselassie, T.H.; Gebre, B.; Kidane, D.; Massawe, A.W.; Mbije, N.E.; Makundi, R.H. Abundance and microhabitat use of rodent species in crop fields and bushland in Ethiopia. J. Vertebr. Biol. 2020, 69, 20054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goüy de Bellocq, J.; Těšíková, J.; Meheretu, Y.; Čížková, D.; Bryjová, A.; Leirs, L.; Bryja, B. Complete genome characterisation and phylogenetic position of Tigray hantavirus from the Ethiopian white-footed mouse, Stenocephalemys albipes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 45, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryja, J.; Kostin, D.; Meheretu, Y.; Šumbera, R.; Bryjová, A.; Kasso, M.; Mikula, O.; Lavrenchenko, L.A. Reticulate Pleistocene evolution of Ethiopian rodent genus along remarkable altitudinal gradient. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 118, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizerovská, D.; Mikula, O.; Meheretu, Y.; Bartáková, V.; Bryjová, A.; Kostin, D.S.; Šumbera, R.; Lavrenchenko, L.A.; Bryja, J. Integrative taxonomic revision of the Ethiopian endemic rodent genus Stenocephalemys (Muridae: Murinae: Praomyini) with the description of two new species. J. Vertebr. Biol. 2020, 69, 20031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meheretu, Y.; Sluydts, V.; Welegerima, K.; Bauer, H.; Teferi, M.; Yirga, G.; Mulungu, L.; Haile, M.; Nyssen, J.; Deckers, J.; et al. Rodent abundance, stone bund density and its effects on crop damage in the Tigray highlands, Ethiopia. Crop Prot. 2014, 55, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancampenhout, K.; Nyssen, J.; Gebremichael, D.; Deckers, J.; Poesen, J.; Haile, M.; Moeyersons, J. Stone bunds for soil conservation in the northern Ethiopian highlands: Impacts on soil fertility and crop yield. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 90, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuria, W.; Veldkamp, E.; Haile, M.; Gebrehiwot, K.; Muys, B.; Nyssen, J. Effectiveness of exclosures to control soil erosion and local community perception on soil erosion in Tigray, Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 4, 365–377. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.E.; Lacher, T.E.; Mittermeier, R.A. (Eds.) Handbook of the Mammals of the World; Rodents II; Lynx Editions: Barcelona, Spain, 2017; Volume 7, p. 1008. [Google Scholar]
- Bryja, J.; Meheretu, Y.; Šumbera, R.; Lavrenchenko, L.A. Annotated checklist, taxonomy and distribution of rodents in Ethiopia. Folia Zool. 2019, 68, 117–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindkvist, M.; Näslund, J.; Ahlm, C.; Bucht, G. Cross-reactive and serospecific epitopes of nucleocapsid proteins of three hantaviruses: Prospects for new diagnostic tools. Virus Res. 2008, 137, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evander, M.; Eriksson, I.; Pettersson, L.; Juto, P.; Ahlm, C.; Olsson, G.E.; Bucht, G.; Allard, A. Puumala hantavirus viremia diagnosed by real-time reverse transcriptase PCR using samples from patients with hemorrhagic fever and renal syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meheretu, Y.; Welegerima, K.; Deckers, S.; Raes, D.; Makundi, R.; Leirs, H. Farmers’ perspectives of rodent damage and management from the highlands of Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstedt Oscarsson, K.; Brorstad, A.; Baudin, M.; Lindberg, A.; Forssén, A.; Evander, M.; Eriksson, M.; Ahlm, C. Human Puumala hantavirus infection in northern Sweden; increased seroprevalence and association to risk and health factors. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wube, T.; Bekele, A. Habitat preference of the African grass rat, Arvicanthis dembeensis (Rodentia, Muridae), in Koka, Central Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the 8th African Small Mammals Symposium, Paris, France, 5–9 July 1999; Denys, C., Granjon, L., Poulet, A., Eds.; Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) Editions: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Meheretu, Y.; Fanos, A.; Dawit, K.; Kiros, W. Stored-grain losses and management practices among smallholder cereal farmers in Northern Ethiopia. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Type of Data Collected | Categories | Definition/Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serostatus (dependent) | Categorical, via IFA analyses of blood samples | Positive Negative | Samples containing orthohantavirus-reactive antibodies were considered to be positive |
| Study area | Categorical, via Questionnaire | Atsbi Hagere Selam | The two areas where TIGV was first discovered in rodents |
| Gender | Categorical, via Questionnaire | Women Men | |
| Age | Quantitative, discrete, via questionnaire categorized in statistical analyses | 18–40 years 41–60 years 61–80 years | |
| Stone bund age | Categorical, via questionnaire | ≤10 years >10 years | Age of majority of stone bunds that belonged to the household. Data collected per household |
| Stone bund density (SBD) | Quantitative, continuous. Assessed via GPS point and GIS. | - | Length (m) of stone bunds within 100 m from human dwellings. Data assessed per household |
| Cat | Categorical, via questionnaire | Yes No | Presence of domestic cat(s) in the household |
| Sightings of rodents | Categorical, via questionnaire | In house or storage Never in house or storage | Location of where participants did see rodents |
| Contact with rodents | Categorical, via questionnaire | Never touch Touch < once/year Touch ≥ once/year | Whether participants ever touched rodents, dead or alive, and in such case how often |
| Rodent bite | Categorical, via questionnaire | Yes No | Whether participants had ever been bitten by a rodent |
| Astbi | Hagere Selam | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Mammals Abundance | ||||||||
| Species | LSBD | HSBD | Enclosure | Total | LSBD | HSBD | Enclosure | Total |
| Acomys cahirinus (North East African Spiny Mouse) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 (12.5) | 6 (12.5) |
| Arvicanthis niloticus (African Grass Rat) | 2 (3.57) | 11 (19.64) | 12 (21.43) | 25 (44.64) | 5 (10.42) | 2 (4.17) | - | 7 (14.58) |
| Crocidura olivieri (African Giant Shrew) | - | - | 4 (7.14) | 4 (7.14) | 2 (4.17) | 3 (6.25) | - | 5 (10.42) |
| Dendromus mystacalis (Chestnut African Climbing Mouse) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 (2.08) | 1 (2.08) |
| Mastomys awashensis (Awash Multimammate Mouse) | - | - | - | - | 3 (6.25) | 1 (2.08) | - | 4 (8.33) |
| Mus proconodon (Rhoads’s Pygmy Mouse) | 4 (7.14) | 2 (3.57) | 11 (19.64) | 17 (30.36) | 4 (8.33) | 6 (12.5) | - | 10 (20.83) |
| Rattus rattus (Roof Rat) | - | - | 1 (1.79) | 1 (1.79) | - | 1 (2.08) | - | 1 (2.08) |
| Stenocephalemys albipes (White-footed Ethiopian Rat) | 2 (3.57) | 5 (8.93) | 2 (3.57) | 9 (16.07) | 6 (12.5) | 6 (12.5) | 2 (4.17) | 14 (29.16) |
| Total | 10 (17.86) | 18 (32.14) | 28 (50) | 56 (100) | 20 (41.67) | 19 (39.58) | 9 (18.75) | 48 (100) |
| Species | Atsbi | Hagere Selam | Overall | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Post-Rainy | Total | Dry | Post-Rainy | Total | ||
| A. cahirinus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| A. niloticus | 19 | 6 | 25 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 32 |
| C. olivieri | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 9 |
| D. mystacalis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| M. awashensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| M. proconodon | 8 | 9 | 17 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 27 |
| R. rattus | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| S. albipes | 9 | 0 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 14 | 23 |
| Total | 36 | 20 | 56 | 24 | 24 | 48 | 104 |
| Independent Variable | Characteristics | Sample Size (% of Study Population) | Seropositive No. (%) | Logistic Regression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Study Population | Only Atsbi Population * | ||||||||
| Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI of OR | p-Value | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI of OR | p-Value | ||||
| Study population | Overall | 114 (100) | 6 (5.26) | 7.27 | 0.82–64.4 | 0.075 | |||
| Study area | Atsbi | 49 (43) | 5 (10.20) | 7.27 | 0.82–64.4 | 0.075 | |||
| Hagere selam | 65 (57) | 1 (1.54) | 1 | - | - | ||||
| Gender | Women | 78 (68) | 5 (6.4) | 2.40 | 0.27–12.3 | 0.443 | 1.9 | 0.19–18.3 | 0.592 |
| Men | 36 (32) | 1 (2.3) | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | |
| Age | 18–40 | 57 (50) | 2 (4.0) | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| 41–60 | 35 (31) | 2 (5.7) | 1.67 | 0.22–12.4 | 0.618 | 0.5 | 0.04–6.02 | 0.585 | |
| 61–80 | 22 (19) | 2 (9.1) | 2.75 | 0.36–20.8 | 0.328 | 2.25 | 0.27–18.9 | 0.455 | |
| Stone bund age (n = 108 **) | ≤10 year | 37 (34) | 4 (10.8) | 8.48 | 0.91–79.9 | 0.060 | 5.25 | 0.50–54.8 | 0.166 |
| >10 year | 71 (66) | 1 (1.4) | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | |
| Cat | Yes | 69 (61) | 4 (5.7) | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| No | 45 (39) | 2 (4.4) | 0.76 | 0.13–4.31 | 0.753 | 5.25 | 0.39–71.4 | 0.213 | |
| Contact with rodents | Never touch | 72 (63) | 4 (5.6) | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| Touch < once/year | 35 (31) | 1 (2.3) | 0.50 | 0.05–4.65 | 0.542 | 0.42 | 0.04–4.38 | 0.469 | |
| Touch ≥ once/year | 7 (6) | 1 (14.3) | 2.83 | 0.27–29.5 | 0.384 | 8.00 | 0.39–164 | 0.177 | |
| Rodent bite (n = 113 ***) | Yes | 9 (8) | 1 (11.1) | 2.48 | 0.26–23.8 | 0.443 | 1.32 | 0.13 –13.7 | 0.815 |
| No | 104 (92) | 5 (4.8) | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | |
| SBD within 100 m from Houses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max | Atsbi | Hagere Selam | T-Test (Ho: diff = 0) | ||
| (±95% CI) | (±95% CI) | T | p-value | ||
| All samples (n = 113 *) | 163–2033 | 591 (±79) | 1300 (±87) | −11.7 | 0.000 |
| Seropositives | Seronegatives | ||||
| Atsbi (n = 49) | 163–1165 | 442 (±199, n = 5) | 608 (±86, n = 44) | 1.99 | 0.085 |
| Hagere Selam (n = 64 *) | 561–2033 | 1504 (n = 1) | 1297 (±88, n = 63) | −4.96 | 0.000 |
| Type | Hagare Selam | Atsbi | Density Difference | Length Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (m/ha) | Length (m) | Density (m/ha) | Length (m) | ||||
| Outside village | Total | 396.91 | 1803.02 | 437.92 | 4628.14 | −41.01 | −2825.12 |
| In village | Total | 134.08 | 609.08 | 91.17 | 963.48 | 42.91 | −354.40 |
| Overall | 455.87 | 2070.88 | 461.34 | 4875.66 | −5.47 | −2804.78 | |
| Outside village | Small | 176.00 | 799.53 | 63.31 | 669.09 | 112.69 | 130.44 |
| Medium | 57.44 | 260.94 | 206.23 | 2179.50 | −148.79 | −1918.56 | |
| Big | 163.46 | 742.55 | 168.38 | 1779.54 | −4.92 | −1036.99 | |
| In village | Small | 1.93 | 8.77 | - | - | - | 8.77 |
| Medium | - | - | 8.22 | 86.87 | - | −86.87 | |
| Big | 132.15 | 600.31 | 82.95 | 876.61 | 49.2 | −276.30 | |
| Fishers Exact Test | Total Study Population | Only Atsbi Population * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sero + | Sero - | Sero + | Sero - | ||
| Sightings of rodents | In house and storage | 6 | 88 | 5 | 41 |
| Never in house or storage | 0 | 20 | 0 | 3 | |
| p-value | p = 0.588 | p = 0.719 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meheretu, Y.; Granberg, Å.; Berhane, G.; Khalil, H.; Lwande, O.W.; Mitiku, M.; Welegerima, K.; Bellocq, J.G.d.; Bryja, J.; Abreha, H.; et al. Prevalence of Orthohantavirus-Reactive Antibodies in Humans and Peri-Domestic Rodents in Northern Ethiopia. Viruses 2021, 13, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061054
Meheretu Y, Granberg Å, Berhane G, Khalil H, Lwande OW, Mitiku M, Welegerima K, Bellocq JGd, Bryja J, Abreha H, et al. Prevalence of Orthohantavirus-Reactive Antibodies in Humans and Peri-Domestic Rodents in Northern Ethiopia. Viruses. 2021; 13(6):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061054
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeheretu, Yonas, Åsa Granberg, Gebregiorgis Berhane, Hussein Khalil, Olivia Wesula Lwande, Mengistu Mitiku, Kiros Welegerima, Joëlle Goüy de Bellocq, Josef Bryja, Hagos Abreha, and et al. 2021. "Prevalence of Orthohantavirus-Reactive Antibodies in Humans and Peri-Domestic Rodents in Northern Ethiopia" Viruses 13, no. 6: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061054
APA StyleMeheretu, Y., Granberg, Å., Berhane, G., Khalil, H., Lwande, O. W., Mitiku, M., Welegerima, K., Bellocq, J. G. d., Bryja, J., Abreha, H., Leirs, H., Ecke, F., & Evander, M. (2021). Prevalence of Orthohantavirus-Reactive Antibodies in Humans and Peri-Domestic Rodents in Northern Ethiopia. Viruses, 13(6), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061054






