Identification, Virulence, and Molecular Characterization of a Recombinant Isolate of Grass Carp Reovirus Genotype I
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Cell Line and Antibody
2.2. Virus Isolation
2.3. Morphology of Virus Particles
2.4. Antigen Identification
2.5. Virus Genome RNA Extraction and SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.6. Regression Infection Test
2.7. Full-Length Genome Amplification
2.8. Sequence Analysis and Recombination Analysis
3. Results
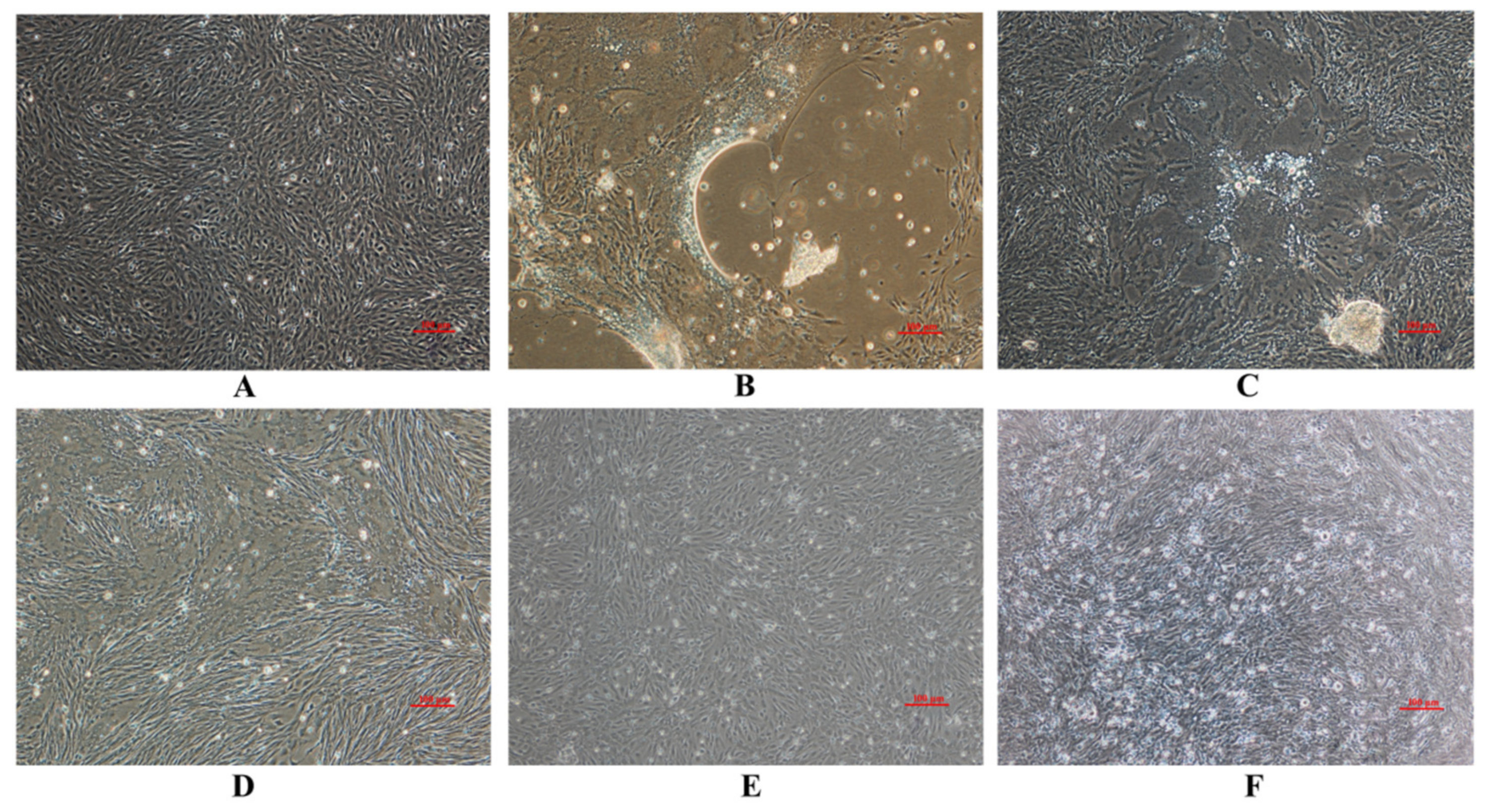
3.1. Virus Isolation
3.2. Morphology under EM
3.3. Antigenic Identification of Isolate GCRV-GZ1208
3.4. Genomic Electrophoretic Patterns
3.5. Virulence Analyses
3.6. Complete Genome Analysis
3.7. Recombination Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, K.; Chen, X.H.; Qi, X.Z.; Yu, X.B.; Du, E.Q.; Ling, F.; Zhu, B.; Wang, G.X. Protective immunity of grass carp induced by DNA vaccine encoding capsid protien gene (vp7) of grass carp reovirus using bacterial ghost as delivery vehicles. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.H.; Yang, C.R.; Su, J.G.; Rao, Y.L.; Gu, T.L. LGP2 plays extensive roles in modulating innate immune responses in Ctenopharyngodon idella kidney (CIK) cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 49, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.; Zhu, Z. Molecular basis and genetic improvement of economically important traits in aquaculture animals. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, H.; Huang, R.; Xia, X.; Feng, Q.; et al. The draft genome of the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) provides insights into its evolution and vegetarian adaptation. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.D.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.S.; Zhou, F.N.; Fu, Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Zeng, Y.Q.; Li, T.M.; Wang, H. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of cathepsin D from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics Yearbook; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sumanta, K.M.; Nupur, J.; Neetu, S.; Krishna, K.; Shivam, S.; Abhay, K.G.; Kushagra, P.; Suresh, C. Characterization and pathogenicity of Aeromonas veronii associated with mortality in cage farmed grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes, 1844) from the Central Himalayan region of India. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2063–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Y.F.; Meng, X.Z.; Lu, J.F.; Liu, L.; Li, J.L. Role of mannose-binding lectin in regulating monocytes/macrophages Functions during Aeromonas hydrophila infection in grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 99, 103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.L.; Lu, L.Q. Quantitative in vivo and in vitro characterization of co-infection by two genetically distant grass carp reoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.D.; Rao, S.J.; Zeng, L.B.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Identification and genomic characterization of a novel fish reovirus, Hubei grass carp disease reovirus, isolated in 2009 in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudeseth, B.E.; Wiulsrød, R.; Fredriksen, B.N.; Lindmo, K.; Lokling, E.K.; Bordevik, M.; Steine, N.; Klevan, A.; Gravningen, K. Status and future perspectives of vaccines for industrialised fin-fish farming. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.L. Hemorrhagic Disease of Grass Carp: Status of Outbreaks, Diagnosis, Surveillance, and Research. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2009, 61, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.D.; Yao, Y.Y.; Cui, Z.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Guo, X.Z.; Zhou, Y.Y. Comparative study of the immunoprotective effect of two grass carp-sourced Bacillus subtilis spore-based vaccines against grass carp reovirus. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.L.; Su, J.G. Insights into the antiviral immunity against grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) reovirus (GCRV) in grass carp. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 670437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y. Studies on the morphological and physico-chemical characterization of the hemorrhagic virus of grass carp. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1983, 28, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Ahne, W. Some properties of the etiological agent of the hemorrhagic disease of grass carp and black carp. In Viruses of Lower Vertebrates; Ahne, W., Kurstak, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Ruan, H.M.; Li, Z.Q.; Jiang, Y. Detection of Grass carp Hemorrhage Virus(GCHV) from Vietnam and Comparison with GCHV Strain form China. High Technol. Lett. 2003, 9, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, C.; Ke, F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y. Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of grass carp reovirus strain 109 (GCReV-109) with other grass carp reovirus strains reveals no significant correlation with regional distribution. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.R.; Li, Y.G.; Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, S.Q. Pathogenicity and tissue distribution of grass carp reovirus after intraperitoneal administration. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attoui, H.; Fang, Q.; Jaafar, F.M.; Cantaloube, J.F.; Biagini, P.; de Micco, P.; de Lamballerie, X. Common evolutionary origin of aquareoviruses and orthoreoviruses revealed by genome characterization of Golden shiner reovirus, grass carp reovirus, striped bass reovirus and golden ide reovirus (genus Aquareovirus, family Reoviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, A.A.C.; Rockemann, D.D.; Hetrick, F.M.; Samal, S.K. Identification of grass carp haemorrhage virus as a new genogroup of aquareovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2399–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.Q.; Yu, L.F.; Ke, L.H.; Cai, Y.Q. Study of infecting other fishes with grass carp hemorrhage virus. Virol. Sin. 1991, 6, 371–373. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.H.; Liu, P.L.; Chen, H.X. Preliminary study on the susceptibility of gobiocypris rarus to hemorrhagic virus of grass carp (GCHV). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1994, 18, 144–149. Available online: http://ir.ihb.ac.cn/handle/152342/5114 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Ye, X.; Tian, Y.Y.; Deng, G.C.; Chi, Y.Y.; Jiang, X.Y. Complete genomic sequence of a reovirus isolated from grass carp reovirus. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.L.; Cui, K.; Li, H.Y.; He, J.X.; Chen, H.L.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Ren, J. Genomic characterization and evolution analysis of a mutant reovirus isolated from grass carp in Anhui. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1385–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hu, H.Z.; Zhou, W.L.; Yin, J.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Bergmann, S.M.; Wu, S.Y.; Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Q. Assessment of a natural grass carp reovirus genotype II avirulent strain GD1108 shows great potential as an avirulent live vaccine. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, W.W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Complete genome sequence of a reovirus isolated from grass carp, indicating different genotypes of GCRV in China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.F.; Jian, J.C.; Wu, Z.H. Phylogenetic analysis of newly isolated grass carp reovirus. Springer Plus 2014, 3, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd, J.F.; Goodwin, M.; Belhouchet, G.; Merry, Q.; Fang, J.F.; Cantaloube, P.; Biagini, P.M.; Mertens, P.P.C.; Attoui, H. Complete characterisation of the American grass carp reovirus genome (genus Aquareovirus: Family Reoviridae) reveals an evolutionary link between aquareoviruses and coltiviruses. Virology 2008, 373, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, W.W.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.Y.; Zheng, S.C.; Shi, C.B. Comparative Study on Physical–Chemical and Biological Characteristics of Grass Carp Reovirus from Different Genotypes. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 47, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Cao, L.; Duetal, J. Grasscarpreovirusinducesapoptosis and oxidative stress in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) kidney cell line. Virus Res. 2014, 185, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Fang, Q.; Cai, Y. Characteristics of a novel isolate of grass carp hemorrhagic virus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1990, 14, 153–159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Isolation and identification of new GCRV strain and primary study on its immunogenicity. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2011, 35, 790–795. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhao, C.C.; Li, Y.Y.; Shi, C.B.; Li, S.J. Immunogenicity of a cell culture-derived inactivated vaccine against, a common virulent isolate of grass carp reovirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.F.; Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Yin, J.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, C.B.; Bergmann, S.M.; Gao, C.X.; Hu, H.Z. Comparison of the blood parameters and histopathology between grass carp infected with a virulent and avirulent isolates of genotype II grass carp reovirus. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Establishment of multiplex PCR for detection of grass carp reovirus and its application. J. Fish. Sci. China 2013, 2, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Sun, X.Y.; Shao, L.; Fang, Q. Functional investigation of grass carp reovirus nonstructural NS80. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gui, J.-F. Virus genomes and virus-host interactions in aquaculture animals. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, H.L.; Zeng, W.W.; Wang, L.C.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Bergmann, S.M. Development of indirect immunofluorescence assay for TCID50 measurement of grass carp reovirus genotype II without cytopathic effect onto cells. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liang, H.R.; Liu, C.; Song, X.J.; Wu, S.Q.; Wang, Q. A one-step duplex rRT-PCR assay for the simultaneous detection of grass carp reovirus genotypes I and II. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 210, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.; Green, T.; Rao, S.; White, S.; Carner, G.; Mertens, P.P.C.; Becnel, J.J. Morphological and molecular characterization of a Cypovirus (Reoviridae) from the mosquito Uranotaenia sapphirina (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9430–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Shi, C.B.; Zeng, W.W.; Liu, Y.K.; Wu, S.Q. Molecular analysis of grass carp reovirus HZ08 genome segments 1–3 and 5–Virus. Genes 2010, 41, 102–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nibert, M.L.; Duncan, R. Bioinformatics of recent aqua-And orthoreovirus isolates from fish: Evolutionary gain or loss of FAST and fiber proteins and taxonomic implications. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Xiao, T.Y.; Li, L.; Zou, G.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.P. Infection Characterizations of four Grass Carp Reovirus (GCRV) strains. Virol. Sin. 2002, 17, 182. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Zhang, A.; Pei, Y.; Chu, P.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Differences in responses of grass carp to different types of grass carp reovirus (GCRV) and the mechanism of hemorrhage revealed by transcriptome sequencing. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.M.; Chang, O.Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Yin, J.Y.; Bergmann, S.M.; Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Q. Establishment of a rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) disease model for grass carp reovirus genotype II. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, L.; Tiehui, W.; Yonglan, Y.; Hanqin, L.; Renhou, L.; Hongxi, C. A detection method for grass carp hemorrhagic virus (GCHV) based on a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1997, 29, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, J.A.; Bowser, P.R.; Grizzle, J.M.; Mitchell, A.J. Fish viruses: A double-stranded RNA icosahedral virus from a North American cyprinid. J. Fish Res. Board Can. 1979, 36, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.M.Q.; Lefkowitz, E.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B. Family—Reoviridae. In Virus Taxonomy: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A.M.Q., Lefkowitz, E., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 541–637. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.M.; Ding, M.Y.; Li, C.F.; Liu, G.Q.; Chen, Z.Y. Construction and characterization of an infectious molecular clone of novel duck reovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydni, C.S.; Jennifer, G.; Julia, R.D.; Michelle, A.W.; Timothy, W.T.; Mark, R.D.; Kristen, M.O. Reovirus RNA recombination is sequence directed and generates internally deleted defective genome segments during passage. J. Virol. 2021, 20, 2120–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Ramig, R.F.; Mustoe, T.A.; Fields, B.N. A genetic map of reovirus. Correlation of genome RNAs between serotypes 1, 2, and 3. Virology 1978, 84, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Virus Strain | Segment | GenBank Accession No. | Length (bp) | Conserved Terminal Sequence | Predicted Function | Homology of Nucleotide (nu) and Amino Acid (aa) Sequence (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCRV-I (873/GCHV) | GSRV | GCRV-II | GCRV-III (HDGRV) | AGCRV | |||||||||||
| nu | aa | nu | aa | nu | aa | nu | aa | nu | aa | ||||||
| GCRV-GZ1208 | S1 | KU240074 | 3949 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | guanylyl transferase/methyl transferase VP1 | 92.6 | 99 | 92.4 | 98.7 | 44.6–44.9 | 31.2–31.5 | 43.2 | 32.1 | 61 | 63.9 |
| S2 | KU240074 | 3877 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase VP2 | 93.7 | 99.4 | 94.5 | 99.1 | 52.9–53.8 | 48.1–49.6 | 50.6 | 43.8 | 68.4 | 74.6 | |
| S3 | KU240074 | 3702 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | NTPase/helicase VP3 | 90.7 | 99.7 | 92.7 | 99.5 | 45.2–46.3 | 34.5–35.7 | 48.2 | 35.6 | 69.1 | 76.8 | |
| S4 | KU240074 | 2320 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | NS1 | 95.9 | 98 | 96.5 | 98.1 | 33.6–34.8 | 19.3–20.4 | 44.3 (S6) | 19.4 (S6) | 53.5 | 41 | |
| S5 | KU240074 | 2239 | GUUAUUU...AUCAUC | putative core protein NTPase/VP5 | 98.3 | 98.8 | 91.7 | 97.1 | 38.8–39.9 | 31.5–32.6 | 46.4 (S4) | 20.4 (S4) | 58.9 | 57.5 | |
| S6 | KU240074 | 2103 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | putative outer capsid VP4 | 94.2 | 99.7 | 93.4 | 99.2 | 45.3–46.2 | 31.6–32.9 | 41.6 (S5) | 19.6 (S5) | 66.9 | 70 | |
| S7 | KU240074 | 1414 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | NS4 | 95.8 | 98.9 | 97.5 | 97.5 | NE | NE | NE | NE | 55.7 | 45.2 | |
| NS5 | 98.5 | 98.1 | |||||||||||||
| S8 | KU240074 | 1296 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | core protein VP6 | 95.2 | 99 | 96.9 | 99.8 | 41.7–42.8(S9) | 27.3–28.6(S9) | 35 | 25.3 | 62.1 | 60.3 | |
| S9 | KU240074 | 1130 | GUUAUUU...AUCAUC | NS2 | 92.8 | 100 | 99.2 | 100 | 42.1–43.4 (S10) | 21.7–23.4 (S10) | NE | NE | 60.4 | 57.8 | |
| S10 | KU240074 | 909 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | outer capsid VP7 | 92.1 | 96.4 | 93.9 | 97.8 | 44.3–45.8 (S11) | 14.6–16.2 (S11) | NE | NE | 48.5 | 26.5 | |
| S11 | KU240074 | 820 | GUUAUUU...UUCAUC | NS3 | 91.5 | 99.2 | 91.5 | 98 | NE | NE | NE | NE | 52.4 | 36.8 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, W.; Bergmannc, S.M.; Dong, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, H. Identification, Virulence, and Molecular Characterization of a Recombinant Isolate of Grass Carp Reovirus Genotype I. Viruses 2021, 13, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050807
Zeng W, Bergmannc SM, Dong H, Yang Y, Wu M, Liu H, Chen Y, Li H. Identification, Virulence, and Molecular Characterization of a Recombinant Isolate of Grass Carp Reovirus Genotype I. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050807
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Weiwei, Sven M. Bergmannc, Hanxu Dong, Ying Yang, Minglin Wu, Hong Liu, Yanfeng Chen, and Hua Li. 2021. "Identification, Virulence, and Molecular Characterization of a Recombinant Isolate of Grass Carp Reovirus Genotype I" Viruses 13, no. 5: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050807
APA StyleZeng, W., Bergmannc, S. M., Dong, H., Yang, Y., Wu, M., Liu, H., Chen, Y., & Li, H. (2021). Identification, Virulence, and Molecular Characterization of a Recombinant Isolate of Grass Carp Reovirus Genotype I. Viruses, 13(5), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050807






