Isolation, Identification, and Genomic Analysis of a Novel Reovirus from Healthy Grass Carp and Its Dynamic Proliferation In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Isolation and Culture
2.2. Artificial Infection
2.3. Physical and Chemical Properties
2.4. Electron Microscopy and SDS-PAGE
2.5. Full-Length Amplification, Cloning, and Nucleotide Sequencing
2.6. Sequence Analysis
2.7. HGCRV Proliferation In Vitro and In Vivo
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
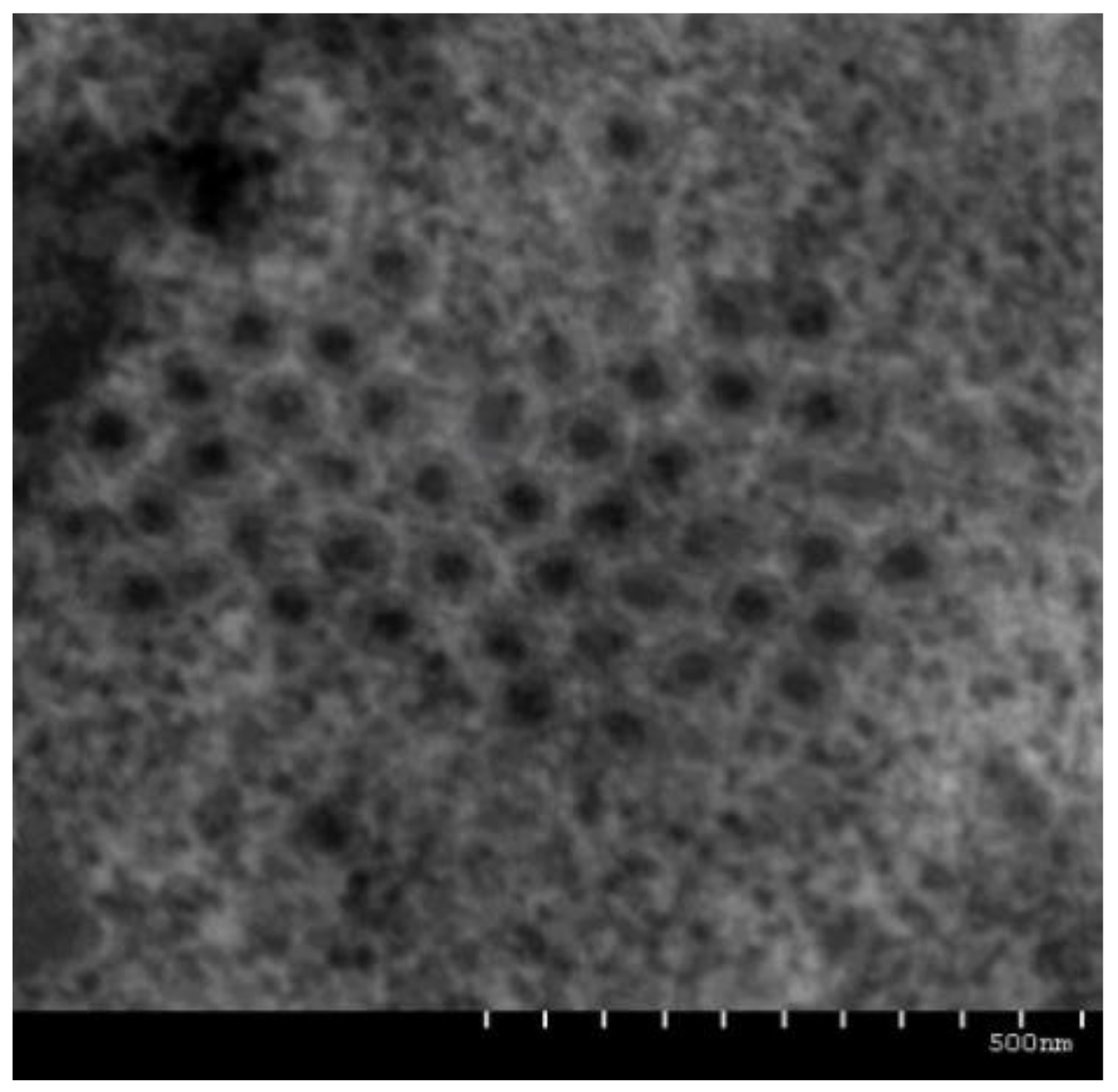
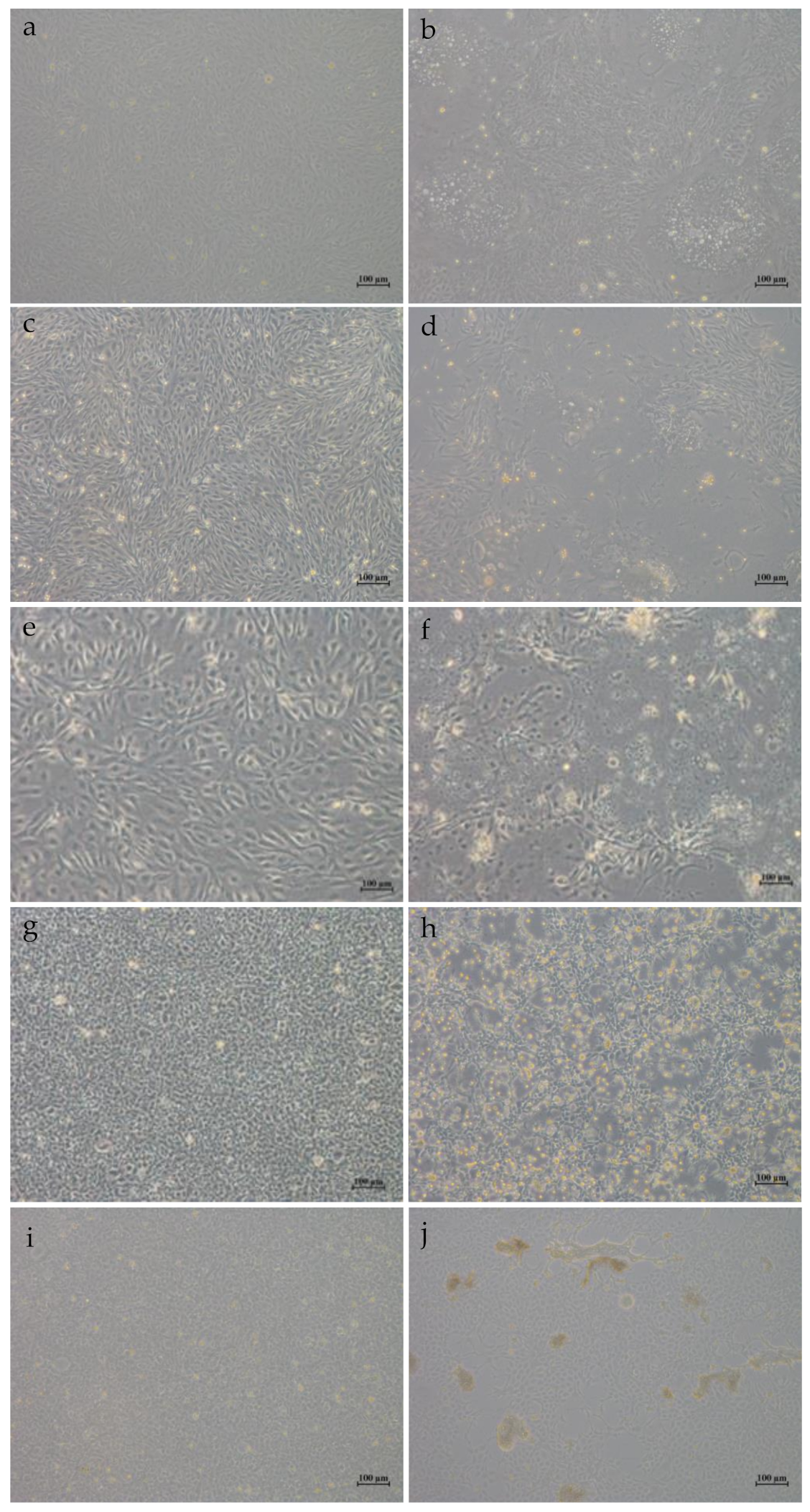
3.1. Pathology and Morphology of HGCRV
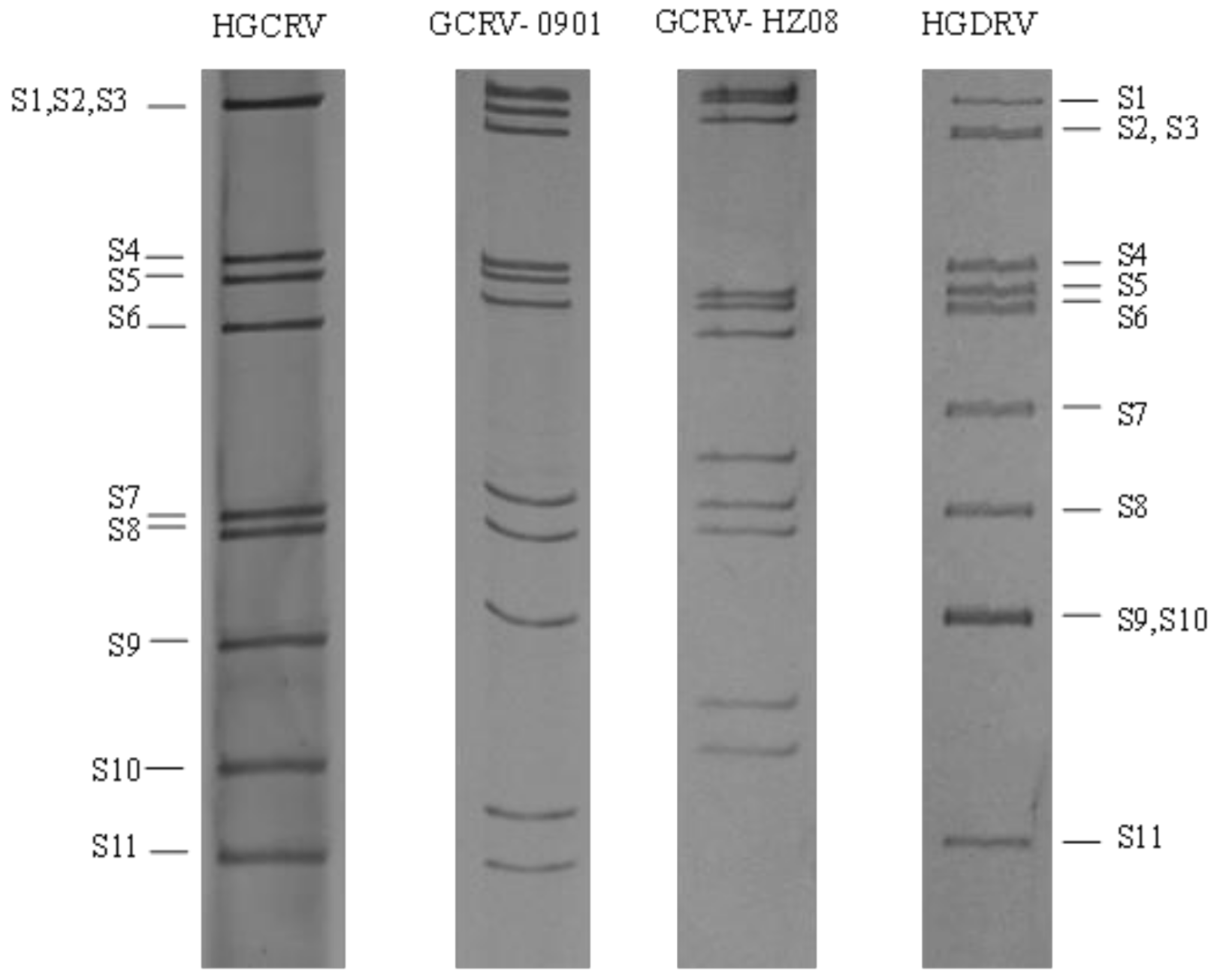
3.2. HGCRV Genome
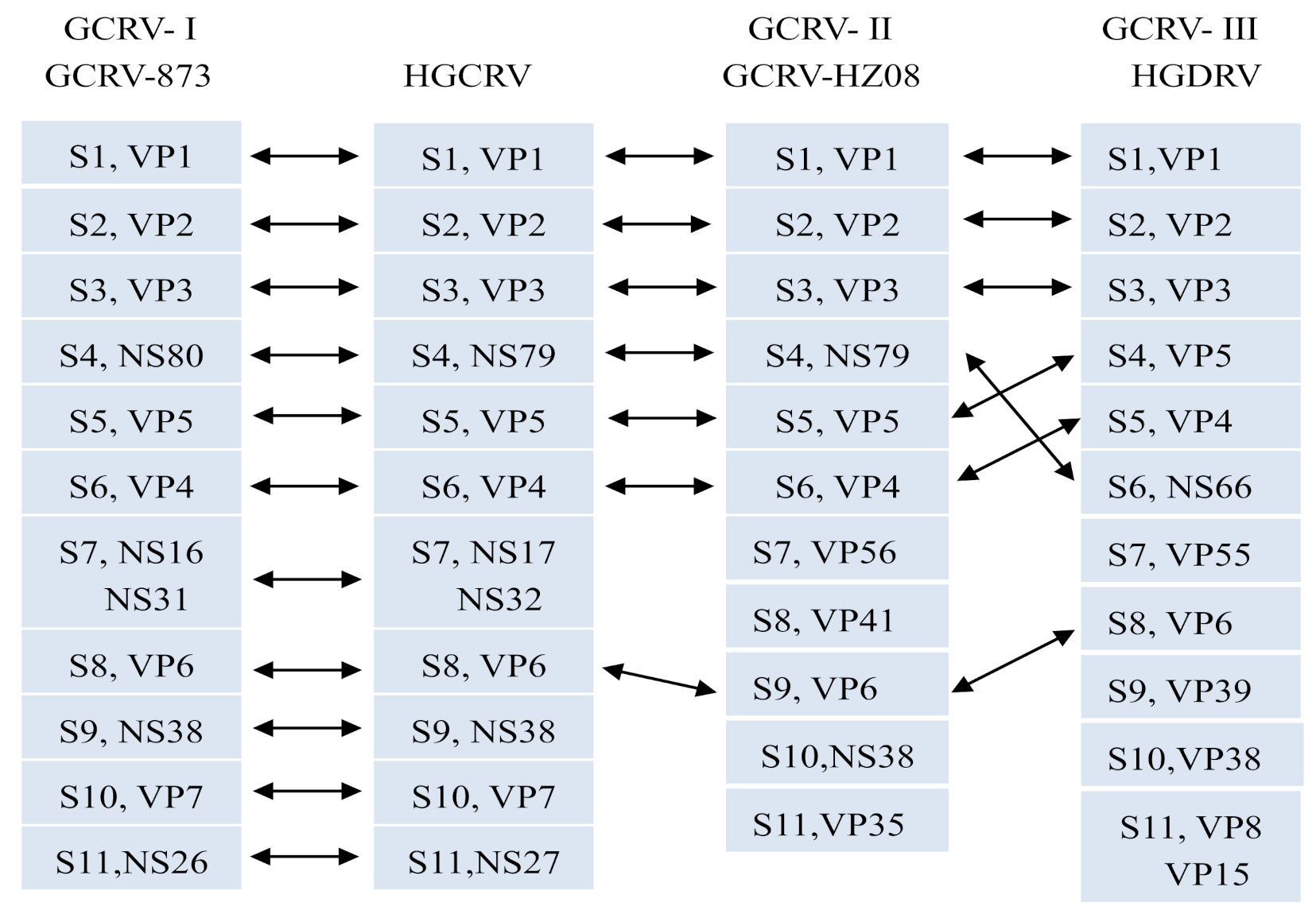
3.3. Sequence Analysis of the HGCRV
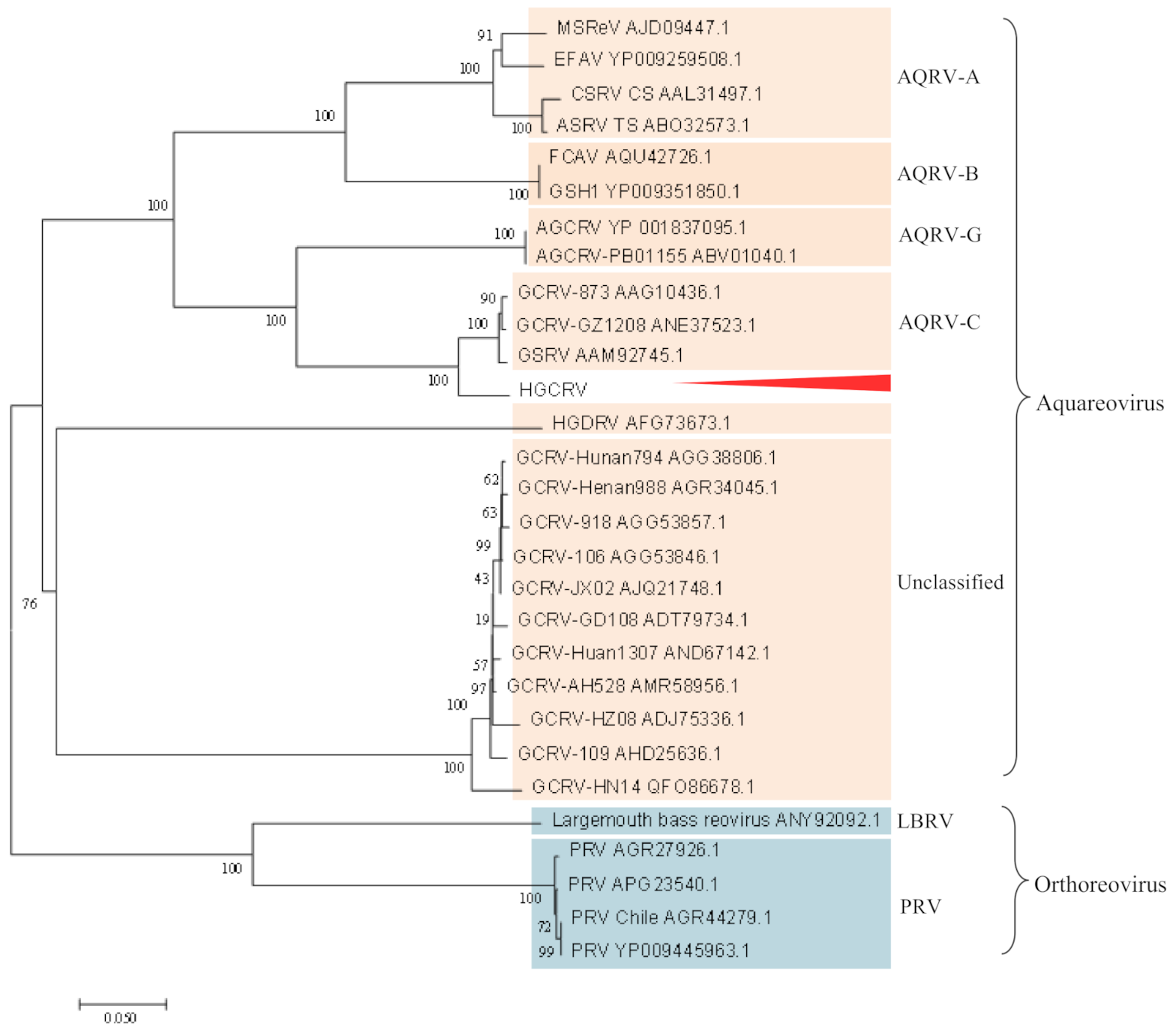
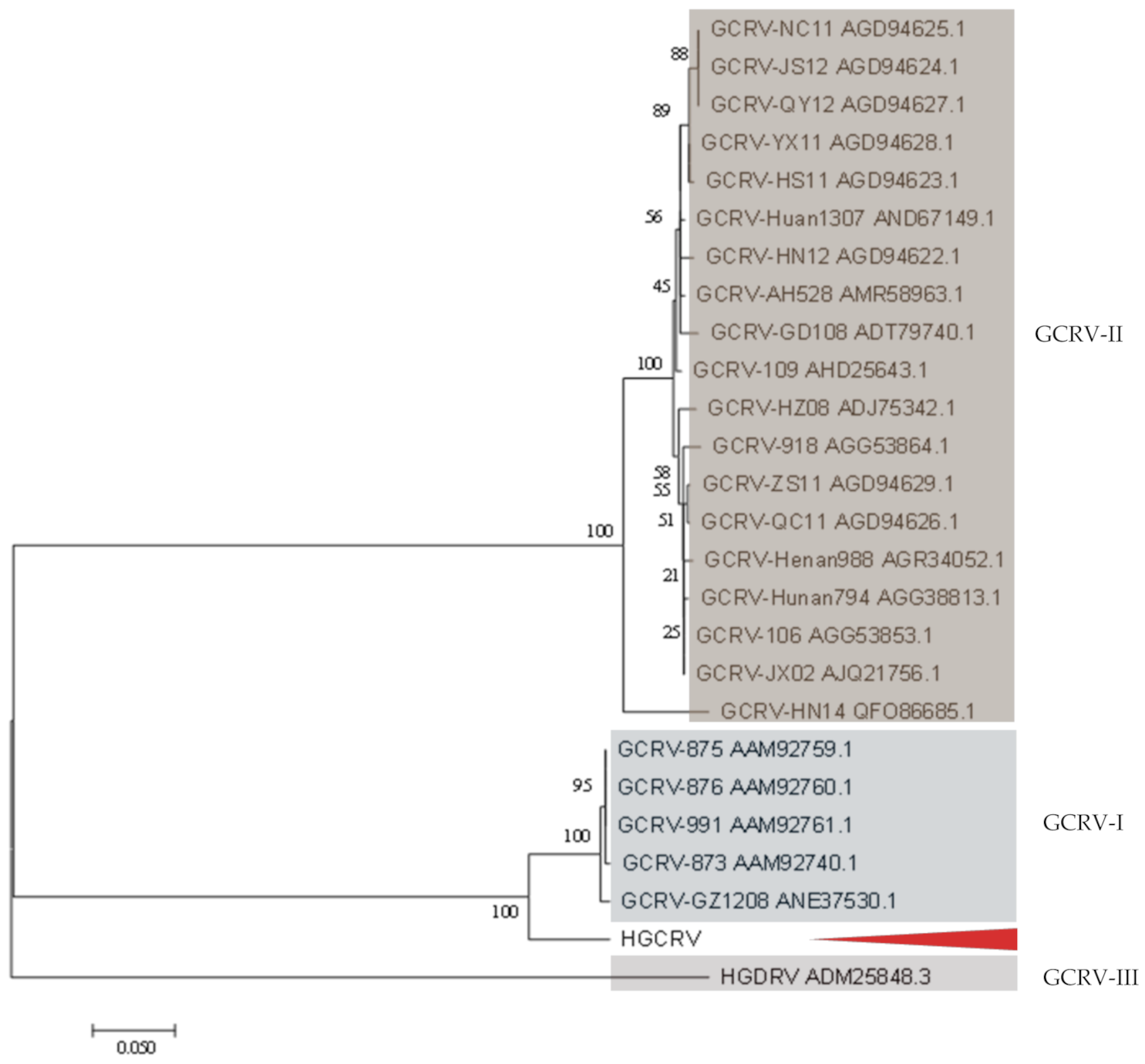
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
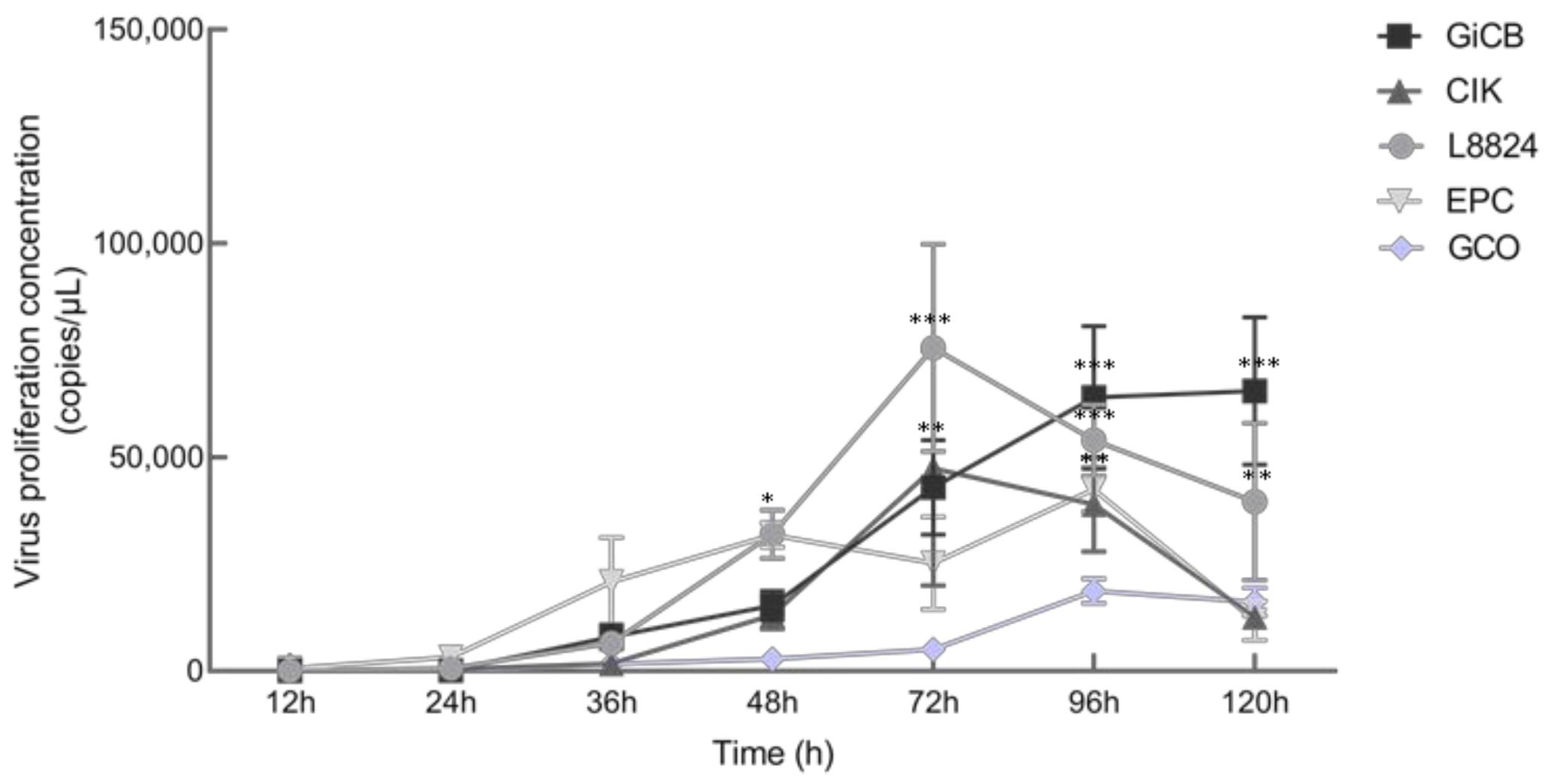
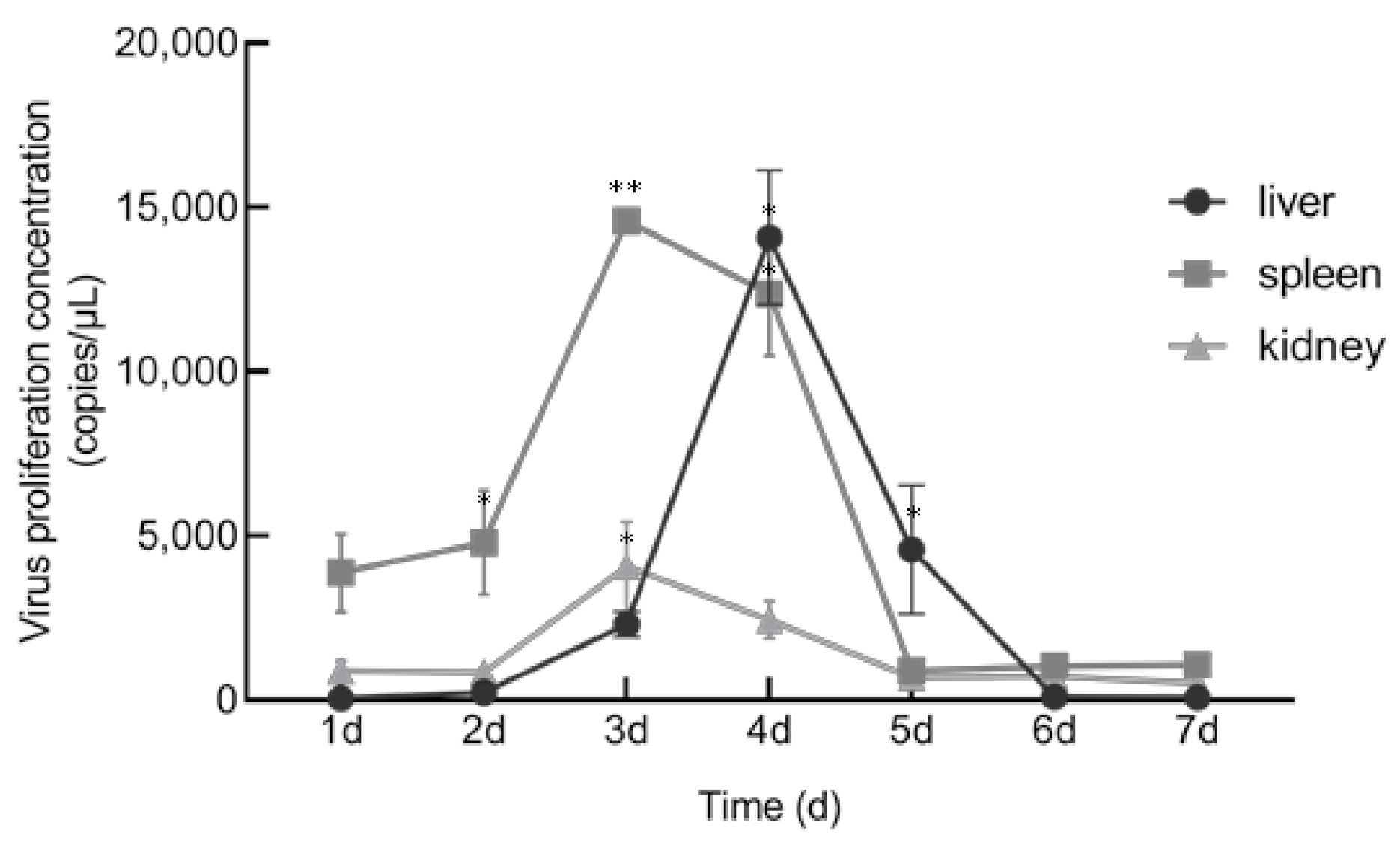
3.5. In Vitro and In Vivo Proliferation Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, C.X.; Zeng, W.W.; Tang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.L.; Wu, J.X.; Liu, S.X.; Yin, J.Y.; Li, Y.Y. Isolation and identification of two new isolates of genotype II grass carp reovirus and comparision of their biological characteristics. J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Ke, L.H.; Cai, Y.Q. Growth characteristics and high titer culture of grass carp hemorrhage virus (GCHV)-873 in vitro. Virol. Sin. 1989, 155, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Grass Carp Hemorrhagic Disease Research Group of Wuhan Institute Virology, Academia Sinica; Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences. Observation of grass carp hemorrhagic virus. Fresh Water Fish. China 1983, 3, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Francki, R.I.B.; Fauquet, C.M.; Knudson, S.L.; Brown, F. Classification and nomenclature of viruses, 5th report of the International Committee on Taxanomy of Viruses. Arch. Virol. 1991, 2, 186–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Attoui, H.; Fang, Q.; Jaafar, F.M.; Cantaloube, J.F.; Biaginin, P.; De Micco, P.; De Lamballerie, X. Common evolutionary origin of aquareoviruses and orthoreoviruses revealed by genome characterization of Golden shiner reovirus, Grass carp reovirus, Striped bass reovirus and golden ide reovirus (genus Aquareovirus, family Reoviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, F.M.; Goodwin, A.E.; Belhouchet, M.; Merry, G.; Fang, Q.; Cantaloube, J.F.; Biagini, P.; De Mieco, P.; Mertens, P.P.C.; Attoui, H. Complete characterization of the American grass carp reovirus genome (genus Aquareovirus: Family Reoviridae) reveals an evolutionary link between aquareoviruses and coltiviruses. Virology 2008, 373, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; He, L.B.; Pei, C.; Zhang, Q.Y. Turbot reovirus (SMReV) genome encoding a FAST protein with a non−AUG start site. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, W.W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Complete genome sequence of a reovirus isolated from grass carp, indicating different genotypes of GCRV in China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Tian, Y.Y.; Deng, G.C.; Chi, Y.Y.; Jiang, X.Y. Complete genomic sequence of a reovirus isolated from grass carp in China. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.D.; Rao, S.J.; Zeng, L.B.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Identification and genomic characterization of a novel fish reovirus, Hubei grass carp disease reovirus, isolated in 2009 in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhsous, N.; Jensen, N.L.; Haman, K.H.; Batts, W.N.; Jerome, K.R.; Winton, J.R.; Greninger, A.L. Isolation and characterization of the fall Chinook aquareovirus. J. Virol. 2017, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skoge, R.H.; Nylund, A.; Solheim, K.; Plarre, H. Complete genome of Atlantic halibut reovirus (AHRV) associated with mortality in production of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) fry. Aquaculture 2019, 509, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.; Ke, F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y. Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of grass carp reovirus strain 109 (GCReV−109) with other grass carp reovirus strains reveals no significant correlation with regional distribution. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Shi, C.B.; Zeng, W.W.; Liu, Y.K.; Wu, S.Q. Isolation and identification of a grass carp reovirus isolate GCRV HZ08. J. Fish. Sci. China 2010, 17, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, G.J.; Shen, J.Y.; Pan, X.Y.; Xu, Y.; Yao, J.Y.; Yin, W.L. Isolation and identification of a strain of Grass carp reovirus in Huzhou. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2011, 32, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.K.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, W.W.; Shi, C.B.; Zhang, C.; Chen, D.Y.; Wu, S.Q. Isolation and identification of grass carp reovirus strain JX−0902. J. Fish. Sci. China 2011, 5, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Xiao, T.Y.; Ding, Q.Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhu, Z.Y. Virological properties of GCRV991 strain. Virol. Sin. 2002, 17, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.F.; Jian, J.C.; Wu, Z.H. Phylogenetic analysis of newly isolated grass carp reovirus. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hao, G.J.; Shen, J.Y.; Zheng, S.J.; Pan, X.Y.; Yao, J.Y.; Yin, W.L. Isolation and identification of two grass carp reovrius strains in Jiangxi province. Freshw. Fish. 2010, 40, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.K.; Zhang, L.S.; Liu, B.Q.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Isolation and identification of new GCRV strain and primary study on its immunogenicity. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2011, 35, 790–795. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, N.N.; Su, J.G.; Lei, C.Z. Cloning and analysis of partial coding sequences of grass carp reovirus 097 strain genome segments L3, M5 and S8. J. Domest. Anim. Ecol. 2015, 3, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, L.H.; Fang, Q.; Cai, Y.Q. Characteristics of a novel isolate of grass carp hemorrhagic virus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1990, 14, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.X.; Wang, Q.; Chang, O.Q.; Zhou, W.L.; Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Y.Y. Preparation and application of synthetic peptide antibody against VP7 protein of grass carp reovirus (GCRV) genotype I. J. South Agric. 2018, 49, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.L.; Cui, K.; Li, H.Y.; He, J.X.; Chen, H.L.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Ren, J. Genomic characterization and evolution analysis of a mutant reovirus isolated from grass carp in Anhui. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1385–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, W.W.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Comparative study on physical–chemical and biological characteristics of grass carp reovirus from different genotypes. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 47, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhu, J.; Hui, W.H.; Zhang, X.; Honig, B.; Fang, Q.; Zhou, Z.H. Backbone model of an aquareovirus virion by cryo−electron microscopy and bioinformatics. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Luongo, C.L. Identification of two histidines necessary for reovirus mRNA guanylyltransferase activity. Virology 2003, 316, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Shao, L.; Fang, Q. Characterization of the nonstructural protein NS80 of grass carp reovirus. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Brown, E.G. Nucleotide sequence comparison of the M1 genome segment of reovirus type 1 Lang and type 3 Dearing. Virus Res. 1992, 22, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.S.; Broering, T.J.; Kim, J.; Higgins, D.E.; Nibert, M.L. Reovirus core protein mu2 determines the filamentous morphology of viral inclusion bodies by interacting with and stabilizing microtubules. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4483–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler−Bauer, A.; Lu, S.; Anderson, J.B.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; DeweeseScott, C.; Fong, J.H.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD: A conserved domain database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Lu, R.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.Y. Molecular characterization and expression of the M6 gene of grass carp hemorrhage virus (GCHV), an aquareovirus. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Gilmore, R.; Leone, G.; Coffey, M.C.; Weber, B.; Lee, P.W. Hsp90 phosphorylation is linked to its chaperoning function. Assembly of the reovirus cell attachment protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32822–32827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazelton, P.R.; Coombs, K.M. The reovirus mutant tsA279 L2 gene is associated with generation of a spikeless core particle: Implications for capsid assembly. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, E.S.; Forrest, J.C.; Connolly, J.L.; Chappell, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Schnell, F.J.; Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C.A.; Dermody, T.S. Junction adhesion molecule is a receptor for reovirus. Cell 2001, 104, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, C.L.; Dryden, K.A.; Farsetta, D.L.; Margraf, R.L.; Severson, T.F.; Olson, N.H.; Fields, B.N.; Baker, T.S.; Nibert, M.L. Localization of a C−terminal region of lambda2 protein in reovirus cores. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8035–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Seng, E.K.; Ding, Q.Q.; Zhang, L.L. Characterization of infectious particles of grass carp reovirus by treatment with proteases. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sun, X.Y.; Yan, L.M.; Shao, L.; Fang, Q. The NS16 protein of aquareovirus-C is a fusion-associated small transmembrane (FAST) protein, and its activity can be enhanced by the nonstructural protein NS26. Virus Res. 2013, 171, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Q.X.; Yan, L.M.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S.C.; Zhang, F.X.; Fang, Q. Identification of a functional motif in the AqRV NS26 protein required for enhancing the fusogenic activity of FAST protein NS16. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahne, W. Viral infectious of aquatic animals with special reference to Asia aquaculture. Ann. Rev. Fish Dis. 1994, 4, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupiani, B.; Subramanian, K.; Samal, S.K. Aquareovirus. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1995, 5, 175–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.L.; Lu, L.Q. Quantitative in vivo and in vitro characterization of co-infection by two genetically distant grass carp reoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.X.; Yang, X.Q.; Chen, H.X. Susceptibility to grass carp reovirus (GCRV) of several fish cell lines. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1985, 9, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zeng, W.W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Song, X.J.; Huang, Q.W.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. The study on the proliferation of GCRV Ⅱ in different fish cell lines. J. Fish. China 2016, 40, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Ding, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhu, Z.Y. Partial characteristic comparison between two aquareovirus isolates. Virol. Sin. 2003, 18, 464–467. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.M.; Yan, J.Y.; Hao, G.J.; Lin, L.Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.Y.; Yin, W.L.; Shen, J.Y. Research on growth characteristics of grass carp reovirus. China Anim. Health Insp. 2018, 35, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.B.; He, L.; Zuo, W.G. Physical−chemical and biological characteristics and genome structure of grass carp hemorrhage virus−854. J. Fish. China 1998, 22, 279–282. [Google Scholar]

| Segments | Primers | Sequence (5′–3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| UPM | UPM-Long prime | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT | |
| UPM-short prime | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC | ||
| S1 | 5′ | GSP-S1-5 | CCGGCAGCGAGATTCGCTAGTAGTCGG |
| NGSP-S1-5 | CGTTGAGTGAGCACACCAACGAAGGC | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S1-3 | CTACCCTAGGCCAACCACCCGTCCCTC | |
| NGSP-S1-3 | CGGCAACGACGCCCAGATCAACTGCG | ||
| S2 | 5′ | GSP-S2-5 | GAAGACCCTGCGGAGCGGCTGGAGGG |
| NGSP-S2-5 | GACTTGCCTAGCCTGGGAGGAGGCG | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S2-3 | GGCATGTCCGATTCGGAAGCGCACC | |
| NGSP-S2-3 | GTTGTGCACTTGTCCATACCCTCGTC | ||
| S3 | 5′ | GSP-S3-5 | GTCAAGGTATGCGGAGAGTGCCTTGG |
| NGSP-S3-5 | GCGACGGACGCGATACTATCAGAAG | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S3-3 | GCTGGCGATTGGGTATATCCAAGCGACG | |
| NGSP-S3-3 | CCCGACGTGTCCACTACGCCTTCACCTC | ||
| S4 | 5′ | GSP-S4-5 | GTCGAGGGAGTCCAGGAGAGGACCAG |
| NGSP-S4-5 | CTCGAACACGAGTTGGTTGAACGCTGC | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S4-3 | CTCGCCGTACTCCAAAGCGTCATGGG | |
| NGSP-S4-3 | GGCTGCTGCTGCTGAACGTGATCAAGC | ||
| S5 | 5′ | GSP-S5-5 | CAGCGTCGACATCGAGGAGGAATGTGCG |
| NGSP-S5-5 | TAGCCACTGGGCGAACCGTTTGGGC | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S5-3 | CGTCGTAAATCTGCTGGCACGTCGA | |
| NGSP-S5-3 | TCGACGGTGACCCACCCTTGTCAG | ||
| S6 | 5′ | GSP-S6-5 | GCATGCGAGCAGCAATAGTGCGTTGC |
| NGSP-S6-5 | CGCGCATGTTCTCGTTGACGAATGAG | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S6-3 | TCCAGTGCTGCTTCGAGAGACCACG | |
| NGSP-S6-3 | TTGGTGACGCCATCCCAGTAGCATC | ||
| S7 | 5′ | GSP-S7-5 | CGGGCTCAATGTGGCGCTCATACGC |
| NGSP-S7-5 | GCTGGGATCTCTACCACCTGGGCGG | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S7-3 | CGTTCAATATGACTCCACGTGGAGC | |
| NGSP-S7-3 | CCACCGTCGACAACATCCGCTGCAT | ||
| S8 | 5′ | GSP-S8-5 | GGACTCCGATGTACGCCATGAGCGC |
| NGSP-S8-5 | GATGGCTGGTGATCTGACCACCGGAG | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S8-3 | CCTTAAATGGAACGATGGAGCCCGT | |
| NGSP-S8-3 | GCGGCTAGACACCTGCAATGGCGTC | ||
| S9 | 5′ | GSP-S9-5 | CCTAACCTATCGGCATGAAGCAGGG |
| NGSP-S9-5 | GTCGACGGGCATTTGGGCGAGGTGAG | ||
| 3′ | GSP-S9-3 | CCCTGCTTCATGCCGATAGGTTAGG | |
| NGSP-S9-3 | GTGGCTCGGCCTCATCTGCGGTCTC |
| Genome Segment | Gene | Protein | Predicted Function | Conserved Terminal Nucleotide Sequences | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (bp) | GC% | 5′ NCR (bp) | 3′ NCR (bp) | Position of ORF (nt) | Length (aa) | Coding Potential | MM (kDa) | Isoelectric Point (pI) | |||
| S1 | 3949 | 56.32 | 12 | 37 | 13–3912 | 1299 | VP1 | 141.26 | 5.85 | Core protein, guanylyltransferase | 5′-GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S2 | 3876 | 54.28 | 12 | 39 | 13–3837 | 1274 | VP2 | 141.24 | 8.22 | Core protein, polymerase | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S3 | 3703 | 55.98 | 12 | 46 | 13–3657 | 1214 | VP3 | 132.15 | 5.88 | NTPase, helicase | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S4 | 2311 | 60.28 | 26 | 65 | 27–2246 | 739 | NS79 | 79.17 | 6.30 | Nonstructural protein | 5′-GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S5 | 2239 | 56.10 | 17 | 35 | 18–2204 | 728 | VP5 | 80.35 | 7.69 | Core protein | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S6 | 2039 | 55.66 | 30 | 62 | 31–1977 | 648 | VP4 | 68.70 | 5.35 | Outer capsid protein | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S7 | 1414 | 56.51 | 13 | 70 | 520–1344 14–484 | 274 156 | NS32 NS17 | 31.70 16.90 | 5.72 8.21 | Nonstructural protein | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S8 | 1298 | 58.32 | 12 | 47 | 13–1251 | 412 | VP6 | 44.37 | 6.66 | Core protein | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S9 | 1128 | 58.78 | 31 | 38 | 32–1090 | 352 | NS38 | 37.95 | 7.21 | Nonstructural protein | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S10 | 910 | 57.58 | 30 | 49 | 31–861 | 276 | VP7 | 29.81 | 6.36 | Outer capsid protein | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| S11 | 821 | 58.95 | 43 | 43 | 44–778 | 244 | NS27 | 26.53 | 6.75 | Nonstructural protein | 5′- GUUAUU…UCAUC-3′ |
| Segment | HGCRV | GCRV—I | GCRV—II | GCRV—III | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCRV-873 | GCRV-GZ1208 | GCRV-HZ08 | GCRV-GD108 | GCReV-109 | HGDRV | ||||||||||
| bp | aa | bp (%) | aa (%) | bp (%) | aa (%) | bp (%) | aa (%) | bp (%) | aa (%) | bp (%) | aa (%) | bp (%) | aa (%) | ||
| S1 | 3949 | 1299 | 3949 (76.85%) | 1299 (90.30%) | 3949 (76.48%) | 1299 (90.76%) | 3927 (41.76%) | 1294 (29.84%) | 3928 (42.07%) | 1294 (30.25%) | 3929 (41.99%) | 1294 (29.71%) | 3943 (44.09%) | 1294 (32.11%) | |
| S2 | 3876 | 1274 | 3877 (77.96%) | 1274 (94.35%) | 3877 (77.60%) | 1274 (94.35%) | 3870 (50.97%) | 1273 (45.85%) | 3867 (51.32%) | 1273 (46.67%) | 3867 (50.86%) | 1273 (46.43%) | 3864 (48.32%) | 1274 (43.39%) | |
| S3 | 3703 | 1214 | 3702 (78.89%) | 1214 (96.71%) | 3702 (79.77%) | 1214 (97.03%) | 3753 (45.65%) | 1232 (35.74%) | 3752 (45.68%) | 1232 (35.58%) | 3753 (45.62%) | 1232 (35.91%) | 3729 (45.79%) | 1224 (36.30%) | |
| S4 | 2311 | 739 | 2320 (75.02%) | 742 (79%) | 2320 (75.17%) | 742 (78.33%) | 2263 (40.67%) | 716 (22.65%) | 2263 (39.98%) | 716 (22.52%) | 2263 (40.53%) | 716 (23.19%) | 2210 (39.29%) | 715 (23.37%) | |
| S5 | 2239 | 728 | 2239 (75.66%) | 728 (85.03%) | 2239 (75.88%) | 728 (85.99%) | 2229 (42.78%) | 726 (26.61%) | 2230 (41.75%) | 726 (26.65%) | 2143 (42.26%) | 726 (26.77%) | 2003 (42.18%) | 638 (29.40%) | |
| S6 | 2039 | 648 | 2039 (77.55%) | 648 (90.43%) | 2039 (77.64%) | 648 (91.05%) | 2030 (44.59%) | 650 (32.63%) | 2028 (44.64%) | 650 (32.63%) | 2029 (44.59%) | 650 (32.48%) | 1912 (36.46%) | 609 (28.46%) | |
| S7 | 1414 | 274/156 | 1414 (73.82%) | 274/146 (72.53%/71.92%) | 1414 (73.61%) | 274/146 (71.79% 71.92%) | 1604 - | 512 - | 1604 - | 512 - | 1605 - | 512 - | 1581 - | 511 - | |
| S8 | 1298 | 412 | 1296 (78.97%) | 412 (90.29%) | 1297 (79.28%) | 412 (91.02%) | 1560 - | 361 - | 1560 - | 361 - | 1560 - | 361 - | 1319 (39.39%) | 418 (24.94%) | |
| S9 | 1128 | 352 | 1130 (78.67%) | 352 (91.48%) | 1130 (79.56%) | 352 (91.76%) | 1320 (40.59%) | 418 (22.86%) | 1320 (41.24%) | 418 (22.86%) | 1320 (40.59%) | 418 (23.12%) | 1141 - | 354 - | |
| S10 | 910 | 276 | 909 (71.04%) | 276 (69.57%) | 909 (71.06%) | 276 (70.29%) | 1124 - | 345 - | 1124 - | 345 - | 1124 - | 345 - | 1122 - | 346 - | |
| S11 | 821 | 244 | 820 (74.91%) | 244 (77.46%) | 820 (74.04%) | 244 (77.05%) | 1027 - | 310 - | 1027 - | 310 - | 1027 - | 310 - | 876 - | 75/140 - | |
| Total genome lengt | 23688 | 7616 | 23695 (71.04–78.97%) | 7609 (69.57–96.71%) | 23696 (71.06–79.77%) | 7609 (70.29–97.03%) | 24707 (40.59–50.97%) | 7837 (22.65–45.85%) | 24703 (39.98–51.32%) | 7837 (22.52–46.67%) | 24620 (40.53–50.86%) | 7837 (23.12–46.43%) | 23706 (36.46–48.32%) | 7598 (23.37–43.39%) | |
| Average | 76.30% | 84.09% | 70.92% | 84.28% | 43.86% | 30.88% | 43.81% | 31.02% | 43.78% | 31.08% | 42.22% | 31.14% | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zeng, L.; Vakharia, V.N.; Fan, Y. Isolation, Identification, and Genomic Analysis of a Novel Reovirus from Healthy Grass Carp and Its Dynamic Proliferation In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses 2021, 13, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040690
Zhang K, Liu W, Li Y, Zhou Y, Meng Y, Zeng L, Vakharia VN, Fan Y. Isolation, Identification, and Genomic Analysis of a Novel Reovirus from Healthy Grass Carp and Its Dynamic Proliferation In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses. 2021; 13(4):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040690
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ke, Wenzhi Liu, Yiqun Li, Yong Zhou, Yan Meng, Lingbing Zeng, Vikram N. Vakharia, and Yuding Fan. 2021. "Isolation, Identification, and Genomic Analysis of a Novel Reovirus from Healthy Grass Carp and Its Dynamic Proliferation In Vitro and In Vivo" Viruses 13, no. 4: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040690
APA StyleZhang, K., Liu, W., Li, Y., Zhou, Y., Meng, Y., Zeng, L., Vakharia, V. N., & Fan, Y. (2021). Isolation, Identification, and Genomic Analysis of a Novel Reovirus from Healthy Grass Carp and Its Dynamic Proliferation In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses, 13(4), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040690







