Emergence and Spread of SARS-CoV-2 Lineages B.1.1.7 and P.1 in Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Data
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
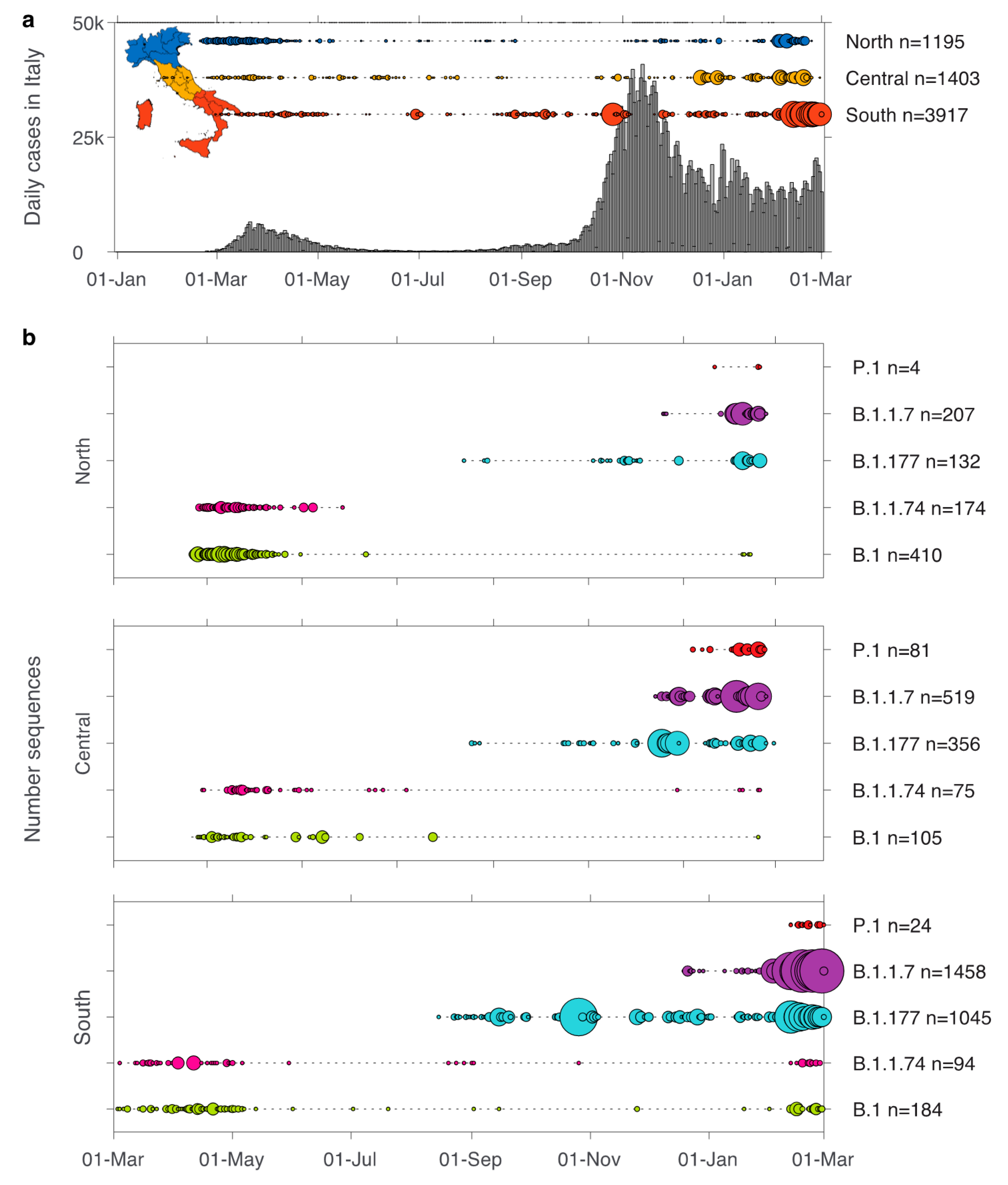
3. Results
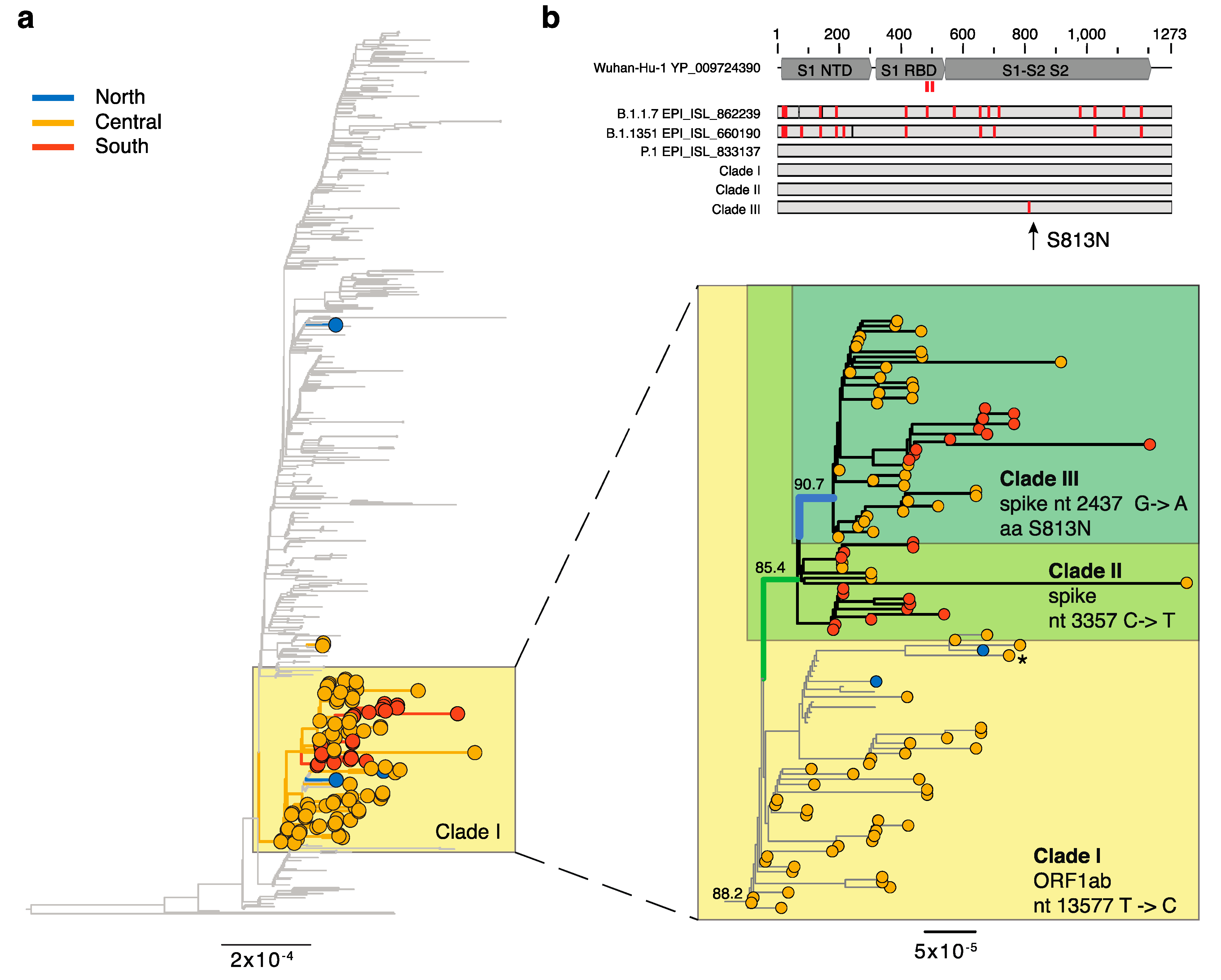
3.1. Emerging Lineages in Italy
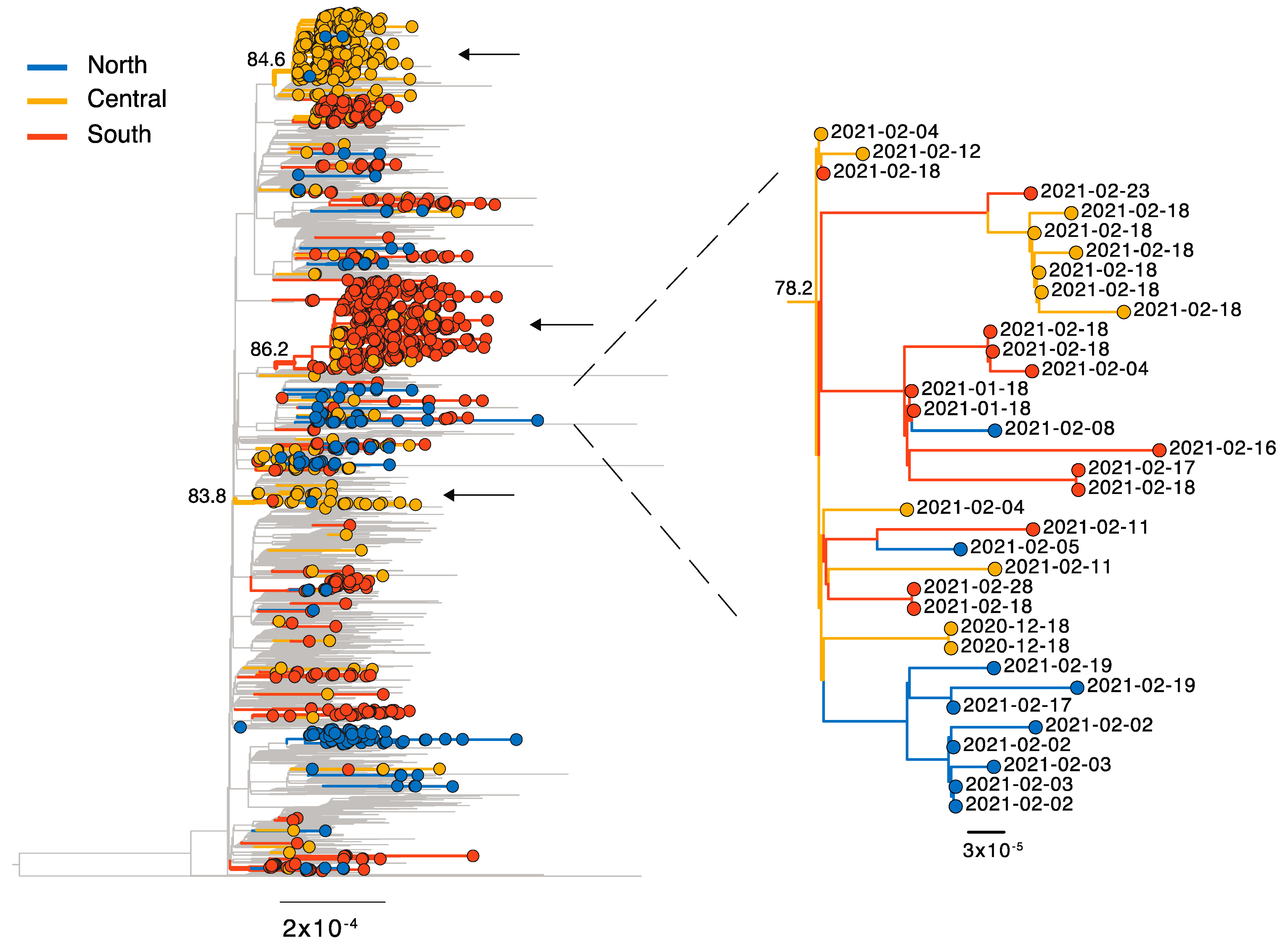
3.2. Lineages of Global Concern—B.1.1.7, P.1, and B.1.351
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Weekly Operational Update on COVID-19—8 March 2021; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Weekly Epidemiological Update—31 August 2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; O’Toole, A.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Ruis, C.; du Plessis, L.; Pybus, O.G. A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Science Brief: Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/more/science-and-research/scientific-brief-emerging-variants.html (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Davies, N.G.; Abbott, S.; Barnard, R.C.; Jarvis, C.I.; Kucharski, A.J.; Munday, J.D.; Pearson, C.A.B.; Russell, T.W.; Tully, D.C.; Washburne, A.D.; et al. Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Science 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Emergence and rapid spread of a new severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) lineage with multiple spike mutations in South Africa. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, A.; Hill, V.; Pybus, O.G.; Watts, A.; Bogoch, I.I.; Khan, K.; Messina, J.P.; consortium, T.C.-G.U.C.-U.; (NGS-SA), N.f.G.S.i.S.A.; Network, B.-U.C.G.; et al. Tracking the International Spread of SARS-CoV-2 lineages B.1.1.7 and B.1.351/501Y-V2. Available online: https://virological.org/t/tracking-the-international-spread-of-sars-cov-2-lineages-b-1-1-7-and-b-1-351-501y-v2/592 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Walensky, R.P.; Walke, H.T.; Fauci, A.S. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern in the United States-Challenges and Opportunities. JAMA 2021, 325, 1037–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabino, E.C.; Buss, L.F.; Carvalho, M.P.S.; Prete, C.A., Jr.; Crispim, M.A.E.; Fraiji, N.A.; Pereira, R.H.M.; Parag, K.V.; da Silva Peixoto, P.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; et al. Resurgence of COVID-19 in Manaus, Brazil, despite high seroprevalence. Lancet 2021, 397, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, P.C.; Bezerra, J.F.; Vasconcelos, R.H.T.d.; Arantes, I.; Appolinario, L.; Mendonça, A.C.; Paixao, A.C.; Rodrigues, A.C.D.; Silva, T.; Rocha, A.S.; et al. Spike E484K Mutation in the First SARS-CoV-2 Reinfection Case Confirmed in Brazil. 2020. Available online: https://virological.org/t/spike-e484k-mutation-in-the-first-sars-cov-2-reinfection-case-confirmed-in-brazil-2020/584 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Naveca, F.; Costa, C.d.; Nascimento, V.; Souza, V.; Corado, A.; Nascimento, F.; Costa, Á.; Duarte, D.; Silva, G.; Mejía, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 reinfection by the new Variant of Concern (VOC) P.1 in Amazonas, Brazil. Available online: https://virological.org/t/sars-cov-2-reinfection-by-the-new-variant-of-concern-voc-p-1-in-amazonas-brazil/596 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Wibmer, C.K.; Ayres, F.; Hermanus, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Kgagudi, P.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; de Oliveira, T.; Vermeulen, M.; van der Berg, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 escapes neutralization by South African COVID-19 donor plasma. Nat. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.C.; Burgers, W.A. SARS-CoV-2 evolution and vaccines: Cause for concern? Lancet Respir. Med. 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.; Fontes-Garfias, C.R.; Xia, H.; Swanson, K.A.; Cutler, M.; Cooper, D.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 spike 69/70 deletion, E484K and N501Y variants by BNT162b2 vaccine-elicited sera. Nat. Med. 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistiche Coronavirus. Statistiche Coronavirus in Italia. Available online: https://statistichecoronavirus.it/coronavirus-italia/ (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Di Giallonardo, F.; Duchene, S.; Puglia, I.; Curini, V.; Profeta, F.; Camma, C.; Marcacci, M.; Calistri, P.; Holmes, E.C.; Lorusso, A. Genomic epidemiology of the first wave of SARS-CoV-2 in Italy. Viruses 2020, 12, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlosser, F.; Maier, B.F.; Jack, O.; Hinrichs, D.; Zachariae, A.; Brockmann, D. COVID-19 lockdown induces disease-mitigating structural changes in mobility networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32883–32890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swadi, T.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Devine, T.; McElnay, C.; Sherwood, J.; Shoemack, P.; Ren, X.; Storey, M.; Jefferies, S.; Smit, E.; et al. Genomic evidence of in-flight transmission of SARS-CoV-2 despite predeparture testing. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R. A Global Phylogeny of hCoV-19 Sequences from GISAID. Available online: https://www.gisaid.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Kuraku, S.; Zmasek, C.M.; Nishimura, O.; Katoh, K. aLeaves facilitates on-demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delli Compagni, E.; Jurisic, L.; Caporale, M.; Baca, F.; Scialabba, S.; Fani, S.; Perullo, A.; Toro, M.; Marchegiano, A.; Martino, M.; et al. Genome sequences of three SARS-CoV-2 P.1 strains identified from patients returning from Brazil to Italy. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novazzi, F.; Genoni, A.; Spezia, P.G.; Focosi, D.; Zago, C.; Colombo, A.; Cassani, G.; Pasciuta, R.; Tamborini, A.; Rossi, A.; et al. Introduction of SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern 20h/501Y.V2 (B.1.351) from Malawi to Italy. Emerg. Microbes Infect 2021, 10, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish Covid-19 Genome Consortium. Genomic overview of SARS-CoV-2 in Denmark. Available online: https://www.covid19genomics.dk/statistics (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Calistri, P.; Amato, L.; Puglia, I.; Cito, F.; Di Giuseppe, A.; Danzetta, M.L.; Morelli, D.; Di Domenico, M.; Caporale, M.; Scialabba, S.; et al. Infection sustained by lineage B.1.1.7 of SARS-CoV-2 is characterised by longer persistence and higher viral RNA loads in nasopharyngeal swabs. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 753–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buss, L.F.; Prete, C.A., Jr.; Abrahim, C.M.M.; Mendrone, A., Jr.; Salomon, T.; de Almeida-Neto, C.; Franca, R.F.O.; Belotti, M.C.; Carvalho, M.; Costa, A.G.; et al. Three-quarters attack rate of SARS-CoV-2 in the Brazilian Amazon during a largely unmitigated epidemic. Science 2021, 371, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, F.; Novazzi, F.; Genoni, A.; Baj, A.; Spezia, P.G.; Focosi, D.; Zago, C.; Colombo, A.; Cassani, G.; Pasciuta, R.; et al. Imported SARS-CoV-2 variant P.1 in traveler returning from Brazil to Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1249–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, J. Covid-19: The E484K mutation and the risks it poses. BMJ 2021, 372, n359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Giallonardo, F.; Puglia, I.; Curini, V.; Cammà, C.; Mangone, I.; Calistri, P.; Cobbin, J.C.A.; Holmes, E.C.; Lorusso, A. Emergence and Spread of SARS-CoV-2 Lineages B.1.1.7 and P.1 in Italy. Viruses 2021, 13, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050794
Di Giallonardo F, Puglia I, Curini V, Cammà C, Mangone I, Calistri P, Cobbin JCA, Holmes EC, Lorusso A. Emergence and Spread of SARS-CoV-2 Lineages B.1.1.7 and P.1 in Italy. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050794
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Giallonardo, Francesca, Ilaria Puglia, Valentina Curini, Cesare Cammà, Iolanda Mangone, Paolo Calistri, Joanna C. A. Cobbin, Edward C. Holmes, and Alessio Lorusso. 2021. "Emergence and Spread of SARS-CoV-2 Lineages B.1.1.7 and P.1 in Italy" Viruses 13, no. 5: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050794
APA StyleDi Giallonardo, F., Puglia, I., Curini, V., Cammà, C., Mangone, I., Calistri, P., Cobbin, J. C. A., Holmes, E. C., & Lorusso, A. (2021). Emergence and Spread of SARS-CoV-2 Lineages B.1.1.7 and P.1 in Italy. Viruses, 13(5), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050794







