Mayaro Virus Infects Human Brain Cells and Induces a Potent Antiviral Response in Human Astrocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus, Cells and Reagents
2.2. Infection of hNPCs, Astrocytes and Pericytes
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Virus Titration
2.5. Extraction and Quantification of Viral RNA
2.6. RT2 Profiler PCR Array
2.7. Real-Time PCR Gene Expression Analysis
2.8. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assays
2.9. ELISA
3. Results
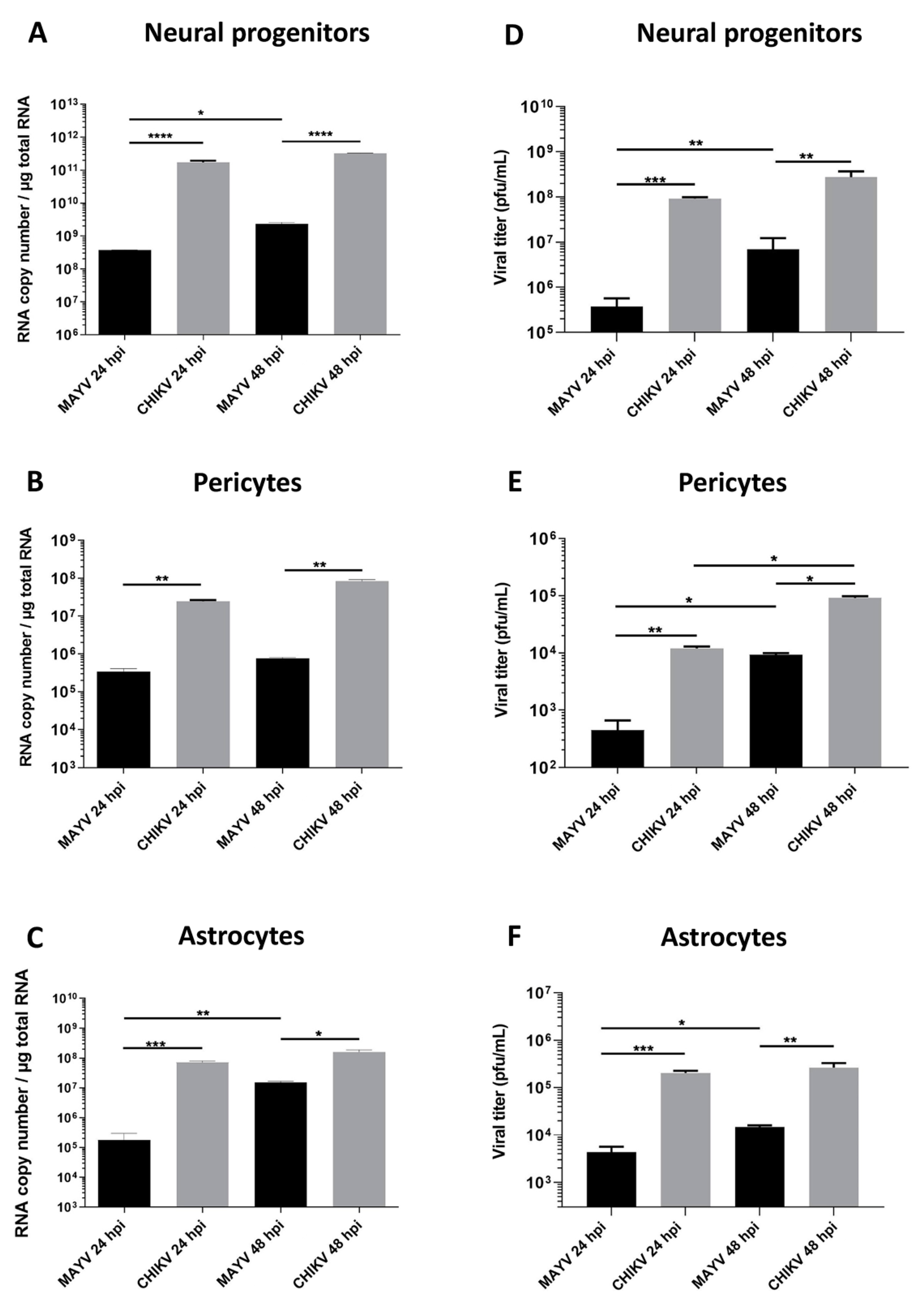
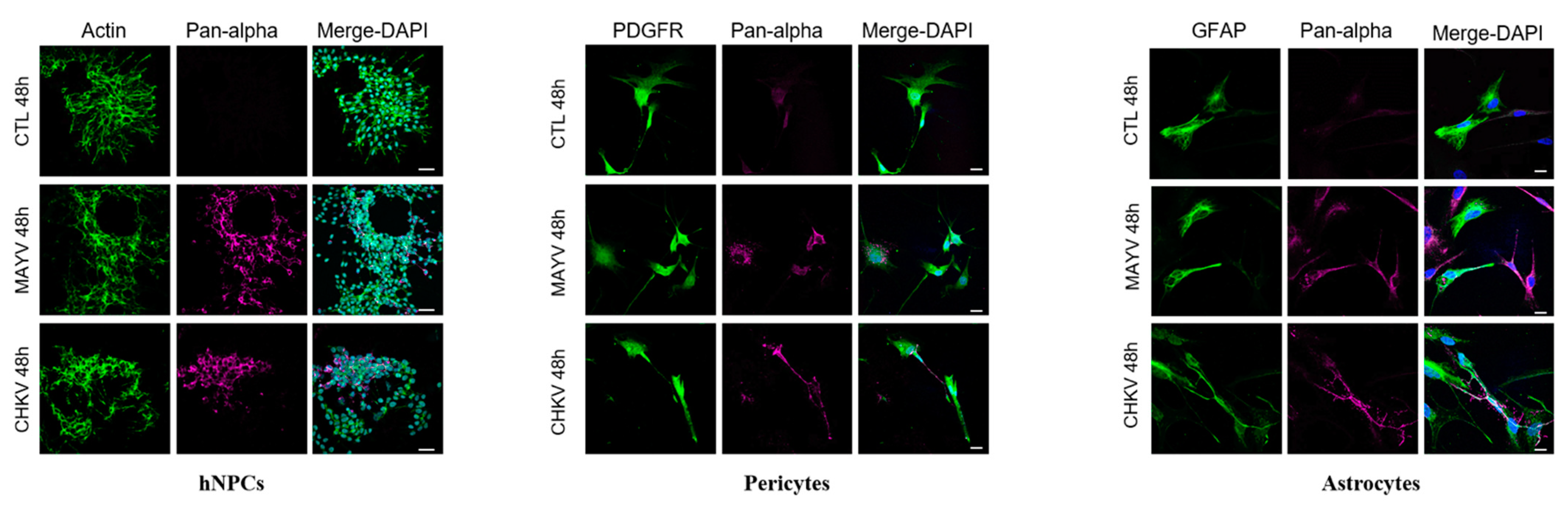
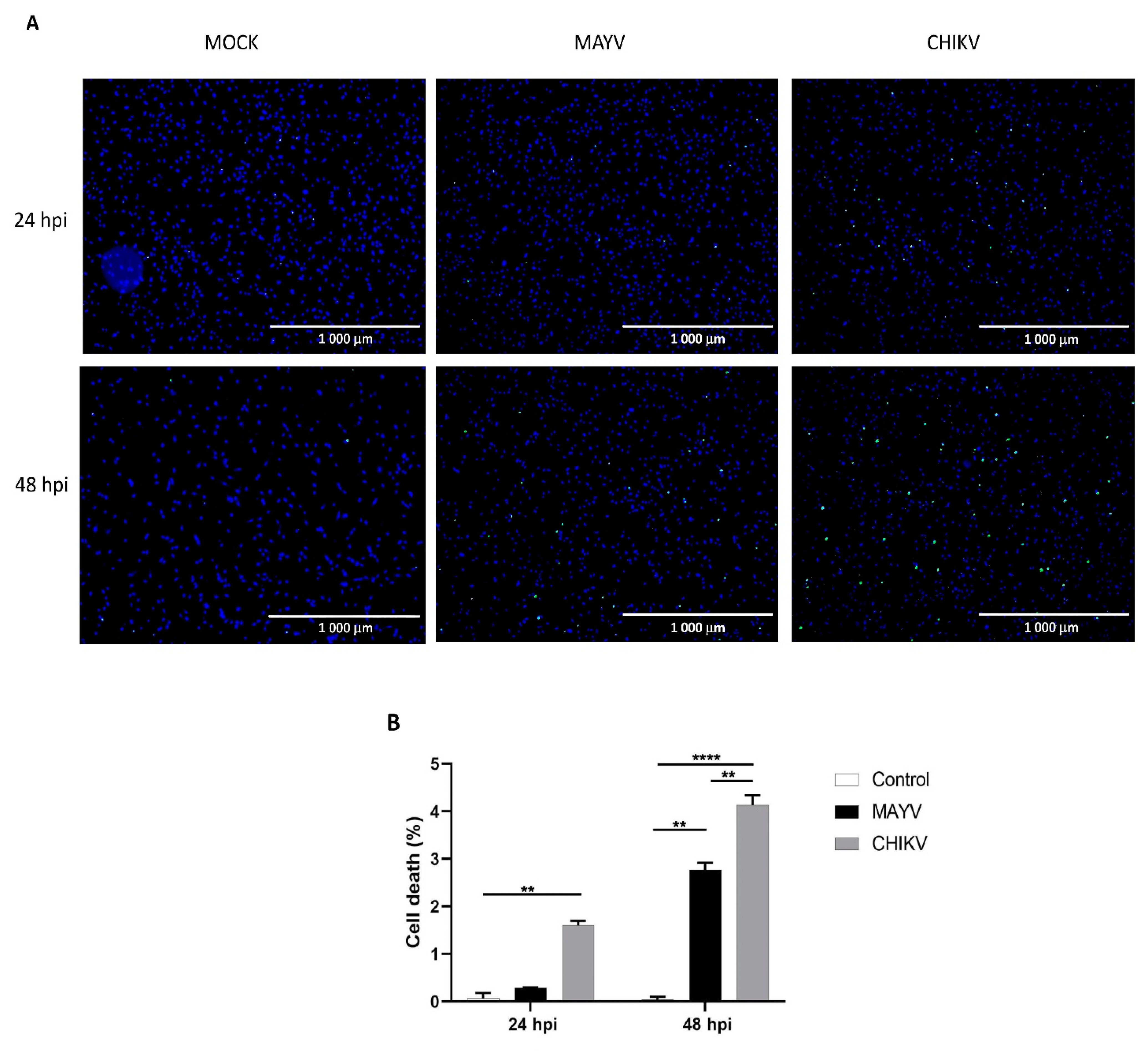
3.1. MAYV Efficiently Infects Human Neural Progenitor Cells, Astrocytes and Pericytes
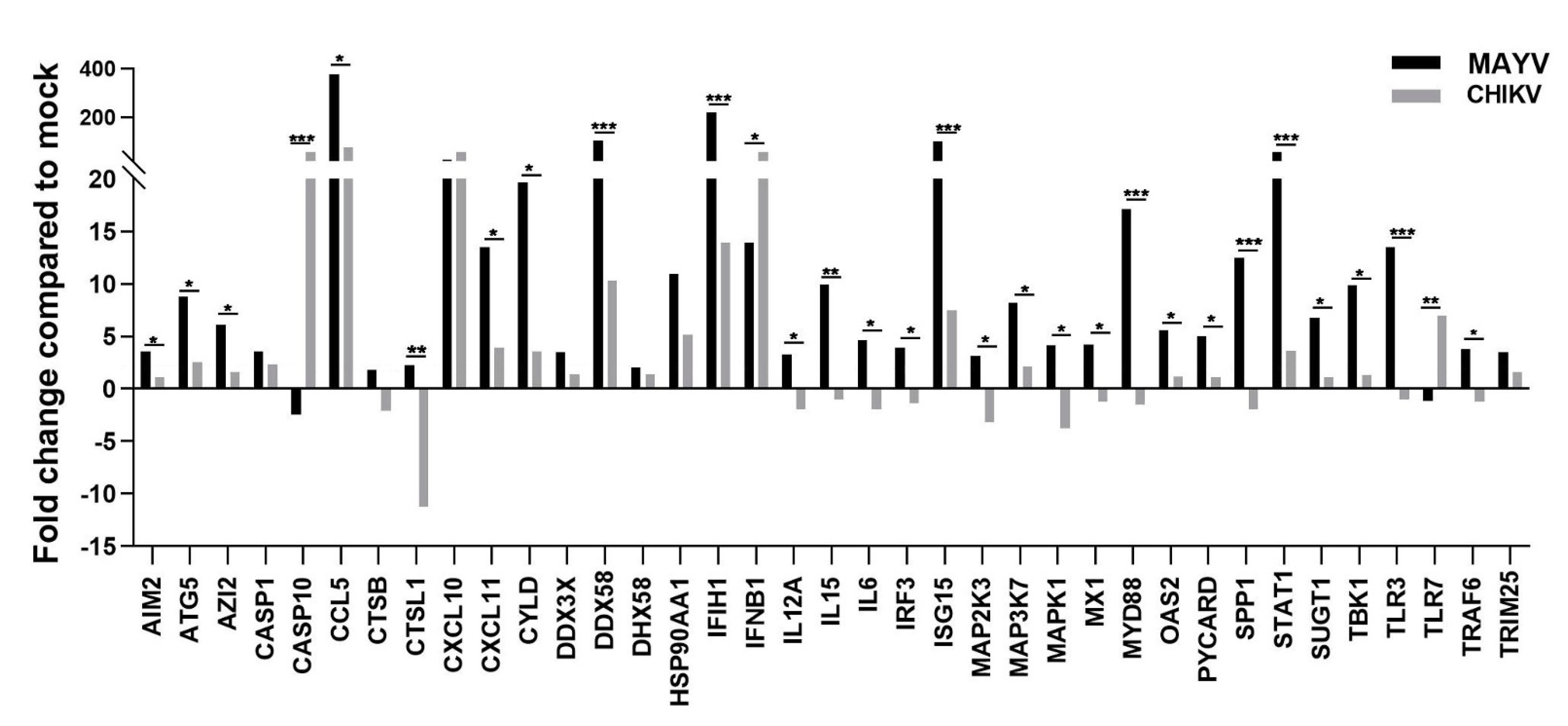
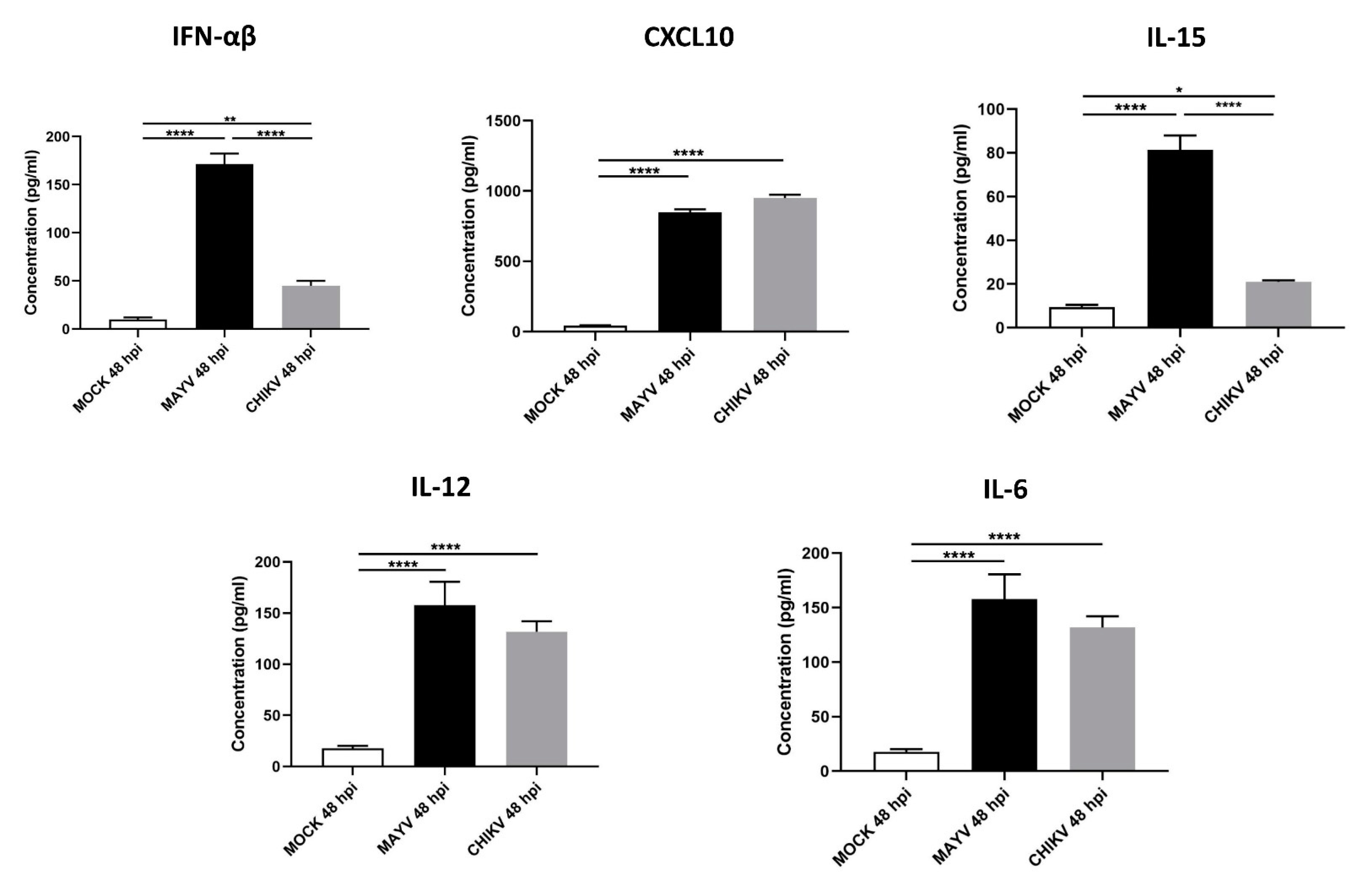
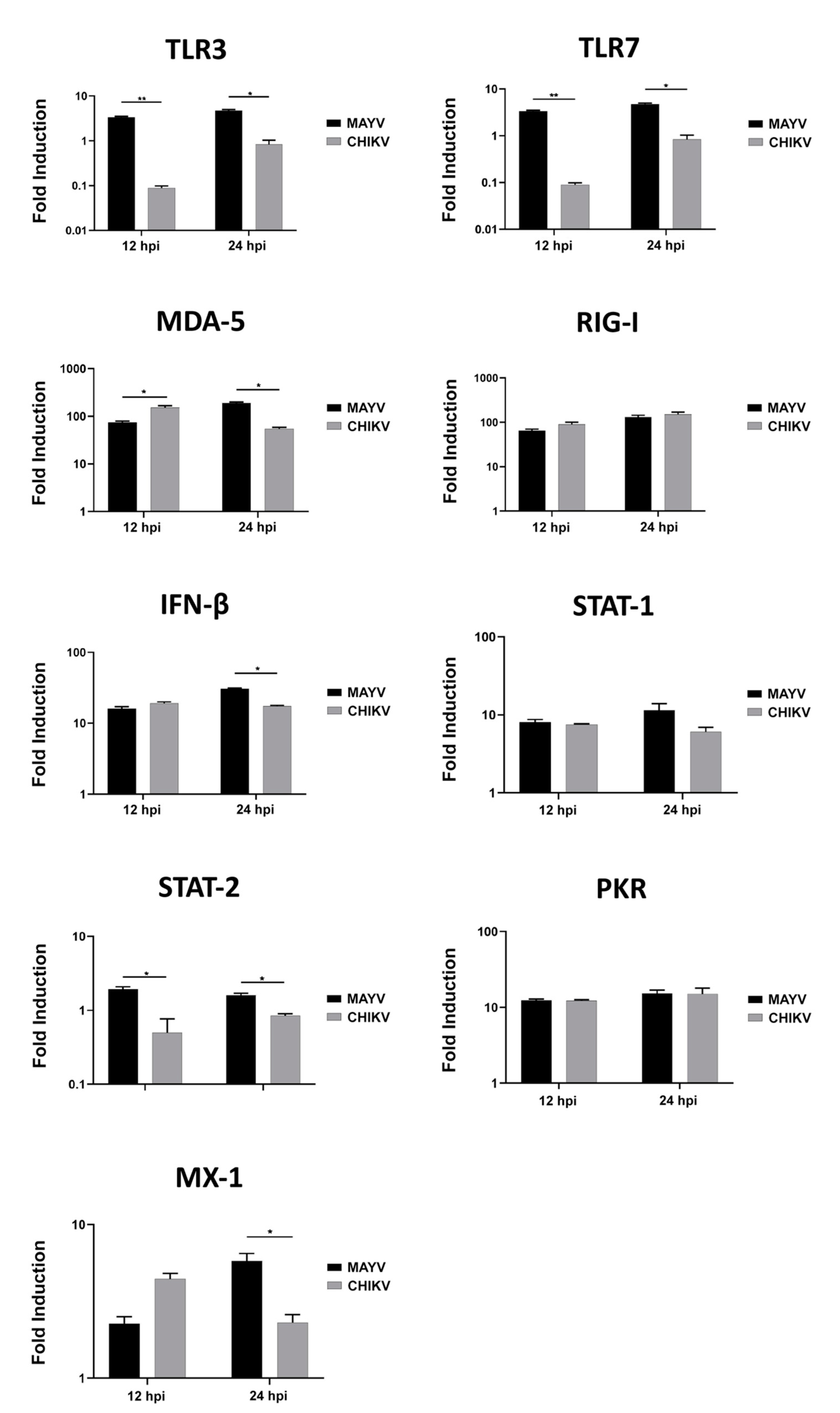
3.2. MAYV Elicits a Strong Antiviral Response in Human Astrocytes
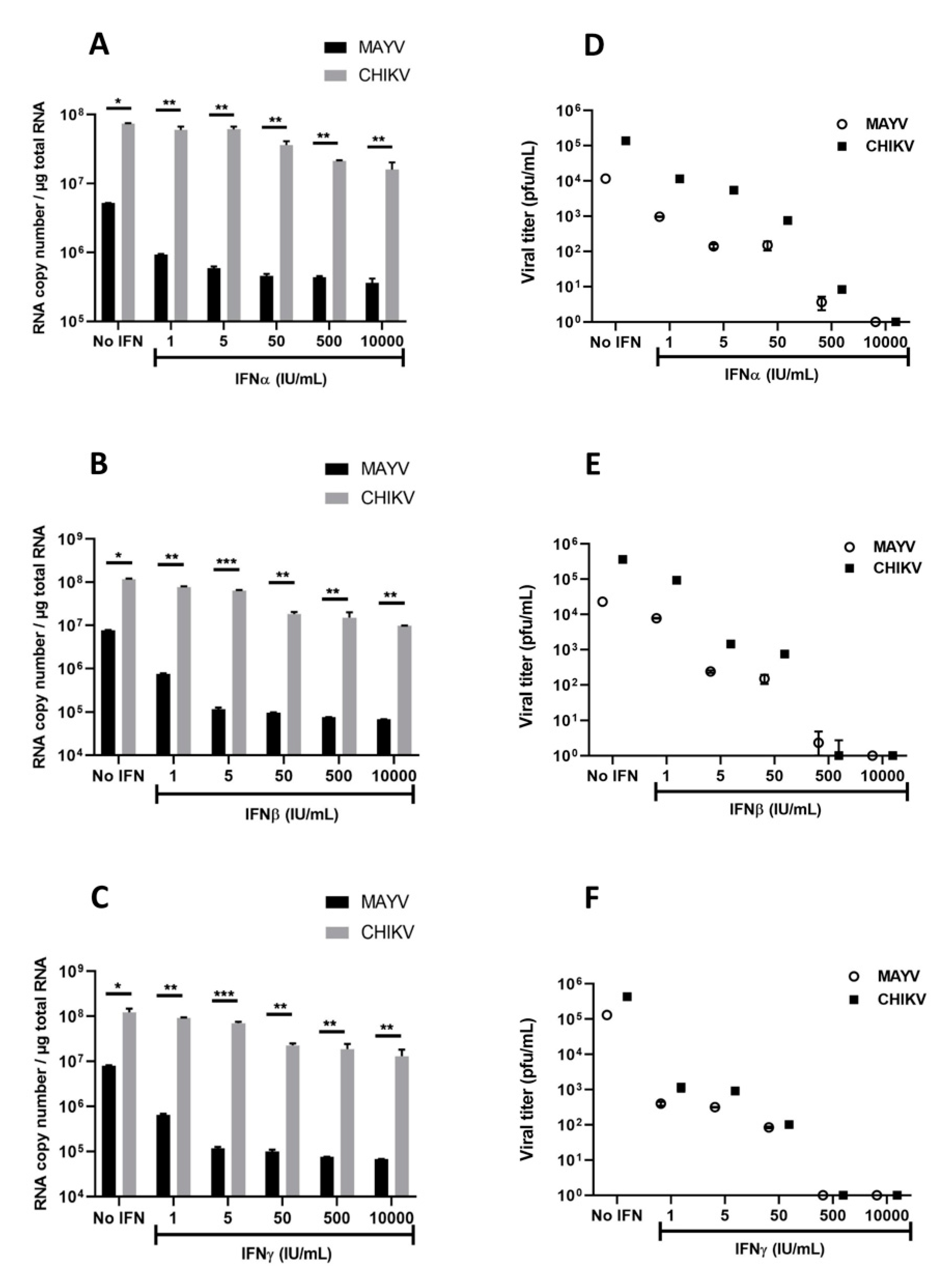
3.3. Interferons Inhibit MAYV Replication in Primary Human Astrocytes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weaver, S.C.; Charlier, C.; Vasilakis, N.; Lecuit, M. Zika, Chikungunya, and Other Emerging Vector-Borne Viral Diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2018, 69, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, E.; Pettersson, J.; Higgs, S.; Charrel, R.; De Lamballerie, X. Emerging arboviruses: Why today? One Health 2017, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.T.O.; Vedovello, D.; Estofolete, C.F.; Malossi, C.D.; Araújo, J.P.; Nogueira, M.L. Complete Genome Sequence of Mayaro Virus Imported from the Amazon Basin to São Paulo State, Brazil. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01341-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustolin, M.; Pujhari, S.; Henderson, C.A.; Rasgon, J.L. Anopheles mosquitoes may drive invasion and transmission of Mayaro virus across geographically diverse regions. Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieme, C.; Ciota, A.T.; Kramer, L.D. Transmission potential of Mayaro virus by Aedes albopictus, and Anopheles quadrimaculatus from the USA. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, F.; Alout, H.; Diagne, C.T.; Bengue, M.; Baronti, C.; Hamel, R.; Talignani, L.; Liegeois, F.; Pompon, J.; Vargas, R.E.M.; et al. Differential Susceptibility and Innate Immune Response of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus to the Haitian Strain of the Mayaro Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, C.T.; Bengue, M.; Choumet, V.; Hamel, R.; Pompon, J.; Missé, D. Mayaro Virus Pathogenesis and Transmission Mechanisms. Pathogens 2020, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E. Mayaro virus: A forest virus primed for a trip to the city? Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednicky, J.; De Rochars, V.M.B.; ElBadry, M.; Loeb, J.; Telisma, T.; Chavannes, S.; Anilis, G.; Cella, E.; Ciccozzi, M.; Okech, B.; et al. Mayaro Virus in Child with Acute Febrile Illness, Haiti, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2000–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavian, C.; Rife, B.D.; Dollar, J.J.; Cella, E.; Ciccozzi, M.; Prosperi, M.C.F.; Lednicky, J.; Morris, J.G.; Capua, I.; Salemi, M. Emergence of recombinant Mayaro virus strains from the Amazon basin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegoureix, I. Mayaro Fever–Epidemiological Alert. Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=15123:1-may-2019-mayaro-fever-epidemiological-alert&Itemid=42346&lang=en (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- Levi, L.I.; Vignuzzi, M. Arthritogenic Alphaviruses: A Worldwide Emerging Threat? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhrbier, A.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.-C.; Gasque, P. Arthritogenic alphaviruses—An overview. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, A.; Burt, F.J.; Liu, X.; Poo, Y.S.; Zandi, K.; Suhrbier, A.; Weaver, S.C.; Texeira, M.M.; Mahalingam, S. Arthritogenic alphaviruses: Epidemiological and clinical perspective on emerging arboviruses. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandale, B.V.; Sathe, P.S.; Arankalle, V.A.; Wadia, R.; Kulkarni, R.; Shah, S.V.; Shah, S.K.; Sheth, J.K.; Sudeep, A.; Tripathy, A.S.; et al. Systemic involvements and fatalities during Chikungunya epidemic in India, 2006. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economopoulou, A.; Dominguez, M.; Helynck, B.; Sissoko, D.; Wichmann, O.; Quenel, P.; Germonneau, P.; Quatresous, I. Atypical Chikungunya virus infections: Clinical manifestations, mortality and risk factors for severe disease during the 2005–2006 outbreak on Réunion. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 137, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmannitya, S.; Halstead, S.B.; Cohen, S.N.; Margiotta, M.R. Dengue and Chikungunya Virus Infection in Man in Thailand, 1962–1964. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1969, 18, 954–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, K.V.; Kalyanasundaram, V.; Rajgopal, J. Clinical and pathological studies on chikungunya fever in Madras city. Indian J. Med Res. 1965, 53, 729–744. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, G.; Botelho, D.; Souza, G.; Braune, C.; Breder, R.; Pupe, C.; Pinheiro, T.; Fillipis, A.M. Chikungunya Virus Meningoencephalitis: A Case Report (4362). Neurology 2020, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Mittal, S.; Bharati, M.J.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Saravanan, S.; Sathe, P.S. Optic Neuritis Associated With Chikungunya Virus Infection in South India. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2007, 125, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Gerardin, P.; De Brito, C.A.A.; Soares, C.N.; Ferreira, M.L.B.; Solomon, T. The neurological complications of chikungunya virus: A systematic review. Rev. Med Virol. 2018, 28, e1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemant, J.; Boisson, V.; Winer, A.; Thibault, L.; André, H.; Tixier, F.; Lemercier, M.; Antok, E.; Cresta, M.P.; Grivard, P.; et al. Serious acute chikungunya virus infection requiring intensive care during the reunion island outbreak in 2005–2006. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.R.; Falleiros-Arlant, L.H.; Dueñas, L.; Pleitez-Navarrete, J.; Salgado, D.M.; Castillo, J.B.-D. Congenital and perinatal complications of chikungunya fever: A Latin American experience. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 51, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerny, T.; Schwarz, M.; Lemant, J.; Gérardin, P.; Keller, E. The Range of Neurological Complications in Chikungunya Fever. Neurocritical Care 2017, 27, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Hoarau, J.J.; Bandjee, M.C.J.; Maquart, M.; Gasque, P. Multifaceted innate immune responses engaged by astrocytes, microglia and resident dendritic cells against Chikungunya neuroinfection. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, F.M.; Lee, K.M.; Chiu, K.B.; Purcell, O.M.; Didier, P.J.; Russell-Lodrigue, K.; Weaver, S.C.; Roy, C.J.; MacLean, A.G.; Russell-Lodrigues, K. Neuropathogenesis of Chikungunya infection: Astrogliosis and innate immune activation. J. Neurovirol. 2015, 22, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-Espinosa, J.; Gómez-Dantés, H. Arbovirus causing hemorrhagic fever at IMSS. Rev. Med. Inst. Mex. Seguro Soc. 2006, 44, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- De-Simone, S.G. Mayaro Virus Disease. J. Hum. Virol. Retrovirol. 2014, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenhoven, J.; Jansson, D.; Smyth, L.C.; Dragunow, M. Brain Pericytes As Mediators of Neuroinflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Astrocytes: Role and Functions in Brain Pathologies. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Zou, Z.; Wang, S.; Jin, M. Insights into Human Astrocyte Response to H5N1 Infection by Microarray Analysis. Viruses 2015, 7, 2618–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potokar, M.; Jorgačevski, J.; Zorec, R. Astrocytes in Flavivirus Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, H.; Cain, M.D.; Jiang, X.; Roth, R.A.; Beatty, W.L.; Sun, C.; Klimstra, W.B.; Hou, J.; Klein, R.S. Encephalitic Alphaviruses Exploit Caveola-Mediated Transcytosis at the Blood-Brain Barrier for Central Nervous System Entry. mBio 2020, 11, e02731-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clé, M.; Barthelemy, J.; Desmetz, C.; Foulongne, V.; Lapeyre, L.; Bolloré, K.; Tuaillon, E.; Erkilic, N.; Kalatzis, V.; Lecollinet, S.; et al. Study of Usutu virus neuropathogenicity in mice and human cellular models. Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.S.; Garber, C.; Funk, K.E.; Salimi, H.; Soung, A.; Kanmogne, M.; Manivasagam, S.; Agner, S.; Cain, M. Neuroinflammation During RNA Viral Infections. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengue, M.; Ferraris, P.; Baronti, C.; Diagne, C.T.; Talignani, L.; Wichit, S.; Liegeois, F.; Bisbal, C.; Nougairède, A.; Missé, D. Mayaro Virus Infects Human Chondrocytes and Induces the Expression of Arthritis-Related Genes Associated with Joint Degradation. Viruses 2019, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, D.; Pöltl, D.; Genewsky, A.; Weng, M.; Waldmann, T.; Schildknecht, S.; Leist, M. Rapid, complete and large-scale generation of post-mitotic neurons from the human LUHMES cell line. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, R.; Dejarnac, O.; Wichit, S.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Neyret, A.; Luplertlop, N.; Perera-Lecoin, M.; Surasombatpattana, P.; Talignani, L.; Thomas, F.; et al. Biology of Zika Virus Infection in Human Skin Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8880–8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryman, K.D.; Klimstra, W.B.; Nguyen, K.B.; Biron, C.A.; Johnston, R.E. Alpha/Beta Interferon Protects Adult Mice from Fatal Sindbis Virus Infection and Is an Important Determinant of Cell and Tissue Tropism. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3366–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clé, M.; Eldin, P.; Briant, L.; Lannuzel, A.; Simonin, Y.; Van De Perre, P.; Cabié, A.; Salinas, S. Neurocognitive impacts of arbovirus infections. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, C.M.; Neris, R.L.D.S.; Gavino-Leopoldino, D.; Da Silva, M.O.L.; Almeida, J.S.; Dos-Santos, J.S.; Figueiredo, C.P.; Bellio, M.; Bozza, M.T.; Assunção-Miranda, I. Mayaro Virus Replication Restriction and Induction of Muscular Inflammation in Mice Are Dependent on Age, Type-I Interferon Response, and Adaptive Immunity. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, J.; Chen, W.; Foo, S.-S.; Lee, S.-A.; Ge, J.; Wang, S.; Goldman, S.A.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Zika Virus NS4A and NS4B Proteins Deregulate Akt-mTOR Signaling in Human Fetal Neural Stem Cells to Inhibit Neurogenesis and Induce Autophagy. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, P.; Cochet, M.; Hamel, R.; Gladwyn-Ng, I.; Alfano, C.; Diop, F.; Garcia, D.; Talignani, L.; Montero-Menei, C.N.; Nougairède, A.; et al. Zika virus differentially infects human neural progenitor cells according to their state of differentiation and dysregulates neurogenesis through the Notch pathway. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Ayyadurai, S.; Zlokovic, B.V. Pericytes of the neurovascular unit: Key functions and signaling pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, R.; Mudaliar, P.; Padmanabhan, A.; Sreekumar, E. Induction of Cytopathogenicity in Human Glioblastoma Cells by Chikungunya Virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, R.; Patro, I.; Parida, M. TLR3 mediated innate immune response in mice brain following infection with Chikungunya virus. Virus Res. 2014, 189, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Her, Z.; Teng, T.; Tan, J.J.L.; Teo, T.; Kam, Y.; Lum, F.; Lee, W.W.L.; Gabriel, C.; Melchiotti, R.; Andiappan, A.K.; et al. Loss of TLR3 aggravates CHIKV replication and pathology due to an altered virus-specific neutralizing antibody response. Embo Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.K.; Tripathi, A. Association of toll-like receptor polymorphisms with susceptibility to chikungunya virus infection. Virology 2017, 511, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirato, K.; Kimura, T.; Mizutani, T.; Kariwa, H.; Takashima, I. Different chemokine expression in lethal and non-lethal murine west nile virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emichlmayr, D.; Lim, J.K. Chemokine receptors as important regulators of pathogenesis during arboviral encephalitis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.S.; Lin, E.; Zhang, B.; Luster, A.D.; Tollett, J.; Samuel, M.A.; Engle, M.; Diamond, M.S. Neuronal CXCL10 Directs CD8+ T-Cell Recruitment and Control of West Nile Virus Encephalitis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11457–11466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Marle, G.; Antony, J.; Ostermann, H.; Dunham, C.; Hunt, T.; Halliday, W.; Maingat, F.; Urbanowski, M.D.; Hobman, T.; Peeling, J.; et al. West Nile Virus-Induced Neuroinflammation: Glial Infection and Capsid Protein-Mediated Neurovirulence. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10933–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, Y.-W.; Leite, J.A.; Lum, F.-M.; Tan, J.J.L.; Lee, B.; Judice, C.C.; Teixeira, D.A.D.T.; Andreata-Santos, R.; Vinolo, M.A.; Angerami, R.; et al. Specific Biomarkers Associated With Neurological Complications and Congenital Central Nervous System Abnormalities From Zika Virus-Infected Patients in Brazil. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, K.L.W.; Troisi, E.M.; Baxter, V.K.; Glowinski, R.; Griffin, D.E. Interferon regulatory factors 3 and 7 have distinct roles in the pathogenesis of alphavirus encephalomyelitis. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Ou, Y.-C.; Li, J.-R.; Chang, C.-Y.; Pan, H.-C.; Lai, C.-Y.; Liao, S.-L.; Raung, S.-L.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-J. Infection of Pericytes In Vitro by Japanese Encephalitis Virus Disrupts the Integrity of the Endothelial Barrier. J. Virol. 2013, 88, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Stone, K.P.; Hsuchou, H.; Manda, V.K.; Zhang, Y.; Kastin, A.J. Cytokine Signaling Modulates Blood-Brain Barrier Function. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, H.E.; Blom-Roosemalen, M.C.; Van Oosten, M.; De Boer, A.G.; Van Berkel, T.J.; Breimer, D.D.; Kuiper, J. The influence of cytokines on the integrity of the blood-brain barrier in vitro. J. Neuroimmunol. 1996, 64, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Her, Z.; Ong, E.K.S.; Chen, J.-M.; Dimatatac, F.; Kwek, D.J.C.; Barkham, T.; Yang, H.; Rénia, L.; Leo, Y.-S.; et al. Persistent Arthralgia Induced by Chikungunya Virus Infection is Associated with Interleukin-6 and Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fros, J.J.; Liu, W.J.; Prow, N.A.; Geertsema, C.; Ligtenberg, M.; VanLandingham, D.L.; Schnettler, E.; Vlak, J.M.; Suhrbier, A.; Khromykh, A.A.; et al. Chikungunya Virus Nonstructural Protein 2 Inhibits Type I/II Interferon-Stimulated JAK-STAT Signaling. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10877–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, J.D.; White, L.J.; Morrison, T.E.; Montgomery, S.A.; Whitmore, A.C.; Johnston, R.E.; Heise, M.T. Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus Disrupts STAT1 Signaling by Distinct Mechanisms Independent of Host Shutoff. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10571–10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, R.; Mundt, F.; Gilthorpe, J.D.; Wölfel, S.; Gekara, N.O.; Kröger, A.; Överby, A.K. Fast type I interferon response protects astrocytes from flavivirus infection and virus-induced cytopathic effects. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detje, C.N.; Lienenklaus, S.; Chhatbar, C.; Spanier, J.; Prajeeth, C.K.; Soldner, C.; Tovey, M.G.; Schlüter, D.; Weiss, S.; Stangel, M.; et al. Upon Intranasal Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Infection, Astrocytes in the Olfactory Bulb Are Important Interferon Beta Producers That Protect from Lethal Encephalitis. J. Virol. 2014, 89, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Gardner, C.L.; Burke, C.W.; Ryman, K.D.; Klimstra, W.B. Similarities and Differences in Antagonism of Neuron Alpha/Beta Interferon Responses by Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis and Sindbis Alphaviruses. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10036–10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.D.L.; Da, F.B.A.L. Characterization of the immune response following in vitro mayaro and chikungunya viruses (Alphavirus, Togaviridae) infection of mononuclear cells. Virus Res. 2018, 256, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Myoung, J. Chikungunya Virus-Encoded nsP2, E2 and E1 Strongly Antagonize the Interferon- ¥Signaling Pathway. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göertz, G.P.; McNally, K.L.; Robertson, S.J.; Best, S.M.; Pijlman, G.P.; Fros, J.J. The Methyltransferase-Like Domain of Chikungunya Virus nsP2 Inhibits the Interferon Response by Promoting the Nuclear Export of STAT1. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meertens, L.; Hafirassou, M.L.; Couderc, T.; Bonnet-Madin, L.; Kril, V.; Kümmerer, B.M.; LaBeau, A.; Brugier, A.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; et al. FHL1 is a major host factor for chikungunya virus infection. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 574, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, B.P.; Holman, D.W.; Cruz-Orengo, L.; Jujjavarapu, H.; Durrant, D.M.; Klein, R.S. Viral Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns Regulate Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity via Competing Innate Cytokine Signals. mBio 2014, 5, e01476-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bengue, M.; Ferraris, P.; Barthelemy, J.; Diagne, C.T.; Hamel, R.; Liégeois, F.; Nougairède, A.; de Lamballerie, X.; Simonin, Y.; Pompon, J.; et al. Mayaro Virus Infects Human Brain Cells and Induces a Potent Antiviral Response in Human Astrocytes. Viruses 2021, 13, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030465
Bengue M, Ferraris P, Barthelemy J, Diagne CT, Hamel R, Liégeois F, Nougairède A, de Lamballerie X, Simonin Y, Pompon J, et al. Mayaro Virus Infects Human Brain Cells and Induces a Potent Antiviral Response in Human Astrocytes. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030465
Chicago/Turabian StyleBengue, Michèle, Pauline Ferraris, Jonathan Barthelemy, Cheikh Tidiane Diagne, Rodolphe Hamel, Florian Liégeois, Antoine Nougairède, Xavier de Lamballerie, Yannick Simonin, Julien Pompon, and et al. 2021. "Mayaro Virus Infects Human Brain Cells and Induces a Potent Antiviral Response in Human Astrocytes" Viruses 13, no. 3: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030465
APA StyleBengue, M., Ferraris, P., Barthelemy, J., Diagne, C. T., Hamel, R., Liégeois, F., Nougairède, A., de Lamballerie, X., Simonin, Y., Pompon, J., Salinas, S., & Missé, D. (2021). Mayaro Virus Infects Human Brain Cells and Induces a Potent Antiviral Response in Human Astrocytes. Viruses, 13(3), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030465










