Recent Progress on Exosomes in RNA Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
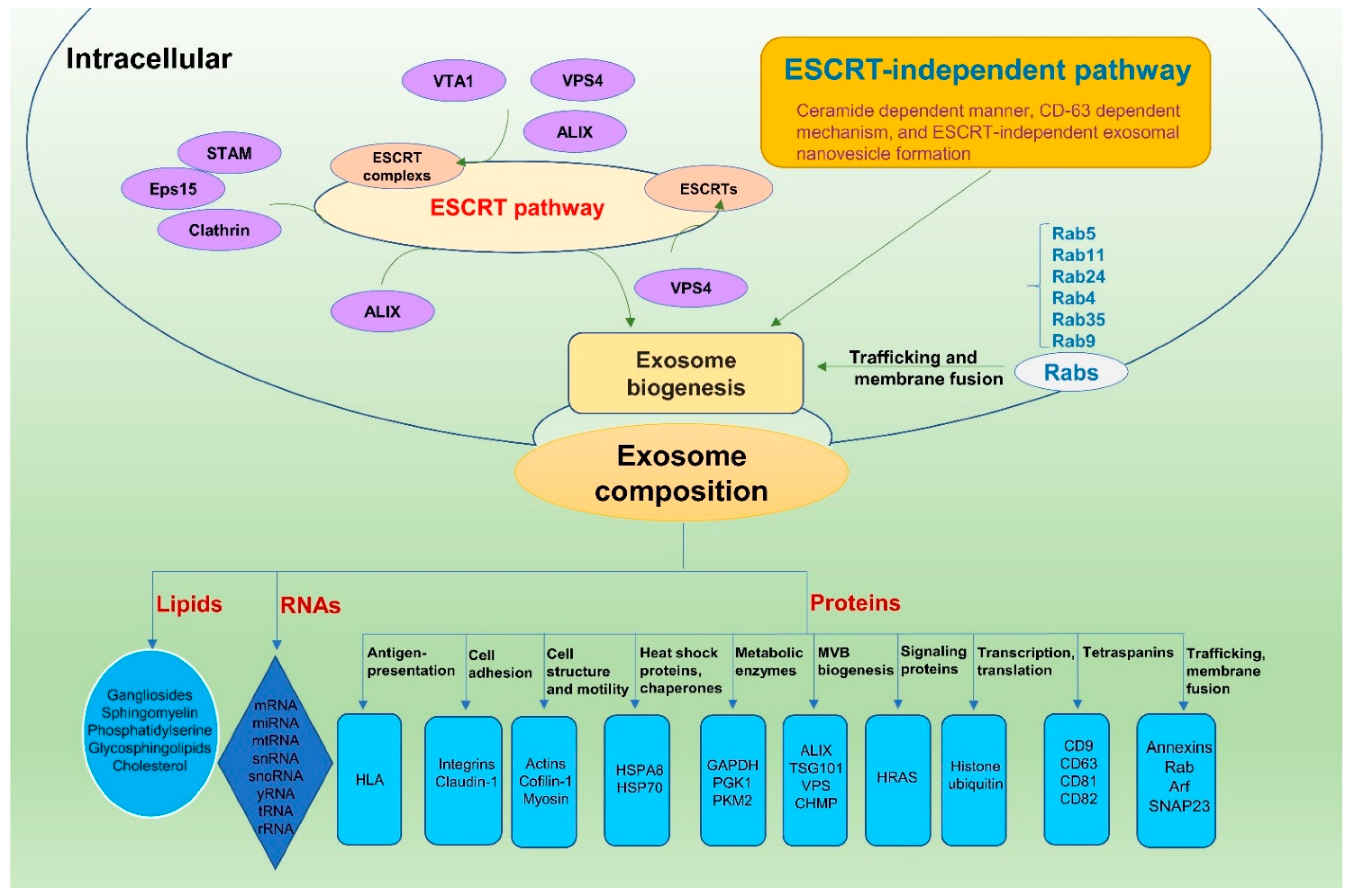
2. Exosome Biogenesis
3. Exosome Composition
4. Roles of Exosomes in the Transmission and Replication of RNA Viruses
4.1. Roles for Exosomes in Enveloped Virus Processes
4.1.1. Exosomes with HIV
4.1.2. Exosomes with HCV
4.1.3. Exosomes and Other Enveloped Viruses
5. Roles of Exosomes in Nonenveloped RNA Virus Processes
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greening, D.W.; Simpson, R.J. Understanding extracellular vesicle diversity—Current status. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 887–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latifkar, A.; Hur, Y.H.; Sanchez, J.C.; Cerione, R.A.; Antonyak, M.A. New insights into extracellular vesicle biogenesis and function. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs222406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Burrola, S.; Wu, J.; Ding, W.-Q. Extracellular vesicles in the development of cancer therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.; Heuser, J.; Stahl, P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 97, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassov, A.V.; Magdaleno, S.; Setterquist, R.; Conrad, R. Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoorvogel, W.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Geuze, H.J.; Raposo, G. The biogenesis and functions of exosomes. Traffic 2002, 3, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenquer, M.; Amorim, M.J. Exosome biogenesis, regulation, and function in viral infection. Viruses 2015, 7, 5066–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrik, J. Immunomodulatory effects of exosomes produced by virus-infected cells. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2016, 55, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; Van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Théry, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuffers, S.; Wegner, C.S.; Stenmark, H.; Brech, A. Multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the absence of ESCRTs. Traffic 2009, 10, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, G.; Charrin, S.; Simoes, S.; Romao, M.; Rochin, L.; Saftig, P.; Marks, M.S.; Rubinstein, E.; Raposo, G. The tetraspanin CD63 regulates ESCRT-independent and -dependent endosomal sorting during melanogenesis. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brügger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghossoub, R.; Lembo, F.; Rubio, A.; Gaillard, C.B.; Bouchet, J.; Vitale, N.; Slavík, J.; Machala, M.; Zimmermann, P. Syntenin-ALIX exosome biogenesis and budding into multivesicular bodies are controlled by ARF6 and PLD2. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henne, W.M.; Buchkovich, N.J.; Emr, S.D. The ESCRT pathway. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H.; Hanson, P.I. Membrane budding and scission by the ESCRT machinery: It’s all in the neck. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 11, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschuschke, M.; Kocherova, I.; Bryja, A.; Mozdziak, P.; Volponi, A.A.; Janowicz, K.; Sibiak, R.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H.; Iżycki, D.; Bukowska, D.; et al. Inclusion biogenesis, methods of isolation and clinical application of human cellular exosomes. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hernandez, D.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Jorge, I.; Lopez-Martin, S.; Ursa, A.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Vazquez, J.; Yanez-Mo, M. The intracellular interactome of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains reveals their function as sorting machineries toward exosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11649–11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, A.; Meyering, S.S.; Lepene, B.; Iordanskiy, S.; van Hoek, M.L.; Hakami, R.M.; Kashanchi, F. Extracellular vesicles from infected cells: Potential for direct pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.G.; Booth, A.; Gould, S.J.; Hildreth, J.E.K. Evidence that HIV budding in primary macrophages occurs through the exosome release pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52347–52354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batagov, A.O.; Kurochkin, I.V. Exosomes secreted by human cells transport largely mRNA fragments that are enriched in the 3′-untranslated regions. Biol. Direct 2013, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; Van Eijndhoven, M.A.J.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; De Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Eisele, A.S.; Pegtel, D.M.; Bervoets, S.; Verhaar, M.C. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of small RNAs in human endothelial cells and exosomes provides insights into localized RNA processing, degradation and sorting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, D.; Vázquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Record, M.; Carayon, K.; Poirot, M.; Silvente-Poirot, S. Exosomes as new vesicular lipid transporters involved in cell–cell communication and various pathophysiologies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2014, 1841, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadiu, I.; Narayanasamy, P.; Dash, P.K.; Zhang, W.; Gendelman, H.E. Biochemical and biologic characterization of exosomes and microvesicles as facilitators of HIV-1 infection in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, R.D.; Gummuluru, S. Immature dendritic cell-derived exosomes can mediate HIV-1 trans infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenassi, M.; Cagney, G.; Liao, M.; Vaupotič, T.; Bartholomeeusen, K.; Cheng, Y.; Krogan, N.J.; Plemenitaš, A.; Peterlin, B. HIV Nef is secreted in exosomes and triggers apoptosis in bystander CD4+ T cells. Traffic 2010, 11, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahar, H.S.; Bao, X.; Casola, A. Exosomes and their role in the life cycle and pathogenesis of RNA viruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 3204–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqil, M.; Naqvi, A.R.; Mallik, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Maulik, U.; Jameel, S. The HIV Nef protein modulates cellular and exosomal miRNA profiles in human monocytic cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.R.; Wonderlich, E.R.; Roeth, J.F.; Leonard, J.A.; Collins, K.L. HIV-1 Nef targets MHC-I and CD4 for degradation via a final common beta-COP-dependent pathway in T cells. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wu, N.; Gan, X.; Yan, W.; Morrell, J.C.; Gould, S.J. Higher-order oligomerization targets plasma membrane proteins and hiv gag to exosomes. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, A.; Iordanskiy, S.; Das, R.; Van Duyne, R.; Santos, S.; Jaworski, E.; Guendel, I.; Sampey, G.; Dalby, E.; Iglesias-Ussel, M.; et al. Exosomes derived from HIV-1-infected cells contain trans-activation response element RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20014–20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, M.A.; Zhao, H.; Yue, S.C.; Anandaiah, A.; Koziel, H.; Tachado, S.D. Novel HIV-1 miRNAs stimulate TNFα release in human macrophages via TLR8 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu, K.A.; Chu, J.; Huang, M.B.; Amancha, P.K.; Armstrong, W.S.; Powell, M.D.; Villinger, F.; Bond, V.C. Association of cytokines with exosomes in the plasma of HIV-1–seropositive individuals. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Brühl, H.; Klier, C.; Nelson, P.J.; Cihak, J.; Plachý, J.; Stangassinger, M.; Erfle, V.; Schlöndorff, D. Transfer of the chemokine receptor CCR5 between cells by membrane-derived microparticles: A mechanism for cellular human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, M.T.; Graham, D.R.; Coren, L.V.; Trubey, C.M.; Bess, J.W., Jr.; Arthur, L.O.; Ott, D.E.; Lifson, J.D. Differential incorporation of CD45, CD80 (B7-1), CD86 (B7-2), and major histocompatibility complex class I and II molecules into human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions and microvesicles: Implications for viral pathogenesis and immune regulation. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6173–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Sun, B.; Gupta, A.; Rempel, H.; Pulliam, L. Monocyte exosomes induce adhesion molecules and cytokines via activation of NF-kappaB in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3097–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenaccio, C.; Chiozzini, C.; Columba-Cabezas, S.; Manfredi, F.; Affabris, E.; Baur, A.; Federico, M. Exosomes from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected cells license quiescent CD4+ T lymphocytes to replicate HIV-1 through a Nef- and ADAM17-dependent mechanism. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11529–11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; et al. Exosomes mediate the cell-to-cell transmission of IFN-α-induced antiviral activity. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admyre, C.; Johansson, S.M.; Paulie, S.; Gabrielsson, S. Direct exosome stimulation of peripheral humanT cells detected by ELISPOT. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, S.D.; Smiley, J.R.; Bushman, F.D. The interferon response inhibits HIV particle production by induction of TRIM22. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, B.R.; Markovitz, D.M.; Woodford, N.L.; Rochford, R.; Strieter, R.M.; Coffey, M.J. TNF-alpha inhibits HIV-1 replication in peripheral blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages by inducing the production of RANTES and decreasing C-C chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) expression. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar]
- Creery, D.; Weiss, W.; Graziani-Bowering, G.; Kumar, R.; Aziz, Z.; Angel, J.B.; Kumar, A. Differential regulation of CXCR4 and CCR5 expression by interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 is associated with inhibition of chemotaxis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 replication but not HIV entry into human monocytes. Viral Immunol. 2006, 19, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, R.-H.; Ho, W.-Z.; Li, J.-L. Exosomes contribute to the transmission of anti-HIV activity from TLR3-activated brain microvascular endothelial cells to macrophages. Antivir. Res. 2016, 134, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, A.K.; Taylor, H.E.; Hildreth, J.E.K.; Popik, W. Exosomes packaging APOBEC3G confer human immunodeficiency virus resistance to recipient cells. J. Virol. 2008, 83, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; He, J.J. Exosome-associated hepatitis C virus in cell cultures and patient plasma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariumi, Y.; Kuroki, M.; Maki, M.; Ikeda, M.; Dansako, H.; Wakita, T.; Kato, N. The ESCRT system is required for hepatitis C virus production. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fénéant, L.; Levy, S.; Cocquerel, L. CD81 and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Viruses 2014, 6, 535–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assil, S.; Webster, B.; Dreux, M. Regulation of the host antiviral state by intercellular communications. Viruses 2015, 7, 4707–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukong, T.N.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Kodys, K.; Bala, S.; Szabo, G. Exosomes from hepatitis C infected patients transmit HCV infection and contain replication competent viral RNA in complex with Ago2-miR122-HSP90. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-C.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Sarnow, P. Supporting role for GTPase Rab27a in hepatitis C virus RNA replication through a novel miR-122-mediated effect. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-K.; Saxena, V.; Tseng, C.-H.; Jeng, K.-S.; Kohara, M.; Lai, M.M.C. Nonstructural protein 5A is incorporated into hepatitis C virus low-density particle through interaction with core protein and microtubules during intracellular transport. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón, V.; Acosta-Rivero, N.; González, S.; Dueñas-Carrera, S.; Martinez-Donato, G.; Menéndez, I.; Garateix, R.; Silva, J.A.; Acosta, E.; Kouri, J.B. Ultrastructural and biochemical basis for hepatitis C virus morphogenesis. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, S.; Kriss, M.; Golden-Mason, L.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Stone, A.E.; Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Mitchell, A.; Khetani, S.R.; Yamane, D.; Stoddard, M.; et al. Hepatitis C virus infection induces autocrine interferon signaling by human liver endothelial cells and release of exosomes, which inhibits viral replication. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 392–402.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longatti, A. The dual role of exosomes in hepatitis A and C virus transmission and viral immune activation. Viruses 2015, 7, 6707–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Ma, T.C.; Song, L.; Wu, J.G.; Li, J.L.; Ho, W.Z. Toll-like receptor 3-activated macrophages confer anti-HCV activity to hepatocytes through exosomes. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4132–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Xu, C.; Fang, S.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, W.; Qi, Z. Exosomal MicroRNAs derived from umbilical mesenchymal stem cells inhibit hepatitis C virus infection. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaguiri, K.K.; Dos Santos, D.F.; Slavov, S.N.; Depieri, L.V.; Palma, P.V.B.; Meirelles, F.V.; Covas, D.T.; da Silveira, J.C.; Kashima, S. TAX-mRNA-carrying exosomes from human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells can induce interferon-gamma production in vitro. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2018, 34, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworski, E.; Narayanan, A.; Van Duyne, R.; Shabbeer-Meyering, S.; Iordanskiy, S.; Saifuddin, M.; Das, R.; Afonso, P.V.; Sampey, G.C.; Chung, M.; et al. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells secrete exosomes that contain tax protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22284–22305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.R.; Pleet, M.L.; Enose-Akahata, Y.; Erickson, J.; Monaco, M.C.; Akpamagbo, Y.; Velluci, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Azodi, S.; Lepene, B.; et al. Viral antigens detectable in CSF exosomes from patients with retrovirus associated neurologic disease: Functional role of exosomes. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzeit, C.; Nagy, N.; Gentile, M.; Lyberg, K.; Gumz, J.; Vallhov, H.; Puga, I.; Klein, E.; Gabrielsson, S.; Cerutti, A.; et al. Correction: Exosomes derived from Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines induce proliferation, differentiation, and class-switch recombination in B cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, J.; Aslan, C.; Ahmadi, M.; Zolbanin, N.M.; Kashanchi, F.; Jafari, R. The versatile role of exosomes in human retroviral infections: From immunopathogenesis to clinical application. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; He, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wen, W.; Huang, X.; Hu, Y.; Lin, C.; Pan, J.; Li, R.; Deng, H.; et al. IFITM3-containing exosome as a novel mediator for anti-viral response in dengue virus infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, E.A.; Digard, P.; Stuart, A.D. The Rab11 pathway is required for influenza A virus budding and filament formation. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5848–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.-H.; Walker, C.M.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ma, P.; Deng, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Long, G. Hepatitis A virus structural protein pX interacts with ALIX and promotes the secretion of virions and foreign proteins through exosome-like vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1716513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Barrientos, R.; Shiota, T.; Madigan, V.; Misumi, I.; McKnight, K.L.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.; Meganck, R.M.; Li, Y.; et al. Gangliosides are essential endosomal receptors for quasi-enveloped and naked hepatitis A virus. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costafreda, M.I.; Abbasi, A.; Lu, H.; Kaplan, G. Exosome mimicry by a HAVCR1-NPC1 pathway of endosomal fusion mediates hepatitis A virus infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costafreda, M.I.; Kaplan, G. HAVCR1 (CD365) and its mouse ortholog are functional hepatitis A virus (HAV) cellular receptors that mediate HAV infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02065-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; McKnight, K.L.; Hensley, L.; Lanford, R.E.; Walker, C.M.; Lemon, S.M. Human pDCs preferentially sense enveloped hepatitis A virions. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.B.; Gudbergsson, J.M.; Skov, M.N.; Pilgaard, L.; Moos, T.; Duroux, M. A comprehensive overview of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles—Endogenous nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2014, 1846, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishiyama, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Yasuda, J.; Mulyanto; Okamoto, H. Multivesicular body sorting and the exosomal pathway are required for the release of rat hepatitis E virus from infected cells. Virus Res. 2020, 278, 197868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanggis; Nishizawa, T.; Nishiyama, T.; Primadharsini, P.P.; Okamoto, H. Characterization of the quasi-enveloped hepatitis E virus particles released by the cellular exosomal pathway. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, S.; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanggis; Nishizawa, T.; Kouki, T.; Yashiro, T.; Okamoto, H. Hepatitis E virus egress depends on the exosomal pathway, with secretory exosomes derived from multivesicular bodies. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Dubois, M.; Plisson-Chastang, C.; Bonnefois, T.; Lhomme, S.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; You, B.; Simoneau, S.; Gleizes, P.E.; Flan, B.; et al. Characterization of the lipid envelope of exosome encapsulated HEV particles protected from the immune response. Biochimie 2017, 141, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, K.; Simpson, K.J.; Petrik, J. Expression profiles of exosomal MicroRNAs from HEV- and HCV-infected blood donors and patients: A pilot study. Viruses 2020, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wu, J.; Shen, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, H. Enterovirus 71 transmission by exosomes establishes a productive infection in human neuroblastoma cells. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Fang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Zou, X.; Jia, X.; Yin, Y.; Shen, L.; Mao, L. Exosomes cloak the virion to transmit Enterovirus 71 non-lytically. Virulence 2020, 11, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Qiu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Exosomes from EV71-infected oral epithelial cells can transfer miR-30a to promote EV71 infection. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr. Exosomal communication goes viral. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5200–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutchy, N.A.; Peeples, E.S.; Sil, S.; Liao, K.; Chivero, E.T.; Hu, G.; Buch, S. Extracellular vesicles in viral infections of the nervous system. Viruses 2020, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, M.N.; Okeoma, C.M. Exosomes: Implications in HIV-1 pathogenesis. Viruses 2015, 7, 4093–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu, K.A.; Huang, M.B.; Roth, W.G.; Armstrong, W.; Powell, M.; Villinger, F.; Bond, V.C. Isolation of exosomes from the plasma of HIV-1 positive individuals. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 107, e53495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, J.V.; De Castro, R.O.; Da Silva, E.Z.M.; Silveira, P.P.; Da Silva-Januário, M.E.; Arruda, E.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C.; Aguiar, R.S.; Da Silva, L.L.P. Nef neutralizes the ability of exosomes from CD4+ T cells to act as decoys during HIV-1 infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Koike, M.; Moriishi, E.; Kawabata, A.; Tang, H.; Oyaizu, H.; Uchiyama, Y.; Yamanishi, K. Human herpesvirus-6 induces MVB formation, and virus egress occurs by an exosomal release pathway. Traffic 2008, 9, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundage, S.C.; Fitzpatrick, A.N. Hepatitis A. Am. Fam. Physician 2006, 73, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vinaiphat, A.; Sze, S.K. Clinical implications of extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, M.W.; Reichert, D.; Susser, S.; Sarrazin, C.; Martinez, Y.; Herrmann, E.; Zeuzem, S.; Piiper, A.; Kronenberger, B. Soluble serum CD81 is elevated in patients with chronic hepatitis C and correlates with alanine aminotransferase serum activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Ramakrishnaiah, V.; Henry, S.; Fouraschen, S.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Tilanus, H.W.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Van Der Laan, L.J.W. Hepatic cell-to-cell transmission of small silencing RNA can extend the therapeutic reach of RNA interference (RNAi). Gut 2011, 61, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Charrier, A.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yu, B.; Agarwal, K.; Tsukamoto, H.; Lee, L.J.; Paulaitis, M.E.; Brigstock, D.R. Epigenetic regulation of connective tissue growth factor by MicroRNA-214 delivery in exosomes from mouse or human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teow, S.-Y.; Nordin, A.C.; Ali, S.A.; Khoo, A.S.-B. Exosomes in human immunodeficiency virus type I pathogenesis: Threat or opportunity? Adv. Virol. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Viruses | Possible Biological Roles | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| HIV | Helps to establish infection, complete assembly, support budding, and escape immune response | [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50] |
| HCV | Affects virus assembly, budding, spreading and immune evasion | [51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62] |
| HTLV | Delivers host and viral components, activate the immune response, stimulate proinflammatory cytokines | [63,64,65,66,67] |
| DENV | Antiviral activities | [68] |
| IAV and RSV | Participates in viral egress | [69] |
| HAV | Involves in membrane fusion, transportation of viral RNA from eHAV into the cytoplasm, virus packing and releasing | [70,71,72,73,74,75] |
| HEV | Participates in virus entry, releasing, and escape immune response | [76,77,78,79,80,81] |
| EV71 | Involves in virus infection, resistant to antibody neutralization, deliver miRNA | [82,83,84] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Ju, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, L. Recent Progress on Exosomes in RNA Virus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020256
Zhang L, Ju Y, Chen S, Ren L. Recent Progress on Exosomes in RNA Virus Infection. Viruses. 2021; 13(2):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020256
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liying, Yichen Ju, Si Chen, and Linzhu Ren. 2021. "Recent Progress on Exosomes in RNA Virus Infection" Viruses 13, no. 2: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020256
APA StyleZhang, L., Ju, Y., Chen, S., & Ren, L. (2021). Recent Progress on Exosomes in RNA Virus Infection. Viruses, 13(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020256







