Emerging Trends in the Epidemiology of COVID-19: The Croatian ‘One Health’ Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
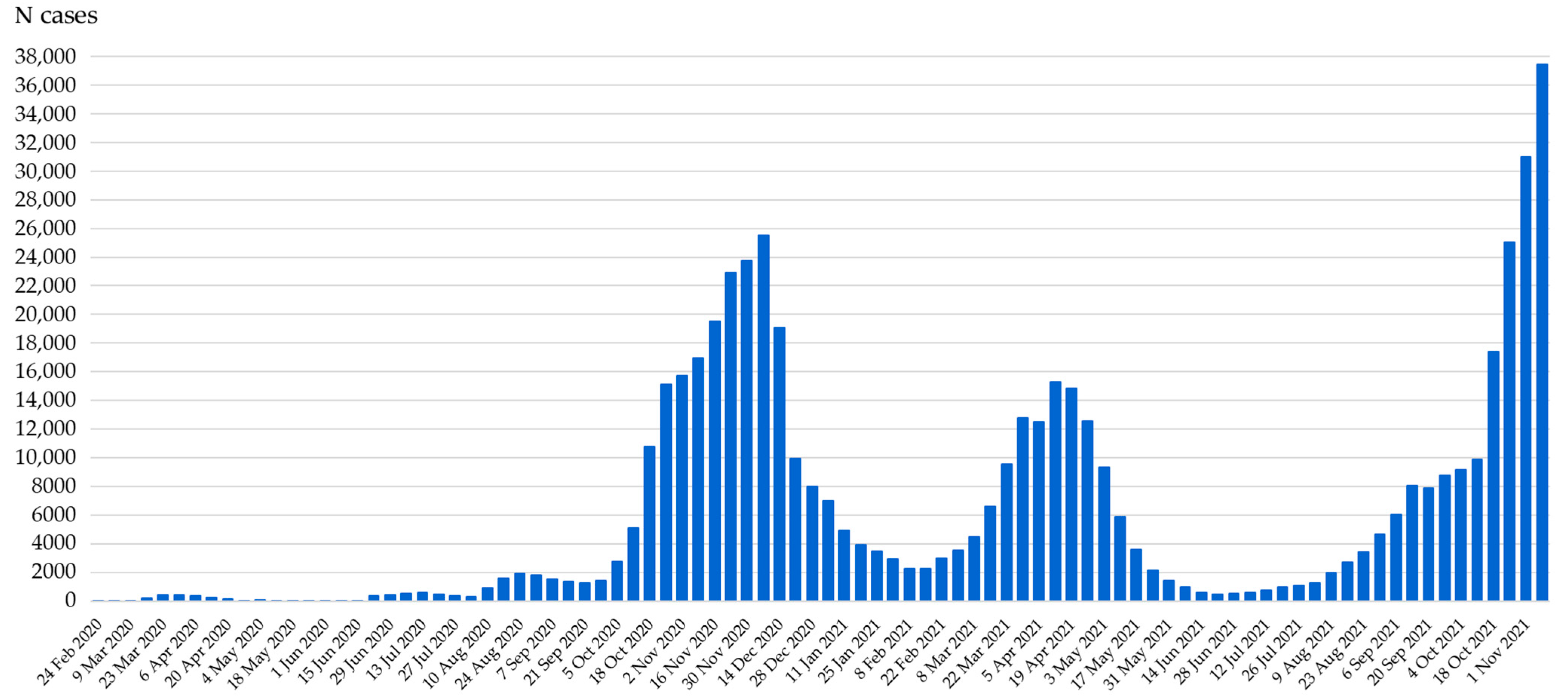
2. COVID-19 in Humans
3. COVID-19 in Pet Animals
4. COVID-19 in Wildlife
5. SARS-CoV-2 in the Environment
5.1. SARS-CoV-2 in Households with COVID-19 Cases
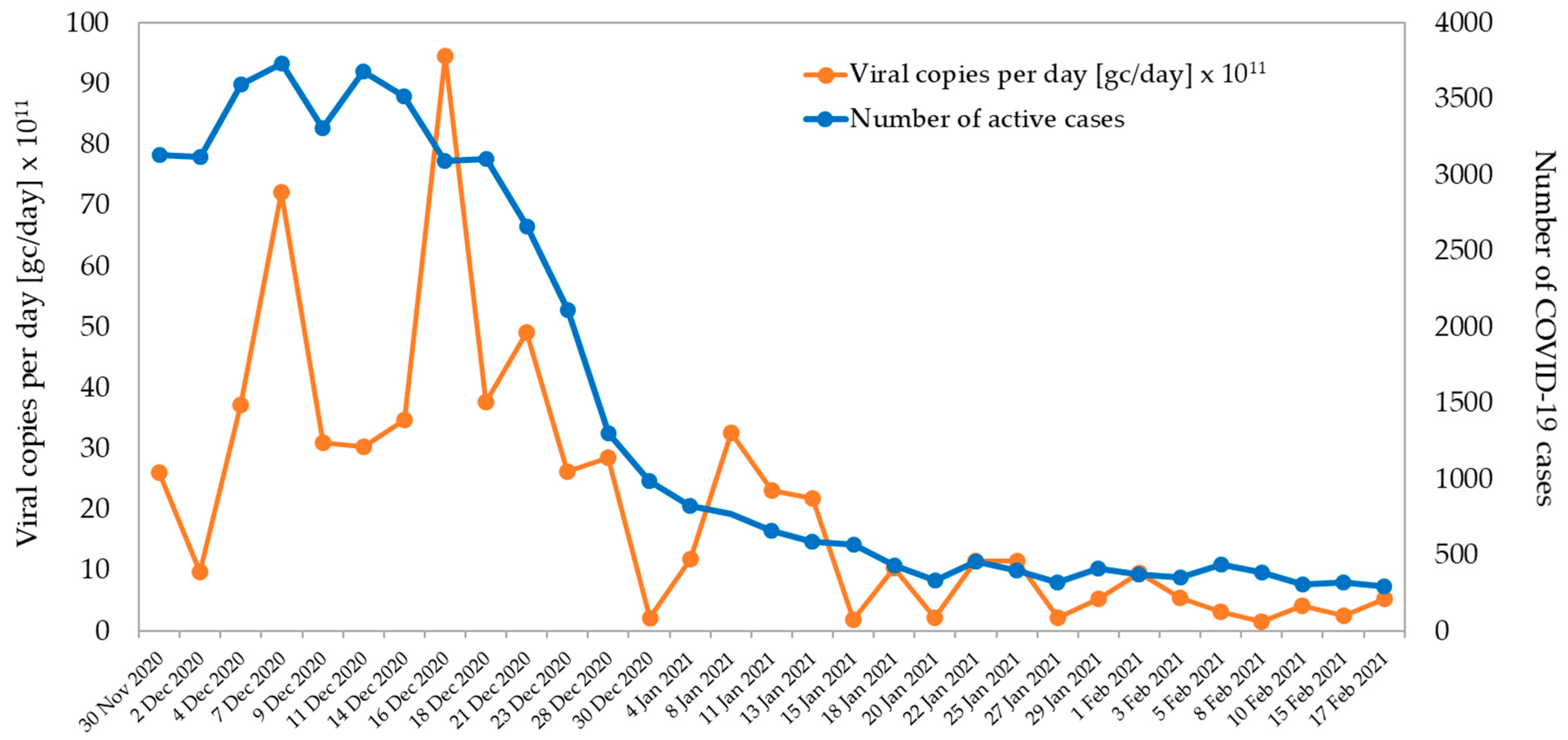
5.2. SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater
6. SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Diversity in Croatia
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-NCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, H.S.; Aziz, M.S.; Hussein, R.H.; Othman, H.H.; Salih Omer, S.H.; Khalid, E.S.; Abdulrahman, N.A.; Amin, K.; Abdullah, R. The Transmission Modes and Sources of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Surg. Open 2020, 26, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, F.-M.; Chen, F.; Lin, Z. Origin and Evolution of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob Machado, D.; Scott, R.; Guirales, S.; Janies, D.A. Fundamental Evolution of All Orthocoronavirinae Including Three Deadly Lineages Descendent from Chiroptera-Hosted Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Cladistics 2021, 37, 461–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; García-Barco, A.; Jimenez-Diaz, S.D.; Bonilla-Aldana, J.L.; Cardona-Trujillo, M.C.; Muñoz-Lara, F.; Zambrano, L.I.; Salas-Matta, L.A.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. SARS-CoV-2 Natural Infection in Animals: A Systematic Review of Studies and Case Reports and Series. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dróżdż, M.; Krzyżek, P.; Dudek, B.; Makuch, S.; Janczura, A.; Paluch, E. Current State of Knowledge about Role of Pets in Zoonotic Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2021, 13, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Bellon, H.; Rodon, J.; Fernández-Bastit, L.; Almagro, V.; Padilla-Solé, P.; Lorca-Oró, C.; Valle, R.; Roca, N.; Grazioli, S.; Trogu, T.; et al. Monitoring Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Lions (Panthera leo) at the Barcelona Zoo: Viral Dynamics and Host Responses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronavirus-Statistical Indicators for Croatia and EU. Available online: https://www.koronavirus.hr/en (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Jerković, I.; Ljubić, T.; Bašić, Ž.; Kružić, I.; Kunac, N.; Bezić, J.; Vuko, A.; Markotić, A.; Anđelinović, Š. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Seroprevalence in Industry Workers in Split-Dalmatia and Šibenik-Knin County, Croatia. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 63, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Stevanovic, V.; Tabain, I.; Betica-Radic, L.; Sabadi, D.; Peric, L.; Bogdanic, M.; Vilibic, M.; Kolaric, B.; Kudumija, B.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Seroprevalence among Personnel in the Healthcare Facilities of Croatia, 2020. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20200458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenicek Krleza, J.; Zrinski Topic, R.; Stevanovic, V.; Lukic-Grlic, A.; Tabain, I.; Misak, Z.; Roic, G.; Kaic, B.; Mayer, D.; Hruskar, Z.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Children in Children’s Hospital Zagreb during the Initial and Second Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic in Croatia. Biochem. Med. 2021, 31, 020706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilibić-Čavlek, T.; Stevanović, V.; Barbić, L.; Tabain, I.; Milašinčić, L.; Antolašić, L.; Hruškar, Ž.; Capak, K.; Mrzljak, A.; Leniček Krleža, J.; et al. Temporal trends of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in Croatia. In Proceedings of the Symposium with International Participation-Veterinarski Dani, Vodice, Croatia, 26–29 October 2021; pp. 9–16. (In Croatian). [Google Scholar]
- Stevanovic, V.; Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Tabain, I.; Benvin, I.; Kovac, S.; Hruskar, Z.; Mauric, M.; Milasincic, L.; Antolasic, L.; Skrinjaric, A.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Pet Animals in Croatia and Potential Public Health Impact. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Stevanovic, V.; Ilic, M.; Barbic, L.; Capak, K.; Tabain, I.; Krleza, J.L.; Ferenc, T.; Hruskar, Z.; Topic, R.Z.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence and Neutralizing Antibody Response after the First and Second COVID-19 Pandemic Wave in Croatia. Pathogens 2021, 10, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrzljak, A.; Jureković, Ž.; Pavičić-Šarić, J.; Stevanović, V.; Tabain, I.; Hruškar, Ž.; Mikulić, D.; Barbić, L.; Vilibić-Čavlek, T. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Croatian Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. Biochem. Med. 2021, 31, 030901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Nair, M.S.; Yin, M.T.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, T.; Mori, K.; Solis, A.G.; Yamashita, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Responses Are More Robust in Patients with Severe Disease. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2091–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccaluga, P.P.; Malerba, G.; Navari, M.; Diani, E.; Concia, E.; Gibellini, D. Cross-Immunization Against Respiratory Coronaviruses May Protect Children From SARS-CoV2: More Than a Simple Hypothesis? Front. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 595539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.S.; Mytton, O.T.; Mullins, E.W.S.; Fowler, T.A.; Falconer, C.L.; Murphy, O.B.; Langenberg, C.; Jayatunga, W.J.P.; Eddy, D.H.; Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.S. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): What Do We Know About Children? A Systematic Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauser, J.; Schwarz, C.; Morgan, J.; Jantsch, J.; Brem, M. SARS-CoV-2 Transmission during an Indoor Professional Sporting Event. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, Z.; Ngo, V.; Pulido, M.; Washburn, F.; Meschyan, G.; Gluck, F.; Kuguru, K.; Reporter, R.; Curley, C.; Civen, R.; et al. Industry Sectors Highly Affected by Worksite Outbreaks of Coronavirus Disease, Los Angeles County, California, USA, 19 March–30 September 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murti, M.; Achonu, C.; Smith, B.T.; Brown, K.A.; Kim, J.H.; Johnson, J.; Ravindran, S.; Buchan, S.A. COVID-19 Workplace Outbreaks by Industry Sector and Their Associated Household Transmission, Ontario, Canada, January to June 2020. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 63, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, D.P.; McCaffrey, K.; Friedrichs, M.; LaCross, N.; Lewis, N.M.; Sage, K.; Barbeau, B.; Vilven, D.; Rose, C.; Braby, S.; et al. Racial and Ethnic Disparities Among COVID-19 Cases in Workplace Outbreaks by Industry Sector-Utah, 6 March–5 June 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauber, C.; Tiwari-Heckler, S.; Pfeiffenberger, J.; Mehrabi, A.; Lund, F.; Gath, P.; Mieth, M.; Merle, U.; Rupp, C. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence and Clinical Features of COVID-19 in a German Liver Transplant Recipient Cohort: A Prospective Serosurvey Study. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevanovic, V.; Tabain, I.; Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Mauric Maljkovic, M.; Benvin, I.; Hruskar, Z.; Kovac, S.; Smit, I.; Miletic, G.; Hadina, S.; et al. The Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 within the Dog Population in Croatia: Host Factors and Clinical Outcome. Viruses 2021, 13, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, B.B.; Kassie, A.M.; Kassaw, M.W.; Aragie, T.G.; Masresha, S.A. Sex Difference in Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stall, N.M.; Wu, W.; Lapointe-Shaw, L.; Fisman, D.N.; Giannakeas, V.; Hillmer, M.P.; Rochon, P.A. Sex- and Age-Specific Differences in COVID-19 Testing, Cases, and Outcomes: A Population-Wide Study in Ontario, Canada. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68, 2188–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-I.; Hu, Y.-L.; Chen, P.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Are Children Less Susceptible to COVID-19? J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laher, N.; Bocchinfuso, S.; Chidiac, M.; Doherty, C.; Persson, A.; Warren, E. The Biopsychosocial Impact of COVID-19 on Older Adults. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 7, 23337214211034274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Talal, N. Sex Hormones and the Immune System--Part 2. Animal Data. Baillieres Clin. Rheumatol. 1990, 4, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissick, H.T.; Sanda, M.G.; Dunn, L.K.; Pellegrini, K.L.; On, S.T.; Noel, J.K.; Arredouani, M.S. Androgens Alter T-Cell Immunity by Inhibiting T-Helper 1 Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9887–9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arredouani, M.S. New Insights into Androgenic Immune Regulation. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e954968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallis, L.J.; Range, F.; Müller, C.A.; Serisier, S.; Huber, L.; Zsó, V. Lifespan Development of Attentiveness in Domestic Dogs: Drawing Parallels with Humans. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, E.I.; Elia, G.; Grassi, A.; Giordano, A.; Desario, C.; Medardo, M.; Smith, S.L.; Anderson, E.R.; Prince, T.; Patterson, G.T.; et al. Evidence of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in Cats and Dogs from Households in Italy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemeršić, L.; Lojkić, I.; Krešić, N.; Keros, T.; Zelenika, T.A.; Jurinović, L.; Skok, D.; Bata, I.; Boras, J.; Habrun, B.; et al. Investigating the Presence of SARS-CoV-2 in Free-Living and Captive Animals. Pathogens 2021, 10, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcenac, P.; Park, G.W.; Duca, L.M.; Lewis, N.M.; Dietrich, E.A.; Barclay, L.; Tamin, A.; Harcourt, J.L.; Thornburg, N.J.; Rispens, J.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 on Surfaces in Households of Persons with COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, E.P.S.; Cortes, M.F.; Noguera, S.V.; Paula, A.V.; de Guimarães, T.; Boas, L.S.V.; Park, M.; da Silva, C.C.; Morales, I.; Perdigão Neto, L.V.; et al. Are Mobile Phones Part of the Chain of Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Hospital Settings? Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2021, 63, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Scheidegger, A.; Bänziger, C.; Cariti, F.; Tuñas Corzon, A.; Ganesanandamoorthy, P.; Lemaitre, J.C.; Ort, C.; Julian, T.R.; Kohn, T. Wastewater Monitoring Outperforms Case Numbers as a Tool to Track COVID-19 Incidence Dynamics When Test Positivity Rates Are High. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovi, T.; Shulman, L.M.; van der Avoort, H.; Deshpande, J.; Roivainen, M.; DE Gourville, E.M. Role of Environmental Poliovirus Surveillance in Global Polio Eradication and Beyond. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, C.; Tang, L.; Hong, Z.; Zhou, J.; Dong, X.; Yin, H.; Xiao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Qu, X.; et al. Prolonged Presence of SARS-CoV-2 Viral RNA in Faecal Samples. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergham, J.; Delerce, J.; Bedotto, M.; La Scola, B.; Moal, V. Isolation of Viable SARS-CoV-2 Virus from Feces of an Immunocompromised Patient Suggesting a Possible Fecal Mode of Transmission. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Angel, N.; Edson, J.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; O’Brien, J.W.; Choi, P.M.; Kitajima, M.; Simpson, S.L.; Li, J.; et al. First Confirmed Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Untreated Wastewater in Australia: A Proof of Concept for the Wastewater Surveillance of COVID-19 in the Community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, G.; Heijnen, L.; Elsinga, G.; Italiaander, R.; Brouwer, A. Presence of SARS-Coronavirus-2 RNA in Sewage and Correlation with Reported COVID-19 Prevalence in the Early Stage of the Epidemic in The Netherlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Orschler, L.; Lackner, S. Long-Term Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Wastewater of the Frankfurt Metropolitan Area in Southern Germany. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.E.; Loeb, S.K.; Wolfe, M.K.; Catoe, D.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N.; Kim, S.; Yamahara, K.M.; Sassoubre, L.M.; Mendoza Grijalva, L.M.; Roldan-Hernandez, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Wastewater Settled Solids Is Associated with COVID-19 Cases in a Large Urban Sewershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisseux, M.; Debroas, D.; Mirand, A.; Archimbaud, C.; Peigue-Lafeuille, H.; Bailly, J.-L.; Henquell, C. Monitoring of Enterovirus Diversity in Wastewater by Ultra-Deep Sequencing: An Effective Complementary Tool for Clinical Enterovirus Surveillance. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. Guidance for Representative and Targeted Genomic SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/guidance-representative-and-targeted-genomic-sars-cov-2-monitoring (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Wahid, M.; Jawed, A.; Mandal, R.K.; Dailah, H.G.; Janahi, E.M.; Dhama, K.; Somvanshi, P.; Haque, S. Variants of SARS-CoV-2, Their Effects on Infection, Transmission and Neutralization by Vaccine-Induced Antibodies. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenčak, I.; Kuzle, J.; Mišić, A.; Stevanović, V.; Bekavac, B.; Hruškar, Ž.; Barbić, L.; Vilibić-Čavlek, T.; Tabain, I. SARS-CoV-2 in Croatia-genomic analysis of the third and fourth epidemic wave. In Proceedings of the 9th International Congress “Veterinary Science and Profession”, Zagreb, Croatia, 9 October 2021; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Ruckert, A.; Zinszer, K.; Zarowsky, C.; Labonté, R.; Carabin, H. What Role for One Health in the COVID-19 Pandemic? Can. J. Public Health 2020, 111, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Population Group | Sampling Time | N Tested | SARS-CoV-2 IgG ELISA | SARS-CoV-2 VNT | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 95% CI | N (%) | 95% CI | ||||
| First pandemic wave | |||||||
| Industry workers | April 2020 | 1494 | 19 (1.27) * | 0.77–1.98 | NT | NT | [12] |
| Healthcare workers | April–May 2020 | 592 | 16 (2.7) | 1.5–4.3 | 9 (1.5) | 0.7–2.9 | [13] |
| Children and adolescents | May 2020 | 240 | 9 (3.9) | 1.7–7.0 | 7 (2.9) | 1.2–5.9 | [14] |
| Hemodialysis patients | May 2020 | 136 | 9 (6.6) | 3.1–12.1 | 0 (0) | 0–2.7 ** | [15] |
| Veterinary personnel | May 2020 | 122 | 6 (4.9) | 1.8–10.4 | 0 (0) | 0–2.9 ** | [15,16] |
| Construction workers | May–June 2020 | 135 | 4 (2.9) | 0.8–7.4 | 3 (2.2) | 0.4–6.4 | [15] |
| General population | May–July 2020 | 1088 | 24 (2.2) | 1.4–3.2 | 2 (0.2) | 0.02–0.7 | [17] |
| Professional athletes | June 2020 | 90 | 10 (11.1) | 5.5–19.5 | 5 (5.5) | 1.8–12.5 | [15] |
| Second pandemic wave | |||||||
| Liver transplant recipients | September–November 2020 | 280 | 59 (21.1) | 16.4–26.3 | 10 (3.6) | 1.7–6.5 | [18] |
| Kidney transplant recipients | September–November 2020 | 232 | 44 (19.0) | 14.1–24.6 | 6 (2.6) | 0.9–5.5 | [18] |
| Children and adolescents | October–November 2020 | 308 | 27 (8.8) | 5.0–12.5 | 26 (8.4) | 5.6–12.1 | [14] |
| General population | December 2020–February 2021 | 1436 | 360 (25.1) | 22.8–27.4 | 268 (18.7) | 16.7–20.8 | [17] |
| Veterinary personnel | March 2021 | 121 | 22 (18.2) | 11.8–26.2 | 11 (9.1) | 4.6–15.7 | [15,16] |
| Population Group | SARS-CoV-2 IgG ELISA | SARS-CoV-2 VNT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI OR | p | OR | 95% CI OR | p | |
| First pandemic wave | ||||||
| General population | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Industry workers * | 0.57 | 0.31–1.05 | 0.07 | NA | NA | NA |
| Healthcare workers | 1.23 | 0.65–2.34 | 0.52 | 8.38 | 1.8–38.20 | 0.002 |
| Children and adolescents | 1.73 | 0.79–3.76 | 0.16 | 16.31 | 3.37–79.30 | <0.001 |
| Hemodialysis patients | 3.14 | 1.43–6.91 | 0.007 | 1.59 | 0.08–33.33 | 1.00 |
| Veterinary personnel | 2.29 | 0.92–5.72 | 0.11 | 1.77 | 0.08–37.16 | 1.00 |
| Construction workers | 1.35 | 0.46–3.96 | 0.54 | 12.34 | 2.04–74.53 | 0.01 |
| Professional athletes | 5.54 | 2.56–11.99 | <0.001 | 31.94 | 6.11–167.09 | <0.001 |
| Second pandemic wave | ||||||
| General population | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Liver transplant recipients | 0.80 | 0.58–1.09 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.08–0.31 | <0.001 |
| Kidney transplant recipients | 0.70 | 0.49–0.99 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.05–0.26 | <0.001 |
| Children and adolescents | 0.29 | 0.19–0.43 | <0.001 | 0.40 | 0.16–0.61 | <0.001 |
| Veterinary personnel | 0.66 | 0.41–1.07 | 0.09 | 0.44 | 0.23–0.82 | 0.008 |
| Sample Origin | SARS-CoV-2 IgG ELISA | OR | 95% CI OR | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N Tested | N Positive (%) | 95% CI | ||||
| Human | 458 | 94 (20.5) | 16.92–24.52 | Ref. | – | – |
| Dog | 167 | 31 (18.6) | 12.97–25.30 | 0.88 | 0.56–1.39 | 0.59 |
| Cat | 29 | 4 (13.8) | 3.89–31.66 | 0.62 | 0.21–1.82 | 0.38 |
| Animal Species | Sampling Time | N Tested | SARS-CoV-2 IgG ELISA | SARS-CoV-2 sVNT | SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 95% CI | N (%) | 95% CI | N (%) | |||
| Yellow-legged gulls (Larus michahellis) | November 2020 | 111 | 0 (0) | 0–3.3 * | 0 (0) | 0–3.3 * | 0 (0) |
| Wild boars (Sus scrofa) | June–December 2020 | 153 | 6 (3.9) | 1.5–8.3% | 0 (0) | 0–2.4 * | 0 (0) |
| Red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) | June–November 2020 | 204 | 6 (2.9) | 1.0–6.2 | 0 (0) | 0–1.8 * | 0 (0) |
| Jackals (Canis aureus moreoticus) | June–October 2020 | 65 | 3 (4.6) | 0.9–12.9 | 0 (0) | 0–5.5 * | 0 (0) |
| Sampling Location | High-Touch Personal Objects 1 | Room 2 | Toilet/Bathroom 3 | Kitchen 4 | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N Positive/N | N Positive/N | N Positive/N | N Positive/N | N Positive/N | % Positive | 95% CI | |
| 1 | 0/3 | 0/5 | 0/3 | - | 0/11 | 0 | 0–28.4 * |
| 2 | 0/2 | 1/1 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 3/11 | 27.2 | 6.0–60.1 |
| 3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/5 | 0/3 | 0/14 | 0 | 0–25.2 * |
| 4 | 1/3 | 1/4 | 0/2 | 0/2 | 2/11 | 18.2 | 2.3–51.8 |
| 5 | 2/4 | 2/4 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 4/12 | 33.3 | 9.9–65.1 |
| 6 | 0/6 | 0/3 | 0/5 | - | 0/14 | 0 | 0–23.2 * |
| 7 | 0/4 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 0/1 | 1/11 | 9.1 | 2.3–49.3 |
| 8 | 0/2 | 2/2 | 0/1 | 1/3 | 3/8 | 37.5 | 8.5–75.5 |
| 9 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 0/2 | 0/1 | 0/9 | 0 | 0–33.6 * |
| 10 | 3/5 | 0/1 | 0/2 | 1/3 | 4/11 | 36.4 | 10.9–69.2 |
| 11 | 0/5 | 0/3 | 0/1 | - | 0/9 | 0 | 0–33.6 * |
| 12 | 0/4 | 0/2 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/12 | 0 | 0–26.5 * |
| 13 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 1/2 | 1/14 | 0 | 0–33.9 |
| 14 | 1/2 | 0/1 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/9 | 1.1 | 2.8–48.2 |
| 15 | 2/4 | 0/1 | 2/6 | 0/4 | 4/15 | 26.7 | 7.8–55.1 |
| Total | 9/52 (17.3%) | 6/41 (14.6%) | 4/48 (8.3%) | 4/30 (13.3%) | 23/171 | 13.5 | 8.7–19.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Stevanovic, V.; Brlek-Gorski, D.; Ferencak, I.; Ferenc, T.; Ujevic-Bosnjak, M.; Tabain, I.; Janev-Holcer, N.; Perkovic, I.; Anticevic, M.; et al. Emerging Trends in the Epidemiology of COVID-19: The Croatian ‘One Health’ Perspective. Viruses 2021, 13, 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122354
Vilibic-Cavlek T, Stevanovic V, Brlek-Gorski D, Ferencak I, Ferenc T, Ujevic-Bosnjak M, Tabain I, Janev-Holcer N, Perkovic I, Anticevic M, et al. Emerging Trends in the Epidemiology of COVID-19: The Croatian ‘One Health’ Perspective. Viruses. 2021; 13(12):2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122354
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilibic-Cavlek, Tatjana, Vladimir Stevanovic, Diana Brlek-Gorski, Ivana Ferencak, Thomas Ferenc, Magdalena Ujevic-Bosnjak, Irena Tabain, Natasa Janev-Holcer, Ivana Perkovic, Mario Anticevic, and et al. 2021. "Emerging Trends in the Epidemiology of COVID-19: The Croatian ‘One Health’ Perspective" Viruses 13, no. 12: 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122354
APA StyleVilibic-Cavlek, T., Stevanovic, V., Brlek-Gorski, D., Ferencak, I., Ferenc, T., Ujevic-Bosnjak, M., Tabain, I., Janev-Holcer, N., Perkovic, I., Anticevic, M., Bekavac, B., Kaic, B., Mrzljak, A., Ganjto, M., Zmak, L., Mauric Maljkovic, M., Jelicic, P., Bucic, L., & Barbic, L. (2021). Emerging Trends in the Epidemiology of COVID-19: The Croatian ‘One Health’ Perspective. Viruses, 13(12), 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122354










