Abstract
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an uncommon, lethal cancer of the skin caused by either Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) or UV-linked mutations. MCPyV is found integrated into MCC tumor genomes, accompanied by truncation mutations that render the MCPyV large T antigen replication incompetent. We used the open access HPV Detector/Cancer-virus Detector tool to determine MCPyV integration sites in whole-exome sequencing data from five MCC cases, thereby adding to the limited published MCPyV integration site junction data. We also systematically reviewed published data on integration for MCPyV in the human genome, presenting a collation of 123 MCC cases and their linked chromosomal sites. We confirmed that there were no highly recurrent specific sites of integration. We found that chromosome 5 was most frequently involved in MCPyV integration and that integration sites were significantly enriched for genes with binding sites for oncogenic transcription factors such as LEF1 and ZEB1, suggesting the possibility of increased open chromatin in these gene sets. Additionally, in one case we found, for the first time, integration involving the tumor suppressor gene KMT2D, adding to previous reports of rare MCPyV integration into host tumor suppressor genes in MCC.
1. Introduction
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive skin cancer (five year overall survival rate of about 44% and disease-specific mortality of 33–46% [1,2]), predominantly arising in the elderly and immunocompromised. MCC is associated with Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) in the majority of cases [2,3]. MCPyV was discovered in 2008 by Feng et al. and found to be integrated into the MCC tumor genome in a mutated, replication-deficient form [3]. MCPyV is a small (5 kb), non-enveloped, circular dsDNA polyomavirus that is commonly found on human skin [2,3,4]. The MCPyV early region expresses large T antigen (LT) and small T antigen (sT) proteins that have been shown to drive tumorigenesis and are likely causative for MCC [5,6]. MCC tumor cells express a truncated form of LT protein that cannot mediate viral replication, but it retains the domain responsible for inhibition of the tumor suppressor Rb [2,3,4,5]. MCC that lack MCPyV display cellular genomic mutations in tumor suppressor genes, especially TP53 and RB1 [7,8,9]. Additional tumor suppressors such as NOTCH family genes and KMT2D are inactivated at lower rates in MCPyV-negative MCC [2,7,8,9].
Integration into the human genome is implicated as an early oncogenic event for many DNA tumor viruses [10,11]. Integration increases the risk of cancer beyond simple viral infection as it can disrupt and deregulate nearby human cancer-associated genes, contribute to genome instability, and create fusion transcripts [11,12]. Various studies show an overall bias for integration near open chromatin regions and SINE (Short Interspersed Nuclear Elements) elements for DNA tumor viruses [12]. Interestingly, there are differences between integration site patterns related to different virus types, cancer types, and disease stages.
Because MCPyV infection is near-ubiquitous [10], demonstrations of viral integration can be helpful in distinguishing tumor-associated viral sequences from spurious detection of background viruses. Furthermore, viral integration can interrupt tumor suppressor genes, representing a potential mechanism for viral tumorigenesis in addition to viral oncogenes. Despite the diagnostic and biologic importance of this question, studies investigating MCPyV integration sites have been relatively few due to the rarity of MCC and limited high-quality tumor samples. Furthermore, the identification of MCPyV integration is technically challenging as the circular genome of the virus does not linearize in a consistent manner. Several approaches have been developed to address this question, often relying upon custom assays or analysis tools (Table 1 and Table S1). A sensitive approach for detecting MCPyV integration sites using commercially available assays and open-access analysis tools has not yet been uniformly validated and adopted.

Table 1.
Summary of studies on MCPyV integration in the human genome.
MCPyV integration sites have been reported across most chromosomes and may occur within genes or in intergenic regions (Table 2). With rare exceptions, the integration site for a particular tumor (and its related metastases) is unique to that case. Despite this variability, several studies have suggested that the distribution of integration sites is non-random, with patterns related to mechanisms of integration [8,9,13,14,15]. Unlike HIV, MCPyV does not carry an integrase, and integration into the host genome is not part of the viral life cycle [3]. Starrett et al. reported that integration is likely mediated through erroneous DNA repair at sites of microhomology between the host and viral genomes, similar to mechanisms identified for HPV genome integration in squamous cell carcinoma tumors [8,9]. Similarly, Czech-Sioli et al. recently observed that MCPyV follows two main types of integration site structure: (1) linear patterns with chromosomal breakpoints related to non-homologous end joining; and (2) complex integration loci dependent on microhomology-mediated break-induced replication [16,17]. Doolittle-Hall et al. conducted the first meta-analysis on 37 MCCs for integration analysis and found that MCPyV integration occurred preferentially near SINEs and BDP1 binding sites [12]. They also confirmed viral preference for transcriptionally active gene-dense regions and accessible chromatin. In addition, they observed a tropism toward integration near specific categories of genes, including sensory perception and G-protein coupled receptor genes [12]. MCPyV integration within cellular genes could also act as a mechanism of tumor suppressor gene inactivation in a subset of tumors, as potentially disruptive integration into genes with tumor suppressor roles (PTPRG, XRCC4) has been described in individual cases. However, recurrent disruption of specific tumor suppressors has not been described [3,8,9,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,20,21] (Table S1 and Table 2).

Table 2.
Summary of host and viral integration sites.
Although most tumors demonstrate a single, unique genomic integration site, rare exceptions have been described. Starrett et al., 2020, found that two independent tumors had overlapping (although non-identical) integration sites on chromosome 1, representing a rare example of a recurrent integration site. An additional case had three distinct integration sites on different chromosomes within a single tumor: one full copy of the viral genome, one smaller segment predicted to retain oncogenic activity (containing NCCR and T antigen coding regions), and one smaller segment predicted to lack oncogenic activity [9].
Patterns by which the circular MCPyV viral genome linearizes and integrates have been defined by several studies (Table 1) [8,9]. For both MCPyV- and HPV-mediated tumors, integration may be followed by the formation of a transiently circular DNA intermediate containing the viral genome and flanking regions of the host genome which can be further amplified through aberrant firing of the viral origin of replication. This piece then reintegrates into the host genome, appearing as amplified regions of the host genome in a tandem head-to-tail conformation interspersed with the viral genome [8,9].
Although the breakpoint in the MCPyV genome is highly variable, most studies describe that junctions are predominantly located in exon 2 of the LT gene after the pRb binding site (Table 2). This could result in a truncated, replication-deficient LT protein equivalent to tumor-specific LT truncating mutations.
More comprehensive characterization of MCPyV integration locations, and thereby preferences, will advance the understanding of virus-mediated tumorigenesis and may reveal therapeutic vulnerabilities. Our study aimed at reviewing published MCPyV integration site data and expanding this repertoire of known MCPyV integration sites. We adapted a bioinformatics tool designed for HPV integration site detection (HPV Detector/Cancer-virus Detector [22]) to detect MCPyV from previously described MCC whole-exome sequencing datasets from patient tumor samples classified as MCPyV-positive by quantitative PCR [7]. Our results identify additional specific viral and host junction sites, including integration into a tumor suppressor gene frequently mutated in MCPyV-negative MCC (KMT2D). Furthermore, we demonstrate the successful use of HPV Detector/Cancer-virus Detector, a simple open-access analysis tool with potential utility in research and clinical testing, for detection of MCPyV integration in standard whole-exome sequencing datasets.
2. Methods
2.1. MCPyV Integration Analysis
MCC whole-exome datasets were taken from a previously published study by Harms et al., Cancer Research, 2015 [7]. The sequencing approach used by this study is briefly summarized here. Exome libraries were generated using an Illumina TruSeq DNA Sample Prep Kit, and paired-end libraries were sequenced with the Illumina HiSeq 2000. Reads that passed the Illumina BaseCall software chastity filter were used for subsequent analysis. Sequence and alignment quality were assessed by FastQC and the Picard package, respectively. More details can be found in the supplement of Harms et al., Cancer Research, 2015 [7].
The HPV Detector used a computational subtraction approach to identify HPV DNA traces from NGS datasets, as published earlier [22]. We modified the HPV Detector to align NGS data to human and MCPyV genomes. In the downstream analysis, we subtracted all NGS reads that were mapped to only the human genome. The remaining reads were either mapped to the MCPyV genome completely or were split reads with parts mapped to the human genome and other parts mapped to the MCPyV genome. We identified all split reads and annotated them using nearby human and MCPyV genome regions through BEDTools [23]. The source code can be accessed via GitHub (https://github.com/pratikchandrani). The sequencing datasets generated previously in Harms et al., 2015 [7], were used for this study. The integration site junctions/genes were further subjected to pathway analysis using GSEA-MSigDB [24] under the default parameters.
2.2. PCR
Primers were designed at the flanking regions (one primer on the human side and another on the viral side) to amplify the integration breakpoints. PCR was performed on genomic DNA from the MCC tumor samples using Platinum Taq DNA Polymerase (catalog # 10966018, Invitrogen, MI, USA), DMSO spike, and 20ng of DNA. Water was used as a negative control.
2.3. MCPyV Integration Site Meta-Analysis
Based on the closest chromosome band for each integration junction on the human genome, the coordinates were taken from UCSC Browser, GRCh38/hg38. The chromosome and start positions were then plotted by Circo plot to represent the integration sites. COSMIC v91 data were downloaded from the Sanger Institute website (https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/census) [25], and the Human Fragile Sites dataset was downloaded from the HumCFS database (https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/humcfs/) [26]. The Circo plot was drawn using Circa Software (OMGenomics http://omgenomics.com/circa/). Of the 123 sites for which the chromosome number was available, 96 (including five from our study) reported information regarding location on the chromosome. Using chromosome band information, a Circo plot was drawn for these 96 sites. Dots on the bars represent the location of genes in which integration sites were found.
3. Result
3.1. Integration Site Detection from Exome Sequencing Data
Of the seven MCC whole-exome sequencing datasets previously published by Harms et al. [7], we predicted viral–host junctions in five (including one primary tumor and four metastases). Similar to previous studies, we found that the integration site was highly variable and at either interchromosomal locations or in introns [8,12,20]. Three of these five sites were found in intergenic regions in chromosomes 4, 7, and 16, whereas for two tumors the sites were found in introns of two genes: KMT2D (intron 34) on chromosome 12 and DCAF7 (intron 3) on chromosome 17 (Table 1, Table 3 and Figure 1A). KMT2D is a lysine methyltransferase and tumor suppressor gene. DCAF7 (DDB1 and CUL4 Associated Factor 7) encodes a scaffold protein for kinase signaling. Unlike findings from a previous report [12], we did not observe a trend toward involvement of sensory genes.

Table 3.
Chimeric Sequences and Novel Integration Breakpoints from Current Study.
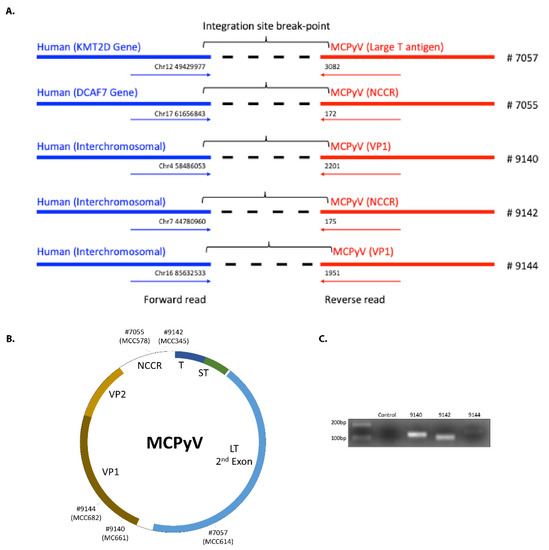
Figure 1.
(A). Integration breakpoints for the different Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) cases. Blue is the human sequence detected and red is the MCPyV sequence. (B) Integration junctions identified for samples from the current study, by sample number and original tumor ID. (C) PCR validation of integration break points. LT: large T antigen, 2nd exon. NCCR: non-coding control region. ST: small T antigen. T: common T antigen exon. VP: viral protein (capsid).
Recent sequencing studies have shown that chromatin remodeling and histone modulators are frequently altered in cancers, with implications for tumor biology. KMT2D (lysine (K)-specific methyltransferase 2D), also known as MLL2 (myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia 2, also known as ALR/MLL4), is one such histone methyltransferase that plays an important role in regulating gene transcription [27]. In particular, it targets lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4) whose methylations serve as a gene activation mark. KMT2D is essential for maintaining the level of global H3K4 monomethylation, with its enzymatic SET domain being directly responsible for this function. Furthermore, most KMT2D binding sites are located in regions of potential enhancer elements. KMT2D has [27] emerged as a frequently mutated gene in about 8.5% of all cancers [28] and has been proposed to play either a tumor suppressor or oncogenic role, depending on cancer type. In MCC, KMT2D predominantly demonstrates inactivating mutations, thus supporting its tumor suppressor role [29].
To determine the integration junction for the viral genome, we mapped the sequences to MCPyV DysKA isolate [30] (GenBank ID # KX781279.1). The sites we found differed from the previously reported pattern in which integration junctions predominantly involved the LT 2nd exon. In our cases we found two integration sites in the NCCR region, two in the VP1 region, and only one in LT 2nd exon (Table 1, Table 3 and Figure 1B). Intriguingly, the sequence we found for LT at the junction is preceded by a TAA sequence in the MCPyV genome, indicating that this integration could also be associated with the generation of a premature LT stop codon, similar to findings by Schrama et al. [18].
Several cases showed integration sites in the NCCR region (of these, our study reports two of the total eight), VP1 (our study reports two of the total 23), and VP2 regions (total of 10 reported). The integration junctions may be disruptive or non-disruptive in gene expression and function, depending on the frame of fused product, mechanism of the integration, number of viral copies integrated, etc. Based upon the previous description of our cases, six of seven tumors had detectable LT protein expression by immunohistochemistry, and six of six tumors with RNASeq data had detectable LT transcript expression (Harms et al., 2015, Supplemental Material) [7]. Therefore, all integration sites were permissive for LT expression, even those involving the NCCR. Of note, our approach is not designed to evaluate effects of integration on LT (especially relevant for integration sites that truncate the protein).
By PCR and using primers flanking the virus–host junctions, followed by Sanger sequencing of the resulting PCR amplicon, we validated the integration sites predicted for three of these cases (Figure 1C). The remaining cases lacked adequate remaining DNA for PCR.
3.2. Correlation with Previously Reported MCPyV Integration Sites
We evaluated our 5 integration site results in the context of 91 other previously reported MCPyV integration sites into the human genome by using Circo plot [31] overlaid with COSMIC gene datasets and fragile sites [26]. Chromosome 5 stands out with the highest (21) MCC cases having integrated MCPyV. There are no integration sites in chromosomes 21, 22, and X. Only five genes of the many associated with MCPyV integration, namely SF3B1, TLX3, CD74, MYC, and KMT2D, are cancer-linked genes listed in the COSMIC database [25]. Additional genes with potential tumor suppressor function that have been shown to be involved in MCPyV integration include PTPRG, GRWD1, and XRCC4 [3,19,21]. Hence, in a minority of MCPyV-positive MCC tumors, MCPyV integration itself may contribute to oncogenesis in a variable and case-specific manner via disruption of cancer genes. Additionally, although there is some overlay with fragile sites as previously reported, this effect did not appear significant. Furthermore, the integration junctions in the human genome were observed to be enriched 91in genes having motifs/binding sites of known oncogenic transcription factors such as LEF1 [32], MYB [33], and AREB6 (ZEB1) [34] along with other pathways (Table S2). We speculate this integration pattern might be related to an increased probability of open chromatin for these gene sets (Figure 2).
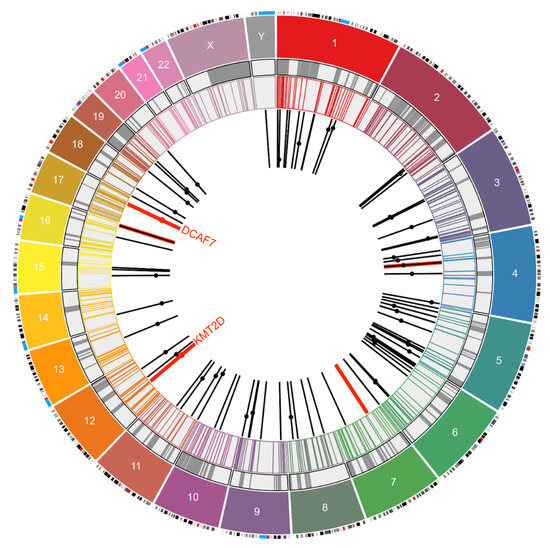
Figure 2.
Circo plot representing 96 integration sites of MCPyV mapped to different chromosomes. The outermost layers represent the chromosomes (color coded) and their respective chromosome bands. The grey circle marks the human fragile sites from the HumCFS database, and the next concentric circle marks the COSMIC database gene sites. The black bars mark 91 integration locations of MCPYV in MCC from previous reports. Dots on the bars represent the human genes associated with this integration event, but their position on the bar is arbitrary. The red bars and dots are data from five MCC cases analyzed using the HPV Detector in this study. The Circo plot was drawn using Circa Software (OMGenomics http://omgenomics.com/circa/).
For the integration junctions in the viral genome (89 in total including this study), we observed the previously reported bias to the T antigen region, with 42 cases displaying junctions in LT, and 4 in sT (Table 2).
3.3. Limitations
We were limited by the amount and quality of available MCC tumor DNA for PCR-Sanger validation, as the majority was used for next generation sequencing. Similarly, previously described inverse PCR approaches for demonstrating viral genome concatemerization [18] were not possible due to limited material. In addition, our approach relies upon identification of off-target capture or shoulder reads of viral sequences within human whole-exome sequencing data, thus generating relatively less sequencing depth than a sequencing approach specifically targeting MCPyV. We also cannot exclude the possibility that the lack of detected integration sites in 2/7 tumors may represent a technical limitation of our approach rather than true absence of viral integration.
4. Conclusions
Our analysis adds to the repertoire of MCPyV integration junction data and systematically collates current information regarding the same. We show unique genetic sites of integration for both the virus and host, confirming the highly variable nature of MCPyV integration. For the first time, we demonstrate integration involving the tumor suppressor gene KMT2D, representing the potential inactivation of a tumor suppressor gene also recurrently inactivated in MCPyV-negative MCC. We also demonstrate that data from tumor whole-exome sequencing data can be effectively interrogated by the simple and open-access Cancervirus Detector tool to demonstrate viral integration sites, thus representing a powerful and accessible new approach for analyzing existing sequencing datasets.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/12/9/966/s1, Table S1: MCPyV Integration Site Genes and Coordinates from Current Study and Published Reports; Table S2: MCPyV Integration Site Genes and Their Associated Biological Pathways.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: R.A.; methodology, R.A. and P.C.; validation, J.E.C.; formal analysis, R.A. and P.C.; investigation, R.A. and P.C.; resources, R.A. And P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A.; writing—review and editing, R.A., P.C., J.E.C., P.W.H.; supervision, R.A.; funding acquisition, R.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust/DBT India Alliance (Early Career Award IA/E/14/1/501773 to Reety Arora).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Sudhir Krishna and Amit Dutt for their valuable support and discussions. We thank Pankaj Vats for assistance with data retrieval and transfer. RA would also like to thank Zaina, Ziyah, and Karan for their love, strength, and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Liu, W.; Huang, Y.-J.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, J.-G.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, F.; Cai, J.-M.; Li, B.-L. Inhibition of TBK1 attenuates radiation-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition of A549 human lung cancer cells via activation of GSK-3β and repression of ZEB1. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, K.L.; Healy, M.A.; Nghiem, P.T.; Sober, A.J.; Johnson, T.M.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Wong, S.L. Analysis of Prognostic Factors from 9387 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Cases Forms the Basis for the New 8th Edition AJCC Staging System. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 3564–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, P.W.; Harms, K.L.; Moore, P.S.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Nghiem, P.T.; Wong, M.K.K.; Brownell, I. The biology and treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma: Current understanding and research priorities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P. Clonal Integration of a Polyomavirus in Human Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. MCV and Merkel cell carcinoma: A molecular success story. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuda, M.; Feng, H.; Kwun, H.J.; Rosen, S.T.; Gjoerup, O.; Moore, P.; Chang, Y. T antigen mutations are a human tumor-specific signature for Merkel cell polyomavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16272–16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Shuda, M.; Weinkam, R.; Schrama, D.; Feng, H.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.; Becker, J.C. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Infected Merkel Cell Carcinoma Cells Require Expression of Viral T Antigens. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7064–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, P.W.; Vats, P.; Verhaegen, M.E.; Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.-M.; Han, S.; Palanisamy, N.; Siddiqui, J.; Cao, X.; Su, F.; et al. The Distinctive Mutational Spectra of Polyomavirus-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3720–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrett, G.J.; Marcelus, C.; Cantalupo, P.G.; Katz, J.P.; Cheng, J.; Akagi, K.; Thakuria, M.; Rabinowits, G.; Wang, L.C.; Symer, D.E.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Exhibits Dominant Control of the Tumor Genome and Transcriptome in Virus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma. mBio 2017, 8, e02079-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrett, G.J.; Thakuria, M.; Chen, T.; Marcelus, C.; Cheng, J.; Nomburg, J.; Thorner, A.R.; Slevin, M.K.; Powers, W.; Burns, R.T.; et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of virus-positive and virus-negative Merkel cell carcinoma. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.; Chang, Y. Common Commensal Cancer Viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, P.; Chang, Y. Why do viruses cause cancer? Highlights of the first century of human tumour virology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrama, D.; Sarosi, E.; Adam, C.; Ritter, C.; Kaemmerer, U.; Klopocki, E.; König, E.; Utikal, J.S.; Becker, J.C.; Houben, R. Characterization of six Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cell lines: Integration pattern suggest that large T antigen truncating events occur before or during integration. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre-Garau, X.; Peter, M.; Avril, M.-F.; Laude, H.; Couturier, J.; Rozenberg, F.; Almeida, A.; Boitier, F.; Carlotti, A.; Couturaud, B.; et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the skin: Pathological and molecular evidence for a causative role of MCV in oncogenesis. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laude, H.C.; Jonchère, B.; Maubec, E.; Carlotti, A.; Marinho, E.; Couturaud, B.; Peter, M.; Sastre-Garau, X.; Avril, M.-F.; Dupin, N.; et al. Distinct Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Molecular Features in Tumour and Non Tumour Specimens from Patients with Merkel Cell Carcinoma. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolittle-Hall, J.M.; Glasspoole, D.C.; Seaman, W.T.; Webster-Cyriaque, J. Meta-Analysis of DNA Tumor-Viral Integration Site Selection Indicates a Role for Repeats, Gene Expression and Epigenetics. Cancers 2015, 7, 2217–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech-Sioli, M.; Guenther, T.; Therre, M.; Spohn, M.; Indenbirken, D.; Theiss, J.; Riethdorf, S.; Qi, M.; Alawi, M.; Wülbeck, C.; et al. High-resolution analysis of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Merkel Cell Carcinoma reveals distinct integration patterns and suggests NHEJ and MMBIR as underlying mechanisms. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, J.E.; Li, Y.; Bell, A.; Hussain, S.S.; Majumdar, R.; Rong-Mullins, X.; Blecua, P.; Damerla, R.; Narang, H.; Ravindran, P.T.; et al. Human papillomavirus 16 promotes microhomology-mediated end-joining. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21573–21579. [Google Scholar]
- Duncavage, E.J.; Magrini, V.; Becker, N.; Armstrong, J.R.; Demeter, R.T.; Wylie, T.; Abel, H.J.; Pfeifer, J.D. Hybrid Capture and Next-Generation Sequencing Identify Viral Integration Sites from Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue. J. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 13, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel-Jantin, C.; Filippone, C.; Cassar, O.; Peter, M.; Tomasic, G.; Vielh, P.; Brière, J.; Petrella, T.; Aubriot-Lorton, M.; Mortier, L.; et al. Genetic variability and integration of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma. Virol. 2012, 426, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.K.; Wollison, B.M.; Powers, W.; Burns, R.T.; Patel, N.; Ducar, M.D.; Starrett, G.J.; Garcia, E.P.; Manning, D.K.; Cheng, J.; et al. ViroPanel: Hybrid Capture and Massively Parallel Sequencing for Simultaneous Detection and Profiling of Oncogenic Virus Infection and Tumor Genome. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 476–487. [Google Scholar]
- García-Mulero, S.; Moratalla-Navarro, F.; Curiel-Olmo, S.; Moreno, V.; Vaque, J.P.; Sanz-Pamplona, R.; Piulats, J.M. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus using whole exome sequencing data. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrani, P.; Kulkarni, V.; Iyer, P.; Upadhyay, P.; Chaubal, R.; Das, P.; Mulherkar, R.; Singh, R.; Dutt, A. NGS-based approach to determine the presence of HPV and their sites of integration in human cancer genome. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, A.R. BEDTools: The Swiss-Army Tool for Genome Feature Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 47, 11.12.1–11.12.34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database Hallmark Gene Set Collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondka, Z.; Bamford, S.; Cole, C.G.; Ward, S.A.; Dunham, I.; Forbes, S.A. The COSMIC Cancer Gene Census: Describing genetic dysfunction across all human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Nagpal, G.; Kumar, V.; Usmani, S.S.; Agrawal, P.; Raghava, G.P.S. HumCFS: A database of fragile sites in human chromosomes. BMC Genom. 2019, 19, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Chen, L.H.; Huang, Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, P.; Pirozzi, C.J.; Qin, X.; Bao, X.; Greer, P.K.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. KMT2D maintains neoplastic cell proliferation and global histone H3 lysine 4 monomethylation. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACR Project GENIE Consortium. The AACR Project GENIE Consortium AACR Project GENIE: Powering Precision Medicine through an International Consortium. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, T.C.; Montesion, M.; Russell, J.S.; Sokol, E.S.; Frampton, G.M.; Miller, V.A.; Albacker, L.A.; McLeod, H.L.; Eroglu, Z.; Khushalani, N.I.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Clinicogenomic Biomarkers of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5961–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Lee, E.; Yue, Y.; Vandergriff, T.; Byekova, G.; Cockerell, C.; Hosler, G.; Pastrana, D.V.; Buck, C.; Wang, R. 569 Human polyomavirus 6 and 7 are associated with pruritic and dyskeratotic dermatoses. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, L.; Daniels, G.; Wang, D.; Deng, F.-M.; Lee, P. Wnt signaling pathway protein LEF1 in cancer, as a biomarker for prognosis and a target for treatment. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1389–1406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Han, L.; Yi, Y. Reassessing the Potential of Myb-targeted Anti-cancer Therapy. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).