Long Term Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol Administration Inhibits Proinflammatory Responses in Minor Salivary Glands of Chronically Simian Immunodeficieny Virus Infected Rhesus Macaques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Care, Ethics and Experimental Procedures
2.2. Animal Model and Experimental Design
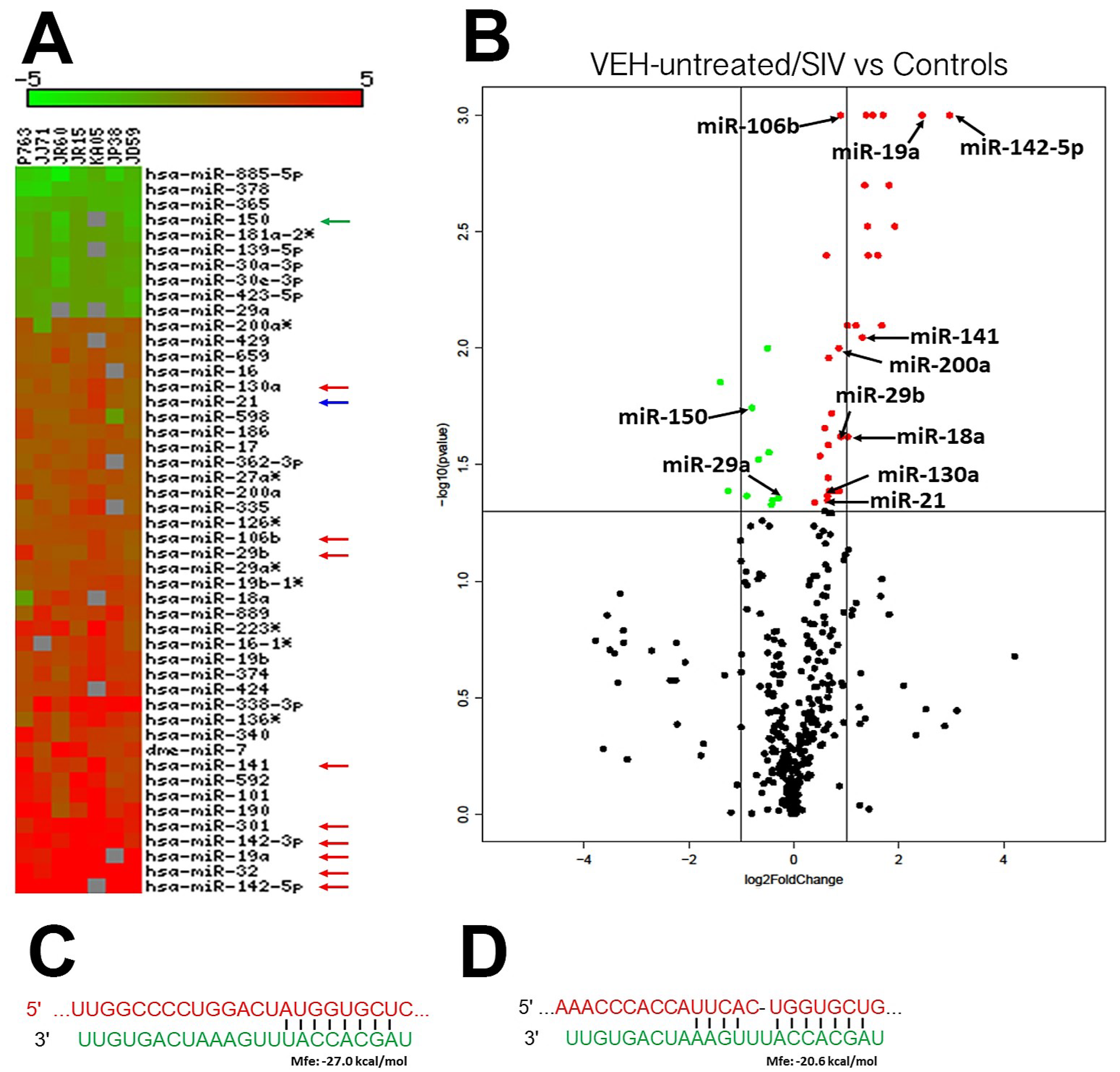
2.3. Global MicroRNA (miRNA) Profiling
2.4. RNA-Seq Library Construction, Clustering and Sequencing
2.5. Cloning of 3′-UTR of AGR2 and TSC22D3 mRNA and Dual-Glo Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
2.6. Immunofluorescence for Cellular Localization of AGR2, WFDC2 and TSC22D3 in OPM Tissues
2.7. Quantitative Image Analysis of OPM Sections
2.8. miR-29b Overexpression Studies
2.9. Quantitation of Mucosal Viral Loads
2.10. Data Analysis and Availability
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Viral Loads, CD4+ and CD8+ T Cell Status and Oral Histopathology
3.2. Genes Associated with Anti-Viral Defense, Interferon Signaling and Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Are Markedly Upregulated in OPM of VEH/SIV but not THC/SIV Rhesus Macaques
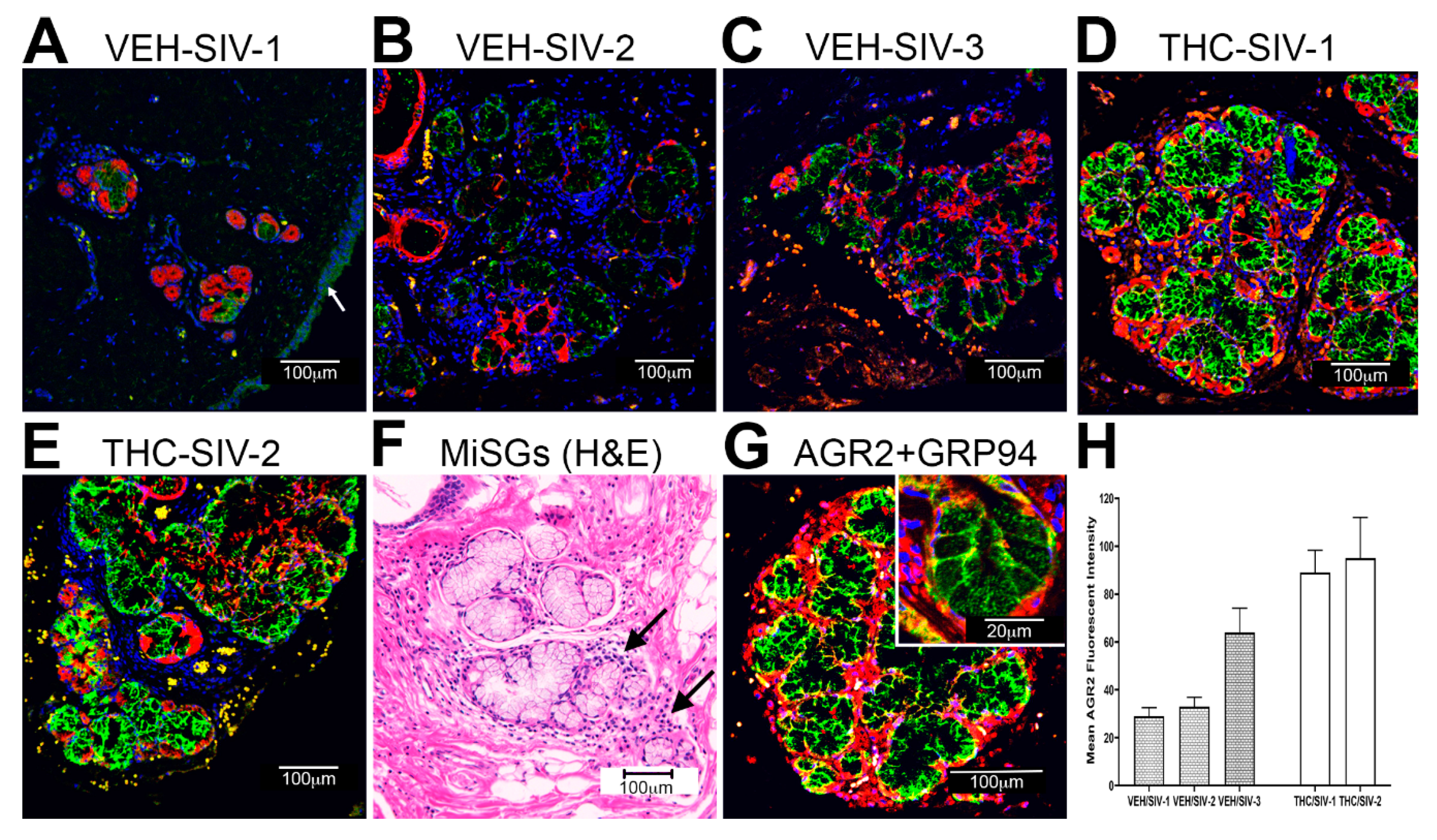
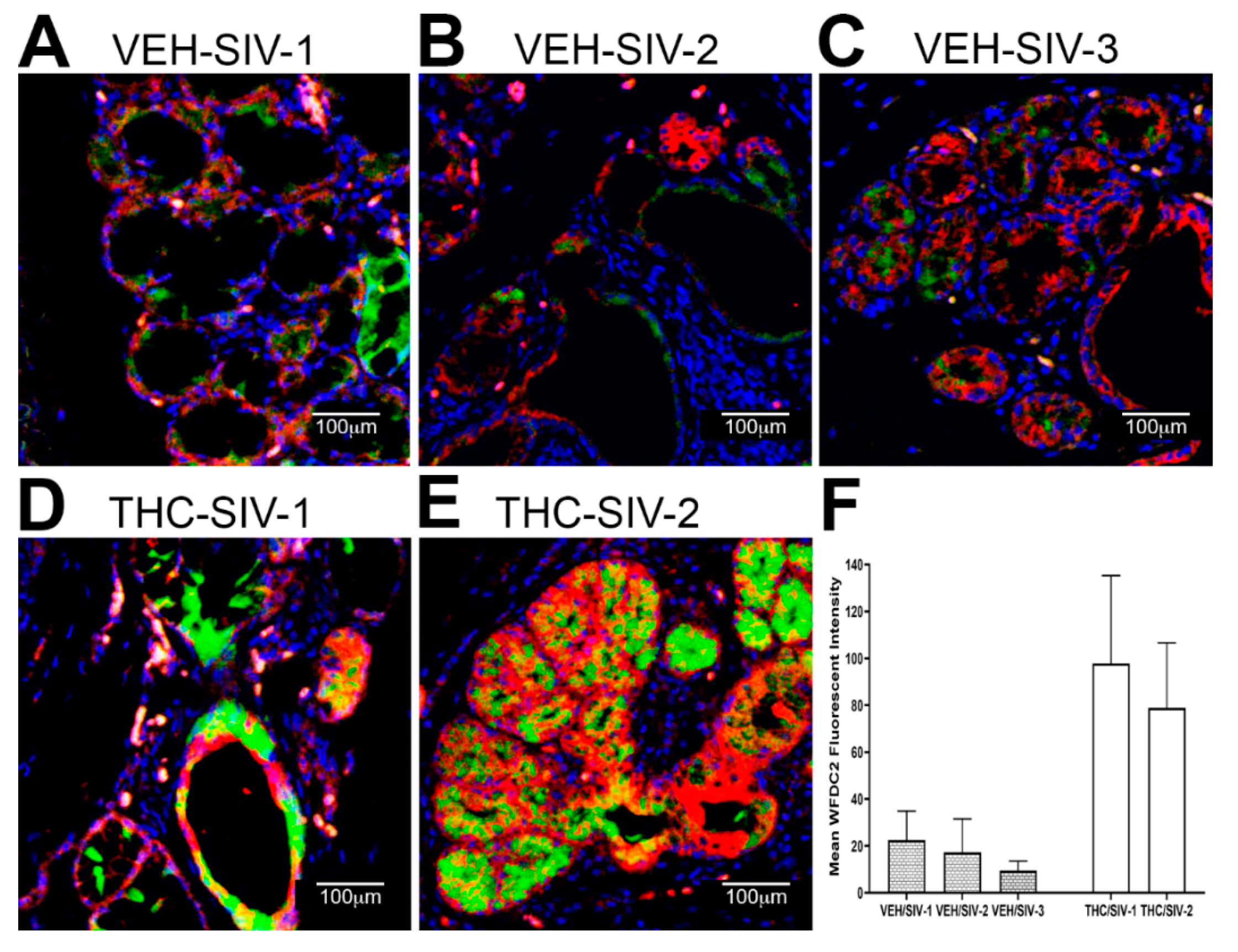
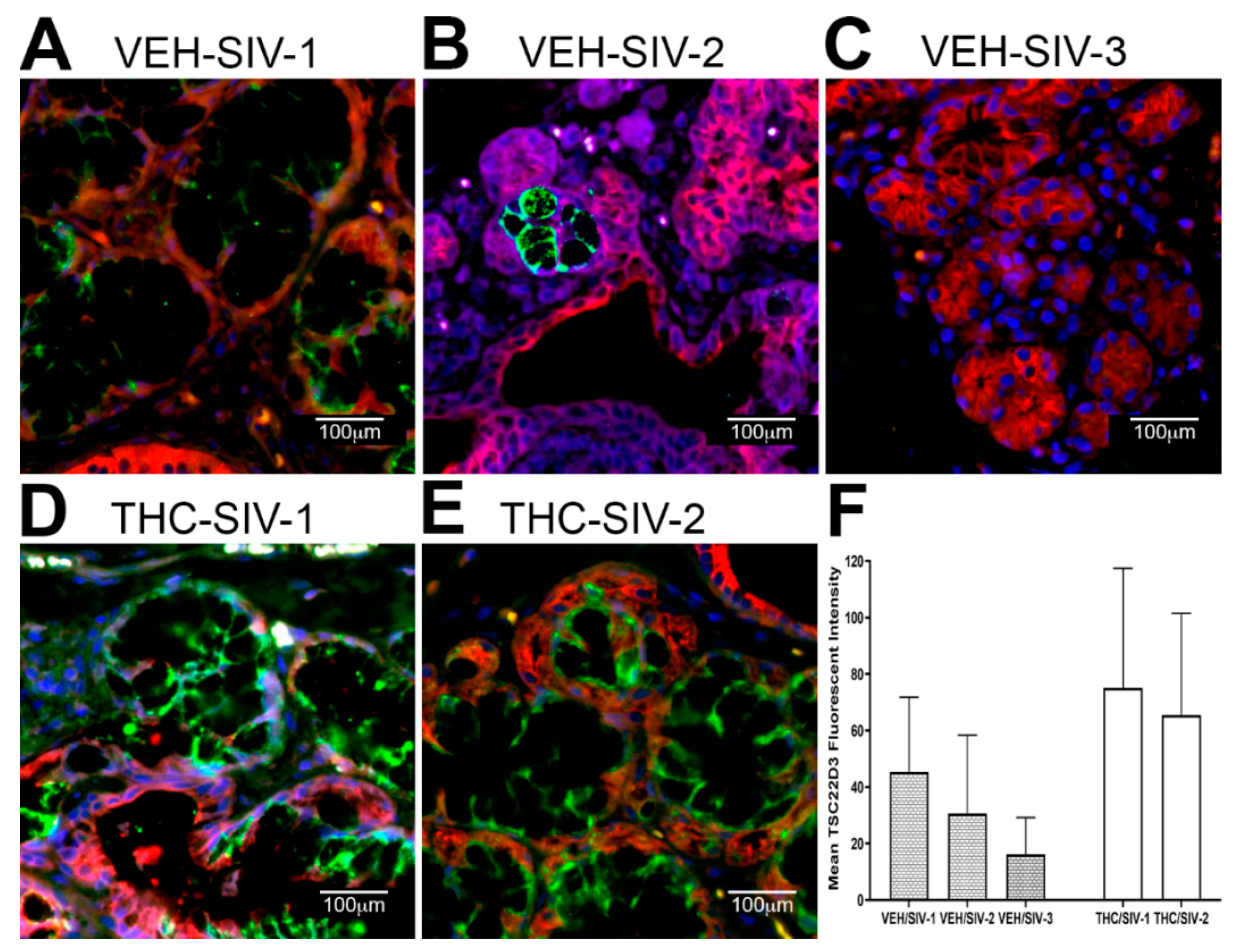
3.3. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress (ER) regulator Anterior Gradient 2 (AGR2), Epithelial Barrier Enhancing WAP Four-Disulfide Core Domain Protein 2 (WFDC2) and the Anti-Inflammatory TSC22D3 Are Significantly Downregulated in OPM of VEH-Untreated/SIV Rhesus Macaques
3.4. Chronic THC Administration Preserved AGR2, WFDC2 and TSC22D3 Protein Expression in Minor Salivary Glands (MiSGs) of Chronic SIV-Infected Rhesus Macaques
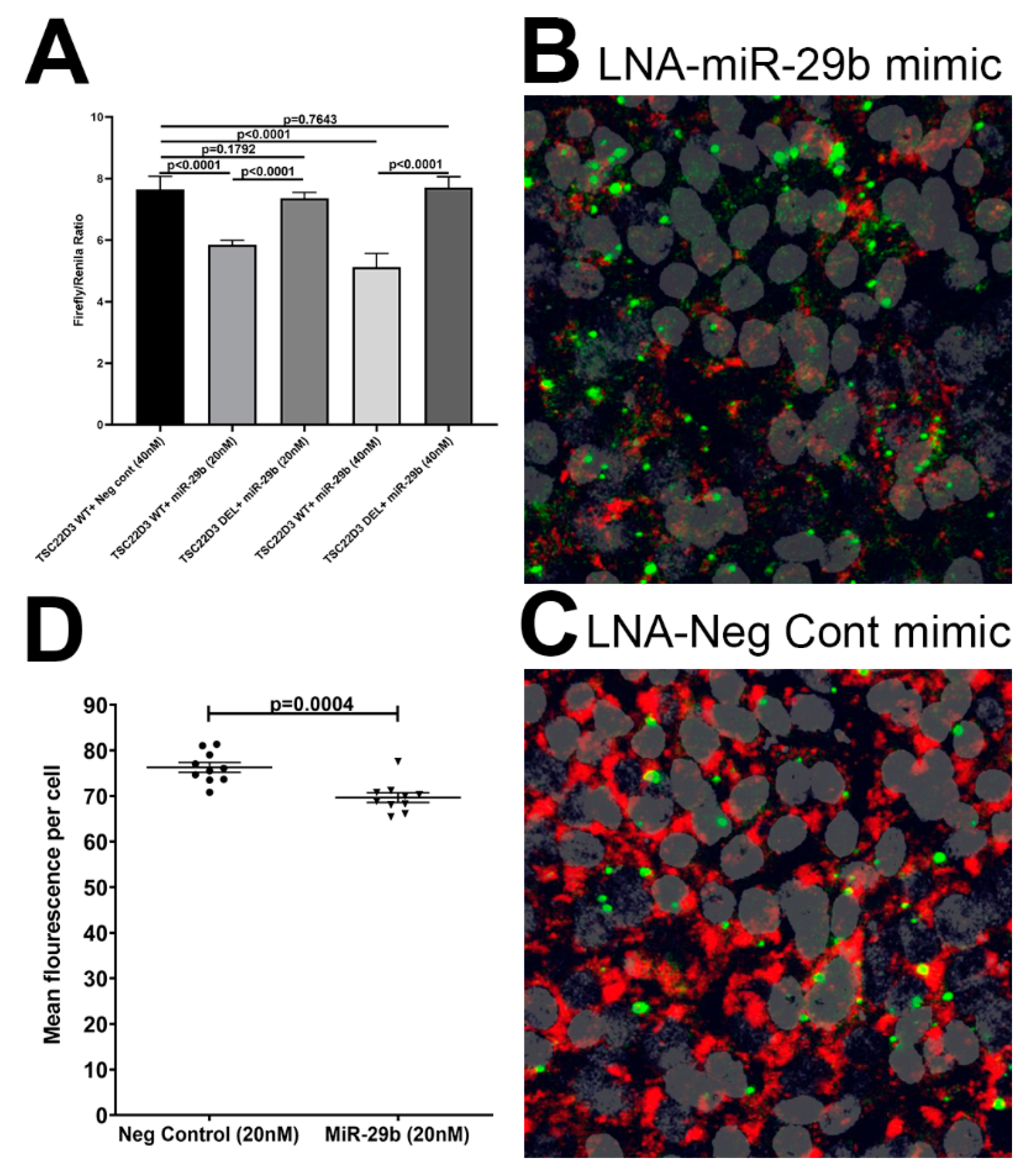
3.5. TSC22D3 Is Post-Transcriptionally Regulated by miR-29b
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, F.; Jacobson, R.S. Oral mucosal immunity and HIV/SIV infection. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nittayananta, W.; Tao, R.; Jiang, L.; Peng, Y.; Huang, Y. Oral innate immunity in HIV infection in HAART era. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2015, 45, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, J.; Saladyanant, T.; Ramsey, K.; Blake, J.; Morelli, T.; Southerland, J.; Quinlivan, E.B.; Phillips, C.; Nelson, J.; Deparis, K.; et al. Impact of periodontal intervention on local inflammation, periodontitis, and HIV outcomes. Oral Dis. 2016, 22 (Suppl. S1) (Suppl. S1), 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, L.T.; Jayashantha, P.; Chidzonga, M.; Komesu, M.; Nair, R.G.; Johnson, N.W. Comorbidities associated with HIV and antiretroviral therapy (clinical sciences): A workshop report. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heron, S.E.; Elahi, S. HIV Infection and Compromised Mucosal Immunity: Oral Manifestations and Systemic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pólvora, T.L.S.; Nobre, Á.V.V.; Tirapelli, C.; Taba, M.; De Macedo, L.D.; Santana, R.C.; Pozzetto, B.; Lourenço, A.G.; Motta, A.C.F. Relationship between human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection and chronic periodontitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annavajhala, M.K.; Khan, S.D.; Sullivan, S.B.; Shah, J.; Pass, L.; Kister, K.; Kunen, H.; Chiang, V.; Monnot, G.C.; Ricupero, C.L.; et al. Oral and Gut Microbial Diversity and Immune Regulation in Patients with HIV on Antiretroviral Therapy. mSphere 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Verhoeven, D.; Sankaran, S.; Glavan, T.; Reay, E.; Dandekar, S. Heightened Cytotoxic Responses and Impaired Biogenesis Contribute to Early Pathogenesis in the Oral Mucosa of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 16, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Saxena, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Abrams, W.R.; Phelan, J.A.; Norman, R.G.; Fisch, G.S.; Corby, P.M.; Dewhirst, F.; et al. HIV Infection and Microbial Diversity in Saliva. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomeli-Martinez, S.M.; Valentin-Gomez, E.; Varela-Hernandez, J.J.; Alvarez-Zavala, M.; Sanchez-Reyes, K.; Ramos-Solano, M.; Cabrera-Silva, R.I.; Ramirez-Anguiano, V.M.; Lomeli-Martinez, M.A.; Martinez-Salazar, S.Y.; et al. Candida spp. Determination and Th1/Th2 Mixed Cytokine Profile in Oral Samples From HIV+ Patients With Chronic Periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittayananta, W.; Kemapunmanus, M.; Yangngam, S.; Talungchit, S.; Sriplung, H. Expression of oral secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in HIV-infected subjects with long-term use of antiretroviral therapy. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2012, 42, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocon, S.; Murphy, C.; Dang, A.T.; Sankaran-Walters, S.; Li, C.-S.; Tarara, R.; Borujerdpur, N.; Dandekar, S.; Paster, B.J.; George, M. Transcription Profiling Reveals Potential Mechanisms of Dysbiosis in the Oral Microbiome of Rhesus Macaques with Chronic Untreated SIV Infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittayananta, W.; Amornthatree, K.; Kemapunmanus, M.; Talungchit, S.; Sriplung, H. Expression of oral cytokines in HIV-infected subjects with long-term use of antiretroviral therapy. Oral Dis. 2013, 20, e57–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patton, L.L.; Ramirez-Amador, V.; Anaya-Saavedra, G.; Nittayananta, W.; Carrozzo, M.; Ranganathan, K. Urban legends series: Oral manifestations of HIV infection. Oral Dis. 2013, 19, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emfietzoglou, R.; Pachymanolis, E.; Piperi, C. Impact of Epigenetic alterations in the development of oral diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, H.; Suzuki, H.I. Systems and Synthetic microRNA Biology: From Biogenesis to Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.; Mona, M.; Lee, K.-E.; Kim, D.H.; Han, K. MicroRNAs in Autoimmune Sjögren’s Syndrome. Genom. Inform. 2018, 16, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.; Uttamani, J.R.; Naqvi, A.R.; Nares, S. microRNAs: Emerging players in oral cancers and inflammatory disorders. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317698379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Zhou, X.; Naqvi, A.; Francis, M.; Foyle, D.; Nares, S.; Diekwisch, T.G. MicroRNAs and immunity in periodontal health and disease. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, M.; Sharma, R.; Panda, N.K.; Khullar, M. Role of non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A narrative review. Oral Dis. 2017, 24, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.Y.; Constantinides, C.; Kebschull, M.; Papapanou, P.N. MicroRNAs Regulate Cytokine Responses in Gingival Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xue, N.; Xie, Y.-F.; Zhu, N.-W.; Dong, Y.-Y.; Wei, C.-C.; Deng, J.-Y. The negative feedback regulation of microRNA-146a in human periodontal ligament cells after Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouhara, K.; Savitri, I.J.; Fujita, T.; Kittaka, M.; Kajiya, M.; Iwata, T.; Miyagawa, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Shiba, H.; Kurihara, H. miR-584 Expressed in Human Gingival Epithelial Cells Is Induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis Stimulation and Regulates Interleukin-8 Production via Lactoferrin Receptor. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, e198–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, L.C.; Kumar, V.; Torben, W.; Vande Stouwe, C.; Winsauer, P.; Amedee, A.; Molina, P.E.; Mohan, M. Chronic administration of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol induces intestinal anti-inflammatory microRNA expression during acute simian immunodeficiency virus infection of rhesus macaques. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Torben, W.; Mansfield, J.; Alvarez, X.; Stouwe, C.V.; Li, J.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Didier, P.J.; Pahar, B.; Molina, P.E.; et al. Cannabinoid Attenuation of Intestinal Inflammation in Chronic SIV-Infected Rhesus Macaques Involves T Cell Modulation and Differential Expression of Micro-RNAs and Pro-inflammatory Genes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, P.E.; Amedee, A.M.; LeCapitaine, N.J.; Zabaleta, J.; Mohan, M.; Winsauer, P.J.; Vande Stouwe, C.; McGoey, R.R.; Auten, M.W.; LaMotte, L.; et al. Modulation of gut-specific mechanisms by chronic delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol administration in male rhesus macaques infected with simian immunodeficiency virus: A systems biology analysis. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2014, 30, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusthen, S.; Kristoffersen, A.K.; Young, A.; Galtung, H.K.; Petrovski, B.É.; Palm, Ø.; Enersen, M.; Jensen, J.L. Dysbiotic salivary microbiota in dry mouth and primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigalou, C.; Stavropoulou, E.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Current Insights in Microbiome Shifts in Sjogren’s Syndrome and Possible Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Meulen, T.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Bootsma, H.; Liefers, S.C.; Vila, A.V.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J.; Wijmenga, C.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Kroese, F.G.M.; et al. Dysbiosis of the buccal mucosa microbiome in primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, P.E.; Winsauer, P.; Zhang, P.; Walker, E.; Birke, L.; Amedee, A.; Stouwe, C.V.; Troxclair, D.; McGoey, R.; Varner, K.; et al. Cannabinoid Administration Attenuates the Progression of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2011, 27, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsauer, P.; Molina, P.E.; Amedee, A.M.; Filipeanu, C.M.; McGoey, R.R.; Troxclair, D.A.; Walker, E.M.; Birke, L.L.; Stouwe, C.V.; Howard, J.M.; et al. Tolerance to chronic delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ⁹-THC) in rhesus macaques infected with simian immunodeficiency virus. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 19, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, L.; Cong, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Qin, C.; Molina, P.; Chen, Z. Chronic Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Administration Reduces IgE+B Cells but Unlikely Enhances Pathogenic SIVmac251 Infection in Male Rhesus Macaques of Chinese Origin. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Mansfield, J.; Fan, R.; MacLean, A.; Li, J.; Mohan, M. miR-130a and miR-212 Disrupt the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier through Modulation of PPARgamma and Occludin Expression in Chronic Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2677–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Torben, W.; Kenway, C.S.; Schiro, F.R.; Mohan, M. Longitudinal Examination of the Intestinal Lamina Propria Cellular Compartment of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques Provides Broader and Deeper Insights into the Link between Aberrant MicroRNA Expression and Persistent Immune Activation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5003–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiernasz, N.; Leroi, F.; Chevalier, F.; Cornet, J.; Cardinal, M.; Rohloff, J.; Passerini, D.; Skırnisdóttir, S.; Pilet, M.-F. Salmon Gravlax Biopreservation With Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Polyphasic Approach to Assessing the Impact on Organoleptic Properties, Microbial Ecosystem and Volatilome Composition. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboulnasr, F.; Paranjape, G.; Badley, A.D. The TRAIL: TRAILshort Axis in HIV Immunopathology. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 38, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; McCarthy, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Okoniewski, M.; Smyth, G.K.; Huber, W.; Robinson, M.D. Count-based differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data using R and Bioconductor. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1765–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersole, J.L.; Peyyala, R.; Gonzalez, O.A. Biofilm-induced profiles of immune response gene expression by oral epithelial cells. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.B.; Xiong, Y.; Pattabiraman, G.; Manavalan, T.T.; Qiu, F.; Medvedev, A.E. Pellino-3 promotes endotoxin tolerance and acts as a negative regulator of TLR2 and TLR4 signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janaka, S.K.; Tavakoli-Tameh, A.; Neidermyer, W.J., Jr.; Serra-Moreno, R.; Hoxie, J.A.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Johnson, R.P.; Lifson, J.D.; Wolinsky, S.M.; Evans, D.T. Polymorphisms in Rhesus Macaque Tetherin Are Associated with Differences in Acute Viremia in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Deltanef-Infected Animals. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, N.; Schenten, V.; Bueb, J.L.; Tolle, F.; Brechard, S. miRNAs Regulate Cytokine Secretion Induced by Phosphorylated S100A8/A9 in Neutrophils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-C.; Xu, W.-D.; Liu, X.-Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Huang, A.-F.; Su, L.; Liu, X.-Y. Biology of IL-36 Signaling and Its Role in Systemic Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqrawi, L.A.; Jensen, J.L.; Øijordsbakken, G.; Ruus, A.-K.; Nygård, S.; Holden, M.; Jonsson, R.; Galtung, H.K.; Skarstein, K. Signalling pathways identified in salivary glands from primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients reveal enhanced adipose tissue development. Autoimmunity 2018, 51, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparber, F.; Dolowschiak, T.; Mertens, S.; Lauener, L.; Clausen, B.E.; Joller, N.; Stoitzner, P.; Tussiwand, R.; LeibundGut-Landmann, S. Langerin+ DCs regulate innate IL-17 production in the oral mucosa during Candida albicans-mediated infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiripolsky, J.; Romano, R.A.; Kasperek, E.M.; Yu, G.; Kramer, J.M. Activation of Myd88-Dependent TLRs Mediates Local and Systemic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, A.; Liu, J.; Martinot, A.J.; Mcmahan, K.; Mercado, N.B.; Peter, L.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Yu, J.; Maliga, Z.; Nekorchuk, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection protects against rechallenge in rhesus macaques. Science 2020, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Bradley, T.; Williams, W.B.; Cain, D.W.; Montefiori, D.C.; Saunders, K.O.; Parks, R.J.; Edwards, R.W.; Ferrari, G.; Mueller, O.; et al. Neonatal Rhesus Macaques Have Distinct Immune Cell Transcriptional Profiles following HIV Envelope Immunization. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1553–1569.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Qi, F.; Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Bao, L.; Deng, W.; Gao, H.; Xiang, Z.; et al. Age-related rhesus macaque models of COVID-19. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2020, 3, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, T.M.; Molloy, E.L.; Masterson, J.C.; Glynn, S.F.; Costello, R.W.; Avdalovic, M.V.; Schelegle, E.S.; Miller, L.A.; Hyde, D.M.; O’Dea, S. SMAD Signaling in the Airways of Healthy Rhesus Macaques versus Rhesus Macaques with Asthma Highlights a Relationship Between Inflammation and Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamperschroer, C.; Goldstein, R.; Schneider, P.A.; Kuang, B.; Eisenbraun, M.D. Utilization of lipopolysaccharide challenge in cynomolgus macaques to assess IL-10 receptor antagonism. J. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 16, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, M.; Rao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xian, Q.; Yu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Bao, R.; Yue, J.; et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Erdman infection of cynomolgus macaques of Chinese origin. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3609–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Ren, S.; Korge, P.; Choi, J.; Dong, Y.; Weiss, J.; Koehler, C.; Chen, J.-N.; Wang, Y. A novel mitochondrial matrix serine/threonine protein phosphatase regulates the mitochondria permeability transition pore and is essential for cellular survival and development. Genome Res. 2007, 21, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.-M.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.-Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Q.; Sheng, R.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; et al. TIGAR inhibits ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory response of astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 2018, 131, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jin, D. A genetic screen in Drosophila implicates Sex comb on midleg (Scm) in tissue overgrowth and mechanisms of Scm degradation by Wds. Mech. Dev. 2015, 136, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herich, S.; Schneider-Hohendorf, T.; Rohlmann, A.; Ghadiri, M.K.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Zondler, L.; Janoschka, C.; Ostkamp, P.; Richter, J.; Breuer, J.; et al. Human CCR5high effector memory cells perform CNS parenchymal immune surveillance via GZMK-mediated transendothelial diapedesis. Brain 2019, 142, 3411–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, M.; Obacz, J.; Avril, T.; Ding, Y.; Papadodima, O.; Treton, X.; Daniel, F.; Pilalis, E.; Hörberg, J.; Hou, W.; et al. Control of anterior GR adient 2 (AGR 2) dimerization links endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis to inflammation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-W.; Zhen, G.; Verhaeghe, C.; Nakagami, Y.; Nguyenvu, L.T.; Barczak, A.J.; Killeen, N.; Erle, D. The protein disulfide isomerase AGR2 is essential for production of intestinal mucus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6950–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingle, L.; Cross, S.; High, A.S.; Wallace, W.A.H.; Rassl, D.; Yuan, G.; Hellstrom, I.; Campos, M.; Bingle, C.D. WFDC2 (HE4): A potential role in the innate immunity of the oral cavity and respiratory tract and the development of adenocarcinomas of the lung. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, K.; Antanaviciute, A.; Fawkner-Corbett, D.; Jagielowicz, M.; Aulicino, A.; Lagerholm, C.; Davis, S.; Kinchen, J.; Chen, H.H.; Alham, N.K.; et al. Colonic epithelial cell diversity in health and inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2019, 567, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.T.; Hoppstädter, J.; Hirschfelder, K.; Hachenthal, N.; Diesel, B.; Kessler, S.M.; Huwer, H.; Kiemer, A.K. Downregulation of the glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) promotes vascular inflammation. Atherosclerosis 2014, 234, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.; Ronchetti, S.; Gabrielli, E.; Pericolini, E.; Gentili, M.; Roselletti, E.; Vecchiarelli, A.; Riccardi, C.; Ricci, E. GILZ restrains neutrophil activation by inhibiting the MAPK pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 105, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchetti, S.; Gentili, M.; Ricci, E.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper as a Druggable Target in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toczewska, J.; Konopka, T. Activity of enzymatic antioxidants in periodontitis: A systematic overview of the literature. Dent. Med. Probl. 2019, 56, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzeldemir-Akcakanat, E.; Alkan, B.; Sunnetci-Akkoyunlu, D.; Gurel, B.; Balta, V.M.; Kan, B.; Akgun, E.; Yilmaz, E.B.; Baykal, A.T.; Çine, N.; et al. Molecular signatures of chronic periodontitis in gingiva: A genomic and proteomic analysis. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denard, B.; Seemann, J.; Chen, Q.; Gay, A.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, J. The Membrane-Bound Transcription Factor CREB3L1 Is Activated in Response to Virus Infection to Inhibit Proliferation of Virus-Infected Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Marusawa, H.; Endo, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Chiba, T. Expression of APOBEC2 is transcriptionally regulated by NF-κB in human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, A.; Olagnier, D.; Lin, R.; Van Grevenynghe, J.; Hiscott, J. SAMHD1 Host Restriction Factor: A Link with Innate Immune Sensing of Retrovirus Infection. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 4981–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, F.; Guo, L.; Wu, B. REV-ERBalpha integrates colon clock with experimental colitis through regulation of NF-kappaB/NLRP3 axis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichnieski, C.; Maheshwari, K.; De Souza, L.C.; Nieves, F.; Tartari, T.; Garlet, G.P.; Carneiro, E.; Letra, A.; Silva, R.M. DNA methylation profiles of immune response-related genes in apical periodontitis. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 52, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayani, J.; Diamandis, E. The physiology and pathobiology of human kallikrein-related peptidase 6 (KLK6). Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmajidi, M.; Shafaee, S.; Bijani, A.; Bagheri, S. VCAM1 and ICAM1 expression in oral lichen planus. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2013, 2, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papathanasiou, E.; Kantarci, A.; Konstantinidis, A.; Gao, H.; Van Dyke, T.E. SOCS-3 Regulates Alveolar Bone Loss in Experimental Periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Su, L.; Duan, X.; Chen, X.; Hays, A.; Upadhyayula, S.; Shivde, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, D.; et al. MicroRNA-21 down-regulates inflammation and inhibits periodontitis. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 101, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Hu, B.; Jadhav, R.R.; Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Cavanagh, M.M.; Akondy, R.S.; Ahmed, R.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Activation of miR-21-Regulated Pathways in Immune Aging Selects against Signatures Characteristic of Memory T Cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2148–2162.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentenero, M.; Bowers, L.; Jayasinghe, R.; Cheong, S.C.; Farah, C.S.; Kerr, A.R.; Alevizos, I. World Workshop on Oral Medicine VII: Functional pathways involving differentially expressed lncRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.-W.; Bartel, B. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos Parra Flores, B.D.C.T.; Lourenco, S.V.; Damascena, A.S.; Kowaslki, L.P.; Soares, F.A.; Coutinho-Camillo, C.M. Altered expression of apoptosis-regulating miRNAs in salivary gland tumors suggests their involvement in salivary gland tumorigenesis. Virchows Arch. 2016, 470, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereshchenko, O.; Migliorati, G.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper: A Novel Anti-inflammatory Molecule. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballegeer, M.; Vandewalle, J.; Eggermont, M.; Van Isterdael, G.; Dejager, L.; De Bus, L.; Decruyenaere, J.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Overexpression of Gilz Protects Mice Against Lethal Septic Peritonitis. Shock 2019, 52, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliasson, L.; Carlén, A. An update on minor salivary gland secretions. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 118, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aframian, D.J.; Keshet, N.; Nadler, C.; Zadik, Y.; Vered, M. Minor salivary glands: Clinical, histological and immunohistochemical features of common and less common pathologies. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 151451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meer, S. Human immunodeficiency virus and salivary gland pathology: An update. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 128, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittayananta, W.; Chanowanna, N.; Pruphetkaew, N.; Nauntofte, B. Relationship between xerostomia and salivary flow rates in HIV-infected individuals. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2013, 4, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, I.; Koulen, P.; McArthur, C. Contribution of HIV Infection, AIDS, and Antiretroviral Therapy to Exocrine Pathogenesis in Salivary and Lacrimal Glands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Arunkumar, G.; Manickavasagam, M.; Rajkumar, K.S.; Rajaraman, R.; Munirajan, A.K. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: MicroRNA expression profiling and integrative analyses for elucidation of tumourigenesis mechanism. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Vella, S.; Tuzzolino, F.; Cuscino, N.; Cecchettini, A.; Ferro, F.; Mosca, M.; Alevizos, I.; Bombardieri, S.; Conaldi, P.G.; et al. MicroRNA-mediated Regulation of Mucin-type O-glycosylation Pathway: A Putative Mechanism of Salivary Gland Dysfunction in Sjögren Syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlacius, G.E.; Wahren-Herlenius, M.; Ronnblom, L. An update on the role of type I interferons in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Animal ID | SIV Inoculum | Duration of Infection | Plasma Viral Loads 106/mL | OPM Viral Loads 106/mg RNA | Opportunistic Infections |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic SIV-Infected and Vehicle Untreated (Group 1) for microRNA and gene expression studies | |||||
| P763 # | SIVmac251 | 145 | NA | 3 | ND |
| JJ71 # * | SIVmac239 | 148 | NA | 0.3 | ND |
| JR60 # * | SIVmac251 | 180 | NA | 10 | ND |
| JR15 # * | SIVmac251 | 180 | NA | 0.3 | ND |
| KA05 # * | SIVmac251 | 90 | NA | 0.7 | ND |
| JP38 # * | SIVmac251 | 180 | NA | 0.1 | ND |
| JD59 # * | SIVmac251 | 150 | NA | 300 | ND |
| IJ60 * | SIVmac251 | 180 | NA | NA | ND |
| Chronic SIV-Infected and Vehicle treated (Group 2) for Immunofluorescence studies | |||||
| JH47 % | SIVmac251 | 180 | 2 | NA | ND |
| JR36 % | SIVmac251 | 180 | 0.5 | 0.02 | ND |
| JD66 % | SIVmac251 | 180 | 0.04 | 0.5 | ND |
| Chronic SIV-Infected and ∆9-THC treated (Group 3) for Immunofluorescence studies | |||||
| JI45 # % * | SIVmac251 | 180 | 3 | 0.02 | ND |
| JT80 # % * | SIVmac251 | 180 | 1 | 9 | ND |
| IV90 # % * | SIVmac251 | 180 | 0.02 | 0.3 | ND |
| Uninfected Controls (Group 4) for microRNA and gene expression studies | |||||
| JC65 # * | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| GJ01 # * | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| GK11 # * | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| GK22 # * | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| JD95 # * | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez, X.; Sestak, K.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Mohan, M. Long Term Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol Administration Inhibits Proinflammatory Responses in Minor Salivary Glands of Chronically Simian Immunodeficieny Virus Infected Rhesus Macaques. Viruses 2020, 12, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070713
Alvarez X, Sestak K, Byrareddy SN, Mohan M. Long Term Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol Administration Inhibits Proinflammatory Responses in Minor Salivary Glands of Chronically Simian Immunodeficieny Virus Infected Rhesus Macaques. Viruses. 2020; 12(7):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070713
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez, Xavier, Karol Sestak, Siddappa N. Byrareddy, and Mahesh Mohan. 2020. "Long Term Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol Administration Inhibits Proinflammatory Responses in Minor Salivary Glands of Chronically Simian Immunodeficieny Virus Infected Rhesus Macaques" Viruses 12, no. 7: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070713
APA StyleAlvarez, X., Sestak, K., Byrareddy, S. N., & Mohan, M. (2020). Long Term Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol Administration Inhibits Proinflammatory Responses in Minor Salivary Glands of Chronically Simian Immunodeficieny Virus Infected Rhesus Macaques. Viruses, 12(7), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070713






