Characterization of Plaque Variants and the Involvement of Quasi-Species in a Population of EV-A71
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Serial Passages of Virus
2.3. Plaque Assay
2.4. Isolation of Plaque Variants
2.5. Re-Infection of the Cells by EV-A71/BP and EV-A71/SP Plaque Variants and the Determination of Their Plaque Sizes
2.6. Growth Kinetics
2.7. Rates of RNA Replication (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Amplification of EV-A71 RNA to cDNA
2.9. Genome Sequencing
2.10. Homology Modelling
2.11. Viral Binding Assay
3. Results
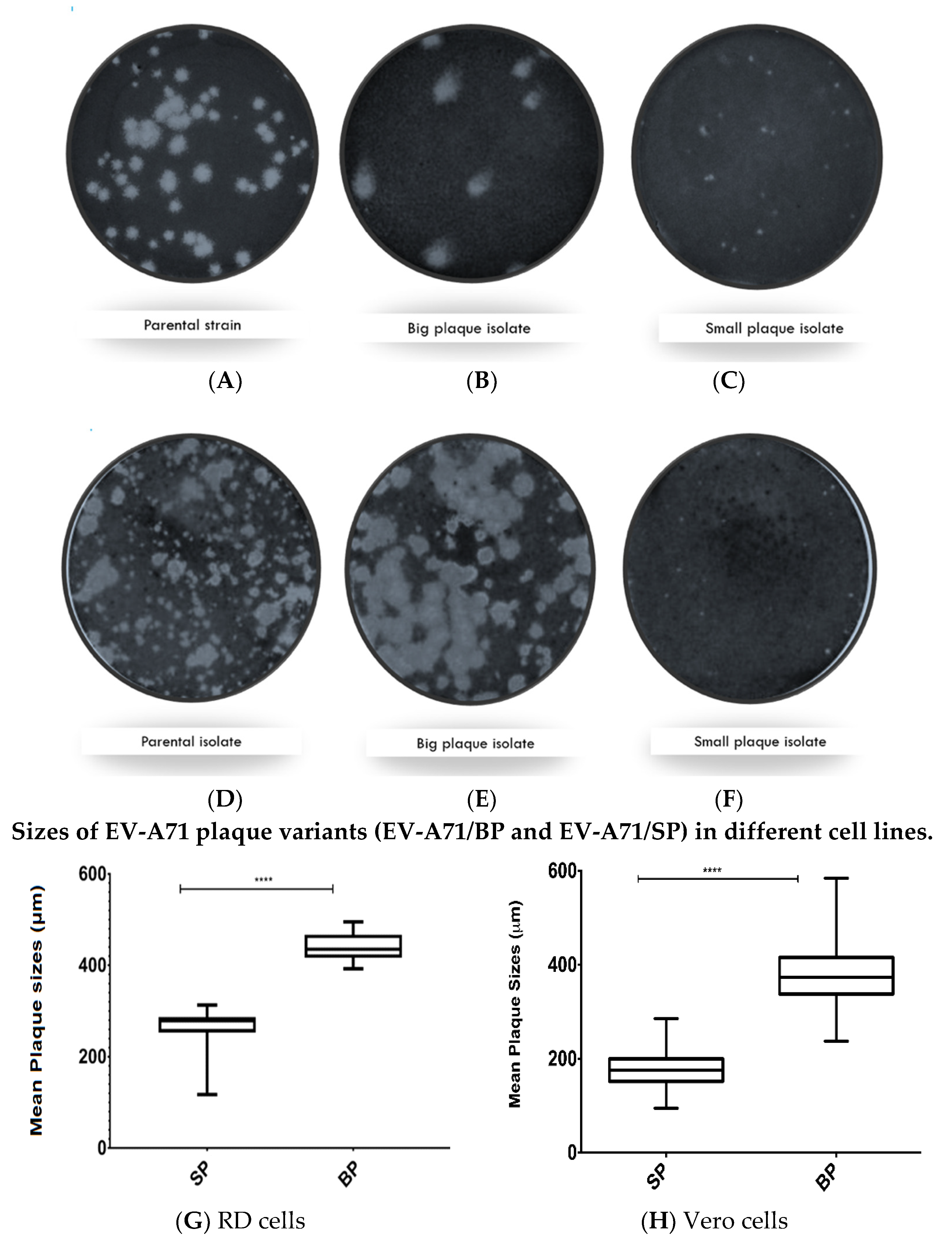
3.1. Isolation of Big-Plaque and Small-Plaque Variants of EV-A71
3.2. In Vitro Assessment of the Big and Small Plaque Variants
3.3. Rates of RNA Replication and Infectivity of EV-A71/BP and EV-A71/SP Plaque Variants
3.4. Sequence Comparison of Small-Plaque and Big-Plaque Variants to the WT
3.5. Analysis of Amino Acid Mutations in the VP1 of the EV-A71 Plaque Variants
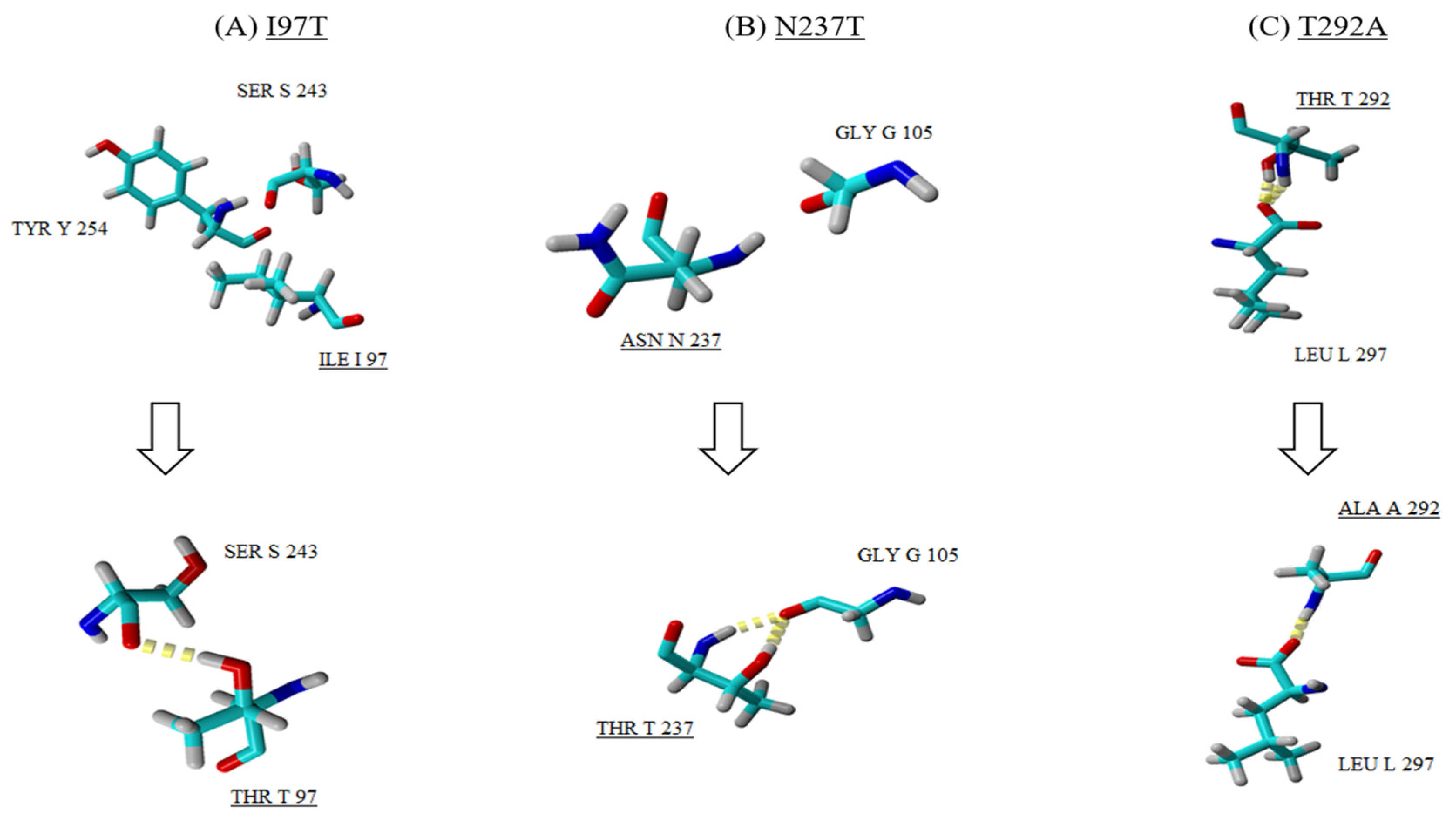
3.6. Impact of Spontaneous Mutations on VP1 Protein Folding
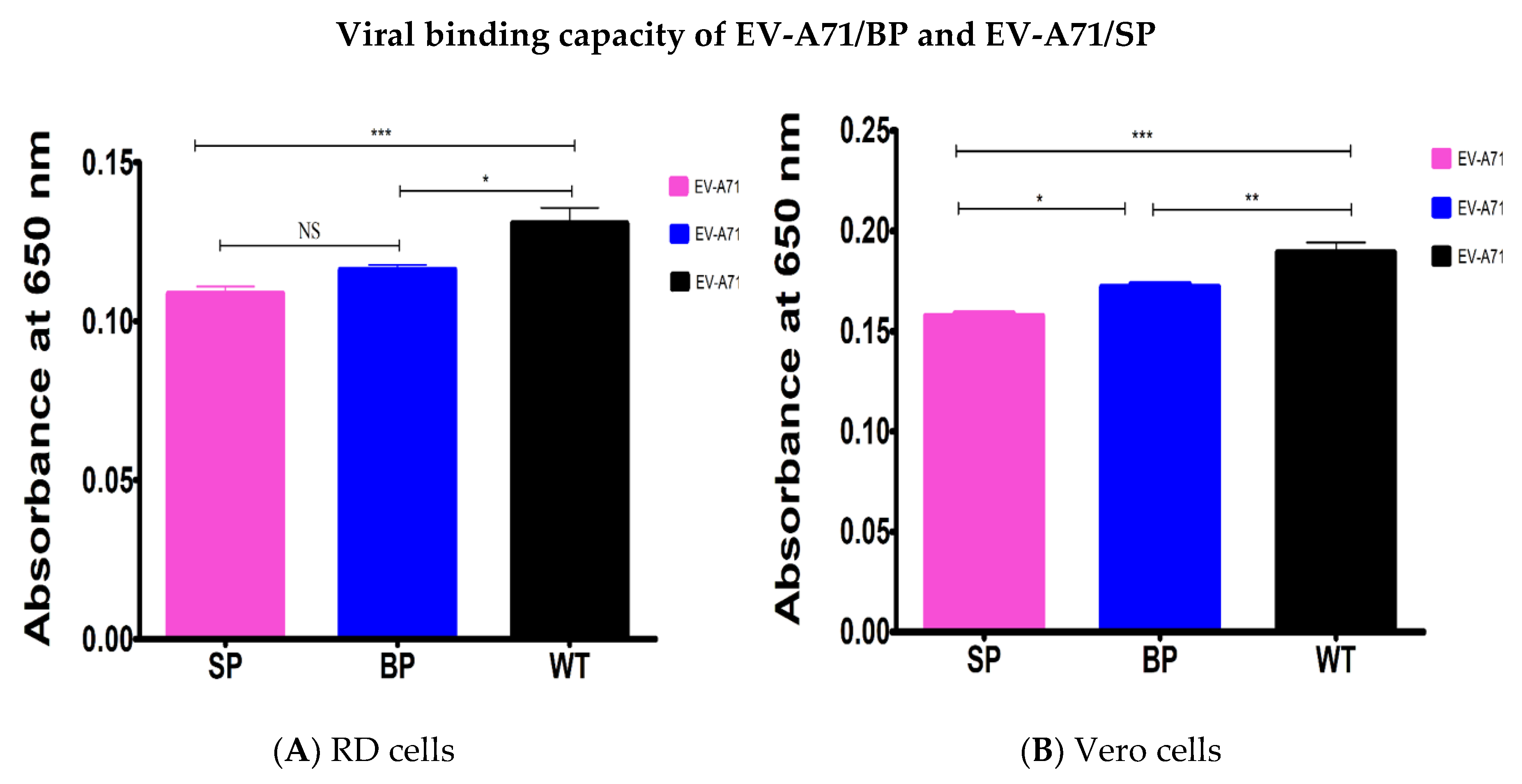
3.7. Viral Binding Ability
4. Discussion
Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmidt, N.J.; Lennette, E.H.; Ho, H.H. An apparently new enterovirus isolated from patients with disease of the central nervous system. J. Infect. Dis. 1974, 129, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Alexander, J.P., Jr.; Kennett, M.L.; Pallansch, M.A. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of enterovirus 71 strains isolated from 1970 to 1998. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9969–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumakov, M.; Voroshilova, M.; Shindarov, L.; Lavrova, I.; Gracheva, L.; Koroleva, G.; Vasilenko, S.; Brodvarova, I.; Nikolova, M.; Gyurova, S.; et al. Enterovirus 71 isolated from cases of epidemic poliomyelitis-like disease in Bulgaria. Arch. Virol. 1979, 60, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, G.; Takatsy, S.; Kukan, E.; Mihaly, I.; Domok, I. Virological diagnosis of enterovirus type 71 infections: Experiences gained during an epidemic of acute CNS diseases in Hungary in 1978. Arch. Virol. 1982, 71, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Sanden, S.M.G.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Verduyn-Lunel, F.; van der Avoort, H.; Galama, J.M.D. Epidemiology of enterovirus 71 in the Netherlands, 1963–2007: Change of dominant subgenogroup in time. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 44, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Liao, Q.; Viboud, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Wu, J.T.; Chang, Z.; Liu, F.; Fang, V.J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in China, 2008–2012: An epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis 2014, 14, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.G.; Parashar, U.D.; Lye, M.S.; Ong, F.G.L.; Zaki, S.R.; Alexander, J.P.; Ho, K.K.; Han, L.L.; Pallansch, M.A.; Abu Bakar, S. Deaths of children during an outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Sarawak, Malaysia: Clinical and pathological characteristics of the disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Tuan, Y.C.; Tsai, H.P.; Yan, J.J.; Liu, C.C.; Su, I.J. Change of major genotype of enterovirus 71 in outbreaks of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Taiwan between 1998 and 2000. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardosa, M.J.; Krishnan, S.; Tio, P.H.; Perera, D.; Wong, S.C. Isolation of subgenus B adenovirus during a fatal outbreak of enterovirus 71-associated hand, foot, and mouth disease in Sibu, Sarawak. Lancet 1999, 354, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.A.; Pallansch, M.A. Complete nucleotide sequence of Enterovirus 71 is distinct from poliovirus. Virus Res. 1995, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessaud, M.; Razafindratsimandresy, R.; Nougairede, A.; Joffret, M.L.; Deshpande, J.M.; Dubot-Peres, A.; Heraud, J.M.; de Lamballerie, X.; Delpeyroux, F.; Bailly, J.L. Molecular comparison and evolutionary analyses of VP1 nucleotide sequences of new African human enterovirus 71 isolates reveal a wide genetic diversity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of Enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volle, R.; Razafindratsimandresy, R.; Joffret, M.L.; Bessaud, M.; Rabemanantsoa, S.; Andriamamonjy, S.; Raharinantoanina, J.; Blondel, B.; Heraud, J.M.; Bailly, J.L.; et al. High permissiveness for genetic exchanges between enteroviruses of species A, including enterovirus 71, favors evolution through intertypic recombination in Madagascar. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01667-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandary, M.B.; Poh, C.L. Changes in the EV-A71 genome through recombination and spontaneous mutations: Impact on virulence. Viruses 2018, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Kiang, D.; Smith, D.J.; Wang, J.R. Evolution of re-emergent virus and its impact on enterovirus 71 epidemics. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuBakar, S.; Chee, H.Y.; Al-Kobaisi, M.F.; Xiaoshan, J.; Chua, K.B.; Lam, S.K. Identification of enterovirus 71 isolates from an outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) with fatal cases of encephalomyelitis in Malaysia. Virus Res. 1999, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podin, Y.; Gias, E.L.M.; Ong, F.; Leong, Y.W.; Yee, S.F.; Yusof, M.A.; Perera, D.; Teo, B.; Wee, T.Y.; Yao, S.C. Sentinel surveillance for human enterovirus 71 in Sarawak, Malaysia: Lessons from the first 7 years. BMC Public Health 2006, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caine, E.A.; Moncla, L.H.; Ronderos, M.D.; Friedrich, T.C.; Osorio, J.E. A single mutation in the VP1 of enterovirus 71 is responsible for increased virulence and neurotropism in adult interferon-deficient mice. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8592–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yue, Y.; Song, N.; Li, B.; Meng, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; An, L.; Qin, L. Genome analysis of enterovirus 71 strains differing in mouse pathogenicity. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Poh, C.L.; Chow, V.T. Complete sequence analyses of enterovirus 71 strains from fatal and non-fatal cases of the hand, foot and mouth disease outbreak in Singapore. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.T.; Wang, S.W.; Yu, C.K.; Lin, K.H.; Lei, H.Y.; Su, I.J.; Wang, J.R. A single nucleotide in stem loop II of 5′-untranslated region contributes to virulence of enterovirus 71 in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R.; Altmeyer, R.; Zou, G. Identification of positively charged residues in enterovirus 71 capsid protein VP1 essential for production of infectious particles. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.; Holland, J.J. RNA virus mutations and fitness for survival. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckels, K.H.; Brandt, W.E.; Harrison, V.R.; McCown, J.M.; Russell, P.K. Isolation of a temperature-sensitive dengue-2 virus under conditions suitable for vaccine development. Infect. Immun. 1976, 14, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.C.M.; Tang, C.K.; Norton, D.C.; Gan, E.S.; Tan, H.C.; Sun, B.; Syenina, A.; Yousuf, A.; Ong, X.M.; Kamaraj, U.S.; et al. Molecular determinants of plaque size as an indicator of dengue virus attenuation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-C.; Lian, W.-C.; Hsu, L.-C.; Liau, M.-Y. Japanese encephalitis virus antigenic variants with characteristic differences in neutralization resistance and mouse virulence. Virus Res. 1997, 51, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Blaney, J.E.; Johnson, D.H.; Firestone, C.-Y.; Hanson, C.T.; Murphy, B.R.; Whitehead, S.S. Chemical mutagenesis of dengue virus type 4 yields mutant viruses which are temperature sensitive in Vero cells or human liver cells and attenuated in mice. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9731–9740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blaney, J.E.; Manipon, G.G.; Murphy, B.R.; Whitehead, S.S. Temperature sensitive mutations in the genes encoding the NS1, NS2A, NS3, and NS5 nonstructural proteins of dengue virus type 4 restrict replication in the brains of mice. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, J.E., Jr.; Johnson, D.H.; Manipon, G.G.; Firestone, C.-Y.; Hanson, C.T.; Murphy, B.R.; Whitehead, S.S. Genetic basis of attenuation of dengue virus type 4 small plaque mutants with restricted replication in suckling mice and in SCID mice transplanted with human liver cells. Virology 2002, 300, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, T.J.; Nickells, M. Neuroadapted yellow fever virus 17D: Genetic and biological characterization of a highly mouse-neurovirulent virus and its infectious molecular clone. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 10912–10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickells, M.; Chambers, T.J. Neuroadapted yellow fever virus 17D: Determinants in the envelope protein govern neuroinvasiveness for SCID mice. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12232–12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Burgon, T.B.; Jenkins, J.A.; Deitz, S.B.; Spagnolo, J.F.; Kirkegaard, K. Bypass suppression of small-plaque phenotypes by a mutation in poliovirus 2A that enhances apoptosis. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10129–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Moudy, R.M.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Ngo, K.A.; Maffei, J.G.; Jerzak, G.V.; Franke, M.A.; Kauffman, E.B.; Kramer, L.D. Characterization of a small plaque variant of West Nile virus isolated in New York in 2000. Virology 2007, 367, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, F.; Tajima, S.; Nakayama, E.; Kawai, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Shibasaki, K.; Taira, M.; Maeki, T.; Lim, C.K.; Takasaki, T. Characterization of large and small-plaque variants in the Zika virus clinical isolate ZIKV/Hu/S36/Chiba/2016. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimipak, T.; Yoksan, S.; Ubol, S.; Pulmanausahakul, R. Small plaque size variant of Chikungunya primary isolate showed reduced virulence in mice. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 36, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.W.; Chan, Y.F.; Sim, K.M.; Tan, E.L.; Poh, C.L. Inhibition of Enterovirus 71 (EV-71) infections by a novel antiviral peptide derived from EV-71 capsid protein VP1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; James, P.; Baden, L.; Pallansch, M.A.; Anderson, L.J. Enterovirus 71 infections and neurologic disease—United States, 1977–1991. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 169, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.Y.; Chang, T.Y.; Chen, S.T.; Li, C.; Liu, H.S. Comparative study of enterovirus 71 infection of human cell lines. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 70, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, L.A.; Boylan, B.T.; Moreira, F.R.; Myers, L.J.; Svenson, E.L.; Fedorova, N.B.; Pickett, B.E.; Bernard, K.A. Growth and adaptation of Zika virus in mammalian and mosquito cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade-Weskott, M.L.; van Schalkwyk, A.; Koekemoer, J.J.O. A correlation between capsid protein VP2 and the plaque morphology of African horse sickness virus in cell culture. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.D.; Barr, K.L.; Heil, G.L.; Friary, J.A.; Gray, G.C. A comparison of viral fitness and virulence between emergent adenovirus 14p1 and prototype adenovirus 14p strains. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 54, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kanno, T.; Mackay, D.; Inoue, T.; Wilsden, G.; Yamakawa, M.; Yamazoe, R.; Yamaguchi, S.; Shirai, J.; Kitching, P.; Murakami, Y. Mapping the genetic determinants of pathogenicity and plaque phenotype in swine vesicular disease virus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2710–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Huang, Y.H.; Tsai, H.P.; Kuo, P.H.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, J.R. A selective bottleneck shapes the evolutionary mutant spectra of enterovirus A71 during viral dissemination in humans. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01062-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigen, M.; Schuster, P. The hypercycle. Naturwissenschaften 1978, 65, 7–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignuzzi, M.; Stone, J.K.; Arnold, J.J.; Cameron, C.E.; Andino, R. Quasispecies diversity determines pathogenesis through cooperative interactions in a viral population. Nature 2006, 439, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, J.; Spindler, K.; Horodyski, F.; Grabau, E.; Nichol, S.; VandePol, S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science 1982, 215, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, P.; Jin, J.; Su, W.; An, D.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Gao, F.; et al. Establishment of cell lines with increased susceptibility to EV71/CA16 by stable overexpression of SCARB2. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Yue, Y.Y.; Li, P.; Song, N.N.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, H.; Jiang, G.S.; Qin, L. MA104 Cell line presents characteristics suitable for enterovirus A71 isolation and proliferation. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 59, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamayoshi, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Li, J.; Hanagata, N.; Minowa, T.; Takemura, T.; Koike, S. Scavenger receptor B2 is a cellular receptor for enterovirus 71. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Lin, H.Y.; Tsou, Y.L.; Chitra, E.; Hsiao, K.N.; Shao, H.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Sia, C.; Chong, P.; Chow, Y.H. Human SCARB2-mediated entry and endocytosis of EV71. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, Y.; Kotecha, A.; Fry, E.E.; Kelly, J.T.; Wang, X.; Rao, Z.; Rowlands, D.J.; Ren, J.; Stuart, D.I. Unexpected mode of engagement between enterovirus 71 and its receptor SCARB2. Nat. Microb. 2019, 4, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Chou, C.T.; Lei, H.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, S.M.; Yan, J.J.; Su, I.J.; Wang, J.R.; Yeh, T.M.; Chen, S.H.; et al. A mouse-adapted enterovirus 71 strain causes neurological disease in mice after oral infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7916–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Yu, C.K.; Su, I.J.; Wang, J.R. Mutations in VP2 and VP1 capsid proteins increase infectivity and mouse lethality of enterovirus 71 by virus binding and RNA accumulation enhancement. Virology 2012, 422, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.M.; Minor, P.D.; Schild, G.S.; Almond, J.W. Critical role of an eight-amino acid sequence of VP1 in neutralization of poliovirus type 3. Nature 1983, 304, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkegaard, K. Mutations in VP1 of poliovirus specifically affect both encapsidation and release of viral RNA. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Sam, I.C.; Lee, V.S.; Wong, H.V.; Chan, Y.F. VP1 residues around the five-fold axis of enterovirus A71 mediate heparan sulfate interaction. Virology 2017, 501, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Wang, E.C.; Jenkins, O.; Borysiewicz, L.K. Analysis of the human T-cell response to picornaviruses: Identification of T-cell epitopes close to B-cell epitopes in poliovirus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, B.Y.; Zell, R.; Kandolf, R. Mapping of a neutralizing antigenic site of coxsackievirus B4 by construction of an antigen chimera. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 3475–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monica, N.; Kupsky, W.J.; Racaniello, V.R. Reduced mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing antigenic variants selected with monoclonal antibodies. Virology 1987, 161, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Wychowski, C.; Couderc, T.; Crainic, R.; Hogle, J.; Girard, M. Engineering a poliovirus type 2 antigenic site on a type 1 capsid results in a chimaeric virus which is neurovirulent for mice. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 2839–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordey, S.; Petty, T.J.; Schibler, M.; Martinez, Y.; Gerlach, D.; van Belle, S.; Turin, L.; Zdobnov, E.; Kaiser, L.; Tapparel, C. Identification of site-specific adaptations conferring increased neural cell tropism during human enterovirus 71 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, K.; Ding, J.; Han, J.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.Y.; He, Y.L.; Qin, C.F.; Chen, R. Human enterovirus 71 uncoating captured at atomic resolution. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3114–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, N.H.; Kolatkar, P.R.; Oliveira, M.A.; Cheng, R.H.; Greve, J.M.; McClelland, A.; Baker, T.S.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of a human rhinovirus complexed with its receptor molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Mueller, S.; Morais, M.C.; Bator, C.M.; Bowman, V.D.; Hafenstein, S.; Wimmer, E.; Rossmann, M.G. Crystal structure of CD155 and electron microscopic studies of its complexes with polioviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18284–18289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricks, C.E.; Hogle, J.M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: Externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1934–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Lee, H.; Hafenstein, S.; Kataoka, C.; Wakita, T.; Bergelson, J.M.; Shimizu, H. Enterovirus 71 binding to PSGL-1 on leukocytes: VP1-145 acts as a molecular switch to control receptor interaction. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Q.; Yang, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Shen, X.; Fry, E.E.R.; et al. Structures of coxsackievirus A16 capsids with native antigenicity: Implications for particle expansion, receptor binding, and immunogenicity. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10500–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, C.; Bao, W.; Zhao, K.; Niu, J.; Yu, X.F.; Zhang, W. Characterization of full-length enterovirus 71 strains from severe and mild disease patients in northeastern China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, I.G.; McCauley, J.; Cox, N.; Daniels, R.; Engelhardt, O.G.; Fukuda, K.; Grohmann, G.; Hay, A.; Kelso, A.; Klimov, A.; et al. Epidemiological, antigenic and genetic characteristics of seasonal influenza A(H1N1), A(H3N2) and B influenza viruses: Basis for the WHO recommendation on the composition of influenza vaccines for use in the 2009-2010 northern hemisphere season. Vaccine 2010, 28, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W.; Tai, C.H.; Fonville, J.M.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Su, I.J.; Smith, D.J.; Wang, J.R. Mapping enterovirus A71 antigenic determinants from viral evolution. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11500–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.; Yabrov, R.; Bittle, J.; Hogle, J.; Baltimore, D. Synthetic peptides from four separate regions of the poliovirus type 1 capsid protein VP1 induce neutralizing antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zou, G.; Liu, Q.; Kong, L.; et al. Coxsackievirus A10 atomic structure facilitating the discovery of a broad-spectrum inhibitor against human enteroviruses. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zou, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Molecular analysis of virulent determinants of enterovirus 71. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, K.; He, Y.L.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, R. Crystal structures of yeast-produced enterovirus 71 and enterovirus 71/coxsackievirus A16 chimeric virus-like particles provide the structural basis for novel vaccine design against hand-foot-and-mouth disease. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6196–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, W.; Ren, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, J.; Lou, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, W.; Shen, X.; Porta, C.; et al. A sensor-adaptor mechanism for enterovirus uncoating from structures of EV71. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuthill, T.J.; Groppelli, E.; Hogle, J.M.; Rowlands, D.J. Picornaviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 343, 43–89. [Google Scholar]
- Colonno, R.J.; Condra, J.H.; Mizutani, S.; Callahan, P.L.; Davies, M.E.; Murcko, M.A. Evidence for the direct involvement of the rhinovirus canyon in receptor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5449–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, M.G.; Arnold, E.; Erickson, J.W.; Frankenberger, E.A.; Griffith, J.P.; Hecht, H.J.; Johnson, J.E.; Kamer, G.; Luo, M.; Mosser, A.G.; et al. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature 1985, 317, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Wang, J.R.; Liu, C.C.; Yang, H.B.; Su, I.J. An outbreak of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan 1998: A comprehensive pathological, virological, and molecular study on a case of fulminant encephalitis. J. Clin. Virol. 2000, 17, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.; Sheldon, J.; Perales, C. Viral quasispecies evolution. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2012, 76, 159–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Han, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Hao, P.; Sheng, J.; Li, X.H.; Yu, D.M.; Gong, Q.M.; Tian, F.; et al. Comparison of next-generation sequencing and clone-based sequencing in analysis of hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase quasispecies heterogeneity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4087–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
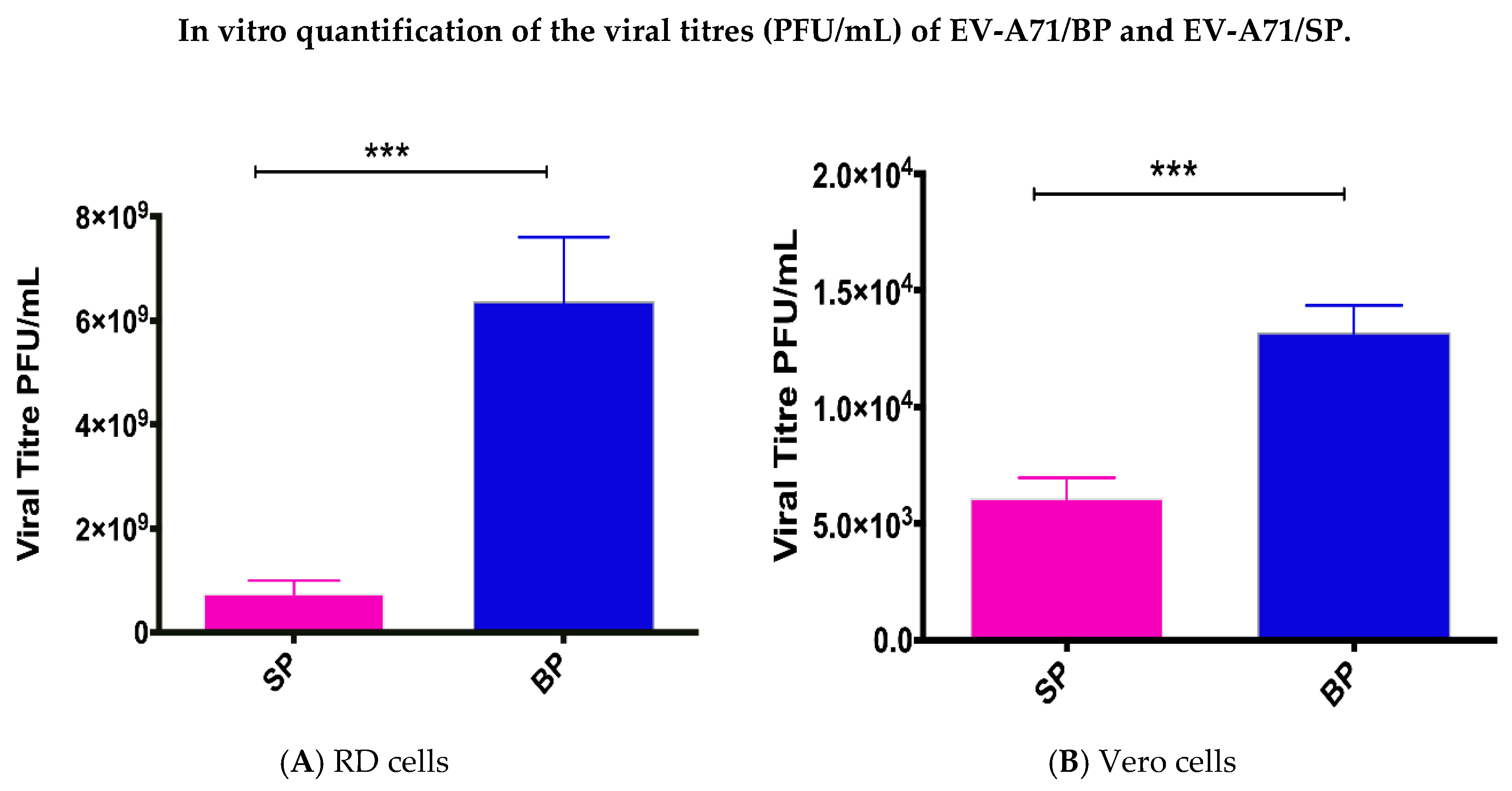


| Plaque Variants of EV-A71 * | Viral Titre in RD Cells (PFU/mL) | Viral Titre in Vero Cells (PFU/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| SP1 | 3.7 × 108 | 6.40 × 103 |
| SP2 | 8.7 × 108 | 6.70 × 103 |
| SP3 | 9.9 × 108 | 6.40 × 103 |
| SP4 | 7.0 × 108 | 4.70 × 103 |
| BP1 | 5.4 × 109 | 1.39 × 104 |
| BP2 | 5.5 × 109 | 1.18 × 104 |
| BP3 | 6.4 × 109 | 1.44 × 104 |
| BP4 | 8.1 × 109 | 1.25 × 104 |
| EV-A71 Variants | RMSD/Å | Hydrogen Bonds Interactions | Secondary Structure Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| EV-A71/WT | 0.00 | 108 | 9.4% helix, 23.9% sheet, 17.5% turn, 47.8% coil, 1.3% 310 helix. |
| EV-A71/BP | 1.76 | 104 | 6.7% helix, 23.2% sheet, 20.9% turn, 47.5% coil, 1.7% 310 helix. |
| EV-A71/SP | 1.35 | 107 | 7.4% helix, 23.2% sheet, 19.9% turn, 48.1% coil, 1.3% 310 helix. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandary, M.B.; Masomian, M.; Ong, S.-K.; Poh, C.L. Characterization of Plaque Variants and the Involvement of Quasi-Species in a Population of EV-A71. Viruses 2020, 12, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060651
Mandary MB, Masomian M, Ong S-K, Poh CL. Characterization of Plaque Variants and the Involvement of Quasi-Species in a Population of EV-A71. Viruses. 2020; 12(6):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060651
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandary, Madiiha Bibi, Malihe Masomian, Seng-Kai Ong, and Chit Laa Poh. 2020. "Characterization of Plaque Variants and the Involvement of Quasi-Species in a Population of EV-A71" Viruses 12, no. 6: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060651
APA StyleMandary, M. B., Masomian, M., Ong, S.-K., & Poh, C. L. (2020). Characterization of Plaque Variants and the Involvement of Quasi-Species in a Population of EV-A71. Viruses, 12(6), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060651





