Isolation and Characterisation of Alongshan Virus in Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Processing of Ticks
2.2. Infection of Tick Cell Line
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.4. Reverse-Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) and Sequencing of Amplified Products
2.5. High-Throughput Sequencing
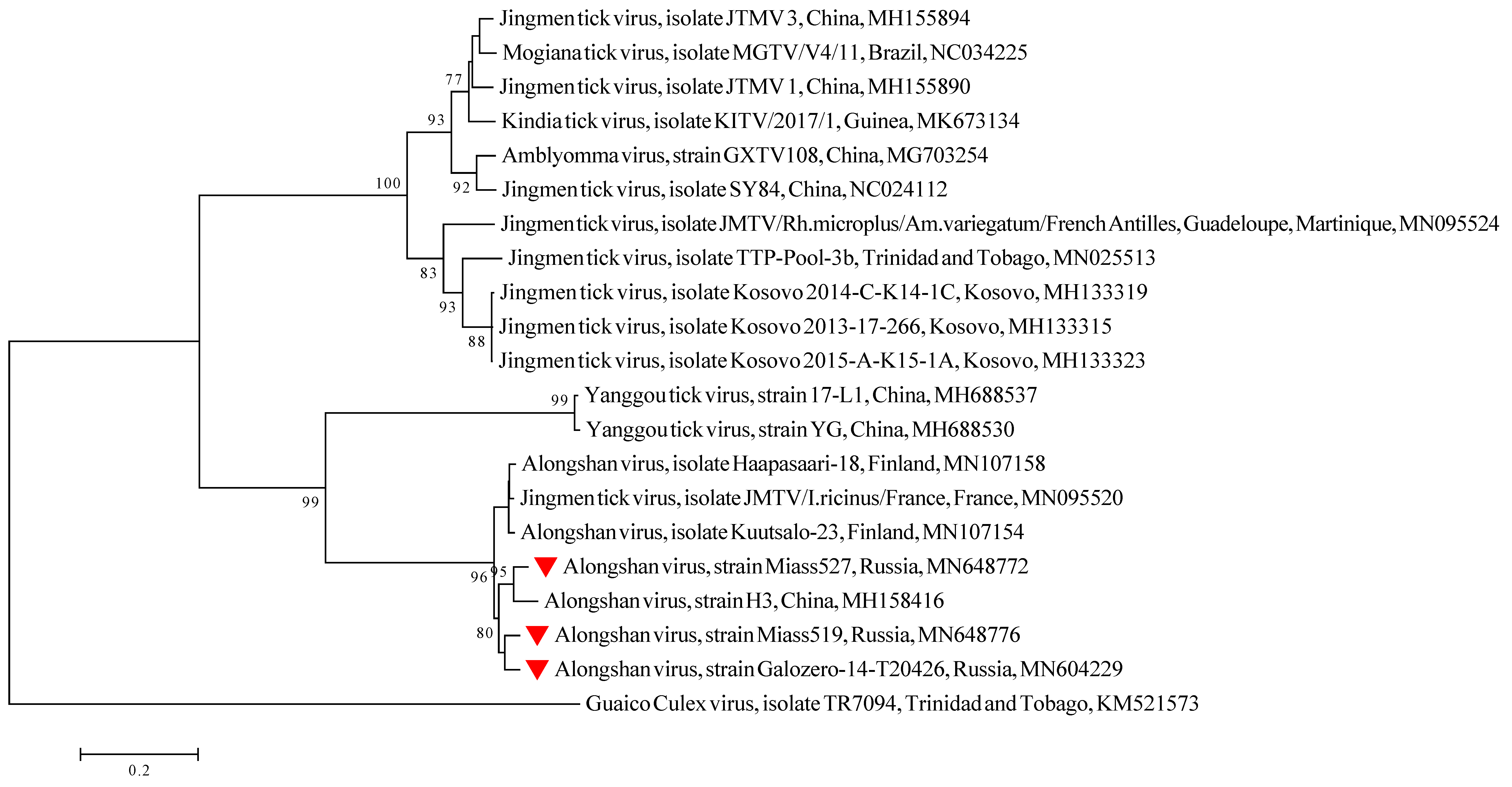
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Bioinformatics Tools Used for Discovery of Overlapping Elements
2.8. Genome Annotation and Visualisation
3. Results
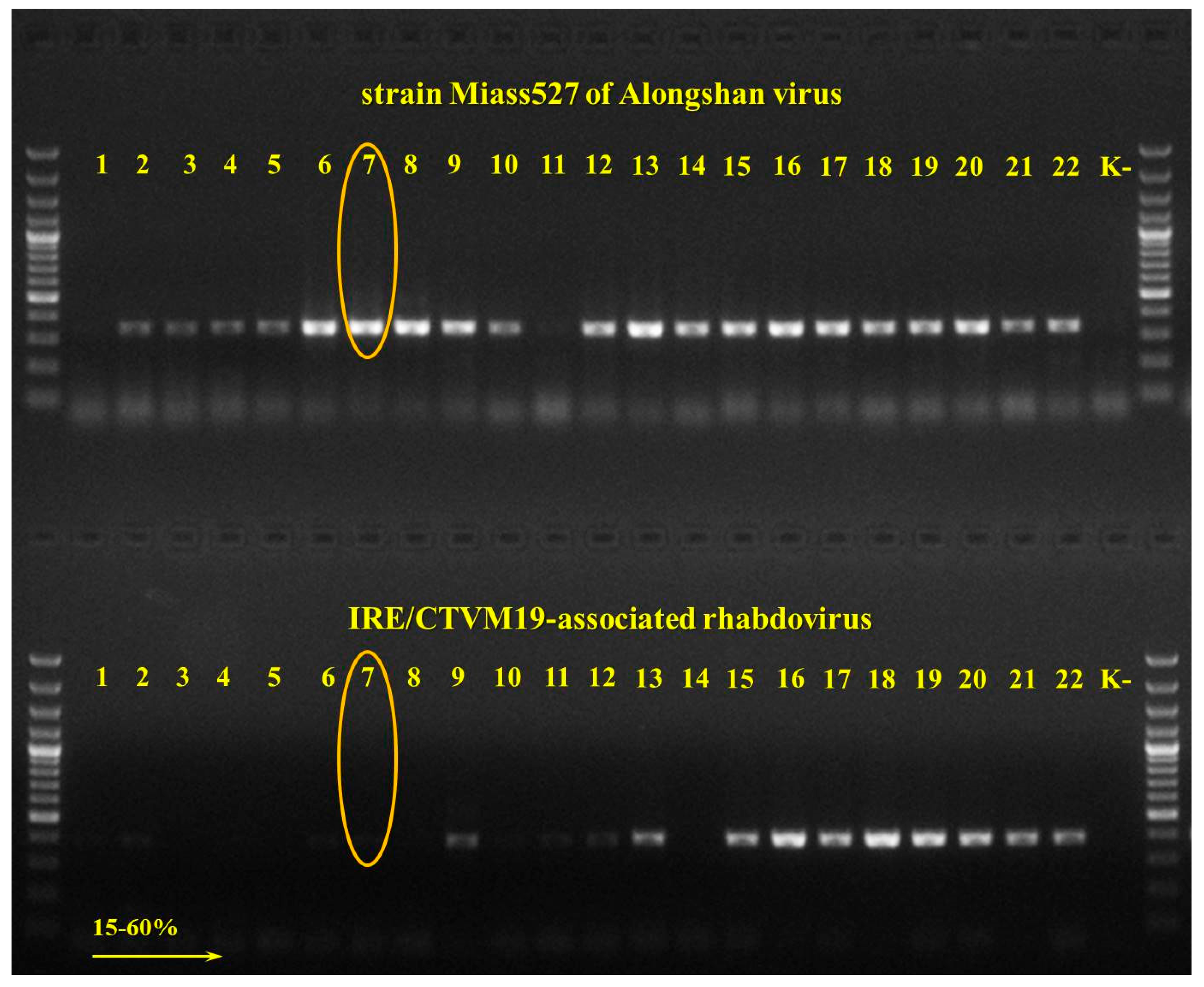
3.1. Detection and Isolation of Alongshan Virus Strains
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
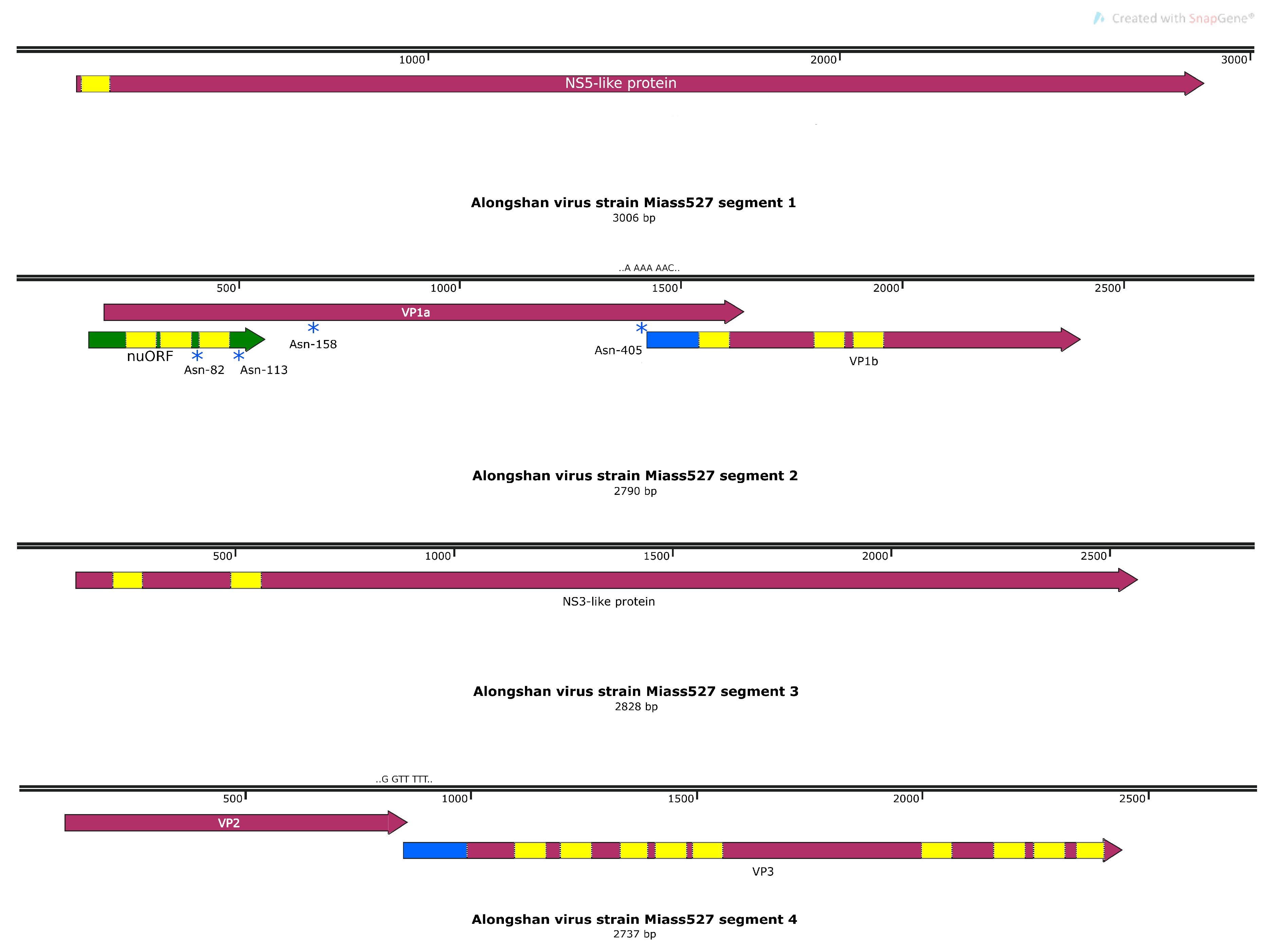
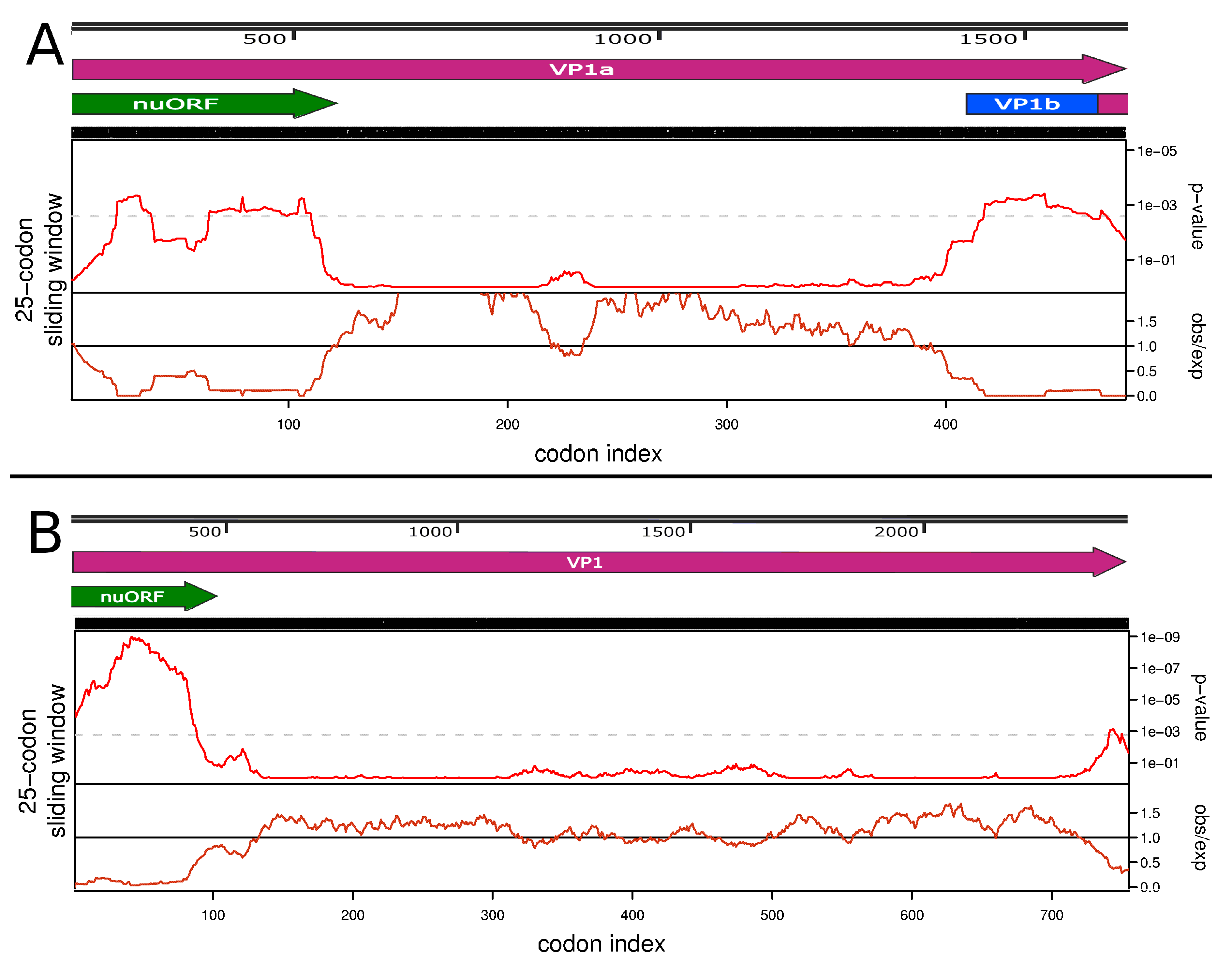
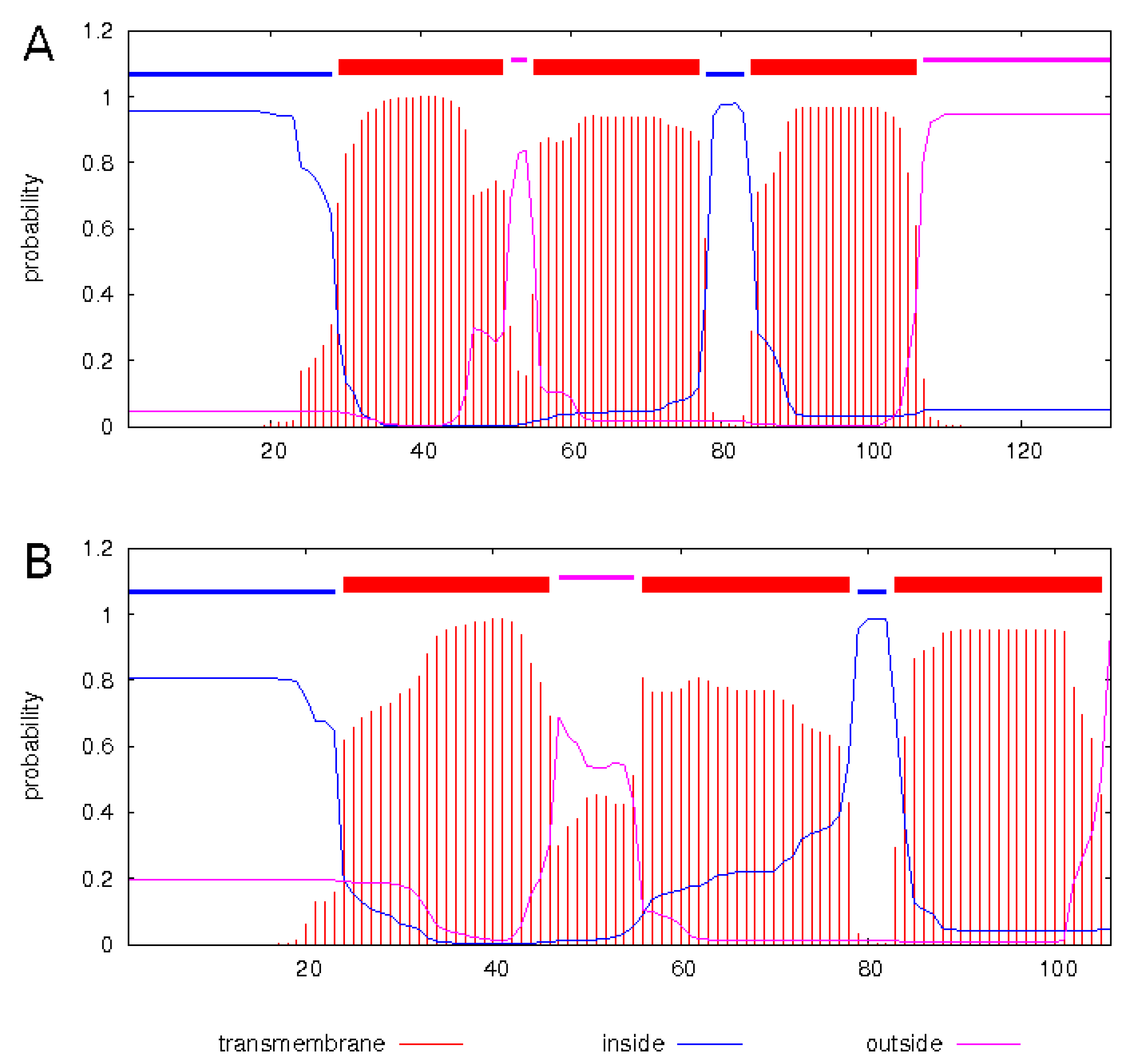
3.3. Full Genome, Genome Structure and Proposed Novel Elements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Vasilakis, N.; Tian, J.-H.; Li, C.-X.; Chen, L.-J.; Eastwood, G.; Diao, X.-N.; Chen, M.-H.; Chen, X.; et al. Divergent Viruses Discovered in Arthropods and Vertebrates Revise the Evolutionary History of the Flaviviridae and Related Viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, J.T.; Wiley, M.R.; Beitzel, B.; Auguste, A.J.; Dupuis, A.P.; Lindquist, M.E.; Sibley, S.D.; Kota, K.P.; Fetterer, D.; Eastwood, G.; et al. A Multicomponent Animal Virus Isolated from Mosquitoes. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.R.; Castro-Jorge, L.A.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Gardinassi, L.G.; Garcia, G.R.; Brandão, L.G.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Okada, M.I.; Abrão, E.P.; Ferreira, B.R.; et al. Characterisation of divergent flavivirus NS3 and NS5 protein sequences detected in Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2014, 109, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.-C.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.-H.; Lin, X.-D.; Gao, D.-Y.; He, J.-R.; Wang, J.-B.; Li, C.-X.; Kang, Y.-J.; Yu, B.; et al. A tick-borne segmented RNA virus contains genome segments derived from unsegmented viral ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-D.; Wang, B.; Wei, F.; Han, S.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.-T.; Yan, Y.; Lv, X.-L.; Li, L.; Wang, S.-C.; et al. A New Segmented Virus Associated with Human Febrile Illness in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Orton, R.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B. Virus taxonomy: The database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D708–D717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.Y.; Yeap, S.K.; Omar, A.R.; Tan, W.S. Advances in the study of nodavirus. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmam, S.; Bigot, T.; Chrétien, D.; Gondard, M.; Pérot, P.; Pommelet, V.; Dufou, E.; Petres, S.; Devillers, E.; Hoem, T.; et al. Insights into the Host Range, Genetic Diversity, and Geographical Distribution of Jingmenviruses. mSphere 2019, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Liu, H.B.; Ni, X.B.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zheng, Y.C.; Song, J.L.; Li, J.; Jiang, B.G.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Emergence of human infection with Jingmen tick virus in China: A retrospective study. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçer, E.; Hacıoğlu, S.; Kar, S.; Emanet, N.; Brinkmann, A.; Nitsche, A.; Özkul, A.; Linton, Y.-M.; Ergünay, K. Survey and Characterization of Jingmen Tick Virus Variants. Viruses 2019, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, P.; Jakupi, X.; von Possel, R.; Berisha, L.; Halili, B.; Günther, S.; Cadar, D.; Ahmeti, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J. Viral metagenomics, genetic and evolutionary characteristics of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever orthonairovirus in humans, Kosovo. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuivanen, S.; Levanov, L.; Kareinen, L.; Sironen, T.; Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Plyusnin, I.; Zakham, F. Detection of novel tick-borne pathogen, Alongshan virus, in Ixodes ricinus ticks, south-eastern Finland. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, E.C.; Maruyama, S.R.; de Miranda-Santos, I.K.F.; Palacios, G.; Ladner, J.T. Complete Coding Genome Sequence for Mogiana Tick Virus, a Jingmenvirus Isolated from Ticks in Brazil. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Pascoal, J.; de Siqueira, S.M.; da Costa Maia, R.; Szabó, M.P.J.; Yokosawa, J. Detection and molecular characterization of Mogiana tick virus (MGTV) in Rhipicephalus microplus collected from cattle in a savannah area, Uberlândia, Brazil. Ticks Tick. Borne. Dis. 2019, 10, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, C.L.; Waldron, F.M.; Robertson, S.; Crowson, D.; Ferrari, G.; Quintana, J.F.; Brouqui, J.M.; Bayne, E.H.; Longdon, B.; Buck, A.H.; et al. The discovery, distribution, and evolution of viruses associated with Drosophila melanogaster. Plos Biol. 2015, 13, e1002210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callister, D.M.; Winter, A.D.; Page, A.P.; Maizels, R.M. Four abundant novel transcript genes from Toxocara canis with unrelated coding sequences share untranslated region tracts implicated in the control of gene expression. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2008, 162, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, K.K.A.; Loukas, A.; Tripp, C.; Maizels, R.M. Identification of abundantly expressed novel and conserved genes from the infective larval stage of Toxocara canis by an expressed sequence tag strategy. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4771–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-D.; Wang, W.; Wang, N.N.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, X.; Tana, G.; Liu, Q. Prevalence of the emerging novel Alongshan virus infection in sheep and cattle in Inner Mongolia, northeastern China. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, N.A. Ixodid Ticks of the Subfamily Ixodinae. Fauna of the USSR: Arachnoides; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1977; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Filippova, N.A. Fauna of Russia and neighbouring countries. Ixodid ticks of Subfamily Amblyomminae. Arachnoidea; Nauka: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1997; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Scaramozzino, N.; Crance, J.-M.; Jouan, A.; DeBriel, D.A.; Stoll, F.; Garin, D. Comparison of Flavivirus universal primer pairs and development of a rapid, highly sensitive heminested reverse transcription-PCR assay for detection of flaviviruses targeted to a conserved region of the NS5 gene sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1922–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zweygarth, E.; Blouin, E.F.; Gould, E.A.; Jongejan, F. Tick cell lines: Tools for tick and tick-borne disease research. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisheit, S.; Villar, M.; Tykalová, H.; Popara, M.; Loecherbach, J.; Watson, M.; Růžek, D.; Grubhoffer, L.; De La Fuente, J.; Fazakerley, J.K.; et al. Ixodes scapularis and Ixodes ricinus tick cell lines respond to infection with tick-borne encephalitis virus: Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitin, N.; Trifonova, E.; Evtushenko, E.; Kirpichnikov, M.; Atabekov, J.; Karpova, O. Comparative study of non-enveloped icosahedral viruses size. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.C.; Chain, P.S.G. Rapid evaluation and quality control of next generation sequencing data with FaQCs. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, A.E. Mapping overlapping functional elements embedded within the protein-coding regions of RNA viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12425–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Jung, E.; Brunak, S. Prediction of N-glycosylation sites in human proteins. 2004. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNGlyc/ (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, È.; Von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Predicting Transmembrane Protein Topology with a Hidden Markov Model: Application to Complete Genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.; Giegerich, R. The RNA shapes studio. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell-Sakyi, L.; Attoui, H. Virus discovery using tick cell lines. Evol. Bioinforma. 2016, 12, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Huhtamo, E.; Putkuri, N.; Kurkela, S.; Manni, T.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O.; Uzcategui, N.Y. Characterization of a Novel Flavivirus from Mosquitoes in Northern Europe That Is Related to Mosquito-Borne Flaviviruses of the Tropics. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9532–9540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtamo, E.; Cook, S.; Moureau, G.; Uzcátegui, N.Y.; Sironen, T.; Kuivanen, S.; Putkuri, N.; Kurkela, S.; Harbach, R.E.; Firth, A.E.; et al. Novel flaviviruses from mosquitoes: Mosquito-specific evolutionary lineages within the phylogenetic group of mosquito-borne flaviviruses. Virology 2014, 464–465, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, O.A.; Litov, A.G.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Romanova, L.I.; Karganova, G.G. Properties of the tick-borne encephalitis virus population during persistent infection of ixodid ticks and tick cell lines. Ticks Tick. Borne. Dis. 2017, 8, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korboukh, V.K.; Lee, C.A.; Acevedo, A.; Vignuzzi, M.; Xiao, Y.; Arnold, J.J.; Hemperly, S.; Graci, J.D.; August, A.; Andino, R.; et al. RNA Virus Population Diversity: An Optimum for Maximal Fitness and Virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29531–29544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcalá, A.C.; Medina, F.; González-Robles, A.; Salazar-Villatoro, L.; Fragoso-Soriano, R.J.; Vásquez, C.; Cervantes-Salazar, M.; del Angel, R.M.; Ludert, J.E. The dengue virus non-structural protein 1 (NS1) is secreted efficiently from infected mosquito cells. Virology 2016, 488, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, D.A.; Landsberg, M.J.; Bletchly, C.; Rothnagel, R.; Waddington, L.; Hankamer, B.; Young, P.R. Structure of the dengue virus glycoprotein non-structural protein 1 by electron microscopy and single-particle analysis. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.; Bromley, E.; Joshi, P.U.; Long, F.; Heldt, C.L. Virus isoelectric point determination using single-particle chemical force microscopy. Langmuir 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Rice, C.M. Molecular biology of flaviviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2003, 59, 23–61. [Google Scholar]
- Shiryaev, S.A.; Chernov, A.V.; Aleshin, A.E.; Shiryaeva, T.N.; Strongin, A.Y. NS4A regulates the ATPase activity of the NS3 helicase: A novel cofactor role of the non-structural protein NS4A from West Nile virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Jordan, J.L.; Sánchez-Burgos, G.G.; Laurent-Rolle, M.; García-Sastre, A. Inhibition of interferon signaling by dengue virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14333–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, C.; Ye, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Zhang, P.; Shi, P.-Y.; Yuan, Z.-M.; Zhang, B. Transmembrane Domains of NS2B Contribute to both Viral RNA Replication and Particle Formation in Japanese Encephalitis Virus. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5735–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMaio, D. Viral Miniproteins. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Coronavirus envelope protein: Current knowledge. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
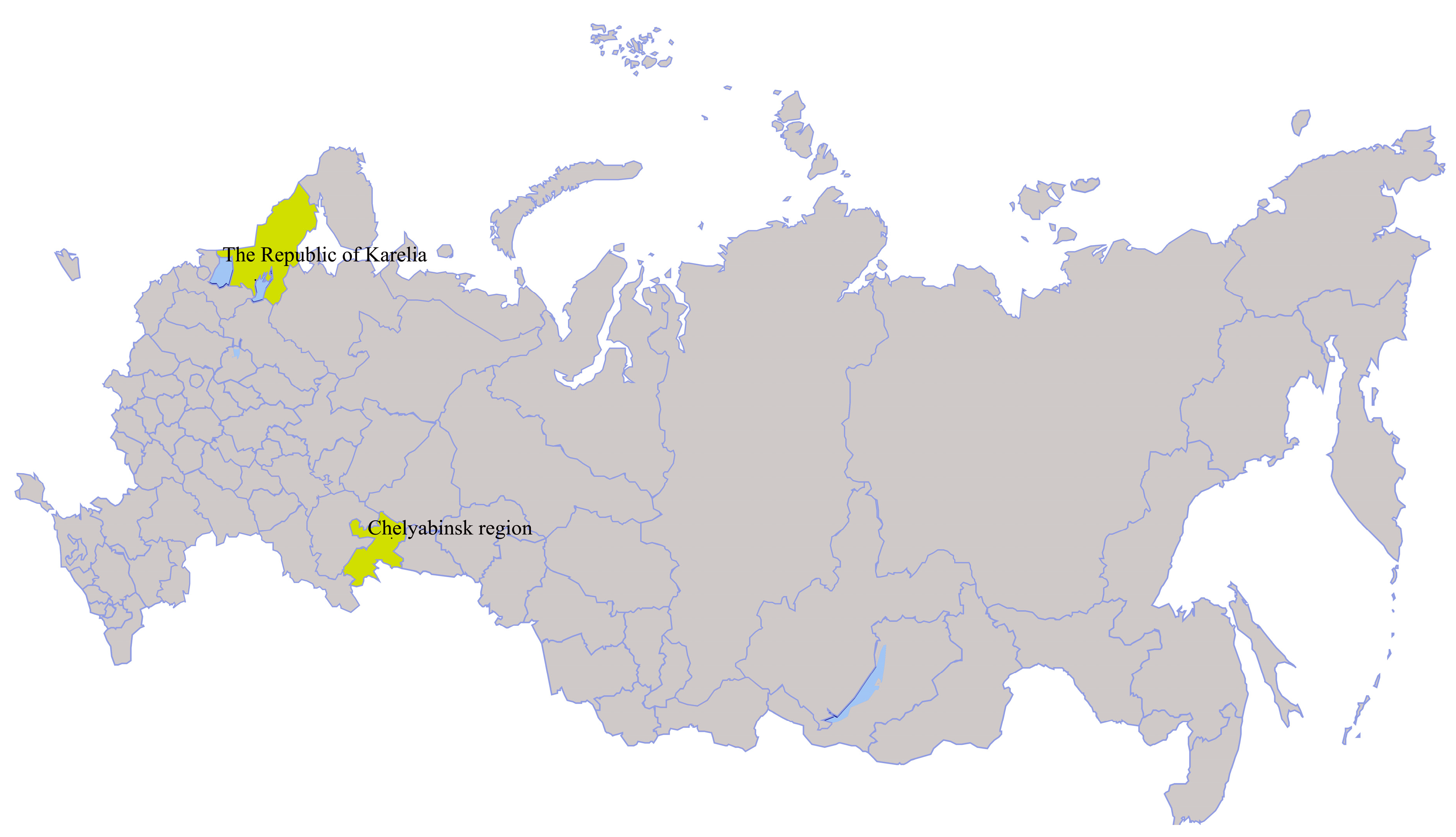

| Strain | Tick Species | Year, Region (GPS) | GenBank Access. No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Miass519 | I. persulcatus | 2014, Chelyabinsk region, Ilmen State Reserve (55°01.287’N 060°10.097´E) | MN648774–MN648777 |
| Miass527 | I. persulcatus | MN648770–MN648773 | |
| Galozero-14-T20426 | I. persulcatus | 2014, The Republic of Karelia (62°4.515´N 33°57.077´E) | MN604229 |
| Strain Miass527 | Strain H3 | Strain Kuutsalo-23 | Strain Haapasaari-18 | Isolate JMTV/I.ricinus/France | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment 1. NS5-like protein | |||||
| Strain Miass519 | 90.6% | 89.0% | 89.2% | 88.9% | 89.1% |
| Strain Miass527 | 89.6% | 89.2% | 88.6% | 89.7% | |
| Strain H3 | 89.6% | 89.2% | 90.1% | ||
| Strain Kuutsalo-23 | 95.6% | 96.0% | |||
| Strain Haapasaari-18 | 95.9% | ||||
| Segment 2. VP1a and VP1b | |||||
| Strain Miass519 | 92.6% | 92.0% | 93.7% | 93.6% | 94.0% |
| Strain Miass527 | 94.7% | 92.4% | 92.2% | 93.0% | |
| Strain H3 | 91.7% | 91.6% | 92.1% | ||
| Strain Kuutsalo-23 | 98.3% | 98.5% | |||
| Strain Haapasaari-18 | 98.6% | ||||
| Segment 3. NS3-like protein | |||||
| Strain Miass519 | 96.7% | 91.2% | 91.3% | 90.9% | 91.2% |
| Strain Miass527 | 90.7% | 91.1% | 90.5% | 91.0% | |
| Strain H3 | 90.9% | 91.3% | 91.5% | ||
| Strain Kuutsalo-23 | 95.0% | 97.4% | |||
| Strain Haapasaari-18 | 94.5% | ||||
| Segment 4. VP2 and VP3 | |||||
| Strain Miass519 | 98.6% | 90.5% | 90.8% | 90.7% | 91.2% |
| Strain Miass527 | 90.6% | 90.7% | 90.8% | 91.3% | |
| Strain H3 | 90.6% | 90.3% | 91.1% | ||
| Strain Kuutsalo-23 | 94.7% | 98.0% | |||
| Strain Haapasaari-18 | 95.3% | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kholodilov, I.S.; Litov, A.G.; Klimentov, A.S.; Belova, O.A.; Polienko, A.E.; Nikitin, N.A.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Ivannikova, A.Y.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Yakovlev, A.S.; et al. Isolation and Characterisation of Alongshan Virus in Russia. Viruses 2020, 12, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040362
Kholodilov IS, Litov AG, Klimentov AS, Belova OA, Polienko AE, Nikitin NA, Shchetinin AM, Ivannikova AY, Bell-Sakyi L, Yakovlev AS, et al. Isolation and Characterisation of Alongshan Virus in Russia. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040362
Chicago/Turabian StyleKholodilov, Ivan S., Alexander G. Litov, Alexander S. Klimentov, Oxana A. Belova, Alexandra E. Polienko, Nikolai A. Nikitin, Alexey M. Shchetinin, Anna Y. Ivannikova, Lesley Bell-Sakyi, Alexander S. Yakovlev, and et al. 2020. "Isolation and Characterisation of Alongshan Virus in Russia" Viruses 12, no. 4: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040362
APA StyleKholodilov, I. S., Litov, A. G., Klimentov, A. S., Belova, O. A., Polienko, A. E., Nikitin, N. A., Shchetinin, A. M., Ivannikova, A. Y., Bell-Sakyi, L., Yakovlev, A. S., Bugmyrin, S. V., Bespyatova, L. A., Gmyl, L. V., Luchinina, S. V., Gmyl, A. P., Gushchin, V. A., & Karganova, G. G. (2020). Isolation and Characterisation of Alongshan Virus in Russia. Viruses, 12(4), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040362






