New Viral Sequences Identified in the Flavescence Dorée Phytoplasma Vector Scaphoideus titanus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, RNA Extraction, Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
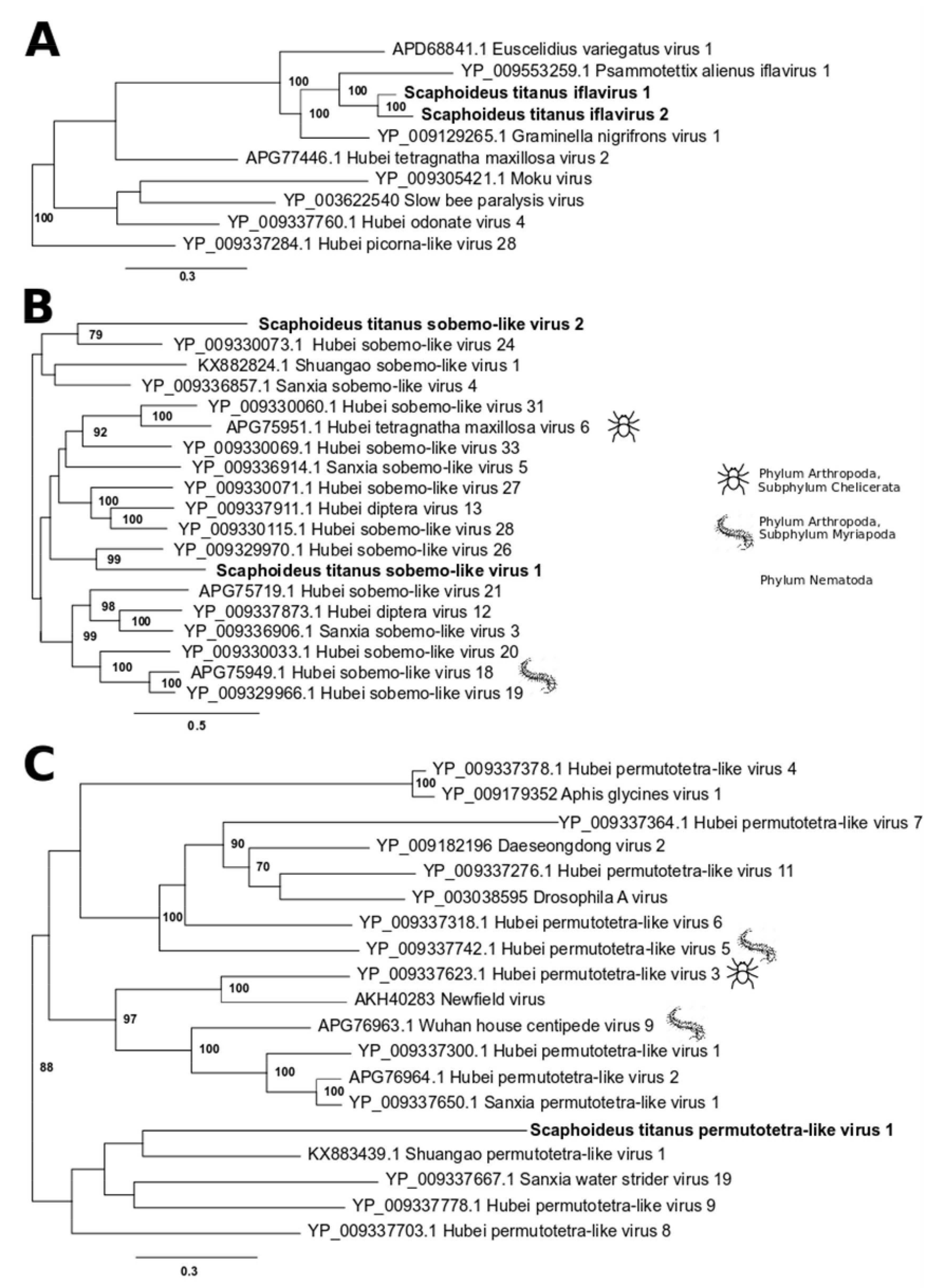
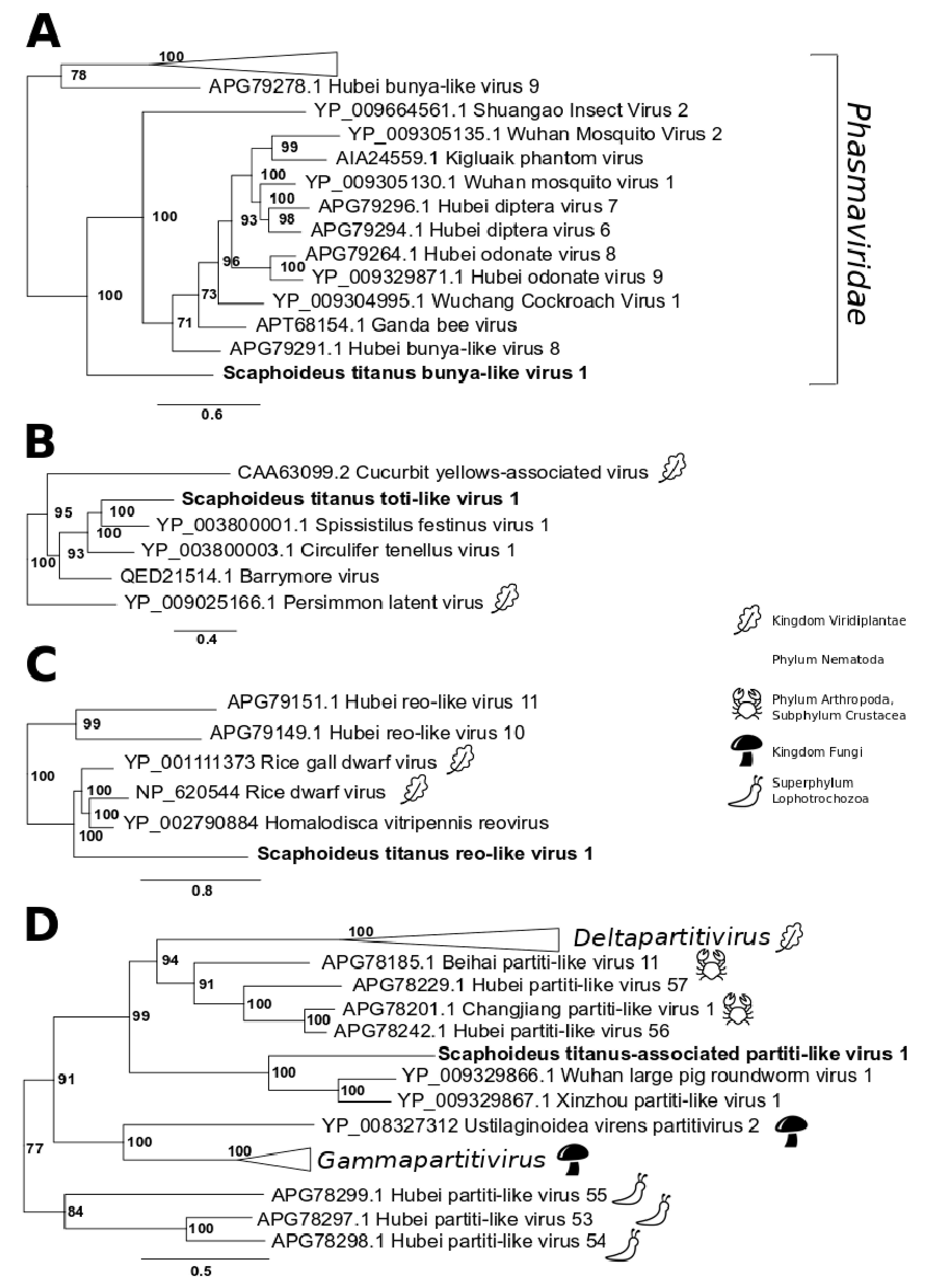
2.4. Phylogenetic Trees
2.5. PCR and RT-PCR
3. Results
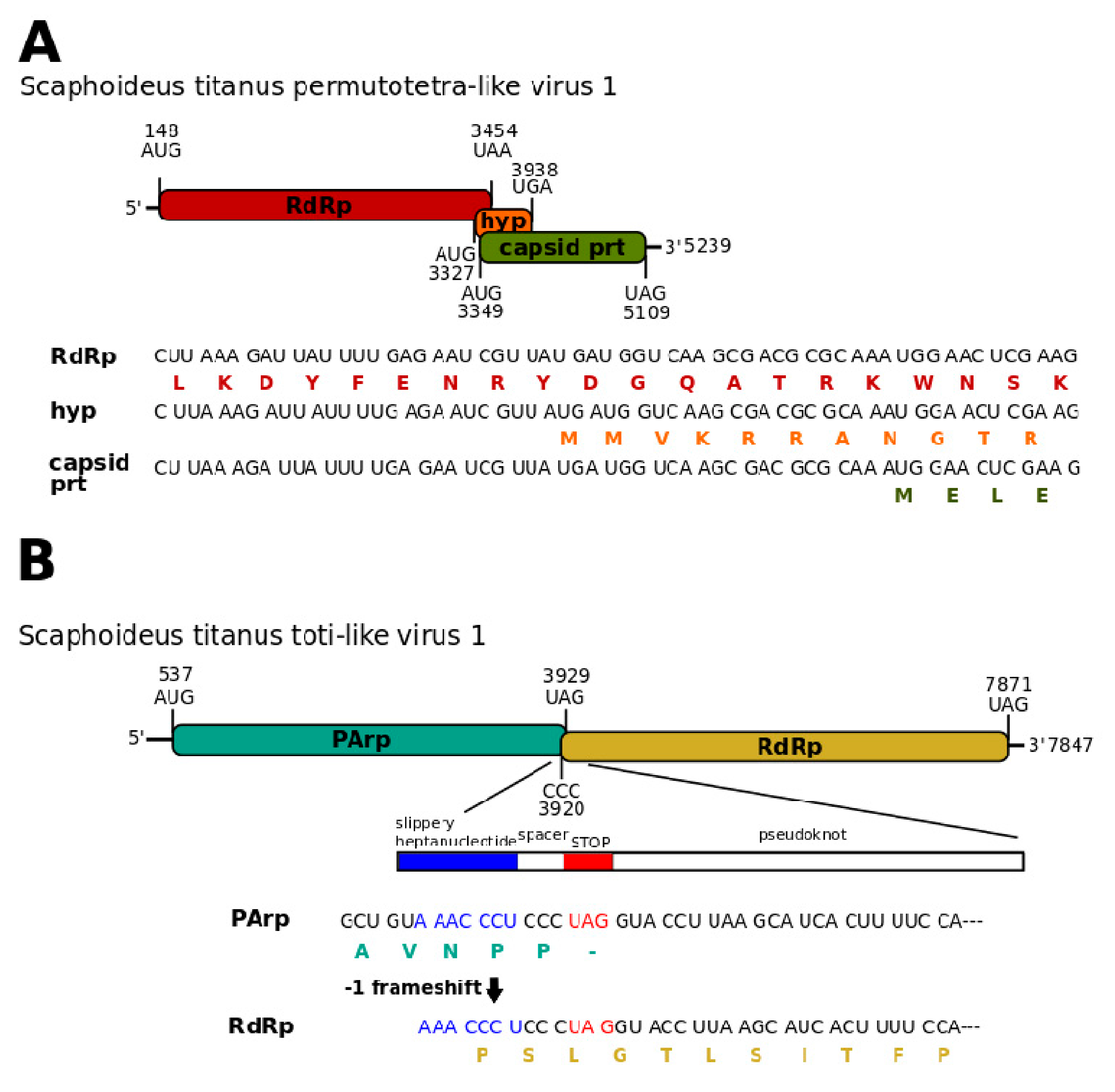
3.1. Single-Stranded Positive-Sense RNA Viruses
3.2. Single-Stranded Negative-Sense RNA Virus
3.3. Double-Stranded RNA Viruses
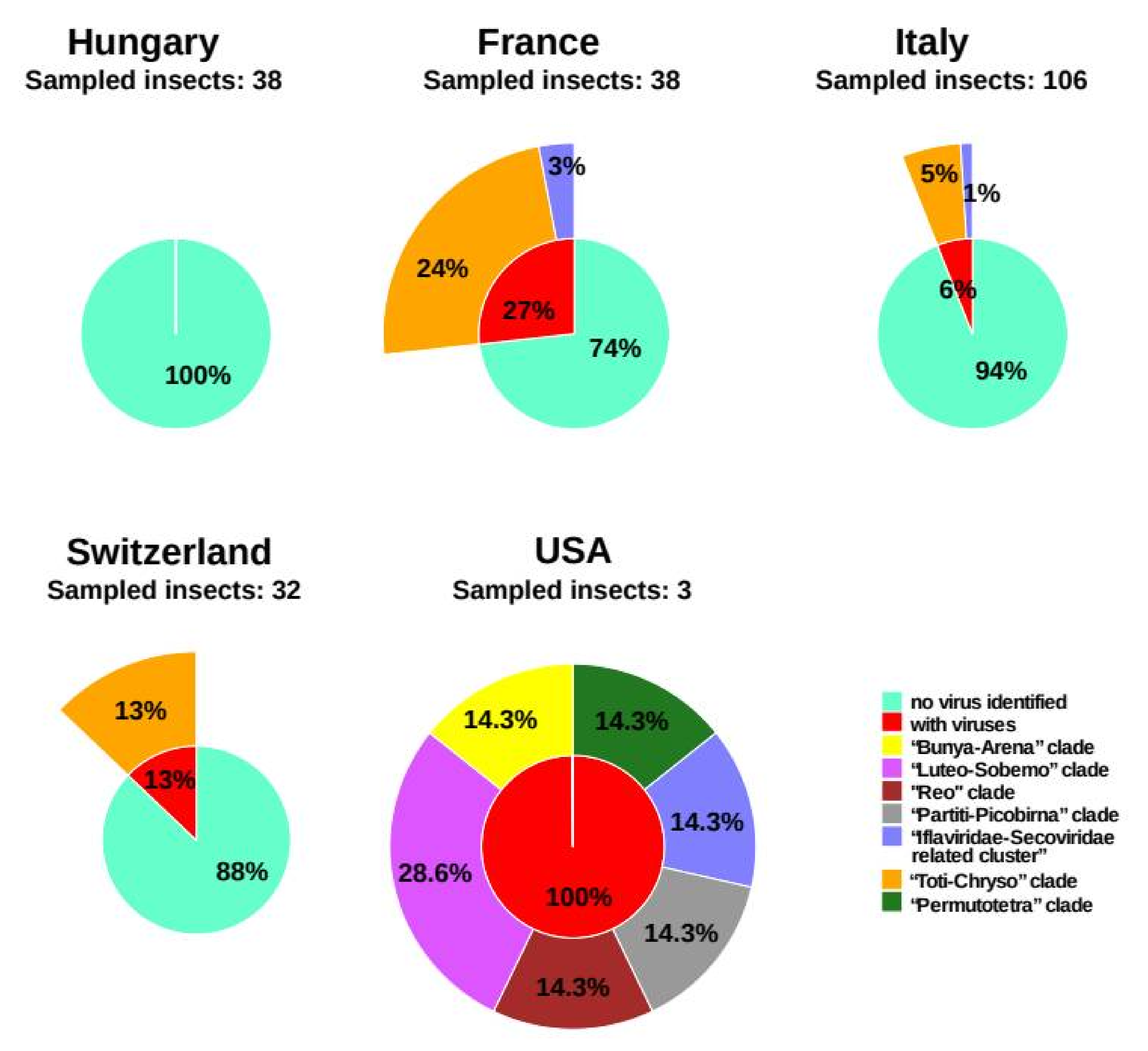
3.4. Virus Prevalence
3.5. Endogenous Viral Elements
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carton, Y.; Sorensen, C.; Smith, J.; Smith, E. Une coopération exemplaire entre entomologistes enançais et américains pendant la crise du Phylloxera en France (1868–1895). Ann. Société Entomol. Fr. NS 2007, 43, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papura, D.; Burban, C.; van Helden, M.; Giresse, X.; Nusillard, B.; Guillemaud, T.; Kerdelhué, C. Microsatellite and Mitochondrial Data Provide Evidence for a Single Major Introduction for the Neartic Leafhopper Scaphoideus titanus in Europe. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maixner, M.; Pearson, R.; Boudon-Padieu, E.; Caudwell, A. Scaphoideus titanus, a possible vector of grapevine yellows in New York. Plant Dis. 1993, 77, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schvester, D.; Moutous, G.; Carle, P. Scaphoideus littoralis Ball (Homopt. Jassidae) cicadelle vectrice de la Flavescence dorée de la vigne. Rev. Zool. Agric. Appl. 1962, 61, 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Krnjajić, S.; Mitrović, M.; Cvrković, T.; Jović, J.; Petrović, A.; Forte, V.; Angelini, E.; Toševski, I. Occurrence and distribution of Scaphoideus titanus in multiple outbreaks of “flavescence dorée” in Serbia. Bull. Insectol. 2012, 60, 197–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lessio, F.; Tota, F.; Alma, A. Tracking the dispersion of Scaphoideus titanus Ball (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) from wild to cultivated grapevine: Use of a novel mark-capture technique. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2014, 104, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, F.; Mori, N.; Bigot, G.; Zandigiacomo, P. Border effect in spatial distribution of Flavescence dorée affected grapevines and outside source of Scaphoideus titanus vectors. Bull. Insectol. 2012, 65, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, M.; Pegoraro, M.; Ripamonti, M.; Abbà, S.; Beal, D.; Giraudo, A.; Veratti, F.; Malembic-Maher, S.; Salar, P.; Bosco, D.; et al. Genetic diversity of Flavescence Dorée phytoplasmas at the vineyard scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e03123-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Murari, E.; Mori, N.; Bertaccini, A. Identification and epidemic distribution of two flavescence dorée—related phytoplasmas in Veneto (Italy). Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudwell, A. Deux Années D’études sur la Flavescence Dorée Nouvelle Maladie Grave de la Vigne; Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique: Paris, France, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Kriston, É.; Krizbai, L.; Szabó, G.; Bujdosó, B.; Orosz, S.; Dancsházy, Z.; Szőnyegi, S. First occurrence of grapevine flavescence doree in Hungary. Növényvédelem 2013, 49, 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Jermini, M.; Gusberti, M.; Schaub, L.; Linder, C.; Gugerli, P.; Schärer, S.; Emery, S. Flavescence dorée and Scaphoideus titanus: Distribution and control in Switzerland. IOBCWPRS Bull. 2008, 36, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub, P.G.; Beanland, L. Insect vectors of phytoplasmas. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morone, C.; Boveri, M.; Giosuè, S.; Gotta, P.; Rossi, V.; Scapin, I.; Marzachì, C. Epidemiology of Flavescence Dorée in Vineyards in Northwestern Italy. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, G.; Bianco, P.; Conti, M. Grapevine yellows in Italy: Past, present and future. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, 303–326. [Google Scholar]
- Chuche, J.; Thiéry, D. Biology and ecology of the Flavescence dorée vector Scaphoideus titanus: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffek, R.; Reisenzein, H.; Zeisner, N. Analysis of the pest risk from Grapevine flavescence dorée phytoplasma to Austrian viticulture. EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Plant Health; Jeger, M.; Bragard, C.; Caffier, D.; Candresse, T.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Gilioli, G.; Jaques Miret, J.A.; MacLeod, A.; et al. Risk to plant health of Flavescence dorée for the EU territory. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04603. [Google Scholar]
- Ignoffo, C.M. Entomopathogens as insecticides. Environ. Lett. 1975, 8, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergoin, M.; Tijssen, P. Biological and molecular properties of densoviruses and their use in protein expression and biological control. In The Insect Viruses; Plenum Publishing, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 141–169. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.A.; Crawford, A.M.; Glare, T.R. Oryctes virus—Time for a new look at a useful biocontrol agent. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 89, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzachì, C.; Veratti, F.; Bosco, D. Direct PCR detection of phytoplasmas in experimentally infected insects. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1998, 133, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBMap. Available online: Sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap/ (accessed on 11 March 2019).
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Madan, A. CAP3: A DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res. 1999, 9, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.-X.; Qin, X.-C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.-P.; Eden, J.-S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.M.; Lefkowitz, E.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B. Iflaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A.M., Lefkowitz, E., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 9, p. 848. [Google Scholar]
- Spear, A.; Sisterson, M.S.; Yokomi, R.; Stenger, D.C. Plant-feeding insects harbor double-stranded RNA viruses encoding a novel proline-alanine rich protein and a polymerase distantly related to that of fungal viruses. Virology 2010, 404, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, R.; Coutts, R. Relationships among Trialeurodes vaporariorum—Transmitted Yellowing Viruses from Europe and North America. J. Phytopathol. 1995, 143, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Suzaki, K.; Nakano, M. Genetic characterization of novel putative rhabdovirus and dsRNA virus from Japanese persimmon. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, D.C.; Sisterson, M.S.; Krugner, R.; Backus, E.A.; Hunter, W.B. A new Phytoreovirus infecting the glassy-winged sharpshooter (Homalodisca vitripennis). Virology 2009, 386, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Breitbart, M.; Salamon, P.; Andresen, B.; Mahaffy, J.M.; Segall, A.M.; Mead, D.; Azam, F.; Rohwer, F. Genomic analysis of uncultured marine viral communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14250–14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obbard, D.J. Expansion of the metazoan virosphere: Progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 31, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Adams, M.J.; Benkő, M.; Breitbart, M.; Brister, J.R.; Carstens, E.B.; Davison, A.J.; Delwart, E.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Harrach, B.; et al. Consensus statement: Virus taxonomy in the age of metagenomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonning, B.C. The Insect Virome: Opportunities and Challenges. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2019, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vainio, E.J.; Chiba, S.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Maiss, E.; Roossinck, M.; Sabanadzovic, S.; Suzuki, N.; Xie, J.; Nibert, M. Ictv Report Consortium ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Partitiviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara Pinto, A.Z.; de Santos de Carvalho, M.; de Melo, F.L.; Ribeiro, A.L.M.; Morais Ribeiro, B.; Dezengrini Slhessarenko, R. Novel viruses in salivary glands of mosquitoes from sylvatic Cerrado, Midwestern Brazil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, H.-O.J.; Shi, M.; Eden, J.-S.; Holmes, C.E.; Hesson, C.J. Meta-Transcriptomic Comparison of the RNA Viromes of the Mosquito Vectors Culex pipiens and Culex torrentium in Northern Europe. Viruses 2019, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivellone, V. (Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, IL, USA). Personal Communication, 2018.
- Keane, R.M.; Crawley, M.J. Exotic plant invasions and the enemy release hypothesis. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colautti, R.I.; Ricciardi, A.; Grigorovich, I.A.; MacIsaac, H.J. Is invasion success explained by the enemy release hypothesis? Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medd, N.C.; Fellous, S.; Waldron, F.M.; Xuéreb, A.; Nakai, M.; Cross, J.V.; Obbard, D.J. The virome of Drosophila suzukii, an invasive pest of soft fruit. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Souza-Neto, J.; Cosme, R.T.; Rovira, J.; Ortiz, A.; Pascale, J.M.; Dimopoulos, G. Reciprocal tripartite interactions between the Aedes aegypti midgut microbiota, innate immune system and dengue virus influences vector competence. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.; Ramirez, J.L.; Dimopoulos, G. The Aedes aegypti toll pathway controls dengue virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, W.; Glick, E.; Paldi, N.; Bextine, B. Advances in RNA interference: dsRNA Treatment in Trees and Grapevines for Insect Pest Suppression. Southwest. Entomol. 2012, 37, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killiny, N.; Hajeri, S.; Tiwari, S.; Gowda, S.; Stelinski, L.L. Double-Stranded RNA Uptake through Topical Application, Mediates Silencing of Five CYP4 Genes and Suppresses Insecticide Resistance in Diaphorina citri. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.; Chung, B.Y.-W.; Bass, D.; Moureau, G.; Tang, S.; McAlister, E.; Culverwell, C.L.; Glücksman, E.; Wang, H.; Brown, T.D.K.; et al. Novel Virus Discovery and Genome Reconstruction from Field RNA Samples Reveals Highly Divergent Viruses in Dipteran Hosts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauver, J.R.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Krajacich, B.J.; Weger-Lucarelli, J.; Lakin, S.M.; Fakoli, L.S., III; Bolay, F.K.; Diclaro, J.W., II; Dabiré, K.R.; Foy, B.D.; et al. West African Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes harbor a taxonomically diverse virome including new insect-specific flaviviruses, mononegaviruses, and totiviruses. Virology 2016, 498, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewski, M.; Rašić, G.; Darbro, J.; Krause, L.; Poo, Y.S.; Filipović, I.; Parry, R.; Asgari, S.; Devine, G.; Suhrbier, A. Mapping the virome in wild-caught Aedes aegypti from Cairns and Bangkok. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Asad, S.; Khromykh, A.A.; Asgari, S. Cell fusing agent virus and dengue virus mutually interact in Aedes aegypti cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Altan, E.; Deng, X.; Barker, C.M.; Fang, Y.; Coffey, L.L.; Delwart, E. Virome of > 12 thousand Culex mosquitoes from throughout California. Virology 2018, 523, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, K.; Capobianco, H.; Ng, T.F.F.; Breitbart, M.; Polston, J.E. RNA viral metagenome of whiteflies leads to the discovery and characterization of a whitefly-transmitted carlavirus in North America. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, S.; Salem, N.; Nigg, J.C.; Falk, B.W. Diverse Array of New Viral Sequences Identified in Worldwide Populations of the Asian Citrus Psyllid (Diaphorina citri) Using Viral Metagenomics. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2434–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamonje, F.O.; Michuki, G.N.; Braidwood, L.A.; Njuguna, J.N.; Musembi Mutuku, J.; Djikeng, A.; Harvey, J.J.W.; Carr, J.P. Viral metagenomics of aphids present in bean and maize plots on mixed-use farms in Kenya reveals the presence of three dicistroviruses including a novel Big Sioux River virus-like dicistrovirus. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atoni, E.; Wang, Y.; Karungu, S.; Waruhiu, C.; Zohaib, A.; Obanda, V.; Agwanda, B.; Mutua, M.; Xia, H.; Yuan, Z. Metagenomic virome analysis of Culex mosquitoes from Kenya and China. Viruses 2018, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanfack-Minkeu, F.; Mitri, C.; Bischoff, E.; Belda, E.; Casademont, I.; Vernick, K.D. Interaction of RNA viruses of the natural virome with the African malaria vector, Anopheles coluzzii. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| RNA-seq LibrariesID | Country | State/Region | Sampling Sites | Latitude (Decimal Degrees) | Longitude (Decimal Degrees) | Sampling Date (yyyy/mm/dd) | Number of Sampled Individuals | Positive to Scaphoideus titanus Iflavirus 1 | Positive to Scaphoideus titanustoti-Like Virus 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St_HU | Hungary | Pest | Monor | 47.354861 | 19.472177 | 2018-07-12 | 20 | 0 | 0 | |
| St_HU | Hungary | Pest | Gomba | 47.349622 | 19.505863 | 2018-07-12 | 18 | 0 | 0 | |
| St_FR | France | Burgundy | Corgoloin | 47.095667 | 4.908233 | 2018-07-06 | 20 | 0 | 8 | |
| St_FR | France | Dordogne | Saint-Nexans | 44.472132 | 0.345279 | 2018-07-10 | 18 | 1 | 1 | |
| St_IT1 | Italy | Piedmont | Asti | 44.921854 | 8.195758 | 2018-07-31 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| St_IT1 | Italy | Piedmont | Montà | 44.807434 | 7.965787 | 2018-07-31 | 12 | 1 | 0 | |
| St_IT1 | Italy | Piedmont | Portacomaro | 44.962898 | 8.26072 | 2018-08-03 | 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| St_IT1 | Italy | Piedmont | Cisterna | 44.82591 | 8.008371 | 2018-08-03 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| St_IT1 | Italy | Lombardy | Ome | 45.6302972 | 10.129867 | 2018-07-11 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| St_IT1 | Italy | Veneto | Verona | 45.4227833 | 11.025431 | 2018-08-08 | 8 | 0 | 0 | |
| St_IT2 | Italy | Friuli-Venezia Giulia | Togliano | 46.1129556 | 13.411311 | 2018-07-30 | 22 | 0 | 2 | |
| St_IT2 | Italy | Friuli-Venezia Giulia | Savorgnano al Torre | 46.161786 | 13.286864 | 2018-07-31 | 24 | 0 | 1 | |
| St_IT2 | Italy | Abruzzo | Vacri | 42.290333 | 14.223861 | 2018-07-16 | 12 | 0 | 2 | |
| St_CH | Switzerland | Canton Vaud | Gland | 46.42616 | 6.28217 | 2018-08-09 | 16 | 0 | 4 | |
| St_CH | Switzerland | Canton Valais | Pramagnon | 46.24987 | 7.45371 | 2018-08-09 | 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| 214 | 2 | 18 | Total | |||||||
| St_USA | USA | Illinois | Muncie | 40.0893 | -87.8323 | 2018-06-11 | 3 | |||
| Insects for DNA extraction1 | Country | State/Region | Sampling Sites | Latitude (Decimal Degrees) | Longitude (Decimal Degrees) | Sampling Date (yyyy/mm/dd) | Number of Sampled Individuals | |||
| Italy | Piedmont | Montà | 44.807434 | 7.965787 | 2018-07-31 | 2 | ||||
| Italy | Piedmont | Dogliani | 44.5362837 | 7.9312913 | 2018-08-20 | 2 |
| Library ID | Accession Numbers | Sequence Length (bp) | Best Blastx Hit Description | % Identity | % Query Coverage | RPKM | Tentative Name | Genome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St_IT1 | MN982380 | 10729 | YP_009129265.1 polyprotein [Graminella nigrifrons virus 1] | 51 | 83 | 0.01 | Scaphoideus titanus iflavirus 1 | +ssRNA (monopartite) |
| St_IT2 | MN982382 | 7847 | YP_003800001.1 RNA-directed RNA polymerase partial [Spissistilus festinus virus 1] | 42 | 37 | 0.002 | Scaphoideus titanus toti-like virus 1 | dsRNA (monopartite) |
| St_CH | MN982383 | 7839 | YP_003800001.1 RNA-directed RNA polymerase partial [Spissistilus festinus virus 1] | 42 | 37 | 0.032 | Scaphoideus titanus toti-like virus 1 | dsRNA (monopartite) |
| St_FR | MN982379 | 10693 | YP_009129265.1 polyprotein [Graminella nigrifrons virus 1] | 51 | 83 | 0.004 | Scaphoideus titanus iflavirus 1 | +ssRNA (monopartite) |
| St_FR | MN982381 | 7871 | YP_003800001.1 RNA-directed RNA polymerase partial [Spissistilus festinus virus 1] | 42 | 37 | 0.023 | Scaphoideus titanus toti-like virus 1 | dsRNA (monopartite) |
| St_USA | MN982384 | 4361 | API65464.1 glycoprotein precursor [Sanxia Water Strider Virus 2] | 25 | 12 | 1.016 | Scaphoideus titanus bunya-like virus 1 | −ssRNA (tripartite): segment M |
| St_USA | MN982385 | 1458 | APG79297.1 putative nucleoprotein [Hubei diptera virus 7] | 27 | 43 | 0.9 | Scaphoideus titanus bunya-like virus 1 | −ssRNA (tripartite): segment S |
| St_USA | MN982386 | 7740 | APT68154.1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [Ganda bee virus] | 33 | 74 | 0.359 | Scaphoideus titanus bunya-like virus 1 | −ssRNA (tripartite): segment L |
| St_USA | MN982387 | 10519 | YP_009129265.1 polyprotein [Graminella nigrifrons virus 1] | 51 | 85 | 0.045 | Scaphoideus titanus iflavirus 2 | +ssRNA (monopartite) |
| St_USA | MN982388 | 1455 | AWA82259.1 hypothetical protein, partial [Naganuma virus] | 38 | 91 | 0.145 | Scaphoideus titanus sobemo-like virus 1 | +ssRNA (bipartite) |
| St_USA | MN982389 | 3213 | YP_009329970.1 hypothetical protein [Hubei sobemo-like virus 26] | 60 | 99 | 0.103 | Scaphoideus titanus sobemo-like virus 1 | +ssRNA (bipartite) |
| St_USA | MN982390 | 1550 | AWA82259.1 hypothetical protein partial [Naganuma virus] | 36 | 77 | 0.231 | Scaphoideus titanus sobemo-like virus 2 | +ssRNA (bipartite) |
| St_USA | MN982391 | 3100 | YP_009330073.1 hypothetical protein 2 [Hubei sobemo-like virus 24] | 46 | 97 | 0.172 | Scaphoideus titanus sobemo-like virus 2 | +ssRNA (bipartite) |
| St_USA | MN982393 | 1303 | YP_009329884.1 hypothetical protein [Wuhan large pig roundworm virus 1] | 35 | 61 | 0.227 | Scaphoideus titanus-associated partiti-like virus 1 | dsRNA (bipartite) |
| St_USA | MN982392 | 1558 | AVV63192.1 RNA-directed RNA polymerase [Wuhan large pig roundworm virus] | 44 | 87 | 0.272 | Scaphoideus titanus-associated partiti-like virus 1 | dsRNA (bipartite) |
| St_USA | MN982394 | 5239 | YP_009337778.1 RdRp [Hubei permutotetra-like virus 9] | 39 | 39 | 0.764 | Scaphoideus titanus permutotetra-like virus 1 | +ssRNA (monopartite) |
| St_USA | MN982397 | 1240 | ADN64742.1 non-structural protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 79 | 58 | 2.378 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 10 |
| St_USA | MN982398 | 1867 | ADN64768.1 minor core protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 83 | 42 | 1.146 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 7 |
| St_USA | MN982399 | 2937 | ADN64783.1 minor core protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 52 | 49 | 2.661 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 5 |
| St_USA | MN982395 | 4957 | ADN64816.1 RNA-directed RNA polymerase [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 87 | 61 | 5.053 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 1 |
| St_USA | MN982400 | 3560 | YP_002790885.1 RNA-binding protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 96 | 49 | 5.444 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 2 |
| St_USA | MN982401 | 1416 | Q85451.1 RecName: Full=Outer capsid protein P8 | 62 | 88 | 1.679 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 8 |
| St_USA | MN982402 | 3179 | ADN64799.1 major core protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 95 | 55 | 1.901 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 3 |
| St_USA | MN982403 | 2648 | YP_002790887.1 zinc-finger protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 73 | 30 | 3.571 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 4 |
| St_USA | MN982404 | 1778 | YP_002790889.1 non-structural protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 78 | 33 | 1.196 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 6 |
| St_USA | MN982396 | 1179 | YP_002790892.1 non-structural protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 68 | 47 | 1.802 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 9 |
| St_USA | MN982405 | 798 | YP_002790894.1 non-structural protein [Homalodisca vitripennis reo-like virus] | 48 | 45 | 4.192 | Scaphoideus titanus reo-like virus 1 | dsRNA (multipartite): segment 11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ottati, S.; Chiapello, M.; Galetto, L.; Bosco, D.; Marzachì, C.; Abbà, S. New Viral Sequences Identified in the Flavescence Dorée Phytoplasma Vector Scaphoideus titanus. Viruses 2020, 12, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030287
Ottati S, Chiapello M, Galetto L, Bosco D, Marzachì C, Abbà S. New Viral Sequences Identified in the Flavescence Dorée Phytoplasma Vector Scaphoideus titanus. Viruses. 2020; 12(3):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030287
Chicago/Turabian StyleOttati, Sara, Marco Chiapello, Luciana Galetto, Domenico Bosco, Cristina Marzachì, and Simona Abbà. 2020. "New Viral Sequences Identified in the Flavescence Dorée Phytoplasma Vector Scaphoideus titanus" Viruses 12, no. 3: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030287
APA StyleOttati, S., Chiapello, M., Galetto, L., Bosco, D., Marzachì, C., & Abbà, S. (2020). New Viral Sequences Identified in the Flavescence Dorée Phytoplasma Vector Scaphoideus titanus. Viruses, 12(3), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030287







