Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: An Emerging Ancient Zoonosis?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
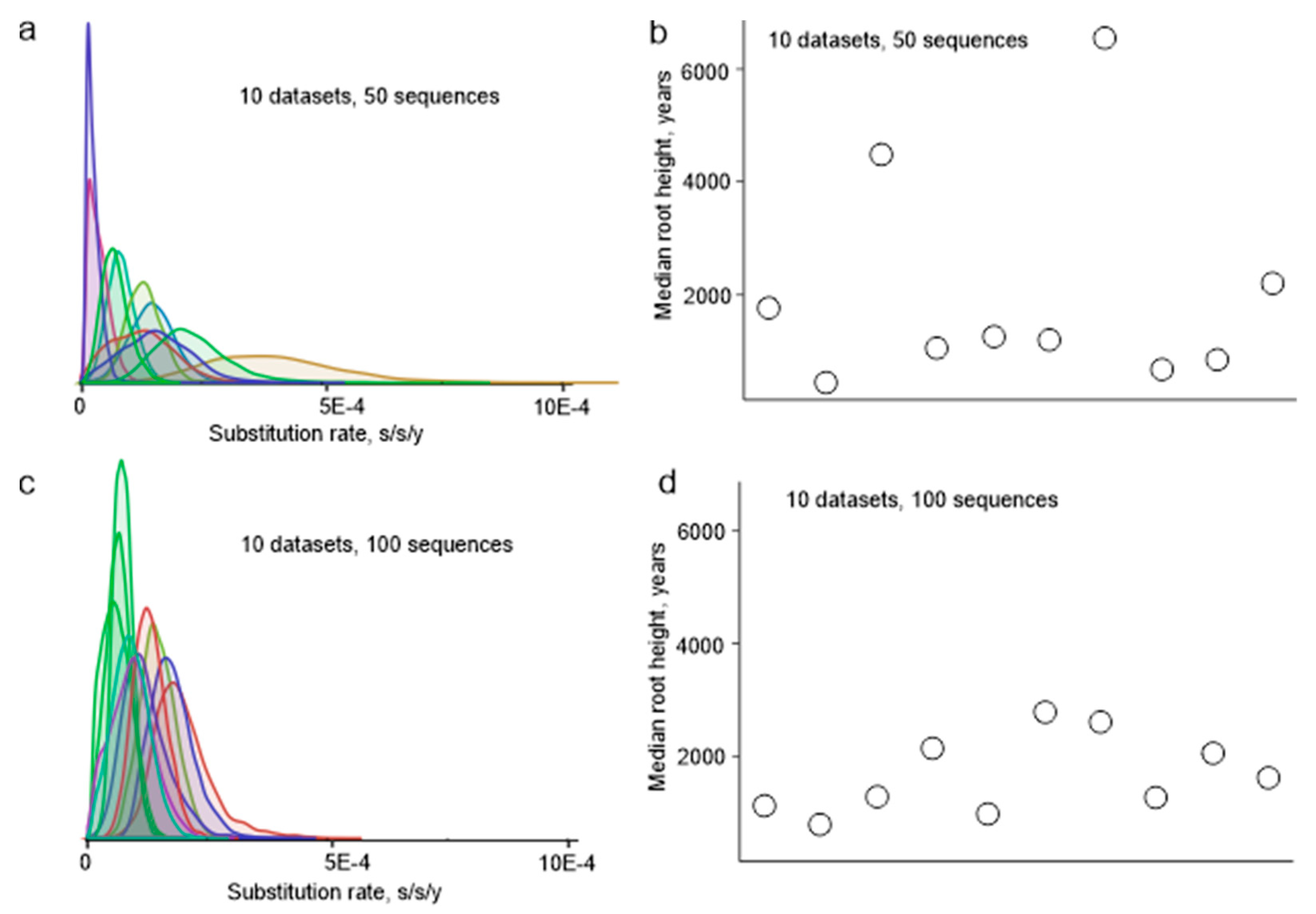
3.1. Sample Selection and Its Effect on the Ancestry Inference Estimates
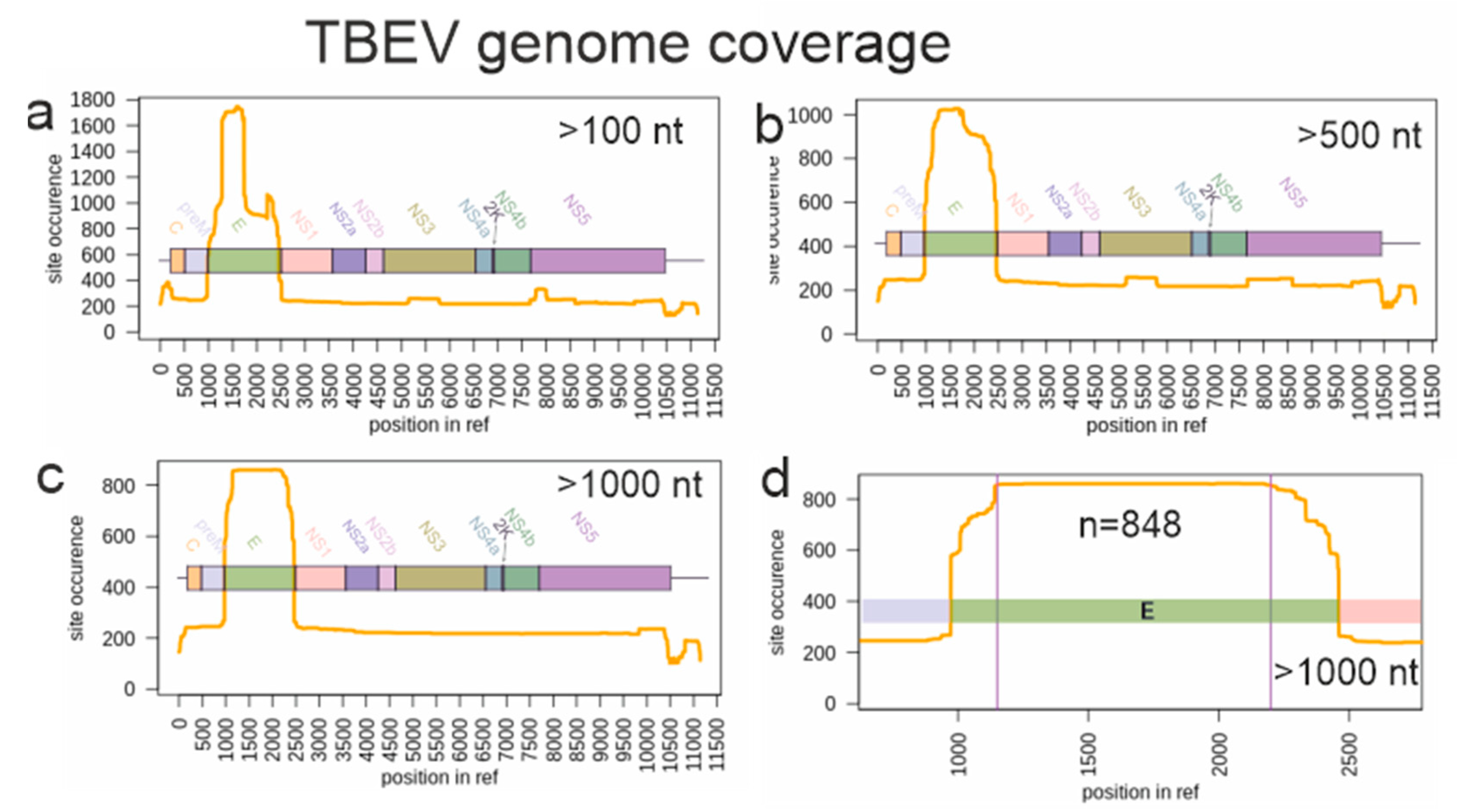
3.2. Suitability of TBEV Genomic Data for Molecular Clock Analysis
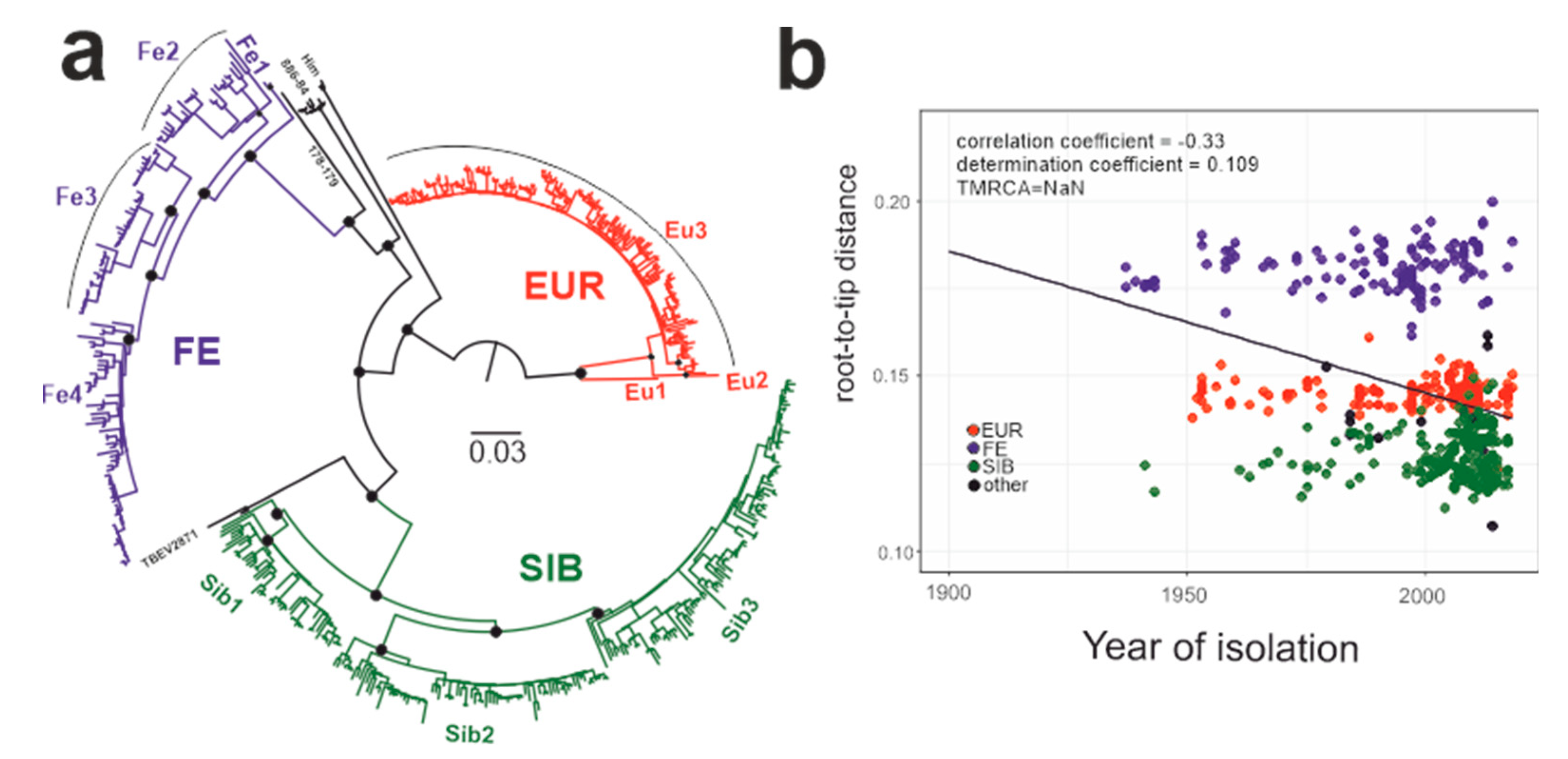
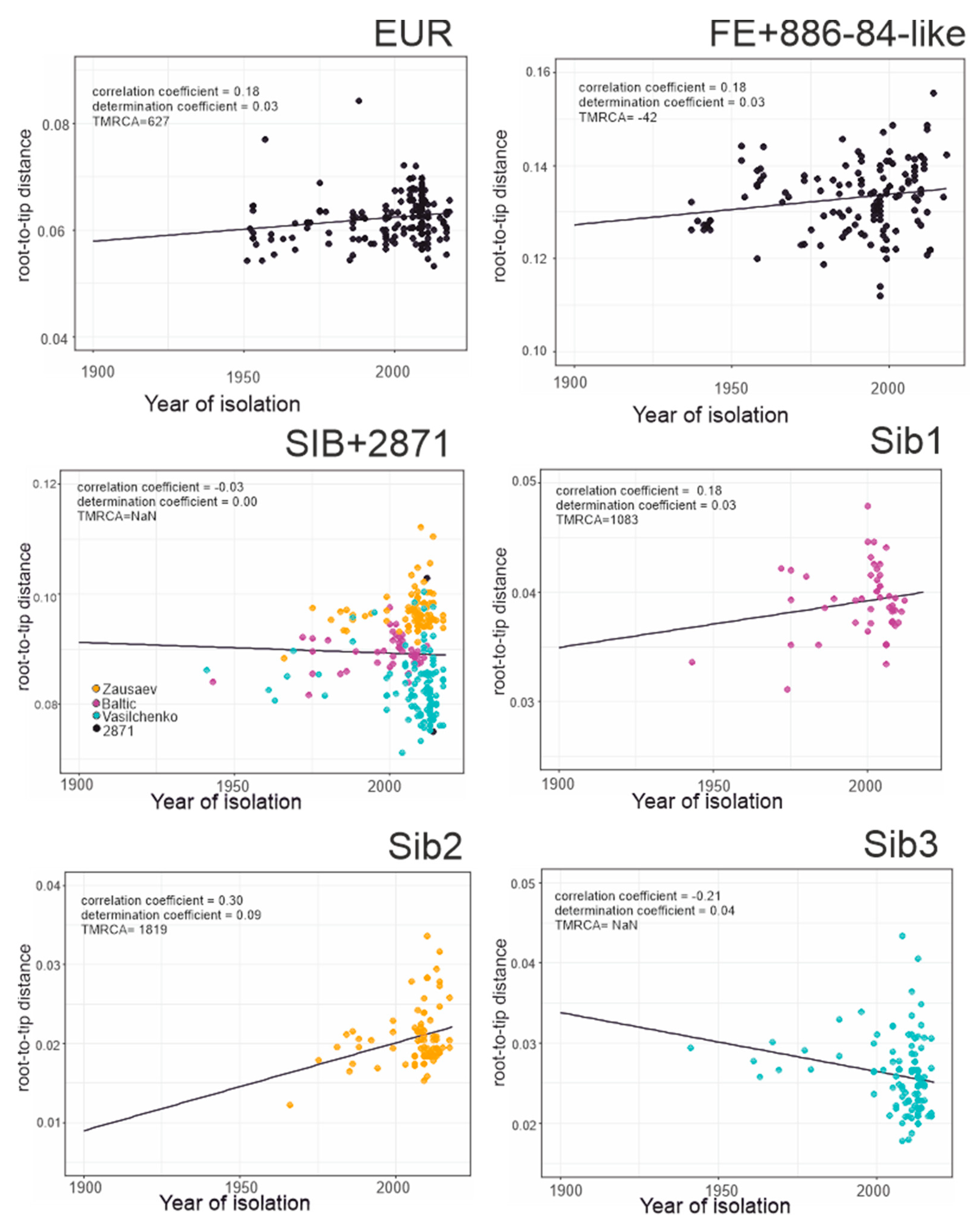
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Population Dynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beauté, J.; Spiteri, G.; Warns-Petit, E.; Zeller, H. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe, 2012 to 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing. Available online: www.rospotrebnadzor.ru/activities/statistical-materials/ (accessed on 24 December 2019).
- Lindquist, L.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, B.; Hubalek, Z.; Marek, M.; Daniel, M.; Strakova, P.; Betasova, L. Results of the Screening of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Antibodies in Human Sera from Eight Districts Collected Two Decades Apart. Vector Bome Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maikova, G.B.; Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Rogova, Y.V.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Romanenko, V.V.; Esyunina, M.S.; Ankudinova, A.A.; Kilyachina, A.S.; Vorovitch, M.F.; et al. Ability of inactivated vaccines based on far-eastern tick-borne encephalitis virus strains to induce humoral immune response in originally seropositive and seronegative recipients. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, M.; Allison, S.L.; Meixner, T.; Heinz, F.X. Sequence analysis and genetic classification of tick-borne encephalitis viruses from Europe and Asia. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrel, R.N.; Attoui, H.; Butenko, A.M.; Clegg, J.C.; Deubel, V.; Frolova, T.V.; Gould, E.A. Tick-borne virus diseases of human interest in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 1040–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, K.; Song, J.Y.; Park, S.-B.B.; Yang, J.; Schmitt, H.-J.J. Tick-borne encephalitis in Japan, Republic of Korea and China. Emergy Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e82. [Google Scholar]
- Jaaskelainen, A.E.; Castren, J.; Subbotina, N.; Sironen, T.; Alekseev, A.N.; Vapalahti, O.; Murueva, G.B.; Vaheri, A.; Alitalo, I. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks in Finland, Russian Karelia and Buryatia. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2706–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovljova, I.; Vene, S.; Sjölander, K.B.; Vasilenko, V.; Plyusnin, A.; Lundkvist, Å. Characterization of tick-borne encephalitis virus from Estonia. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukhovskaya, N.; Morozova, O.; Belozerova, N.; Bakhmetyeva, S.; Vysochina, N.; Zdanovskaya, N.; Ivanov, L. Comparative analysis of genomes of tick-borne encephalitis virus strains isolated from mosquitoes and ticks. Vopr. Virusol. 2017, 60, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tkachev, S.E.; Babkin, I.V.; Chicherina, G.S.; Kozlova, I.V.; Verkhozina, M.M.; Demina, T.V.; Lisak, O.V.; Doroshchenko, E.K.; Dzhioev, Y.P.; Suntsova, O.V.; et al. Ticks and Tick-borne Diseases Genetic diversity and geographical distribution of the Siberian subtype of the tick-borne encephalitis virus. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2019, 101327. [Google Scholar]
- Muto, M.; Bazartseren, B.; Tsevel, B.; Dashzevge, E.; Yoshii, K.; Kariwa, H. Isolation and characterization of tick-borne encephalitis virus from Ixodes persulcatus in Mongolia in 2012. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2015, 6, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, B.J.; Atkinson, B.; Czechowski, D.M.; Larsen, P.A.; Meeks, H.N.; Carrera, J.P.; Duplechin, R.M.; Hewson, R.; Junushov, A.T.; Gavrilova, O.N.; et al. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus, Kyrgyzstan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomareva, E.P.; Mikryukova, T.P.; Gori, A.V.; Kartashov, M.Y.; Protopopova, E.V.; Chausov, E.V.; Konovalova, S.N.; Tupota, N.L.; Gheorghita, S.D.; Burlacu, V.I.; et al. Detection of Far-Eastern subtype of tick-borne encephalitis viral RNA in ticks collected in the Republic of Moldova. J. Vector Bome Dis. 2015, 52, 334–336. [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenko, O.O.; Dubina, D.O.; Vynograd, N.O.; Gonzalez, J.-P. Partial Characterization of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Isolates from Ticks of Southern Ukraine. Vector Bome Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demina, T.; Dzhioev, Y.; Kozlova, I.; Verkhozina, M.; Tkachev, S.; Doroshchenko, E.; Lisak, O.; Paramonov, A.; Zlobin, V. genotypes 4 and 5 of the tick-Borne encephalitis Virus: Features of the genome Structure and Possible Scenario for its formation. Vopr. Virusol. 2012, 57, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Shang, G.; Lu, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. A new subtype of eastern tick-borne encephalitis virus discovered in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelshin, R.V.; Sidorova, E.A.; Bondaryuk, A.N.; Trukhina, A.G.; Sherbakov, D.Y.; White, R.A., III; Andaev, E.I.; Balakhonov, S.V. “886-84-like” tick-borne encephalitis virus strains: Intraspecific status elucidated by comparative genomics. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2019, 10, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, M.; Laverman, G.D.; de Vries, A.; Reimerink, J.; Geeraedts, F. Emergence of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in the Netherlands. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2019, 10, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzek, D.; Avšič Županc, T.; Borde, J.; Chrdle, A.; Eyer, L.; Karganova, G.; Kholodilov, I.; Knap, N.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Matveev, A.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and Russia: Review of pathogenesis, clinical features, therapy, and vaccines. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.; Hagedorn, P.; Schulze, Y.; Hellenbrand, W.; Pfeffer, M.; Niedrig, M. Review: Sentinels of tick-borne encephalitis risk. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2015, 6, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukhovskaya, N.M.; Morozova, O.V.; Vysochina, N.P.; Belozerova, N.B.; Bakhmetyeva, S.V.; Zdanovskaya, N.I.; Seligman, S.J.; Ivanov, L.I. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in arthropod vectors in the Far East of Russia. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2018, 9, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kholodilov, I.; Belova, O.; Burenkova, L.; Korotkov, Y.; Romanova, L.; Morozova, L.; Kudriavtsev, V.; Gmyl, L.; Belyaletdinova, I.; Chumakov, A.; et al. Ixodid ticks and tick-borne encephalitis virus prevalence in the South Asian part of Russia (Republic of Tuva). Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2019, 10, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, D.M.; Gould, E.A.; Forrester, N.L. Revisiting the Clinal Concept of Evolution and Dispersal for the Tick-Borne Flaviviruses by Using Phylogenetic and Biogeographic Analyses. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8663–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Pakskina, N.D. Current distribution area of tick-borne encephalitis in the russian federation. Med. Virol. 2016, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suss, J. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and beyond--the epidemiological situation as of 2007. Euro Surveill. 2008, 13, 717–727. [Google Scholar]
- Revich, B.; Tokarevich, N.; Parkinson, A.J. Climate change and zoonotic infections in the Russian Arctic. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2012, 71, 18792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarevich, N.K.; Tronin, A.A.; Blinova, O.V.; Buzinov, R.V.; Boltenkov, V.P.; Yurasova, E.D.; Nurse, J. The impact of climate change on the expansion of Ixodes persulcatus habitat and the incidence of tick-borne encephalitis in the north of European Russia. Glob. Health Action 2011, 4, 8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugmyrin, S.V.; Bespyatova, L.A.; Korotkov, Y.S.; Burenkova, L.A.; Belova, O.A.; Romanova, L.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Karganova, G.G.; Ieshko, E.P. Distribution of Ixodes ricinus and I. persulcatus ticks in southern Karelia (Russia). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybek, M.; Alsarraf, M.; Tołkacz, K.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Biernat, B.; Stańczak, J.; Strachecka, A.; Guz, L.; Szczepaniak, K.; Paleolog, J.; et al. Seroprevalence of TBEV in bank voles from Poland—A long-term approach. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorenko, M.; Radzievskaja, J.; Rosef, O.; Paulauskas, A. Investigation of the tick-borne encephalitis virus in Norway. Biologija 2018, 64, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Hjertqvist, M.; Bergström, T.; Lundkvist, A. Why is tick-borne encephalitis increasing? A review of the key factors causing the increasing incidence of human TBE in Sweden. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonteri, E.; Jokelainen, P.; Matala, J.; Pusenius, J.; Vapalahti, O. Serological evidence of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in moose and deer in Finland: Sentinels for virus circulation. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baasandavga, U.; Badrakh, B.; Burged, N.; Davaajav, O.; Khurelsukh, T.; Barnes, A.; Ulaankhuu, U.; Nyamdorj, T. A case series of fatal meningoencephalitis in Mongolia: Epidemiological and molecular characteristics of tick-borne encephalitis virus. West. Pacific Surveill Response J. 2019, 10, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabec, M.; Daniel, M.; Malý, M.; Danielová, V.; Kříž, B.; Kott, I.; Beneš, Č. Analysis of meteorological effects on the incidence of tick-borne encephalitis in the Czech Republic over a thirty-year period. Virol. Res. Rev. 2017, 1, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martello, E.; Mannelli, A.; Ragagli, C.; Ambrogi, C.; Selmi, M.; Ceballos, L.A.; Tomassone, L. Range expansion of Ixodes ricinus to higher altitude, and co-infestation of small rodents with Dermacentor marginatus in the Northern Apennines, Italy. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2014, 5, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, J.A.; Reimerink, J.H.; Voorn, G.P.; Bij de Vaate, E.A.; de Vries, A.; Rockx, B.; Schuitemaker, A.; Hira, V. First human case of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection acquired in The Netherlands, July 2016. Euro Surveill 2016, 21, 30323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velay, A.; Solis, M.; Kack-Kack, W.; Gantner, P.; Maquart, M.; Martinot, M.; Augereau, O.; De Briel, D.; Kieffer, P.; Lohmann, C.; et al. A new hot spot for tick-borne encephalitis (TBE): A marked increase of TBE cases in France in 2016. Ticks Tick Bome Dis. 2018, 9, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holding, M.; Dowall, S.D.; Medlock, J.M.; Carter, D.P.; Pullan, S.T.; Lewis, J.; Vipond, R.; Rocchi, M.S.; Baylis, M.; Hewson, R. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus, United Kingdom. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agergaard, C.N.; Rosenstierne, M.W.; Bødker, R.; Rasmussen, M.; Andersen, P.H.S.; Fomsgaard, A. New tick-borne encephalitis virus hot spot in Northern Zealand, Denmark, October 2019. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1900639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.R.; Drummond, A.J. bModelTest: Bayesian phylogenetic site model averaging and model comparison. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kuhnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A Software Platform for Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, V.; Baele, G. Bayesian Estimation of Past Population Dynamics in BEAST 1.10 Using the Skygrid Coalescent Model. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2620–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakulenko, Y.; Deviatkin, A.; Lukashev, A. The Effect of Sample Bias and Experimental Artefacts on the Statistical Phylogenetic Analysis of Picornaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbotina, E.L.; Loktev, V.B. Molecular evolution of the tick-borne encephalitis and Powassan viruses. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachev, S.E.; Chicherina, G.S.; Golovljova, I.; Belokopytova, P.S.; Tikunov, A.Y.; Zadora, O.V.; Glupov, V.V.; Tikunova, N.V. New genetic lineage within the Siberian subtype of tick-borne encephalitis virus found in Western Siberia, Russia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 56, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahfari, S.; De Vries, A.; Rijks, J.M.; Van Gucht, S.; Vennema, H.; Sprong, H.; Rockx, B. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks and roe deer, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1028–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritsun, T.S.; Lashkevich, V.A.; Gould, E.A. Tick-borne encephalitis. Antiviral Res. 2003, 57, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonova, G.N.; Belikov, S.I.; Kondratov, I.G.; Takashima, I. Comprehensive assessment of the genetics and virulence of tick-borne encephalitis virus strains isolated from patients with inapparent and clinical forms of the infection in the Russian Far East. Virology 2013, 443, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smura, T.; Tonteri, E.; Jääskeläinen, A.; Von Troil, G.; Kuivanen, S.; Huitu, O.; Kareinen, L.; Uusitalo, J.; Uusitalo, R.; Hannila-Handelberg, T.; et al. Recent establishment of tick-borne encephalitis foci with distinct viral lineages in the Helsinki area, Finland. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashev, A.N.; Vakulenko, Y.A. Molecular evolution of types in non-polio enteroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2968–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deviatkin, A.A.; Lukashev, A.N.; Poleshchuk, E.M.; Dedkov, V.G.; Tkachev, S.E.; Sidorov, G.N.; Karganova, G.G.; Galkina, I.V.; Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Shipulin, G.A. The phylodynamics of the rabies virus in the Russian Federation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikryukova, T.P.; Moskvitina, N.S.; Kononova, Y.V.; Korobitsyn, I.G.; Kartashov, M.Y.; Tyuten’kov, O.Y.; Protopopova, E.V.; Romanenko, V.N.; Chausov, E.V.; Gashkov, S.I.; et al. Surveillance of tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild birds and ticks in Tomsk city and its suburbs (Western Siberia). Ticks Tick. Bome Dis. 2014, 5, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, S.Y.; Chernykh, D.N.; Kokorev, V.S.; Snitkovskaya, T.E.; Romanenko, V.V. Origin and distribution of tick-borne encephalitis virus strains of the Siberian subtype in the Middle Urals, the north-west of Russia and the Baltic countries. J. Gen. Virol 2009, 90, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, S.; Oehme, R.; Buckenmaier, T.; Beer, M.; Jeffery-Smith, A.; Spannenkrebs, M.; Haag-Milz, S.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Schlegel, C.; Fritz, J.; et al. A cluster of two human cases of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) transmitted by unpasteurised goat milk and cheese in Germany, May 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuivanen, S.; Smura, T.; Rantanen, K.; Kämppi, L.; Kantonen, J.; Kero, M.; Jääskeläinen, A.; Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Sane, J.; Myllykangas, L.; et al. Fatal Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infections Caused by Siberian and European Subtypes, Finland, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, A.; Tonteri, E.; Pieninkeroinen, I.; Sironen, T.; Voutilainen, L.; Kuusi, M.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Siberian subtype tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes ricinus in a newly emerged focus, Finland. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makenov, M.; Karan, L.; Shashina, N.; Akhmetshina, M.; Zhurenkova, O.; Kholodilov, I.; Karganova, G.; Smirnova, N.; Grigoreva, Y.; Yankovskaya, Y.; et al. First detection of tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes ricinus ticks and their rodent hosts in Moscow, Russia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogstraal, H. Ticks in relation to human diseases caused by viruses. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1966, 11, 261–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Ito, T.; Chiba, M.; Takahashi, K.; Niioka, T.; Takashima, I. Isolation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus from Ixodes ovatus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Japan. J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.M.; Song, B.G.; Choi, W.; Park, W.I.; Kim, S.Y.; Roh, J.Y.; Ryou, J.; Ju, Y.R.; Park, C.; Shin, E.H. Prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in ixodid ticks collected from the republic of Korea during 2011–2012. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2012, 3, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


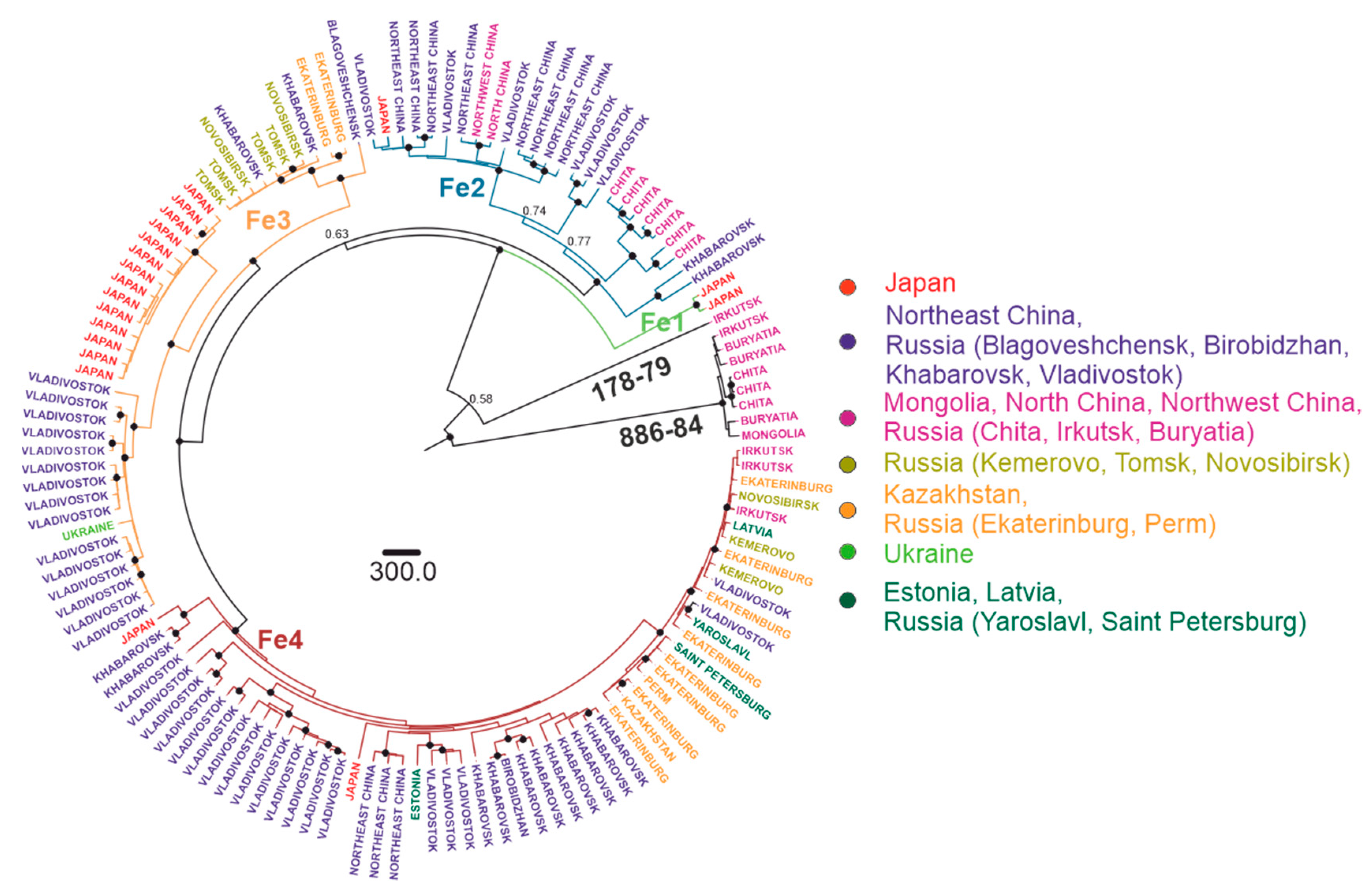
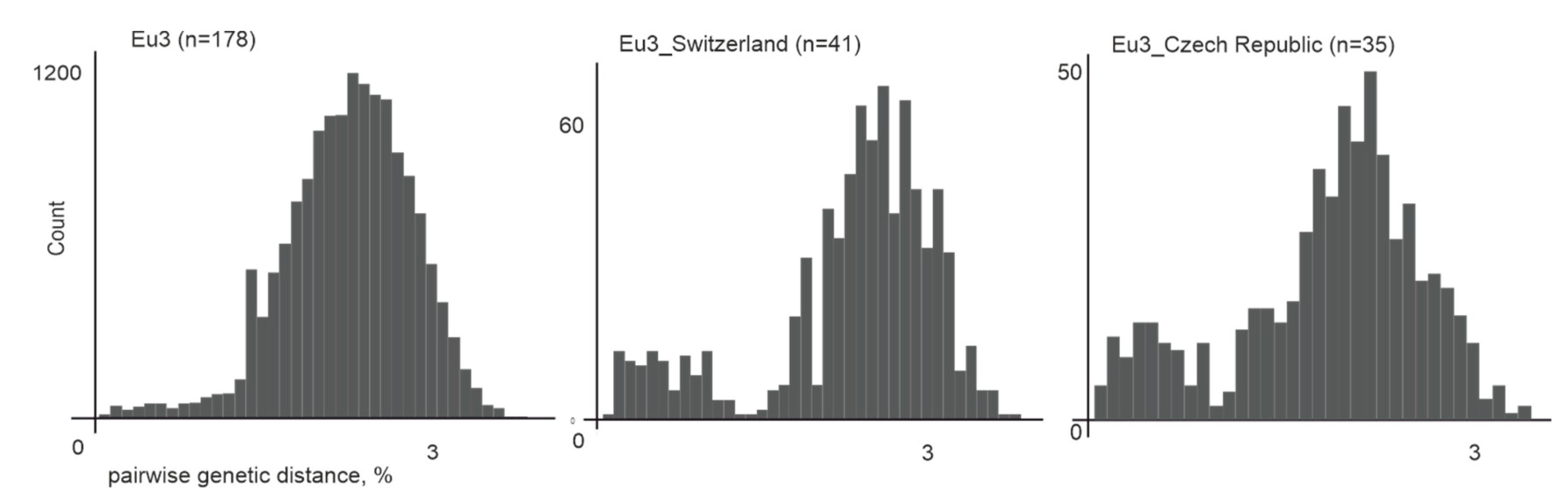
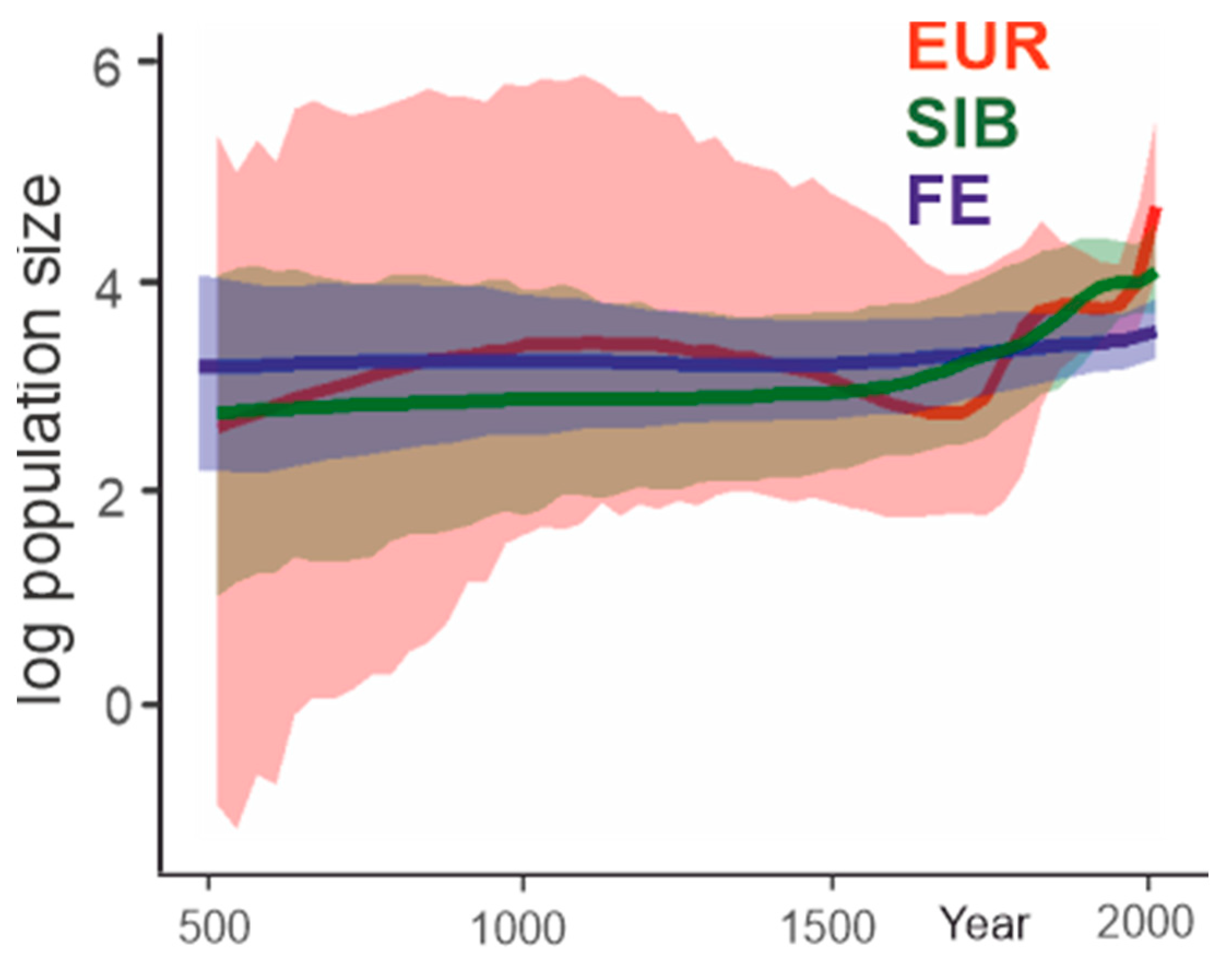
| Strain | Nearest Neighbor in Terms of Genetic Distance (Nearly Identical Sequences from the Same Place Were Omitted) | Nt Sequence Identity between Strain of Interest and Its Nearest Neighbor, % | Approximate Direct Air Distance, km | tMRCA (95% HPD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EUR | ||||
| Eu3 MH663428 Russia Moscow 2017 | Eu3 JQ654701 Slovenia 1992 | 98.1 | 2000 | 1681 (1228–1799) |
| Eu3 MK801803 Finland 2005 | Eu3 JF501414 Czech Republic 1986 | 99,3 | 1300 | 1876 (1541–1937) |
| Eu3 AF091007 France Alsace 1975 | Eu3 JF501408 Czech Republic 1978 | 99,4 | 500 | 1898 (1745–1950) |
| Eu3 AJ319583 Latvia 1997 | Eu3 MH704574 Germany Battaune 2017 | 99,91 | 950 | 1967 (1882–1996) |
| Eu3 KY069126 Russia Altai 1986 | Eu3 AF091005 Russia Saint Petersburg 1951 | 99.91 | 3200 | 1934 (1851–1951) |
| Eu3 MH021184 Netherlands 2016 | Eu3 AF091005 Russia Saint Petersburg 1951 | 98.39 | 1750 | 1624 (814–1793) |
| Eu3 KJ994330 Italy 2013 | Eu3 AF091005 Russia Saint Petersburg 1951 | 99.43 | 1900 | 1724 (1468–1836) |
| SIB | ||||
| Sib3 KF826916 Russia Sakhalin 2011 | Sib3 KC422663 Russia Chita 2000 | 100.00 | 2200 | 1993 (1973–2000) |
| Sib1 FJ214123 Russia Ekaterinburg 2006 | Sib1 FJ214145 Russia Yaroslavl 2001 | 98.54 | 1200 | 1855 (1699–1940) |
| Sib1 GQ845418 Russia Ekaterinburg 2009 | Sib1 Baltic GQ845439 Russia Yaroslavl 2008 | 98.73 | 1200 | 1883 (1764–1057) |
| Sib1 FJ214131 Russia Kurgan 2007 | Sib1 FJ214153 Russia Vologda 2007 | 99.90 | 1600 | 1995 (1956–2007) |
| Sib1 KY319395 Russia Kurgan 2010 | Sib1 GQ845440 Russia Yaroslavl 2008 | 100.00 | 1600 | 2003 (1986–2008) |
| Sib2 GQ845427 Russia Ekaterinburg 2009 | Sib2 MG598843 Russia Novosibirsk 2013 | 98.86 | 1400 | 1873 (1751–1944) |
| Sib2 FJ214150 Russia Kurgan 2007 | Sib2 FJ214137 Russia Vologda 1975 | 98.10 | 1600 | 1882 (1766–1956) |
| Sib2 AF527415 Russia Tomsk Zausaev 1985 | Sib2 KR633032 Russia Kirov 2012 | 98.54 | 2100 | 1757 (1560–1875) |
| Sib2 JF274481 Mongolia Bulgan 2010 | Sib2 MG598825 Russia Novosibirsk 2011 | 98.01 | 1700 | 1756 (1543–1879) |
| Sib2 KC417475 Russia Irkutsk 2010 | Sib2 KR633015 Russia Kemerovo 2014 | 98.39 | 1200 | 1872 (1741–1952) |
| Sib2 MF161158 Russia Irkutsk 2015 | Sib2 GQ845421 Russia Ekaterinburg 2009 | 99.05 | 2800 | 1863 (1741–1933) |
| Sib3 KF826916 Russia Sakhalin 2011 | Sib3 KC422663 Russia Chita 2000 | 100.00 | 2200 | 1993 (1972–2000) |
| FE | ||||
| Fe2 LC440460 Japan-Nanporo 2018 | Fe2 GU121642 Russia Vladivostok 2008 | 98.96 | 800 | 1946 (1884–1989) |
| Fe3 JX987281 Russia Khabarovsk 1973 | Fe3 KJ739731 Russia Tomsk Sorex araneus 2006 | 100.00 | 3400 | 1949 (1916–1969) |
| Fe3 FJ214120 Russia Ekaterinburg 1959 | Fe3 KJ739731 Russia Tomsk Sorex araneus 2006 | 99.43 | 1500 | 1898 (1831–1944) |
| Fe3 AF091008 Ukraine 1987 | Fe3 AY169390 Russia Prymorye Prymorye-332 human blood 1991 | 99.53 | 7300 | 1905 (1850–1951) |
| Fe4 LC440459 Japan- Sapporo Ixodes ovatus 2017 | Fe4 KP869172 Russia-Khabarovsk 1985 | 97.91 | 780 | 1810 (1639–1927) |
| Fe4 DQ393779 Estonia Laanemaa 1996 | Fe4 AB049345 Russia-Vladivostok 1999 | 98.48 | 6900 | 1835 (1725–1919) |
| Fe4 FJ214119 Russia Ekaterinburg 1943 | Fe4 FJ214119 Russia- SaintPetersburg 1943 | 99.81 | 1800 | 1924 (1901–1940) |
| Fe4 FJ214147 Russia Yaroslavl 1989 | Fe4 AF091013 Russia Vladivostok 1979 | 99.72 | 6200 | 1954 (1917–1977) |
| Fe4 AF091016 Latvia 1977 | Fe4 FJ214133 Russia Kemerovo 1967 | 99.72 | 3700 | 1961 (1948–1967) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deviatkin, A.A.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Vakulenko, Y.A.; Karganova, G.G.; Lukashev, A.N. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: An Emerging Ancient Zoonosis? Viruses 2020, 12, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020247
Deviatkin AA, Kholodilov IS, Vakulenko YA, Karganova GG, Lukashev AN. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: An Emerging Ancient Zoonosis? Viruses. 2020; 12(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020247
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeviatkin, Andrei A., Ivan S. Kholodilov, Yulia A. Vakulenko, Galina G. Karganova, and Alexander N. Lukashev. 2020. "Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: An Emerging Ancient Zoonosis?" Viruses 12, no. 2: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020247
APA StyleDeviatkin, A. A., Kholodilov, I. S., Vakulenko, Y. A., Karganova, G. G., & Lukashev, A. N. (2020). Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: An Emerging Ancient Zoonosis? Viruses, 12(2), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020247





