Abstract
Hepatitis B remains one of the major global health problems more than 40 years after the identification of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) as the causative agent. A critical turning point in combating this virus was the development of a preventative vaccine composed of the HBV surface (envelope) protein (HBsAg) to reduce the risk of new infections. The isolation of HBsAg sub-viral particles (SVPs) from the blood of asymptomatic HBV carriers as antigens for the first-generation vaccines, followed by the development of recombinant HBsAg SVPs produced in yeast as the antigenic components of the second-generation vaccines, represent landmark advancements in biotechnology and medicine. The ability of the HBsAg SVPs to accept and present foreign antigenic sequences provides the basis of a chimeric particulate delivery platform, and resulted in the development of a vaccine against malaria (RTS,S/AS01, MosquirixTM), and various preclinical vaccine candidates to overcome infectious diseases for which there are no effective vaccines. Biomedical modifications of the HBsAg subunits allowed the identification of strategies to enhance the HBsAg SVP immunogenicity to build potent vaccines for preventative and possibly therapeutic applications. The review provides an overview of the formation and assembly of the HBsAg SVPs and highlights the utilization of the particles in key effective vaccines.
1. Introduction
Hepatitis B is globally one of the most common infectious diseases in humans, which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Approximately 2 billion people worldwide have been infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and approximately 257 million people live with chronic HBV infections. An estimated 887,000 persons died in 2015 from acute or chronic consequences of hepatitis B [1,2,3,4]. The ability of the HBV structural proteins, including the hepatitis B surface (envelope) proteins (HBsAg) to assemble into non-infectious sub-viral particles (SVPs), allows the generation of highly organized particles displaying neutralizing epitopes that promote protective immune responses against the parent virus. The approval of the recombinant hepatitis B vaccine Recombivax HB (Merck Sharp and Dohme) in 1986, based on HBsAg SVPs and produced in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, was the first developed vaccine using recombinant DNA technology. The recombinant vaccine, together with the recombinant products, human insulin (licensed 1982), human growth hormone (licensed 1985), and alpha interferon (licensed 1986), demonstrated the capability of biotechnological approaches to generate innovative medicines [1]. The ability to accept foreign antigenic sequences into the SVP structure can provide the basis for the development of delivery platforms for targeted medically relevant sequences, as in the case of the RTS,S/AS01 (Mosquirix™) vaccine against malaria. The antigenic components of Mosquirix™ are chimeric SVPs containing HBsAg proteins fused to a Plasmodium falciparum-specific circumsporozoite (CS) polypeptide [5,6,7]. The design and generation of chimeric SVPs holds enormous potential in the treatment of infectious diseases, for which there are no effective vaccines [8,9,10].
2. Hepatitis B Virus, Classification, and Gene Products
HBV is a hepatocyte-tropic virus and is assigned to the family of hepatitis DNA viruses, Hepadnaviridae [11,12,13]. HBV is divided into 10 main genotypes, A–J, which differ by more than 8% at the nucleotide level [14,15]. The HBV genome has a size of approximately 3.2 kilobases (kb), and is represented by a relaxed circular, partially double-stranded DNA (rcDNA), which is delivered to the nucleus of the host cell and converted into a covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) molecule [12]. The cccDNA represents a non-integrated stable episome and forms the template for all viral RNA transcripts. In the absence of an origin of replication site required for DNA-dependent DNA amplification, one of the viral transcripts, the pre-genomic RNA (pgRNA), serves as the template for replication to generate rcDNA via reverse transcription [12]. HBV contains four open reading frames (C, P, S, and X) and encodes seven proteins (polymerase, X protein, HBcAg, HBeAg, HBsAgL, HBsAgM, and HBsAgS). The polymerase is essential for several steps in the replication pathway through its reverse transcriptase, RNaseH, and priming activities. The X protein supports efficient infection and replication in vivo [11,12,16]. The core protein (HBcAg) constitutes the subunit of the viral capsid and is essential for the formation of virions. The e-antigen (HBeAg) is derived from the pre-core protein by proteolytic processing and is not part of the viral capsid. It is involved in modulating the host immune response against HBV and represents an important serological marker [11,12,13]. The virus encodes for three related surface (envelope) proteins (HBsAg) that share a common S-domain. They are translated from different in-frame start codons and hence are distinguished by their N-terminal extensions. The small HBsAg (HBsAgS) comprises only the S-domain with a size of 226 amino acids (aa), the middle HBsAg protein (HBsAgM) has an N-terminal extension of 55 aa (pre-S2 domain), and the large HBsAg (HBsAgL) has an additional extension of 108 or 119 aa (preS1-domain) depending on the genotype [17] (Figure 1A,B). In addition to the classification by genotypes, HBV is distinguished by four main serotypes based on the reactivity against HBsAg. All genotypes have a common serotypic reactivity against a major antigenic site called the “a”-determinant, but further express two mutually exclusive allelic antigenic determinants “d” or “y” and “w” or “r” [18,19,20]. The antigenic determinants of HBsAg are located in an exposed loop region of the S-domain. HBsAg and antibodies against HBsAg (anti-HBs) are important serological markers. The loss of HBsAg and seroconversion to anti-HBs antibodies are a sign of immunity and recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B [13].
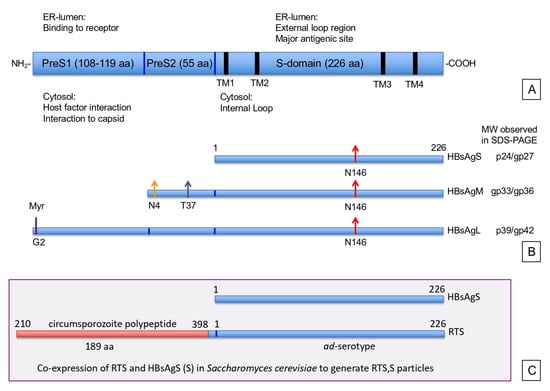
Figure 1.
The surface (envelope) proteins (HBsAg) of hepatitis B virus (HBV): (A) The open reading frame encoding the complete hepatitis B surface antigen is depicted. The domain organization of preS1, preS2, and S, with the number of amino acids (aa) of the individual domains are specified. The four transmembrane regions (TM1–4) are indicated by the thick black lines. The function of the different domains in relation to their orientation towards the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or cytosol is indicated. (B) The individual HBsAg open reading frames for the small (HBsAgS), middle (HBsAgM), and large (HBsAgL) proteins, and their post-translational modifications are shown. The size of the HBsAgS protein is indicated by the number of amino acids. Arrows represent the utilized glycosylation sites. Red arrows mark asparagine 146 (N146) in the S-domain. Orange and purple arrows represent the N-4 and threonine 37 (T37) respectively, in the preS2 domain. The glycine residue at position 2 (G2) of the preS1 domain, indicated by a purple line, is myristolated. The observed molecular weights (MW) of the glycosylated (gp) and non-glycosylated proteins (p) separated under reducing conditions on a SDS-PAGE are indicated on the right. (C) Design of the RTS,S vaccine that is produced by co-expressing HBsAgS (aa 1–226) and the chimeric protein that is a fusion of the circumsporozoite polypeptide (210–398 aa) to the N-terminus of HBsAgS, including 4 aa from the preS2 domain.
Characteristic of a HBV infection is the generation of a large quantity of HBsAg SVPs and filaments devoid of capsid and of the viral genome. SVPs exceed the presence of infectious virions in host sera by a factor between 102 and 105 [17,21,22,23,24]. SVPs are predominately composed of HBsAgS, and their presence in the sera does not seem to interfere with HBV particle entry into hepatocytes, suggesting that SVPs represent decoys by binding to virus-neutralizing antibodies [25]. HBsAgS SVPs share important immunological determinants with the mature virus, and therefore, SVPs derived from patient serum or recombinant SVPs represent effective immunogens for the induction of a protective immune response [26,27,28]. Vaccinated individuals develop antibodies targeting the “a”-determinant region, which provides protection against the infection of all HBV serotypes [20,29]. The discovery and characterization of “empty” genome-free virions containing HBsAg and capsid is reviewed by Hu and Liu, 2017 [30].
3. Role of HBsAg in HBV, Filament, and SVP Formation
An essential step in the formation of virions, filaments, or SVPs is the cotranslational insertion of the HBsAgS protein into the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with a short luminal exposed N-terminal sequence, two transmembrane regions separated by a cytosolic loop, and a luminal domain, followed by a hydrophobic C-terminal region. The luminal domain corresponds to the external loop region of the S-domain, which contains multiple epitopes, including the immunodominant “a”-determinant region that is common to all HBV genotypes, and the allelic antigenic determinants “d/y” and “w/r” [17,31]. A conformational heparan sulfate binding site also overlaps with the “a”-determinant region and is essential to infectivity [32].
HBV virion formation depends on the presence of the viral capsid containing rcDNA and the HBsAg proteins for envelopment. The preS1 region of HBsAgL is essential for the assembly of infectious HBV particles by interacting with the capsid [17,33], possibly contributes to the binding to a proteoglycan attachment site [34,35], and is required for binding to the hepatocyte entry receptor, sodium taurochlorate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) [36,37]. Chaperones of the heat shock protein (hsp) 70 family facilitate the interaction of the HBsAgL preS1 domain with the capsid by retaining the preS1/preS2 sequence in the cytosolic (internal) orientation at the ER [38,39,40]. Virion secretion depends on host factors of the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) and sorting into late endosomal multivesicular bodies (MVBs), and finally, release of its intraluminal content at the hepatocyte surface [41,42,43]. The mature HBV virions are spherical, enveloped particles with a diameter of 42 nm with an inner capsid of 22 nm in diameter [11,12,13]. Due to the elevated presence of HBsAgL in virions and filaments compared to the SVPs, filaments seem to follow the secretion pathway taken by the virions (Figure 2) [44]. The filaments have a width of approximately 20 nm and are variable in length [12,23,45].
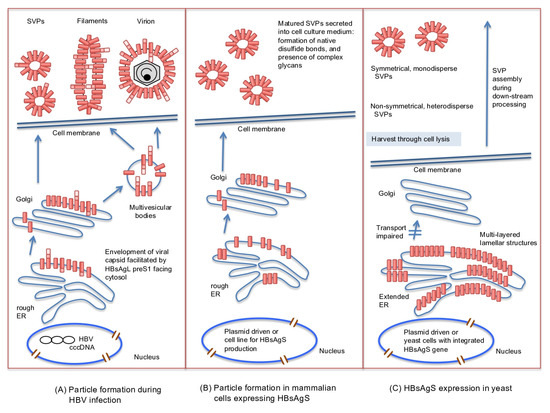
Figure 2.
Illustration of HBsAg protein synthesis and assembly pathways during a natural infection (A), HBsAgS expression and assembly in mammalian cells in the absence of other viral gene products (B), or expressed in yeast (C). During a natural infection, virions and filaments are formed by budding from multivesicular bodies. The spherical subviral particles (SVPs) are produced and secreted through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Golgi complex. The HBsAg subunits of the virions, filaments, and SVPs form intra- and intermolecular disulfide bonds, and are partially glycosylated (not shown) (A). Expression of the HBsAgS gene in mammalian cell lines leads to the formation of SVPs exclusively composed of HBsAgS permitting the formation of disulfide bonds and partial glycosylation (not shown) (B). HBsAgS protein expressed in yeast accumulates in the ER, causes an extended ER and forms multilayered lamellar structures. HBsAgS protein complexes are harvested from the cell lysate, and SVPs are assembled during down-stream processing (C). cccDNA: covalently closed circular DNA.
In contrast to the formation of infectious particles, the formation of SVP does not depend on the preS1 domain. HBsAgS proteins have the ability to assemble into secretion-competent SVPs and are composed solely of envelope proteins, lipids, and glycans. Contrary to virion secretion, SVP assembly follows the constitutive secretory pathway of the host cell for release [43,44]. The non-infectious SVPs are 17 to 25 nm in diameter. SVPs isolated from HBV carriers show spike-like features protruding from the surface similar to the surface projections observed on filaments and infectious virions (Dane particles) [24,45,46,47,48]. An alternative structure for recombinant SVPs expressed in transgenic mice has been proposed to possess an octahedral symmetry [49]. Mammalian cell lines expressing HBsAgS in the absence of any other viral component secrete SVPs, which are morphologically indistinguishable from serum-derived SVPs (Figure 2) [50,51,52,53,54]. Thus, particle morphogenesis substantially differs between SVPs and virions, but they have identical antigenic structures due to the S-domain, which is encoded by all HBV envelope proteins (Figure 1A,B).
3.1. Topology of HBsAgS
The correct folding of HBsAgS depends on two topogenic signal sequences, which determine the orientation of the S-domains in relation to the lipid layer. The insertion of the HBsAgS N-terminus into the ER membrane requires the presence of the topogenic N-terminal signal sequence 1 (transmembrane region 1, TM1, aa 8–22), which is not proteolytically cleaved by the host’s peptidases, and allows the translocation of the N-terminus across the ER membrane. The second internal topogenic transmembrane sequence (TM2), which is located between aa 80 and 98, supports the translocation of flanking C-terminal sequences and serves as an anchor to hold the sequence in the membrane [17,55,56]. Both topogenic signal sequences are required for the correct folding of HBsAgS, resulting in the formation of a cytosolic loop (aa 23 to 79), and a loop reaching into the ER lumen (aa 99 to approximately 155), followed by a proposed amphipathic helix (aa 156 to 169) and the hydrophobic C-terminal region (aa 170 to 226) embedded in the ER membrane (Figure 1A and Figure 3) [57]. The luminal loop region of the S-domain is located at the external surface of the mature SVPs and also infectious virions, and harbors the major HBsAg protein epitopes (“a”-determinant, and “d/y”, “w/r” determinants) [13]. The hydrophobic C-terminal region (aa 170 to 226) possibly contains two additional transmembrane regions, as indicated by topological models [58,59]. The presence of transmembrane passages is supported by experimental data suggesting that the C-terminal sequences are exposed at internal and external surfaces. The sequence between residues 196 and 201 is important for packaging of hepatitis delta virus (HDV), a satellite of HBV, and therefore expected to be accessible to facilitate the interaction with the HDV ribonucleoprotein complex [60]. A second site between residue 178 and 186 is targeted by an anti-HBs monoclonal antibody, indicating surface exposure [61].
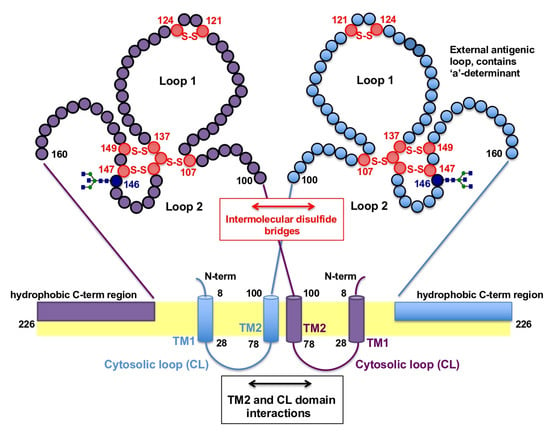
Figure 3.
Proposed model for the formation of the HBsAgS homodimer based on Suffner et al. [57]. Dimerization of two HBsAgS monomers represented in purple and blue is facilitated by interactions of the transmembrane domains (TM2), cytosolic loops (CL) and intermolecular disulfide bridges (S-S) between cysteine residues (red circles) in the external loop region. The facultative N-glycosylation site at position N146 is indicated (dark blue). The orientation of the hydrophobic C-terminal region is illustrated in a simplified form.
HBsAg proteins contain 14 cysteine (cys) residues located in the S-domain, which are highly conserved among different HBV genotypes; the preS1 and preS2 domains do not contain additional cysteine residues [12,17]. Eight cysteine residues are located in the external loop region, forming disulfide bonds which are important for the integrity of the major antigenic determinants [62,63], such as cys-107 in the external loop for retaining the “a”-determinant specific antigenicity [64]. The identification of HBsAgS oligomers and polymers by electrophoresis under non-reducing conditions suggests that the disulfide bonding is heterogeneous, consistent with the finding that only a fraction of HBsAgS subunits are exclusively linked by disulfide bonds formed between cys-121 and cys-147 (Figure 3) [62,63,65]. Reduction or absence of intermolecular disulfide bridges interferes with the native HBsAgS antigenicity but allows SVP formation [62,65,66].
The S-domain shared by the HBsAg proteins harbors an N-glycosylation site at position asparagine-146 (N146), which is partially utilized by the oligosaccharyltransferase [17,67], and hence, HBsAgS proteins are synthesized as unglycosylated p24 and N-glycosylated gp27 versions (Figure 1B). HBsAgS p24 and gp27 have identical transmembrane topologies and dimerize without preference for a specific pairing and form heterologous dimers with HBsAgM and HBsAgL [66]. Synthesis and secretion of HBsAgS SVPs do not depend on N-glycosylation at position N146 in the external loop region, in contrast to the formation and release of infectious HBV particles [67,68,69,70].
3.2. Topology of HBsAgM
The middle HBsAg protein has the same transmembrane topology as HBsAgS, and hence is partly glycosylated at N146 in the S-domain. Translocation of the preS2 domain of HBsAgM is mediated by the topologic signal TM1 located in the S-domain [71]. The translocation event across the ER membrane into the lumen allows the N-glycosylation of the asparagine-4 (N4) residue in the preS2 domain, which is always glycosylated [72], resulting in glycoproteins with a molecular weight of 33 kDa and 36 kDa (Figure 1B). In addition to the N-glycosylation site in the preS2 domain, the preS2 domain can be partially O-glycosylated, depending on the genotype and the presence of the threonine (T37) (Figure 1B) [73]. Similar to HBsAgS, HBsAgM proteins assemble into SVPs and can be secreted independently from other viral proteins [74,75,76,77]. HBsAgM, however, is not essential for virion morphogenesis and infectivity [78].
3.3. Topology of HBsAgL
The large HBsAg protein adopts two distinguished transmembrane topologies facilitating an internal or external location of the preS1/S2 domain (Figure 1A) [17,79,80,81]. The internal orientation allows preS1/S2 to interact with the viral capsid, a critical step in viral morphogenesis. The preS2 region of the HBsAgL protein serves as a possible spacer to facilitate conformational changes of the preS1/S2 domain [17,81,82]. During the maturation process, the preS1/S2 domain is translocated to adopt an external orientation, which is essential for virus attachment to the host cell through a specific interaction with heparan sulfate proteoglycan [34,35] and binding to the entry receptor [36,37]. In addition, the preS1 domain is myristoylated at the N-terminus, which is required for efficient HBV entry into hepatocytes (Figure 1B) [83,84]. The potential N- and O-glycosylation sites in the HBsAgL preS1/S2 domain are not utilized due to the cytosolic orientation of the preS1/preS2 domain after translation. HBsAgL molecules have molecular weights of 39 kD (p39) or 42kD (gp42) depending on the glycosylation status at position N146 in the S-domain (Figure 1B). Expression of HBsAgL in mammalian cells in the absence of HBsAgS and HBsAgM does lead to particle formation, but not secretion, and it is retained in post-ER and pre-Golgi compartments [85]. HBsAgL causes a dose-dependent inhibition of particle release if co-expressed with HBsAgS [86,87].
Taken together, the S-domain is shared by the HBV envelope proteins and defines the backbone of the particle due to the presence of the topogenic transmembrane regions, glycans at position N146, cysteine residues to form inter- and intra-molecular disulfide bonds, and the external loop region. The correct folding of the external loop defines the HBsAg-specific antigenic determinants.
4. Biochemical Properties of SVPs
The proportion of the HBsAgL, -M, and -S proteins differ between Dane particles, filaments, and SVPs generated during a natural infection. It is estimated that the envelope of Dane particles contains HBsAgL, HBsAgM, and HBsAgS at a ratio of approximately 3:2:5, and filaments at a ratio of 1:1:4. SVPs contain less HBsAgM compared to filaments with trace amounts of HBsAgL [46,83,88]. HBsAgS SVPs have a molecular weight of 2–4 × 106, and are composed of protein (75% by weight), carbohydrates (in form of glycoproteins) and lipids (25% by weight) [89]. Approximately 100 HBsAgS proteins assemble with lipids into lipoprotein particles, fifty HBsAgS dimers were identified in SVPs purified from sera of transgenic mice [49,89,90]. Three different regions of the S-domain contribute to the oligomerization of the HBsAg proteins, the cytosolic loop, TM2, and the luminal loop (Figure 3) [57]. The SVPs are compact particles with a reported density of 1.21 g/mL in caesium chloride (CsCl) compared to a density of infectious virions between 1.24 and 1.26 g/mL [23,91,92]. The compact structure of the SVPs is due to the large number of intra- and inter-molecular disulfide bonds within and between the S-domains of the individual HBsAg subunits [62,65,90,93,94,95]. Kinetic studies demonstrated that disulfide-linked HBsAgS dimers are formed in the ER, then the immature particle precursors are transported to a post-ER, pre-Golgi compartment, which excludes the enzyme “protein disulfide isomerase” and allows the formation of HBsAgS oligomers [96]. Intracellular HBsAgS particles contain high-mannose oligosaccharide chains, and after secretion, SVPs contain complex oligosaccharide chains with terminal sialic acid N-acetylglucosamine residues representing glycosylation patterns conforming with the HBsAg movement from the ER through the Golgi cisternae [12,67,97].
Cryo-EM studies and biophysical analyses of the SVPs produced in cell culture or purified from sera of transgenic mice demonstrates a tight HBsAgS protein–lipid interaction. The lipid composition of HBsAgS SVPs purified from the plasma of several HBV carriers showed that phospholipids, in particular, phosphatidylcholine is a major lipid class; with palmitic, stearic, oleic, and linoleic acids being the major fatty acid components [89]. Consistently, SVPs produced in human hepatoma cell lines predominantly contain phospholipids, with phosphatidylcholine being the dominant component [98]. The tight protein–lipid interaction restricts lipid movement suggesting that the lipids are not aligned in a typical bilayer structure. HBsAg particles seem to contain the lipids in an unusual arrangement, with the lipids being closely intercalated with the proteins, located on the particle surface, and are hence likely arranged in a lipid monolayer [99,100]. HBsAg proteins contain a high content of alpha helices (45%–52%), which are lipid-associated, and provide an arrangement which allows the disposal of the loop regions in the particle interior or on its surface [100,101]. Assessing yeast (Hansenula polymorpha)-derived SVPs, the particles have an ordered and rigid lipid interface, possibly organized as a phospholipid monolayer, with a hydrophobic and fluid inner core. HBsAgS proteins penetrate into the lipid core, with parts of the protein protruding from the particle surface [89,102,103]. The lipids contribute to the antigenic activity of HBsAg particles [100], likely by stabilizing the proper helical structure of the HBsAg proteins and the conformation of their hydrophilic region, which contains the antigenic site. Removal of lipids decreases the helical content and reduces the antigenic activity of the particles [100]. S-domain antigenic structures seem to be strongly impacted by the lipid–protein interface, which defines the formation of alpha-helical structures and accommodates the arrangement of proper disulfide bonding patterns and the correct folding of HBsAg.
5. The First Vaccine Generation Against HBV: Vaccine Derived from Patient Plasma
The first vaccine against HBV was based on the unique approach to purify the HBsAg immunogen directly from the blood of asymptomatic HBV carriers [104]. The identification of the HBsAg as an important immune target was based on observations that anti-HBs human immunoglobulins conferred passive protection against hepatitis B [105,106]. Consistently, active immunization studies with HBsAg protected chimpanzees from hepatitis B [29,107,108], and clinical studies with recipients of blood transfusion indicated that patients who developed anti-HBs were less likely to develop hepatitis [109]. Patients on a renal dialysis unit and staff were less likely to acquire hepatitis if they had anti-HBs antibodies [110]. The first reported vaccination against hepatitis B was performed with a diluted, heat-inactivated HBsAg-positive serum in children, then the children challenged with infectious HBV, resulting in an incomplete but considerable protection [111]. For the generation of a proper vaccine, methodologies were developed to purify HBsAg using isopycnic banding and rate-zonal separation [26,27,112,113], affinity columns [114], adsorption onto colloidal silicate and desorption, differential polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitations and gel filtration [27]. To minimize the risk of infections due to the presence of hepatitis B virions, the vaccine preparations were inactivated with formalin [112,114]. Plasma was from “ad” and “ay” donors, the SVPs mixed, then adsorbed onto aluminium hydroxide, or used in the absence of an adjuvant [26,27]. The pilot vaccines demonstrated that the plasma-derived SVPs induced anti-HBs antibody responses in different animal models [26]. Safety testing in chimpanzees, which are susceptible to HBV infection, did not provide any evidence of hepatitis in chimpanzees, which had received the inactivated plasma-derived SVP vaccine. Vaccinated chimpanzees were protected from a challenge with infectious HBV and did not show any indication of a hepatitis B infection [26,108].
The use of the first plasma-derived vaccines, Heptavax-B (Merck Sharp and Dohme, MSD) and Hevac-B (Institute Pasteur) provided good protection rates, and they were safe [114,115,116,117]. Depending on the purification and inactivation procedure, the composition of the plasma-derived HBsAg SVPs can vary, and they may or may not contain small quantities of HBsAgM, providing the preS2 domain in addition to HBsAgS. The Hevac-B vaccine contained 1%–2% HBsAgM. In contrast, the Heptavax-B vaccine did not contain preS2 proteins due to a treatment step with proteases, which however did not interfere with HBsAg-specific antigenicity [118,119,120]. Similar serum-derived vaccines were then produced from various manufacturers, such as Hepavax-B (Green Cross, Korea), Hepaccine-B (Cheil, Korea), and GCC VAC (Green Cross Corporation, Osaka) (Table 1). Limitations given by the supply of human plasma from chronically infected patients, and the risk associated with human-derived products due to contaminating proteins and the potential presence of other pathogens transmitted by blood, in particular a non-A non-B hepatitis virus, confronted the use of human plasma-derived HBsAg SVP vaccines [121,122,123]. Safety concerns about products from human sources, together with the advances in recombinant DNA technology and biotechnology, led to the development of recombinant hepatitis B vaccines.

Table 1.
Key vaccines against HBV utilizing hepatitis B surface antigens.
6. The Second Vaccine Generation Against HBV: Yeast-Derived Recombinant HBsAgS SVPs
The identification of HBsAgS as the major HBV envelope protein of plasma-derived HBsAg SVPs and encoding the major antigenic determinants prompted the expression of HBsAgS in mammalian cell lines and yeast [13]. Yeast cell strains (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris, Hansenula polymorpha) were developed which express HBsAgS in high quantities. HBsAgS SVPs are isolated from yeast cell extracts with a sedimentation rate and buoyant density similar to particles from human samples or expressed in cell culture [138,139,140]. Yeast-derived SVPs have reduced antigenic reactivity compared to SVPs derived from human plasma but immunization studies established that yeast-derived SVPs induce anti-HBs antibody responses, which provide protection of immunized chimpanzees following a challenge with HBV. Importantly, the yeast-derived HBsAgS SVP vaccine of the “adw” subtype conferred protection against HBV subtypes “adr” and “ayw” [28]. Clinical trials using different age groups, healthy individuals, and special target populations confirmed that the yeast-derived vaccine is highly immunogenic, and generated qualitative and quantitative anti-HBs antibody responses with a protective efficacy similar to the plasma-derived vaccines [141]. The vaccines achieved 99% seroprotection rates in healthy children and adolescents but approximately 5%–7% of the adult population are non-responders and the rate can increase to 70% in elderly persons and in special risk groups [13,129,136,142]. Also, genetically determined resistance may contribute to non-responsiveness to HBsAgS SVP vaccines [143,144,145]. At the molecular level, yeast-derived HBsAg SVPs are not N-glycosylated at the N146 position within the S-domain, in contrast to SVPs produced in mammalian cell lines and harvested from the cell culture medium, or isolated from the blood of chronic hepatitis B patients. HBsAgS expressed in yeast generate SVPs [146], but experimental evidence indicates that the SVP are not formed within the yeast cell and generated during the down-stream purification procedures. HBsAgS expression in Pichia pastoris showed that HBsAgS assembles at the ER into multi-layered lamellar structures [147]. Monitoring SVP assembly during the purification procedure demonstrated that particulate structures are formed after eluting HBsAg bound to colloidal silica. Irregular SVP-like structures were visualized, and morphological changes observed after pH adjustment (colloidal silica eluate pH 10.8 to 8.0), ion-exchange, and size-exclusion chromatography. The monodispersity improved after potassium thiocyanate (KSCN) treatment, also the SVPs have a more-fine structured surface [148,149,150]. The correct disulfide bonding is the molecular basis for the formation of native epitopes as probed with an anti-HBs antibody [151]. Lipid-containing SVPs undergo KSCN-induced maturation by the formation of intra- and inter-molecular disulfide bonds to generate fully disulfide-bonded SVPs, resulting in a decreased conformational flexibility of HBsAgS in the matured particles [149,152]. Restricted conformational flexibility is possibly required for the formation of native HBsAg-specific antigenic structures, which allows epitope recognition by anti-HBs antibodies, and importantly in eliciting neutralizing antibodies [149]. The particle size (diameter) of yeast-derived SVPs is consistent with the data obtained from mammalian-cell-derived SVPs, but the size distribution can vary depending on the SVP maturation level [148,153]. Yeast-derived SVPs have a high content of alpha-helical structures, and the movement of the HBsAgS proteins is restricted due to the tight association with the lipid membrane [102,154]. Similarly, the lipid composition is characterized by high levels of phospholipids, in particular, phosphatidylcholine consistent with mammalian cell-derived SVPs [154,155,156]. No significant differences in the anti-HBs response induced by the plasma-derived or yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccines was observed [123,157].
The widely distributed, yeast cell-derived hepatitis B vaccines, Engerix®-B (GlaxoSmithKline) and Recombivax HB™ (Merck Sharp and Dohme) use aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxyphosphate sulfate as adjuvanting substances, respectively. Aluminium-based adjuvants are widely used and activate the inflammasome pathway [158,159,160]. The adsorption of HBsAgS SVPs on aluminium hydroxide is mediated by binding of the phosphate groups of the HBsAgS SVPs phospholipids with hydroxyl groups of aluminium hydroxide through a ligand-exchange mechanism [161,162]. After vaccine administration, the SVPs are eluted from the aluminium adjuvant upon contact with the interstitial fluid [163,164]. Adsorption of HBsAgS SVPs derived from Hansenula polymorpha on an aluminium gel followed by a mild desorption step using competing phosphate anions demonstrated that the conformation of the HBsAgS protein is retained, and consistently, no significant changes of the lipid core and lipid membrane surface of the SVPs were identified [165]. To improve immunization outcomes in adults at risk of a hepatitis B infection, HBsAgS SVPs synthesized in Hansenula polymorpha are formulated with a Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR 9) agonist, cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG-ODN) 1018 as an adjuvant (Heplisav-B™, Dynavax Technologies). TLR9 is a pattern recognition receptor of the innate immune system, which induces the production of cytokines such as interleukin-12 and interferon-alpha to stimulate the adaptive immune response [134,166]. Heplisav-B™ induced earlier seroprotection rates allowing a two-dose regimen compared to three doses required for the Engerix-B vaccine, but it caused more injection-site reactions [134].
The ability of HBsAgS subunits expressed in yeast cells to form SVPs during down-stream procedures, and to reproduce native antigenic structures, allowed the development of a highly successful preventative vaccine. The advancement of the vaccine adjuvant technology allowed new HBsAgS SVP formulations and demonstrated strategies to enhance the magnitude of the anti-HBs immune response with immediate practical applications
7. Third Generation Vaccine Concepts against HBV
The development of third-generation HBsAg vaccines providing the S-domain in combination with preS1 and/or preS2 sequences was directed by the objective to enhance the protective efficacy of the human plasma-derived vaccines (which consisted predominantly of HBsAgS subunits), and the second-generation recombinant yeast-derived vaccines (which consisted exclusively of HBsAgS subunits). The third-generation vaccines attracted interest to improve the immunization outcomes in persons who do not respond to the conventional HBsAgS vaccines [13]. The importance of the preS1 domain for viral entry and assembly makes it a potential target for vaccine development, anti-preS1 antibodies protected chimpanzees from HBV infection [167]. PreS1/S2 sequences provide additional B-cell epitopes to generate protective antibody responses [167,168,169] and may also serve as a T cell immunogen to overcome the non-responsiveness to the S-domain [170,171,172]. Small quantities of HBsAgL present in the HBsAgS vaccine induced significant T-cell activation measured as in vitro proliferation specific for the preS domain [172]. In addition, preS2 peptide vaccines protect chimpanzees against a challenge with HBV [169], and the use of SVPs with preS1 and/or preS2 sequences generated anti-HBs immune responses in mouse strains, which are non-responsive to the standard yeast-derived HBsAgS SVP vaccine [173].
For the generation of third-generation vaccines, different yeast expression systems and mammalian cell lines were utilized to synthesize SVPs composed of HBsAgM and HBsAgL proteins in the presence or absence of HBsAgS. Utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the expression of a modified HBsAgM in the absence of HBsAgS allowed the formation of SVPs. The modified HBsAgM protein (P31c) contains a deletion of six amino acids to make it resistant to trypsin-like proteases in S. cerevisiae. The HBsAgM-P31c proteins assembled into SVPs with a diameter of approximately 20 nm and retained HBsAg antigenicity [174,175]. Immunization studies in BALB/c mice and guinea pigs demonstrated that anti-HBs antibody titres can be induced comparable to the plasma-derived Heptavax-B vaccine (MSD). Also, anti-preS2 antibodies were detected in animals immunized with the HBsAgM-P31c SVP vaccine. In contrast to the yeast-derived HBsAgS vaccine, the HBsAgM-P31c SVPs are glycosylated with N- and O-linked glycans located in the preS2 domain [174,175], which may facilitate interactions with lectin receptors expressed by antigen-presenting cells. In an independent study, HBsAgM SVPs induced anti-S and anti-preS2 antibodies in healthy young adults but the anti-S response was lower than in the patient group who received HBsAgS SVPs, and hence, the HBsAgM vaccine failed to achieve the objective of inducing an early and strong anti-S and anti-preS2 immune response [176]. The HBsAgM-P31c SVPs, however, were used to formulate a new vaccine (TGP-943, Takeda) and demonstrated a protective effect in the chimpanzee model and also generated protective levels of anti-preS2 antibodies in humans [177,178]. Clinical studies demonstrated that the vaccine TGP-943 induced both anti-S and anti-preS2 antibodies, approximately 50% of non-responders became positive for either or both anti-S and anti-preS2 [131].
For the development of a HBsAgL-based vaccine, HBsAgL expression during the exponential S. cerevisiae growth phase generated high levels of HBsAgL but did not assemble into the typical 20–25 nm SVPs, but generated a polydisperse population of small (2–3 nm) and large aggregates (15–50 nm) [179]. HBsAgL was glycosylated by N- and O-linked glycans in the preS1/S2 domain indicating that HBsAgL accessed the lumen of the ER of the yeast cell and caused morphological changes in the ER compartment [179,180]. The presence of N-linked and O-linked glycans in the preS1/S2 domain of yeast-derived HBsAgL proteins is in contrast to preS1/preS2 of HBsAgL isolated from human plasma due to the cytoplasmic exposure of the preS1/S2 domain during the orderly and regulated process of virion morphogenesis [83,88,179,180]. Particle formation using S. cerevisiae could be rescued providing an N-terminal signal sequence, which possibly allows a correct entry into the secretory pathway, and after purification from the yeast lysate, spheres and filaments with a diameter of 23 nm were obtained, the length of the filaments was in the range of 40 to 120 nm, visualized by negative staining electron microscopy. HBsAgL proteins expressed in the absence of the signal sequence did not form such an ordered structure [181]. The visualization of the particles by atomic force microscopy (AFM) demonstrated a heterogeneous population of rugged spherical forms between 50 and 500 nm in diameter [182]. Immunization of mice with the yeast-derived HBsAgL SVPs elicited anti-S, anti-preS2, and anti-preS1 antibodies, and the effective dose (ED50) for anti-S and anti-preS2 antibodies were similar to those achieved with HBsAgM particles [182]. Using an alternative strategy, hybrid SVPs were generated in S. cerevisiae composed of HBsAgS and a modified HBsAgL (HBsAgL*). HBsAgL* contains a truncated preS1/S2 region with sequences relevant for the hepatocyte-binding site and immunologically important B- and T-helper epitopes but does not contain sites for proteolysis and the binding site for polymerized human serum albumin. The hybrid SVPs contained HBsAgS and HBsAgL* at a ratio of 75:25 [176]. The immunization of BALB/c mice with HBsAgL*/HBsAgS SVPs generated anti-S and anti-preS1 antibodies. The anti-S titers were similar to those found after immunization with Engerix B. Immunizations of African Green Monkeys (Ceropithecus aethiops) using HBsAgL*/HBsAgS SVPs induced anti-S, anti-preS2, and anti-preS1 antibodies [176]. Safety and immunogenicity studies in young, healthy adult persons, and in poor responders to hepatitis B vaccines demonstrated that the presence of the preS1/preS2 domain did not enhance the anti-S response compared to the control Engerix B vaccine (GSK) [183,184], in spite of the preS1 sequence present as a strong T-cell immunogen [170]. The HBsAgL*/HBsAgS vaccine induced anti-preS1 antibodies in a young, healthy adult person cohort, and possibly provides additional neutralizing activity [183].
With the availability of mammalian cell culture technologies, recombinant hepatitis B vaccines composed of SVPs have been developed containing the HBsAgS and HBsAgM (GenHevacB, Sanofi Pasteur Vaccins) and the additional HBsAgL subunits (Sci-B-Vac, VBI Vaccines; Hepacare, Medeva Pharma) (Table 1). Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells (GenHevacB, Sci-B-Vac) [120,136] or murine cells (C1271) (Hepacare, Medeva Pharma) [137] were used to generate the vaccines. The GenHevac B vaccine is composed of HBsAgS/HBsAgM SVPs at a ratio 80:20, and compared in a clinical setting to the human plasma-derived Hevac B vaccine, both vaccines induced antibodies to the HBsAg in >90% of the participants (497 persons in the age range of 18–40 years). Compared to the plasma-derived vaccine, the recombinant vaccine produced early and high levels of anti-preS2 antibodies, which may provide an additional advantage in prevention of a HBV infection [120,185].
For Sci-B-Vac, the complete HBsAg gene encoding HBsAgS, -M, and -L, including native promoter, enhancer, and poly(A) signal, were used to establish a producer CHO cell line, which contains more than 100 HBsAg coding copies/cell [173]. Protein analysis of the secreted SVPs revealed the presence of all three HBsAg proteins and its glycosylated isoforms (HBsAgS p24 and gp27; HBsAgM gp33 and gp36, HBsAgL p39 and gp42). Sci-B-Vac induced anti-S and anti-preS1 antibody responses in BALB/c mice, and also in mouse strains which are resistant to immunizations with HBsAgS SVPs and/or HBsAgM [136,173]. Sci-B-Vac demonstrated an excellent safety record in clinical studies, which included healthy individuals, children, and neonates. In comparison with yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccines, more than 50% of vaccinees receiving Sci-B-Vac developed earlier seroprotection against HBV [136]. Sci-B-Vac performed superior to yeast-derived HBsAgS vaccines in specific patient risk groups and provided vaccine boosts in persons with no or low response to preceding immunizations with the conventional yeast-derived HBV vaccine. Specific risk groups including patients with renal failure, with overweight and immune-suppressed patients responded with higher seroprotection rates compared to conventional yeast derived vaccines. The Sci-B-Vac vaccine is widely used in Israel and licensed in various countries [136].
8. HBsAgS SVPs as Platforms for Medically Relevant Antigenic Sequences
SVPs display an array of antigenic sequences to the innate immune system facilitating the subsequent activation of the adaptive system [8,10,186,187]. The ability to accept foreign inserts into the SVP structure provides the basis for advanced delivery platforms for medically relevant sequences, such as malaria antigens. Chimeric SVPs can be constructed from viral capsid proteins, such as capsids from HBV, human papilloma virus, and Qβ phage that have been re-engineered to express foreign antigenic sequences at a high antigenic density [8,187]. Similarly, SVPs derived from the HBV envelope assemble into highly compact lipid-containing particles, and have been exploited as carrier platforms for foreign antigenic sequences by introducing N- or C-terminal extensions [188,189,190,191], N-terminal extensions in addition to substitutions of the HBsAgS N-terminal sequence [192], by replacing the HBsAgM preS2-domain [193,194], by insertions into the external loop region including replacing antigenic determinants [195,196,197,198,199,200,201], or by replacing HBsAgS-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitopes [202] (Table 2). The insertion of a poliovirus-specific epitope with a length of 11 amino acids into the external loop region of HBsAgS allowed the expression of the chimeric, assembly and secretion competent HBsPolioAg proteins in a mouse cell line [201,203]. The chimeric SVPs contained glycosylated and non-glycosylated HBsPolioAg subunits and formed particles with 22 nm in diameter, similar to wild-type HBsAgS proteins. HBsPolioAg SVPs were used in mouse immunization studies and induced anti-poliovirus peptide-specific antibodies with neutralizing activity and a low level of anti-HBs antibodies, possibly due to a partial loss of HBsAg-specific antigenicity. The co-expression of both wild-type HBsAgS proteins and HBsPolioAg generated hybrid SVPs composed of both proteins, which facilitated the induction of anti-HBs and anti-poliovirus epitope antibodies [203]. Similar studies inserting heterologous B-cell epitopes in an exposed site in the external loop region reduced HBsAg-specific antigenicity depending on the length of the insert, but the recombinant proteins retained the ability to induce anti-HBs antibodies [195,196,198,204]. Chimeric SVPs composed of subunits distinguished by the number of inserted epitope repeats from the Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite (CS) protein demonstrated that the CS epitope number influenced the activity of the anti-CS epitope antibodies. The effect of the epitope-specific density on the antibody quality may instruct chimeric SVP designs to optimize immunological outcomes and vaccine efficacy [195]. The RTS,S/AS01 vaccine (Mosquirix™) is the most advanced vaccine with a heterologous antigenic sequence arrayed on SVPs. The RTS,S vaccine is based on the fusion of a Plasmodium falciparum CS polypeptide of 189 aa with selected tandem repeats of B-cell and T-cell epitopes to the HBsAgS N-terminus (RTS) (Figure 1C). The CS-protein is expressed on the Plasmodium sporozoite surface, and essential for hepatocyte invasion and for establishing a productive infection, and therefore an important target for the development of a pre-erythrocyte vaccine [205]. The genes for HBsAgS and RTS are integrated into the genome of S. cerevisiae and co-expressed at a ratio RTS:HBsAgS of 1:4 to generate non-glycosylated mixed (hybrid) lipoprotein particles [190,191]. The RTS,S vaccine is well-tolerated, safe, and immunogenic, and is considered to be the first advanced vaccine against the pre-erythrocyte stage of the malaria parasite, and induces both anti-HBs and anti-CS protein antibodies. The anti-malaria RTS,S/AS01 vaccine in children of five months or older reduced clinical malaria episodes by 39% and life-threatening severe malaria episodes by 29%. The vaccine is licensed in three African countries [5,6,206]. Mosquirix™ (RTS,S/AS01) is adjuvanted with AS01, which is a liposome formulation and contains monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) and the saponin QS-21. RTS,S in combination with AS01 resulted in higher anti-CS protein immune responses than AS02, which is an oil-in-water emulsion-based adjuvant [7,205,206,207]. To enhance the vaccine efficacy against malaria, a RTS,S-related vaccine (R21) with an increased proportion of CS-polypeptides was developed. CS-polypeptide-HBsAg fusion proteins were expressed in Pichia pastoris, and SVPs were obtained after caesium chloride density ultracentrifugation and gel filtration [208]. The R21 vaccine induces a sterile protection in mice against a challenge with transgenic sporozoites. The induction of anti-HBs antibodies is compromised, possibly because the high content of the CS-polypeptide blocks access to the HBsAg external loop region, which contains the antigenic “a”-determinant [208].

Table 2.
Selection of chimeric HBsAg SVP platforms and vaccines.
Preexisting immunity against vaccine vectors can impose a negative effect on the outcome of the vaccination [210,211,212,213]. HBsAgS SVPs are widely used in immunization programs to combat HBV, and therefore, the use of chimeric SVPs could pose a problem for recipients previously immunized against hepatitis B. Immunization studies in mice using chimeric SVPs with a foreign epitope inserted into the external loop of HBsAgS or fused to the N-terminus of HBsAgS demonstrated that pre-existing anti-HBs antibodies do not compromise the immunogenicity of the foreign antigenic sequence presented by the chimeric HBsAgS SVPs [214,215]. Consistently, clinical studies with human volunteers to assess the RTS,S malaria vaccine did not provide any evidence that a pre-existing anti-HBs status prevented an anti-CS-protein immune response [190]. In relation to a HBV chronic carrier status and the use of the RTS,S vaccine, there was no evidence that chronic HBV carriers (HBsAg positive) and HBsAg-negative individuals respond differently regarding an antibody response to the CS-protein [216].
9. Enhancement of Platform Immunogenicity through Biochemical Modifications
Based on the importance of SVPs as medical tools and platforms for the presentation of native viral antigenic sequences, it is critical to understand their immunogenicity in relation to antigen structure in order to enhance or to modulate their immunogenicity. Depending on the SVP type, targeted biochemical modifications of the SVP subunits may allow the generation of SVP variants with enhanced immunogenicity. HBsAgS SVPs are glycosylated lipoprotein particles and are stabilized by extensive intra- and inter-molecular disulfide bonds, which allows targeted modifications of the glycan content and level of disulphide bonding.
Changing disulfide bonding impacts on antigen processing and epitope selection by modifying the conformational flexibility [217]. The three-dimensional structure guides processing and presentation of T helper (Th) and CTL epitopes, and subtle changes in antigen structure can modulate T cell responses due to qualitative and quantitative differences in protein processing [217,218,219,220]. Distinct Th cell epitope profiles emerged from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 molecules after destabilizing the three-dimensional structure as a consequence of deleted cysteine residues [221]. In an attempt to enhance immunogenicity, HBsAgS SVPs with a reduced level of disulfide bonds were generated. The biochemically modified SVPs showed a higher protease sensitivity, potentially due to introducing structural changes associated with enhanced cellular immunogenicity [65]. Altering SVP structure may represent an attractive strategy to modulate proteolytic sensitivity to influence antigen processing and promoting an enhanced immune response and/or a changed hierarchy of epitope presentation [218,222].
Manipulation of protein glycosylation represents an alternative strategy to promote antigen internalization and antigen presentation via MHC class I and class II molecules to enhance the adaptive immune responses [223,224]. The glycosylation status and glycan density of the immunogen impacts on its interaction with antigen-presenting cells and recognition by lectins [224]. Glycan-mediated interactions with immunocompetent cells impact on protein uptake and can enhance or modulate cell-mediated and humoral immune responses [225,226,227,228,229]. Contrarily, glycans can shield protein epitopes to evade recognition by antibodies and can block antigen processing [230]. Mannosylation provided an efficient strategy to improve uptake and processing of a SVP derived from the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus [225]. Consistently, mannosylated solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with HBsAg induced stronger cellular responses than nanoparticles devoid of mannose [229]. Mutant HBsAgS subunits with additional N-glycosylation sites assembled into hyperglycosylated SVP. Antigenic fingerprints indicated that additional glycans do not extensively shield HBsAg-specific antigenic sites. Immunization studies demonstrated that the hyperglycosylated SVPs induced earlier and longer-lasting antibody responses than hypoglycosylated SVPs or wild type SVPs [231]. The ability of biochemically modified SVPs to promote immune responses possibly due to differences in their glycosylation-related interaction with cells of the innate immune system illustrates approaches for the design of immunogens with superior immunological characteristics.
10. Concluding Remarks
The development of preventative vaccines against hepatitis B resulted in remarkable advances in reducing HBV associated liver diseases. However, chronic hepatitis B is still difficult to control due to continuous viral replication driven by the episomal cccDNA present in the nuclei of infected hepatocytes. Novel strategies to generate vaccines based on structurally modified subunits to enhance immunogenicity and/or to modify antigen processing to change the hierarchy of epitope presentation may represent a pathway to overcome chronic viral infections or may complement a vaccine based on native proteins [65,218,224,225,226,231]. HBsAgS SVPs have been used as carrier platforms for various antigenic sequences to induce anti-foreign humoral and cellular immune responses [8,186]. One of the most advanced chimeric vaccines with a foreign antigenic sequence arrayed on a particulate carrier is based on the HBsAgS backbone fused to a P. falciparum CS-polypeptide [5,6]. For the design of next generation vaccines with therapeutic capabilities, formulations based on antigen combinations, such as mixtures of HBsAgS SVPs and SVPs composed of the HBV nucleocapsid antigen (HBcAg), may allow the induction of broad CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses suitable for therapeutic outcomes [232]. Alternatively, the assessment of synergistic effects between biochemically modified immunogens and adjuvant compounds possibly represent an avenue for the generation of optimized vaccines and delivery platforms, which may be suitable for therapeutic applications to overcome established chronic infections.
Author Contributions
H.-J.N. wrote the original draft version; J.K.-T.H. and B.J.-R. edited and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
HJN was partly supported by a grant awarded by the Australian Centre for HIV and Viral Hepatitis Research (ACH2).
Conflicts of Interest
The author H.-J.N. of this publication has an equity interest in, and serves as a consultant to ClearB Therapeutics. ClearB Therapeutics had no role in the design and writing of the review article.
References
- Huzair, F.; Sturdy, S. Biotechnology and the transformation of vaccine innovation: The case of the hepatitis B vaccines 1968–2000. Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 64, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millman, I. The development of the hepatitis B vaccine. In Hepatitis B. The Virus, the Disease, and the Vaccine; Millman, I., Eisenstein, T.K., Blumberg, B.S., Eds.; Plenum Publishing Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. Key Facts; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Prevention and Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection. Framework for Global Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Adepoju, P. RTS, S malaria vaccine pilots in three African countries. Lancet 2019, 393, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuerman, L. RTS, S malaria vaccine could provide major public health benefits. Lancet 2019, 394, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Nussenzweig, V.; Nussenzweig, R.; Vekemans, J.; Leach, A. From the circumsporozoite protein to the RTS, S/AS candidate vaccine. Hum. Vaccines 2010, 6, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Zha, L.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; Bachmann, M.F. Major findings and recent advances in virus-like particle (VLP)-based vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 34, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sagaseta, J.; Malito, E.; Rappuoli, R.; Bottomley, M.J. Self-assembling protein nanoparticles in the design of vaccines. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Recent advancements in combination subunit vaccine development. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, D.-S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.-L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection. Virology 2015, 479–480, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H. Medical virology of hepatitis B: How it began and where we are now. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A. Genotypes and genetic variability of hepatitis B virus. Intervirology 2014, 57, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norder, H.; Couroucé, A.M.; Coursaget, P.; Echevarria, J.M.; Lee, S.D.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Robertson, B.H.; Locarnini, S.; Magnius, L.O. Genetic diversity of hepatitis B virus strains derived worldwide: Genotypes, subgenotypes and HBsAg subtypes. Intervirology 2004, 47, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagle, B.L.; Bouchard, M.J. Role of HBx in hepatitis B virus persistence and its therapeutic implications. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 30, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruss, V. Hepatitis B virus morphogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bouvier, G.L. The heterogeneity of Australia antigen. J. Infect. Dis. 1971, 123, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, W.H.; Mundon, F.K.; Russell, P.K. Detection of additional antigenic determinants of hepatitis B antigen. J. Immunol. 1972, 109, 842–848. [Google Scholar]
- Jazayeri, S.M.; Alavian, S.M.; Dindoost, P.; Thomas, H.C.; Karayiannis, P. Molecular variants of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). In Viral Hepatitis, 4th ed.; Thomas, H.C., Lok, A.S.F., Locarnini, S.A., Zuckerman, A.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Désiré, N.; Ngo, Y.; Franetich, J.-F.; Dembele, L.; Mazier, D.; Vaillant, J.-C.; Poynard, T.; Thibault, V. Definition of an HBsAg to DNA international unit conversion factor by enrichment of circulating hepatitis B forms. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 718–726. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto, M.R. A new role for an old marker, HBsAg. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreesman, G.R.; Hollinger, F.B.; Suriano, J.R.; Fujioka, R.S.; Brunschwig, J.P.; Melnick, J.L. Biophysical and biochemical heterogeneity of purified hepatitis B antigen. J. Virol. 1972, 10, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, D.S.; Cameron, C.H.; Briggs, M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen associated hepatitis. Lancet 1970, 1, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydell, G.E.; Prakash, K.; Norder, H.; Lindh, M. Hepatitis B surface antigen on subviral particles reduces the neutralizing effect of anti-HBs antibodies on hepatitis B viral particles in vitro. Virology 2017, 509, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilleman, M.R.; Bertland, A.U.; Buynak, E.B.; Lampson, G.P.; McAleer, W.J.; McLean, A.A.; Roehm, R.R.; Tytell, A.A. Clinical and laboratory studies of HBsAg vaccine. In Viral Hepatitis; Vyas, G.N., Cohen, S.N., Schmid, R., Eds.; The Franklin Institute Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1978; pp. 525–537. [Google Scholar]
- Maupas, P.; Goudeau, A.; Coursaget, P.; Drucker, J.; Barin, F.; André, M. Immunization against hepatitis B in man: A pilot study of two years’ duration. In Viral Hepatitis; Vyas, G.N., Cohen, S.N., Schmid, R., Eds.; The Franklin Institute Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1978; pp. 539–556. [Google Scholar]
- McAleer, W.J.; Buynak, E.B.; Maigetter, R.Z.; Wampler, D.E.; Miller, W.J.; Hilleman, M.R. Human hepatitis B vaccine from recombinant yeast. Nature 1984, 307, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.L.; Maynard, J.E.; Le Bouvier, G.L. Viral subtypes and cross-presentation in hepatitis B virus infections of chimpanzees. Intervirology 1974, 3, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, K. Complete and incomplete hepatitis B virus particles: Formation, function, and application. Viruses 2017, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selzer, L.; Zlotnick, A. Assembly and release of hepatitis B virus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureau, C.; Salisse, J. A conformational heparan sulfate binding site essential to infectivity overlaps with the conserved hepatitis B virus a-determinant. Hepatology 2013, 57, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruss, V.; Vieluf, K. Functions of the internal pre-S domain of the large surface protein in hepatitis B virus particle morphogenesis. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6652–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Gripon, P.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, C.M.; Gruen-Bernhard, S.; Glebe, D. Role of glycosaminoglycans for binding and infection of hepatitis B virus. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, A.R.; Kent, S.B.H.; Strick, N.; Parker, K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell 1986, 46, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.; Prange, R. Chaperone action in the posttranslational topological reorientation of the hepatitis B virus large envelope protein: Implications for translocational regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5199–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.Y.; Yang, G.H.; Ryu, C.J.; Hong, H.J. Molecular chaperone GRP78/BiP interacts with the large surface protein of hepatitis B virus in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2784–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Löffler-Mary, H.; Werr, M.; Prange, R. Sequence-specific repression of cotranslational translocation of the hepatitis B virus envelope proteins coincides with binding of heat shock protein Hsc70. Virology 1997, 235, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieler, J.T.; Prange, R. Involvement of ESCRT-II in hepatitis B virus morphogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.; Döring, T.; Prange, R. Hepatitis B virus maturation is sensitive to functional inhibition of ESCRT-III, Vps4, and γ2-Adaptin. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9050–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Sorensen, E.M.; Naito, A.; Schott, M.; Kim, S.; Ahlquist, P. Involvement of host cellular multivesicular body functions in hepatitis B virus budding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10205–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Himmelsbach, K.; Ren, H.; Boller, K.; Hildt, E. Subviral hepatitis B virus filaments, like infectious viral particles, are released via multivesicular bodies. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3330–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairez, R.; Hollinger, F.B.; Melnick, J.L.; Dreesman, G.R. Biophysical properties of purified morphologic forms of hepatitis B antigen. Intervirology 1974, 3, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, J.M.; Chen, S.; Roseman, A.M.; Butler, P.J.G.; Crowther, R.A. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen from subviral tubes determined by electron cryomicroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 390, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, K.A.; Wieland, S.F.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Gerin, J.L.; Chisari, F.V.; Yeager, M. Native hepatitis B virions and capsids visualized by electron cryomicroscopy. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, P. Cryo-EM structure of native spherical subviral particles isolated from HBV carriers. Virus Res. 2019, 259, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.J.C.; Beales, L.; Blond, D.; Simon, M.N.; Lin, B.Y.; Chisari, F.V.; Stuart, D.I.; Rowlands, D.J. Hepatitis B small surface antigen particles are octahedral. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14783–14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, C.W.; Liu, C.-C.; Levinson, A.D. Plasmid-directed synthesis of hepatitis B surface antigen in monkey cells. Moll. Cell. Biol. 1983, 3, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Yansura, D.; Levinson, A.D. Direct expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in monkey cells from an SV40 vector. DNA 1982, 1, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarty, A.M.; Hoyer, B.H.; Shih, J.W.K.; Gerin, J.L.; Hamer, D.H. Expression of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene in cell culture by using a simian virus 40 vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 2606–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.F.; Pourcel, C.; Rousset, S.; Chany, C.; Tiollais, P. Excretion of hepatitis B surface antigen particles from mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 4549–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, B.K.; Choi, E.-C. Physiochemical properties of recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen expressed in mammalian cell (C127). Arch. Pharm. Res. 1998, 21, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, B.E.; Lingappa, V.R.; Ganem, D. Hepatitis B surface antigen: An unusual secreted protein initially synthesized as a transmembrane polypeptide. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1986, 6, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, B.E.; MacRae, D.R.; Lingappa, V.R.; Ganem, D. Multiple topogenic sequences determine the transmembrane orientation of hepatitis B surface antigen. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1987, 7, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffner, S.; Gerstenberg, N.; Patra, M.; Ruibal, P.; Orabi, A.; Schindler, M.; Bruss, V. Domains of the hepatitis B virus small surface protein S mediating oligomerization. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02232-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirk, H.J.; Thornton, J.M.; Howard, C.R. A topological model for hepatitis B surface antigen. Intervirology 1992, 33, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berting, A.; Hahnen, J.; Kröger, M.; Gerlich, W.H. Computer-aided studies on the spatial structure of the small hepatitis B surface protein. Intervirology 1995, 38, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komla-Soukha, I.; Sureau, C. A tryptophan-rich motif in the carboxyl terminus of the small envelope protein of hepatitis B virus is central to the assembly of hepatitis delta virus particles. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4648–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulij, W.P.; de Wit, P.L.M.; Sünnen, C.M.G.; van Roosmalen, M.H.; Petersen-van Ettekoven, A.; Cooreman, M.P.; Heijtink, R.A. Localization of a unique hepatitis B virus epitope sheds new light on the structure of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangold, C.M.T.; Unckell, F.; Werr, M.; Streeck, R.E. Analysis of intermolecular disulfide bonds and free sulfhydryl groups in hepatitis B surface antigen particles. Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangold, C.M.T.; Streeck, R.E. Mutational analysis of the cysteine residues in the hepatitis B virus small envelope protein. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4588–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, C.M.T.; Unckell, F.; Werr, M.; Streeck, R.E. Secretion and antigenicity of hepatitis B virus small envelope proteins lacking cysteines in the major antigenic region. Virology 1995, 211, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, W.S.; Hyakumura, M.; Yuen, L.; Warner, N.; Locarnini, S.; Netter, H.J. Modulation of the immunogenicity of virus-like particles composed of mutant hepatitis B virus envelope subunits. Antivir. Res. 2012, 93, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, G.; Bruss, V. Characterization of early hepatitis B virus surface protein oligomers. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzer, E.J.; Nakamura, G.R.; Yaffe, A. Intracellular transport and secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Mehta, A.; Dwek, R.; Butters, T.; Block, T. Evidence that N-linked glycosylation is necessary for hepatitis B virus secretion. Virology 1995, 213, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Qin, Y.; Guarnieri, M.; Garcia, T.; Kwei, K.; Mizokami, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wands, J.R.; Tong, S. Impairment of hepatitis B virus virion secretion by single-amino-acid substitutions in the small envelope protein and rescue by a novel glycosylation site. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12850–12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julithe, R.; Abou-Jaoudé, G.; Sureau, C. Modification of the hepatitis B virus envelope protein glycosylation pattern interferes with secretion of viral particles, infectivity, and susceptibility to neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9049–9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eble, B.E.; Lingappa, V.R.; Ganem, D. The N-terminal (pre-S2) domain of a hepatitis B virus surface glycoprotein is translocated across membranes by downstream signal sequences. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stibbe, W.; Gerlich, W.H. Characterization of pre-s gene products in hepatitis B surface antigen. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1983, 54, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, S.; Glebe, D.; Tolle, T.K.; Lochnit, G.; Linder, D.; Geyer, R.; Gerlich, W.H. Structure of pre-S2 N- and O-linked glycans in surface proteins from different genotypes of hepatitis B virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-C.; Moss, B. Selective synthesis and secretion of particles composed of the hepatitis B virus middle surface protein directed by a recombinant vaccinia virus: Induction of antibodies to pre-S and S epitopes. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, A.; Milich, D.R.; Raney, A.K.; Riggs, M.G.; Hughes, J.L.; Sorge, J.; Chisari, F.V. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface and core antigens: Influences of pre-S and precore sequences. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar-Kimber, K.L.; Jarocki-Witek, V.; Dheer, S.K.; Vernon, S.K.; Conley, A.J.; Davis, A.R.; Hung, P.P. Distinctive properties of the hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, S.Y.; Lo, S.J. Biogenesis of the hepatitis B viral middle (M) surface protein in a human hepatoma cell line: Demonstration of an alternative secretion pathway. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 3031–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernholz, D.; Galle, P.R.; Stemler, M.; Brunetto, M.; Bonino, F.; Will, H. Infectious hepatitis B virus variant defective in pre-S2 protein expression in a chronic carrier. Virology 1993, 194, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostapchuk, P.; Hearing, P.; Ganem, D. A dramatic shift in the transmembrane topology of a viral envelope glycoprotein accompanies hepatitis B viral morphogenesis. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prange, R.; Streeck, R.E. Novel transmembrane topology of the hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, S.; Iancu, C.; Volz, T.; Mier, W.; Dandri, M.; Urban, S.; Bartenschlager, R. A slow maturation process renders hepatitis B virus infectious. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Sonnabend, J.; Seitz, S.; Urban, S. The pre-S2 domain of the hepatitis B virus is dispensable for infectivity but serves a spacer function for L-protein-connected virus assembly. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3879–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruss, V.; Gerhardt, E.; Vieluf, K.; Wunderlich, G. Functions of the large hepatitis B virus surface protein in viral particle morphogenesis. Intervirology 1996, 39, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Le Seyec, J.; Rumin, S.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Myristylation of the hepatitis B virus large surface protein is essential for viral infectivity. Virology 1995, 213, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Bruss, V.; Yen, T.S.B. Formation of intracellular particles by hepatitis B virus large surface protein. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5487–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persing, D.H.; Varmus, H.E.; Ganem, D. Inhibition of secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen by a related presurface polypeptide. Science 1986, 234, 1388–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.H.; Rutter, W.J. Regulation of secretion of the hepatitis B virus major surface antigen by the preS-1 protein. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heermann, K.H.; Goldmann, U.; Schwartz, W.; Seyffarth, T.; Baumgarten, H.; Gerlich, W.H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J. Virol. 1984, 52, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavilanes, F.; Gonzalez-Ros, J.M.; Peterson, D.L. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 7770–7777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.L. The structure of hepatitis B surface antigen and its antigenic sites. BioEssays 1987, 6, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.; Li, L.S.; Roychoudhury, S.; Ho, M.H. In vitro propagation of human hepatitis B virus in a rat hepatoma cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6323–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruska, J.F.; Robinson, W.S. The proteins of hepatitis B Dane particle cores. J. Med. Virol. 1977, 1, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukeno, N.; Shirachi, R.; Yamaguchi, J.; Ishida, N. Reduction and reoxidation of Australia antigen: Loss and reconstitution of particle structure and antigenicity. J. Virol. 1972, 9, 182–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, G.N.; Rao, K.R.; Ibrahim, A.B. Australia antigen (hepatitis B antigen): A conformational antigen dependent of disulfide bonds. Science 1972, 178, 1300–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Gotoh, A.; Nishioka, K.; Kurashina, S.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. Antigenicity of reduced and alkylated Australia antigen. J. Immunol. 1974, 112, 416–419. [Google Scholar]
- Huovila, A.-P.J.; Eder, A.M.; Fuller, S.D. Hepatitis B surface antigen assembles in a post-ER, pre-Golgi compartment. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzer, E.J.; Nakamura, G.R.; Simonsen, C.C.; Levinson, A.D.; Brands, R. Intracellular assembly and packaging of hepatitis B surface antigen particles occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Virol. 1986, 58, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, O.; Umeda, M.; Imai, H.; Tunoo, H.; Inoue, K. Lipid composition of hepatitis B surface antigen particles and the particle-producing human hepatoma cell lines. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Satoh, O.; Imai, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Miyamura, T.; Utsumi, H.; Inoue, K.; Umeda, M. Membrane structure of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen particle. J. Biochem. 2000, 127, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavilanes, F.; Gomez-Gutierrez, J.; Aracil, M.; Gonzales-Ros, J.M.; Ferragut, J.A.; Guerrero, E.; Peterson, D.L. Hepatitis B surface antigen. Role of lipids in maintaining the structural and antigenic properties of protein components. Biochem. J. 1990, 265, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, E.; Gavilanes, F.; Peterson, D.L. Model for the protein arrangement in HBsAg particles based on physical and chemical studies. In Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease; Zuckerman, A.J., Ed.; Alan, R. Liss Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 606–613. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner, V.J.; Egelé, C.; Oncul, S.; Ronzon, F.; Manin, C.; Klymchenko, A.; Mély, Y. Characterization of the lipid and protein organization in HBsAg viral particles by steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochimie 2010, 92, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhiet, P.-E.; Dosset, P.; Godefroy, C.; Le Grimellec, C.; Guigner, J.M.; Larquet, E.; Ronzon, F.; Manin, C. Nanoscale topography of hepatitis B antigen particles by atomic force microscopy. Biochimie 2011, 93, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, B.S. Australia antigen and the biology of hepatitis B. Science 1977, 197, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couroucé-Pauty, A.M.; Delons, S.; Soulier, J.P. Attempt to prevent hepatitis by using specific anti-HBs immunoglobulin. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1975, 270, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Iwarson, S.; Kjellman, H.; Ahlmén, J.; Ljunggren, C.; Eriksson, E.; Selander, D.; Hermodsson, S. Hepatitis B immune serum globulin and standard gamma globulin in prevention of hepatitis B infection among hospital staff: A preliminary report. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1975, 270, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilleman, M.R.; Buynak, E.B.; Roehm, R.R.; Tytell, A.A.; Bertland, A.U.; Lampson, G.P. Purified and inactivated human hepatitis B vaccine: Progress report. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1975, 270, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, R.H.; Gerin, J.L. Hepatitis B subunit vaccine: A preliminary report of safety and efficacy tests in chimpanzees. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1975, 270, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okochi, K.; Murakami, S.; Ninomiya, K.; Kaneko, M. Australia antigen, transfusion and hepatitis. Vox Sang. 1970, 18, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, W.T.; Drew, J.S.; Lustbader, E.D.; Werner, B.G.; Blumberg, B.S. Host responses to hepatitis B infection in patients in a chronic hemodialysis unit. Kidney Int. 1977, 12, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krugman, S.; Giles, J.P.; Hammond, J. Viral Hepatitis, type B (MS-2 strain). Studies on active immunization. JAMA 1971, 217, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buynak, E.B.; Roehm, R.R.; Tytell, A.A.; Bertland, A.U., II; Lampson, G.P.; Hilleman, M.R. Vaccine against human hepatitis B. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1976, 235, 2832–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerin, J.L.; Holland, P.V.; Purcell, R.H. Australia antigen: Large-scale purification from human serum and biochemical studies of its proteins. J. Virol. 1971, 7, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maupas, P.; Goudeau, A.; Coursaget, P.; Drucker, J.; Bagros, P. Immunisation against hepatitis B in man. Lancet 1976, 307, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, B.J.; Helminiak, C.; Wainwright, R.B.; Bulkow, L.; Trimble, B.A.; Wainwright, K. Frequency of adverse reactions to hepatitis B vaccine in 43,618 persons. Am. J. Med. 1992, 92, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmuness, W.; Stevens, C.E.; Zang, E.A.; Harley, E.J.; Kellner, A. A controlled clinical trial of the efficacy of the hepatitis B vaccine (Heptavax B): A final report. Hepatol 1981, 1, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, F.E.; Graham, D.J.; Guess, H.A.; Milstien, J.B.; Johnson, J.M.; Schatz, G.C.; Hadler, S.C.; Kuritsky, J.N.; Hiner, E.E.; Bregman, D.J.; et al. Postmarketing surveillance for neurologic adverse events reported after hepatitis B vaccination. Experience of the first three years. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1988, 127, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, A.R.; Strick, N.; Kent, S.B.H.; Offensperger, W.; Wahl, S.; Christman, J.K.; Acs, G. Enzyme-linked immunoassay of pre-S gene-coded sequences in hepatitis B vaccines. J. Virol. Method 1985, 12, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, A.R.; Kent, S.B.H.; Strick, N.; Taylor, P.; Stevens, C.E. Hepatitis B virus contains pre-S gene-encoded domains. Nature 1985, 315, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coursaget, P.; Bringer, L.; Sarr, G.; Bourdil, C.; Fritzell, B.; Blondeau, C.; Yvonnet, B.; Chiron, J.P.; Jeannée, E.; Guindo, S.; et al. Comparative immunogenicity in children of mammalian cell-derived recombinant hepatitis B vaccine and plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccine. Vaccine 1992, 10, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, A.J. Hepatitis-B vaccine. Safety criteria and non-B infection. Lancet 1976, 307, 1396–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilleman, M.R.; Ellis, R. Vaccines made from recombinant yeast cells. Vaccine 1986, 4, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenne, J. Recombinant versus plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccines: Issues of safety, immunogenicity and cost-effectiveness. Vaccine 1988, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coursaget, P.; Adamowicz, P.; Bourdil, C.; Yvonnet, B.; Buisson, Y.; Barrès, J.L.; Saliou, P.; Chiron, J.P.; Diop Mar, I. Anti-preS2 antibodies in natural hepatitis B virus infection and after immunization. Vaccine 1988, 6, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.Y.N.; Lai, C.L.; Wu, P.C.; Lin, H.J. Comparison of two plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccines: Long-term report of a prospective, randomized trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1989, 4, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, C.Y. Seroepidemiology of HBV and HCV in Korea: The decreasing prevalence rate of HBV infection after launching HB vaccination program. Int. Hepatol. Commun. 1996, 5, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayanarooj, S.; Vaughn, D.W.; Ariyasriwatana, C.; Snitbhan, R. Protective antibody after a ‘one dollar’ hepatitis B vaccine. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1996, 27, 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Schoub, B.D.; Matai, U.; Singh, B.; Blackburn, N.K.; Levin, J.B. Universal immunization of infants with low doses of a low-cost, plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccine in South Africa. Bull. World Health Organ. 2002, 80, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coates, T.; Wilson, R.; Patrick, G.; André, F.; Watson, V. Hepatitis B vaccines: Assessment of the seroprotective efficacy of two recombinant DNA vaccines. Clin. Ther. 2001, 23, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bernal, F.; Aguilar-Betancourt, A.; Aljovin, V.; Arias, G.; Valenzuela, C.; de Alejo, K.P.; Hernández, K.; Oquendo, O.; Figueredo, N.; Figueroa, N.; et al. Comparison of four recombinant hepatitis B vaccines applied on an accelerated schedule in healthy adults. Hum. Vaccine 2011, 7, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Iino, S.; Shiraki, K.; Akahane, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Domoto, K.; Mishiro, S. Safety and efficacy of a recombinant yeast-derived pre-S2 + S-containing hepatitis B vaccine (TGP-943): Phase 1, 2 and 3 clinical testing. Vaccine 1994, 12, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, S.A.; Martins, R.M.B.; Lopes, C.L.R.; dos Santos Carneiro, M.A.; Souza, K.P.; Yoshida, C.F.T. Immunogenicity of a recombinant hepatitis B vaccine (Euvax-B) in haemodialysis patients and staff. Eur.J. Epidemiol. 2001, 17, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, P.; Mistry, F.P.; Bapat, M.R.; Sharma, G.; Reddy, G.R.; Prasad, K.S.N.; Ramanna, V. Evaluation of a new recombinant DNA hepatitis B vaccine (Shanvac-B). Vaccine 1999, 17, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. A two-dose hepatitis B vaccine for adults (Heplisav-B). Med. Lett. Drugs Ther. 2018, 60, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Deckx, H.; Roten, R.; Michiels, B.; Sarnecki, M. Comparative efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of Hepavax-Gene TF and Engerix-B recombinant hepatitis B vaccines in neonates in China. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, D.; Roggendorf, H.; Roggendorf, M. Enhanced immune response to hepatitis B vaccination through immunization with a Pre-S1/Pre-S2/S vaccine. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Schneider, D.L.; Zuckerman, A.J.; Du, W.; Dickson, B.; Maddrey, W.C. Adult hepatitis B vaccination using a novel triple antigen recombinant vaccine. Hepatology 2001, 34, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, P.; Medina, A.; Rutter, W.J.; Ammerer, G.; Hall, B.D. Synthesis and assembly of hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles in yeast. Nature 1982, 298, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harford, N.; Cabezon, T.; Crabeel, M.; Simoen, E.; Rutgers, A.; De Wilde, M. Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in yeast. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1983, 54, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyanohara, A.; Toh-e, A.; Nozaki, C.; Hamada, F.; Ohtomo, N.; Matsubara, K. Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen gene in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.E. Overview of a 5-year clinical experience with a yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccine. Vaccine 1990, 8 (Suppl. 1), S74–S78. [Google Scholar]
- Wolters, B.; Junge, U.; Dziuba, S.; Roggendorf, M. Immunogenicity of combined hepatitis A and B vaccine in elderly persons. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3623–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zou, G.; Li, J.; Lu, M. Host genetic determinants of hepatitis B virus infection. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K.; Nie, J.J.; Li, J.; Zhuang, H. The effec t of HLA on immunological response to hepatitis B vaccine in healthy people: A meta-analysis. Vaccine 2013, 31, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milich, D.R.; Leroux-Roels, G.G. Immunogenetics of the response to HBsAg vaccination. Autoimmun. Rev. 2003, 2, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cregg, J.M.; Tschopp, J.F.; Stillman, C.; Siegel, R.; Akong, M.; Craig, W.S.; Buckholz, R.G.; Madden, K.R.; Kellaris, P.A.; Davis, G.R.; et al. High-level expression and efficient assembly of hepatitis B surface antigen in the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology 1987, 5, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünsdorf, H.; Gurramkonda, C.; Adnan, A.; Khanna, N.; Rinas, U. Virus-like particle production with yeast: Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical insights into Pichia pastoris producing high levels of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Lünsdorf, H.; Rinas, U. Assessing stability and assembly of the hepatitis B surface antigen into virus-like particles during down-stream processing. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3739–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Freed, D.; Fu, T.-M.; Gimenez, J.A.; Sitrin, R.D.; Washabaugh, M.W. Maturation of recombinant hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles. Hum. Vaccines 2006, 2, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurramkonda, C.; Zahid, M.; Nemani, S.K.; Adnan, A.; Gudi, S.K.; Khanna, N.; Ebensen, T.; Lünsdorf, H.; Guzmán, C.A.; Rinas, U. Purification of hepatitis B surface antigen virus-like particles from recombinant Pichia pastoris and in vivo analysis of their immunogenic properties. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 940, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Towne, V.; Brown, M.; Wang, Y.; Abraham, D.; Oswald, C.B.; Gimenez, J.A.; Washabaugh, M.W.; Kennedy, R.; Sitrin, R.D. In-depth process understanding of RECOMBIVAX HB® maturation and potential epitope improvements with redox treatment: Multifaceted biochemical and immunochemical characterization. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7936–7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wampler, D.E.; Lehman, E.D.; Boger, J.; McAleer, W.J.; Scolnick, E.M. Multiple chemical forms of hepatitis B surface antigen produced in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6830–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Sugahara, K.; Shiosaki, K.; Mizokami, H.; Takeo, K. Fine structure of hepatitis B virus surface antigen produced by recombinant yeast: Comparison with HBsAg of human origin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 165, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonveaux, N.; Conrath, K.; Capiau, C.; Brasseur, R.; Goormaghtigh, E.; Ruysschaert, J.M. The topology of the S protein in the yeast-derived hepatitis B surface antigen particles. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 25637–25645. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meeren, P.; Van Criekinge, W.; Vanderdeelen, J.; Baert, L. Phospholipid composition of r-DNA hepatitis B surface antigens. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 106, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diminsky, D.; Schirmbeck, R.; Reimann, J.; Barenholz, Y. Comparison between hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) particles derived from mammalian cells (CHO) and yeast cells (Hansenula polymorpha): Composition, structure and immunogenicity. Vaccine 1997, 15, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.E.; Stanley, C.; Howard, C.R.; Zuckerman, A.J.; Steward, M.W. Antibody responses to recombinant and plasma derived hepatitis B vaccines. Br. Med. J. 1986, 292, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Núñez, G. The Nlrp3 inflammasome is critical for aluminium hydroxide-mediated IL-1β secretion but dispensible for adjuvant activity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 2085–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Willingham, S.B.; Ting, J.P.-Y.; Re, F. Cutting Edge: Inflammasome activation by alum and alum’s adjuvant effect are mediated by NLRP3. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; Pétrilli, V.; De Smedt, T.; Rolaz, A.; Hammad, H.; van Nimwegen, M.; Bergen, I.M.; Castillo, R.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Tschopp, J. Cutting edge: Alum adjuvant stimulates inflammatory dendritic cells through activation of the NALP3 inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3755–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HogenEsch, H. Mechanism of immunopotentiation and safety of aluminum adjuvants. Front. Immunol. 2013, 3, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.; Robinett, R.S.R.; HogenEsch, H.; Hem, S.L. Mechanism of adsorption of hepatitis B surface antigen by aluminum hydroxide adjuvant. Vaccine 2004, 22, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.; Belfast, M.; Soung, G.; Song, L.; Egan, P.M.; Capen, R.; HogenEsch, H.; Mancinelli, R.; Hem, S.L. Effect of the strength of adsorption of hepatitis B surface antigen to aluminum hydroxide adjuvant on the immune response. Vaccine 2009, 27, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; HogenEsch, H.; Hem, S.L. Change in the degree of adsorption of proteins by aluminum-containing adjuvants following exposure to interstitial fluid: Freshly prepared and aged model vaccines. Vaccine 2002, 20, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, V.J.; Ronzon, F.; Larquet, E.; Desbat, B.; Estèves, C.; Bonvin, J.; Gréco, F.; Manin, C.; Klymchenko, A.S.; Mély, Y. The structure of HBsAg particles is not modified upon their adsorption on aluminium hydroxide gel. Vaccine 2012, 30, 5240–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.; Lentino, J.; Kopp, J.; Murray, L.; Ellison, W.; Rhee, M.; Shockey, G.; Akella, L.; Erby, K.; Heyward, W.L.; et al. Immunogenicity of a two-dose investigational hepatitits B vaccine, HBsAg-1018, using a toll-like receptor 9 agonist adjuvant compared with a licensed hepatitis B vaccine in adults. Vaccine 2018, 36, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, A.R.; Seto, B.; Strick, N. Antibodies to synthetic peptides from the preS1 region of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) envelope (env) protein are virus-neutralizing and protective. Vaccine 1989, 7, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, A.R.; Kent, S.B.H.; Parker, K.; Prince, A.M.; Strick, N.; Brotman, B.; Sproul, P. Anrtibodies to a synthetic peptide from the preS 120-145 region of the hepatitis B virus envelope are virus-neutralizing. Vaccine 1986, 4, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Takai, E.; Ohnuma, H.; Kitajima, K.; Tsuda, F.; Machida, A.; Mishiro, S.; Nakamura, T.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. A synthetic peptide vaccine involving the product of the pre-S(2) region of hepatitis B virus DNA: Protective efficacy in chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 9174–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C.; Penna, A.; Bertoletti, A.; Cavalli, A.; Valli, A.; Schianchi, C.; Fiaccadori, F. The preS1 antigen of hepatitis B virus is highly immunogenic at the T cell level in man. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milich, D.R. T- and B-cell recognition of hepatitis B viral antigens. Immunol. Today 1988, 9, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milich, D.R.; McLachlan, A.; Chisari, F.V.; Kent, S.B.H.; Thornton, G.B. Immune response to the pre-S(1) region of the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): A pre-S(1)-specific T cell response can bypass nonresponsiveness to the pre-S(2) and S regions of HBsAg. J. Immunol. 1986, 137, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Shouval, D.; Ilan, Y.; Adler, R.; Deepen, R.; Panet, A.; Even-Chen, Z.; Gorecki, M.; Gerlich, W.H. Improved immunogenicity in mice of a mammalian cell-derived recombinant hepatitis B vaccine containing pre-S1 and pre-S2 antigens as compared with conventional yeast-derived vaccines. Vaccine 1994, 12, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Asano, T.; Utsunomiya, M.; Itoh, Y.; Fijisawa, Y.; Nishimura, O.; Kato, K.; Kakinuma, A. Recombinant hepatitis B virus surface antigen carrying the pre-S2 region derived from yeast: Purification and characterization. J. Biotechnol. 1988, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Fujisawa, Y. Synthesis in yeast of hepatitis B virus surface antigen modified P31 particles by gene modification. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 141, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, M.; Rutgers, T.; Cabezon, T.; Hauser, P.; van Opstal, O.; Harford, N.; van Wijnendaele, F.; Desmons, P.; Comberbach, M.; Roelants, P.; et al. PreS-containing HBsAg particles from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Production, antigenicity, and immunogenicity. In Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease; Hollinger, F.B., Lemon, S.M., Margolis, H., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1991; pp. 732–736. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, S.; Fujisawa, Y.; Iino, S.; Akahane, Y.; Suzuki, H. Induction of protection level of anti-pre-S2 antibodies in humans immunized with a novel hepatitis B vaccine consisting of M (pre-S2+S) protein particles (a third generation vaccine). Vaccine 1991, 9, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Van Eerd, P.M.C.A.; Schellekens, H.; Kakinuma, A. Protective efficacy of a novel hepatitis B vaccine consisting of M (pre-S2+S) protein particles (a third generation vaccine). Vaccine 1990, 8, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniskern, P.J.; Hagopian, A.; Burke, P.; Dunn, N.; Emini, E.A.; Miller, W.J.; Yamazaki, S.; Ellis, R.W. A candidate vaccine for hepatitis B containing the complete viral surface protein. Hepatology 1988, 8, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemans, R.; Thines, D.; Rutgers, T.; de Wilde, M.; Cabezon, T. The large surface protein of hepatitis B virus is retained in the yeast endoplasmic reticulum and provokes its unique enlargement. DNA Cell Biol. 1991, 10, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, S.; Otaka, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Nakao, M.; Fujisawa, Y. Hepatitis B virus envelope L protein particles. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Iwabuki, H.; Kanno, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kawai, T.; Fukuda, H.; Kondo, A.; Seno, M.; Tanizawa, K.; Kuroda, S. Physicochemical and immunological characterization of hepatitis B virus envelope particels exclusively consisting of the entire L (pre-S1+pre-S2+S) protein. Vaccine 2001, 19, 3154–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux-Roels, G.; Desombere, I.; De Tollenaere, G.; Petit, M.A.; Desmons, P.; Hauser, P.; Delem, A.; De Grave, D.; Safary, A. Hepatitis B vaccine containing surface antigen and selected preS1 and preS2 sequences. 1. Safety and immunogenicity in young, healthy adults. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux-Roels, G.; Desombere, I.; Cobbaut, L.; Petit, M.A.; Desmons, P.; Hauser, P.; Delem, A.; De Grave, D.; Safary, A. Hepatitis B vaccine containing surface antigen and selected preS1 and preS2 sequences. 2. Immunogenicity in poor responders to hepatitis B vaccines. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tron, F.; Degos, F.; Bréchot, C.; Couroucé, A.M.; Goudeau, A.; Marie, F.N.; Adamowicz, P.; Saliou, P.; Laplanche, A.; Benhamou, J.P.; et al. Randomized dose range study of a recombinant hepatitis B vaccine produced in mammalian cells and containing the S and preS2 sequences. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 160, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Wei, Y.Q.; Guo, H.C.; Sun, S.Q. The application of virus-like particles as vaccines and biological vehicles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10415–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushko, P.; Pumpens, P.; Grens, E. Development of virus-like particle technology from small highly symmetric to large complex virus-like particle structures. Intervirology 2013, 56, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, V.; Arora, U.; Shukla, R.; Poddar, A.; Shanmugam, R.K.; White, L.J.; Mattocks, M.M.; Raut, R.; Perween, A.; Tyagi, P.; et al. A tetravalent virus-like particle vaccine designed to display domain III of dengue envelope proteins induces multi-serotype neutralizing antibodies in mice and macaques which confer protection against antibody dependent enhancement in AG129 mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, 0006191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkower, I.; Raymond, M.; Muller, J.; Spadaccini, A.; Aberdeen, A. Assembly, structure, and antigenic properties of virus-like particles rich in HIV-1 envelope gp120. Virology 2004, 321, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.M.; McGovern, T.W.; Krzych, U.; Cohen, J.C.; Schneider, I.; LaChance, R.; Heppner, D.G.; Yuan, G.; Hollingdale, M.; Slaoui, M.; et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of a recombinantly produced Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein-hepatitis B surface antigen subunit vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 171, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutgers, T.; Gordon, D.; Gathoye, A.M.; Hollingdale, M.; Hockmeyer, W.; Rosenberg, M.; De Wilde, M. Hepatitis B surface antigen as carrier matrix for the repetitive epitope of the circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium falciparum. Bio/Technology 1988, 6, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, E.; Patient, R.; Hourioux, C.; Dimier-Poisson, I.; Roingeard, P. Chimeric hepatitis B virus/hepatitis C virus envelope proteins elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies and constitute a potential bivalent prophylactic vaccine. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes Gonzalez, M.; Kostrzak, A.; Guetard, D.; Pniewski, T.; Sala, M. HIV-1 derived peptides fused to HBsAg affects its immunogenicity. Virus Res. 2009, 146, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlienger, K.; Mancini, M.; Rivière, Y.; Dormont, D.; Tiollais, P.; Michel, M.L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 major nautralizing determinant exposed on hepatitis B surface antigen particles is highly immunogenic in primates. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2570–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, N.J.; Kurtovic, L.; Walsh, R.; Joe, C.; Lovrecz, G.; Locarnini, S.; Beeson, J.G.; Netter, H.J. Hepatitis B virus-like particles expressing Plasmodium falciparum epitopes induce complement-fixing antibodies against the circumsporozoite protein. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Lei, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Shu, F.; Wei, X.; Lin, F.; Li, B.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Neutralization effects of antibody elicited by chimeric HBV S antigen viral-like particles presenting HCV neutralization epitopes. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotiw, M.; Johnson, M.; Pandey, M.; Fry, S.; Hazell, S.L.; Netter, H.J.; Good, M.F.; Olive, C. Immunological response to parenteral vaccination with recombinant hepatitis B virus surface antigen virus-like particles expressing Helicobacter pylori KatA epitopes in a murine H. pylori challenge model. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietheer, P.T.K.; Boo, I.; Drummer, H.E.; Netter, H.J. Immunizations with chimeric hepatitis B virus-like particles to induce potential anti-hepatitis C virus neutralizing antibodies. Antivir. Ther. 2007, 12, 477–487. [Google Scholar]
- Pumpens, P.; Razanskas, R.; Pushko, P.; Renhof, R.; Gusars, I.; Skrastina, D.; Ose, V.; Borisova, G.; Sominskaya, I.; Petrovskis, I.; et al. Evaluation of HBs, HBc, and frCP virus-like particles for expression of human papillomavirus 16 E7 oncoprotein epitopes. Intervirology 2002, 45, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brunn, A.; Früh, K.; Müller, H.M.; Zentgraf, H.W.; Bujard, H. Epitopes of the human malaria parasite P. falciparum carried on the surface of HBsAg particles elicit an immune response against the parasite. Vaccine 1991, 9, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpeyroux, F.; Chenciner, N.; Lim, A.; Malpièce, Y.; Blondel, B.; Crainic, R.; van der Werf, S.; Streeck, R.E. A poliovirus neutralization epitope expressed on hybrid hepatitis B surface antigen particles. Science 1986, 233, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, W.S.; Reiseger, J.; Turner, S.J.; Boyd, R.; Netter, H.J. Chimeric virus-like particles for the delivery of an inserted influenza A-specific CTL epitope. Antivir. Res. 2009, 81, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpeyroux, F.; Peillon, N.; Blondel, B.; Crainic, R.; Streeck, R.E. Presentation and immunogenicity of the hepatitis B surface antigen and a poliovirus neutralization antigen on mixed empty envelope particles. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 1836–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netter, H.J.; Macnaughton, T.B.; Woo, W.P.; Tindle, R.; Gowans, E.J. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of novel chimeric hepatitis B surface antigen particles with exposed hepatitis C virus epitopes. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, S.; Brumeanu, T.D.; Richie, T.L. The RTS, S malaria vaccine. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4880–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RTS,S Clinical Trials Partnership. Efficacy and safety of RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine with or without a booster dose in infants and children in Africa: Final results of a phase 3, individually randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kester, K.E.; Cummings, J.F.; Ofori-Anyinam, O.; Ockenhouse, C.F.; Krzych, U.; Moris, P.; Schwenk, R.; Nielsen, R.A.; Debebe, Z.; Pinelis, E.; et al. Randomized, double-blind, phase 2a trial of falciparum malaria vaccines RTS,S/AS01B and RTS,S/AS02A in malaria-naive adults: Safety, efficacy, and immunologic associates of protection. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.A.; Snaith, R.; Cottingham, M.G.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hill, A.V.S. Enhancing protective immunity to malaria with a highly immunogenic virus-like particle vaccine. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patient, R.; Hourioux, C.; Vaudin, P.; Pagès, J.C.; Roingeard, P. Chimeric hepatitis B and C viruses envelope proteins can form subviral particles: Implications for the design of new vaccine strategies. New Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCluskie, M.J.; Evans, D.M.; Zhang, N.; Benoit, M.; McElhiney, S.P.; Unnithan, M.; DeMarco, S.C.; Clay, B.; Huber, C.; Deora, A.; et al. The effect of pre-existing anti-carrier immunity on subsequent responses to CRM197 or Qb-VLP conjugate vaccines. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 38, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, M.; Van, T.T.H.; Baird, F.J.; Coloe, P.J.; Smooker, P.M. Pre-existing immunity against vaccine vectors—Friend or foe? Microbiology 2013, 159, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegerlehner, A.; Wiesel, M.; Dietmeier, K.; Zabel, F.; Gatto, D.; Saudan, P.; Bachmann, M.F. Carrier induced epitopic suppression of antibody responses induced by virus-like particles is a dynamic phenomenon caused by carrier-specific antibodies. Vaccine 2010, 28, 5503–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutze, M.P.; Leclerc, C.; Jolivet, M.; Audibert, F.; Chedid, L. Carrier-induced epitopic suppression, a major issue for future synthetic vaccines. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 2319–2322. [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont, E.; Roingeard, P. Chimeric hepatitis B virus (HBV)/hepatitis C virus (HCV) subviral envelope particles induce efficient anti-HCV antibody production in animals pre-immunized with HBV vaccine. Vaccine 2015, 33, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netter, H.J.; Woo, W.P.; Tindle, R.; Macfarlan, R.I.; Gowans, E.J. Immunogenicity of recombinant HBsAg/HCV particles in mice pre-immunised with hepatitis B virus-specific vaccine. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2692–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojang, K.A.; Milligan, P.J.M.; Pinder, M.; Vigneron, L.; Alloueche, A.; Kester, K.E.; Ballou, W.R.; Conway, D.J.; Reece, W.H.H.; Gothard, P.; et al. Efficacy of RTS,S/AS02 malaria vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum infection in semi-immune adult men in The Gambia: A randomised trial. Lancet 2001, 358, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Haque, M.A.; Blum, J.S. Role of disulfide bonds in regulating antigen processing and epitope selection. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 2444–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmicle, S.; Steede, N.K.; Landry, S.J. Antigen three-dimensional structure guides the processing and presentation of helper T-cell epitopes. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prato, S.; Fleming, J.; Schmidt, C.W.; Corradin, G.; Lopez, J.A. Cross-presentation of a human malaria CTL epitope is conformation dependent. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, G.; Carmicle, S.; Steede, N.K.; Landry, S.J. Structural basis for helper T-cell and antibody epitope immunodominance in bacteriophage T4 Hsp10. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirano-Bascos, D.; Steede, N.K.; Robinson, J.E.; Landry, S.J. Influence of disulfide-stabilized structure on the specificity of helper T-cell and antibody responses to HIV envelope glycoprotein gp120. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3303–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Landry, S.J. Three-dimensional structure determines the pattern of CD4+ T-cell epitope dominance in influenza virus hemagglutinin. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfert, M.A.; Boons, G.J. Adaptive immune activation: Glycosylation does matter. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, T.K.; Brewer, C.F. Lectins as pattern recognition molecules: The effects of epitope density in innate immunity. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Barwani, F.; Young, S.L.; Baird, M.A.; Larsen, D.S.; Ward, V.K. Mannosylation of virus-like particles enhances internalization by antigen-presenting cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, T.; Zhang, X.; Dériaud, E.; Ganneau, C.; Vichier-Guerre, S.; Azria, E.; Launay, O.; Lo-Man, R.; Bay, S.; Leclerc, C. Glycosidic Tn-based vaccines targeting dermal dendritic cells favor germinal center B-cell development and potent antibody response in the absence of adjuvant. Blood 2010, 116, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.C.; Kalkanidis, M.; Pouniotis, D.S.; Esparon, S.; Tang, C.K.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Pietersz, G.A. Delivery of antigen using a novel mannosylated dendrimer potentiates immunogenicity in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, B.; Steimer, K.S.; Walker, C.M. Induction of HIV-1 envelope (gp120)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in mice by recombinant CHO cell-derived gp120 is enhanced by enzymatic removal of N-linked glycans. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, H.; Mishra, D.; Mishra, P.K.; Nahar, M.; Dubey, V.; Jain, N.K. Evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles as carriers for delivery of hepatitis B surface antigen for vaccination using subcutaneous route. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 13, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigerust, D.J.; Shepherd, V.L. Virus glycosylation: Role in virulence and immune interactions. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyakumura, M.; Walsh, R.; Thaysen-Andersen, M.; Kingston, N.J.; La, M.; Lu, L.; Lovrecz, G.; Packer, N.H.; Locarnini, S.; Netter, H.J. Modification of asparagine-linked glycan density for the design of hepatitis B virus virus-like particles with enhanced immunogenicity. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11312–11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.; Rodriguez, E.N.; Lobaina, Y.; Musacchio, A.; Falcon, V.; Guillen, G.; Aguilar, J.C. Characterization of the size distribution and aggregation of virus-like nanoparticles used as active ingredients of the HeberNasvac therapeutic vaccine against chronic hepatitis B. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).