Abstract
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is an acute, high-mortality-rate, severe infectious disease caused by an emerging MERS coronavirus (MERS-CoV) that causes severe respiratory diseases. The continuous spread and great pandemic potential of MERS-CoV make it necessarily important to develop effective vaccines. We previously demonstrated that the application of Gram-positive enhancer matrix (GEM) particles as a bacterial vector displaying the MERS-CoV receptor-binding domain (RBD) is a very promising MERS vaccine candidate that is capable of producing potential neutralization antibodies. We have also used the rabies virus (RV) as a viral vector to design a recombinant vaccine by expressing the MERS-CoV S1 (spike) protein on the surface of the RV. In this study, we compared the immunological efficacy of the vaccine candidates in BALB/c mice in terms of the levels of humoral and cellular immune responses. The results show that the rabies virus vector-based vaccine can induce remarkably earlier antibody response and higher levels of cellular immunity than the GEM particles vector. However, the GEM particles vector-based vaccine candidate can induce remarkably higher antibody response, even at a very low dose of 1 µg. These results indicate that vaccines constructed using different vaccine vector platforms for the same pathogen have different rates and trends in humoral and cellular immune responses in the same animal model. This discovery not only provides more alternative vaccine development platforms for MERS-CoV vaccine development, but also provides a theoretical basis for our future selection of vaccine vector platforms for other specific pathogens.
1. Introduction
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) was first identified in Saudi Arabia in 2012 [1]. Soon after its first report, some imported cases occurred in many other countries outside the Arabian Peninsula through infected travelers, most notably the outbreak in South Korea in 2015 [2]. The clinical signs of MERS-CoV-infected patients are similar to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), the outbreaks of which in China in 2003 caused acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans [3]. Bats and dromedaries are considered as the natural reservoirs of MERS-CoV [3]. Up to now, a continuous increase of human cases in the endemic areas has been reported [4], highlighting that it is urgent to develop and make available effective therapeutic drugs and prophylactic vaccines to protect against MERS-CoV.
To date, many promising approaches toward MERS-CoV vaccine candidates have been developed, such as recombinant viral vectors [4,5,6,7,8,9,10], protein-based platforms [11,12], bacterial-based platform [13], and DNA vaccines [14,15,16]. Most of MERS-CoV vaccine candidates have focused on the major immune-dominant antigen, the S protein of the virion, which plays a significant role in mediating viral entry into target cells and in inducing neutralizing antibodies in experimental animals and infected individuals [17]. The receptor-binding domain (RBD) within the S1 domain of the S protein of the MERS-CoV virus decides the host range and cellular tropism [18,19,20]. As such, we developed two promising MERS-CoV vaccine candidates using two different platforms. One uses the rabies virus (RV) as a vector to express S1 domains of the MERS-CoV S gene to develop a recombinant MERS-CoV vaccine, and the other applies gram-positive enhancer matrix (GEM) particles as a vector to construct a MERS bacterium (Lactococcus lactis)-like particle (BLP) vaccine by displaying the RBD [13]. A previous study has utilized the RV (BNSP333) vector modified from the RV vaccine vector SPBN to successfully design a vaccine against MERS-CoV infection [10,21], whereas the RV vector (SRV9 strain) used in our study is screened from the Street Alabama Dufferin (SAD) strain by plaque purification on baby Syrian hamster kidney cells (BHK-21) cells, which have been proven to be safe and have good immunogenicity [22]. The GEM-PA system is a novel surface display system consisting of nonliving and genetically unmodified GEM particles and a protein anchor (PA) from the Lactococcus lactis peptidoglycan hydrolase AcmA. We utilized the system to successfully display the RBD protein fragment of MERS-CoV, inducing high neutralizing antibodies with intramuscular vaccination and robust antigen-specific local and systemic immune responses by intranasal vaccination [13]. The head-to-head comparison of available vaccine vectors is necessary in vaccine design [23]. The difference in immune response induced by two different MERS-CoV vaccine candidates and the effect of antigen displayed in viral and bacterial vectors on the immune response are still questionable.
In this study, we evaluated the immunological efficacy of MERS BLP at different doses and the inactivated recombinant MERS antigen in BABL/c mice. Specifically, we compared the ability of these two vaccines to induce MERS-CoV-specific humoral immune response and T-cell-mediated immune response, as well as neutralizing antibodies against MERS-CoV.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
All animal works were strictly in accordance with the welfare and ethical guidance on Chinese laboratory animals (GB 14925-2001). The agreement was approved by the Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee of the Institute of Veterinary Medicine of the Changchun Veterinary Research Institute (Laboratory Animal Care and Use Committee Authorization, permit number JSY-DW-2019-05).
2.2. Cells and Virus
Baby Syrian hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells were cultured in serum-free medium (VirusPro®, Shanghai, China) at 37 °C with 5% CO2 on an orbital shaker at 130 rpm in suspension culture for virus infection. Mouse neuroblastoma (NA) cells were cultured with Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) plus 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Biological Industries, Kibbutz Beit Haemek, Israel) for determination of viral titer and verification of virus inactivation. Spodoptera frugiperda 9 (Sf9, Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) insect cells were grown in Sf-900TM II medium (Life Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA) for protein expression. The recombinant RV expressing MERS-CoV S1 protein (RV/MERS) was constructed and stored in our laboratory.
2.3. Production of the RV/MERS in BHK-21 Cells
The RV/MERS virus was cultivated in BHK-21 cells. Briefly, BHK-21 cells (2 × 106 cells per mL) grown in shake flask cultures were infected with RV/MERS virus at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.05. RV/MERS was harvested from the culture supernatant of cell culture on two days post-infection (DPI). The titers of the recombinant virus were determined by the median endpoint of the 50% tissue culture infectious dose units (TCID50) in NA cells as described previously [24]. Recombinant virus was inactivated with 0.025% β-propiolactone (v/v); the mixtures were incubated at 4 °C overnight and then treated at 37 °C for 2 h. The verification of the virus’ complete inactivation was detected in NA cells. The completely inactivated virus was purified with 500KD Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration Column and Sepharose Fast Flow 4 Gel. Fractions were harvested and analyzed by immunoblotting. The total protein concentration of the purified product was determined by the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay.
2.4. Production of the MERS Bacterium-Like Particles
The MERS BLP was produced as previously described [13]. Briefly, the fusion protein of RBD-linker-PA3 was expressed in a baculovirus expression system. The GEM particles were used as vectors to construct MERS BLP by externally displaying the RBD through the PA3. The fusion protein concentration of the MERS BLP was detected densitometrically using Quantity One image analysis software, version 4.6.7.
2.5. Size of the Particles
The size (Hydrodynamic diameter, in nm) and size distribution (polydispersity index, PDI) of the RV/MERS and MERS BLP were determined using a laser particle size analyzer (NANO ZS90, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK), which the fresh prepared RV/MERS and MERS BLP suspension were determined under almost the same humidity and temperature at 25 °C, and each sample measurement was performed in triplicate simultaneously.
2.6. Animal Immunization and Sera Collection
Four- to six-week-old female BALB/c mice were purchased from Changchun Yisi Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. (Changchun, China). Female BALB/c mice were randomized into five groups of 10. Mice were intramuscularly prime-immunized with 8 µg purified RV/MERS virus; 1, 5, and 20 µg MERS BLP; mixed with the compound adjuvants consisting of ISA201VG (Seppic, Paris, France) and Poly I: C (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA); and boosted twice with an equal volume antigen as the primary vaccination at 3-week intervals. Compound adjuvants only were immunized as negative control. Blood samples were collected before immunization and two weeks after each vaccination. Serum samples were inactivated at 56 °C for 30 min before determining MERS-CoV RBD-specific antibodies and neutralizing antibodies. Five mice selected randomly from each group were euthanized on day 7 after the third immunization, and their splenocytes were collected for cytokines analysis.
2.7. ELISA for MERS-CoV Specific Antibody Test
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was applied to analyze MERS-CoV RBD-specific IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c, and IgG3 antibodies. Serially diluted sera were added to 96-well microtiter plates (Corning-Costar, Corning, NY, USA) that were pre-coated overnight with MERS-RBD protein (1 μg/mL) produced in Escherichia coli. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h and washed three times with PBST before being incubated with the following horseradish peroxidase (HRP) labeled anti-mouse IgG (1:5000, BioWorld, St. Louis, MN, USA), IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c, and IgG3 (1:2000, Southern Biotech, Birmingham, AL, USA) at 37 °C for 1 h. Plates were then washed three times, and 100 µL TMB (3′,3′,5′,5′-tetramethylbenzidine) per well was added. Then, the color development was stopped by adding H2SO4. Optical density values were read at 450 nm using an ELISA plate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
2.8. Virus Neutralizing Assay
Neutralizing titers of mice sera were detected by using a MERS-CoV pseudovirus reported in our previous study [11]. Briefly, serially diluted mouse sera mixed with an equal volume of 100× TCID50 of MERS-pseudotyped viruses were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min, and then, the mixture was incubated with Huh 7 cells at 37 °C for 4 h. After the incubation, the medium was replaced with complete DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin–streptomycin, and then, the samples were incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. The luciferase activity was detected by using an Infinite M200 Microplate Spectrophotometer (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland).
2.9. Cytokines Analysis in Splenocytes Culture Supernatants
To evaluate antigen-specific T-cell responses, splenocytes were harvested on day 7 after the third immunization and stimulated with 1 μM MERS-CoV peptide S291 for 24 h at 37 °C [25]. Secreted tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and interleukin 2 (IL-2) in the supernatants were detected with the mouse ELISA cytokine kits (MABTECH, Nacka, Sweden).
2.10. Statistics
All statistical analysis was performed by using the Graphpad 8.0.2 software. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD, and significance in their differences between groups were analyzed using a Student’s t-test.
3. Results
3.1. The Particle Size of RV/MERS and MERS BLP
The particle size and polydispersity index of RV/MERS and MERS BLP were measured by a dynamic light scattering (DLS) device before immunization of mice. As shown in Figure 1, the size of RV/MERS is about 167 nm (Figure 1a); the size of MERS BLP is about 2161 nm (Figure 1b).
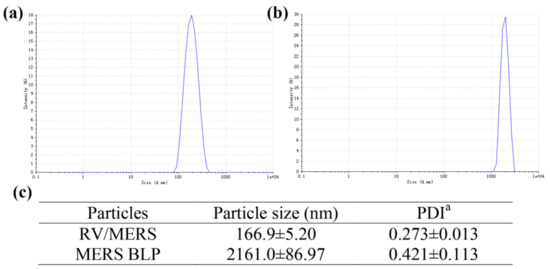
Figure 1.
The particle size of recombinant RV expressing MERS-CoV S1 protein (RV/MERS) and MERS bacterium-like particle (MERS BLP). The particle size distribution of RV/MERS (a) and MERS BLP (b). The particle size and polydispersity index (PDI) of RV/MERS and MERS BLP (c). Data was shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). a PDI, polydispersity index from dynamic light scattering (DLS).
3.2. Neutralizing Antibody Response by Pseudovirions Neutralization Assay
To compare the immunological efficacy of two MERS-CoV vaccines derived from two different vectors, we studied the impact on the immunogenicity of MERS-CoV BLP with different doses and the immunogenicity of RV/MERS with only one certain dose in mice. The schematic diagram for group design, immunizations, and immunological characterization is shown in Figure 2a. A total of five groups of mice (G1–G5) were administered three immunizations with a combined adjuvant through an intramuscular (i.m.) route; G1 was immunized with PBS as negative control; G2 was immunized with 8 µg inactivated and purified RV/MERS; G3–G5 were immunized with 1 µg (low dose), 5 µg (medium dose), and 20 µg (high dose) MERS-CoV BLP, respectively. Sequential sera samples were collected at weeks 0, 2, 5, and 8 and detected for neutralizing activity against pseudotyped MERS-CoV and the binding activity. Splenocytes were harvested at 7 weeks after the last immunization for cytokines analysis. As shown in Figure 2b, G2 developed neutralizing antibody response at 2 weeks after the first immunization, and the neutralizing antibodies of G3, G4, and G5 were not detected at this point. However, the neutralizing antibody of G3, G4, and G5 was significantly higher than G2 at 5 and 8 weeks after immunization. There were also no significant differences in the neutralizing activity among G3, G4, and G5, indicating that 1 µg MERS-CoV BLP can efficiently induce MERS-CoV neutralizing antibodies in mice. Overall, these results show that the RV/MERS can rapidly induce neutralizing antibody response, and the MERS BLP can induce higher antibody response in mice.
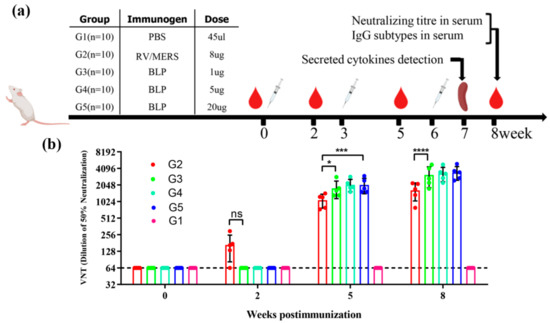
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of immunization and neutralizing antibody responses. (a) The vaccination schedule and characterization of immunologic responses in BALB/c mice. A total of five groups of mice were immunized and detected for virus-neutralizing antibody, IgG subtypes, and cytokines release. Group 1 (G1) was negative controls; group 2 (G2) was vaccinated with inactivated and purified rabies virus (RV)/Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS); group 3, group 4, and group 5 (G3, G4, G5) were vaccinated with varying doses of the MERS bacterium (Lactococcus lactis)-like particle (BLP). All groups received a second and third identical vaccination boost with a combined adjuvant at 3-week intervals after the primary immunization. (b) Neutralizing activity was detected by using MERS coronavirus (MERS-CoV) pseudovirus, and the data are shown as the mean ± SD from five mice in each group and were analyzed by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, n = 5).
3.3. MERS-CoV RBD-Specific IgG Subtypes Responses by Indirect ELISA
We next detected the MERS-CoV RBD-specific IgG and IgG subtypes’ antibodies level in the serum at 8 weeks post-immunization. ELISA results indicate that both MERS antigen-induced IgG antibodies can specifically bind to MERS-CoV RBD protein. Particularly, G3–G5 acquired a stronger binding to MERS-CoV RBD protein than G2, whereas G1, the control samples, were detected to have negligible binding activity (Figure 3a), indicating the specificity of the IgG antibody response induced by this RBD protein. Additionally, the endpoint titers of the IgG antibody level showed that the immunogenicity of G3–G5 was much stronger than G2 in inducing MERS-CoV RBD-specific IgG antibody response in mice after three vaccinations (Figure 3b). Furthermore, no significant difference was shown for IgG titers among groups G3, G4, and G5, suggesting that 1 µg antigen protein on the bacterial vector is sufficient to induce high RBD-specific antibody level in mice. Thus, the MERS-CoV antigen protein displayed on the surface of the bacterial vector can significantly enhance the immunogenicity of the RBD fragments.
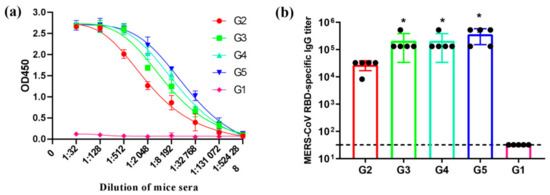
Figure 3.
MERS-CoV receptor-binding domain (RBD)-specific IgG antibodies. Sera from 2 weeks after the last immunization were tested for MERS-CoV RBD-specific IgG antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The data are shown as the mean ± SD from five mice in each group and were analyzed by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05, n = 5). (a) The total IgG antibodies specific to MERS-CoV RBD protein were assessed by ELISA. The level of the MERS-CoV RBD-specific IgG (b) antibodies was determined by ELISA and is shown as end-point dilution titers.
T helper 2 (Th2) response is associated with IgG1, and T helper 1 (Th1) response correlates with IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c, and IgG3 in mice [26]. In order to evaluate the IgG subtypes’ levels in serum from immunized mice, the production of IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c, and IgG3 in sera were detected. Observation of sera IgG subtypes showed that the sera in G3–G5 induced significantly higher levels of IgG1 antibody than those of G2 (Figure 4a); the sera in G4–G5 induced significantly higher levels of IgG2a and IgG2b antibodies than those of G2 (Figure 4b,c); there was no significant difference in IgG2c antibody level between G2–G5 (Figure 4d); the sera in G5 induced significantly higher levels of IgG3 antibody than those of G2 (Figure 4e). However, further analysis of the ratios of IgG2a/IgG1 revealed that the sera in G2 were remarkably higher than those in G3–G5 (Figure 4f). Collectively, these results suggest that the MERS-CoV antigen protein displayed on the surface of the viral vector appears to induce a stronger Th1-biased immune response than that on the bacterial vector.
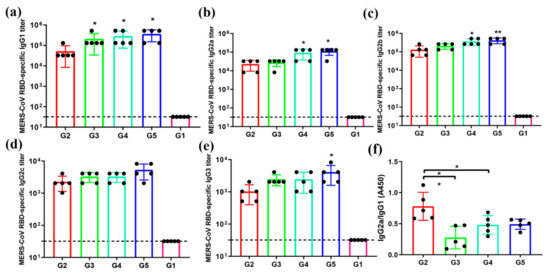
Figure 4.
MERS-CoV RBD-specific antibody subtypes response. Sera from 2 weeks after the last immunization were tested for MERS-CoV RBD-specific IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c, and IgG3 antibodies by ELISA. The data are shown as the mean ± SD from five mice in each group and were analyzed by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, n = 5). The level of the MERS-CoV RBD-specific IgG1 (a), IgG2a (b), IgG2b (c), IgG2c (d), and IgG3 (e) antibodies were determined by ELISA and are shown as end-point dilution titers. The ratios between IgG1 and IgG2a antibody responses were also calculated (f).
3.4. Antigen-Specific T-Cell Immune Responses
Next, in order to analyze the MERS-CoV specific T-cell immune responses, we detected the levels of secreted IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α from the splenocytes after re-stimulation with MERS S291 peptide. The levels of IFN-γ and IL-2 in G3 were significantly higher than those in G4 and G5, suggesting that 1 µg of antigen protein on the bacterial vector is sufficient to induce potent IFN-γ/IL-2-expressing T-cell responses, whereas the levels of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α in G2 were remarkably higher than those in G3–G5 at 7 weeks post-immunization (w.p.i.) (Figure 5). These results indicate that MERS-CoV antigen protein displayed on the viral vector induces a superior cellular immune response than that on the bacterial vector.
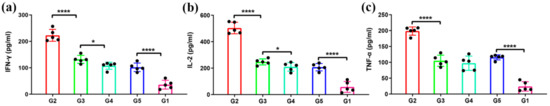
Figure 5.
Immunization induced a significant cytokine response in mice. In order to evaluate antigen-specific T-cell responses, splenocytes were harvested from five mice in each group and were stimulated by MERS-CoV peptide S291 for 24 h. The level of secreted IFN-γ (a), IL-2 (b), and TNF-α (c) in the supernatants was detected by mouse ELISA kits. The data are shown as the mean ± SD and were analyzed by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001, n = 5).
4. Discussion
MERS-CoV continues to infect humans, causing morbidity and mortality since several outbreaks in 2012 that have caused a potential global MERS-CoV pandemic. However, no prophylactics and therapeutics available to protect against MERS have currently been licensed, although researchers have developed and tested several MERS-CoV vaccine candidates in many animal models. Each of these candidate vaccines has several advantages and challenges, such as preexisting immunity, immunogenicity, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we have developed two promising MERS-CoV vaccine candidates using two different platforms. One is the recombinant RV expressing MERS-CoV S1 protein fragment, and the other uses GEM particles as a vector to display the MERS-CoV RBD protein fragment. In this study, we compared the humoral and cellular responses in a BALB/c mouse model. The results indicate that the RV/MERS vaccine induces rapidly neutralizing antibody and stronger T-cell immune responses than the MERS-CoV BLP vaccine. However, the MERS-CoV BLP vaccine can induce a higher level of neutralizing antibodies than that of the RV/MERS vaccine.
Two unique aspects can be highlighted in our study. The first is about the RV vector, besides the MERS-CoV, which has been proven to be successfully utilized for many other emergent infectious diseases, such as the Ebola virus (EBOV) [27], Lassa virus (LASV) [28], Marburg virus (MARV) [29], human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) [30], and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) [31]. Additionally, the Ebola virus vaccine is close to clinical trials [29]. Notably, chemically inactivated rabies virus vaccines have been widely used for vaccination of humans, dogs, cats, and ferrets, which shows that they are safe for humans and animals [32]. Therefore, the inactivated rabies virus-based vaccine is also safe and can induce neutralizing antibodies against the target pathogen. Here, the results show that the inactivated rabies virus vectors have very safe and immunogenic profiles in animals and highlight their promise for vaccine development.
The second unique aspect of this study is the GEM-PA system, a novel surface display system, which is a flexible, effective, cost-effective, and easy-to-handle alternative for heterologous proteins to be displayed on the GEM particles [33]. The GEM particles are from the Lactococcus lactis boiled in acids and mainly contain the bacterial-shaped peptidoglycan spheres, lacking other cell components [34]. Additionally, Lactococcus lactis has been safely applied in foods in recent years [35]. As such, the GEM-based vaccine is recognized as being safe. Furthermore, the GEM particles have been proven to enhance immune response as a carrier displaying the antigen with high density or adjuvant in vaccine development [36,37,38,39]. GEM particles can also improve the humoral and cellular immune response by activating the maturation of the dendritic cells, enhancing the antigen-presenting capacity, and stimulating the DCs to produce cytokines [40]. Besides that, peptidoglycan, the main component of the GEM particles, is a toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 ligand [38,40,41]. Moreover, GEM particles can efficiently bind the antigen protein at room temperature to obtain the purified proteins with only a one-step centrifugation process [33]. It is convenient and economical to scale up in vaccine development. GEM particles can also bind to different antigen proteins in the same particles to develop multivalent vaccines [42]. The system has successfully displayed a variety of heterologous proteins from pathogens, showing strong antigen-specific immune responses with parenteral vaccination or mucosal vaccination, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites [38,43,44,45,46]. In our study, the results suggest that the RBD protein of MERS-CoV displayed on the GEM particles could induce strong humoral and cellular immune response even when the dose is as low as 1 µg.
The two vaccine platforms in this study have their own advantages and disadvantages. The RV-based MERS-CoV vaccine platform can rapidly induce antibody immune response and higher cellular immune response than the GEM-based vaccine platform. However, there is a risk of incomplete inactivation in the process of inactivating the RV/MERS. Additionally, RV/MERS vaccine needs to be purified through many purification steps. These factors must be considered in vaccine production. Antigen protein density and distribution on a particle are two key parameters in eliciting an efficient immune response in vaccine design; a high density and ordered antigenic array displayed on a particle makes binding events between the host B-cell surface immunoglobulins and the particle occur more easily, which is an important step in inducing sequential immune response [47]. The GEM-based vaccine platform could display antigen protein in a high density, while the RV-based vaccine platform not only displayed the antigen protein but also expressed the RV GP protein. This may be why the GEM-based vaccine of MERS-CoV induces a much stronger humoral immune response in mice than that of the RV-based vaccine. Micro-particles could promote a humoral immune response, and nano-particles are much easier to induce a cellular immune response [48,49]. The size of the RV/MERS virion is about 167 nm, and the diameter of the MERS BLP particles is about 2161 nm. This may be a critical factor in inducing a different cellular immune response by two different vectors of vaccine platforms. Specific molecules of microbial origin, as intrinsic innate immune triggers, are endowed with adjuvant activity, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), bacterial lipopeptides, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic acid (RNA), and other conserved molecules [50]. The receptors for these molecules are the mammalian Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Members of the TLRs have been confirmed on the cell surface membrane (TLR1/2/4/5/6/10) and on the membrane of endosomes (TLR3/7/8/9) [51]. Peptidoglycan, the main component of the GEM particles, is a TLR 2 ligand which is an activation of TLR-2 receptors in human peripheralblood mononuclear cells inducing a Th1-type immune response [52]. Single stranded RNA, the component of inactivated rabies virus, is a TLR 7 ligand [51,53]. TLR7/8 agonists have shown Th1 polarizing effects on the immune response. Different receptors play an important role in delivering different signals to the host cells. The activated antigen presenting cells (APCs) precisely define the nature of the perceived danger and send this information to the secondary lymphoid organs, inducing relevant adaptive immune response. This may be another ignored factor of inducing a different immune response by the immune system thinking that the danger is from a virus infection or a bacterial infection. The immune system is triggered by a combination of events and stimuli in vaccine immunology. The compound adjuvants containing the emulsion and PolyI:C (TLR 3 ligand) may be another assignable cause. The speed of the antibodies’ production and cellular immune response needs to be further improved in future study of the GEM-based vaccine platform. To solve the problems, we can try to screen optimum adjuvants for the vaccine or co-displaying protein-adjuvants on GEM particles, such as flagellin (TLR 5 ligand). Furthermore, the GEM-based vaccine platform may be more suitable to develop mucosal vaccines considering that Lactococcus lactis has been safely used as a probiotic in our foods. Understanding the modes of action of the GEM-based vaccine platform will allow us to design a much safer, cost-effective, and protective vaccine with the desired immune response.
The goal of this study was to test vaccine vectors through a head-to-head comparison of immunogenicity of two MERS-CoV vaccine candidates as they might be used in real vaccines for humans or animals. This study provides an important reference for selecting a suitable vaccine platform in developing the MERS-CoV vaccine or other special pathogens in further study.
Author Contributions
X.X., S.Y., and Y.Z. designed the experiments. E.L., F.Y., and P.H. performed the experiment. E.L., H.C., S.X., G.L., C.L., N.F., and H.W. analyzed the data. E.L. and F.Y. wrote the manuscript. X.X., S.Y., F.Y., and Y.Z. reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31902306) and the National Project for Prevention and Control of Transboundary Animal Diseases (Grant No. 2017YFD0501804).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest, and all the authors approved this manuscript for publication.
References
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M. 2015 MERS outbreak in Korea: Hospital-to-hospital transmission. Epidemiol. Health 2015, 37, e2015033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Channappanavar, R.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, P.; Xu, J.; Shan, S.; Shi, X.; et al. Single intranasal immunization with chimpanzee adenovirus-based vaccine induces sustained and protective immunity against MERS-CoV infection. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haagmans, B.L.; van den Brand, J.M.; Raj, V.S.; Volz, A.; Wohlsein, P.; Smits, S.L.; Schipper, D.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Okba, N.; Fux, R.; et al. An orthopoxvirus-based vaccine reduces virus excretion after MERS-CoV infection in dromedary camels. Science 2016, 351, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, A.; Kupke, A.; Song, F.; Jany, S.; Fux, R.; Shams-Eldin, H.; Schmidt, J.; Becker, C.; Eickmann, M.; Becker, S.; et al. Protective Efficacy of Recombinant Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Delivering Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8651–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Lan, J.; Wang, W.; Zou, X.; Hung, T.; Lu, Z.; Tan, W. Systemic and mucosal immunity in mice elicited by a single immunization with human adenovirus type 5 or 41 vector-based vaccines carrying the spike protein of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Immunology 2015, 145, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.Q.; Ge, J.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, J.L.; Wen, Z.Y.; Bu, Z.G. Newcastle disease virus-based MERS-CoV candidate vaccine elicits high-level and lasting neutralizing antibodies in Bactrian camels. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczyk, A.H.; Kupke, A.; Prufer, S.; Scheuplein, V.A.; Hutzler, S.; Kreuz, D.; Beissert, T.; Bauer, S.; Hubich-Rau, S.; Tondera, C.; et al. A Highly Immunogenic and Protective Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Vaccine Based on a Recombinant Measles Virus Vaccine Platform. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11654–11667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirblich, C.; Coleman, C.M.; Kurup, D.; Abraham, T.S.; Bernbaum, J.G.; Jahrling, P.B.; Hensley, L.E.; Johnson, R.F.; Frieman, M.B.; Schnell, M.J. One-Health: A Safe, Efficient, Dual-Use Vaccine for Humans and Animals against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus and Rabies Virus. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, X.X.; Gai, W.W.; Wong, G.; Wang, H.L.; Jin, H.L.; Feng, N.; Zhao, Y.K.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, N.; et al. Novel chimeric virus-like particles vaccine displaying MERS-CoV receptor-binding domain induce specific humoral and cellular immune response in mice. Antivir. Res. 2017, 140, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, X.X.; Gai, W.W.; Zhao, Y.K.; Wang, H.L.; Wang, H.J.; Feng, N.; Chi, H.; Qiu, B.N.; Li, N.; et al. MERS-CoV virus-like particles produced in insect cells induce specific humoural and cellular imminity in rhesus macaques. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12686–12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.; Chi, H.; Huang, P.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Mo, R.; et al. A Novel Bacterium-Like Particle Vaccine Displaying the MERS-CoV Receptor-Binding Domain Induces Specific Mucosal and Systemic Immune Responses in Mice. Viruses 2019, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Gai, W.; Perlman, S.; Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Xia, X. DNA vaccine encoding Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus S1 protein induces protective immune responses in mice. Vaccine 2017, 35, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amri, S.S.; Abbas, A.T.; Siddiq, L.A.; Alghamdi, A.; Sanki, M.A.; Al-Muhanna, M.K.; Alhabbab, R.Y.; Azhar, E.I.; Li, X.; Hashem, A.M. Immunogenicity of Candidate MERS-CoV DNA Vaccines Based on the Spike Protein. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthumani, K.; Falzarano, D.; Reuschel, E.L.; Tingey, C.; Flingai, S.; Villarreal, D.O.; Wise, M.; Patel, A.; Izmirly, A.; Aljuaid, A.; et al. A synthetic consensus anti-spike protein DNA vaccine induces protective immunity against Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in nonhuman primates. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 301ra132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, F.; Jiang, S. MERS-CoV spike protein: A key target for antivirals. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.W.; Hu, Y.W.; Wang, Q.H.; Qi, J.X.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Bao, J.K.; et al. Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26. Nature 2013, 500, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Yang, Y.; Agnihothram, S.S.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.L.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Crystal structure of the receptor-binding domain from newly emerged Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10777–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.S.; Shi, X.L.; Jiang, L.W.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, D.L.; Tong, P.; Guo, D.X.; Fu, L.L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Structure of MERS-CoV spike receptor-binding domain complexed with human receptor DPP4. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettigan, J.P.; Pomerantz, R.J.; Siler, C.A.; McKenna, P.M.; Foley, H.D.; Dietzschold, B.; Schnell, M.J. Second-generation rabies virus-based vaccine vectors expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag have greatly reduced pathogenicity but are highly immunogenic. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, H.L.; Jin, H.L.; Feng, N.; Zheng, X.X.; Li, L.; Qi, Y.L.; Liang, M.; Zhao, Y.K.; Wang, T.C.; Gao, Y.W.; et al. Using rabies virus vaccine strain SRV9 as viral vector to express exogenous gene. Virus Genes 2015, 50, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barefoot, B.; Thornburg, N.J.; Barouch, D.H.; Yu, J.S.; Sample, C.; Johnston, R.E.; Liao, H.X.; Kepler, T.B.; Haynes, B.F.; Ramsburg, E. Comparison of multiple vaccine vectors in a single heterologous prime-boost trial. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6108–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.H.; Zheng, X.X.; Wang, H.L.; Ma, J.Z.; Li, L.; Gai, W.W.; Wang, T.C.; Yang, S.T.; Xia, X.Z. An inactivated recombinant rabies CVS-11 virus expressing two copies of the glycoprotein elicits a higher level of neutralizing antibodies and provides better protection in mice. Virus Genes 2014, 48, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.C.; Li, K.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Agnihothram, S.S.; Fett, C.; Zhao, J.X.; Gale, M.J.; Baric, R.S.; Enjuanes, L.; Gallagher, T.; et al. Rapid generation of a mouse model for Middle East respiratory syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4970–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Suzuki, J.; Sakai, N.; Isome, M.; Nozawa, R.; Tanji, M.; Suzuki, H. Evaluation of T helper-1/-2 balance on the basis of IgG subclasses and serum cytokines in children with glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2004, 44, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, J.E.; Wirblich, C.; Papaneri, A.B.; Johnson, R.F.; Myers, C.J.; Juelich, T.L.; Holbrook, M.R.; Freiberg, A.N.; Bernbaum, J.G.; Jahrling, P.B.; et al. Inactivated or live-attenuated bivalent vaccines that confer protection against rabies and Ebola viruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10605–10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Mota, T.; Hagen, K.R.; Cooper, K.; Jahrling, P.B.; Tan, G.; Wirblich, C.; Johnson, R.F.; Schnell, M.J. Non-neutralizing antibodies elicited by recombinant Lassa-Rabies vaccine are critical for protection against Lassa fever. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willet, M.; Kurup, D.; Papaneri, A.; Wirblich, C.; Hooper, J.W.; Kwilas, S.A.; Keshwara, R.; Hudacek, A.; Beilfuss, S.; Rudolph, G.; et al. Preclinical Development of Inactivated Rabies Virus-Based Polyvalent Vaccine Against Rabies and Filoviruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, S414–S424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McGettigan, J.P.; Foley, H.D.; Belyakov, I.M.; Berzofsky, J.A.; Pomerantz, R.J.; Schnell, M.J. Rabies virus-based vectors expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope protein induce a strong, cross-reactive cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response against envelope proteins from different HIV-1 isolates. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4430–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama-Ito, M.; Lim, C.K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Posadas-Herrera, G.; Kato, H.; Iizuka, I.; Islam, M.T.; Morimoto, K.; Saijo, M. Replication-incompetent rabies virus vector harboring glycoprotein gene of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) protects mice from LCMV challenge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliquet, F.; Aubert, M. Elimination of terrestrial rabies in western European countries. Dev. Biol. 2004, 119, 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Bosma, T.; Kanninga, R.; Neef, J.; Audouy, S.A.L.; van Roosmalen, M.L.; Steen, A.; Buist, G.; Kok, J.; Kuipers, O.P.; Robillard, G.; et al. Novel surface display system for proteins on non-genetically modified gram-positive bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roosmalen, M.L.; Kanninga, R.; El Khattabi, M.; Neef, J.; Audouy, S.; Bosma, T.; Kuipers, A.; Post, E.; Steen, A.; Kok, J.; et al. Mucosal vaccine delivery of antigens tightly bound to an adjuvant particle made from food-grade bacteria. Methods 2006, 38, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, S.; von Wright, A.; Morelli, L.; Marteau, P.; Brassart, D.; de Vos, W.M.; Fonden, R.; Saxelin, M.; Collins, K.; Mogensen, G.; et al. Demonstration of safety of probiotics—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 44, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, R.; Yasawardena, S.; Zomer, A.; Venema, G.; Kok, J.; Leenhouts, K. Immunogenicity of a malaria parasite antigen displayed by Lactococcus lactis in oral immunisations. Vaccine 2006, 24, 3900–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audouy, S.A.L.; van Selm, S.; van Roosmalen, M.L.; Post, E.; Kanninga, R.; Neef, J.; Estevao, S.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E.S.; Adrian, P.V.; Leenhouts, K.; et al. Development of lactococcal GEM-based pneumococcal vaccines. Vaccine 2007, 25, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.; Ditamo, Y.; Rodriguez, L.; Picking, W.L.; van Roosmalen, M.L.; Leenhouts, K.; Pasetti, M.F. Neonatal mucosal immunization with a non-living, non-genetically modified Lactococcus lactis vaccine carrier induces systemic and local Th1-type immunity and protects against lethal bacterial infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2010, 3, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, V.; Visser, M.R.; van Roosmalen, M.L.; Leenhouts, K.; Huckriede, A.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Frijlink, H.W. Gastro-intestinal delivery of influenza subunit vaccine formulation adjuvanted with Gram-positive enhancer matrix (GEM) particles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, T.; Hara, H.; Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, N.; Akira, S.; Saito, T. Cutting edge: TLR2 directly triggers Th1 effector functions. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6715–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.C.; Chen, J.B.; Zhong, L.Y.; Wang, R.; Jiang, L.F.; Cai, J.Y.; Yan, L.; Huang, D.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, Z.W. NSOM- and AFM-based nanotechnology elucidates nano-structural and atomic-force features of a Y-pestis V immunogen-containing particle vaccine capable of eliciting robust response. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Braeckel-Budimir, N.; Haijema, B.J.; Leenhouts, K. Bacterium-like particles for efficient immune stimulation of existing vaccines and new subunit vaccines in mucosal applications. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigter, A.; Widjaja, I.; Versantvoort, H.; Coenjaerts, F.E.; van Roosmalen, M.; Leenhouts, K.; Rottier, P.J.; Haijema, B.J.; de Haan, C.A. A protective and safe intranasal RSV vaccine based on a recombinant prefusion-like form of the F protein bound to bacterium-like particles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.C.; Qiao, X.W.; Zheng, Q.S.; Hou, J.B. Immunogenicity and immunoprotection of porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) Cap protein displayed by Lactococcus lactis. Vaccine 2016, 34, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, S.J.; Franco-Mahecha, O.L.; Chen, X.; Choudhari, S.; Blackwelder, W.C.; van Roosmalen, M.L.; Leenhouts, K.; Picking, W.L.; Pasetti, M.F. Shigella IpaB and IpaD displayed on L. lactis bacterium-like particles induce protective immunity in adult and infant mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nganou-Makamdop, K.; van Roosmalen, M.L.; Audouy, S.A.; van Gemert, G.J.; Leenhouts, K.; Hermsen, C.C.; Sauerwein, R.W. Bacterium-like particles as multi-epitope delivery platform for Plasmodium berghei circumsporozoite protein induce complete protection against malaria in mice. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sagaseta, J.; Malito, E.; Rappuoli, R.; Bottomley, M.J. Self-assembling protein nanoparticles in the design of vaccines. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchan, V.; Panda, A.K. Interactions of antigen-loaded polylactide particles with macrophages and their correlation with the immune response. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5344–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, A.; Sparnacci, K.; Ensoli, B.; Tondelli, L. Functional polymeric nano/microparticles for surface adsorption and delivery of protein and DNA vaccines. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovsky, N.; Aguilar, J.C. Vaccine adjuvants: Current state and future trends. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaji, E.N.; Carvalho, E.; Oliveira, M.L.; Raw, I.; Ho, P.L. Trends in adjuvant development for vaccines: DAMPs and PAMPs as potential new adjuvants. Braz. J. Med Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. Pesqui. Med. Biol. 2011, 44, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brull, F.; Mensink, R.P.; van den Hurk, K.; Duijvestijn, A.; Plat, J. TLR2 activation is essential to induce a Th1 shift in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by plant stanols and plant sterols. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 2951–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudin, Y. Rabies virus-induced membrane fusion pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).