CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines Expression Profiles in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Infected with Different Subtypes of KoRV from Koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) in a Japanese Zoo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Hematological Examination
2.3. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) Culture
2.4. Extraction of Genomic DNA from PBMCs and Determination of KoRV Subtypes
2.5. Extraction of RNA from Koala Tissues
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. KoRV Infection Status of Koalas
3.2. Hematological Examination of Koalas
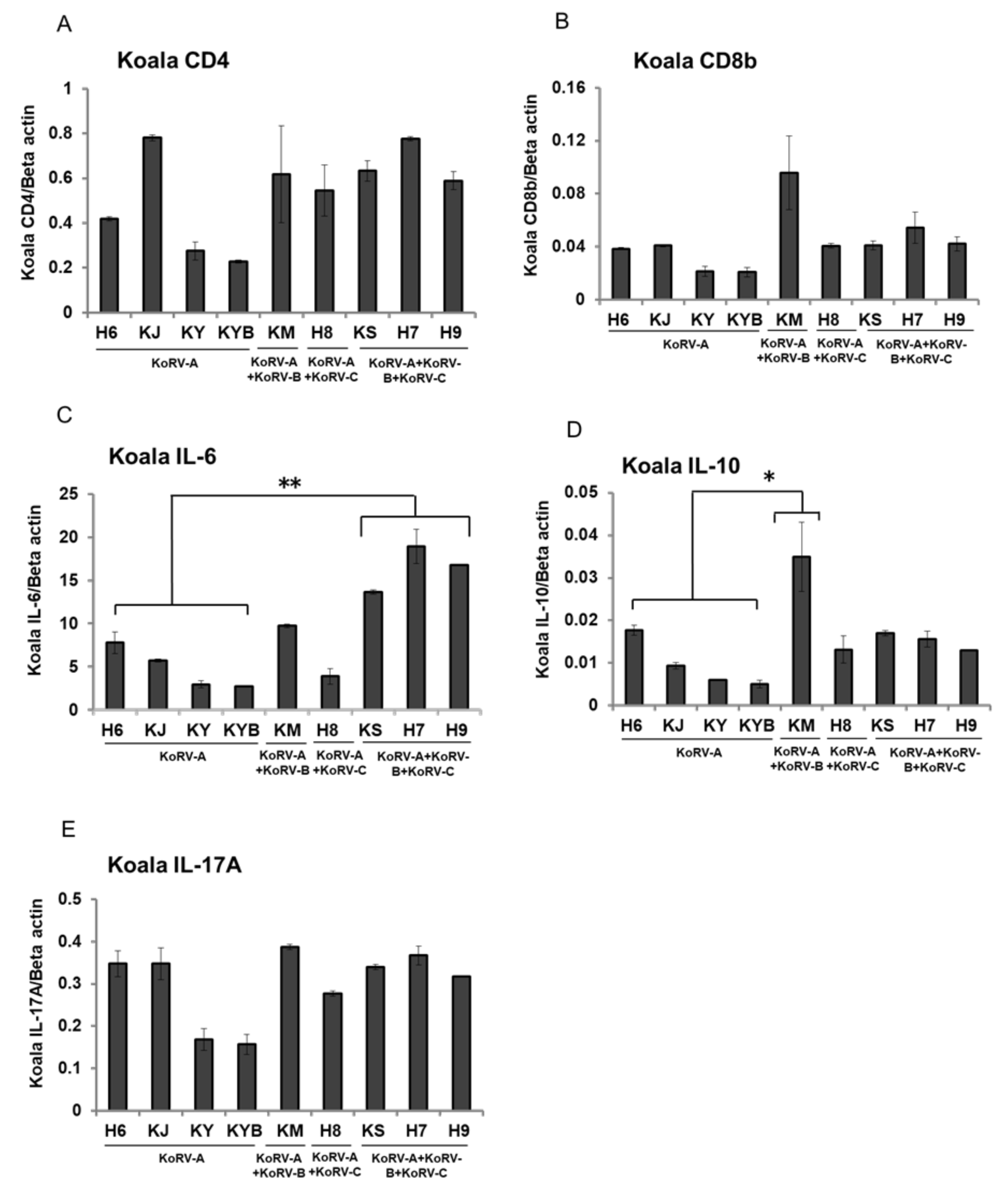
3.3. Changes of CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines mRNA Expression in Unstimulated Koala PBMCs
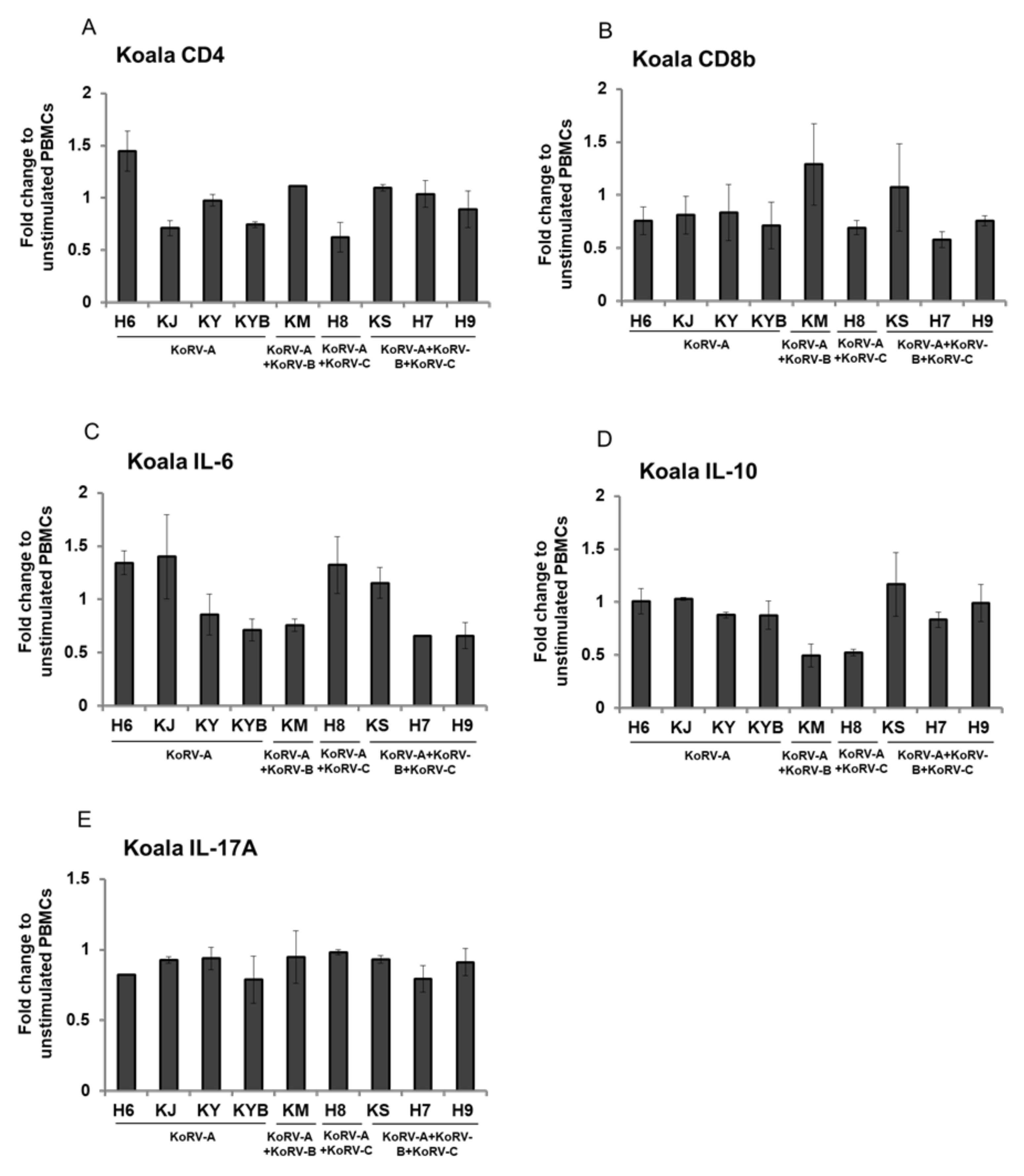
3.4. Fold Change of CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines Expression in Stimulated Koala PBMCs
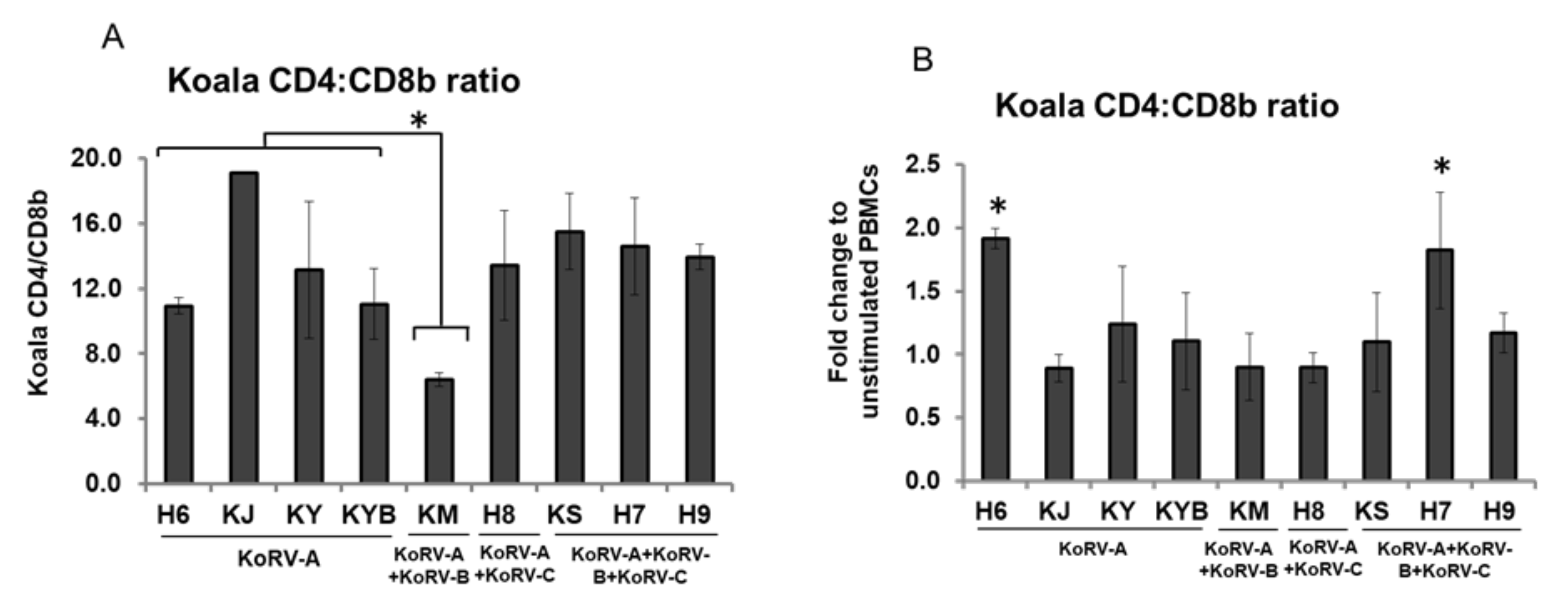
3.5. Changes in CD4 and CD8b Ratio
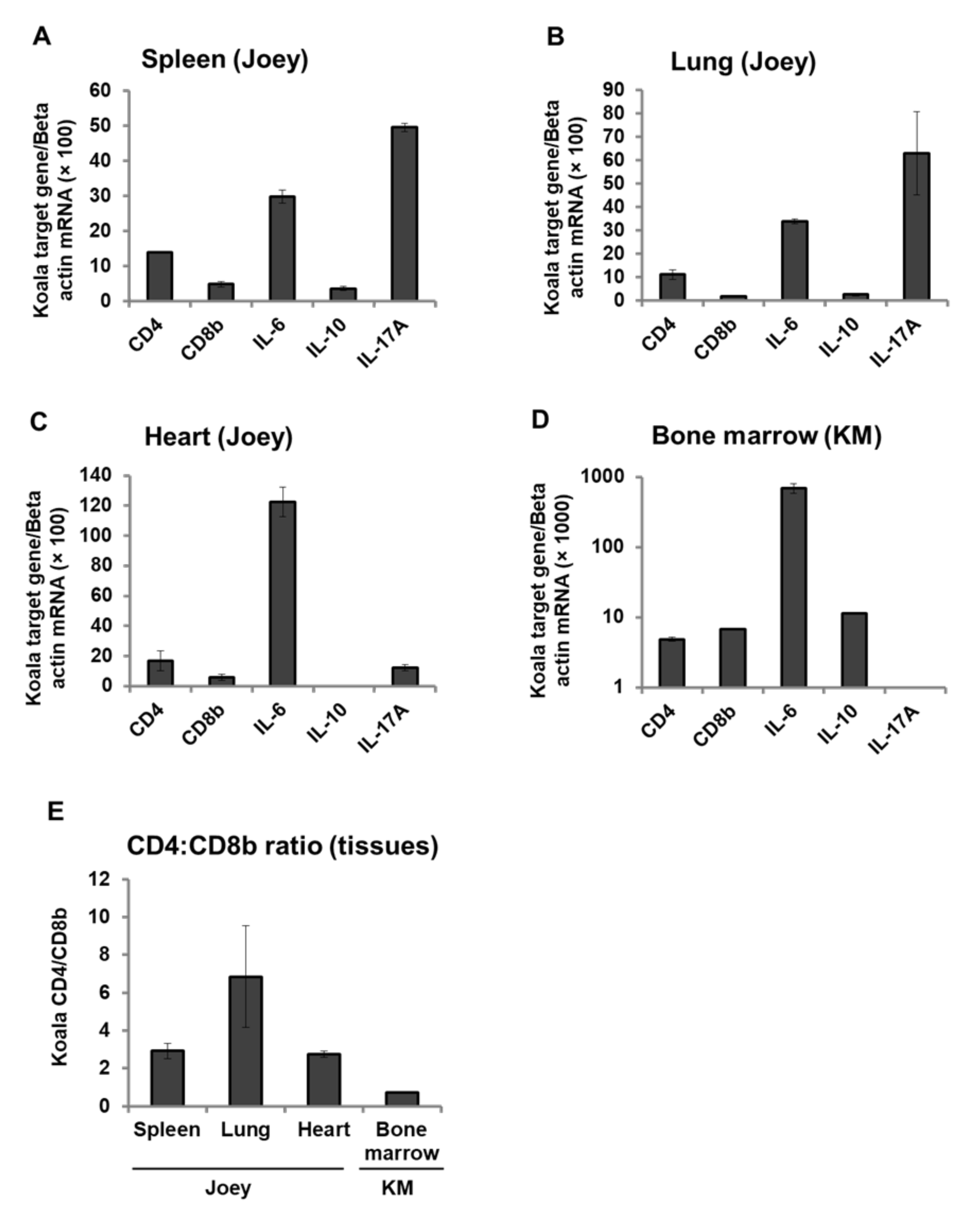
3.6. Expression Pattern of CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines mRNA in Koala Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities. Koala Populations in Queensland, New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory and National Environment Law. 2013. Available online: http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/threatened/publications/koala-species-listing.html (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Connolly, J.H.; Canfield, P.J.; Hemsley, S.; Spencer, A.J. Lymphoid neoplasia in the koala. Aust. Vet. J. 1998, 76, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlinton, R.; Meers, J.; Hanger, J.; Young, P. Real-time reverse transcriptase PCR for the endogenous koala retrovirus reveals an association between plasma viral load and neoplastic disease in koalas. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlinton, R.; Meers, J.; Young, P. Biology and evolution of the endogenous koala retrovirus. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Stadler, C.K.; Gorman, K.; Jensen, N.; Kim, D.; Zheng, H.Q.; Tang, S.; Switzer, W.M.; Pye, G.W.; Eiden, M.V. An exogenous retrovirus isolated from koalas with malignant neoplasias in a US zoo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11547–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denner, J.; Young, P.R. Koala retroviruses: Characterization and impact on the life of koalas. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabijan, J.; Woolford, L.; Lathe, S.; Simmons, G.; Hemmatzadeh, F.; Trott, D.J.; Speight, K.N. Lymphoma, koala retrovirus infection and reproductive chlamydiosis in a koala (Phascolarctos cinereus). J. Comp. Pathol. 2017, 157, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waugh, C.A.; Hanger, J.; Loader, J.; King, A.; Hobbs, M.; Johnson, R.; Timms, P. Infection with koala retrovirus subgroup B (KoRV-B), but not KoRV-A, is associated with chlamydial disease in free-ranging koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canfield, P.J.; Sabine, J.M.; Love, D.N. Virus particles associated with leukaemia in a koala. Aust. Vet. J. 1988, 65, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanger, J.J.; Bromham, L.D.; McKee, J.J.; O’Brien, T.M.; Robinson, W.F. The nucleotide sequence of Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) retrovirus: A novel type C endogenous virus related to Gibbon ape leukemia virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4264–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarlinton, R.E.; Meers, J.; Young, P.R. Retroviral invasion of the koala genome. Nature 2006, 442, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denner, J. Transspecies Transmission of Gammaretroviruses and the Origin of the Gibbon Ape Leukaemia Virus (GaLV) and the Koala Retrovirus (KoRV). Viruses 2016, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simmons, G.; Clarke, D.; McKee, J.; Young, P.; Meers, J. Discovery of a novel retrovirus sequence in an Australian native rodent (Melomys burtoni): A putative link between gibbon ape leukemia virus and koala retrovirus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishida, Y.; Zhao, K.; Greenwood, A.D.; Roca, A.L. Proliferation of endogenous retroviruses in the early stages of a host germ line invasion. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, N.; Michaux, J.; Fabre, P.H.; Morand, S.; Alpin, K.; Tsangaras, K.; Löber, U.; Fitriana, Y.; Semiadi, G.; Ishida, Y.; et al. Endogenous gibbon ape leukemia virus identified in a rodent (Melomys burtoni subsp.) from Wallacea (Indonesia). J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8169–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayward, J.A.; Tachedjian, M.; Kohl, C.; Johnson, A.; Dearnley, M.; Jesaveluk, B.; Langer, C.; Solymosi, P.D.; Hille, G.; Nitsche, A.; et al. Infectious KoRV-related retroviruses circulating in Australian bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9529–9536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Pan, Y.; Tang, S.; Pye, G.W.; Stadler, C.K.; Vogelnest, L.; Herrin, K.V.; Rideout, B.A.; Switzer, W.M. Koala retrovirus diversity, transmissibility, and disease associations. Retrovirology 2020, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayesh, M.E.H.; Hashem, M.A.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K. Koala retrovirus epidemiology, transmission mode, pathogenesis, and host immune response in koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus): A review. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, B.L.; Timms, P. Helping koalas battle disease—Recent advances in Chlamydia and koala retrovirus (KoRV) disease understanding and treatment in koalas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 583–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, G.S.; Young, P.R.; Hanger, J.J.; Jones, K.; Clarke, D.; McKee, J.J.; Meers, J. Prevalence of koala retrovirus in geographically diverse populations in Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2012, 90, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, B.L.; Ong, V.A.; Hanger, J.; Timms, P. Molecular dynamics and mode of transmission of koala retrovirus as it invades and spreads through a wild Queensland koala population. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01871-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabijan, J.; Miller, D.; Olagoke, O.; Woolford, L.; Boardman, W.; Timms, P.; Polkinghorne, A.; Simmons, G.; Hemmatzadeh, F.; Trott, D.J.; et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of koala retrovirus in two South Australian koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) populations. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, N.; Fabijan, J.; Seddon, J.; Tarlinton, R.; Owen, H.; Simmons, G.; Thia, J.; Blanchard, A.M.; Speight, N.; Kaler, J.; et al. Genetic diversity of Koala retrovirus env gene subtypes: Insights into northern and southern koala populations. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, M.A.; Maetani, F.; Kayesh, M.E.H.; Eiei, T.; Mochizuki, K.; Ito, A.; Sakurai, H.; Asai, T.; Kohara, K.T. Transmission of koala retrovirus from parent koalas to a joey in a Japanese zoo. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00019–e00020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denner, J.; Norley, S.; Kurth, R. The immunosuppressive peptide of HIV-1: Functional domains and immune response in AIDS patients. Aids 1994, 8, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; McCallister, C.; Nikolaidis, N.; Tsangaras, K.; Helgen, K.M.; Greenwood, A.D.; Roca, A.L. Sequence variation of koala retrovirus transmembrane protein p15E among koalas from different geographic regions. Virology 2015, 475, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maher, I.E.; Griffith, J.E.; Lau, Q.; Reeves, T.; Higgins, D.P. Expression profiles of the immune genes CD4, CD8β, IFNγ, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 in mitogen-stimulated koala lymphocytes (Phascolarctos cinereus) by qRT-PCR. Peer J. 2014, 2, e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abts, K.C.; Ivy, J.A.; DeWoody, J.A. Immunomics of the koala (Phascolarctos cinereus). Immunogenetics 2015, 67, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, I.E.; Higgins, D.P. Altered Immune Cytokine Expression Associated with KoRV B Infection and Season in Captive Koalas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olagoke, O.; Miller, D.; Hemmatzadeh, F.; Stephenson, T.; Fabijan, J.; Hutt, P.; Finch, S.; Speight, N.; Timms, P. Induction of neutralizing antibody response against koala retrovirus (KoRV) and reduction in viral load in koalas following vaccination with recombinant KoRV envelope protein. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olagoke, O.; Quigley, B.L.; Eiden, M.V.; Timms, P. Antibody response against koala retrovirus (KoRV) in koalas harboring KoRV-A in the presence or absence of KoRV-B. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, I.E.; Patterson, J.; Curnick, M.; Devlin, J.; Higgins, D.P. Altered immune parameters associated with koala retrovirus (KoRV) and chlamydial infection in free ranging Victorian koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus). Sci. Rep. 2019, 11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyazawa, T.; Shojima, T.; Yoshikawa, R.; Ohata, T. Isolation of koala retroviruses from koalas in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayesh, M.E.H.; Yamato, O.; Rahman, M.M.; Hashem, M.A.; Maetani, F.; Eiei, T.; Mochizuki, K.; Sakurai, H.; Kohara, K.T. Molecular dynamics of koala retrovirus infection in captive koalas in Japan. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, M.A.; Kayesh, M.E.H.; Yamato, O.; Maetani, F.; Eiei, T.; Mochizuki, K.; Sakurai, H.; Ito, A.; Kannno, H.; Kohara, K.T.; et al. Coinfection with koala retrovirus subtypes A and B and its impact on captive koalas in Japanese zoos. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, U.; Hartmann, M.G.; Bannert, N.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. Transspecies transmission of the endogenous koala retrovirus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5651–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, J.M.; Fahey, J.L.; Detels, R.; Giorgi, J.V. CD4 percentage, CD4 number, and CD4: CD8 ratio in HIV infection: Which to choose and how to use. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1989, 2, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Margolick, J.B.; Gange, S.J.; Detels, R.; O’Gorman, M.R.G.; Rinaldo, C.R.J.; Lai, S. Impact of inversion of the CD4/CD8 ratio on the natural history of HIV-1 infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 42, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Villar, S.; Sainz, T.; Lee, S.A.; Hunt, P.W.; Sinclair, E.; Shacklett, B.L.; Ferre, A.L.; Hayes, T.L.; Somsouk, M.; Hsue, P.Y.; et al. HIV-infected individuals with low CD4/CD8 ratio despite effective antiretroviral therapy exhibit altered T cell subsets, heightened CD8+ T cell activation, and increased risk of non-AIDS morbidity and mortality. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Mehraj, V.; Vyboh, K.; Cao, W.; Li, T.; Routy, J.P. CD4:CD8 ratio as a frontier marker for clinical outcome, immune dysfunction and viral reservoir size in virologically suppressed HIV-positive patients. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2015, 18, 20052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Koala | Age | Sex | KoRV Subtypes | Health Status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KoRV-A | KoRV-B | KoRV-C | ||||
| KS | 1 y 6 m | Male | Positive | Positive | Positive | Lymphoma |
| KM | 12 y | Female | Positive | Positive | Negative | Lymphoma (subsequently died) |
| KY | 2 y | Female | Positive | Negative | Negative | Apparently healthy |
| KYB | 1 y | Female | Positive | Negative | Negative | Apparently healthy |
| H6 | 3 y 9 m | Female | Positive | Negative | Negative | Apparently healthy |
| H7 | 3 y 1 m | Female | Positive | Positive | Positive | Apparently healthy |
| H8 | 5 y 5 m | Female | Positive | Negative | Positive | Apparently healthy |
| H9 | 10 y 3 m | Female | Positive | Positive | Positive | Apparently healthy |
| KJ | 6 y | Female | Positive | Negative | Negative | Apparently healthy |
| Joey | 6 m | Male | Positive | Negative | Positive | Dead |
| Gene | Forward (5′ to 3′) | Reverse (5′ to 3′) | Product Size | Reference or GenBank Accession Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pol (KoRV) | CCTTGGACCACCAAGAGACTTTTGA | TCAAATCTTGGACTGGCCGA | 523 | [11] |
| Env (KoRV-A) | TCCTGGGAACTGGAAAAGAC | GGGTTCCCCAAGTGATCTG | 321 | [8] |
| Env (KoRV-B) | TCCTGGGAACTGGAAAAGAC | GGCGCAGACTGTTGAGATTC | 271 | [5] |
| Env (KoRV-C) | TCCTGGGAACTGGAAAAGAC | AAGGCTGGTCCCGCGAAGGT | 290 | [24] |
| CD4 (Koala) | GCCAACCCAAGTGACTCTGT | TCTCCTGGACCACTCCATTC | 105 | [27] |
| CD8b (Koala) | GCATTGGCTTCTAATTGCTAGTATC | CACTTTCTATCATGCAAAGTAACCC | 88 | XM_020969485 |
| IL-6 (Koala) | TGGATGAGCTGAACTGTACCC | GCTTGCCAAGGATTGTGAGT | 119 | [27] |
| IL-10 (Koala) | ACCAGAGACAAGCTCGAAAC | TCTTCCAGCAAAGATTTGTCTATC | 50 | XM_021002936 |
| IL-17A (Koala) | GAGGCTAGGTGCCGTCATTC | TGCTGGATTTCGACGGAGTT | 80 | KJ174517 |
| Beta actin (Koala) | AGATCATTGCCCCACCT | TGGAAGGCCCAGATTC | 123 | [11] |
| Koala | Blood Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (102/μL) | RBC (104/μL) | HGB (g/dL) | PCV (%) | MCV (fL) | MCH (pg) | MCHC (g/dL) | |
| KS | 4000 | 23.4 | 8.8 | 26 | 111.1 | 37.6 | 33.8 |
| KM | 2275 | 241 | 8.8 | 25.4 | 105.4 | 36.5 | 34.6 |
| KY | 102 | 360 | 14.1 | 40.5 | 112.5 | 39.2 | 34.8 |
| KYB | 52 | 308 | 12 | 35.9 | 116.6 | 39 | 33.4 |
| H6 | 70 | 390 | 14 | 41.6 | 106.7 | 35.9 | 33.7 |
| H7 | 99 | 349 | 13.7 | 39.1 | 112 | 39.3 | 35 |
| H8 | 82 | 342 | 13 | 38 | 111.1 | 38 | 34.2 |
| H9 | 52 | 319 | 11 | 33.8 | 106 | 34.5 | 32.5 |
| KJ | 125 | 359 | 13.2 | 37.8 | 105.3 | 36.8 | 34.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kayesh, M.E.H.; Hashem, M.A.; Maetani, F.; Eiei, T.; Mochizuki, K.; Ochiai, S.; Ito, A.; Ito, N.; Sakurai, H.; Asai, T.; et al. CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines Expression Profiles in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Infected with Different Subtypes of KoRV from Koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) in a Japanese Zoo. Viruses 2020, 12, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121415
Kayesh MEH, Hashem MA, Maetani F, Eiei T, Mochizuki K, Ochiai S, Ito A, Ito N, Sakurai H, Asai T, et al. CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines Expression Profiles in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Infected with Different Subtypes of KoRV from Koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) in a Japanese Zoo. Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121415
Chicago/Turabian StyleKayesh, Mohammad Enamul Hoque, Md Abul Hashem, Fumie Maetani, Taiki Eiei, Kyoya Mochizuki, Shinsaku Ochiai, Ayaka Ito, Nanao Ito, Hiroko Sakurai, Takayuki Asai, and et al. 2020. "CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines Expression Profiles in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Infected with Different Subtypes of KoRV from Koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) in a Japanese Zoo" Viruses 12, no. 12: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121415
APA StyleKayesh, M. E. H., Hashem, M. A., Maetani, F., Eiei, T., Mochizuki, K., Ochiai, S., Ito, A., Ito, N., Sakurai, H., Asai, T., & Tsukiyama-Kohara, K. (2020). CD4, CD8b, and Cytokines Expression Profiles in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Infected with Different Subtypes of KoRV from Koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) in a Japanese Zoo. Viruses, 12(12), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121415






