Mapping Influenza-Induced Posttranslational Modifications on Histones from CD8+ T Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
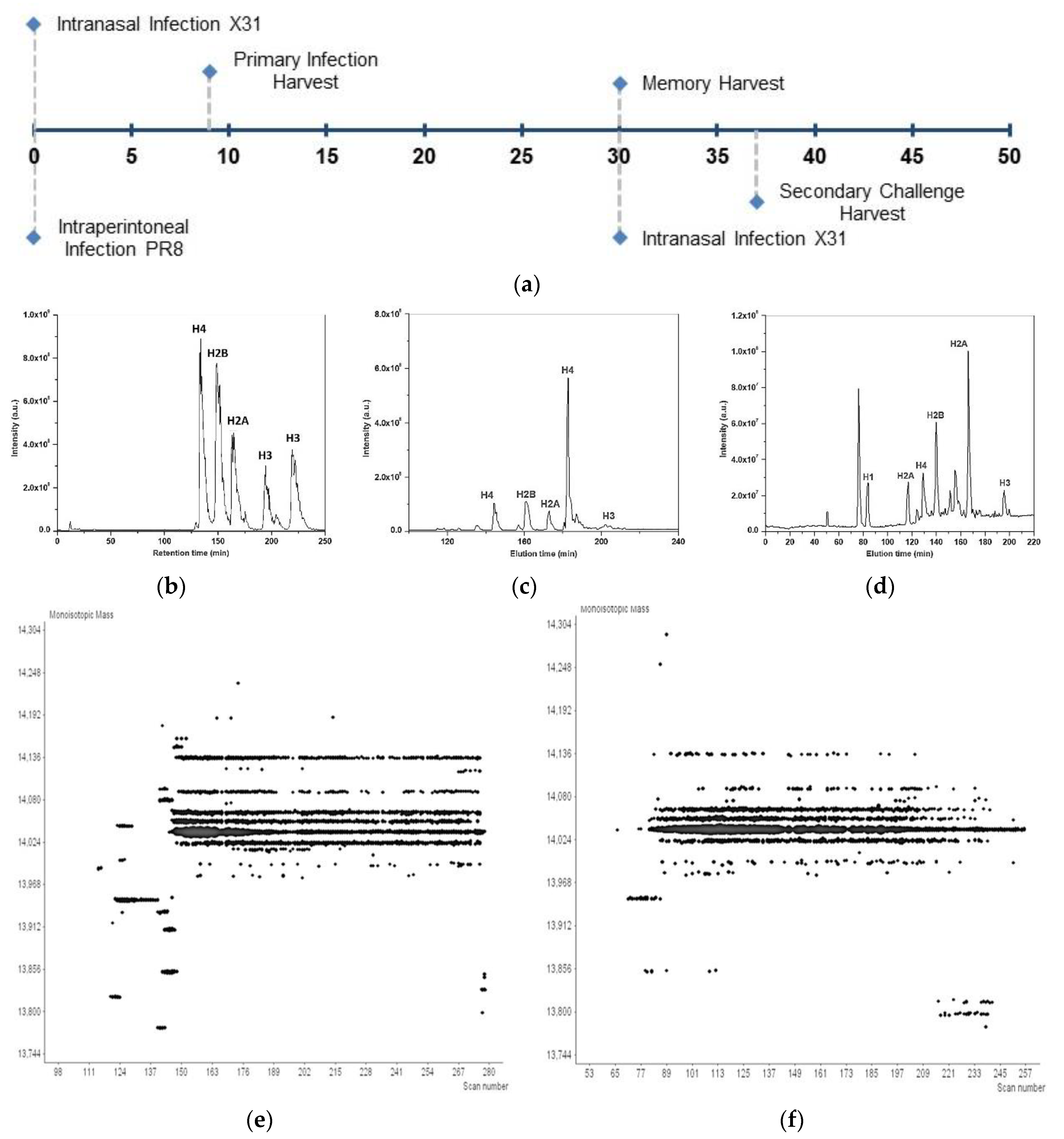
2.1. Infections and T Cell Extraction
2.2. Mass Spectra Acquisition
2.3. Data Analysis
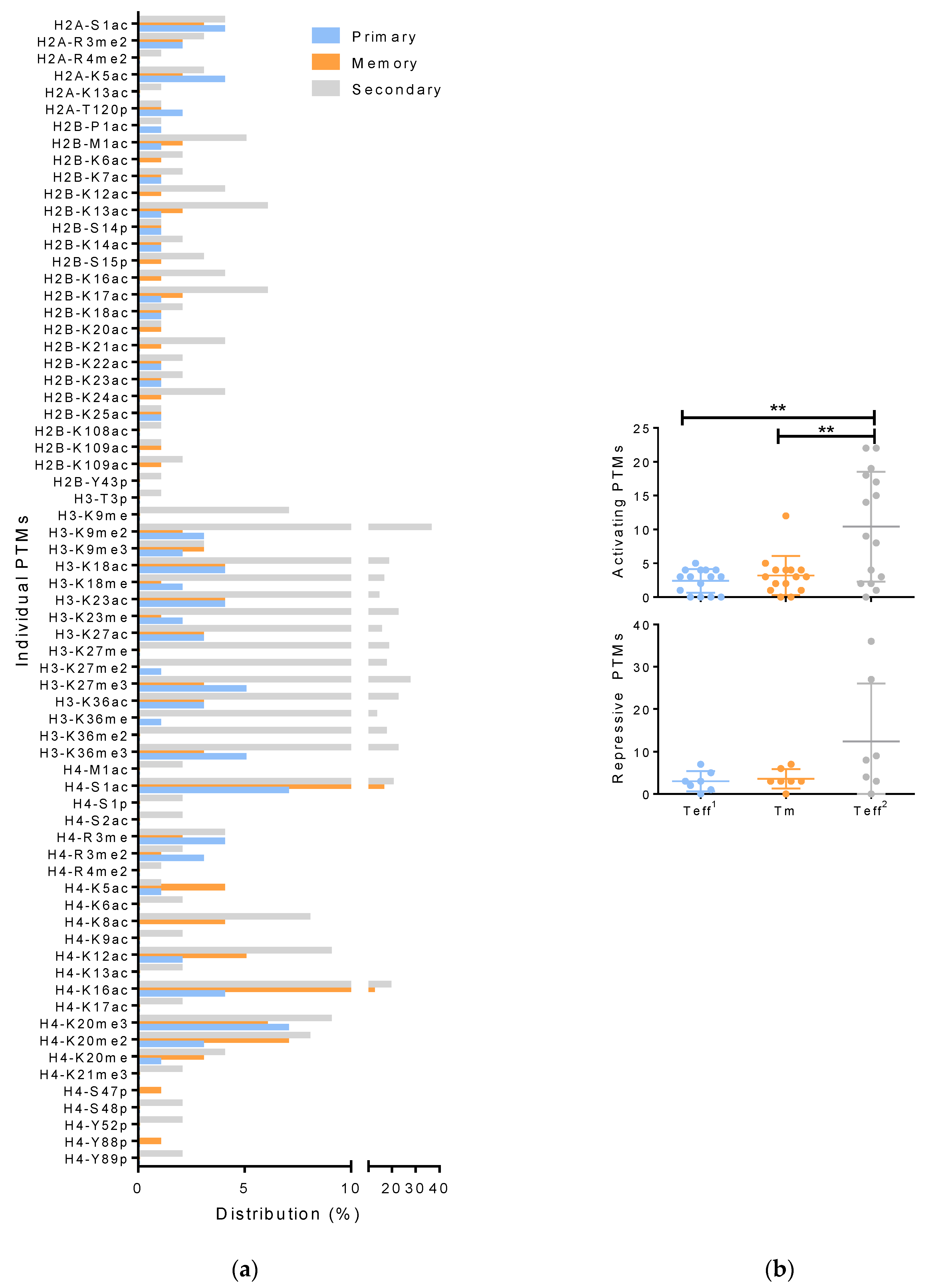
3. Results
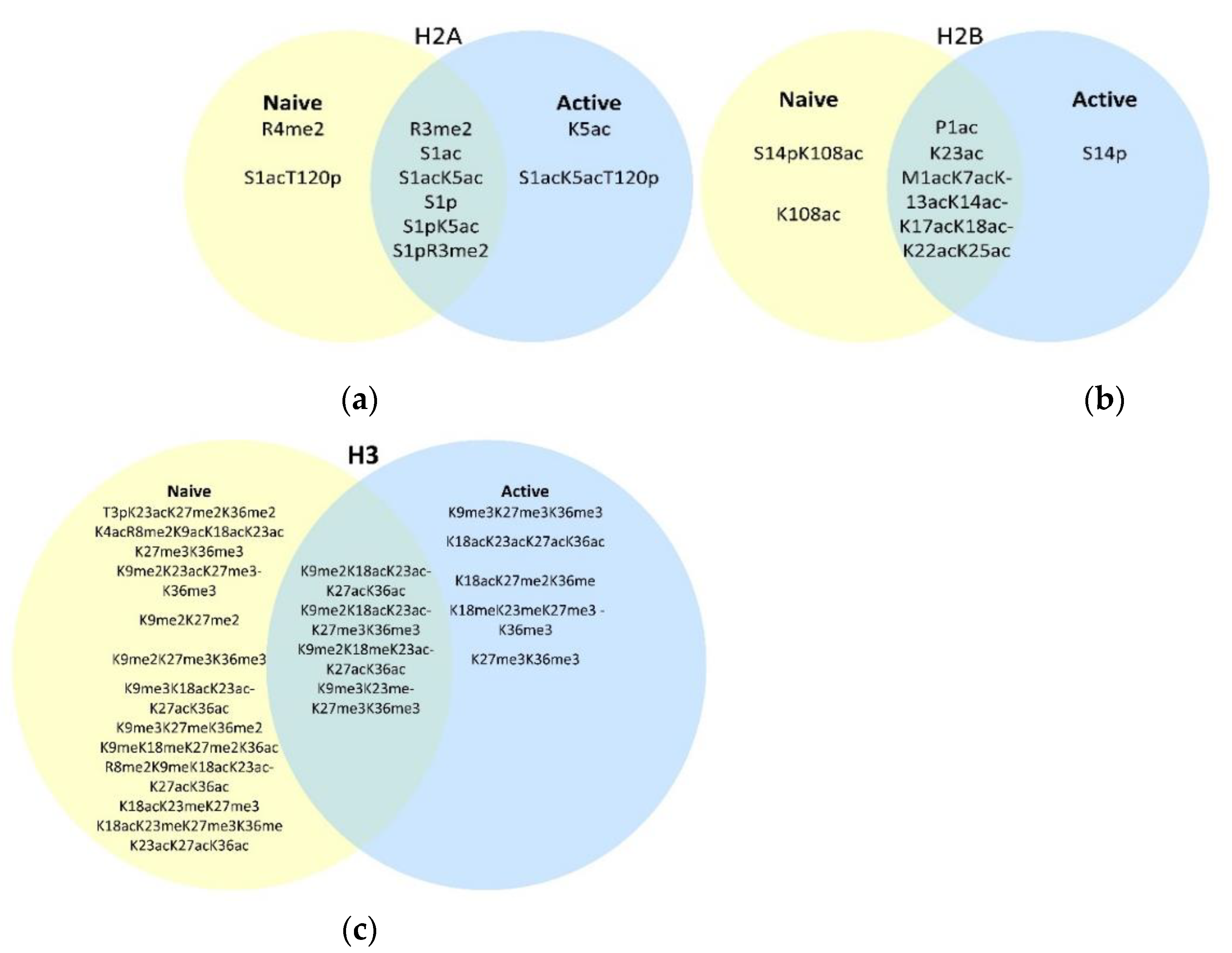
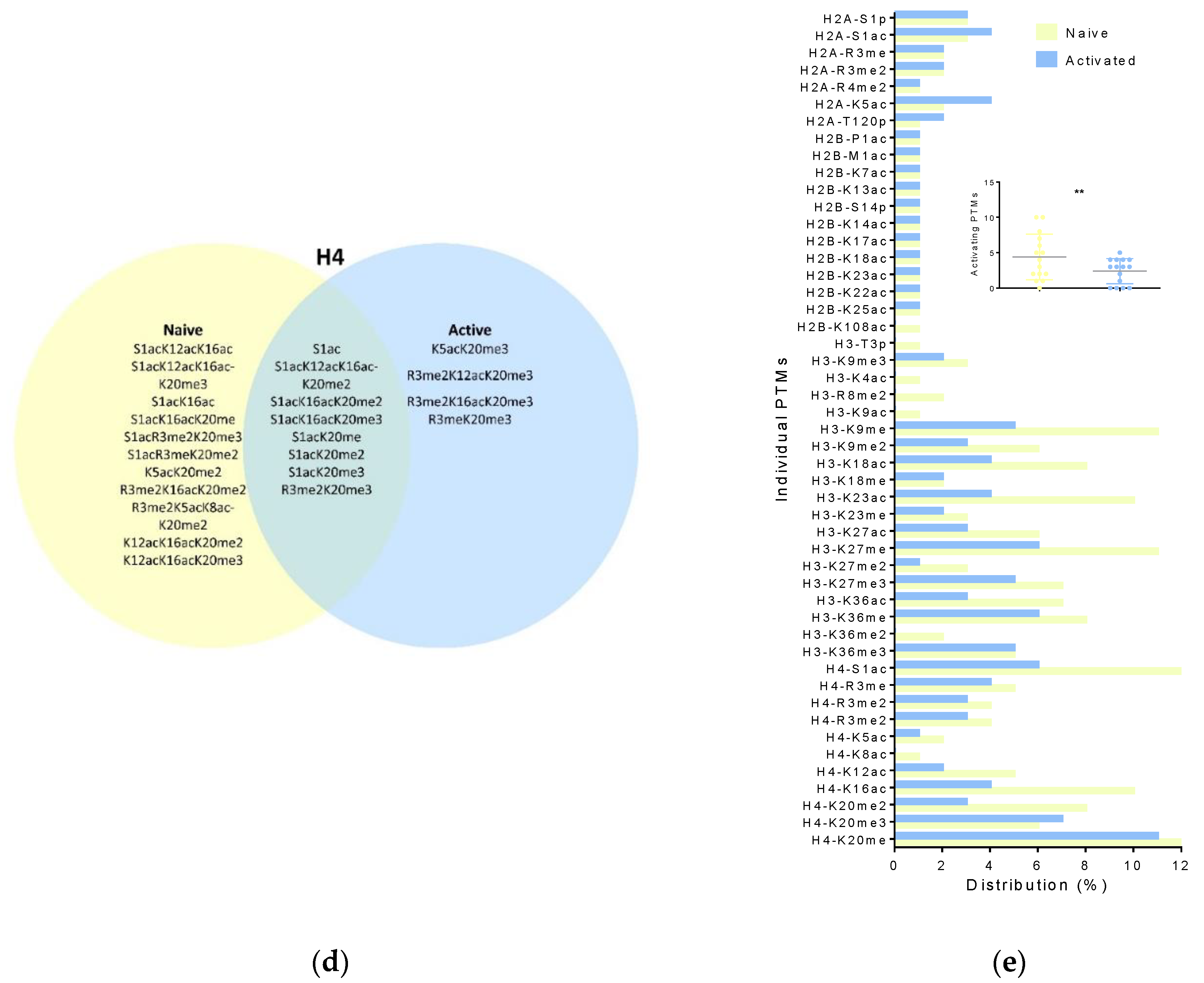
3.1. Naïve Versus Activated T Cell Histone Modifications
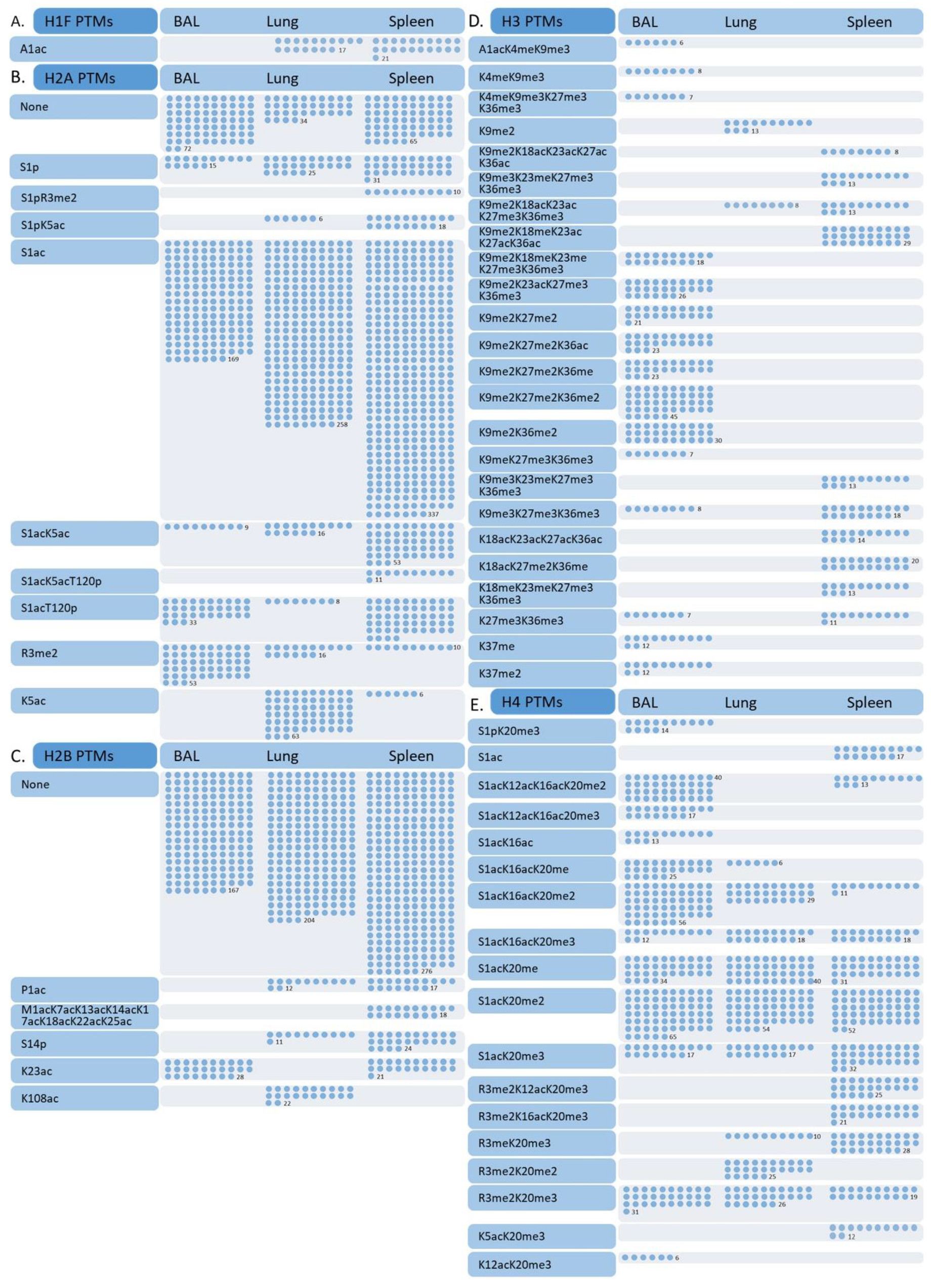
3.2. Differences in Effector T Cell Histone Modification from the Spleen, Lung, and Bronchial Lavage
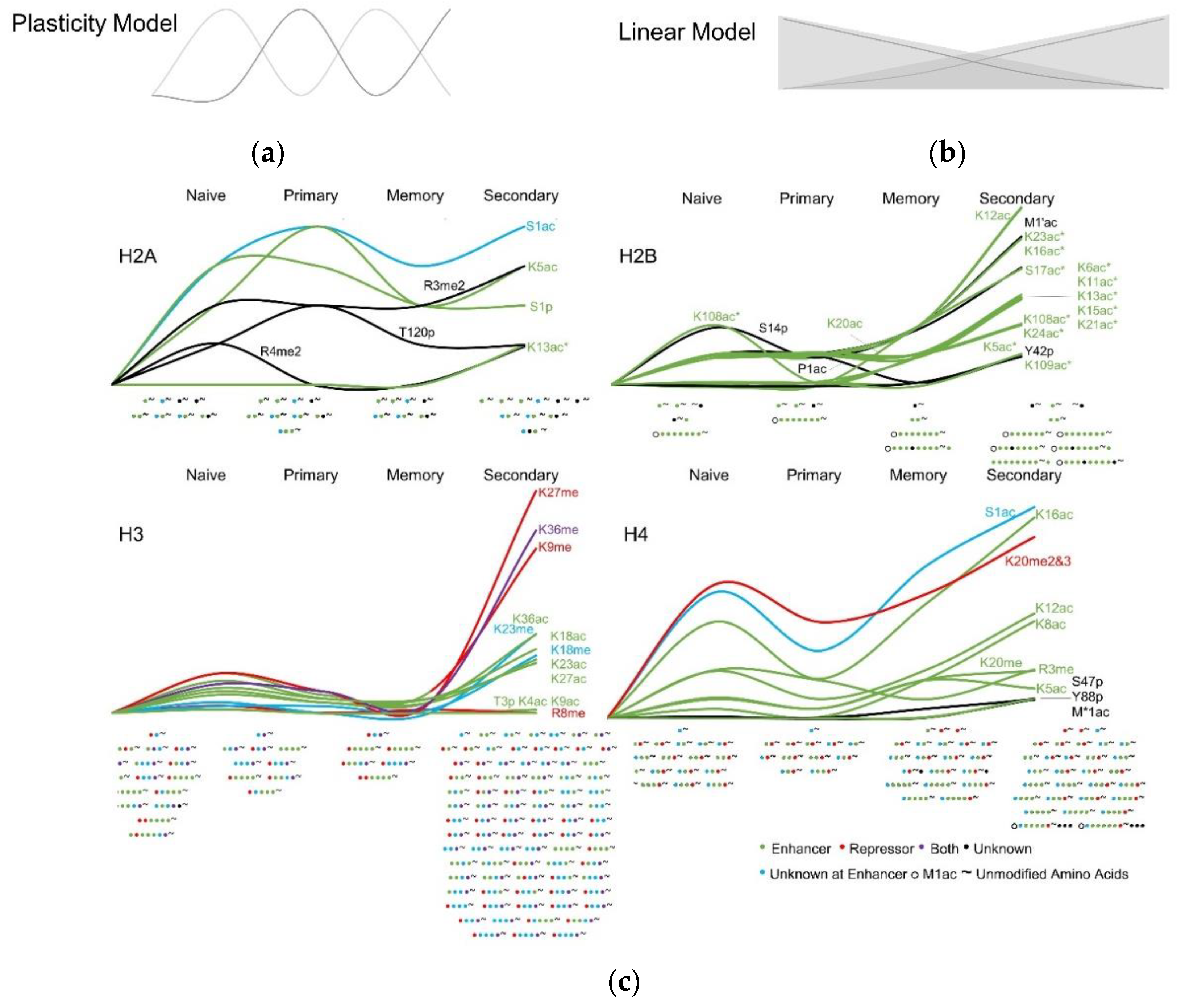
3.3. Histone Modifications in Memory and Effector T Cells Following Influenza Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, S.J.; Kedzierska, K.; La Gruta, N.L.; Webby, R.; Doherty, P.C. Characterization of CD8+ T cell repertoire diversity and persistence in the influenza A virus model of localized, transient infection. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Gruta, N.L.; Turner, S.J.; Doherty, P.C. Hierarchies in cytokine expression profiles for acute and resolving influenza virus-specific CD8+ T cell responses: Correlation of cytokine profile and TCR avidity. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5553–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russ, B.E.; Olshanksy, M.; Smallwood, H.S.; Li, J.; Denton, A.E.; Prier, J.E.; Stock, A.T.; Croom, H.A.; Cullen, J.G.; Nguyen, M.L.; et al. Distinct epigenetic signatures delineate transcriptional programs during virus-specific CD8(+) T cell differentiation. Immunity 2014, 41, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, S.; Thomas, P.G. Balancing Immune Protection and Immune Pathology by CD8(+) T-Cell Responses to Influenza Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, S.; Meliopoulos, V.A.; McClaren, J.L.; Guo, X.Z.; Sanders, C.J.; Smallwood, H.S.; Webby, R.J.; Schultz-Cherry, S.L.; Doherty, P.C.; Thomas, P.G. Diverse heterologous primary infections radically alter immunodominance hierarchies and clinical outcomes following H7N9 influenza challenge in mice. PLoS Pathogens. 2015, 11, e1004642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veiga-Fernandes, H.; Walter, U.; Bourgeois, C.; McLean, A.; Rocha, B. Response of naive and memory CD8+ T cells to antigen stimulation in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaech, S.M.; Hemby, S.; Kersh, E.; Ahmed, R. Molecular and functional profiling of memory CD8 T cell differentiation. Cell 2002, 111, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzolla, A.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sant, S.; Jaffar, J.; Loudovaris, T.; Mannering, S.I.; Thomas, P.G.; Westall, G.P.; Kedzierska, K.; Wakim, L.M. Influenza-specific lung-resident memory T cells are proliferative and polyfunctional and maintain diverse TCR profiles. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreansky, S.S.; Stambas, J.; Thomas, P.G.; Xie, W.; Webby, R.J.; Doherty, P.C. Consequences of immunodominant epitope deletion for minor influenza virus-specific CD8+-T-cell responses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4329–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keating, R.; Morris, M.Y.; Yue, W.; Reynolds, C.E.; Harris, T.L.; Brown, S.A.; Doherty, P.C.; Thomas, P.G.; McGargill, M.A. Potential killers exposed: Tracking endogenous influenza-specific CD8(+) T cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 1104–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souquette, A.; Thomas, P.G. Past Life and Future Effects-How Heterologous Infections Alter Immunity to Influenza Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannan, A.; Huang, W.; Huang, F.; August, A. Signal transduction via the T cell antigen receptor in naive and effector/memory T cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghoneim, H.E.; Fan, Y.; Moustaki, A.; Abdelsamed, H.A.; Dash, P.; Dogra, P.; Carter, R.; Awad, W.; Neale, G.; Thomas, P.G.; et al. De Novo Epigenetic Programs Inhibit PD-1 Blockade-Mediated T Cell Rejuvenation. Cell 2017, 170, 142–157.e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelsamed, H.A.; Zebley, C.C.; Youngblood, B. Epigenetic Maintenance of Acquired Gene Expression Programs during Memory CD8 T Cell Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblood, B.; Noto, A.; Porichis, F.; Akondy, R.S.; Ndhlovu, Z.M.; Austin, J.W.; Bordi, R.; Procopio, F.A.; Miura, T.; Allen, T.M.; et al. Cutting edge: Prolonged exposure to HIV reinforces a poised epigenetic program for PD-1 expression in virus-specific CD8 T cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harland, K.L.; Day, E.B.; Apte, S.H.; Russ, B.E.; Doherty, P.C.; Turner, S.J.; Kelso, A. Epigenetic plasticity of Cd8a locus during CD8(+) T-cell development and effector differentiation and reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denton, A.E.; Russ, B.E.; Doherty, P.C.; Rao, S.; Turner, S.J. Differentiation-dependent functional and epigenetic landscapes for cytokine genes in virus-specific CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15306–15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juelich, T.; Sutcliffe, E.L.; Denton, A.; He, Y.; Doherty, P.C.; Parish, C.R.; Turner, S.J.; Tremethick, D.J.; Rao, S. Interplay between chromatin remodeling and epigenetic changes during lineage-specific commitment to granzyme B expression. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7063–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; The Consortium for Top Down Proteomics. Proteoform: A single term describing protein complexity. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.I.; Lessard, J.; Crabtree, G.R. Understanding the words of chromatin regulation. Cell 2009, 136, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, T.K.; De Carvalho, D.D.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetic modifications as therapeutic targets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadakierska-Chudy, A.; Filip, M. A comprehensive view of the epigenetic landscape. Part II: Histone post-translational modification, nucleosome level, and chromatin regulation by ncRNAs. Neurotox Res. 2015, 27, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burgess, R.J.; Zhang, Z. Histone chaperones in nucleosome assembly and human disease. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eberharter, A.; Becker, P.B. Histone acetylation: A switch between repressive and permissive chromatin. Second Rev. Ser. Chromatin Dyn. Embo Rep. 2002, 3, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, K.R.; Zhao, Y.; Klus, N.J.; Kaiser, J.F.; Gordy, L.E.; Joyce, S.; Hiebert, S.W.; Summers, A.R. Histone Deacetylase 3 Is Required for Efficient T Cell Development. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 3854–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dovey, O.M.; Foster, C.T.; Conte, N.; Edwards, S.A.; Edwards, J.M.; Singh, R.; Vassiliou, G.; Bradley, A.; Cowley, S.M. Histone deacetylase 1 and 2 are essential for normal T-cell development and genomic stability in mice. Blood 2013, 121, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heideman, M.R.; Wilting, R.H.; Yanover, E.; Velds, A.; de Jong, J.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; Jacobs, H.; Wessels, L.F.; Dannenberg, J.H. Dosage-dependent tumor suppression by histone deacetylases 1 and 2 through regulation of c-Myc collaborating genes and p53 function. Blood 2013, 121, 2038–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Jiao, J.; Wang, L.; O’Brien, S.; Newick, K.; Wang, L.C.; Falkensammer, E.; Liu, Y.; Han, R.; Kapoor, V.; et al. HDAC5 controls the functions of Foxp3(+) T-regulatory and CD8(+) T cells. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, G.; Okiyama, N.; Villarroel, V.A.; Katz, S.I. Histone deacetylase 6 inhibition impairs effector CD8 T-cell functions during skin inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunez-Andrade, N.; Iborra, S.; Trullo, A.; Moreno-Gonzalo, O.; Calvo, E.; Catalan, E.; Menasche, G.; Sancho, D.; Vazquez, J.; Yao, T.P.; et al. HDAC6 regulates the dynamics of lytic granules in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tschismarov, R.; Firner, S.; Gil-Cruz, C.; Goschl, L.; Boucheron, N.; Steiner, G.; Matthias, P.; Seiser, C.; Ludewig, B.; Ellmeier, W. HDAC1 controls CD8+ T cell homeostasis and antiviral response. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exner, V.; Aichinger, E.; Shu, H.; Wildhaber, T.; Alfarano, P.; Caflisch, A.; Gruissem, W.; Kohler, C.; Hennig, L. The chromodomain of LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN 1 is essential for H3K27me3 binding and function during Arabidopsis development. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, K.H.; Bracken, A.P.; Pasini, D.; Dietrich, N.; Gehani, S.S.; Monrad, A.; Rappsilber, J.; Lerdrup, M.; Helin, K. A model for transmission of the H3K27me3 epigenetic mark. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, K.; Marley, K.E.; Jeong, B.R.; Xu, J.; Hesson, J.; Cerny, R.L.; Waterborg, J.H.; Cerutti, H. Monomethyl histone H3 lysine 4 as an epigenetic mark for silenced euchromatin in Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2439–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nightingale, K.P.; Gendreizig, S.; White, D.A.; Bradbury, C.; Hollfelder, F.; Turner, B.M. Cross-talk between histone modifications in response to histone deacetylase inhibitors: MLL4 links histone H3 acetylation and histone H3K4 methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 4408–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taverna, S.D.; Ilin, S.; Rogers, R.S.; Tanny, J.C.; Lavender, H.; Li, H.; Baker, L.; Boyle, J.; Blair, L.P.; Chait, B.T.; et al. Yng1 PHD finger binding to H3 trimethylated at K4 promotes NuA3 HAT activity at K14 of H3 and transcription at a subset of targeted ORFs. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roh, T.Y.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Zhao, K. The genomic landscape of histone modifications in human T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15782–15787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akkers, R.C.; van Heeringen, S.J.; Jacobi, U.G.; Janssen-Megens, E.M.; Francoijs, K.J.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Veenstra, G.J. A hierarchy of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 acquisition in spatial gene regulation in Xenopus embryos. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Paz Sanchez, M.; Gutierrez, C. Arabidopsis ORC1 is a PHD-containing H3K4me3 effector that regulates transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2065–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strahl, B.D.; Allis, C.D. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 2000, 403, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tong, Q.; Bishop, D.K.; Zhang, Y. Histone methyltransferase and histone methylation in inflammatory T-cell responses. Immunotherapy 2013, 5, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, B.E.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Xie, X.; Kamal, M.; Huebert, D.J.; Cuff, J.; Fry, B.; Meissner, A.; Wernig, M.; Plath, K.; et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell 2006, 125, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stock, J.K.; Giadrossi, S.; Casanova, M.; Brookes, E.; Vidal, M.; Koseki, H.; Brockdorff, N.; Fisher, A.G.; Pombo, A. Ring1-mediated ubiquitination of H2A restrains poised RNA polymerase II at bivalent genes in mouse ES cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, H.F.; Azuara, V.; Amoils, S.; Spivakov, M.; Terry, A.; Nesterova, T.; Cobb, B.S.; Ramsahoye, B.; Merkenschlager, M.; Fisher, A.G. The impact of chromatin modifiers on the timing of locus replication in mouse embryonic stem cells. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueberheide, B.M.; Mollah, S. Deciphering the histone code using mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 259, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, R.; Hertz, T.; Wehenkel, M.; Harris, T.L.; Edwards, B.A.; McClaren, J.L.; Brown, S.A.; Surman, S.; Wilson, Z.S.; Bradley, P.; et al. The kinase mTOR modulates the antibody response to provide cross-protective immunity to lethal infection with influenza virus. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; Tolić, N.; Zhao, R.; Moore, R.J.; Hengel, S.M.; Robinson, E.W.; Stenoien, D.L.; Wu, S.; Smith, R.D.; Paša-Tolić, L. Enhanced top-down characterization of histone post-translational modifications. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karch, K.R.; Sidoli, S.; Garcia, B.A. Identification and Quantification of Histone PTMs Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Methods Enzymol. 2016, 574, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiMaggio, P.A., Jr.; Young, N.L.; Baliban, R.C.; Garcia, B.A.; Floudas, C.A. A mixed integer linear optimization framework for the identification and quantification of targeted post-translational modifications of highly modified proteins using multiplexed electron transfer dissociation tandem mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2009, 8, 2527–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, S.; Burlingame, A.L. Data processing algorithms for analysis of high resolution MSMS spectra of peptides with complex patterns of posttranslational modifications. Mol. Cell. Proteom. Mcp 2010, 9, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, A.M.; Pesavento, J.J.; Mizzen, C.A.; Kelleher, N.L.; Pevzner, P.A. Interpreting top-down mass spectra using spectral alignment. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, H.S.; Duan, S.; Morfouace, M.; Rezinciuc, S.; Shulkin, B.L.; Shelat, A.; Zink, E.E.; Milasta, S.; Bajracharya, R.; Oluwaseum, A.J.; et al. Targeting Metabolic Reprogramming by Influenza Infection for Therapeutic Intervention. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1640–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, P.A.; Eberharter, A.; John, S.; Cook, R.G.; Turner, B.M.; Workman, J.L. Expanded lysine acetylation specificity of Gcn5 in native complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5895–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Garcia, B.A. Comprehensive Catalog of Currently Documented Histone Modifications. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2015, 7, a025064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamaru, H.; Selker, E.U. A histone H3 methyltransferase controls DNA methylation in Neurospora crassa. Nature 2001, 414, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Cao, X.; Jacobsen, S. Interplay between two epigenetic marks. DNA methylation and histone H3 lysine 9 methylation. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barber, C.M.; Turner, F.B.; Wang, Y.; Hagstrom, K.; Taverna, S.D.; Mollah, S.; Ueberheide, B.; Meyer, B.J.; Hunt, D.F.; Cheung, P.; et al. The enhancement of histone H4 and H2A serine 1 phosphorylation during mitosis and S-phase is evolutionarily conserved. Chromosoma 2004, 112, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Griffin, K.; Mondal, N.; Parvin, J.D. Phosphorylation of histone H2A inhibits transcription on chromatin templates. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 21866–21872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caterino, T.L.; Hayes, J.J. Structure of the H1 C-terminal domain and function in chromatin condensation. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossetto, D.; Avvakumov, N.; Cote, J. Histone phosphorylation: A chromatin modification involved in diverse nuclear events. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, A.S.; Lowell, J.E.; Jacobson, S.J.; Pillus, L. Esa1p is an essential histone acetyltransferase required for cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, A.; Horikoshi, M. Tip60 acetylates six lysines of a specific class in core histones in vitro. Genes Cells 1998, 3, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiltz, R.L.; Mizzen, C.A.; Vassilev, A.; Cook, R.G.; Allis, C.D.; Nakatani, Y. Overlapping but distinct patterns of histone acetylation by the human coactivators p300 and PCAF within nucleosomal substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verreault, A.; Kaufman, P.D.; Kobayashi, R.; Stillman, B. Nucleosomal DNA regulates the core-histone-binding subunit of the human Hat1 acetyltransferase. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aihara, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Mizusaki, H.; Yoneda, M.; Kato, M.; Doiguchi, M.; Imamura, Y.; Higashi, M.; Ikura, T.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Histone H2A T120 Phosphorylation Promotes Oncogenic Transformation via Upregulation of Cyclin D1. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Liang, C.; Chen, Q.; Yan, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Lu, W.; et al. Histone H2A phosphorylation recruits topoisomerase IIalpha to centromeres to safeguard genomic stability. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e101863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füllgrabe, J.; Hajji, N.; Joseph, B. Cracking the death code: Apoptosis-related histone modifications. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, H.C.; Nielsen, E.C.; Matthiesen, R.; Jensen, L.H.; Sehested, M.; Finn, P.; Grauslund, M.; Hansen, A.M.; Jensen, O.N. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Post-translational Modifications of Human Histones. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 1314–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Eugeni, E.E.; Parthun, M.R.; Freitas, M.A. Identification of novel histone post-translational modifications by peptide mass fingerprinting. Chromosoma 2003, 112, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Sprung, R.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ball, H.; Pei, J.; Cheng, T.; Kho, Y.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, L.; et al. Substrate and functional diversity of lysine acetylation revealed by a proteomics survey. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Mann, M. Nepsilon-formylation of lysine is a widespread post-translational modification of nuclear proteins occurring at residues involved in regulation of chromatin function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Blum, R.; Bowman, C.; Hu, D.; Shilatifard, A.; Shen, S.; Dynlacht, B.D. A role for H3K4 monomethylation in gene repression and partitioning of chromatin readers. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Briggs, S.D.; Bryk, M.; Strahl, B.D.; Cheung, W.L.; Davie, J.K.; Dent, S.Y.; Winston, F.; Allis, C.D. Histone H3 lysine 4 methylation is mediated by Set1 and required for cell growth and rDNA silencing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, T.; Mori, T.; Tada, S.; Krajewski, W.; Rozovskaia, T.; Wassell, R.; Dubois, G.; Mazo, A.; Croce, C.M.; Canaani, E. ALL-1 is a histone methyltransferase that assembles a supercomplex of proteins involved in transcriptional regulation. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bernatavichute, Y.V.; Cokus, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Jacobsen, S.E. Genome-wide analysis of mono-, di- and trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 4 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pace, L.; Goudot, C.; Zueva, E.; Gueguen, P.; Burgdorf, N.; Waterfall, J.J.; Quivy, J.-P.; Almouzni, G.; Amigorena, S. The epigenetic control of stemness in CD8+ T cell fate commitment. Science 2018, 359, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruenjaiman, V.; Butta, P.; Leu, Y.W.; Pongpanich, M.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Kueanjinda, P.; Palaga, T. Profile of Histone H3 Lysine 4 Trimethylation and the Effect of Lipopolysaccharide/Immune Complex-Activated Macrophages on Endotoxemia. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Epigenetic regulation of macrophages: From homeostasis maintenance to host defense. Cell Mol. Immunol 2020, 17, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, G.; Wei, L.; Zhu, J.; Zang, C.; Hu-Li, J.; Yao, Z.; Cui, K.; Kanno, Y.; Roh, T.Y.; Watford, W.T.; et al. Global mapping of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 reveals specificity and plasticity in lineage fate determination of differentiating CD4+ T cells. Immunity 2009, 30, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaMere, S.A.; Thompson, R.C.; Meng, X.; Komori, H.K.; Mark, A.; Salomon, D.R. H3K27 Methylation Dynamics during CD4 T Cell Activation: Regulation of JAK/STAT and IL12RB2 Expression by JMJD3. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3158–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araki, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zang, C.; Wood, W.H., 3rd; Schones, D.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.Y.; Lhotsky, B.; Wersto, R.P.; Peng, W.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of histone methylation reveals chromatin state-based regulation of gene transcription and function of memory CD8+ T cells. Immunity 2009, 30, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; Aune, T.M. Dynamic changes in histone-methylation ‘marks’ across the locus encoding interferon-gamma during the differentiation of T helper type 2 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Merwe, M.M.; Smith, J.E. The community health nurse in the next decades. Nurs. RSA 1991, 6, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Woltring, D.; Gerondakis, S.; Shannon, M.F. Histone dynamics on the interleukin-2 gene in response to T-cell activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiza, V.; Molina-Serrano, D.; Kyriakou, D.; Hadjiantoniou, A.; Kirmizis, A. N-alpha-terminal acetylation of histone H4 regulates arginine methylation and ribosomal DNA silencing. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ju, J.; Chen, A.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nie, M.; Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Yao, B.; et al. NatD promotes lung cancer progression by preventing histone H4 serine phosphorylation to activate Slug expression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olp, M.D.; Zhu, N.; Smith, B.C. Metabolically Derived Lysine Acylations and Neighboring Modifications Tune the Binding of the BET Bromodomains to Histone H4. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 5485–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.G.; Keating, R.; Hulse-Post, D.J.; Doherty, P.C. Cell-mediated protection in influenza infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, Y.C.; Camporeale, G.; Kothapalli, N.; Sarath, G.; Zempleni, J. Lysine residues in N-terminal and C-terminal regions of human histone H2A are targets for biotinylation by biotinidase. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 17, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kothapalli, N.; Camporeale, G.; Kueh, A.; Chew, Y.C.; Oommen, A.M.; Griffin, J.B.; Zempleni, J. Biological functions of biotinylated histones. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odegard, V.H.; Kim, S.T.; Anderson, S.M.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Schatz, D.G. Histone modifications associated with somatic hypermutation. Immunity 2005, 23, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molden, R.C.; Bhanu, N.V.; LeRoy, G.; Arnaudo, A.M.; Garcia, B.A. Multi-faceted quantitative proteomics analysis of histone H2B isoforms and their modifications. Epigenetics Chromatin 2015, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, P.D.; Gamble, M.J. MacroH2A1 chromatin specification requires its docking domain and acetylation of H2B lysine 20. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creyghton, M.P.; Cheng, A.W.; Welstead, G.G.; Kooistra, T.; Carey, B.W.; Steine, E.J.; Hanna, J.; Lodato, M.A.; Frampton, G.M.; Sharp, P.A.; et al. Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised enhancers and predicts developmental state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21931–21936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, S.A.; Rao, B.; Garcia, B.A.; Hake, S.B.; Diaz, R.L.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Allis, C.D.; Lieb, J.D.; Strahl, B.D. Identification of histone H3 lysine 36 acetylation as a highly conserved histone modification. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7632–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beisel, C.; Imhof, A.; Greene, J.; Kremmer, E.; Sauer, F. Histone methylation by the Drosophila epigenetic transcriptional regulator Ash1. Nature 2002, 419, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.E., Jr. Decreased heart rate variability in congestive heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 69, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daujat, S.; Bauer, U.M.; Shah, V.; Turner, B.; Berger, S.; Kouzarides, T. Crosstalk between CARM1 methylation and CBP acetylation on histone H3. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.; Vishwanath, S.N.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Sif, S. Human SWI/SNF-associated PRMT5 methylates histone H3 arginine 8 and negatively regulates expression of ST7 and NM23 tumor suppressor genes. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 9630–9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teoh, P.C.; Tan, L.K.; Chia, B.L.; Chao, T.C.; Tambyah, J.A.; Feng, P.H. Non-specific aorto-arteritis in Singapore with special reference to hypertension. Am. Heart J. 1978, 95, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suka, N.; Suka, Y.; Carmen, A.A.; Wu, J.; Grunstein, M. Highly specific antibodies determine histone acetylation site usage in yeast heterochromatin and euchromatin. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, S.; Eisenhaber, F.; O’Carroll, D.; Strahl, B.D.; Sun, Z.W.; Schmid, M.; Opravil, S.; Mechtler, K.; Ponting, C.P.; Allis, C.D.; et al. Regulation of chromatin structure by site-specific histone H3 methyltransferases. Nature 2000, 406, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, J.; Rice, J.C.; Strahl, B.D.; Allis, C.D.; Grewal, S.I. Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly. Science 2001, 292, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tachibana, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Fukushima, T.; Shinkai, Y. Set domain-containing protein, G9a, is a novel lysine-preferring mammalian histone methyltransferase with hyperactivity and specific selectivity to lysines 9 and 27 of histone H3. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25309–25317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, D.C.; Ayyanathan, K.; Negorev, D.; Maul, G.G.; Rauscher, F.J., 3rd. SETDB1: A novel KAP-1-associated histone H3, lysine 9-specific methyltransferase that contributes to HP1-mediated silencing of euchromatic genes by KRAB zinc-finger proteins. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Jones, R.S.; Zhang, Y. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 2002, 298, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKittrick, E.; Gafken, P.R.; Ahmad, K.; Henikoff, S. Histone H3.3 is enriched in covalent modifications associated with active chromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hake, S.B.; Garcia, B.A.; Duncan, E.M.; Kauer, M.; Dellaire, G.; Shabanowitz, J.; Bazett-Jones, D.P.; Allis, C.D.; Hunt, D.F. Expression patterns and post-translational modifications associated with mammalian histone H3 variants. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Z.Q.; Xia, L.; Feng, Q.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Strahl, B.D.; Briggs, S.D.; Allis, C.D.; Wong, J.; Tempst, P.; et al. Methylation of histone H4 at arginine 3 facilitating transcriptional activation by nuclear hormone receptor. Science 2001, 293, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahl, B.D.; Briggs, S.D.; Brame, C.J.; Caldwell, J.A.; Koh, S.S.; Ma, H.; Cook, R.G.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Stallcup, M.R.; et al. Methylation of histone H4 at arginine 3 occurs in vivo and is mediated by the nuclear receptor coactivator PRMT1. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishioka, K.; Rice, J.C.; Sarma, K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Werner, J.; Wang, Y.; Chuikov, S.; Valenzuela, P.; Tempst, P.; Steward, R.; et al. PR-Set7 is a nucleosome-specific methyltransferase that modifies lysine 20 of histone H4 and is associated with silent chromatin. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotta, G.; Lachner, M.; Sarma, K.; Ebert, A.; Sengupta, R.; Reuter, G.; Reinberg, D.; Jenuwein, T. A silencing pathway to induce H3-K9 and H4-K20 trimethylation at constitutive heterochromatin. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Feng, Q.; Ketel, C.S.; Wang, H.; Cao, R.; Xia, L.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Simon, J.A.; Zhang, Y. Purification and functional characterization of SET8, a nucleosomal histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, M.H.; Brownell, J.E.; Sobel, R.E.; Ranalli, T.A.; Cook, R.G.; Edmondson, D.G.; Roth, S.Y.; Allis, C.D. Transcription-linked acetylation by Gcn5p of histones H3 and H4 at specific lysines. Nature 1996, 383, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, G.S.; Kristjuhan, A.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Svejstrup, J.Q. Elongator is a histone H3 and H4 acetyltransferase important for normal histone acetylation levels in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3517–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilfiker, A.; Hilfiker-Kleiner, D.; Pannuti, A.; Lucchesi, J.C. mof, a putative acetyl transferase gene related to the Tip60 and MOZ human genes and to the SAS genes of yeast, is required for dosage compensation in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaskhar Alhamwe, B.; Khalaila, R.; Wolf, J.; von Bulow, V.; Harb, H.; Alhamdan, F.; Hii, C.S.; Prescott, S.L.; Ferrante, A.; Renz, H.; et al. Histone modifications and their role in epigenetics of atopy and allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schafer, A.; Baric, R.S. Epigenetic Landscape during Coronavirus Infection. Pathogens 2017, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Meng, J.L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Niu, S.L.; Yu, X.Z.; Li, Y.B.; Guan, Y.T.; Sun, B.X.; Zhao, Z.H. Changes in methylation of genomic DNA from chicken immune organs in response to H5N1 influenza virus infection. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Vipat, V.C.; Chakrabarti, A.K. Infection with influenza A viruses causes changes in promoter DNA methylation of inflammatory genes. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2013, 7, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, N. Interleukin-6 expression was regulated by epigenetic mechanisms in response to influenza virus infection or dsRNA treatment. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Eisfeld, A.J.; Schafer, A.; Josset, L.; Sims, A.C.; Proll, S.; Fan, S.; Li, C.; Neumann, G.; Tilton, S.C.; et al. Pathogenic influenza viruses and coronaviruses utilize similar and contrasting approaches to control interferon-stimulated gene responses. mBio 2014, 5, e01174-01114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcos-Villar, L.; Diaz-Colunga, J.; Sandoval, J.; Zamarreno, N.; Landeras-Bueno, S.; Esteller, M.; Falcon, A.; Nieto, A. Epigenetic control of influenza virus: Role of H3K79 methylation in interferon-induced antiviral response. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcos-Villar, L.; Pazo, A.; Nieto, A. Influenza Virus and Chromatin: Role of the CHD1 Chromatin Remodeler in the Virus Life Cycle. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3694–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huarte, M.; Sanz-Ezquerro, J.J.; Roncal, F.; Ortin, J.; Nieto, A. PA subunit from influenza virus polymerase complex interacts with a cellular protein with homology to a family of transcriptional activators. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8597–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alfonso, R.; Lutz, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Chavez, J.P.; Rodriguez, P.; Gutierrez, S.; Nieto, A. CHD6 chromatin remodeler is a negative modulator of influenza virus replication that relocates to inactive chromatin upon infection. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1894–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavin, Y.; Winter, D.; Blecher-Gonen, R.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Merad, M.; Jung, S.; Amit, I. Tissue-resident macrophage enhancer landscapes are shaped by the local microenvironment. Cell 2014, 159, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayward, S.L.; Scharer, C.D.; Cartwright, E.K.; Takamura, S.; Li, Z.T.; Boss, J.M.; Kohlmeier, J.E. Environmental cues regulate epigenetic reprogramming of airway-resident memory CD8(+) T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Egervari, G.; Wang, Y.; Berger, S.L.; Lu, Z. Regulation of chromatin and gene expression by metabolic enzymes and metabolites. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D. The metabolic spectrum of memory T cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Tu, B.P. Acetyl-CoA and the regulation of metabolism: Mechanisms and consequences. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 33, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, J.; Villa, M.; Sanin, D.E.; Buck, M.D.; O’Sullivan, D.; Ching, R.; Matsushita, M.; Grzes, K.M.; Winkler, F.; Chang, C.H.; et al. Acetate Promotes T Cell Effector Function during Glucose Restriction. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2063–2074.e2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandele, A.; Joshi, N.S.; Zhu, J.; Paul, W.E.; Leonard, W.J.; Kaech, S.M. Formation of IL-7Ralphahigh and IL-7Ralphalow CD8 T cells during infection is regulated by the opposing functions of GABPalpha and Gfi-1. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5309–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarro, M.N.; Goebel, J.; Feijoo-Carnero, C.; Morrice, N.; Cantrell, D.A. Phosphoproteomic analysis reveals an intrinsic pathway for the regulation of histone deacetylase 7 that controls the function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, A.J.; Kouzarides, T. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tough, D.F.; Rioja, I.; Modis, L.K.; Prinjha, R.K. Epigenetic Regulation of T Cell Memory: Recalling Therapeutic Implications. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, P.; Ghoneim, H.E.; Abdelsamed, H.A.; Youngblood, B. Generating long-lived CD8(+) T-cell memory: Insights from epigenetic programs. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1548–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henning, A.N.; Roychoudhuri, R.; Restifo, N.P. Epigenetic control of CD8(+) T cell differentiation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belz, G.T.; Xie, W.; Altman, J.D.; Doherty, P.C. A previously unrecognized H-2D(b)-restricted peptide prominent in the primary influenza A virus-specific CD8(+) T-cell response is much less apparent following secondary challenge. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Xing, S.; Chen, C.; Gao, P.; Teng, L.; Shan, Q.; Gullicksrud, J.A.; Martin, M.D.; Yu, S.; Harty, J.T.; et al. CD8(+) T Cells Utilize Highly Dynamic Enhancer Repertoires and Regulatory Circuitry in Response to Infections. Immunity 2016, 45, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.M.; Kapoor, V.; Guan, T.; Kaech, S.M.; Welsh, R.M.; Berg, L.J. Epigenetic modifications induced by Blimp-1 Regulate CD8(+) T cell memory progression during acute virus infection. Immunity 2013, 39, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zediak, V.P.; Johnnidis, J.B.; Wherry, E.J.; Berger, S.L. Cutting edge: Persistently open chromatin at effector gene loci in resting memory CD8+ T cells independent of transcriptional status. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2705–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araki, Y.; Fann, M.; Wersto, R.; Weng, N.P. Histone acetylation facilitates rapid and robust memory CD8 T cell response through differential expression of effector molecules (eomesodermin and its targets: Perforin and granzyme B). J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 8102–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.M. Cellular memory and the histone code. Cell 2002, 111, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Ren, C.; Freitas, M.A. Mass spectrometry-based strategies for characterization of histones and their post-translational modifications. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2007, 4, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidoli, S.; Vandamme, J.; Salcini, A.E.; Jensen, O.N. Dynamic changes of histone H3 marks during Caenorhabditis elegans lifecycle revealed by middle-down proteomics. Proteomics 2016, 16, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwammle, V.; Sidoli, S.; Ruminowicz, C.; Wu, X.; Lee, C.F.; Helin, K.; Jensen, O.N. Systems Level Analysis of Histone H3 Post-translational Modifications (PTMs) Reveals Features of PTM Crosstalk in Chromatin Regulation. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2016, 15, 2715–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sidoli, S.; Lopes, M.; Lund, P.J.; Goldman, N.; Fasolino, M.; Coradin, M.; Kulej, K.; Bhanu, N.V.; Vahedi, G.; Garcia, B.A. A mass spectrometry-based assay using metabolic labeling to rapidly monitor chromatin accessibility of modified histone proteins. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoli, S.; Lu, C.; Coradin, M.; Wang, X.; Karch, K.R.; Ruminowicz, C.; Garcia, B.A. Metabolic labeling in middle-down proteomics allows for investigation of the dynamics of the histone code. Epigenetics Chromatin 2017, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britton, L.-M.P.; Gonzales-Cope, M.; Zee, B.M.; Garcia, B.A. Breaking the histone code with quantitative mass spectrometry. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2011, 8, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| H1F | H2A | H2B | H3 | H4 | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naive | Identified | 30 | 18 | 18 | 25 | 91 | |
| Fragments | 832 | 443 | 291 | 598 | 2164 | ||
| Unique | 9 | 6 | 16 | 19 | 50 | ||
| Active | Identified | 1 | 39 | 12 | 10 | 13 | 75 |
| Fragments | 21 | 635 | 356 | 139 | 279 | 1430 | |
| Unique | 1 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 36 |
| H2A | Teff1 | Tm | Teff2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) | |
| S1ac | 15 | 377 | 21 | 304 | 26 | 749 |
| S1p | 2 | 31 | 2 | 26 | 4 | 75 |
| R3me2 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 13 |
| R4me2 | 1 | 20 | ||||
| K5ac | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| S1acK5ac | 4 | 53 | 2 | 59 | 5 | 95 |
| S1acR3me2K5ac | 2 | 21 | ||||
| S1acK5acT120p | 1 | 11 | ||||
| S1acT120p | 4 | 54 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 98 |
| S1pK5ac | 2 | 18 | ||||
| S1pR3me2 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 74 |
| K13ac | 1 | 12 | ||||
| None | 2 | 65 | 5 | 155 | 8 | 158 |
| H2B | Teff1 | TM | Teff2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modifications | Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) |
| P1ac | 1 | 17 | ||||
| P1acK6acK12acK13acK16acK17acK21acK24acK109ac | 1 | 15 | ||||
| M’acK5acK11acK12acS14pK15acK16acK20acK23acY42p | 2 | 59 | ||||
| M1′acK6acK12acK13acK16acK17acK21ac | 1 | 23 | ||||
| M’acK6acK12acK13acK16acK17acK21acK24ac | 1 | 18 | 1 | 24 | 2 | 56 |
| M’acK11acK12acS14pK15acK16acK20acK23ac | 1 | 28 | ||||
| M’acK11acK12acS14pK15acK16acK20acK23acK108ac | 1 | 15 | 1 | 16 | ||
| S14p | 1 | 24 | 2 | 35 | 5 | 135 |
| K20acK23ac | 3 | 31 | 8 | 310 | ||
| K23ac | 1 | 21 | 7 | 259 | ||
| K108ac | 2 | 83 | ||||
| None | 8 | 267 | 10 | 286 | 22 | 804 |
| H3 | Teff1 | TM | Teff2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modifications | Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) |
| T3pK9me3K27me3K36me | 1 | 11 | ||||
| R8me2K9meK18acK23acK27acK36ac | 1 | 10 | ||||
| K9me2K18me | 1 | 29 | ||||
| K9meK18meK23meK27me | 1 | 32 | ||||
| K9meK18meK23meK27meK36me | 1 | 10 | 2 | 58 | ||
| K9me2K18meK27me | 1 | 27 | ||||
| K9meK18meK27me2K36me | 4 | 124 | ||||
| K9me2K18meK36me3 | 1 | 22 | ||||
| K9me2K18meK23acK27acK36ac | 2 | 29 | 1 | 28 | ||
| K9meK18meK27meK36ac | 2 | 61 | ||||
| K9meK18acK23acK27acK36ac | 1 | 8 | 2 | 26 | ||
| K9me2K18acK23acK27me3K36me3 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 9 | 1 | 25 |
| K9me2K18acK36ac | 1 | 24 | ||||
| K9me2K23meK27me | 2 | 58 | ||||
| K9meK23meK27meK36me | 1 | 13 | 4 | 98 | ||
| K9me2K23meK36me3 | 1 | 26 | ||||
| K9me2K23meK27meK36ac | 1 | 31 | ||||
| K9me2K23acK27acK36ac | 1 | 24 | ||||
| K9me2K23acK27me3K36me3 | 2 | 47 | ||||
| K9me3K23acK27acK36me3 | 1 | 24 | ||||
| K9me2K27me | 6 | 168 | ||||
| K9meK27meK36me | 1 | 18 | 1 | 7 | 17 | 501 |
| K9me2K27ac | 2 | 53 | ||||
| K9me2K27acK36me | 2 | 47 | ||||
| K9me2K27acK36ac | 1 | 29 | ||||
| K9me2K27me2K36ac | 3 | 76 | ||||
| K9me2K36ac | 3 | 77 | ||||
| K9me2K36me | 4 | 110 | ||||
| K18meK23meK27me3K36me3 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 26 | ||
| K18acK23meK27me3K36me | 2 | 49 | ||||
| K18acK23acK27acK36ac | 1 | 14 | 1 | 23 | ||
| K18acK23meK27acK36ac | 2 | 56 | ||||
| K18acK23acK27meK36ac | 1 | 26 | ||||
| K18acK23acK27meK36me | 4 | 109 | ||||
| K18acK23meK27me2K36ac | 1 | 22 | ||||
| K18acK23meK27me3 | 1 | 32 | ||||
| K18meK27me3K36me3 | 1 | 16 | ||||
| K18acK27acK36ac | 2 | 52 | ||||
| K18acK27acK36me | 4 | 100 | ||||
| K18acK27meK36me | 1 | 20 | 2 | 61 | ||
| K18acK27meK36ac | 2 | 48 | ||||
| K23meK27me3 | 3 | 72 | ||||
| K23meK27me3K36me | 7 | 185 | ||||
| K23meK27meK36ac | 2 | 60 | ||||
| K23acK27me | 1 | 31 | ||||
| K23acK27me3K36ac | 1 | 22 | ||||
| K23acK27meK36me | 4 | 107 | ||||
| K27acK36ac | 5 | 137 | ||||
| K27acK36me | 4 | 119 | ||||
| K27me2 | 1 | 30 | ||||
| K27meK36me | 1 | 11 | 10 | 268 | ||
| K27meK36ac | 3 | 89 | ||||
| H4 | Teff1 | TM | Teff2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modifications | Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) | Intact ID | Frag (#) |
| S1ac | 1 | 17 | 1 | 15 | ||
| S1pR3me | 1 | 6 | ||||
| S1pR3meK20me3 | 2 | 23 | ||||
| S1acR3meK20me2 | 1 | 14 | ||||
| S1acK5acK8acK12acK16ac | 2 | 22 | ||||
| S1acK5acK8acK12acK16ac | 1 | 19 | ||||
| S1acK5acK8acK12acK16acK20me2 | 1 | 13 | ||||
| S1acK5acK8acK16acK20me | 1 | 23 | ||||
| S1acK5acK12acK16acK20me | 1 | 27 | ||||
| S1acK8acK12acK16ac | 2 | 43 | ||||
| S1acK8acK12acK16acK20me | 1 | 56 | 3 | 48 | ||
| S1acK8acK16acK20me | 5 | 135 | ||||
| S1acK12acK16ac | 3 | 69 | ||||
| S1acK12acK16acK20me | 1 | 13 | 2 | 78 | 7 | 202 |
| S1acK16ac | 1 | 12 | 4 | 79 | ||
| S1acK16acK20me | 2 | 29 | 5 | 191 | 10 | 301 |
| S1acK16acK20me3S47p | 1 | 9 | ||||
| S1acK20me | 4 | 115 | 6 | 241 | 9 | 266 |
| S1acK20me3Y88p | 1 | 19 | ||||
| R3me2K12acK20me3 | 1 | 25 | ||||
| R3me2K16acK20me | 1 | 21 | 1 | 10 | ||
| R3meK20me | 2 | 47 | 1 | 23 | 2 | 25 |
| K5acK20me3 | 1 | 12 | ||||
| K16ac | 1 | 13 | ||||
| K16acK20me | 2 | 31 | ||||
| K20me | 2 | 97 | 2 | 34 | ||
| M1acS2acK6acK9acK13acK17acK21me3-S48pY52pY89p | 1 | 6 | ||||
| M1acS2acR4me2K6acK9acK13acK17ac- K21me3S48pY52pY89p | 1 | 6 | ||||
| None | 2 | 24 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezinciuc, S.; Tian, Z.; Wu, S.; Hengel, S.; Pasa-Tolic, L.; Smallwood, H.S. Mapping Influenza-Induced Posttranslational Modifications on Histones from CD8+ T Cells. Viruses 2020, 12, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121409
Rezinciuc S, Tian Z, Wu S, Hengel S, Pasa-Tolic L, Smallwood HS. Mapping Influenza-Induced Posttranslational Modifications on Histones from CD8+ T Cells. Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121409
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezinciuc, Svetlana, Zhixin Tian, Si Wu, Shawna Hengel, Ljiljana Pasa-Tolic, and Heather S. Smallwood. 2020. "Mapping Influenza-Induced Posttranslational Modifications on Histones from CD8+ T Cells" Viruses 12, no. 12: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121409
APA StyleRezinciuc, S., Tian, Z., Wu, S., Hengel, S., Pasa-Tolic, L., & Smallwood, H. S. (2020). Mapping Influenza-Induced Posttranslational Modifications on Histones from CD8+ T Cells. Viruses, 12(12), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121409







