Influenza A Viruses in Ruddy Turnstones (Arenaria interpres); Connecting Wintering and Migratory Sites with an Ecological Hotspot at Delaware Bay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surveillance of Arenaria interpres for IAVs—Southeastern and DE Bay Sites
2.2. Virus Isolation and Subtyping
2.3. Molecular Analyses
2.4. Barcoding Fecal Samples
3. Results
3.1. Virus Isolation and Subtyping
3.2. Molecular Analyses
3.3. Fecal Barcoding
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rappole, J.H.; Derrickson, S.R.; Hubálek, Z. Migratory birds and spread of West Nile virus in the Western Hemisphere. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, A.M.; Reeves, A.B.; Sonsthagen, S.A.; TeSlaa, J.L.; Nashold, S.; Donnelly, T.; Casler, B.; Hall, J.S. Dispersal of H9N2 influenza A viruses between East Asia and North America by wild birds. Virology 2015, 482, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, A.M.; Reed, J.A.; Walther, P.; Link, P.; Schmutz, J.A.; Douglas, D.C.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Soos, C. Evidence for the exchange of blood parasites between North America and the Neotropics in blue-winged teal (Anas discors). Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3923–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramey, A.M.; Reeves, A.B.; Ogawa, H.; Ip, H.S.; Imai, K.; Bui, V.N.; Yamaguchi, E.; Silko, N.Y.; Afonso, C.L. Genetic diversity and mutation of avian paramyxovirus serotype 1 (Newcastle disease virus) in wild birds and evidence for intercontinental spread. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Toor, M.L.; Avril, A.; Wu, G.; Holan, S.H.; Waldenström, J. As the duck flies - estimating the dispersal of low-pathogenic avian influenza viruses by migrating mallards. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, J.; Krauss, S.; Kuhnert, D.; Fourment, M.; Raven, G.; Pryor, S.P.; Niles, L.J.; Danner, A.; Walker, D.; Mendenhall, I.H.; et al. Influenza a virus migration and persistence in North American wild birds. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinshaw, V.S.; Webster, R.G.; Turner, B. Water-bone transmission of influenza A viruses? Intervirology 1979, 11, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, S.; Walker, D.; Pryor, S.P.; Niles, L.; Chenghong, L.; Hinshaw, V.S.; Webster, R.G. Influenza A viruses of migrating wild aquatic birds in North America. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2004, 4, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Atkinson, P.W.; Clark, N.A. Arrival and weight gain of Red Knot Calidris canutus, Ruddy Turnstone Arenaria interpres and Sanderling Calidris alba staging in Delaware Bay in spring. In BTO Research Report; BTO: Thetford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, K.E.; Niles, L.J.; Burger, J. Abundance and distribution of migrant shorebirds in Delaware Bay. Condor 1993, 95, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, S.; Atkinson, P.W.; Bardsley, S.L.; Clark, N.A.; Love, S.E.; Robinson, R.A.; Stillman, R.A.; Weber, R.G. Shorebird predation of horseshoe crab eggs in Delaware Bay: species contrasts and availability constraints. J. Anim. Ecol. 2007, 76, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, S.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Negovetich, N.J.; Niles, L.J.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G. Coincident ruddy turnstone migration and horseshoe crab spawning creates an ecological ’hot spot’ for influenza viruses. Proc. R. Soc. B 2010, 277, 3373–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallknecht, D.; Luttrell, M.; Poulson, R.; Goekjian, V.; Niles, L.; Dey, A.; Krauss, S.; Webster, R. Detection of avian influenza viruses from shorebirds: Evaluation of surveillance and testing approaches. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaoka, Y.; Chambers, T.M.; Sladen, W.L.; Webster, R.G. Is the gene pool of influenza viruses in shorebirds and gulls different from that in wild ducks? Virology 1988, 163, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallknecht, D.; Poulson, R.; Krauss, S.; Webster, R. Influenza A viruses and Delaware Bay Shorebirds. Inter. Wader Stud. 2020, 21. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxted, A.M.; Luttrell, M.P.; Goekjian, V.H.; Brown, J.D.; Niles, L.J.; Dey, A.D.; Kalasz, K.S.; Swayne, D.E.; Stallknecht, D.E. Avian influenza virus infection dynamics in shorebird hosts. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araujo, J.; de Azevedo, S.M. Jr.; Gaidet, N.; Hurtado, R.F.; Walker, D.; Thomazelli, L.M.; Ometto, T.; Seixas, M.M.; Rodrigues, R.; Galindo, D.B.; et al. Avian influenza virus (H11N9) in migratory shorebirds wintering in the Amazon Region, Brazil. PLoS One 2014, 9, e110141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidet, N.; El Mamy, A.B.O.; Cappelle, J.; Caron, A.; Cumming, G.S.; Grosbois, V.; Gil, P.; Hammoumi, S.; de Almeida, R.S.; Fereidouni, S.R.; et al. Investigating Avian Influenza Infection Hotspots in Old-World Shorebirds. PLoS One 2012, 7, e46049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, R.; Fabrizio, T.; Vanstreels, R.E.; Krauss, S.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G.; Durigon, E.L. Molecular Characterization of Subtype H11N9 Avian Influenza Virus Isolated from Shorebirds in Brazil. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0145627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, A.M.; Reeves, A.B. Ecology of Influenza A Viruses in Wild Birds and Wetlands of Alaska. Avian Dis. 2020, 64, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleship, D.N. Ruddy Turnstone (Arenaria interpres). In The Birds of North America Online; Poole, A., Ed.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe, N.B.; Furness, R.W. Survival, winter population stability and site fidelity in the Turnstone Arenaria interpres. Bird Study 1985, 32, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghersi, B.M.; Blazes, D.L.; Icochea, E.; Gonzalez, R.I.; Kochel, T.; Tinoco, Y.; Sovero, M.M.; Lindstrom, S.; Shu, B.; Klimov, A. Avian influenza in wild birds, central coast of Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.I.; Pollett, S.; Ghersi, B.; Silva, M.; Simons, M.P.; Icochea, E.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Segovia, K.; Kasper, M.R.; Montgomery, J.M. The Genetic Diversity of Influenza A Viruses in Wild Birds in Peru. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, M.L. Hemagglutination assay for the avian influenza virus. Method. Mol. Biol. 2008, 436, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Herfst, S.; Van Der Kemp, L.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D. Detection of influenza A viruses from different species by PCR amplification of conserved sequences in the matrix gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4096–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebarbenchon, C.; Poulson, R.; Shannon, K.; Slagter, J.; Slusher, M.J.; Wilcox, B.R.; Berdeen, J.; Knutsen, G.A.; Cardona, C.J.; Stallknecht, D.E. Isolation of influenza A viruses from wild ducks and feathers in Minnesota (2010–2011). Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, B.A.; Luttrell, M.P.; Goekjian, V.H.; Niles, L.; Swayne, D.E.; Senne, D.A.; Stallknecht, D.E. Is the occurrence of avian influenza virus in Charadriiformes species and location dependent? J. Wildl. Dis. 2008, 44, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramey, A.M.; Pearce, J.M.; Flint, P.L.; Ip, H.S.; Derksen, D.V.; Franson, J.C.; Petrula, M.J.; Scotton, B.D.; Sowl, K.M.; Wege, M.L.; et al. Intercontinental reassortment and genomic variation of low pathogenic avian influenza viruses isolated from northern pintails (Anas acuta) in Alaska: Examining the evidence through space and time. Virology 2010, 401, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S. A practical approach to genetic screening for influenza virus variants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2623–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.; Stech, J.; Guan, Y.; Webster, R.G.; Perez, D.R. Universal primer set for the full-length amplification of all influenza A viruses. Arch Virol 2001, 146, 2275–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, L.P.; Essen, S.C.; Brown, I.H. Genetic subtyping of influenza A viruses using RT-PCR with a single set of primers based on conserved sequences within the HA2 coding region. J. Virol. Methods. 2004, 122, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragstad, K.; Jorgensen, P.H.; Handberg, K.J.; Mellergaard, S.; Corbet, S.; Fomsgaard, A. New avian influenza A virus subtype combination H5N7 identified in Danish mallard ducks. Virus. Res. 2005, 109, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obenauer, J.C.; Denson, J.; Mehta, P.K.; Su, X.; Mukatira, S.; Finkelstein, D.B.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; et al. Large-scale sequence analysis of avian influenza isolates. Science 2006, 311, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, O.T.; Barr, I.; Leung, C.Y.; Chen, H.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.S.; Poon, L.L. Reliable universal RT-PCR assays for studying influenza polymerase subunit gene sequences from all 16 haemagglutinin subtypes. J. Virol. Methods. 2007, 142, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.M.; Reeves, A.B.; Ramey, A.M.; Hupp, J.W.; Ip, H.S.; Bertram, M.; Petrula, M.J.; Scotton, B.D.; Trust, K.A.; Meixell, B.W.; et al. Interspecific exchange of avian influenza virus genes in Alaska: The influence of trans-hemispheric migratory tendency and breeding ground sympatry. Mol. Ecol. 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Bolotov, P.; Dernovoy, D.; Kiryutin, B.; Zaslavsky, L.; Tatusova, T.; Ostell, J.; Lipman, D. The influenza virus resource at the National Center for Biotechnology Information. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, A.B.; Pearce, J.M.; Ramey, A.M.; Meixell, B.W.; Runstadler, J.A. Interspecies transmission and limited persistence of low pathogenic avian influenza genomes among Alaska dabbling ducks. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.P.; Leung, Y.H.; Chow, C.K.; Ng, C.F.; Tsang, C.L.; Wu, Y.O.; Ma, S.K.; Sia, S.F.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.S. Identifying the species-origin of faecal droppings used for avian influenza virus surveillance in wild-birds. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, E.S.; Baker, A.J. Single mitochondrial gene barcodes reliably identify sister-species in diverse clades of birds. BMC Evol Biol 2008, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. Bold: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C.; Moreno, V.; Pedersen, J.; Jeria, J.; Agredo, M.; Gutierrez, C.; Garcia, A.; Vasquez, M.; Avalos, P.; Retamal, P. Avian Influenza in wild birds from Chile, 2007-2009. Virus Res. 2015, 199, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, H.D.; Rohani, P.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Brown, J.; Drake, J.M. Subtype diversity and reassortment potential for co-circulating avian influenza viruses at a diversity hot spot. J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 83, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, NWS Jacksonville, FL [Local Climate page]. Available online: https://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=jax (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- Brown, J.D.; Goekjian, G.; Poulson, R.; Valeika, S.; Stallknecht, D.E. Avian influenza virus in water: infectivity is dependent on pH, salinity and temperature. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 136, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.S.; Kelly, A.; Runstadler, J.A. Prevalence and diversity of avian influenza viruses in environmental reservoirs. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, J.; Haumacher, R.; Ike, A.; Stumpf, P.; Bohm, R.; Marschang, R.E. Long-term study on tenacity of avian influenza viruses in water (distilled water, normal saline, and surface water) at different temperatures. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, J.; Haumacher, R.; Ike, A.C.; Marschang, R.E. Persistence of avian influenza viruses in lake sediment, duck feces, and duck meat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4981–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulson, R.L.; Luttrell, P.M.; Slusher, M.J.; Wilcox, B.R.; Niles, L.J.; Dey, A.D.; Berghaus, R.D.; Krauss, S.; Webster, R.G.; Stallknecht, D.E. Influenza A virus: sampling of the unique shorebird habitat at Delaware Bay, USA. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 171420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
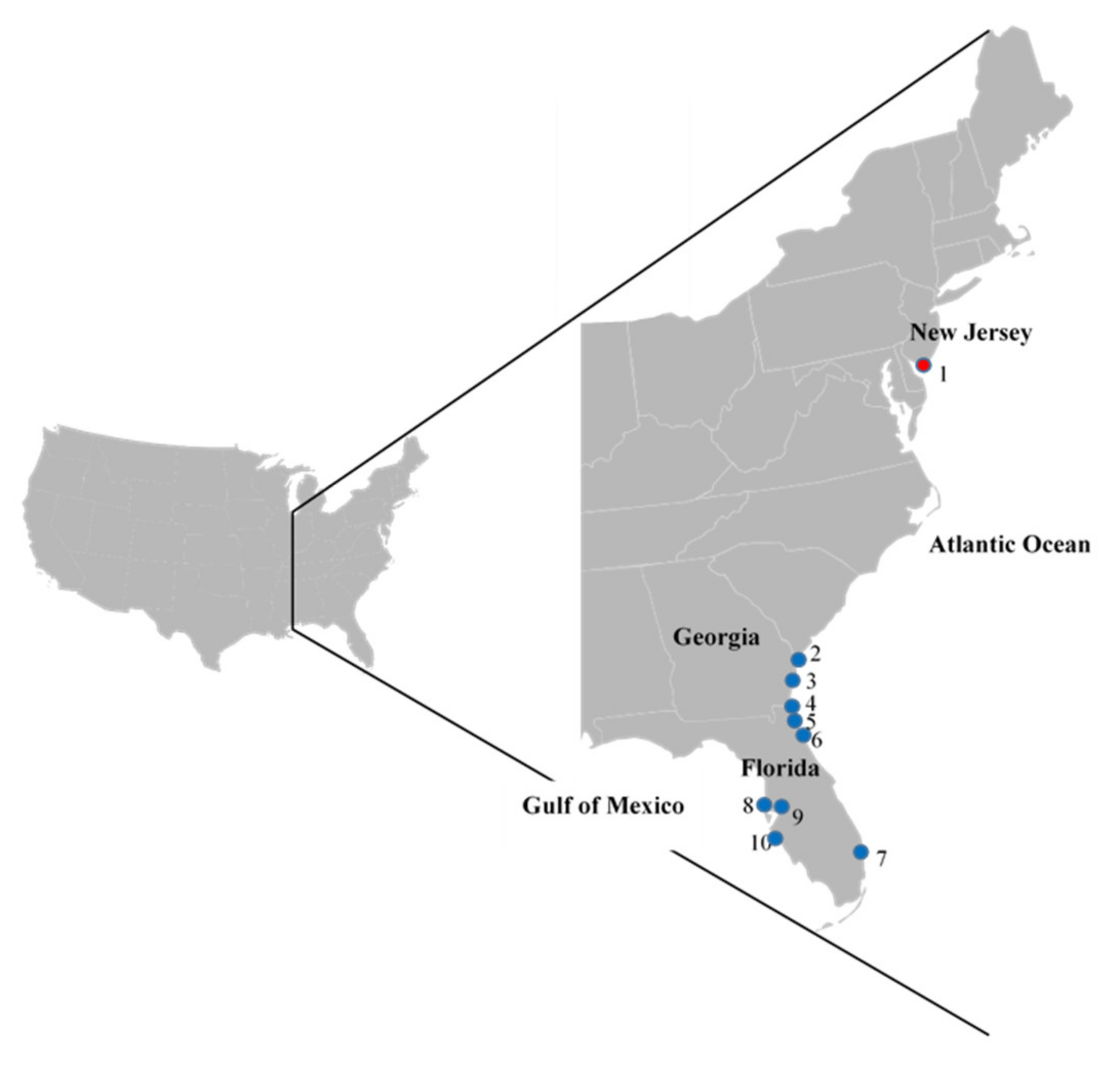
| Year | Month | Location (Figure 1) | IAV Isolated/Total Collected (% Recovery) | Subtypes (#) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | February | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 0/8 | |
| Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/26 | |||
| March | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 0/50 | ||
| Pinellas Co. FL (8) | 0/106 | |||
| April | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 0/71 | ||
| Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/26 | |||
| Longboat Keys (10) | 0/14 | |||
| 2011 | January | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 1/39 (2.6) | H3N8 (1) |
| Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/7 | |||
| February | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 0/81 | ||
| Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/99 | |||
| March | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 0/118 | ||
| Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/85 | |||
| April | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 0/1 | ||
| Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/50 | |||
| 2012 | January | Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/68 | |
| St. John’s Co. FL (6) | 0/31 | |||
| March | Duval Co. FL (5) | 3/64 (4.7) | LPAI H5N9 (3) | |
| Pinellas Co. FL (8) | 0/19 | |||
| May | Duval Co. FL (5) | 9/378 (2.4) | H6N1 (9) | |
| 2013 | January | Nassau Co. FL (4) | 1/36 (2.8) | H12N2 (1) |
| March | Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/164 | ||
| April | Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/1 | ||
| Nassau Co. FL (4) | 0/199 | |||
| 2014 | December | Duval Co. FL (5) | 7/13 (53.8) | H3N4 (7) |
| Nassau Co. FL (4) | 4/176 (2.2) | H3N4 (4) | ||
| Palm Beach Co. FL (7) | 0/19 | |||
| 2015 | January | Chatham Co. GA (2) | 0/69 | |
| Glynn Co. GA (3) | 0/65 | |||
| Nassau Co. FL (4) | 0/89 | |||
| February | Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/12 | ||
| Hillsborough Co. FL (9) | 0/34 | |||
| Nassau Co. FL (4) | 0/26 | |||
| Pinellas Co. FL (8) | 0/52 | |||
| March | Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/94 | ||
| Nassau Co. FL (4) | 0/80 | |||
| Pinellas Co. FL (8) | 0/1 | |||
| December | Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/109 | ||
| Nassau Co. FL (4) | 0/92 | |||
| 2016 | February | Duval Co. FL (5) | 0/109 | |
| Nassau Co. FL (4) | 0/42 | |||
| All Sites (2–10) | 25/2823 (0.9) | |||
| Atlantic Coast (2–7) | 25/2597 (1.0) | |||
| Gulf Coast (8–10) | 0/226 |
| DB 2010 | Southeast 2010/2011c | DB 2011 | Southeast 2011/2012 | DB 2012 | Southeast 2012/2013 | DB 2013 | Southeast 2013/2014 | DB 2014 | Southeast 2014/2015 | DB 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H6N1 (13) b | H7N3 (16) b | H1N1 (38) | H10N7 (90) b | H12N4 (69) | H7N3 (99) b | |||||
| H8N4 (4) | H9N7 (10) b | H12N3 (27) b | H12N2 (1) | H10N8 (33) b | H13N6 (16) b | H1N1 (71) b | ||||
| H5N2 (3) | H5N2 (9) b | H12N1 (15) | H10N1 (22) b | H6N2 (9) b | H1N3 (21) b | |||||
| H6N8 (2) b | H9N2 (3) b | H1N8 (10) b | H10N2 (20) b | H11N2 (8) b | H7N1 (12) | |||||
| H2N3 (1) | H7N7 (2) | H6N1(9) | H6N1 (8) b | H10N9 (18) b | H6N4 (6) a | H1N2 (2) a | ||||
| H2N9 (1) | H10N6 (2) a | H6N4 (4) a | H11N2 (17) b | No Collection | H3N6 (5) b | H1N8 (2) b | ||||
| H3N2 (1) | H10N9 (2) | H7N7 (4) | H11N8 (7) | H6N1 (5) | H11N2 (2) b | |||||
| H3N8 (1) | H3N8 (1) | H5N3 (1) a | H12N8 (2) | H11N7 (5) b | H3N4 (2) | H3N4 (11) | H16N3 (2) a | |||
| H6N4 (1) a | H5N6 (1) | H13N6(2) b | H6N8 (3) b | H6N8 (2) b | H6N8 (1) a | |||||
| H13N6 (1) a | H7N2 (1) a | H16N6 (2) a | H1N8 (1) a | H1N8 (1) | ||||||
| H9N6 (1) a | H1N3 (1) | H16N3 (1) | H4N4 (1) | |||||||
| H10N3 (1) | H5N3(1) | H7N3 (1) | ||||||||
| H5N9 (1)a | H5N9 (3) | H5N9(1) | H12N1 (1) | |||||||
| H11N2 (1)a | H7N3 (1) | H16N6 (1) a | ||||||||
| H11N3 (1) | H9N1 (1) | |||||||||
| H12N2 (1) | H10N8 (1) |
| Virus | Percent Nucleotide Similarity to Reference Sequence 3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB2 | PB1 | PA | NP | MA | NS | HA | NA | ||
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ 1/AI11-1678/2011(H7N7) | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | N/A (H7) | N/A (N7) | Reference 4 |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL 2/AI12-1161/2012/H5N9 | 92.0 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 91.9 | 96.9 | 95.1 | ref | ref | Southeastern viruses —this study |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1244/2012/H5N9 | 92.0 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 91.9 | 96.9 | 95.1 | 99.9 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1476/2012/H5N9 | 91.9 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 91.9 | 96.9 | 95.2 | 99.8 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1541/2012/H6N1 | 91.9 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | ref | ref | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1590/2012/H6N1 | 91.7 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1591/2012/H6N1 | 91.9 | 99.2 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | 99.9 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1592/2012/H6N1 | 91.9 | 99.2 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | 99.9 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1593/2012/H6N1 | 91.9 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1683/2012/H6N1 | 91.9 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | 99.9 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1638/2012/H6N1 | 91.9 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | 99.9 | 99.9 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1340/2012/H6N1 | 91.9 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 91.7 | 99.1 | 95.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/FL/AI12-1368/2012/H6N1 | 92.0 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 93.7 | 99.1 | 95.1 | 99.9 | 99.9 | |
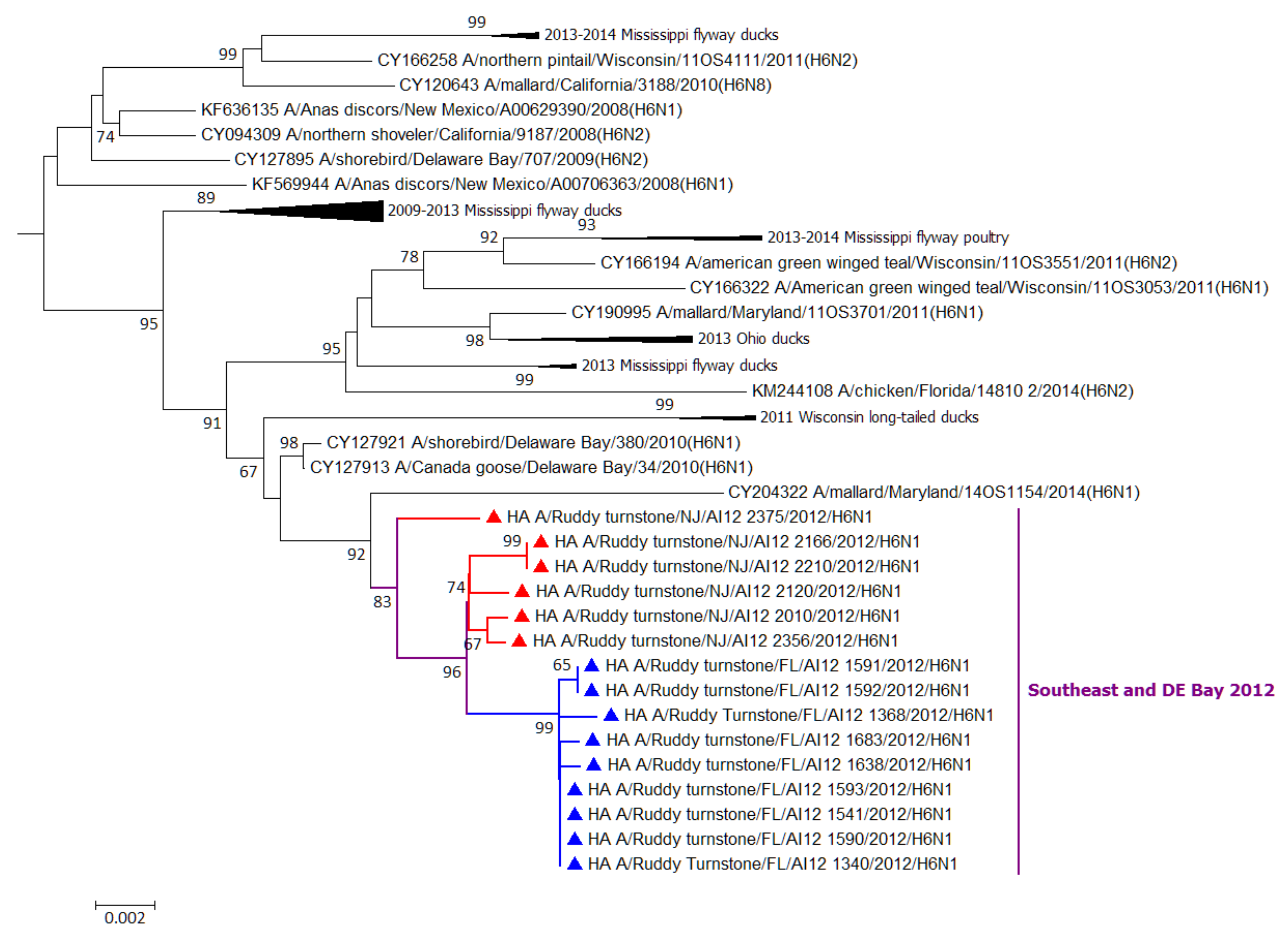
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2120/2012/H6N1 | 99.6 | 99.5 | 87.4 | 91.7 | 99.7 | 98.0 | 99.6 | 99.6 | DE Bay viruses —this study |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2279/2012/H5N9 | 99.6 | 99.5 | 87.4 | 91.7 | 99.5 | 95.3 | 99.4 | 99.3 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2166/2012/H6N1 | 99.6 | 96.1 | 87.4 | 91.7 | 96.7 | 98.2 | 99.5 | 99.5 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2356/2012/H6N1 | 99.6 | 99.4 | 87.5 | 91.7 | 99.7 | 98.2 | 99.6 | 99.6 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2375/2012/H6N1 | 91.8 | 93.5 | 99.4 | 93.8 | 96.8 | 95.1 | 99.2 | 93.0 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2871/2012/H5N3 | 96.8 | 94.1 | 87.4 | 91.6 | 96.9 | 97.8 | 97.7 | N/A | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2010/2012/H6N1 | 99.6 | 99.4 | 87.4 | 91.7 | 99.6 | 98.2 | 99.6 | 99.6 | |
| A/Ruddy turnstone/NJ/AI12-2210/2012/H6N1 | 99.6 | 96.2 | 87.4 | 91.7 | 96.9 | 98.3 | 99.5 | 99.6 | |
| A/gull/MA 3/13JR00943/2013(H9N1) | 91.9 | 96.0 | 87.7 | 93.7 | 97.5 | 97.0 | N/A (H9) | 93.0 | Reference 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulson, R.; Carter, D.; Beville, S.; Niles, L.; Dey, A.; Minton, C.; McKenzie, P.; Krauss, S.; Webby, R.; Webster, R.; et al. Influenza A Viruses in Ruddy Turnstones (Arenaria interpres); Connecting Wintering and Migratory Sites with an Ecological Hotspot at Delaware Bay. Viruses 2020, 12, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111205
Poulson R, Carter D, Beville S, Niles L, Dey A, Minton C, McKenzie P, Krauss S, Webby R, Webster R, et al. Influenza A Viruses in Ruddy Turnstones (Arenaria interpres); Connecting Wintering and Migratory Sites with an Ecological Hotspot at Delaware Bay. Viruses. 2020; 12(11):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111205
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulson, Rebecca, Deborah Carter, Shelley Beville, Lawrence Niles, Amanda Dey, Clive Minton, Pamela McKenzie, Scott Krauss, Richard Webby, Robert Webster, and et al. 2020. "Influenza A Viruses in Ruddy Turnstones (Arenaria interpres); Connecting Wintering and Migratory Sites with an Ecological Hotspot at Delaware Bay" Viruses 12, no. 11: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111205
APA StylePoulson, R., Carter, D., Beville, S., Niles, L., Dey, A., Minton, C., McKenzie, P., Krauss, S., Webby, R., Webster, R., & Stallknecht, D. E. (2020). Influenza A Viruses in Ruddy Turnstones (Arenaria interpres); Connecting Wintering and Migratory Sites with an Ecological Hotspot at Delaware Bay. Viruses, 12(11), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111205






