Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Associated with Increased Colorectal Cancer Risk in Taiwanese Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
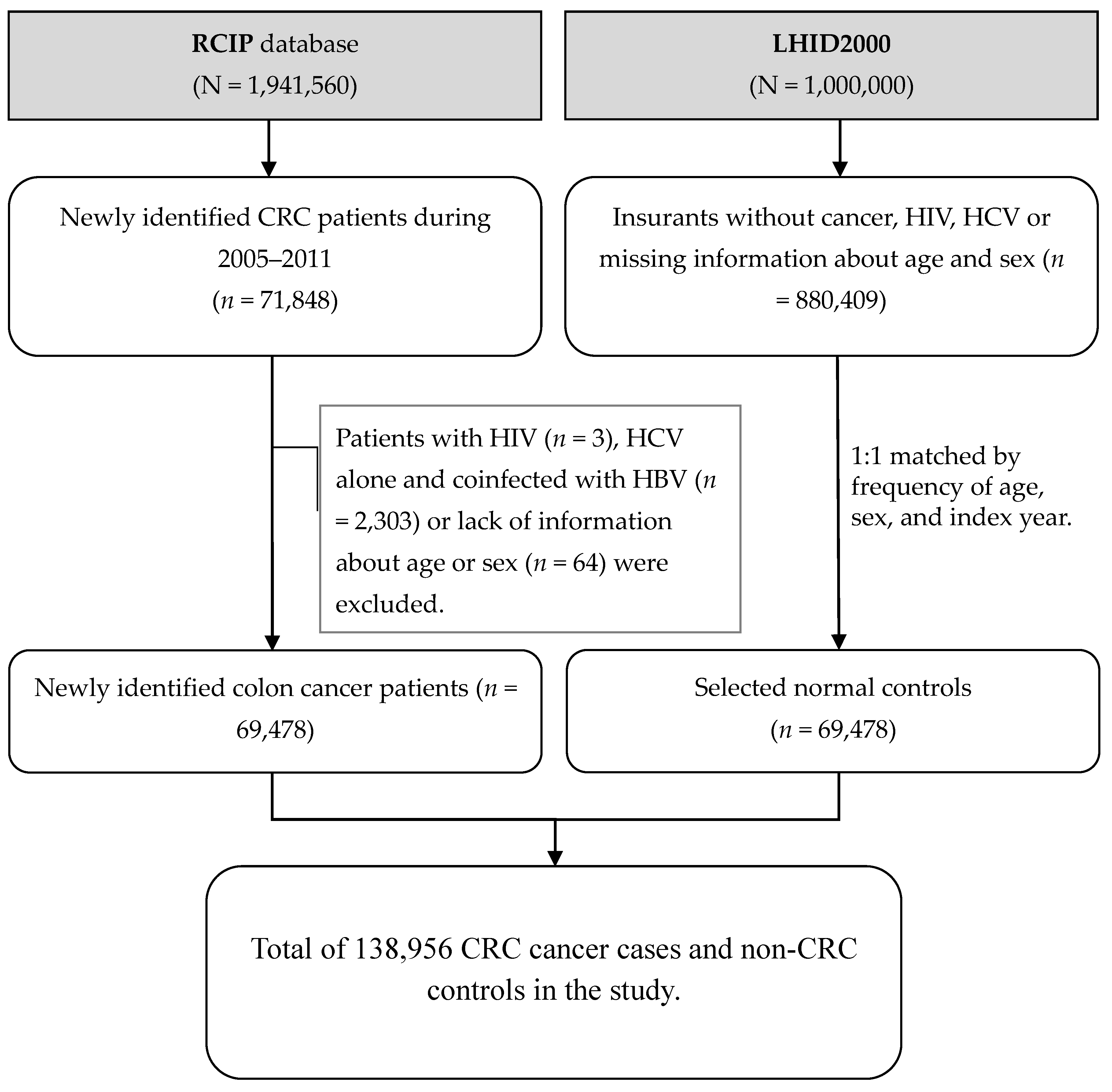
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Patients
3.2. Overall Risk of CRC in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection
3.3. Age-Specific Risk of CRC in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection
3.4. Sex-Specific Risk of CRC in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.J.; Chiu, H.M.; Jung, K.W.; Jun, J.K.; Sekiguchi, M.; Matsuda, T.; Kyaw, M.H. Increasing Trend in Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer in Asia: More Cancers in Men and More Rectal Cancers. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureau of Health Promotion Administration. Cancer Registry Annual Report; 2016; Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=269&pid=10227 (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; van de Velde, C.J.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, R.P.; Hwang, L.Y. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. Semin. Liver Dis. 1984, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organiztion (WHO). Global Hepatitis Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: http://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- Sung, J.L. Hepatitis B virus infection and its sequelae in Taiwan. Gastroenterol. Jpn. 1984, 19, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Chen, R.Y.; Su, C.T.; Wang, W.C.; Bai, C.H.; Chan, C.F.; Su, F.H. Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus in Taiwan 30 years after the commencement of the national vaccination program. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, A.; Wick, M.; White, H.; Perrillo, R. Hepatitis B virus replication in diverse cell types during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 1993, 18, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejean, A.; Lugassy, C.; Zafrani, S.; Tiollais, P.; Brechot, C. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in pancreas, kidney and skin of two human carriers of the virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1984, 65 Pt 3, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.L.; Bai, L.; Deng, T.; Zhang, C.; Kong, Q.Y.; Chen, H. Expression of hepatitis B virus antigen and Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric mucosa of patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis. Int. 2004, 3, 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Iloeje, U.H.; Yang, H.I.; Jen, C.L.; Su, J.; Wang, L.Y.; You, S.L.; Lu, S.N.; Chen, C.J. Risk of pancreatic cancer in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: Data from the REVEAL-HBV cohort study. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Qiu, M.Z.; Jin, Y.; Huang, Y.X.; Wang, R.Y.; Chen, W.W.; Wang, D.S.; Wang, F.; Luo, H.Y.; Zhang, D.S.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection is associated with gastric cancer in China: An endemic area of both diseases. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engels, E.A.; Cho, E.R.; Jee, S.H. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in South Korea: A cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fwu, C.W.; Chien, Y.C.; You, S.L.; Nelson, K.E.; Kirk, G.D.; Kuo, H.S.; Feinleib, M.; Chen, C.J. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A cohort study of parous women in Taiwan. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.B.; Lipka, S.; Shen, H.; Davis-Yadley, A.H.; Viswanathan, P. Establishing the link between hepatitis B virus infection and colorectal adenoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, K.L.; Lee, S.; Koh, S.J.; Jeong, J.B.; Kim, B.G. Hepatitis B Virus Infection Is Independently Associated With Advanced Colorectal Adenoma. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.G.; Ge, Z.; Zhu, J.; Dai, J.; Du, L.B.; Yu, C.; Guo, Y. Associations Between Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Risk of All Cancer Types. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019, 2, e195718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanchiang, C. Current issue: New IC health insurance card expected to offer many benefits. Taiwan Today. 2 January 2004. Available online: http://www.taiwantoday.tw/ct.asp?xItem520439&CtNode5122 (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Su, F.H.; Chang, S.N.; Chen, P.C.; Sung, F.C.; Su, C.T.; Yeh, C.C. Association between chronic viral hepatitis infection and breast cancer risk: A nationwide population-based case-control study. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of National Health Insurance Taiwan. Regulations for Exempting NHI Insured Persons from the Co-Payment. Available online: http://www.nhi.gov.tw/English/webdata/webdata.aspx?menu=11&menu_id=295&WD_ID=295&webdata_id=2431 (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Zur Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.M. Cancer “causation” by infections—Individual contributions and synergistic networks. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.H. Hepatitis B virus infection. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007, 12, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, C.A.; Summers, J. Genomic DNA double-strand breaks are targets for hepadnaviral DNA integration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11135–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedia, V.K.; Singha, A.; Dubeya, S.K.; Hettab, H.F.; Johnd, J.; Sing, M.P. Molecular mechanistic insight of hepatitis B virus mediated hepatocellular carcinoma. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, W.K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrero, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64 (Suppl. 1), S84–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.H.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.X.; Li, W.Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.P.; Zhuang, X.H.; Lin, C. Genomic and oncogenic preference of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A. Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10238–10248. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, Y.; Ichida, T. Impact of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein on the DNA Damage Response during Hepatocarcinogenesis. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2009, 42, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, M.C. Hepatitis B Virus x Protein in the Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B Virus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, H.S.; Ji, J.H.; Cho, M.Y.; Yoo, Y.S.; Park, Y.Y.; Cha, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Cho, H. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Activates the ATM-Chk2 Pathway and Delays Cell Cycle Progression. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahal, A.H.; el Razig, S.A.; Suliman, S.H.; Ibrahim, S.Z.; Tigani, A.E. Gastrointestinal tract cancer in association with hepatitis and HIV infection. East Afr. Med. J. 1995, 72, 424–426. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, J.; Wu, Y.; Ni, B. Hepatitis B virus X protein-induced aberrant epigenetic modifications contributing to human hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arababadi, M.K.; Nasiri Ahmadabadi, B.; Kennedy, D. Current information on the immunologic status of occult hepatitis B infection. Transfusion 2012, 52, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irby, K.; Anderson, W.F.; Henson, D.E.; Devesa, S.S. Emerging and widening colorectal carcinoma disparities between Blacks and Whites in the United States (1975–2002). Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2006, 15, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, K.A.; Tanapanpanit, O.; Reddy, K.R. Hepatitis B and C in African Americans: Current status and continued challenges. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Bhupinderjit, A.; Bhutani, M.S.; Boardman, L.; Nguyen, C.; Romero, Y.; Srinivasan, R.; Figueroa-Moseley, C.; Committee of Minority Affairs and Cultural Diversity, American College of Gastroenterology. Colorectal cancer in African Americans. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.J.; Lau, J.Y.; Goh, K.L.; Leung, W.K.; Asia Pacific Working Group on Colorectal C. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in Asia: Implications for screening. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Controls (N = 69,478) | Cases (N = 69,478) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | (%) | n | (%) | p Value * | |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||||
| Women | 29,750 | (42.8) | 29,750 | (42.8) | |
| Men | 39,728 | (57.2) | 39,728 | (57.2) | |
| Age, years | 1.000 | ||||
| <20 | 37 | (0.05) | 37 | (0.05) | |
| 20–29 | 484 | (0.70) | 484 | (0.70) | |
| 30–39 | 2252 | (3.24) | 2252 | (3.24) | |
| 40–49 | 6347 | (9.14) | 6347 | (9.14) | |
| 50–59 | 14,545 | (20.9) | 14,545 | (20.9) | |
| 60–69 | 16,440 | (23.7) | 16,440 | (23.7) | |
| 70–79 | 18,304 | (26.4) | 18,304 | (26.4) | |
| ≥80 | 11,069 | (15.9) | 11,069 | (15.9) | |
| Geographical region | <0.001 | ||||
| Northern | 29,565 | (42.6) | 29,740 | (42.8) | |
| Central | 14,241 | (20.5) | 13,803 | (19.9) | |
| Southern | 21,763 | (31.3) | 22,535 | (32.4) | |
| Eastern and islands | 3909 | (5.63) | 3400 | (4.89) | |
| Occupation | <0.001 | ||||
| White collar | 32,227 | (46.4) | 33,665 | (48.5) | |
| Blue collar | 29,023 | (41.8) | 28,421 | (40.9) | |
| Retired and others | 8228 | (11.8) | 7392 | (10.6) | |
| Urbanization level | <0.001 | ||||
| Urban | 18,776 | (27.0) | 19,396 | (27.9) | |
| Suburban | 31,055 | (44.7) | 31,778 | (45.7) | |
| Rural | 19,647 | (28.3) | 18,304 | (26.4) | |
| Monthly income, USD | 0.011 | ||||
| <528 | 21,815 | (31.4) | 21,894 | (31.5) | |
| 528–832 | 33,119 | (47.7) | 32,640 | (47.0) | |
| ≥833 | 14,544 | (20.9) | 14,944 | (21.5) | |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Diabetes | 16,706 | (24.1) | 19,165 | (27.6) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 36,709 | (52.8) | 38,189 | (55.0) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 22,072 | (31.8) | 22,029 | (31.7) | 0.804 |
| CAD | 19,995 | (28.8) | 19,464 | (28.0) | 0.002 |
| Renal disease | 10,898 | (15.7) | 10,998 | (15.8) | 0.462 |
| COPD | 26,943 | (38.8) | 24,707 | (35.6) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 1055 | (1.52) | 1055 | (1.52) | 1.000 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 16,166 | (23.3) | 15,845 | (22.8) | 0.041 |
| HBV | Controls | Cases | Crude | Adjusted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | (%) | n | (%) | OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) b | p Value | |
| No | 66,554 | (95.8) | 65,942 | (94.9) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) | ||
| Yes a | 2924 | (4.21) | 3536 | (5.09) | 1.22 (1.16–1.28) | <0.001 | 1.27 (1.20–1.33) | <0.001 |
| HBV only | 2722 | (3.92) | 3315 | (4.77) | 1.23 (1.17–1.29) | <0.001 | 1.27 (1.21–1.34) | <0.001 |
| HBV + HDV | 202 | (0.29) | 221 | (0.32) | 1.10 (0.91–1.34) | 0.31 | 1.15 (0.95–1.39) | 0.16 |
| Age | HBV | Controls | Cases | Adjusted OR (95% CI) a | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <55 | No | 14,900 | 14,439 | 1.00 (ref) | |
| Yes | 808 | 1269 | 1.63 (1.48–1.79) | <0.001 | |
| Odds | 0.054 | 0.088 | |||
| 55–64 | No | 14,773 | 14,618 | 1.00 (ref) | |
| Yes | 847 | 1002 | 1.24 (1.13–1.37) | <0.001 | |
| Odds | 0.057 | 0.069 | |||
| 65–74 | No | 17,184 | 17,188 | 1.00 (ref) | |
| Yes | 762 | 758 | 1.02 (0.92–1.13) | 0.739 | |
| Odds | 0.044 | 0.044 | |||
| ≥75 | No | 19,697 | 19,697 | 1.00 (ref) | |
| Yes | 507 | 507 | 1.03 (0.91–1.17) | 0.611 | |
| Odds | 0.026 | 0.026 |
| Sex | HBV | Controls | Cases | Adjusted OR (95% CI) a | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | No | 28,668 | 28,416 | 1.00 (ref) | |
| Yes | 1082 | 1334 | 1.29 (1.18–1.40) | <0.001 | |
| Odds | 0.038 | 0.047 | |||
| Men | No | 37,886 | 37,526 | 1.00 (ref) | |
| Yes | 1842 | 2202 | 1.25 (1.17–1.34) | <0.001 | |
| Odds | 0.049 | 0.059 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, F.-H.; Le, T.N.; Muo, C.-H.; Te, S.A.; Sung, F.-C.; Yeh, C.-C. Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Associated with Increased Colorectal Cancer Risk in Taiwanese Population. Viruses 2020, 12, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010097
Su F-H, Le TN, Muo C-H, Te SA, Sung F-C, Yeh C-C. Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Associated with Increased Colorectal Cancer Risk in Taiwanese Population. Viruses. 2020; 12(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010097
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Fu-Hsiung, Thi Nga Le, Chih-Hsin Muo, Sister Arlene Te, Fung-Chang Sung, and Chih-Ching Yeh. 2020. "Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Associated with Increased Colorectal Cancer Risk in Taiwanese Population" Viruses 12, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010097
APA StyleSu, F.-H., Le, T. N., Muo, C.-H., Te, S. A., Sung, F.-C., & Yeh, C.-C. (2020). Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Associated with Increased Colorectal Cancer Risk in Taiwanese Population. Viruses, 12(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010097






