A Novel RNA Virus in the Parasitoid Wasp Lysiphlebus fabarum: Genomic Structure, Prevalence, and Transmission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Material
2.2. PCR-Based Viral Screening
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.4. Assembly of Viral Genome
2.5. Phylogenetic Placement of LysV
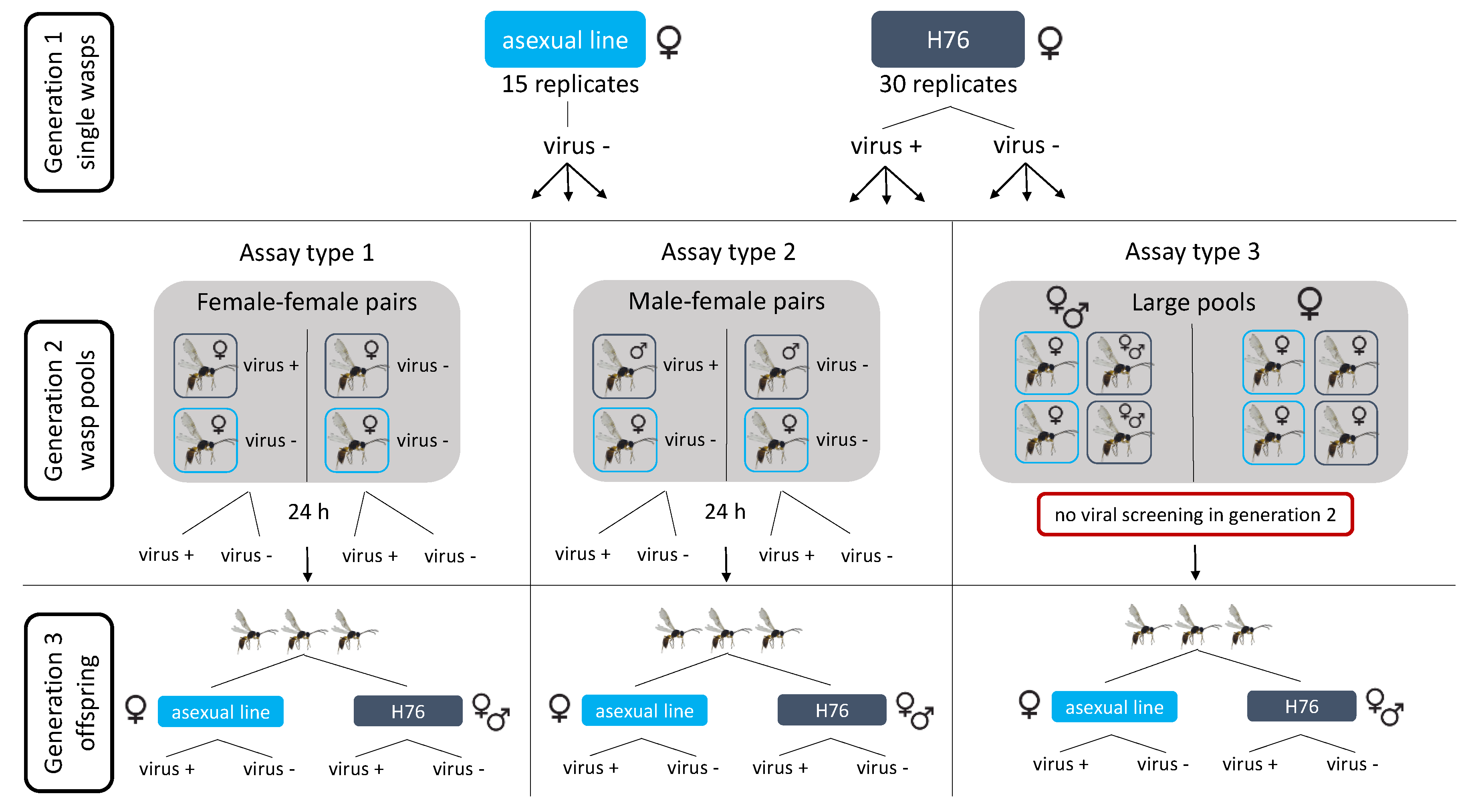
2.6. Transmission Assay
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
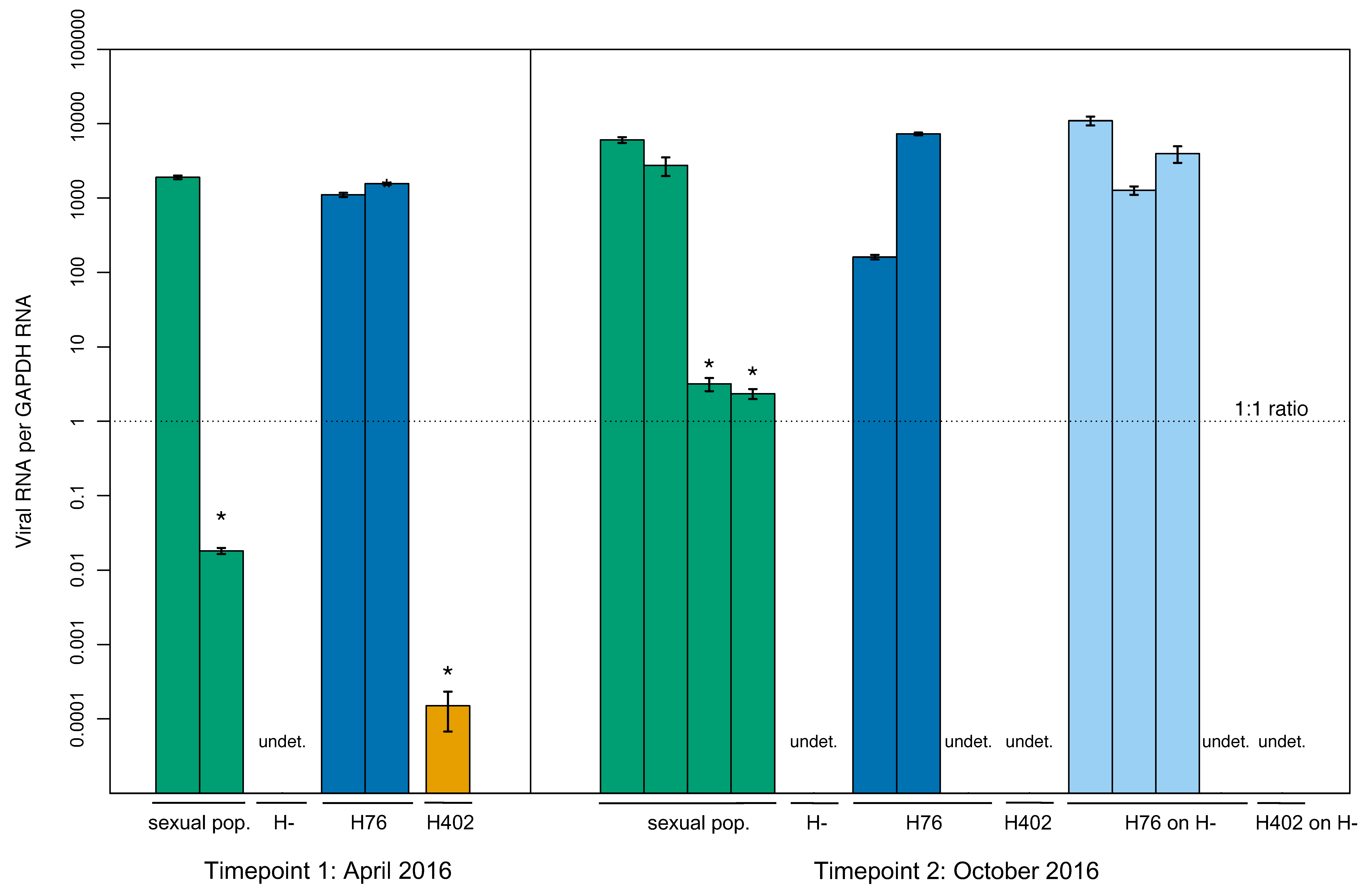
3.1. Lab Populations
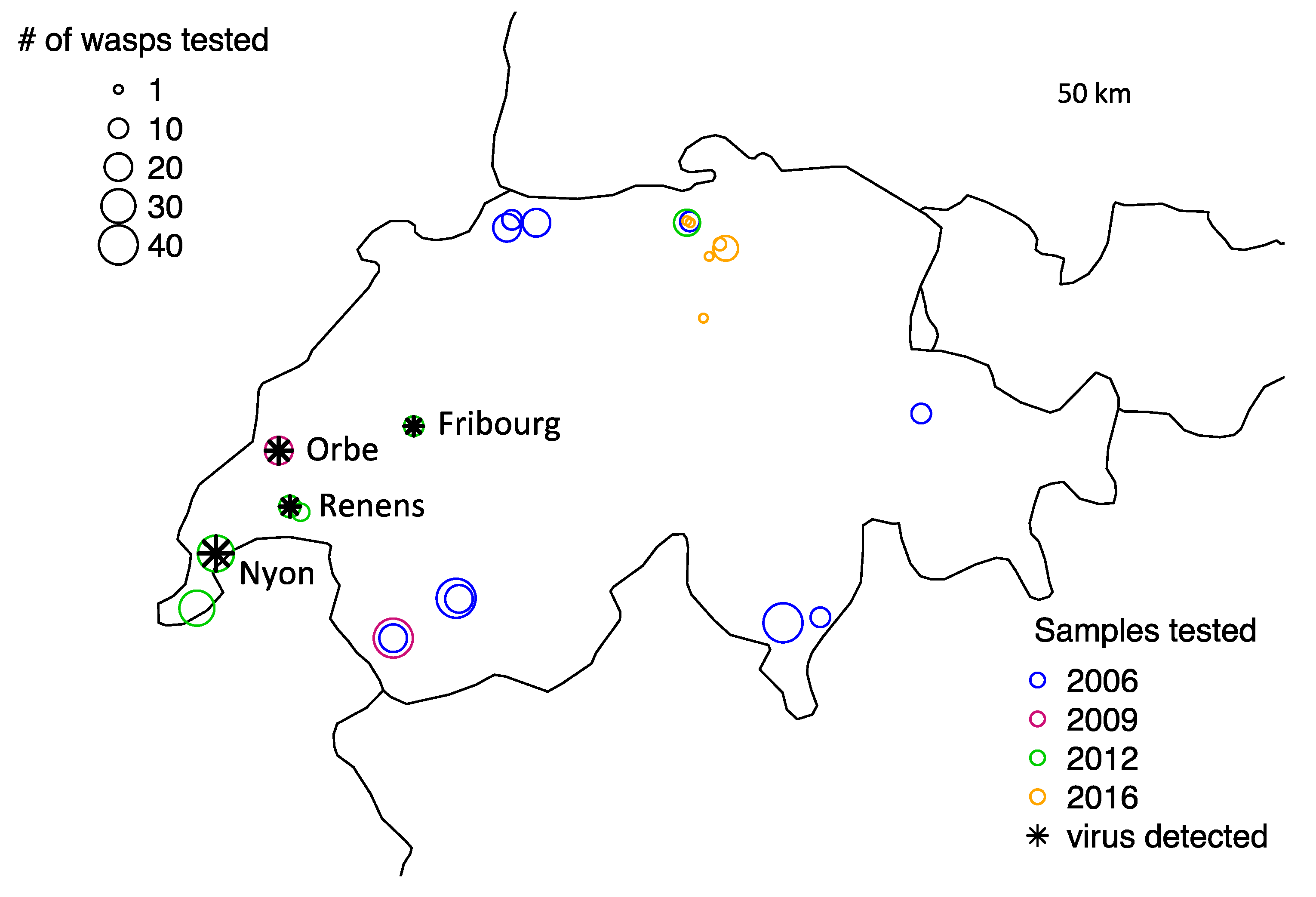
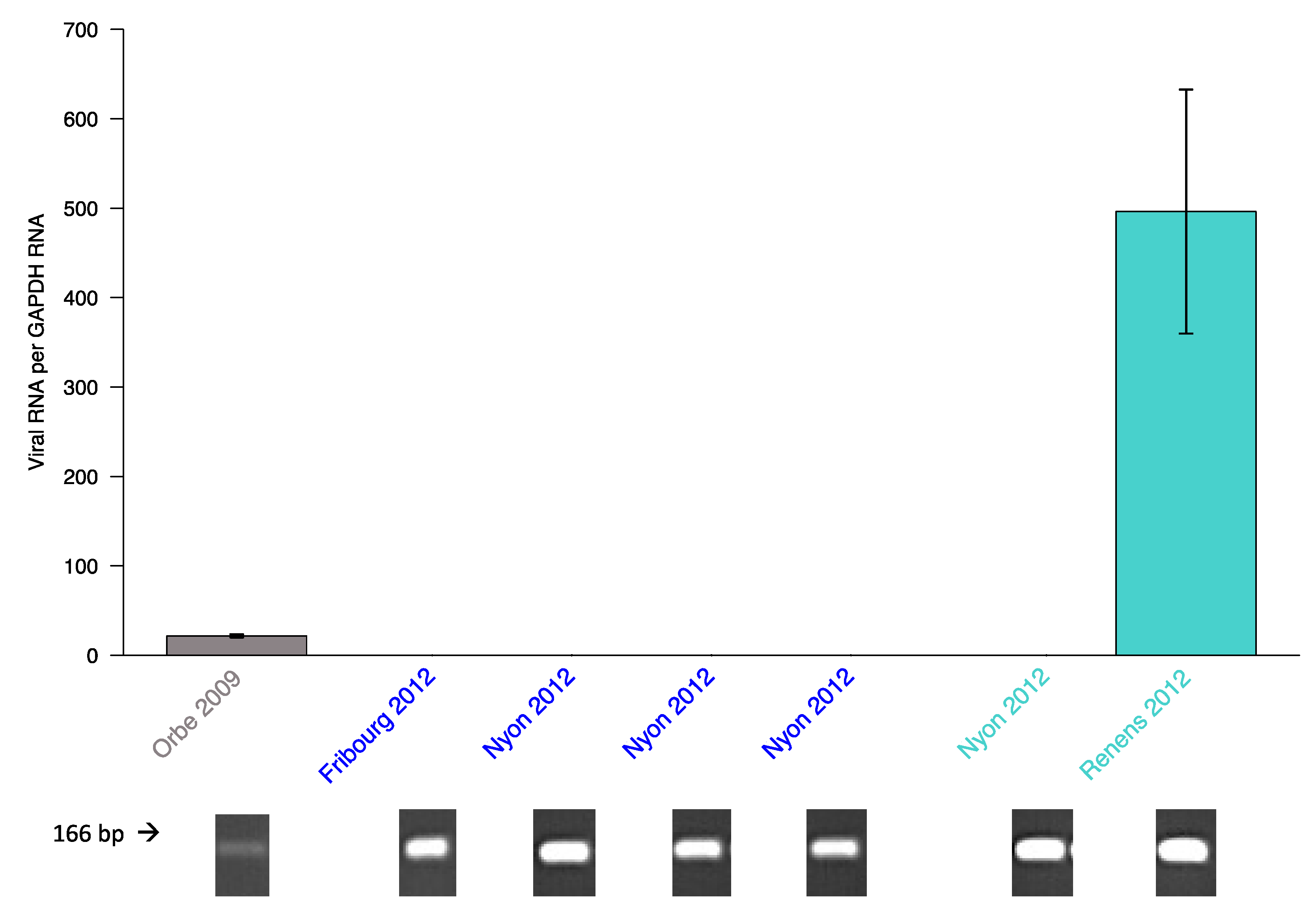
3.2. Wild Populations
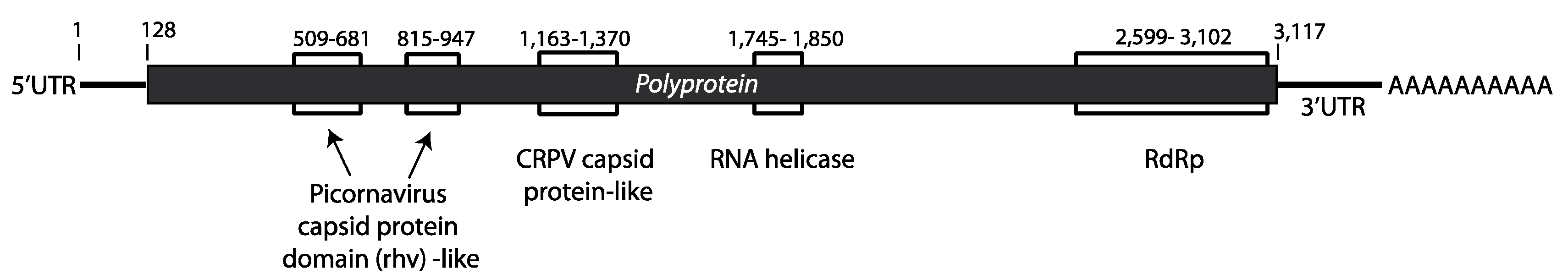
3.3. Description of the Viral Genome
3.4. Phylogenetic Placement of LysV
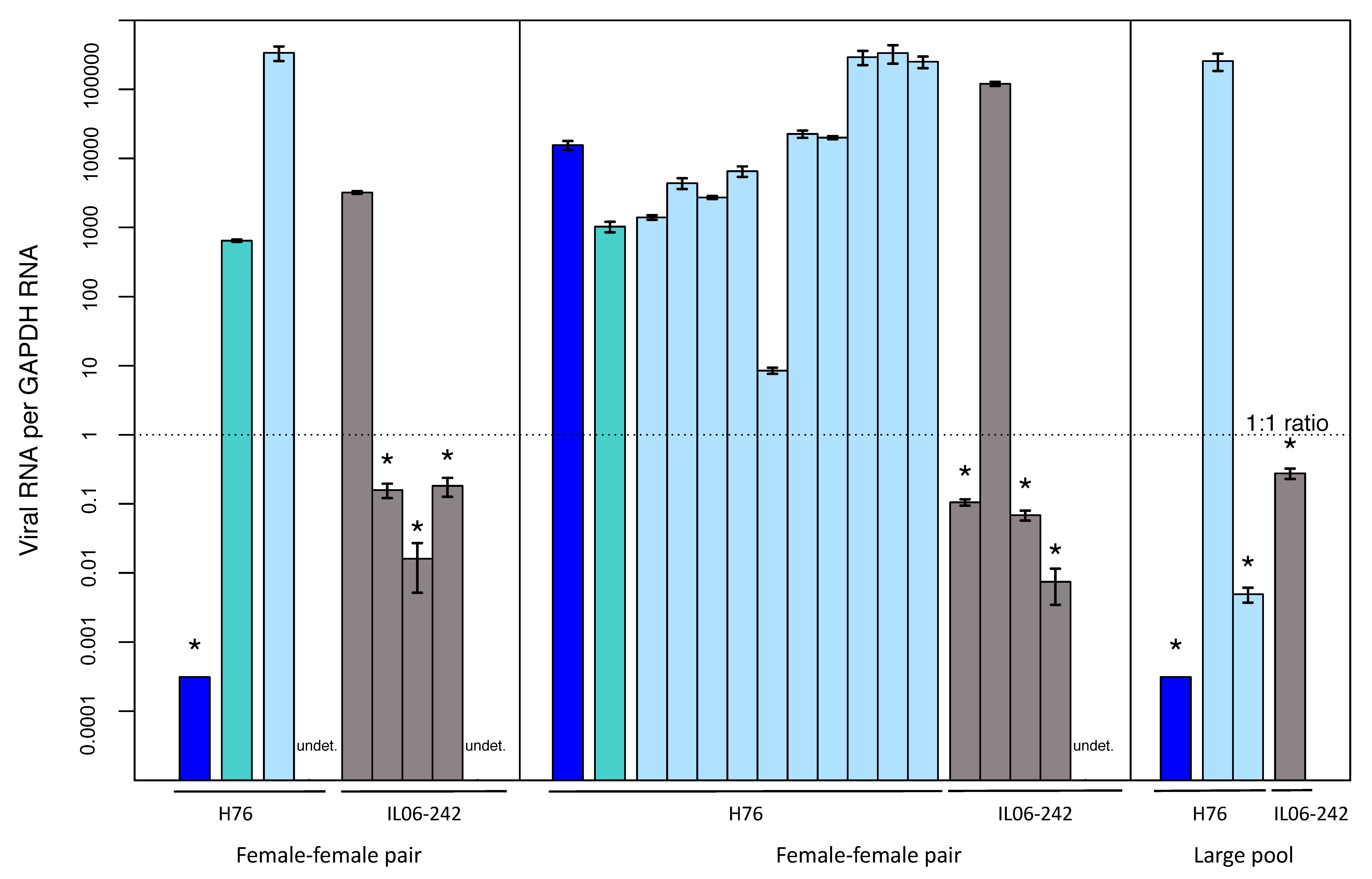
3.5. Transmission of LysV
4. Discussion
4.1. A New RNA Virus
4.2. Viral Haplotype Variation in Wild Populations
4.3. Symptoms
4.4. Viral Transmission
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Vijayendran, D.; Bonning, B.C. Next generation sequencing technologies for insect virus discovery. Viruses 2011, 3, 1849–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Lepetit, D.; Ravallec, M.; Fleury, F.; Varaldi, J. An additional heritable virus in the parasitic wasp Leptopilina boulardi: Prevalence, transmission and phenotypic effects. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dheilly, N.M.; Maure, F.; Ravallec, M.; Galinier, R.; Doyon, J.; Duval, D.; Leger, L.; Volkoff, A.N.; Misse, D.; Nidelet, S.; et al. Who is the puppet master? Replication of a parasitic wasp-associated virus correlates with host behaviour manipulation. Proc. R. Soc. B 2015, 282, 2014–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Bonning, B.C. RNA virus discovery in insects. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2015, 8, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Chen, X.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Eden, J.S.; Shen, J.J.; Liu, L.; et al. The evolutionary history of vertebrate RNA viruses. Nature 2018, 556, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.M.; Banerjee, N. Mechanisms of arthropod transmission of plant and animal viruses. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 128–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounibos, L.P. Invasions by insect vectors of human disease. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, J.R.; Genersch, E. Deformed wing virus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103 (Suppl. 1), S48–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, V.; Blanchard, P.; Chaouch, S.; Lallemand, P.; Schurr, F.; Celle, O.; Dubois, E.; Tordo, N.; Thiery, R.; Houlgatte, R.; et al. Molecular characterisation and phylogenetic analysis of Chronic bee paralysis virus, a honey bee virus. Virus Res. 2008, 132, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Pettis, J.S.; Collins, A.; Feldlaufer, M.F. Prevalence and transmission of honeybee viruses. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2006, 72, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozinger, C.M.; Flenniken, M.L. Bee Viruses: Ecology, Pathogenicity, and Impacts. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscardi, F. Assessment of the application of baculoviruses for control of Lepidoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, B.; Hoyos-Carvajal, L.; Paluszek, M.; Skrzecz, I.; Lobo de Souza, M. Baculoviruses—Re-emerging biopesticides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonet, A. Parasitoid Wasps, Natural Enemies of Insects. In Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems—Tropical Biology and Conservation Management—Phytopathology and Entomology; Del Claro, K., Oliveira, P.S., Rico-Gray, V., Eds.; EOLSS Publishers Co. Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, A.A.; Bagley, R.K.; Beer, M.A.; Hippee, A.C.; Widmayer, H.A. Quantifying the unquantifiable: Why Hymenoptera, not Coleoptera, is the most speciose animal order. BMC Ecol. 2018, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, G.R.; Strand, M.R. Systematic analysis of a wasp parasitism arsenal. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids, Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994; p. 473. [Google Scholar]
- Völkl, W.; Stechmann, D.-H. Parasitism of the black bean aphid (Aphis fabae) by Lysiphlebus fabarum (Hym., Aphidiidae): The influence of host plant and habitat. J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 122, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Sandrock, C.; Schirrmeister, B.E.; Vorburger, C. Evolution of reproductive mode variation and host associations in a sexual-asexual complex of aphid parasitoids. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothacher, L.; Ferrer-Suay, M.; Vorburger, C. Bacterial endosymbionts protect aphids in the field and alter parasitoid community composition. Ecology 2016, 97, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Herbaceous Plants and Shrubs; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, K.M.; Degnan, P.H.; Burke, G.R.; Moran, N.A. Facultative symbionts in aphids and the horizontal transfer of ecologically important traits. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, K.M.; Russell, J.A.; Moran, N.A.; Hunter, M.S. Facultative bacterial symbionts in aphids confer resistance to parasitic wasps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Sieber, R.; Zimmermann, Y.-S.; Vorburger, C. Development, specificity and sublethal effects of symbiont-conferred resistance to parasitoids in aphids. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.W.; Chevignon, G.; Oliver, K.M.; Strand, M.R. Culture of an aphid heritable symbiont demonstrates its direct role in defence against parasitoids. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2017, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, K.M.; Degnan, P.H.; Hunter, M.S.; Moran, N.A. Bacteriophages encode factors required for protection in a symbiotic mutualism. Science 2009, 325, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roossinck, M.J. The good viruses: Viral mutualistic symbioses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reineke, A.; Asgari, S. Presence of a novel small RNA-containing virus in a laboratory culture of the endoparasitic wasp Venturia canescens (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.C.; Hunter, W.B.; Ng, J.; Desjardins, C.A.; Dang, P.M.; Werren, J.H. Data mining cDNAs reveals three new single stranded RNA viruses in Nasonia (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19 (Suppl. 1), 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, S.; Stasiak, K.; Federici, B.; Bigot, Y. Commensal and mutualistic relationships of reoviruses with their parasitoid wasp hosts. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.A. Polydnavirus Biology, Genome Structure, and Evolution. In The Insect Viruses; Miller, L.K., Ball, L.A., Eds.; Plenum Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 105–139. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, G.R.; Strand, M.R. Polydnaviruses of Parasitic Wasps: Domestication of Viruses To Act as Gene Delivery Vectors. Insects 2012, 3, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, S. RNA viruses in parasitoid wasps. In Parasitoid Viruses: Symbionts and Pathogens; Beckage, N.E., Drezen, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, A.B.; Patel, V.; Oliver, K.M.; Vorburger, C. Parasitoid gene expression changes after adaptation to symbiont-protected hosts. Evolution 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchet, R.; Vorburger, C. Experimental evolution of parasitoid infectivity on symbiont-protected hosts leads to the emergence of genotype specificity. Evolution 2014, 68, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrock, C.; Vorburger, C. Single-locus recessive inheritance of asexual reproduction in a parasitoid wasp. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorburger, C.; Rouchet, R. Are aphid parasitoids locally adapted to the prevalence of defensive symbionts in their hosts? Bmc. Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorburger, C. Eawag, Wild populations of L. fabarum wasps collected across Europe. Eawag - Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, Dübendorf, Switzerland, Unpublished work. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandrock, C.; Frauenfelder, N.; von Burg, S.; Vorburger, C. Microsatellite DNA markers for the aphid parasitoid Lysiphlebus fabarum and their applicability to related species. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharlaken, B.; de Graaf, D.C.; Goossens, K.; Brunain, M.; Peelman, L.J.; Jacobs, F.J. Reference gene selection for insect expression studies using quantitative real-time PCR: The head of the honeybee, Apis mellifera, after a bacterial challenge. J. Insect Sci. 2008, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; An, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, F.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X. Identification and validation of reference genes for normalization of gene expression analysis using qRT-PCR in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Gene 2015, 555, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y. Research Progress on Reference Genes of Insect for Quantitative Real-time Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR). Univ. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 3, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maroniche, G.A.; Sagadin, M.; Mongelli, V.C.; Truol, G.A.; del Vas, M. Reference gene selection for gene expression studies using RT-qPCR in virus-infected planthoppers. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, Development Core Team. 2008. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 17 November 2019).
- Dennis, A.B.; Käch, H.; Vorburger, C. Dual RNA-seq in an aphid parasitoid reveals plastic and evolved adaptation to symbiont-conferred resistance. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckmann, B.; Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R.; Blatter, M.C.; Estreicher, A.; Gasteiger, E.; Martin, M.J.; Michoud, K.; O’Donovan, C.; Phan, I.; et al. The SWISS-PROT protein knowledgebase and its supplement TrEMBL in 2003. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, P.; Schurr, F.; Olivier, V.; Celle, O.; Antunez, K.; Bakonyi, T.; Berthoud, H.; Haubruge, E.; Higes, M.; Kasprzak, S.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and a predicted structural protein (pSP) of the Chronic bee paralysis virus (CBPV) isolated from various geographic regions. Virus Res. 2009, 144, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V. Evolution and taxonomy of positive-strand RNA viruses: Implications of comparative analysis of amino acid sequences. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 28, 375–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, Y.; Mise, K.; Nagasaki, K.; Okuno, T.; Honda, D. Complete nucleotide sequence and genome organization of a single-stranded RNA virus infecting the marine fungoid protist Schizochytrium sp. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamer, G.; Argos, P. Primary structural comparison of RNA-dependent polymerases from plant, animal and bacterial viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 7269–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruenn, J.A. Relationships among the positive strand and double-strand RNA viruses as viewed through their RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabrial, S.A. Origin, adaptation and evolutionary pathways of fungal viruses. Virus Genes 1998, 16, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Chumakov, K.M. Tentative identification of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of dsRNA viruses and their relationship to positive strand RNA viral polymerases. FEBS Lett. 1989, 252, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Choi, G.H.; Nuss, D.L.; Shapira, R.; Carrington, J.C. Evidence for common ancestry of a chestnut blight hypovirulence-associated double-stranded RNA and a group of positive-strand RNA plant viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10647–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICTV. Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses: Ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Part II: Order—Picornavirales. In Virus Taxonomy; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 835–839. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest: Selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2104–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starý, P.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Petrović, A.; Zikić, V.; Rakhshani, E.; Tomanović, S.; Tomanović, Z.; Havelka, J. Interference of Field Evidence, Morphology, and DNA Analyses of Three Related Lysiphlebus Aphid Parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae). J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Varaldi, J.; Ravallec, M.; Labrosse, C.; Lopez-Ferber, M.; Bouletreau, M.; Fleury, F. Artifical transfer and morphological description of virus particles associated with superparasitism behaviour in a parasitoid wasp. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaldi, J.; Fouillet, P.; Ravallec, M.; Lopez-Ferber, M.; Bouletreau, M.; Fleury, F. Infectious behavior in a parasitoid. Science 2003, 302, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. R. Package Version 2.0-29. 2015. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lmerTest (accessed on 17 November 2019).
- Millan-Leiva, A.; Jakubowska, A.K.; Ferre, J.; Herrero, S. Genome sequence of SeIV-1, a novel virus from the Iflaviridae family infective to Spodoptera exigua. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 109, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICTV. Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses: Ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Part II: Family—Iflaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 846–849. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, A.B.; Ballesteros, G.I.; Robin, S.; Schrader, L.; Bast, J.; Berghöfer, J.; Beukeboom, L.; Belghazi, M.; Bretaudeau, A.; Büllesbach, J.; et al. Functional insights from the GC-poor genomes of two aphid parasitoids, Aphidius ervi and Lysiphlebus fabarum. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.; Menendez-Arias, L.; Holland, J.J. RNA virus fitness. Rev. Med. Virol. 1997, 7, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.; Holland, J.J. RNA virus mutations and fitness for survival. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigot, Y.; Rabouille, A.; Doury, G.; Sizaret, P.Y.; Delbost, F.; Hamelin, M.H.; Periquet, G. Biological and molecular features of the relationships between Diadromus pulchellus ascovirus, a parasitoid hymenopteran wasp (Diadromus pulchellus) and its lepidopteran host, Acrolepiopsis assectella. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78 Pt 5, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltz, D.; Makkay, A. Co-replication of a reovirus and a polydnavirus in the ichneumonid parasitoid Hyposoter exiguae. Virology 2000, 278, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, P.O. Purification and partial characterization of an entomopoxvirus (DLEPV) from a parasitic wasp of tephritid fruit flies. J. Insect Sci. 2002, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Ye, G.Y.; Fang, Q.; Wu, M.L.; Hu, C. A pathogenic picorna-like virus from the endoparasitoid wasp, Pteromalus puparum: Initial discovery and partial genomic characterization. Virus Res. 2008, 138, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longdon, B.; Jiggins, F.M. Vertically transmitted viral endosymbionts of insects: Do sigma viruses walk alone? Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3889–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Schroder, M.; Bienefeld, K.; Genersch, E. Detection of viral sequences in semen of honeybees (Apis mellifera): Evidence for vertical transmission of viruses through drones. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2006, 92, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longdon, B.; Day, J.P.; Schulz, N.; Leftwich, P.T.; de Jong, M.A.; Breuker, C.J.; Gibbs, M.; Obbard, D.J.; Wilfert, L.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Vertically transmitted rhabdoviruses are found across three insect families and have dynamic interactions with their hosts. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20162381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
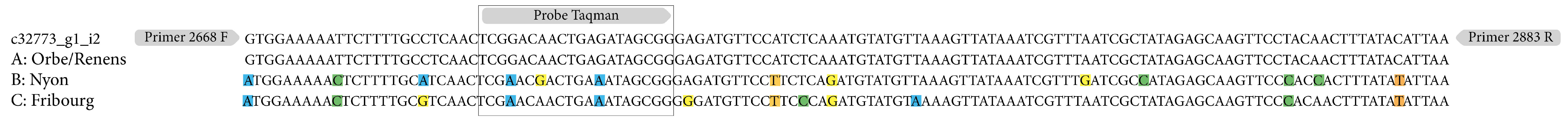

| Population | April 2016 | October 2016 | Fisher’s Exact Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental evolution populations | H– | 0% (n = 10) | 0% (n = 18) | p = 1 |
| H76 | 91.8% (n = 98) | 19.1% (n = 21) | p < 0.001 | |
| H402 | 0% (n = 78) | 0% (n = 17) | p = 1 | |
| H76 on H– | 50% (n = 8) | 17.6% (n = 17) | p = 0.156 | |
| H402 on H– | 25% (n = 4) | 0% (n = 19) | p = 0.174 | |
| Asexual populations | IL06-242 | 0% (n = 15) | 0% (n = 20) | p = 1 |
| IL06–680 | 0% (n = 15) | 0% (n = 20) | p = 1 | |
| IL07–64 | 33.3% (n = 15) | 0% (n = 20) | p = 0.009 | |
| IL09–402 | 0% (n = 15) | 0% (n = 20) | p = 1 | |
| IL09–554 | 33.3% (n = 15) | 0% (n = 20) | p = 0.009 | |
| Sexual population | sexual mixed population | 75% (n = 20) | 92.9% (n = 42) | p = 0.098 |
| Population | Number of Wasps Tested (PCR) | Number of Samples Infected (PCR) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild populations | 2006 | 250 | 0 |
| 2009 | 40 | 1 | |
| 2012 | 12 | 0 | |
| 2012 founding populations before lab | 17 | 4 | |
| 2012 founding populations after lab | 36 | 2 (samples of 4 wasps each) | |
| 2016 | 13 | 0 | |
| Population | Generation | # of Wasps Tested (PCR) | # of Wasps Infected (PCR) | Infection Percentage | Type of Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H76 (sexual) | 1 | 28 | 4 | 14.3% | Horizontal |
| 2 | 71 | 36 | 50.7% | Vertical and horizontal | |
| 3 | 93 | 11 | 11.8% | Vertical and horizontal | |
| IL06-242 (asexual) | 1 | 13 | 0 | 0% | NA |
| 2 | 15 | 0 | 0% | NA | |
| 3 | 82 | 2 | 0.02% | Horizontal |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lüthi, M.N.; Vorburger, C.; Dennis, A.B. A Novel RNA Virus in the Parasitoid Wasp Lysiphlebus fabarum: Genomic Structure, Prevalence, and Transmission. Viruses 2020, 12, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010059
Lüthi MN, Vorburger C, Dennis AB. A Novel RNA Virus in the Parasitoid Wasp Lysiphlebus fabarum: Genomic Structure, Prevalence, and Transmission. Viruses. 2020; 12(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLüthi, Martina N., Christoph Vorburger, and Alice B. Dennis. 2020. "A Novel RNA Virus in the Parasitoid Wasp Lysiphlebus fabarum: Genomic Structure, Prevalence, and Transmission" Viruses 12, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010059
APA StyleLüthi, M. N., Vorburger, C., & Dennis, A. B. (2020). A Novel RNA Virus in the Parasitoid Wasp Lysiphlebus fabarum: Genomic Structure, Prevalence, and Transmission. Viruses, 12(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010059





