The Deoptimization of Rabies Virus Matrix Protein Impacts Viral Transcription and Replication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses, and Antibodies
2.2. Construction of Codon-Deoptimized and Codon-Optimized M and Virus Rescue
2.3. Virus Propagation and Titration
2.4. Virus Growth Assays
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Assessment of Virus Spread
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Construction of RABV-M Variants
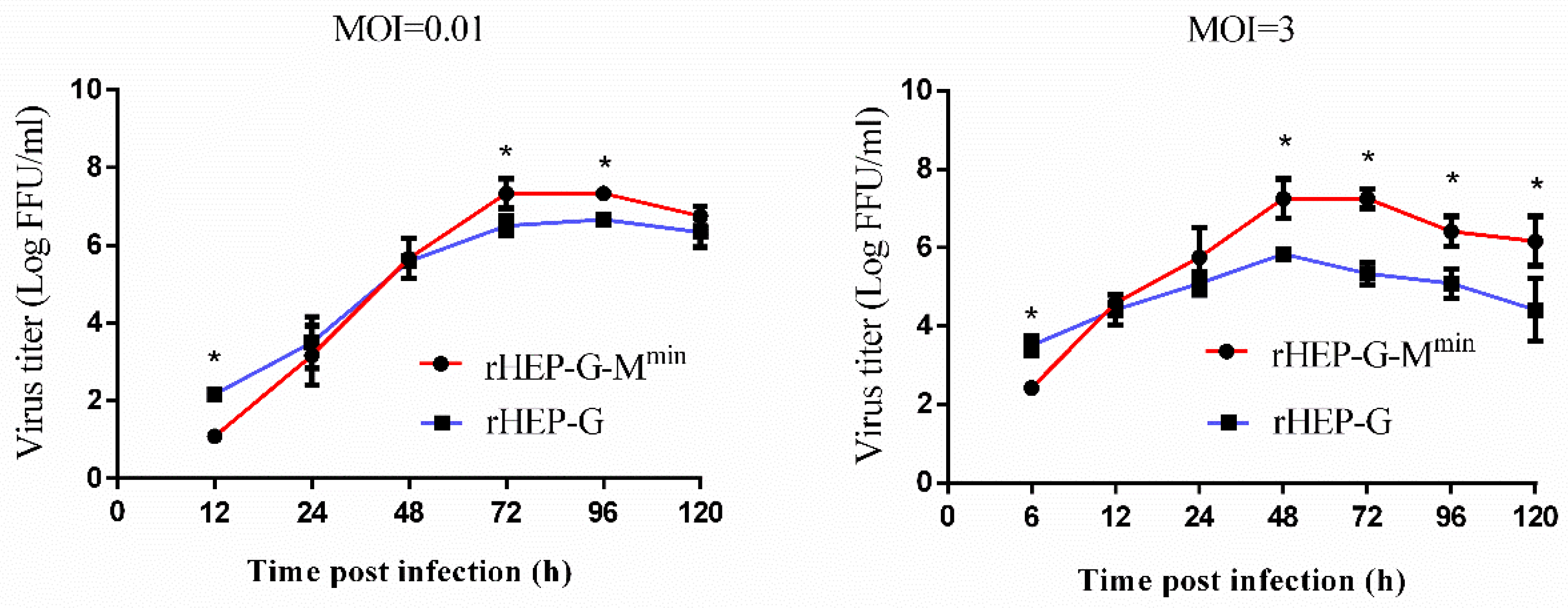
3.2. Codon-Deoptimized M Decreases Virus Production during the Early Stages of Virus Infection, but Increases Virus Production at Later Stages
3.3. Codon-Deoptimized M Regulates Intracellular Genomic RNA and mRNA Synthesis
3.4. Codon-Deoptimized M Regulates Transcription
3.5. Codon-Deoptimized M Increases G Expression
3.6. Codon-Deoptimized M Fails to Increase G Expression in DF-1 Cells
3.7. Attenuating M Expression does not Influence RABV Spread in NA Cells
3.8. rHEP-G-Mmin Induces Stronger Apoptosis in NA Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mebatsion, T.; Weiland, F.; Conzelmann, K.K. Matrix protein of rabies virus is responsible for the assembly and budding of bullet-shaped particles and interacts with the transmembrane spike glycoprotein G. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara, K.; Ohnuma, H.; Sugita, S.; Yasuoka, K.; Nakahara, T.; Tochikura, T.S.; Kawai, A. Intracellular behavior of rabies virus matrix protein (M) is determined by the viral glycoprotein (G). Microbiol. Immunol. 1999, 43, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, S.; Mueller-Waldeck, R.; Conzelmann, K.K. Rabies virus matrix protein regulates the balance of virus transcription and replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, K.Y.; Luco, S.; Besson, B.; Sonthonnax, F.; Archambaud, M.; Grimes, J.M.; Larrous, F.; Bourhy, H. The matrix protein of rabies virus binds to RelAp43 to modulate NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression related to innate immunity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39420. [Google Scholar]
- Besson, B.; Sonthonnax, F.; Duchateau, M.; Ben, K.Y.; Larrous, F.; Eun, H.; Hourdel, V.; Matondo, M.; Chamot-Rooke, J.; Grailhe, R.; et al. Regulation of NF-kappaB by the p105-ABIN2-TPL2 complex and RelAp43 during rabies virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luco, S.; Delmas, O.; Vidalain, P.O.; Tangy, F.; Weil, R.; Bourhy, H. RelAp43, a member of the NF-kappaB family involved in innate immune response against Lyssavirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, D.N.; Mo, K.K.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, B.L.; Gu, J.Y.; Liao, M.; Zhou, J.Y. Rabies virus infection induces microtubule depolymerization to facilitate viral RNA synthesis by upregulating HDAC6. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, S.; Conzelmann, K.K. Dissociation of rabies virus matrix protein functions in regulation of viral RNA synthesis and virus assembly. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12074–12082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Peng, J.J.; Liang, H.R.; Yang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.F.; Wu, X.W.; Pan, J.J.; Luo, Y.W.; Guo, X.F. Gene order rearrangement of the M gene in the rabies virus leads to slower replication. Virusdisease 2014, 25, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A. Codon bias is a major factor explaining phage evolution in translationally biased hosts. J. Mol. Evol. 2008, 66, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.R.; Papamichail, D.; Skiena, S.; Futcher, B.; Wimmer, E.; Mueller, S. Virus attenuation by genome-scale changes in codon pair bias. Science 2008, 320, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Papamichail, D.; Coleman, J.R.; Skiena, S.; Wimmer, E. Reduction of the rate of poliovirus protein synthesis through large-scale codon deoptimization causes attenuation of viral virulence by lowering specific infectivity. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9687–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yang, C.; Tekes, G.; Mueller, S.; Paul, A.; Whelan, S.P.; Wimmer, E. Recoding of the vesicular stomatitis virus L gene by computer-aided design provides a live, attenuated vaccine candidate. MBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirblich, C.; Schnell, M.J. Rabies virus (RV) glycoprotein expression levels are not critical for pathogenicity of RV. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, J.; Ai, J.; Dun, C.; Fu, Z.F.; Niu, X.; Guo, X. A recombinant rabies virus encoding two copies of the glycoprotein gene confers protection in dogs against a virulent challenge. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhao, J.; Tian, Q.; Mo, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, X. A recombinant rabies virus carrying GFP between N and P affects viral transcription in vitro. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Luo, J.; Mo, W.; Peng, J.; Niu, X.; Luo, Y.; Guo, X. Recombinant rabies virus expressing IFNalpha1 enhanced immune responses resulting in its attenuation and stronger immunogenicity. Virology 2014, 468, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Tian, Q.; Mo, M.; Long, T.; Mei, M.; Fan, R.; Lyu, Z.; Jiang, H.; et al. Recombinant rabies virus expressing interleukin-6 enhances the immune response in mouse brain. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, M.; Long, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Tian, Q.; Peng, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Guo, X. Phenotypic consequences in vivo and in vitro of rearranging the P gene of RABV HEP-Flury. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Faber, M.; Faber, M.L.; Papaneri, A.; Bette, M.; Weihe, E.; Dietzschold, B.; Schnell, M.J. A single amino acid change in rabies virus glycoprotein increases virus spread and enhances virus pathogenicity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14141–14148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, G.; Coller, J. Codon optimality, bias and usage in translation and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabi, R.; Tuller, T. Modelling the efficiency of codon-tRNA interactions based on codon usage bias. DNA Res. 2014, 21, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Tuohy, T.M.; Mosurski, K.R. Codon usage in yeast: Cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucl. Acids Res. 1986, 14, 5125–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, S.; Conzelmann, K.K. Replication strategies of rabies virus. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, A.A.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Blondel, D. Rabies virus transcription and replication. Adv. Virus Res. 2011, 79, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jayakar, H.R.; Jeetendra, E.; Whitt, M.A. Rhabdovirus assembly and budding. Virus Res. 2004, 106, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebatsion, T.; Konig, M.; Conzelmann, K.K. Budding of rabies virus particles in the absence of the spike glycoprotein. Cell 1996, 84, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, A.V.; Real, E.; Borman, A.M.; Brocard, M.; England, P.; Tordo, N.; Hershey, J.W.; Kean, K.M.; Jacob, Y. Rabies virus matrix protein interplay with eIF3, new insights into rabies virus pathogenesis. Nucl. Acids Res. 2007, 35, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.L.; Brewer, G.; Lyles, D.S. Effect of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein on host-directed translation in vivo. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, J.H.; Lyles, D.S. Inhibition of host and viral translation during vesicular stomatitis virus infection. eIF2 is responsible for the inhibition of viral but not host translation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13512–13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.H.; Mckenzie, M.O.; Lyles, D.S. Role of residues 121 to 124 of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in virus assembly and virus-host interaction. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 3701–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Ito, N.; Saito, S.; Masatani, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Atoji, Y.; Sugiyama, M. Amino acid substitutions at positions 242, 255 and 268 in rabies virus glycoprotein affect spread of viral infection. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 54, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, J.; Mei, M.; Luo, Y.; Guo, X. Rescue of a wild-type rabies virus from cloned cDNA and assessment of the proliferative capacity of recombinant viruses. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prehaud, C.; Lay, S.; Dietzschold, B.; Lafon, M. Glycoprotein of nonpathogenic rabies viruses is a key determinant of human cell apoptosis. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10537–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, M.; Pulmanausahakul, R.; Hodawadekar, S.S.; Spitsin, S.; Mcgettigan, J.P.; Schnell, M.J.; Dietzschold, B. Overexpression of the rabies virus glycoprotein results in enhancement of apoptosis and antiviral immune response. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3374–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, K.; Hooper, D.C.; Spitsin, S.; Koprowski, H.; Dietzschold, B. Pathogenicity of different rabies virus variants inversely correlates with apoptosis and rabies virus glycoprotein expression in infected primary neuron cultures. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Navid, M.T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Cui, M.; Fu, Z.F.; Tang, L.; Zhao, L. Comparison of the immunogenicity of two inactivated recombinant rabies viruses overexpressing the glycoprotein. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Mo, M.; Tian, Q.; Zhao, J.; Mei, M.; Guo, X. The Deoptimization of Rabies Virus Matrix Protein Impacts Viral Transcription and Replication. Viruses 2020, 12, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010004
Luo J, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Wu Y, Zhang B, Mo M, Tian Q, Zhao J, Mei M, Guo X. The Deoptimization of Rabies Virus Matrix Protein Impacts Viral Transcription and Replication. Viruses. 2020; 12(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jun, Yue Zhang, Qiong Zhang, Yuting Wu, Boyue Zhang, Meijun Mo, Qin Tian, Jing Zhao, Mingzhu Mei, and Xiaofeng Guo. 2020. "The Deoptimization of Rabies Virus Matrix Protein Impacts Viral Transcription and Replication" Viruses 12, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010004
APA StyleLuo, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q., Wu, Y., Zhang, B., Mo, M., Tian, Q., Zhao, J., Mei, M., & Guo, X. (2020). The Deoptimization of Rabies Virus Matrix Protein Impacts Viral Transcription and Replication. Viruses, 12(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010004




