Novel Genetic Rearrangements Termed “Structural Variation Polymorphisms“ Contribute to the Genetic Diversity of Orthohepadnaviruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reference Sequences
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Sequence Gap Analysis
2.4. Sequence Identity Analysis
2.5. Multiple Alignment Analysis
2.6. Sequence Similarity Search
3. Results
3.1. The Genetic Sequences of Orthohepadnaviruses
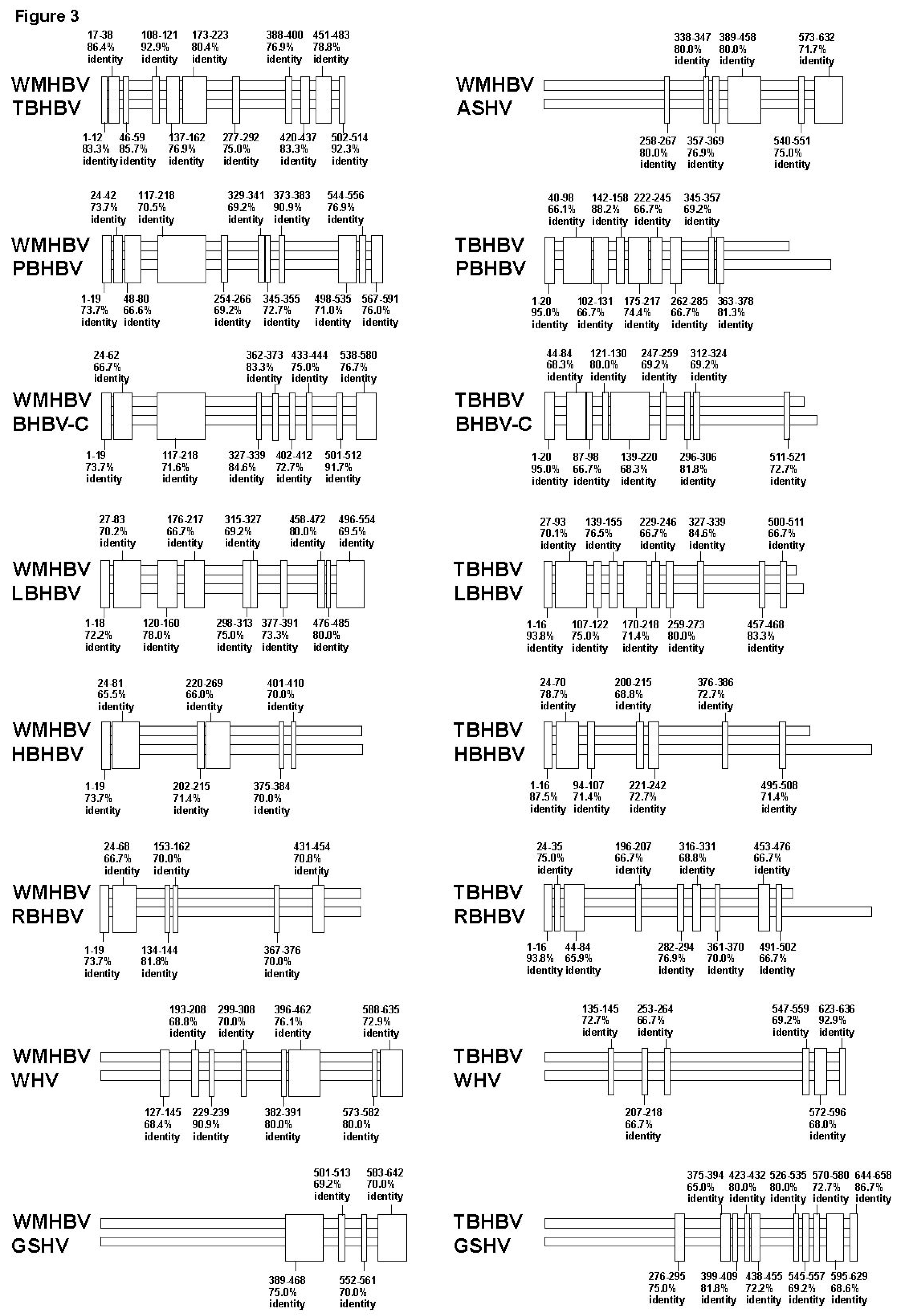
3.2. Analyses of the Sequence Gaps and Percentage Identities among WMHBV, Bat HBVs, and Rodent HBVs
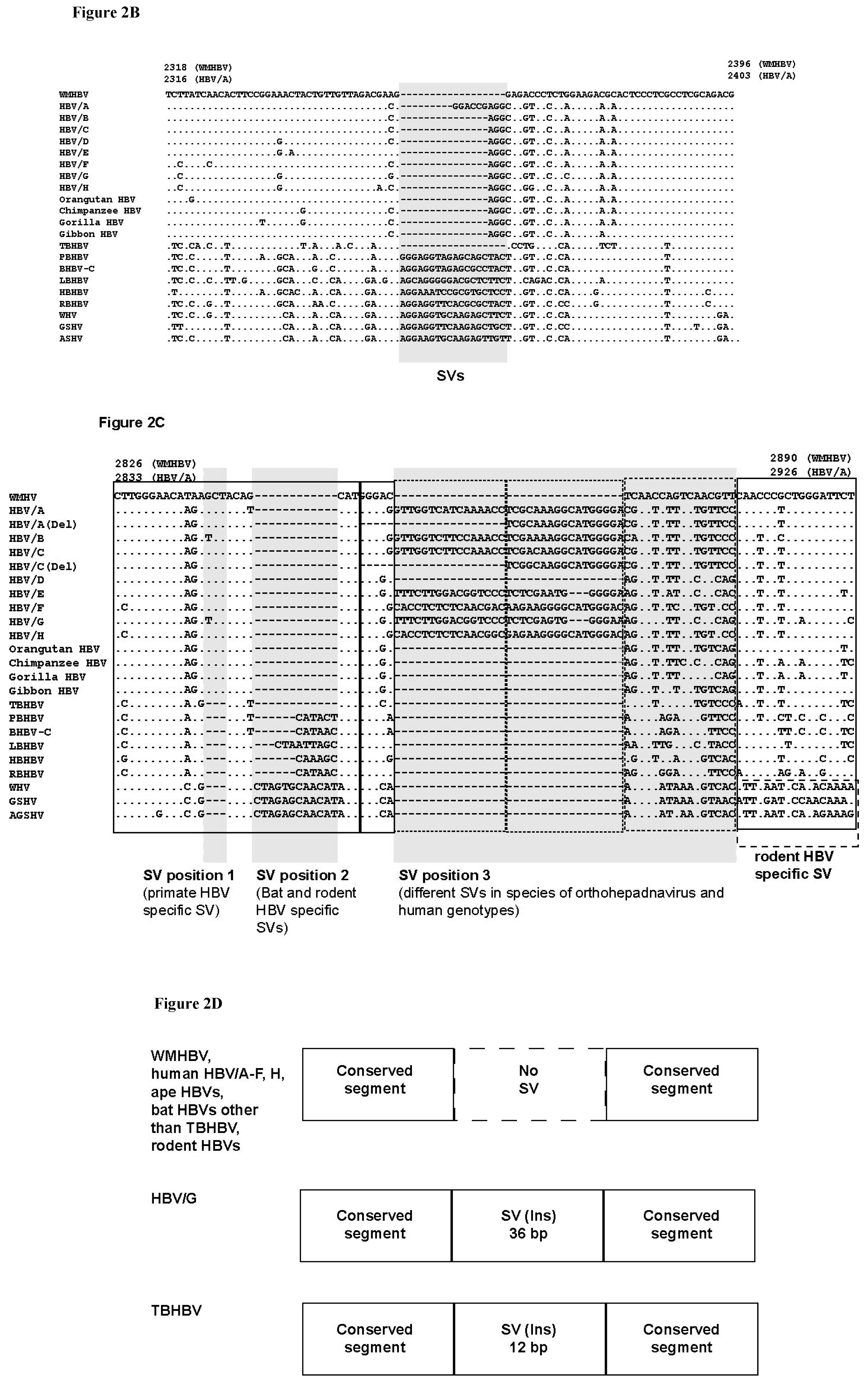
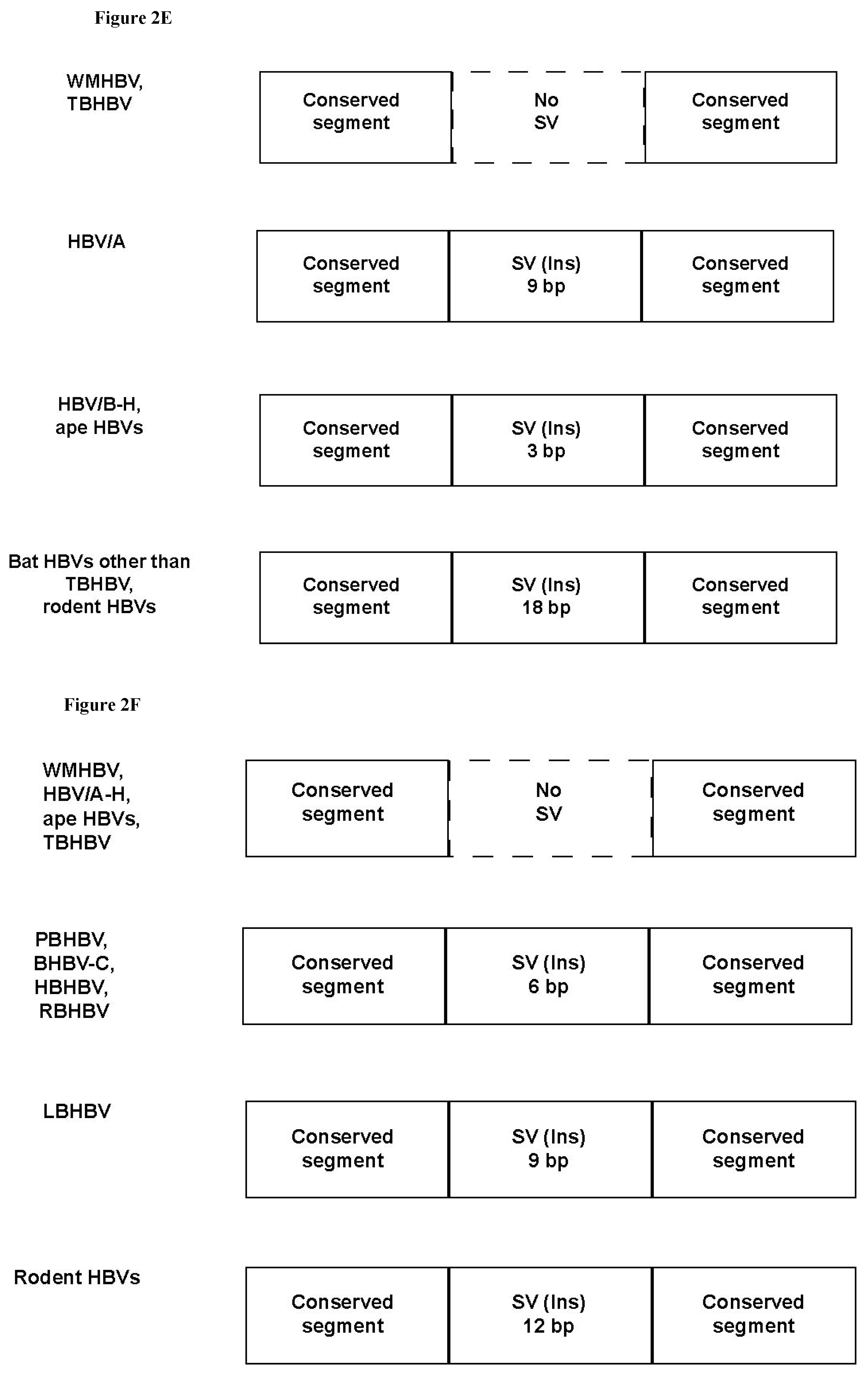
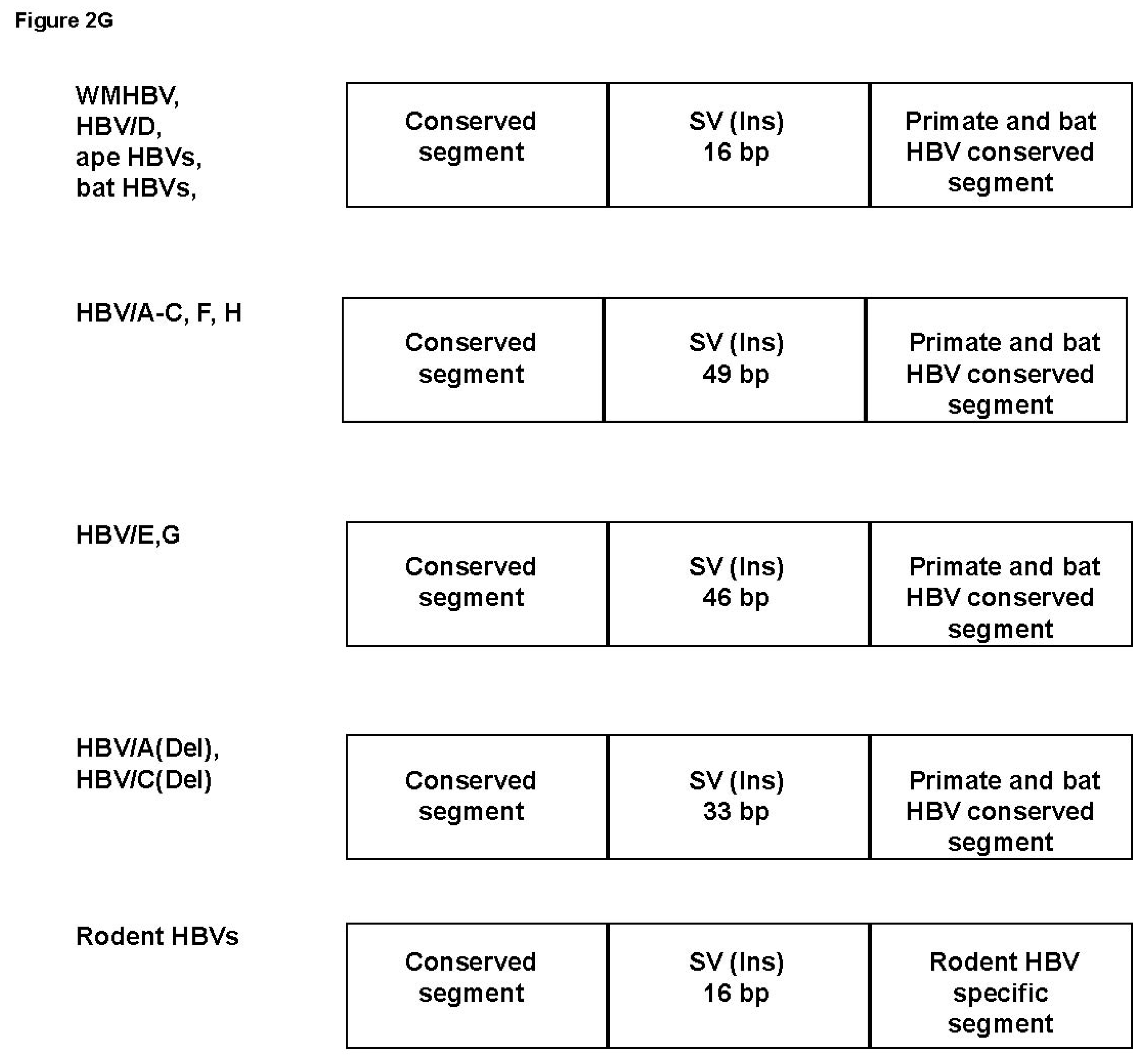
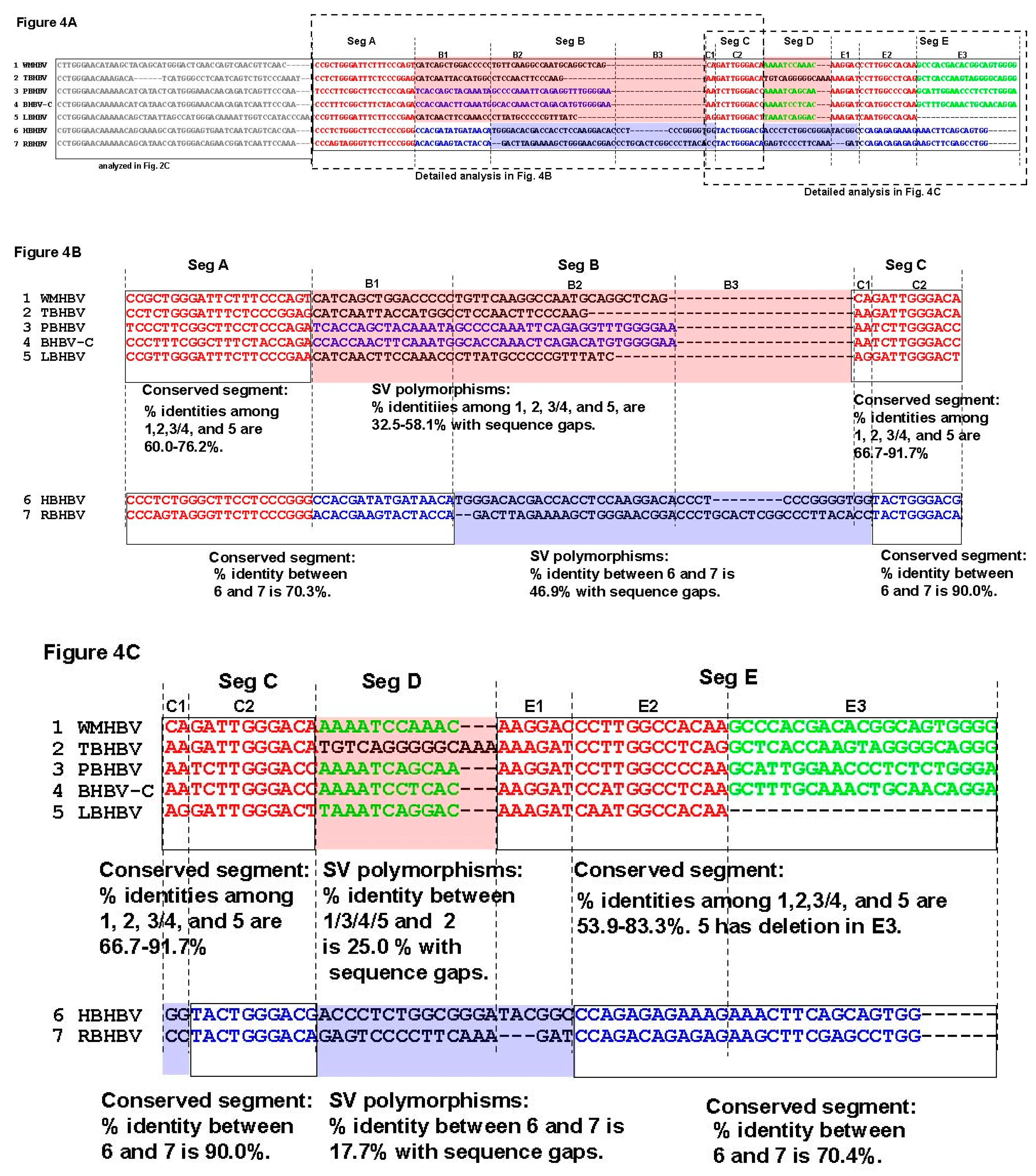
3.3. Unique SVs in the Core and Pre-S1 Promoter to pre-S1 ORF Start Site Regions
3.4. Analysis of the Pre-S1-S2 Region
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, J. Risk of hepatitis B reactivation in HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive patients with undetectable serum HBV DNA after treatment with rituximab for lymphoma: A meta-analysis. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B Reactivation Associated with Immune Suppressive and Biological Modifier Therapies: Current Concepts, Management Strategies, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohn, M.; Locarnini, S.; Yuen, L. Origins and Evolution of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis D Virus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a021360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norder, H.; Ebert, J.W.; Fields, H.A.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Magnius, L.O. Complete sequencing of a gibbon hepatitis B virus genome reveals a unique genotype distantly related to the chimpanzee hepatitis B virus. Virology 1996, 218, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lanford, R.E.; Chavez, D.; Brasky, K.M.; Burns, R.B., 3rd; Rico-Hesse, R. Isolation of a hepadnavirus from the woolly monkey, a New World primate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5757–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, K.S.; Heeney, J.L.; Swan, R.A.; Heriyanto; Verschoor, E.J. A new group of hepadnaviruses naturally infecting orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus). J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7860–7865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grethe, S.; Heckel, J.O.; Rietschel, W.; Hufert, F.T. Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis B virus variants in nonhuman primates. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5377–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, B.H.; Margolis, H.S. Primate hepatitis B viruses—Genetic diversity, geography and evolution. Rev. Med. Virol. 2002, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sall, A.A.; Starkman, S.; Reynes, J.M.; Lay, S.; Nhim, T.; Hunt, M.; Marx, N.; Simmonds, P. Frequent infection of Hylobates pileatus (pileated gibbon) with species-associated variants of hepatitis B virus in Cambodia. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P. The origin and evolution of hepatitis viruses in humans. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.F.; Geipel, A.; Konig, A.; Corman, V.M.; van Riel, D.; Leijten, L.M.; Bremer, C.M.; Rasche, A.; Cottontail, V.M.; Maganga, G.D.; et al. Bats carry pathogenic hepadnaviruses antigenically related to hepatitis B virus and capable of infecting human hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16151–16156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Fan, Q.; Yang, F.; Hu, T.; Qiu, W.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; et al. Hepatitis virus in long-fingered bats, Myanmar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Zhang, F.; Xia, L.; Hu, T.; Chen, G.; Qiu, W.; Fan, Q.; Feng, Y.; Guo, H.; Tu, C. Identification of a novel Orthohepadnavirus in pomona roundleaf bats in China. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowyer, S.M.; Sim, J.G. Relationships within and between genotypes of hepatitis B virus at points across the genome: Footprints of recombination in certain isolates. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Midgley, S. Recombination in the genesis and evolution of hepatitis B virus genotypes. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15467–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasche, A.; Souza, B.; Drexler, J.F. Bat hepadnaviruses and the origins of primate hepatitis B viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 16, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Clark, R.A.; Sokolova, S.; Leibowitz, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Hurles, M.E.; Mell, J.C.; Hall, I.M. Genome-wide mapping and assembly of structural variant breakpoints in the mouse genome. Genome. Res. 2010, 20, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. Characterizing complex structural variation in germline and somatic genomes. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, B.; Wong, K.; Bhomra, A.; Goodson, M.; Keane, T.M.; Adams, D.J.; Flint, J. The fine-scale architecture of structural variants in 17 mouse genomes. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Paulon, E.; Orito, E.; Sugiyama, M.; Ito, K.; Ueda, R.; Mizokami, M.; Naoumov, N.V. Novel type of hepatitis B virus mutation: Replacement mutation involving a hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 binding site tandem repeat in chronic hepatitis B virus genotype E. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14404–14410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Matsunami, K.; Iio, E.; Nojiri, S.; Joh, T. Novel non-canonical genetic rearrangements termed “complex structural variations” in HBV genome. Virus Res. 2017, 238, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Matsuura, K.; Matsunami, K.; Iio, E.; Nojiri, S. Characterization of hepatitis B virus with complex structural variations. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyver, L.; De Gendt, S.; Van Geyt, C.; Zoulim, F.; Fried, M.; Schinazi, R.F.; Rossau, R. A new genotype of hepatitis B virus: Complete genome and phylogenetic relatedness. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norder, H.; Courouce, A.M.; Magnius, L.O. Complete genomes, phylogenetic relatedness, and structural proteins of six strains of the hepatitis B virus, four of which represent two new genotypes. Virology 1994, 198, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, M.A.; Holmes, E.C. A revised evolutionary history of hepatitis B virus (HBV). J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xi, Q.; Deng, R.; Wang, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, X. Identification of interspecies recombination among hepadnaviruses infecting cross-species hosts. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.; Sharp, C.; LeBreton, M.; Djoko, C.F.; Kiyang, J.A.; Lankester, F.; Bibila, T.G.; Tamoufe, U.; Fair, J.; Wolfe, N.D.; et al. Species association of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in non-human apes; evidence for recombination between gorilla and chimpanzee variants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, A.; Brosius, J.; Schmitz, J.; Kriegs, J.O. The genome of a Mesozoic paleovirus reveals the evolution of hepatitis B viruses. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.; Seitz, S.; Mattei, S.; Suh, A.; Beck, J.; Herstein, J.; Borold, J.; Salzburger, W.; Kaderali, L.; Briggs, J.A.G.; et al. Deciphering the Origin and Evolution of Hepatitis B Viruses by Means of a Family of Non-enveloped Fish Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Falth, M.; Stindt, J.; Koniger, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Full | Small S | X | Core | Pre-S1-S2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaps | 131 | 23 | 20 | 14 | 74 |
| Identity | 67.1 ± 7.1 | 79.5 ± 6.0 | 69.1 ± 7.6 | 69.3 ± 7.5 | 52.5 ± 10.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujiwara, K.; Matsuura, K.; Matsunami, K.; Iio, E.; Nagura, Y.; Nojiri, S.; Kataoka, H. Novel Genetic Rearrangements Termed “Structural Variation Polymorphisms“ Contribute to the Genetic Diversity of Orthohepadnaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090871
Fujiwara K, Matsuura K, Matsunami K, Iio E, Nagura Y, Nojiri S, Kataoka H. Novel Genetic Rearrangements Termed “Structural Variation Polymorphisms“ Contribute to the Genetic Diversity of Orthohepadnaviruses. Viruses. 2019; 11(9):871. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090871
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujiwara, Kei, Kentaro Matsuura, Kayoko Matsunami, Etsuko Iio, Yoshihito Nagura, Shunsuke Nojiri, and Hiromi Kataoka. 2019. "Novel Genetic Rearrangements Termed “Structural Variation Polymorphisms“ Contribute to the Genetic Diversity of Orthohepadnaviruses" Viruses 11, no. 9: 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090871
APA StyleFujiwara, K., Matsuura, K., Matsunami, K., Iio, E., Nagura, Y., Nojiri, S., & Kataoka, H. (2019). Novel Genetic Rearrangements Termed “Structural Variation Polymorphisms“ Contribute to the Genetic Diversity of Orthohepadnaviruses. Viruses, 11(9), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090871




