Hepatitis C Core-Antigen Testing from Dried Blood Spots
Abstract
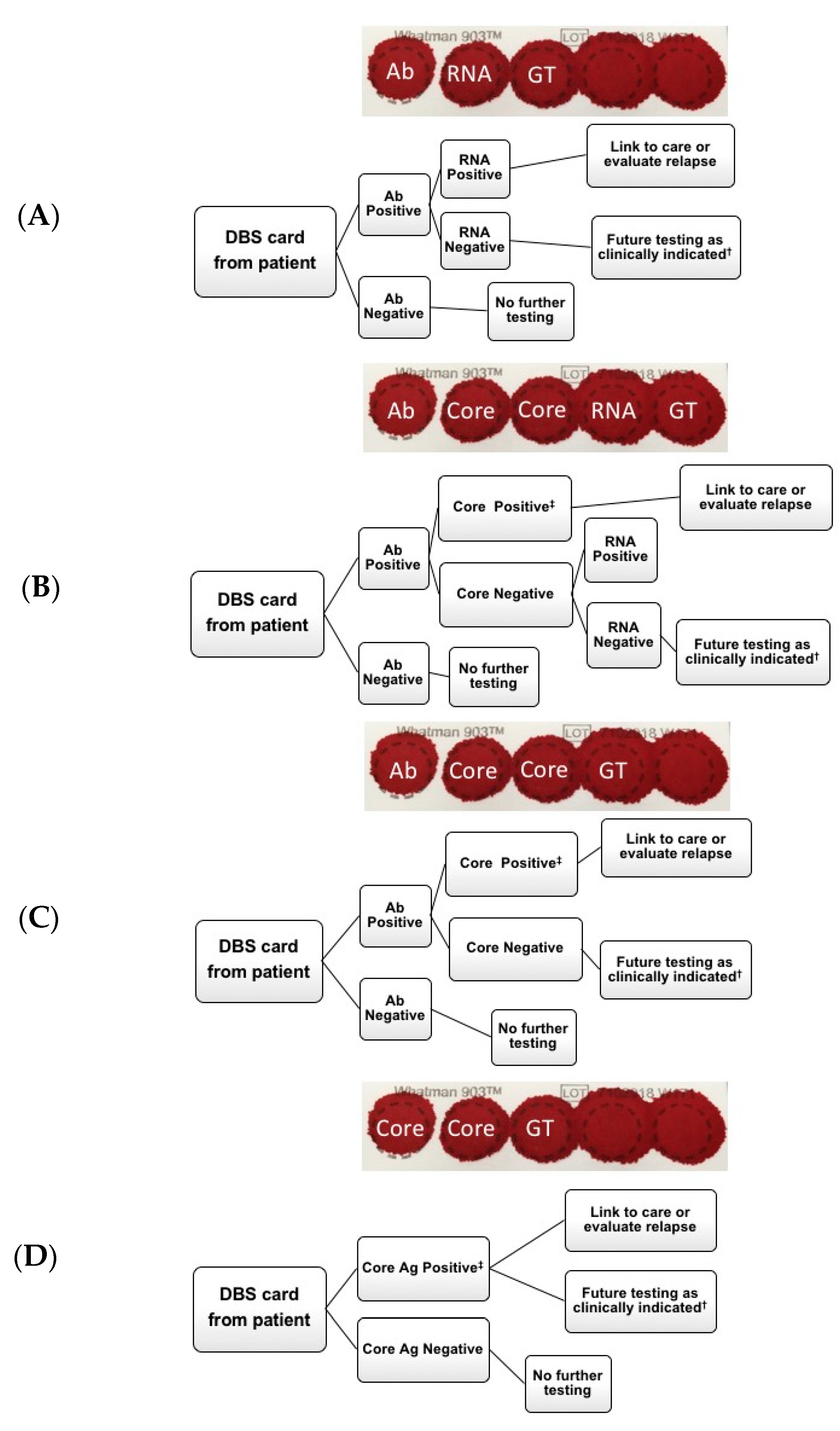
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Dried Blood Spots (DBS) and Serum Sample Collection
2.3. Dried Blood Spots (DBS) Anti-Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Core-Antigen (Ag) Elution and Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
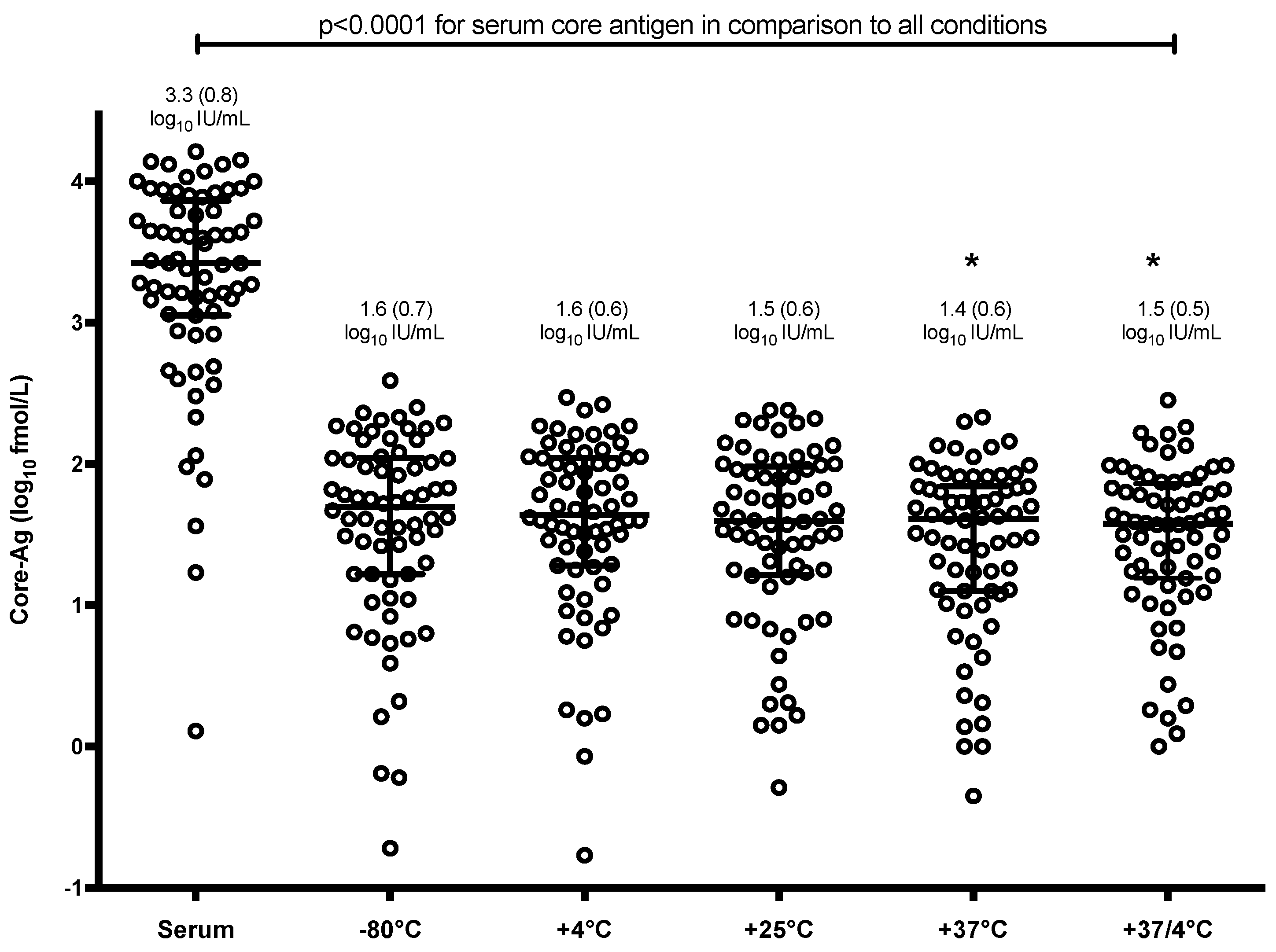
3.2. Detection of Core-Antigen (Ag) Is Unaffected by Changes in Storage Temperature
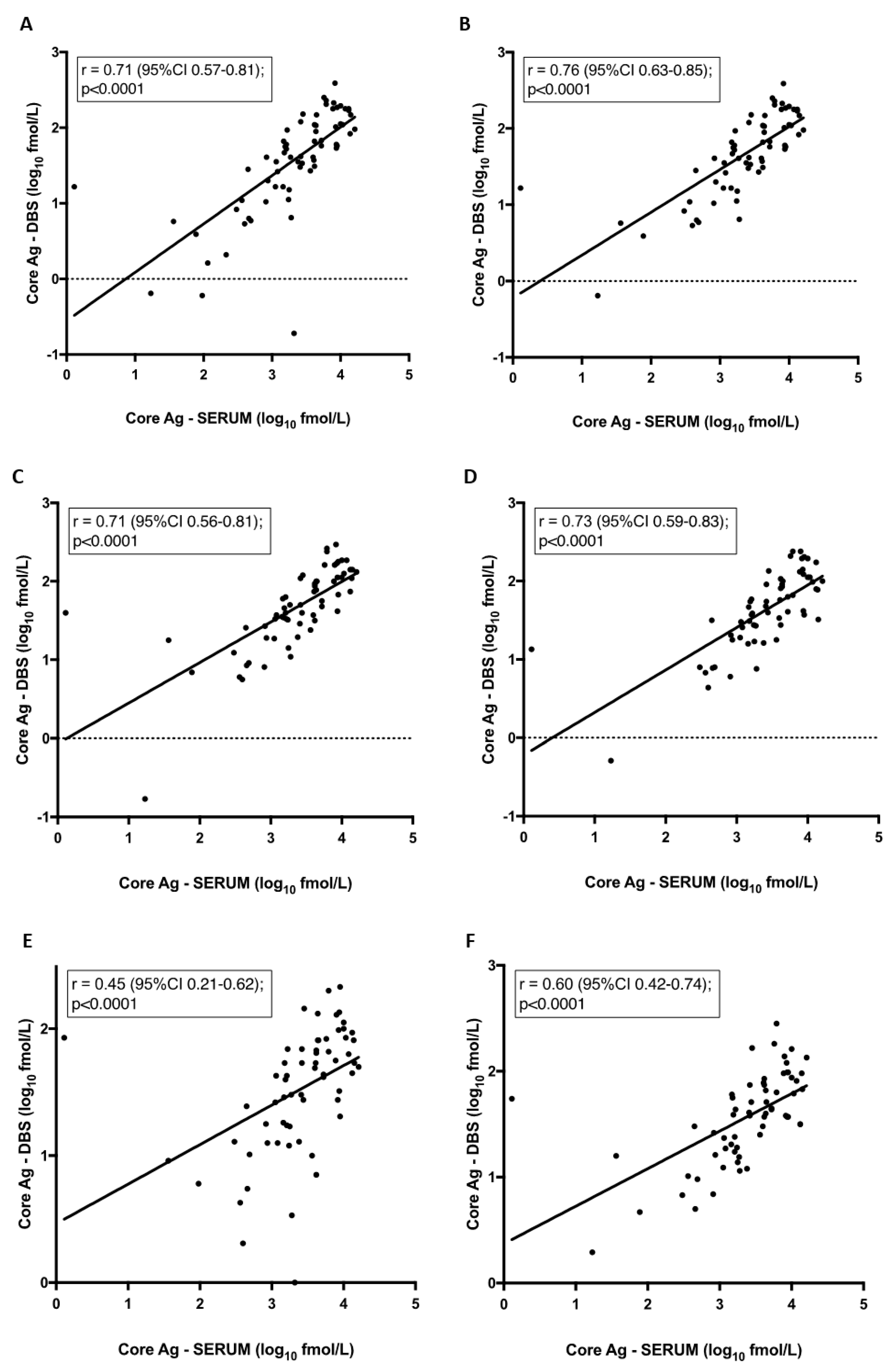
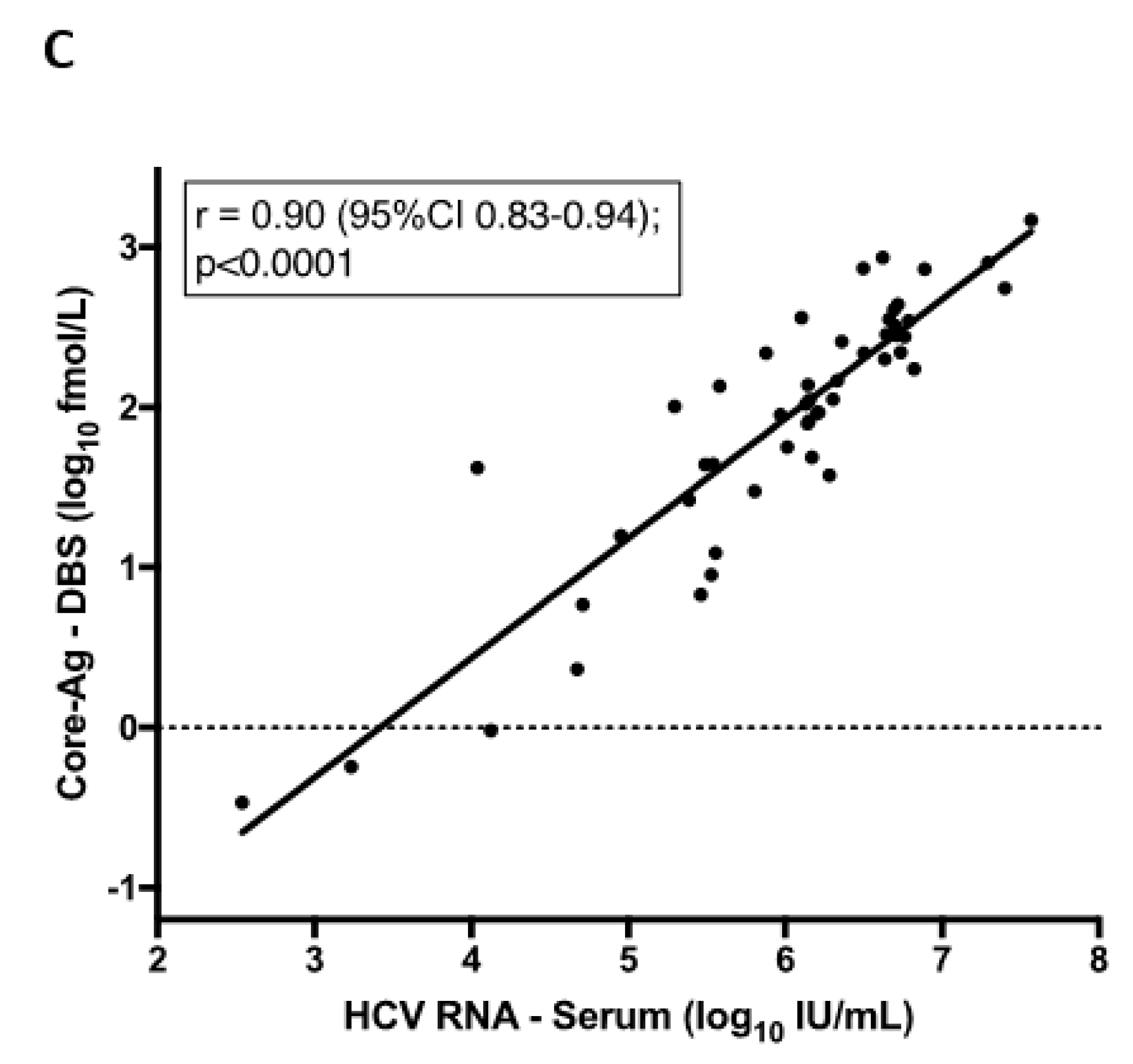
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Core-Antigen (Ag) from Dried Blood Spots (DBS)
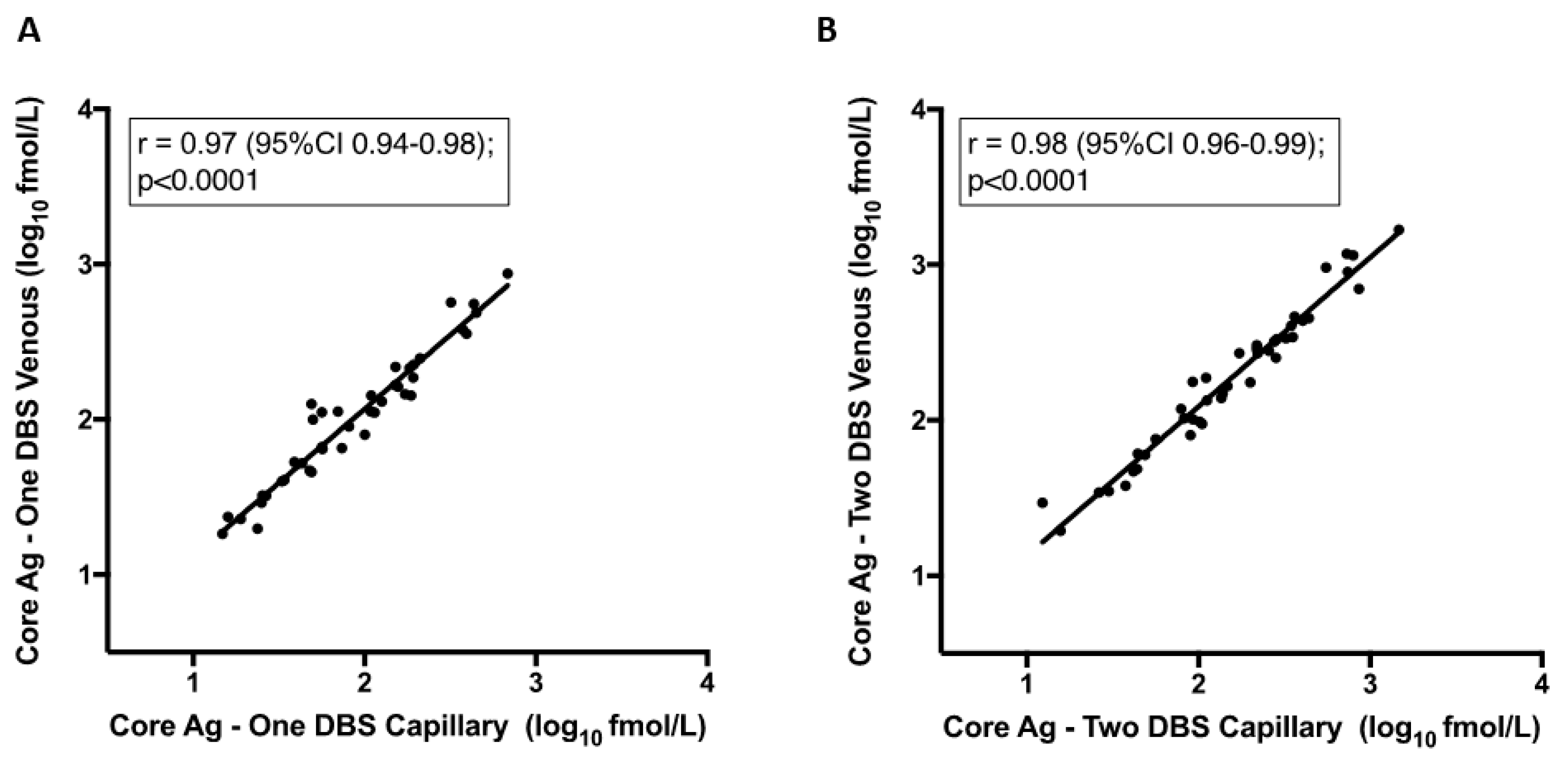
3.4. Core Antigen (Ag) Sensitivity Is Increased by Dried Blood Spots (DBS) Number
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Hepatitis B and C Testing; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=44848&Itemid=270&lang=en (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Grebely, J.; Applegate, T.L.; Cunningham, P.; Feld, J.J. Hepatitis C point-of-care diagnostics: In search of a single visit diagnosis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiman, J.M.; Tran, T.M.; Schumacher, S.G.; White, L.F.; Ongarello, S.; Cohn, J.; Easterbrook, P.J.; Linas, B.P.; Denkinger, C.M. Hepatitis C Core Antigen Testing for Diagnosis of Hepatitis C Virus Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, L.; Njouom, R.; Lissock, F.; Tamko-Mella, G.F.; Rallier, S.; Poiteau, L.; Soulier, A.; Chevaliez, S.; Vernet, G.; Rouveau, N.; et al. HCV Ag quantification as a one-step procedure in diagnosing chronic hepatitis C infection in Cameroon: The ANRS 12336 study. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2017, 20, 21446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Surveillance of Hepatitis C; Public Health Agency of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2017; Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/hepatitis-c/surveillance-hepatitis-c.html (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Gower, E.; Estes, C.; Blach, S.; Razavi-Shearer, K.; Razavi, H. Global epidemiology and genotype distribution of the hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S45–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, G.J.; Ward, J.; Thursz, M. Hepatitis C disease burden and strategies to manage the burden (Guest Editors Mark Thursz, Gregory Dore and John Ward). J. Viral. Hepat. 2014, 21 (Suppl. 1), 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M.; Thursz, M. Hepatitis C, a global issue: Access to care and new therapeutic and preventive approaches in resource-constrained areas. Semin. Liver. Dis. 2014, 34, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Konerman, M.A.; Lok, A.S. Hepatitis C Treatment and Barriers to Eradication. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.E.; Perlman, D.C.; Reed, J.; Smith, D.J.; Hagan, H. Patterns and Gaps Identified in a Systematic Review of the Hepatitis C Virus Care Continuum in Studies among People Who Use Drugs. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradling, P.R.; Tong, X.; Rupp, L.B.; Moorman, A.C.; Lu, M.; Teshale, E.H.; Gordon, S.C.; Vijayadeva, V.; Boscarino, J.A.; Schmidt, M.A.; et al. Trends in HCV RNA testing among HCV antibody-positive persons in care, 2003–2010. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGibbon, E.; Bornschlegel, K.; Balter, S. Half a diagnosis: Gap in confirming infection among hepatitis C antibody-positive patients. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, P.W.; Sollis, K.A.; Fiscus, S.; Ford, N.; Vitoria, M.; Essajee, S.; Barnett, D.; Cheng, B.; Crowe, S.M.; Denny, T.; et al. Systematic review of the use of dried blood spots for monitoring HIV viral load and for early infant diagnosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebely, J.; Bruneau, J.; Lazarus, J.V.; Dalgard, O.; Bruggmann, P.; Treloar, C.; Hickman, M.; Hellard, M.; Roberts, T.; Crooks, L.; et al. Research priorities to achieve universal access to hepatitis C prevention, management and direct-acting antiviral treatment among people who inject drugs. Int. J. Drug Policy 2017, 47, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.; Mbwambo, J.; Shimakawa, Y.; Poiteau, L.; Chevaliez, S.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Rwegasha, J.; Bhagani, S.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Makani, J.; et al. Clinical utility of HCV core antigen detection and quantification using serum samples and dried blood spots in people who inject drugs in Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2017, 20, 21856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulier, A.; Poiteau, L.; Rosa, I.; Hezode, C.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Chevaliez, S. Dried Blood Spots: A Tool to Ensure Broad Access to Hepatitis C Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Monitoring. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoury, F.M.J.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Soker, A.; Martinez, D.; Quek, C.; Cunningham, P.; Catlett, B.; Cloherty, G.; Marks, P.; Amin, J.; et al. Evaluation of a Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen Assay in Plasma and Dried Blood Spot Samples. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Annexes to WHO Guidelines on Hepatitis B and C Testing: Dried Blood Spots; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/guidelines-hepatitis-c-b-testing-annexes/en/ (accessed on 15 December 2017).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Hepatitis B and C Testing; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/guidelines-hepatitis-c-b-testing/en/ (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Lamoury, F.M.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Soker, A.; Martinez, D.; Quek, C.; Cunningham, P.; Catlett, B.; Cloherty, G.A.; Marks, P.; Amin, J.; et al. Hepatitis C virus core antigen and dried blood spots as simplified hepatitis C virus diagnostic tools. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 66, S710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterbrook, P.J.; Group, W.H.O.G.D. Who to test and how to test for chronic hepatitis C infection - 2016 WHO testing guidance for low- and middle-income countries. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, S46–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, G.; Innes, H.; McLeod, A.; Dillon, J.F.; Hayes, P.C.; Fox, R.; Barclay, S.T.; Templeton, K.; Aitken, C.; Gunson, R.; et al. Uptake of hepatitis C specialist services and treatment following diagnosis by dried blood spot in Scotland. J. Clin. Virol 2014, 61, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radley, A.; Melville, K.; Tait, J.; Stephens, B.; Evans, J.M.M.; Dillon, J.F. A quasi-experimental evaluation of dried blood spot testing through community pharmacies in the Tayside region of Scotland. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.K.; Hickman, M.; Miners, A.; Hutchinson, S.J.; Taylor, A.; Vickerman, P. Cost-effectiveness of HCV case-finding for people who inject drugs via dried blood spot testing in specialist addiction services and prisons. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardin, F.; Hearmon, N.; Negro, F.; Eddowes, L.; Bruggmann, P.; Castro, E. Increasing hepatitis C virus screening in people who inject drugs in Switzerland using rapid antibody saliva and dried blood spot testing: A cost-effectiveness analysis. J. Viral Hepat 2019, 26, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertisch, B.; Brezzi, M.; Negro, F.; Mullhaupt, B.; Ottiger, C.; Kunzler-Heule, P.; Schmid, P.; Giudici, F.; Clerc, O.; Moriggia, A.; et al. Very low hepatitis C viral loads in treatment-naive persons: Do they compromise hepatitis C virus antigen testing? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisyah, D.N.; Shallcross, L.; Hully, A.J.; O’Brien, A.; Hayward, A. Assessing hepatitis C spontaneous clearance and understanding associated factors-A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat 2018, 25, 680–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, D.; Deutsch, M. The spectrum of HBV/HCV coinfection: Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, viralinteractions and management. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Sagnelli, E.; Coppola, N.; Pisaturo, M.; Masiello, A.; Tonziello, G.; Sagnelli, C.; Messina, V.; Filippini, P. HBV superinfection in HCV chronic carriers: A disease that is frequently severe but associated with the eradication of HCV. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Storage Condition | HCV Antibody | HCV Core Antigen | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (95% CI) n = 68 | Sensitivity >3 fmol/L (95% CI) n = 68 | Sensitivity >10 fmol/L (95% CI) n = 68 | |
| −80 °C | 100% (100–100) (68/68) | 94.1% (88.5–99.7) (64/68) | 85.3% (76.4–94.2) (58/68) |
| +4 °C | 100% (100–100) (68/68) | 94.1% (88.5–99.7) (64/68) | 85.3% (76.4–94.2) (58/68) |
| +21 °C | 100% (100–100) (68/68) | 91.2% (84.3–98.1) (62/68) | 80.9% (70.8–91.0) (55/68) |
| +37 °C | 98.6% (96.6–100) (67/68) | 92.7% (86.4–98.9) (63/68) | 80.9% (70.8–91.0) (55/68) |
| +37 °C/+4 °C | 98.6% (96.6–100) (67/68) | 92.7% (86.4–98.9) (63/68) | 85.3% (76.4–94.2) (58/68) |
| Test | Biondi et al. | Mohamed et al. [15] | Lamoury et al. [17] | Soulier et al. [16] | WHO Meta-Analysis [19] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity † | Specificity | Sensitivity † | Specificity † | Sensitivity † | Specificity † | Sensitivity † | Specificity † | Sensitivity † | Specificity † | |
| HCV-Ab | 98.0% (98.0–100) | 100% (100–100) | ||||||||
| HCV RNA | 100% (100–100) | 99.9% (99.5–100) | ||||||||
| HCV-Ab DBS | 100% (96.4–100) | 99.1% (97.4–99.8) | 98.2% (94.9–99.6) | 98.0% (94.0–99.0) | 99.0% (97.0–100) | |||||
| HCV RNA DBS ‡ | 98.1% (95.9–99.1) | 100% (97.8–100) | 96.0% (93.4–97.6) | 97.7% (94.7–99.0) | ||||||
| Core-Ag DBS (−80 °C) | 94.1% (88.5–99.7) | 15/15 | 76.7% | 97.3% | 82.9% (74–90) | 96.1% (78–100) | 64.1% (58.5–69.3) | 100% (97.8–100) | ||
| HCV-Core-Ag DBS (21–24 °C) | 91.2% (84.3–98.1) | 5/5 | 64.1% (58.5–69.3) | 100% (97.8–100) | ||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biondi, M.J.; van Tilborg, M.; Smookler, D.; Heymann, G.; Aquino, A.; Perusini, S.; Mandel, E.; Kozak, R.A.; Cherepanov, V.; Kowgier, M.; et al. Hepatitis C Core-Antigen Testing from Dried Blood Spots. Viruses 2019, 11, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090830
Biondi MJ, van Tilborg M, Smookler D, Heymann G, Aquino A, Perusini S, Mandel E, Kozak RA, Cherepanov V, Kowgier M, et al. Hepatitis C Core-Antigen Testing from Dried Blood Spots. Viruses. 2019; 11(9):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090830
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiondi, Mia J., Marjolein van Tilborg, David Smookler, Gregory Heymann, Analiza Aquino, Stephen Perusini, Erin Mandel, Robert A. Kozak, Vera Cherepanov, Matthew Kowgier, and et al. 2019. "Hepatitis C Core-Antigen Testing from Dried Blood Spots" Viruses 11, no. 9: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090830
APA StyleBiondi, M. J., van Tilborg, M., Smookler, D., Heymann, G., Aquino, A., Perusini, S., Mandel, E., Kozak, R. A., Cherepanov, V., Kowgier, M., Hansen, B., Goneau, L. W., Janssen, H. L. A., Mazzulli, T., Cloherty, G., de Knegt, R. J., & Feld, J. J. (2019). Hepatitis C Core-Antigen Testing from Dried Blood Spots. Viruses, 11(9), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090830





