Clinical Evaluation of QuickNaviTM-Ebola in the 2018 Outbreak of Ebola Virus Disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
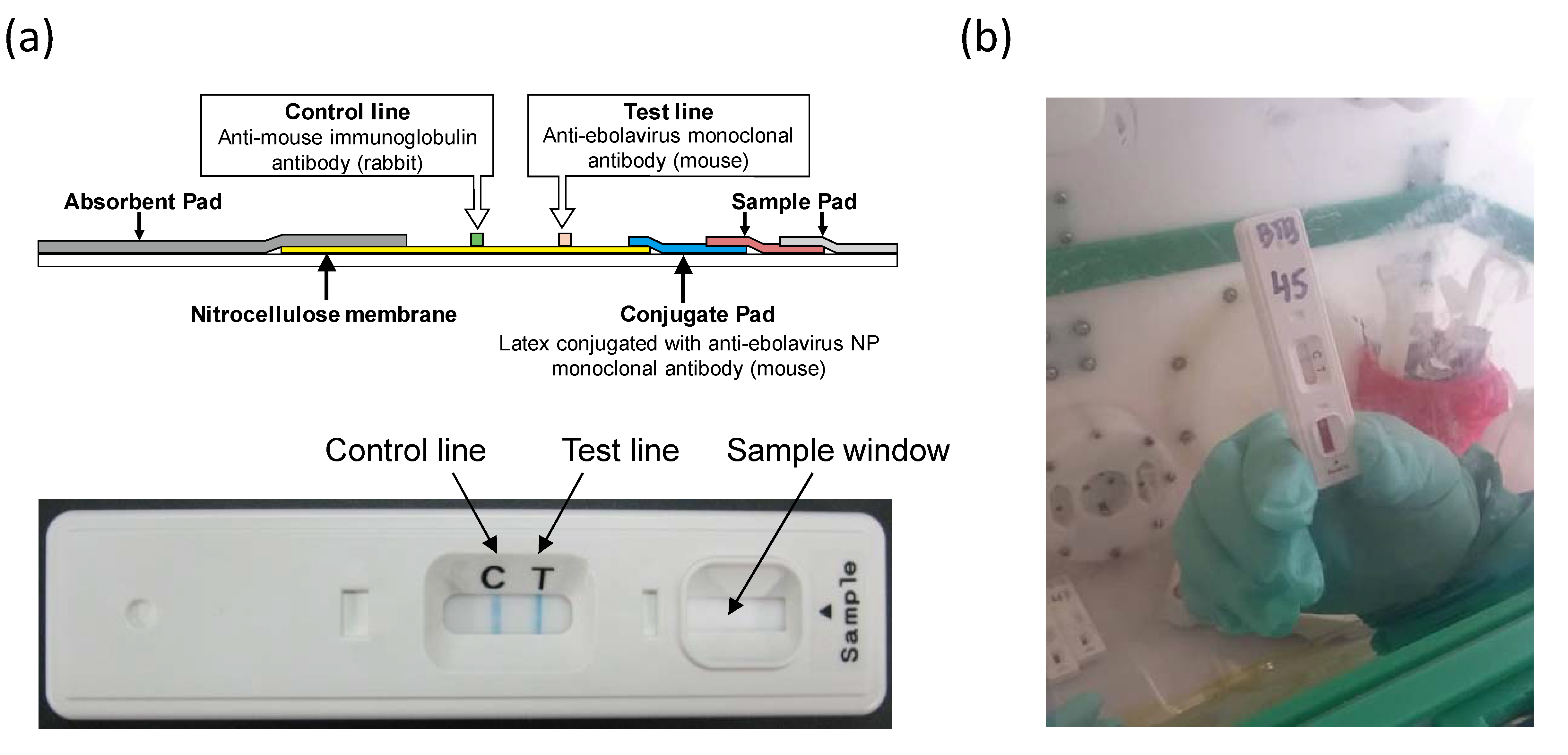
2.1. Devices
2.2. Realtime PCR
2.3. Sample Collection and Detection of the Virus
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldmann, H.; Sanchez, A.; Geisbert, T.W. Filoviridae: Marburg and Ebola Viruses. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams &Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 923–956. [Google Scholar]
- Disease Outbreak News (DONs). Available online: https://www.who.int/ebola/situation-reports/drc-2018/en/ (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Yoshida, R.; Muramatsu, S.; Akita, H.; Saito, Y.; Kuwahara, M.; Kato, D.; Changula, K.; Miyamoto, H.; Kajihara, M.; Manzoor, R.; et al. Development of an immunochromatography assay (QuickNavi-Ebola) to detect multiple species of ebolaviruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S185–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Butler, D. Speedy Ebola tests help contain Africa’s latest outbreak. Nature 2018, 558, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebola Research and Development Landscape of Clinical Candidates and Trials. Available online: http://www.who.int/medicines/ebola-treatment/EbolaR_D_public-report_updt2015.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- FDA Authorizes Emergency Use of First Ebola Fingerstick Test with Portable Reader. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm625502.htm (accessed on 9 November 2018).
- Cnops, L.; De Smet, B.; Mbala-Kingebeni, P.; van Griensven, J.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Ariën, K.K. Where are the Ebola diagnostics from last time? Nature 2019, 565, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbala-Kingebeni, P.; Aziza, A.; Di Paola, N.; Wiley, M.R.; Makiala-Mandanda, S.; Caviness, K.; Pratt, C.B.; Ladner, J.T.; Kugelman, J.R.; Prieto, K.; et al. Medical countermeasures during the 2018 Ebola virus disease outbreak in the North Kivu and Ituri Provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo: A rapid genomic assessment. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Emergency Use Assessment and Listing for Ebola Virus Disease IVDs PUBLIC REPORT. Available online: https://www.who.int/diagnostics_laboratory/160324_final_public_report_ea_0023_021_00.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Bharat, T.A.; Noda, T.; Riches, J.D.; Kraehling, V.; Kolesnikova, L.; Becker, S.; Kawaoka, Y.; Briggs, J.A. Structural dissection of Ebola virus and its assembly determinants using cryo-electron tomography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4275–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, Y.; Matsunami, H.; Kawaoka, Y.; Noda, T.; Wolf, M. Cryo-EM structure of the Ebola virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex at 3.6 Å resolution. Nature 2018, 563, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changula, K.; Yoshida, R.; Noyori, O.; Marzi, A.; Miyamoto, H.; Ishijima, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Kajihara, M.; Feldmann, H.; Mweene, A.S.; et al. Mapping of conserved and species-specific antibody epitopes on the Ebola virus nucleoprotein. Virus Res. 2013, 176, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngom, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Bi, D. Development and application of lateral flow test strip technology for detection of infectious agents and chemical contaminants: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1113–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, A.; Farnon, E.C.; Morgan, O.W.; Gould, P.; Boehmer, T.K.; Blaney, D.D.; Wiersma, P.; Tappero, J.W.; Nichol, S.T.; Ksiazek, T.G.; et al. Filovirus outbreak detection and surveillance: Lessons from Bundibugyo. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, S761–S767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample ID | Outbreaks (Month) | QuickNaviTM-Ebola | Real-Time PCR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18M-1 | 1st (May) | Negative | Negative† |
| 18M-2 | 1st (May) | Positive | Positive (23.6/28.7)† |
| 18M-3 | 1st (May) | Negative | Negative† |
| 18M-4 | 1st (May) | Negative | Negative† |
| 18M-5 | 1st (May) | Negative | Negative† |
| 18M-6 | 1st (May) | Positive | Positive (22.3/22.3)† |
| 18A-1 | 2nd (August) | Negative | Positive/Negative (39.6/NA)ठ|
| 18A-2 | 2nd (August) | Negative | Negative‡ |
| 18A-3 | 2nd (August) | Positive | Positive (21.6/25.0)‡ |
| 18A-4 | 2nd (August) | Positive | Positive (28.3/30.7)‡ |
| 18A-5 | 2nd (August) | Negative | Negative‡ |
| 18A-6 | 2nd (August) | Positive | Positive (20.1/23.7)‡ |
| GeneXpert Ebola | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | |
| QuickNaviTM-Ebola Positive | 68 | 2 | 70 |
| QuickNaviTM-Ebola Negative | 12 | 846 | 858 |
| Total | 80 | 848 | 928 |
| Sample | QuickNaviTM-Ebola | GeneXpert Ebola | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | CT (NP) | GP | CT (GP) | ||
| 1 | Negative | Positive | 38.7 | Negative | NA† |
| 2 | Negative | Positive | 39.9 | Negative | NA |
| 3 | Negative | Positive | 38.1 | Positive | 40.2 |
| 4 | Negative | Positive | 38.7 | Negative | NA |
| 5 | Negative | Positive | 26.1 | Positive | 31.6 |
| 6 | Negative | Positive | 34.2 | Positive | 42.3 |
| 7 | Negative | Positive | 36.0 | Positive | 41.1 |
| 8 | Negative | Positive | 33.6 | Positive | 37.9 |
| 9 | Negative | Positive | 38.0 | Negative | NA |
| 10 | Negative | Positive | 36.8 | Negative | NA |
| 11 | Negative | Positive | 37.7 | Negative | NA |
| 12 | Negative | Positive | 13.9 | Positive | 19.1 |
| Statistics | QuickNaviTM-Ebola Positive (n = 68) | QuickNaviTM-Ebola Negative (n = 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 14.20 | 13.90 |
| 25 percentile | 17.98 | 34.05 |
| Median | 21.00 | 37.25 |
| 75 percentile | 24.88 | 38.25 |
| Maximum | 35.60 | 39.90 |
| Mean | 21.76 | 34.31 |
| Standard deviation | 4.69 | 7.40 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makiala, S.; Mukadi, D.; De Weggheleire, A.; Muramatsu, S.; Kato, D.; Inano, K.; Gondaira, F.; Kajihara, M.; Yoshida, R.; Changula, K.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of QuickNaviTM-Ebola in the 2018 Outbreak of Ebola Virus Disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Viruses 2019, 11, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070589
Makiala S, Mukadi D, De Weggheleire A, Muramatsu S, Kato D, Inano K, Gondaira F, Kajihara M, Yoshida R, Changula K, et al. Clinical Evaluation of QuickNaviTM-Ebola in the 2018 Outbreak of Ebola Virus Disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Viruses. 2019; 11(7):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070589
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakiala, Sheila, Daniel Mukadi, Anja De Weggheleire, Shino Muramatsu, Daisuke Kato, Koichi Inano, Fumio Gondaira, Masahiro Kajihara, Reiko Yoshida, Katendi Changula, and et al. 2019. "Clinical Evaluation of QuickNaviTM-Ebola in the 2018 Outbreak of Ebola Virus Disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo" Viruses 11, no. 7: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070589
APA StyleMakiala, S., Mukadi, D., De Weggheleire, A., Muramatsu, S., Kato, D., Inano, K., Gondaira, F., Kajihara, M., Yoshida, R., Changula, K., Mweene, A., Mbala-Kingebeni, P., Muyembe-Tamfum, J.-J., Masumu, J., Ahuka, S., & Takada, A. (2019). Clinical Evaluation of QuickNaviTM-Ebola in the 2018 Outbreak of Ebola Virus Disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Viruses, 11(7), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070589







