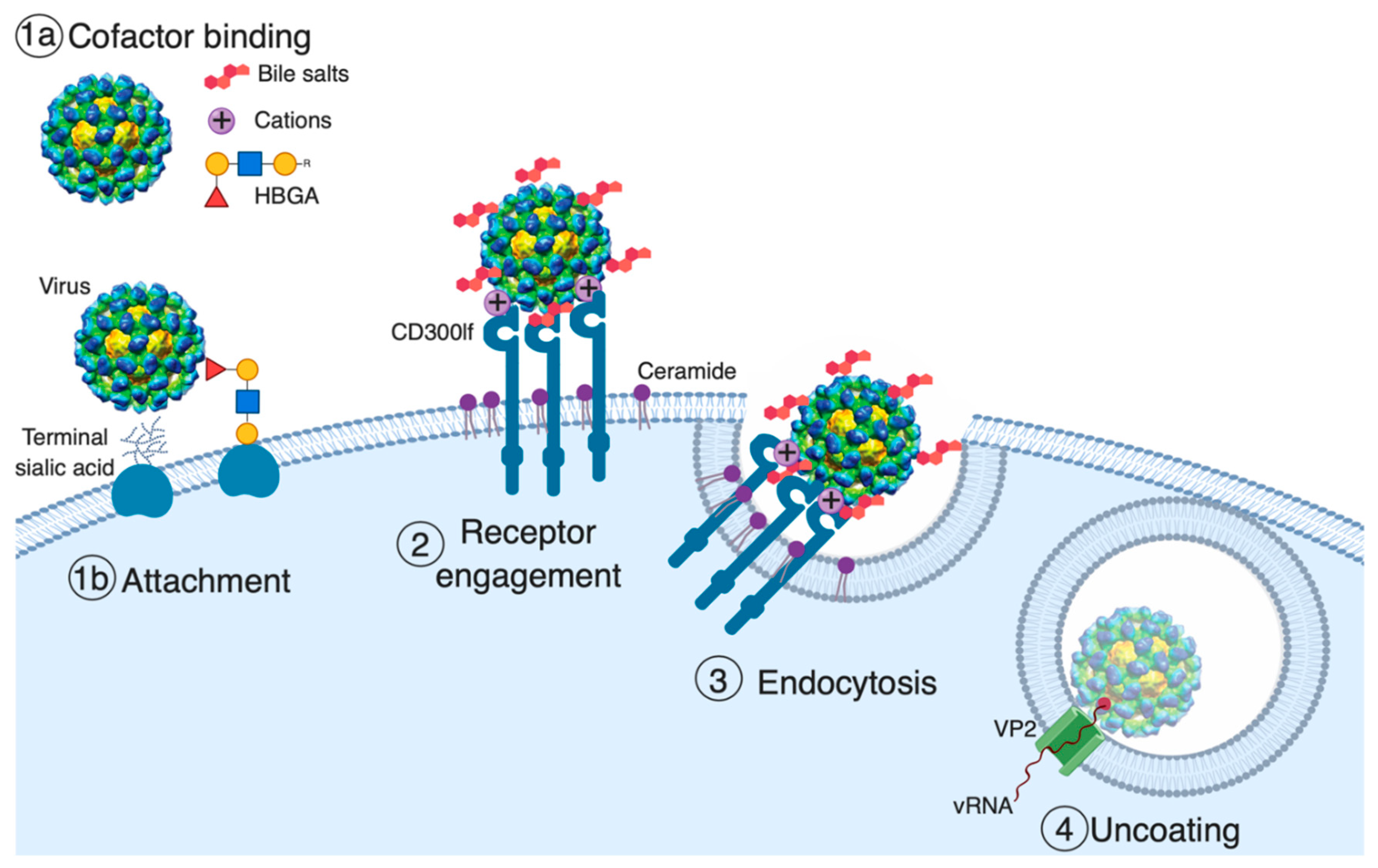
Norovirus Attachment and Entry
Abstract
1. Background
2. The Role of Glycans in Norovirus Attachment
3. The Role of Non-Glycans in Norovirus Attachment
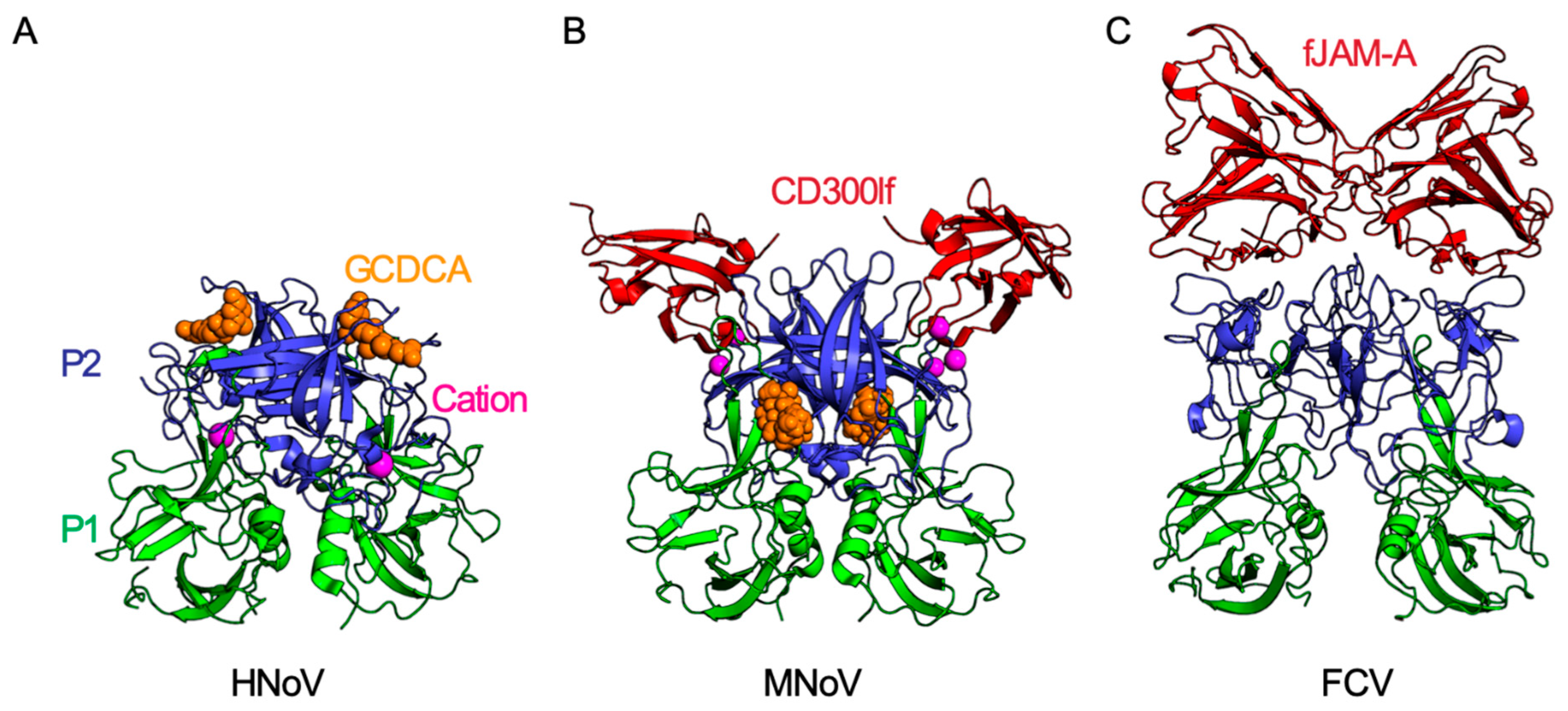
4. Receptor Engagement
5. Endocytosis and Uncoating
6. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopman, B.A.; Steele, D.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Parashar, U.D. The vast and varied global burden of norovirus: Prospects for prevention and control. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1001999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.M.; Widdowson, M.A.; Glass, R.I.; Akazawa, K.; Vinjé, J.; Parashar, U.D. Systematic literature review of role of noroviruses in sporadic gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karst, S.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Goodfellow, I.G.; Green, K.Y.; Virgin, H.W. Advances in norovirus biology. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K.; Atmar, R.L. Prospects and challenges in the development of a norovirus vaccine. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, M.; Helenius, A. Virus entry: Open sesame. Cell 2006, 124, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilen, C.B.; Lee, S.; Hsieh, L.L.; Orchard, R.C.; Desai, C.; Hykes, B.L.; McAllaster, M.R.; Balce, D.R.; Feehley, T.; Brestoff, J.R.; et al. Tropism for tuft cells determines immune promotion of norovirus pathogenesis. Science 2018, 360, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilen, C.B.; Tilton, J.C.; Doms, R.W. Hiv: Cell binding and entry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Med. 2012, 2, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, R.I.; Parashar, U.D.; Estes, M.K. Norovirus gastroenteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, S.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K. Epidemiology of human noroviruses and updates on vaccine development. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubitt, W.D.; Pead, P.J.; Saeed, A.A. A new serotype of calicivirus associated with an outbreak of gastroenteritis in a residential home for the elderly. J. Clin. Pathol. 1981, 34, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, K.; Hardy, M.E.; Nakata, S.; Chiba, S.; Estes, M.K. Molecular characterization of morphologically typical human calicivirus sapporo. Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 1537–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martella, V.; Lorusso, E.; Decaro, N.; Elia, G.; Radogna, A.; D’Abramo, M.; Desario, C.; Cavalli, A.; Corrente, M.; Camero, M.; et al. Detection and molecular characterization of a canine norovirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caddy, S.; Breiman, A.; le Pendu, J.; Goodfellow, I. Genogroup iv and vi canine noroviruses interact with histo-blood group antigens. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10377–10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrino, T.A.; Schreiber, D.S.; Trier, J.S.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Blacklow, N.R. Clinical immunity in acute gastroenteritis caused by norwalk agent. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woode, G.N.; Bridger, J.C. Isolation of small viruses resembling astroviruses and caliciviruses from acute enteritis of calves. J. Med. Microbiol. 1978, 11, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karst, S.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Lay, M.; Davidson, J.; Virgin, H.W. Stat1-dependent innate immunity to a norwalk-like virus. Science 2003, 299, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Han, M.G.; Cheetham, S.; Souza, M.; Funk, J.A.; Saif, L.J. Porcine noroviruses related to human noroviruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Williamson, W.; Hewitt, J.; Lin, S.; Rivera-Aban, M.; Ball, A.; Scholes, P.; Savill, M.; Greening, G.E. Molecular detection of norovirus in sheep and pigs in new zealand farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 133, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford-Siltz, L.A.; Mullis, L.; Sanad, Y.M.; Tohma, K.; Lepore, C.J.; Azevedo, M.; Parra, G.I. Genomics analyses of giv and gvi noroviruses reveal the distinct clustering of human and animal viruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, L.J.; Hardy, M.E.; Estes, M.K. Biochemical characterization of a smaller form of recombinant norwalk virus capsids assembled in insect cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8066–8072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K. Expression, self-assembly, and antigenicity of the norwalk virus capsid protein. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6527–6532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, G.; Ettayebi, K.; Atmar, R.L.; Bombardi, R.G.; Kose, N.; Estes, M.K.; Crowe, J.E. Human monoclonal antibodies that neutralize pandemic gii.4 noroviruses. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolawole, A.O.; Smith, H.Q.; Svoboda, S.A.; Lewis, M.S.; Sherman, M.B.; Lynch, G.C.; Pettitt, B.M.; Smith, T.J.; Wobus, C.E. Norovirus escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies is limited to allostery-like mechanisms. mSphere 2017, 2, e00334-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobus, C.E.; Karst, S.M.; Thackray, L.B.; Chang, K.O.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Belliot, G.; Krug, A.; Mackenzie, J.M.; Green, K.Y.; Virgin, H.W. Replication of norovirus in cell culture reveals a tropism for dendritic cells and macrophages. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.A.; Wilen, C.B.; Dai, Y.N.; Orchard, R.C.; Kim, A.S.; Stegeman, R.A.; Hsieh, L.L.; Smith, T.J.; Virgin, H.W.; Fremont, D.H. Structural basis for murine norovirus engagement of bile acids and the cd300lf receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9201–E9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, R.C.; Wilen, C.B.; Doench, J.G.; Baldridge, M.T.; McCune, B.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, S.; Pruett-Miller, S.M.; Nelson, C.A.; Fremont, D.H.; et al. Discovery of a proteinaceous cellular receptor for a norovirus. Science 2016, 353, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, T.; Koromyslova, A.; Malak, V.; Hansman, G.S. Atomic structure of the murine norovirus protruding domain and soluble cd300lf receptor complex. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00413-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, M.A.; Chung, L.M.; Chaudhry, Y.; Bailey, D.; Goodfellow, I. Development of an optimized rna-based murine norovirus reverse genetics system. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, V.K.; McCormick, C.J.; Clarke, I.N.; Salim, O.; Wobus, C.E.; Thackray, L.B.; Virgin, H.W.; Lambden, P.R. Recovery of infectious murine norovirus using pol ii-driven expression of full-length cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnovtsev, S.; Green, K.Y. RNA transcripts derived from a cloned full-length copy of the feline calicivirus genome do not require vpg for infectivity. Virology 1995, 210, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Watanabe, M.; Zhu, S.; Graves, C.L.; Keyes, L.R.; Grau, K.R.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.B.; Iovine, N.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Vinjé, J.; et al. Enteric bacteria promote human and mouse norovirus infection of b cells. Science 2014, 346, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, K.; Fujimoto, A.; Takai-Todaka, R.; Miki, M.; Doan, Y.H.; Murakami, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Murata, K.; Nakanishi, A.; Katayama, K. Functional receptor molecules cd300lf and cd300ld within the cd300 family enable murine noroviruses to infect cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6248–E6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, M.J.; McElwee, M.; Azmi, L.; Gabrielsen, M.; Byron, O.; Goodfellow, I.G.; Bhella, D. Calicivirus vp2 forms a portal-like assembly following receptor engagement. Nature 2019, 565, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossiboff, R.J.; Parker, J.S. Identification of regions and residues in feline junctional adhesion molecule required for feline calicivirus binding and infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13608–13621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossiboff, R.J.; Zhou, Y.; Lightfoot, P.J.; Prasad, B.V.; Parker, J.S. Conformational changes in the capsid of a calicivirus upon interaction with its functional receptor. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5550–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, S.; Perry, J.W.; Yetming, K.; Patel, S.P.; Auble, H.; Shu, L.; Nawar, H.F.; Lee, C.H.; Connell, T.D.; Shayman, J.A.; et al. Ganglioside-linked terminal sialic acid moieties on murine macrophages function as attachment receptors for murine noroviruses. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, T.; Koromyslova, A.; Hansman, G.S. Structural basis for human norovirus capsid binding to bile acids. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e015581-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.; Moe, C.; Marionneau, S.; Ruvoen, N.; Jiang, X.; Lindblad, L.; Stewart, P.; LePendu, J.; Baric, R. Human susceptibility and resistance to norwalk virus infection. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, A.M.; Atmar, R.L.; Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus infection and disease is associated with abo histo-blood group type. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marionneau, S.; Ruvoën, N.; Le Moullac-Vaidye, B.; Clement, M.; Cailleau-Thomas, A.; Ruiz-Palacois, G.; Huang, P.; Jiang, X.; Le Pendu, J. Norwalk virus binds to histo-blood group antigens present on gastroduodenal epithelial cells of secretor individuals. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; Shimojima, M.; Miyazawa, T.; Kato, K.; Tohya, Y.; Akashi, H. Junctional adhesion molecule 1 is a functional receptor for feline calicivirus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4482–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapikian, A.Z.; Wyatt, R.G.; Dolin, R.; Thornhill, T.S.; Kalica, A.R.; Chanock, R.M. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J. Virol. 1972, 10, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.C.; Mathewson, J.J.; DuPont, H.L.; Greenberg, H.B. Multiple-challenge study of host susceptibility to norwalk gastroenteritis in us adults. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, S.M.; Greenberg, H.B. Immunity to calicivirus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181 (Suppl. 2), S331–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquier, S.; Lowe, J.B.; Kelly, R.J.; Fertitta, A.L.; Lennon, G.G.; Giorgi, D. Molecular cloning of a human genomic region containing the h blood group alpha(1,2)fucosyltransferase gene and two h locus-related DNA restriction fragments. Isolation of a candidate for the human secretor blood group locus. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 4632–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, Y.; Tachida, H.; Pang, H.; Liu, Y.; Soejima, M.; Ghaderi, A.A.; Takenaka, O.; Kimura, H. Contrasting patterns of polymorphisms at the abo-secretor gene (fut2) and plasma alpha(1,3)fucosyltransferase gene (fut6) in human populations. Genetics 2001, 158, 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Koda, Y.; Soejima, M.; Pang, H.; Schlaphoff, T.; du Toit, E.D.; Kimura, H. Extensive polymorphism of the fut2 gene in an african (xhosa) population of south africa. Hum. Genet. 1998, 103, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeck, A.; Kavanagh, O.; Estes, M.K.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Graham, D.Y.; Atmar, R.L. Serological correlate of protection against norovirus-induced gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, P.R.; Lindesmith, L.; Yount, B.; Moe, C.L.; Baric, R.S. Binding of norwalk virus-like particles to abh histo-blood group antigens is blocked by antisera from infected human volunteers or experimentally vaccinated mice. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12335–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koromyslova, A.D.; Morozov, V.A.; Hefele, L.; Hansman, G.S. Human norovirus neutralized by a monoclonal antibody targeting the histo-blood group antigen pocket. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02174-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordgren, J.; Svensson, L. Genetic susceptibility to human norovirus infection: An update. Viruses 2019, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, B.; Kindberg, E.; Buesa, J.; Rydell, G.E.; Lidón, M.F.; Montava, R.; Abu Mallouh, R.; Grahn, A.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Bellido, J.; et al. The g428a nonsense mutation in fut2 provides strong but not absolute protection against symptomatic gii.4 norovirus infection. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopman, B.A.; Trivedi, T.; Vicuña, Y.; Costantini, V.; Collins, N.; Gregoricus, N.; Parashar, U.; Sandoval, C.; Broncano, N.; Vaca, M.; et al. Norovirus infection and disease in an ecuadorian birth cohort: Association of certain norovirus genotypes with host fut2 secretor status. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currier, R.L.; Payne, D.C.; Staat, M.A.; Selvarangan, R.; Shirley, S.H.; Halasa, N.; Boom, J.A.; Englund, J.A.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Harrison, C.J.; et al. Innate susceptibility to norovirus infections influenced by fut2 genotype in a united states pediatric population. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karangwa, C.K.; Parra, G.I.; Bok, K.; Johnson, J.A.; Levenson, E.A.; Green, K.Y. Sequential gastroenteritis outbreaks in a single year caused by norovirus genotypes gii.2 and gii.6 in an institutional setting. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansman, G.S.; Shahzad-Ul-Hussan, S.; McLellan, J.S.; Chuang, G.Y.; Georgiev, I.; Shimoike, T.; Katayama, K.; Bewley, C.A.; Kwong, P.D. Structural basis for norovirus inhibition and fucose mimicry by citrate. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Lou, Z.; Tan, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Rao, Z. Structural basis for the recognition of blood group trisaccharides by norovirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5949–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Leuthold, M.M.; Hansman, G.S. Human noroviruses’ fondness for histo-blood group antigens. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Farkas, T.; Marionneau, S.; Zhong, W.; Ruvoën-Clouet, N.; Morrow, A.L.; Altaye, M.; Pickering, L.K.; Newburg, D.S.; LePendu, J.; et al. Noroviruses bind to human abo, lewis, and secretor histo-blood group antigens: Identification of 4 distinct strain-specific patterns. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guix, S.; Asanaka, M.; Katayama, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Neill, F.H.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus rna is infectious in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12238–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, T.; Stoltzfus, G.T.; Zhu, C.; Jung, K.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J. Attempts to grow human noroviruses, a sapovirus, and a bovine norovirus in vitro. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0178157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldridge, M.T.; Nice, T.J.; McCune, B.T.; Yokoyama, C.C.; Kambal, A.; Wheadon, M.; Diamond, M.S.; Ivanova, Y.; Artyomov, M.; Virgin, H.W. Commensal microbes and interferon-λ determine persistence of enteric murine norovirus infection. Science 2015, 347, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, A.D.; Brown, T.D. Alpha2,6-linked sialic acid acts as a receptor for feline calicivirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, S.; Perry, J.W.; McGreevy, E.; Yetming, K.; Perkins, C.; Henderson, K.; Wobus, C.E. Murine noroviruses bind glycolipid and glycoprotein attachment receptors in a strain-dependent manner. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5584–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.O.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Belliot, G.; Kim, Y.; Saif, L.J.; Green, K.Y. Bile acids are essential for porcine enteric calicivirus replication in association with down-regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8733–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, N. Deconjugation of bile salts by bacteroids and clostridium. Microbiol. Immunol. 1981, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Bajaj, J.S. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanna, V.; Kim, Y.; Chang, K.O. The crucial role of bile acids in the entry of porcine enteric calicivirus. Virology 2014, 456-457, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, R.C.; Wilen, C.B.; Virgin, H.W. Sphingolipid biosynthesis induces a conformational change in the murine norovirus receptor and facilitates viral infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1632, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, L.R.; Ruiz-Argüello, M.B.; Goñi, F.M.; Alonso, A. Membrane restructuring via ceramide results in enhanced solute efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11788–11794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, K.; Isobe, M.; Matsukawa, T.; Ito, S.; Maehara, A.; Takahashi, M.; Yamanishi, Y.; Kaitani, A.; Oki, T.; Okumura, K.; et al. Sphingomyelin and ceramide are physiological ligands for human lmir3/cd300f, inhibiting fcεri-mediated mast cell activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, e271–e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanna, V.; Kim, Y.; Chang, K.O. Ceramide formation mediated by acid sphingomyelinase facilitates endosomal escape of caliciviruses. Virology 2015, 483, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingemann, M.; Taube, S. Open sesame: New keys to unlocking the gate to norovirus infection. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhella, D.; Goodfellow, I.G. The cryo-electron microscopy structure of feline calicivirus bound to junctional adhesion molecule a at 9-angstrom resolution reveals receptor-induced flexibility and two distinct conformational changes in the capsid protein vp1. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11381–11390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Sandoval-Jaime, C.; Parra, G.I.; Tin, C.M.; Jones, R.W.; Soden, J.; Barnes, D.; Freeth, J.; Smith, A.W.; Green, K.Y. Identification of human junctional adhesion molecule 1 as a functional receptor for the hom-1 calicivirus on human cells. MBio 2017, 8, e00031-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Nusrat, A.; Schnell, F.J.; Reaves, T.A.; Walsh, S.; Pochet, M.; Parkos, C.A. Human junction adhesion molecule regulates tight junction resealing in epithelia. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 (Pt 13), 2363–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Borrego, F. The cd300 molecules: An emerging family of regulators of the immune system. Blood 2013, 121, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolawole, A.O.; Xia, C.; Li, M.; Gamez, M.; Yu, C.; Rippinger, C.M.; Yucha, R.E.; Smith, T.J.; Wobus, C.E. Newly isolated mabs broaden the neutralizing epitope in murine norovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Choi, S.C.; Murakami, Y.; Allen, J.; Morse, H.C.; Qi, C.F.; Krzewski, K.; Coligan, J.E. P85α recruitment by the cd300f phosphatidylserine receptor mediates apoptotic cell clearance required for autoimmunity suppression. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez, J.A.; Galfré, E.; Dupeux, F.; Flot, D.; Moran, O.; Dimasi, N. The crystal structure of the extracellular domain of the inhibitor receptor expressed on myeloid cells irem-1. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taube, S.; Rubin, J.R.; Katpally, U.; Smith, T.J.; Kendall, A.; Stuckey, J.A.; Wobus, C.E. High-resolution x-ray structure and functional analysis of the murine norovirus 1 capsid protein protruding domain. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5695–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolawole, A.O.; Li, M.; Xia, C.; Fischer, A.E.; Giacobbi, N.S.; Rippinger, C.M.; Proescher, J.B.; Wu, S.K.; Bessling, S.L.; Gamez, M.; et al. Flexibility in surface-exposed loops in a virus capsid mediates escape from antibody neutralization. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4543–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.M.; Hutson, A.M.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V. Atomic resolution structural characterization of recognition of histo-blood group antigens by norwalk virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9175–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, J.E.; Vaney, M.C.; Duquerroy, S.; Vonrhein, C.; Girard-Blanc, C.; Crublet, E.; Thompson, A.; Bricogne, G.; Rey, F.A. Glycoprotein organization of chikungunya virus particles revealed by x-ray crystallography. Nature 2010, 468, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.W.; Taube, S.; Wobus, C.E. Murine norovirus-1 entry into permissive macrophages and dendritic cells is ph-independent. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, A.D.; Brown, T.D. Entry of feline calicivirus is dependent on clathrin-mediated endocytosis and acidification in endosomes. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7500–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanna, V.; Kim, Y.; Chang, K.O. Endosomal acidification and cathepsin l activity is required for calicivirus replication. Virology 2014, 464–465, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerondopoulos, A.; Jackson, T.; Monaghan, P.; Doyle, N.; Roberts, L.O. Murine norovirus-1 cell entry is mediated through a non-clathrin-, non-caveolae-, dynamin- and cholesterol-dependent pathway. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiana, M.; Ghosh, S.; Ho, B.A.; Rajasekaran, V.; Du, W.L.; Mutsafi, Y.; De Jésus-Diaz, D.A.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Levenson, E.A.; Parra, G.I.; et al. Vesicle-cloaked virus clusters are optimal units for inter-organismal viral transmission. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 208–220.e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Du, W.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Takvorian, P.M.; Pau, C.; Cali, A.; Brantner, C.A.; Stempinski, E.S.; Connelly, P.S.; Ma, H.C.; et al. Phosphatidylserine vesicles enable efficient en bloc transmission of enteroviruses. Cell 2015, 160, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Serrano, E.E.; González-López, O.; Das, A.; Lemon, S.M. Cellular entry and uncoating of naked and quasi-enveloped human hepatoviruses. Elife 2019, 8, e43983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.; Dey, D.; Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, M. Breach: Host membrane penetration and entry by nonenveloped viruses. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti-Ciarlet, A.; Crawford, S.E.; Hutson, A.M.; Estes, M.K. The 3′ end of norwalk virus mrna contains determinants that regulate the expression and stability of the viral capsid protein vp1: A novel function for the vp2 protein. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11603–11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongpunsawad, S.; Venkataram Prasad, B.V.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus minor capsid protein vp2 associates within the vp1 shell domain. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4818–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti-Ciarlet, A.; White, L.J.; Chen, R.; Prasad, B.V.; Estes, M.K. Structural requirements for the assembly of norwalk virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4044–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graziano, V.R.; Wei, J.; Wilen, C.B. Norovirus Attachment and Entry. Viruses 2019, 11, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060495
Graziano VR, Wei J, Wilen CB. Norovirus Attachment and Entry. Viruses. 2019; 11(6):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060495
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraziano, Vincent R., Jin Wei, and Craig B. Wilen. 2019. "Norovirus Attachment and Entry" Viruses 11, no. 6: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060495
APA StyleGraziano, V. R., Wei, J., & Wilen, C. B. (2019). Norovirus Attachment and Entry. Viruses, 11(6), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060495




