Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Enhance Cell Killing and Block Interferon-Beta Synthesis Elicited by Infection with an Oncolytic Parainfluenza Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses, and Infections
2.2. Chemical Preparation
2.3. Cell Viability and Caspase Assays
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Fluorescence Microscopy and IRF-3 immunostaining
2.6. Human IFN-β ELISA
2.7. Reverse Transcription and Real Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
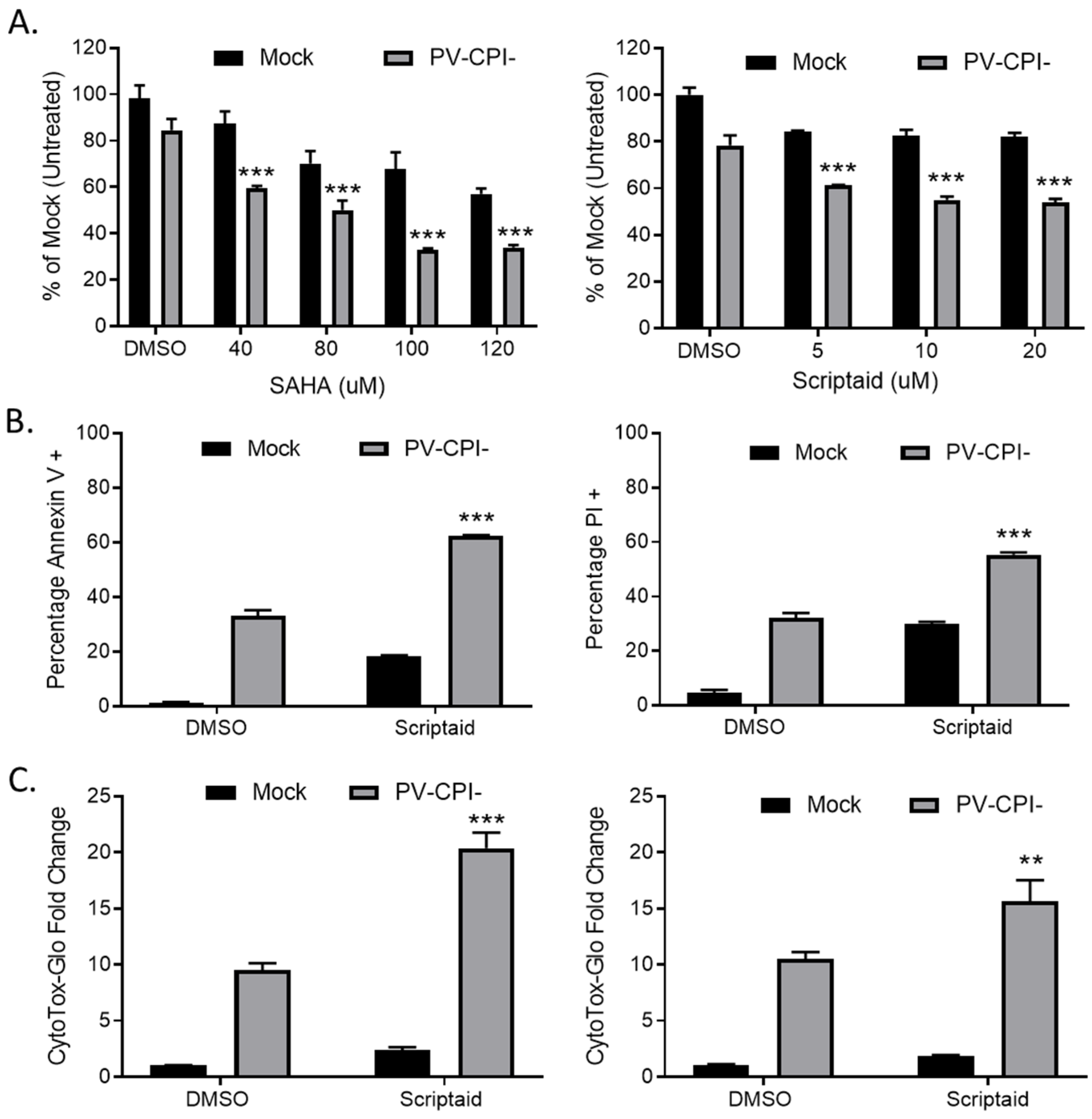
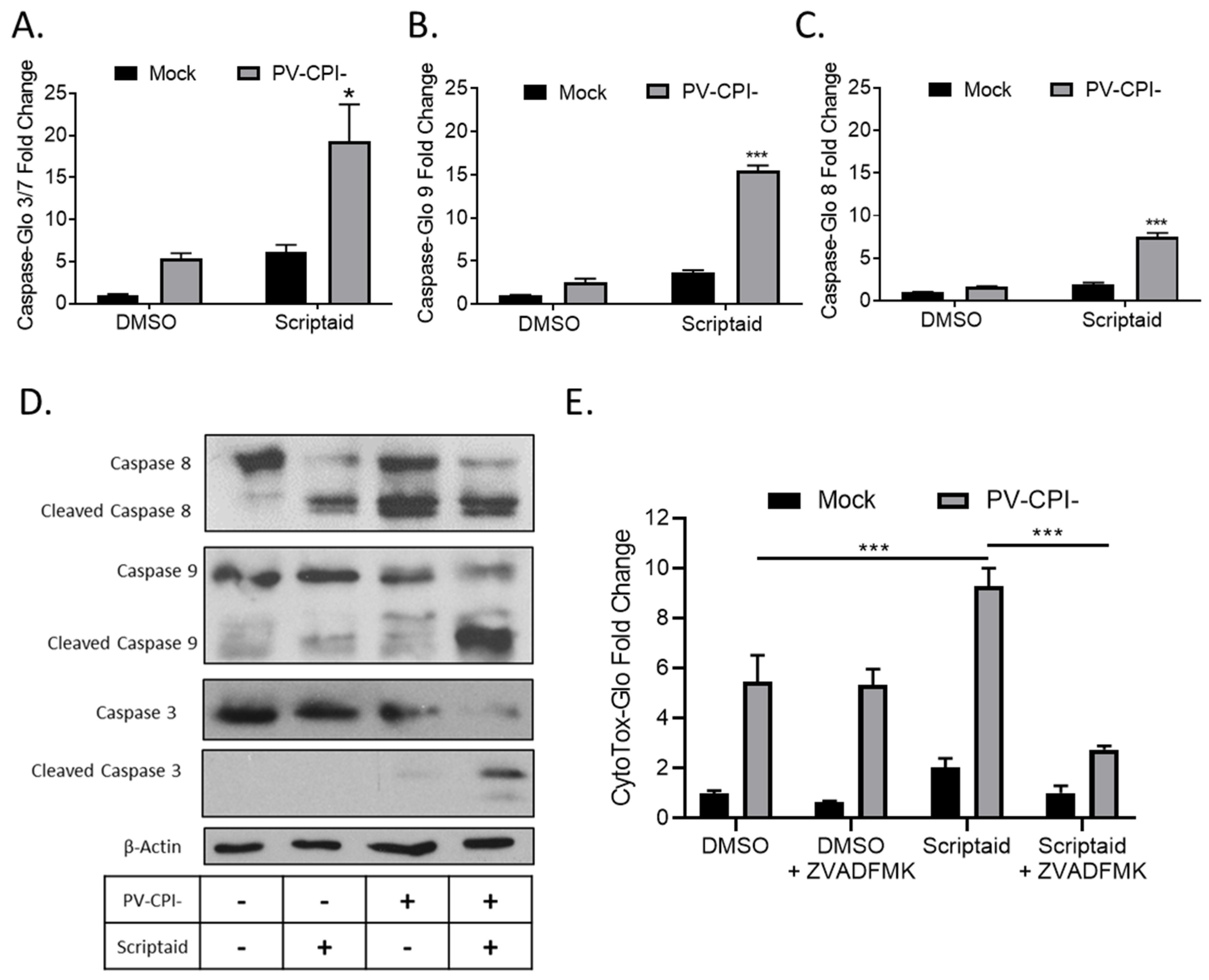
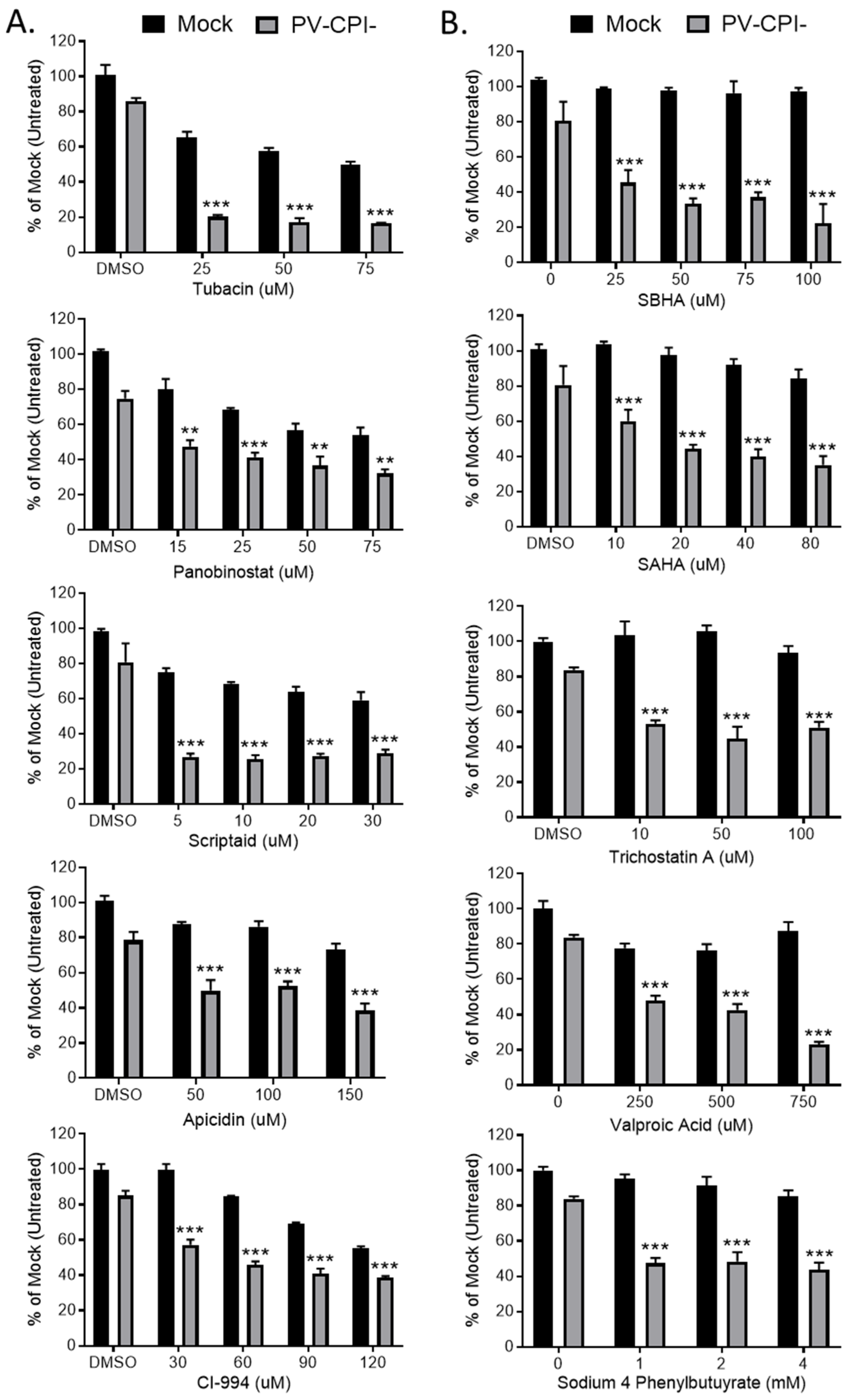
3.1. HDAC Inhibitors Enhance Killing of Lung Cancer Cells by the P/V-CPI- Mutant through Increases in Caspase Activity
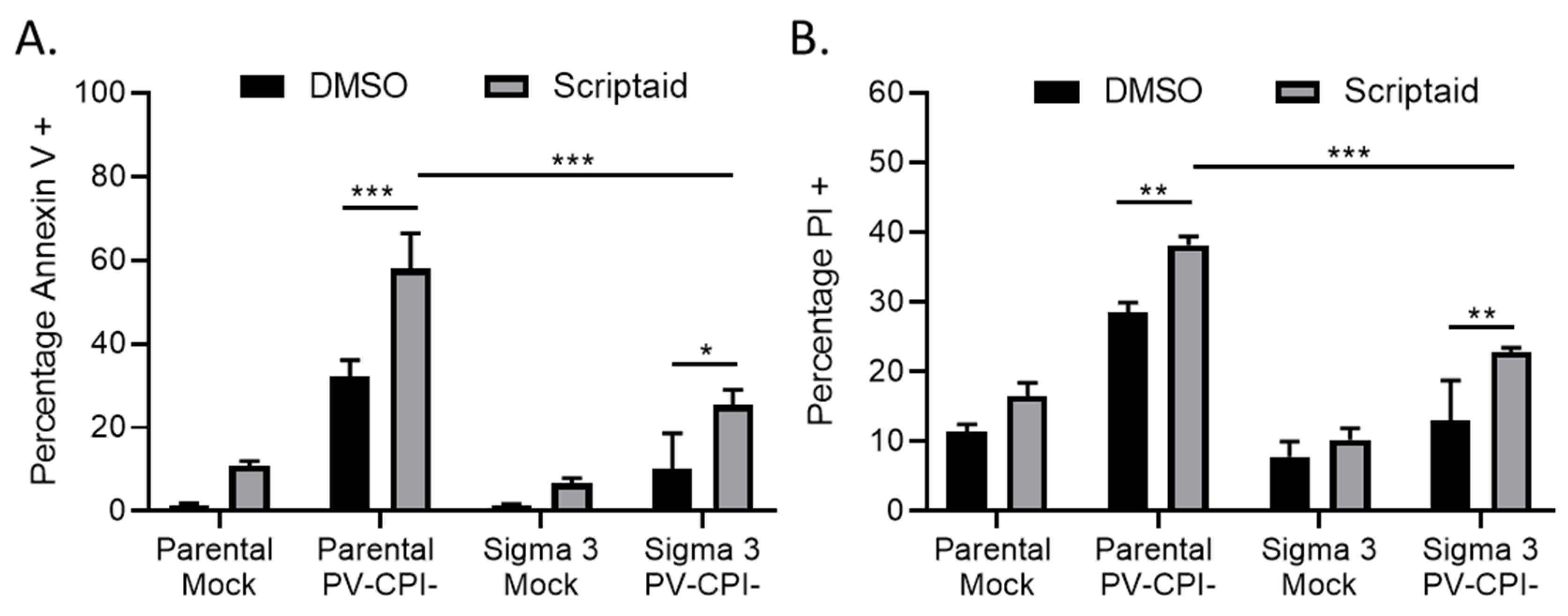
3.2. Double Stranded RNA Contributes to scriptaid-Mediated Enhancement of Cell Killing by the P/V-CPI- Virus
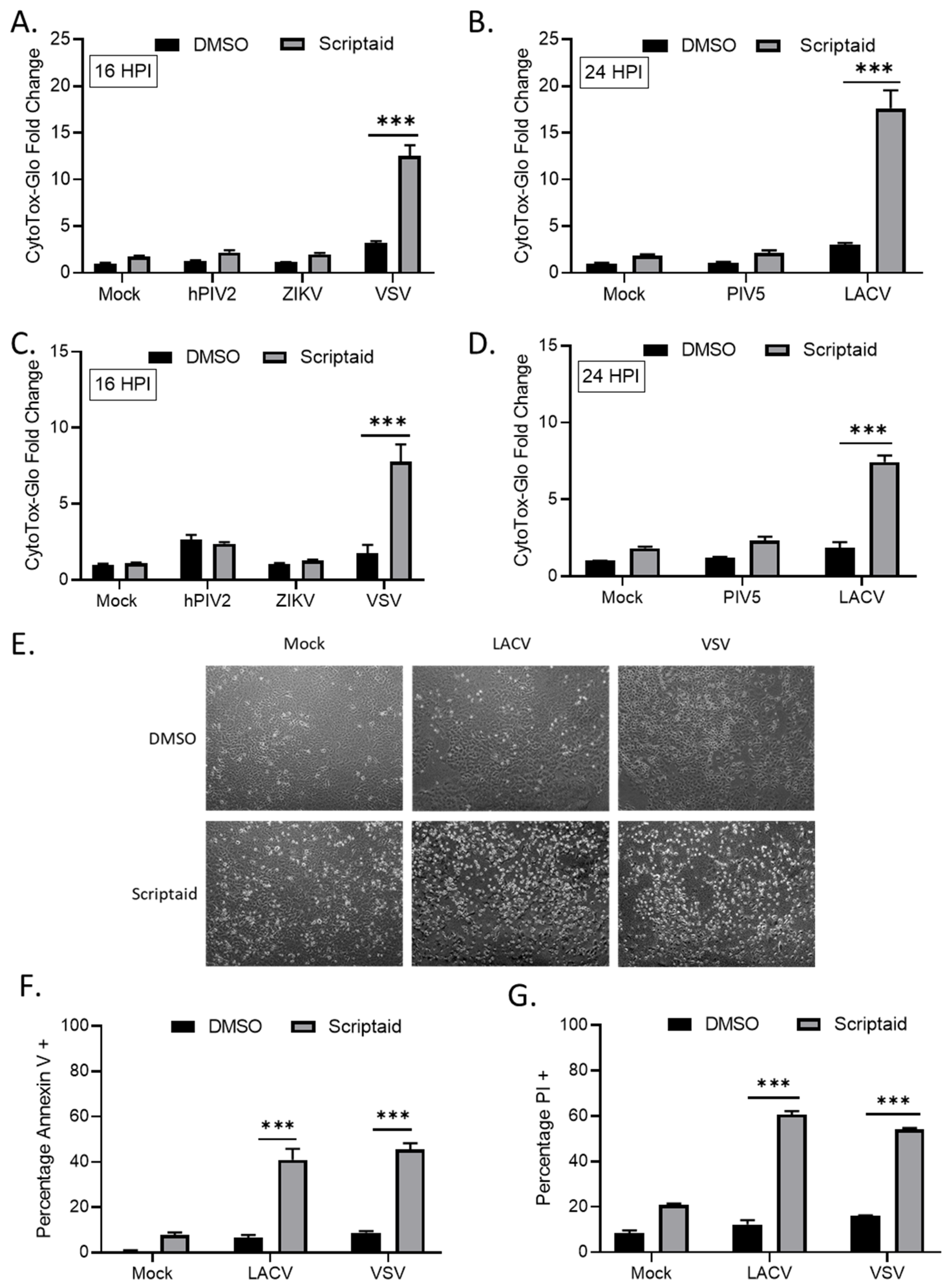
3.3. Scriptaid Pretreatment Enhances Killing of Lung Cancer Cells Infected with LACV and VSV
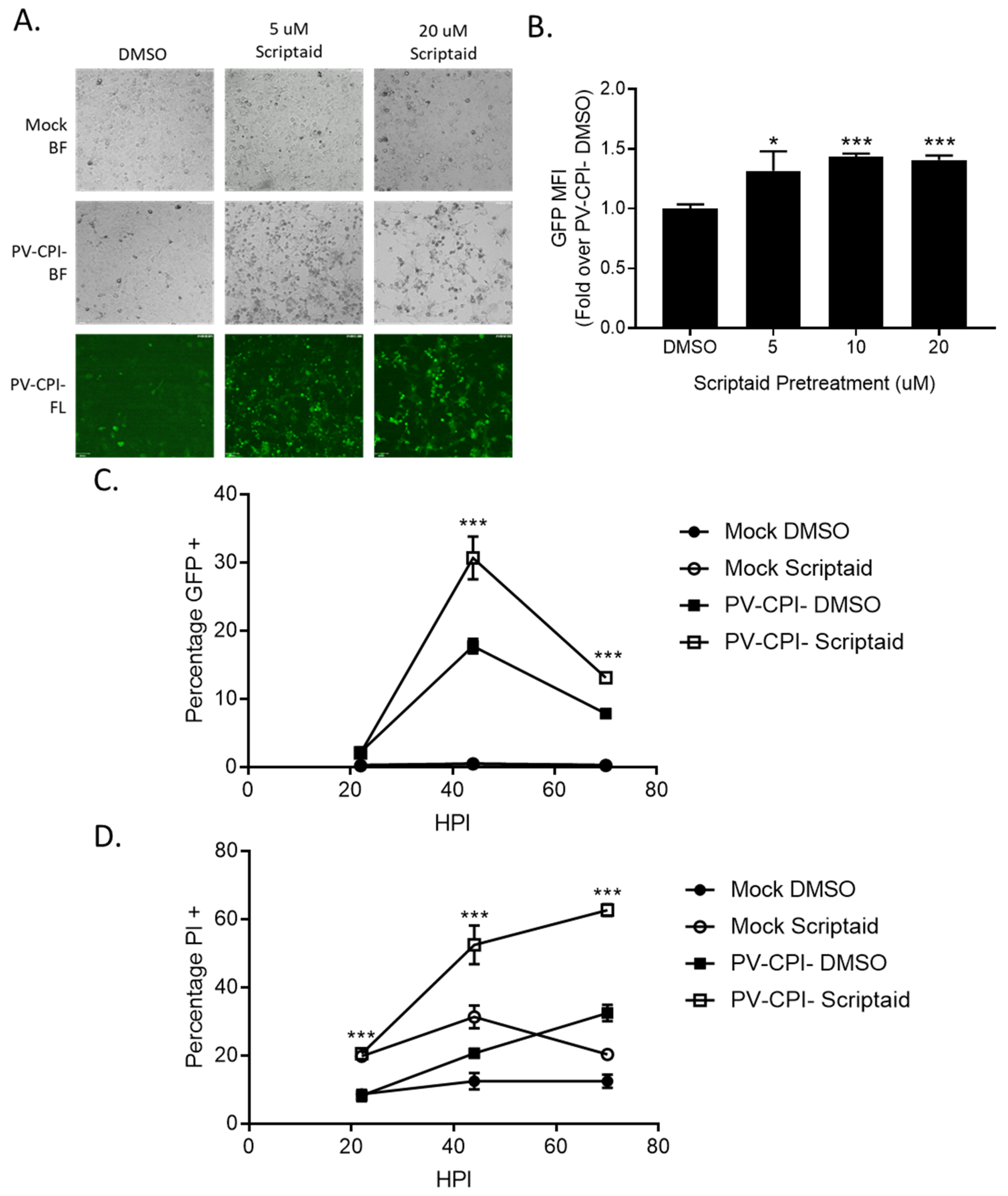
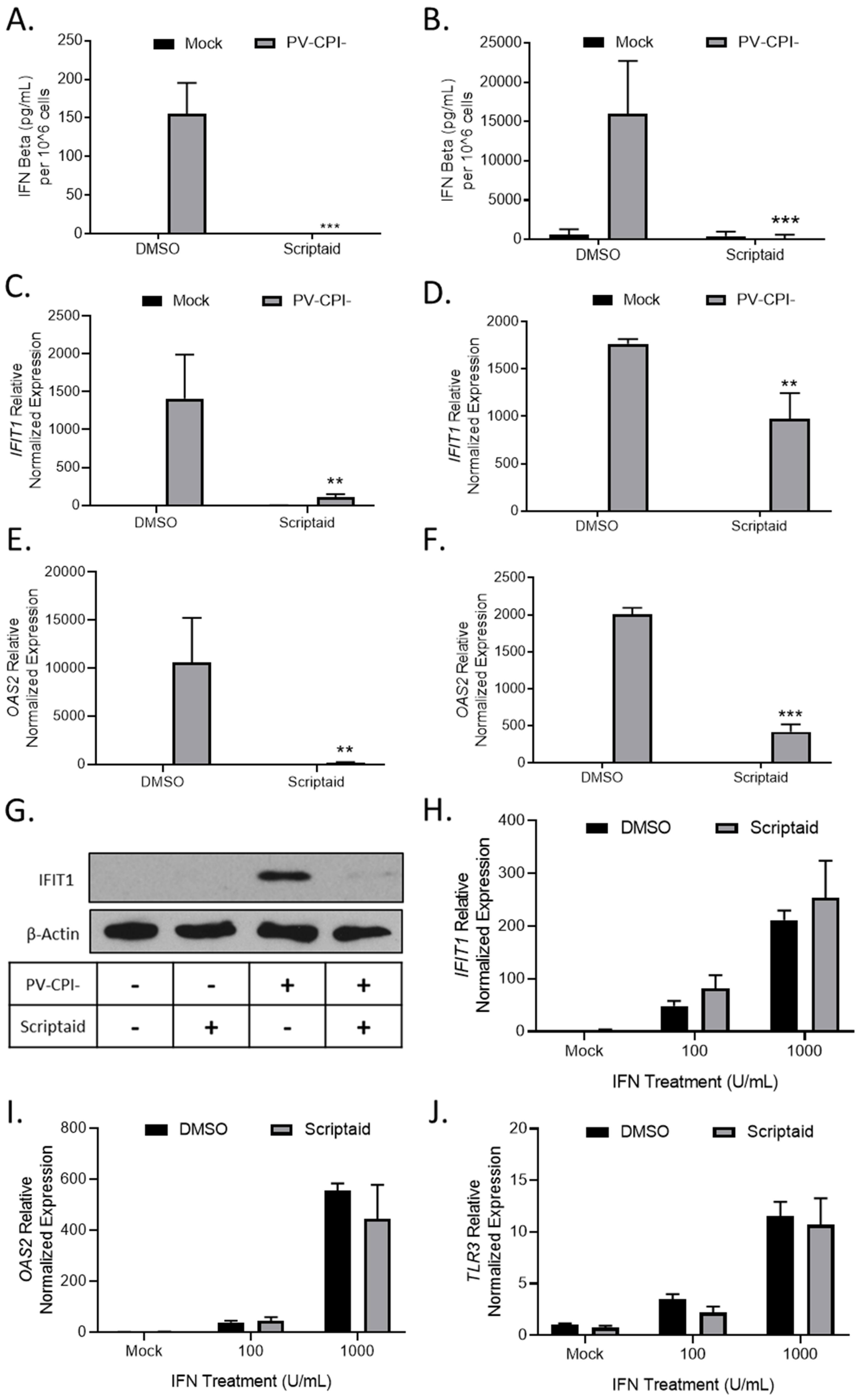
3.4. HDAC Inhibitor Pretreatment Downregulates IFN-β Production and Enhances Spread of the P/V-CPI- Mutant
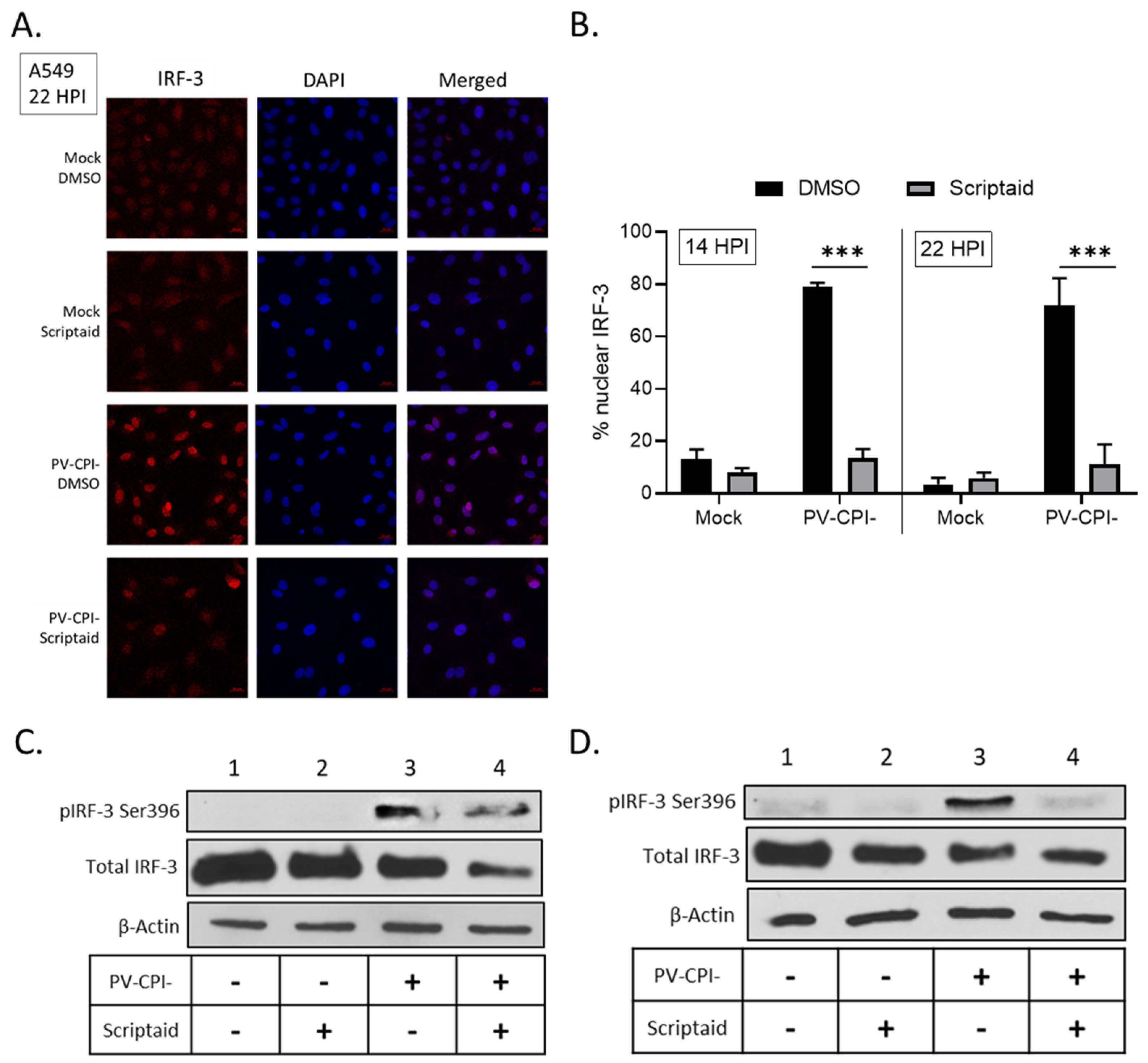
3.5. Scriptaid Treatment Reduces P/V-CPI-Induced Nuclear Localization of IRF-3
3.6. Post-Infection Treatment of P/V-CPI-Infected Cells with a Panel of HDAC Inhibitors Reveals Two Cell Killing Profiles
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, H.L.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Zloza, A. Oncolytic viruses: A new class of immunotherapy drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 642–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, H.; Ino, Y.; Todo, T. Oncolytic virus therapy: A new era of cancer treatment at dawn. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J.; Peng, K.W.; Bell, J.C. Oncolytic virotherapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elankumaran, S.; Rockemann, D.; Samal, S.K. Newcastle disease virus exerts oncolysis by both intrinsic and extrinsic caspase-dependent pathways of cell death. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7522–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoh, H.; Inoue, M.; Washizawa, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Fujikawa, S.; Tokusumi, Y.; Iida, A.; Nagai, Y.; Hasegawa, M. Generation of a recombinant Sendai virus that is selectively activated and lyses human tumor cells expressing matrix metalloproteinases. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lorence, R.M.; Reichard, K.W.; Katubig, B.B.; Reyes, H.M.; Phuangsab, A.; Mitchell, B.R.; Cascino, C.J.; Walter, R.J.; Peeples, M.E. Complete regression of human neuroblastoma xenografts in athymic mice after local Newcastle disease virus therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1994, 86, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.; Greiner, S.; Harvey, M.; Soeffker, D.; Frenzke, M.; Abraham, K.; Shaw, A.; Rozenblatt, S.; Federspiel, M.J.; Russell, S.J.; et al. Oncolytic activities of approved mumps and measles vaccines for therapy of ovarian cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.W.; Donovan, K.A.; Schneider, U.; Cattaneo, R.; Lust, J.A.; Russell, S.J. Oncolytic measles viruses displaying a single-chain antibody against CD38, a myeloma cell marker. Blood 2003, 101, 2557–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Puckett, S.; Antinozzi, P.A.; Cramer, S.D.; Lyles, D.S. Changes in Susceptibility to Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus during Progression of Prostate Cancer. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5250–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Matveeva, O.V.; Guo, Z.S.; Senin, V.M.; Senina, A.V.; Shabalina, S.A.; Chumakov, P.M. Oncolysis by paramyxoviruses: Preclinical and clinical studies. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choppin, P.W. MULTIPLICATION OF A MYXOVIRUS (SV5) WITH MINIMAL CYTOPATHIC EFFECTS AND WITHOUT INTERFERENCE. Virology 1964, 23, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Lin, G.Y.; Durbin, J.E.; Durbin, R.K.; Lamb, R.A. The SH Integral Membrane Protein of the Paramyxovirus Simian Virus 5 Is Required To Block Apoptosis in MDBK Cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4068–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, G.D.; Young, V.A.; Koumenis, C.; Wansley, E.K.; Layer, J.L.; Cooke, K.M. Controlled Cell Killing by a Recombinant Nonsegmented Negative-Strand RNA Virus. Virology 2002, 293, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, M.; Rothermel, T.A.; Shuman, L.; Aligo, J.A.; Xu, S.; Lin, Y.; Lamb, R.A.; He, B. Conserved cysteine-rich domain of paramyxovirus simian virus 5 V protein plays an important role in blocking apoptosis. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5068–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.J.; Wansley, E.K.; Young, V.A.; Alexander-Miller, M.A.; Parks, G.D. Exchange of P/V genes between two non-cytopathic simian virus 5 variants results in a recombinant virus that kills cells through death pathways that are sensitive to caspase inhibitors. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3643–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wansley, E.K.; Parks, G.D. Naturally occurring substitutions in the P/V gene convert the noncytopathic paramyxovirus simian virus 5 into a virus that induces alpha/beta interferon synthesis and cell death. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10109–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, R.A.; Parks, G.D. Paramyxoviridae: The viruses and their replication. In Fields virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1449–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn, S.; Didcock, L.; Randall, R.E. Interferons: Cell signaling, immune modulation, antiviral response and virus countermeasures. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2341–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didcock, L.; Young, D.F.; Goodbourn, S.; Randall, R.E. The V protein of simian virus 5 inhibits interferon signalling by targeting STAT1 for proteasome-mediated degradation. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9928–9933. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, K.; Stock, N.; Ross, C.; Andrejeva, J.; Hilton, L.; Skinner, M.; Randall, R.; Goodbourn, S. mda-5, but not RIG-I, is a common target for paramyxovirus V proteins. Virology 2007, 359, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wansley, E.K.; Dillon, P.J.; Gainey, M.D.; Tam, J.; Cramer, S.D.; Parks, G.D. Growth sensitivity of a recombinant simian virus 5 P/V mutant to type I interferon differs between tumor cell lines and normal primary cells. Virology 2005, 335, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, V.A.; Dillon, P.J.; Parks, G.D. Variants of the paramyxovirus Simian virus 5 with accelerated or delayed viral gene expression activate proinflammatory cytokine synthesis. Virology 2006, 350, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainey, M.D.; Manuse, M.J.; Parks, G.D. A hyperfusogenic F protein enhances the oncolytic potency of a paramyxovirus simian virus 5 P/V mutant without compromising sensitivity to type I interferon. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9369–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainey, M.D.; Dillon, P.J.; Clark, K.M.; Manuse, M.J.; Parks, G.D. Paramyxovirus-induced shutoff of host and viral protein synthesis: Role of the P and V proteins in limiting PKR activation. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wansley, E.K.; Grayson, J.M.; Parks, G.D. Apoptosis induction and interferon signaling but not IFN-beta promoter induction by an SV5 P/V mutant are rescued by coinfection with wild-type SV5. Virology 2003, 316, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.R.; Parks, G.D. Parainfluenza Virus Infection Sensitizes Cancer Cells to DNA-Damaging Agents: Implications for Oncolytic Virus Therapy. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamiya, Y.; Ono, T.; Saito, H.; Takahashi, N.; Ito, M.; Mitsui, M.; Motoyama, S.; Ogawa, J. Expression of histone deacetylase 1 correlates with a poor prognosis in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Chiang, C.P.; Hung, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Deng, Y.T.; Kuo, M.Y. Histone deacetylase 2 expression predicts poorer prognosis in oral cancer patients. Oral. Oncol. 2009, 45, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination Therapy With Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi) for the Treatment of Cancer: Achieving the Full Therapeutic Potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuse, M.J.; Parks, G.D. Role for the paramyxovirus genomic promoter in limiting host cell antiviral responses and cell killing. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9057–9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Antar, A.A.; Boehme, K.W.; Danthi, P.; Eby, E.A.; Guglielmi, K.M.; Holm, G.H.; Johnson, E.M.; Maginnis, M.S.; Naik, S.; et al. A plasmid-based reverse genetics system for animal double-stranded RNA viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Paterson, R.G.; Ward, C.D.; Lamb, R.A. Recovery of infectious SV5 from cloned DNA and expression of a foreign gene. Virology 1997, 237, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, P.J.; Parks, G.D. Role for the phosphoprotein P subunit of the paramyxovirus polymerase in limiting induction of host cell antiviral responses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11116–11127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, A.A.; Sobek, K.M.; Cummings, J.L.; Green, W.R.; Bacich, D.J.; O’Keefe, D.S. Activation of innate anti-viral immune response genes in symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Reyes, S.; Marin, L.; Gonzalez, L.; Gonzalez, L.O.; del Casar, J.M.; Lamelas, M.L.; Gonzalez-Quintana, J.M.; Vizoso, F.J. Study of TLR3, TLR4 and TLR9 in breast carcinomas and their association with metastasis. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Shatkin, A.J. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) is regulated by reovirus structural proteins. Virology 1997, 234, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ai, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Yao, C. Poly I:C-induced tumor cell apoptosis mediated by pattern-recognition receptors. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2012, 27, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiscott, J.; Pitha, P.; Genin, P.; Nguyen, H.; Heylbroeck, C.; Mamane, Y.; Algarte, M.; Lin, R. Triggering the interferon response: The role of IRF-3 transcription factor. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robey, R.W.; Chakraborty, A.R.; Basseville, A.; Luchenko, V.; Bahr, J.; Zhan, Z.; Bates, S.E. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Emerging mechanisms of resistance. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, A.; Patel, A.; Kasai, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kurozumi, K.; Antonio Chiocca, E.; Saeki, Y. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Augment Antitumor Efficacy of Herpes-based Oncolytic Viruses. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Negishi, H.; Idogawa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Mita, H.; Toyota, M.; Shinomura, Y.; Imai, K.; Tokino, T. Histone deacetylase inhibitor FK228 enhances adenovirus-mediated p53 family gene therapy in cancer models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, M.E.; Aguila, A.; Steadman, K.; Martinez, A.; Steinberg, S.M.; Alley, M.C.; Waud, W.R.; Bates, S.E.; Fojo, T. The histone deacetylase inhibitor FK228 given prior to adenovirus infection can boost infection in melanoma xenograft model systems. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacTavish, H.; Diallo, J.S.; Huang, B.; Stanford, M.; Le Boeuf, F.; De Silva, N.; Cox, J.; Simmons, J.G.; Guimond, T.; Falls, T.; et al. Enhancement of vaccinia virus based oncolysis with histone deacetylase inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoti, N.; Chowdhury, W.; Hsieh, J.T.; Sachs, M.D.; Lupold, S.E.; Rodriguez, R. Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is an antagonist for oncolytic adenoviral gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2006, 14, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, H.; Nguyen, T.; Chiocca, E.A. Combining HDAC inhibitors with oncolytic virotherapy for cancer therapy. Oncolytic Virother. 2015, 4, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchini, A.; Scott, E.M.; Rommelaere, J. Overcoming Barriers in Oncolytic Virotherapy with HDAC Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Viruses 2016, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.L.-A.; Wilson, M.G.; Hiscott, J. Oncolytic viruses and histone deacetylase inhibitors—A multi-pronged strategy to target tumor cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulak, L.; Beljanski, V.; Chiang, C.; Dutta, S.M.; Van Grevenynghe, J.; Belgnaoui, S.M.; Nguyên, T.L.-A.; Di Lenardo, T.; Semmes, O.J.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate vesicular stomatitis virus oncolysis in prostate cancer cells by modulating NF-κB-dependent autophagy. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2927–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellerhoff, T.P.; Berchtold, S.; Venturelli, S.; Burkard, M.; Smirnow, I.; Wulff, T.; Lauer, U.M. Novel epi-virotherapeutic treatment of pancreatic cancer combining the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor resminostat with oncolytic measles vaccine virus. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusinzon, I.; Horvath, C.M. Interferon-stimulated transcription and innate antiviral immunity require deacetylase activity and histone deacetylase 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14742–14747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Dai, Y.; Pei, X.Y.; Grant, S. Bim upregulation by histone deacetylase inhibitors mediates interactions with the Bcl-2 antagonist ABT-737: Evidence for distinct roles for Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 6149–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xargay-Torrent, S.; Lopez-Guerra, M.; Saborit-Villarroya, I.; Rosich, L.; Campo, E.; Roue, G.; Colomer, D. Vorinostat-induced apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma is mediated by acetylation of proapoptotic BH3-only gene promoters. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3956–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Riley, J.; Gant, T.W.; Dyer, M.J.; Cohen, G.M. Apoptosis induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors in leukemic cells is mediated by Bim and Noxa. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, T.; Murakami, K.; Takimoto, R.; Takahashi, M.; Takada, K.; Murakami, T.; Minami, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Takayama, T.; Kato, J.; et al. Induction of PIG3 and NOXA through acetylation of p53 at 320 and 373 lysine residues as a mechanism for apoptotic cell death by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8948–8954. [Google Scholar]
- Aron, J.L.; Parthun, M.R.; Marcucci, G.; Kitada, S.; Mone, A.P.; Davis, M.E.; Shen, T.; Murphy, T.; Wickham, J.; Kanakry, C.; et al. Depsipeptide (FR901228) induces histone acetylation and inhibition of histone deacetylase in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells concurrent with activation of caspase 8-mediated apoptosis and down-regulation of c-FLIP protein. Blood 2003, 102, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, R.R.; Almenara, J.A.; Kolla, S.S.; Maggio, S.C.; Coe, S.; Gimenez, M.S.; Dent, P.; Grant, S. Mechanism and functional role of XIAP and Mcl-1 down-regulation in flavopiridol/vorinostat antileukemic interactions. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, T.; Okamoto, T.; Uchida, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Iida, S.; Kayukawa, S.; Suzuki, T.; Oshizawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Miyata, N.; et al. Proteome analyses of the growth inhibitory effects of NCH-51, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, on lymphoid malignant cells. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, R.D.; Swendeman, S.L.; Coffey, D.C.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M.; La Quaglia, M.P. Hybrid polar histone deacetylase inhibitor induces apoptosis and CD95/CD95 ligand expression in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 1999, 59, 4392–4399. [Google Scholar]
- Insinga, A.; Monestiroli, S.; Ronzoni, S.; Gelmetti, V.; Marchesi, F.; Viale, A.; Altucci, L.; Nervi, C.; Minucci, S.; Pelicci, P.G. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor pathway. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebbioso, A.; Clarke, N.; Voltz, E.; Germain, E.; Ambrosino, C.; Bontempo, P.; Alvarez, R.; Schiavone, E.M.; Ferrara, F.; Bresciani, F.; et al. Tumor-selective action of HDAC inhibitors involves TRAIL induction in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, S.; Yoshida, T.; Horinaka, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Wakada, M.; Sakai, T. Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate death receptor 5/TRAIL-R2 and sensitize apoptosis induced by TRAIL/APO2-L in human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A.; Guerra, S.; Gil, J.; Jimenez, V.; Esteban, M. Anti-apoptotic and oncogenic properties of the dsRNA-binding protein of vaccinia virus, E3L. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8379–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazar, J.; Li, Y.; Rosado, A.; Phelan, P.; Kedarinath, K.; Parks, G.D.; Alexander, K.A.; Westmoreland, T.J. Zika virus as an oncolytic treatment of human neuroblastoma cells requires CD24. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemington, E.K. Herpesvirus lytic replication and the cell cycle: Arresting new developments. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4475–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fox, C.R.; Parks, G.D. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Enhance Cell Killing and Block Interferon-Beta Synthesis Elicited by Infection with an Oncolytic Parainfluenza Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050431
Fox CR, Parks GD. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Enhance Cell Killing and Block Interferon-Beta Synthesis Elicited by Infection with an Oncolytic Parainfluenza Virus. Viruses. 2019; 11(5):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050431
Chicago/Turabian StyleFox, Candace R., and Griffith D. Parks. 2019. "Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Enhance Cell Killing and Block Interferon-Beta Synthesis Elicited by Infection with an Oncolytic Parainfluenza Virus" Viruses 11, no. 5: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050431
APA StyleFox, C. R., & Parks, G. D. (2019). Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Enhance Cell Killing and Block Interferon-Beta Synthesis Elicited by Infection with an Oncolytic Parainfluenza Virus. Viruses, 11(5), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050431




