NF-κB-Dependent Production of ROS and Restriction of HSV-1 Infection in U937 Monocytic Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
2.3. Virus, Infections and Treatments
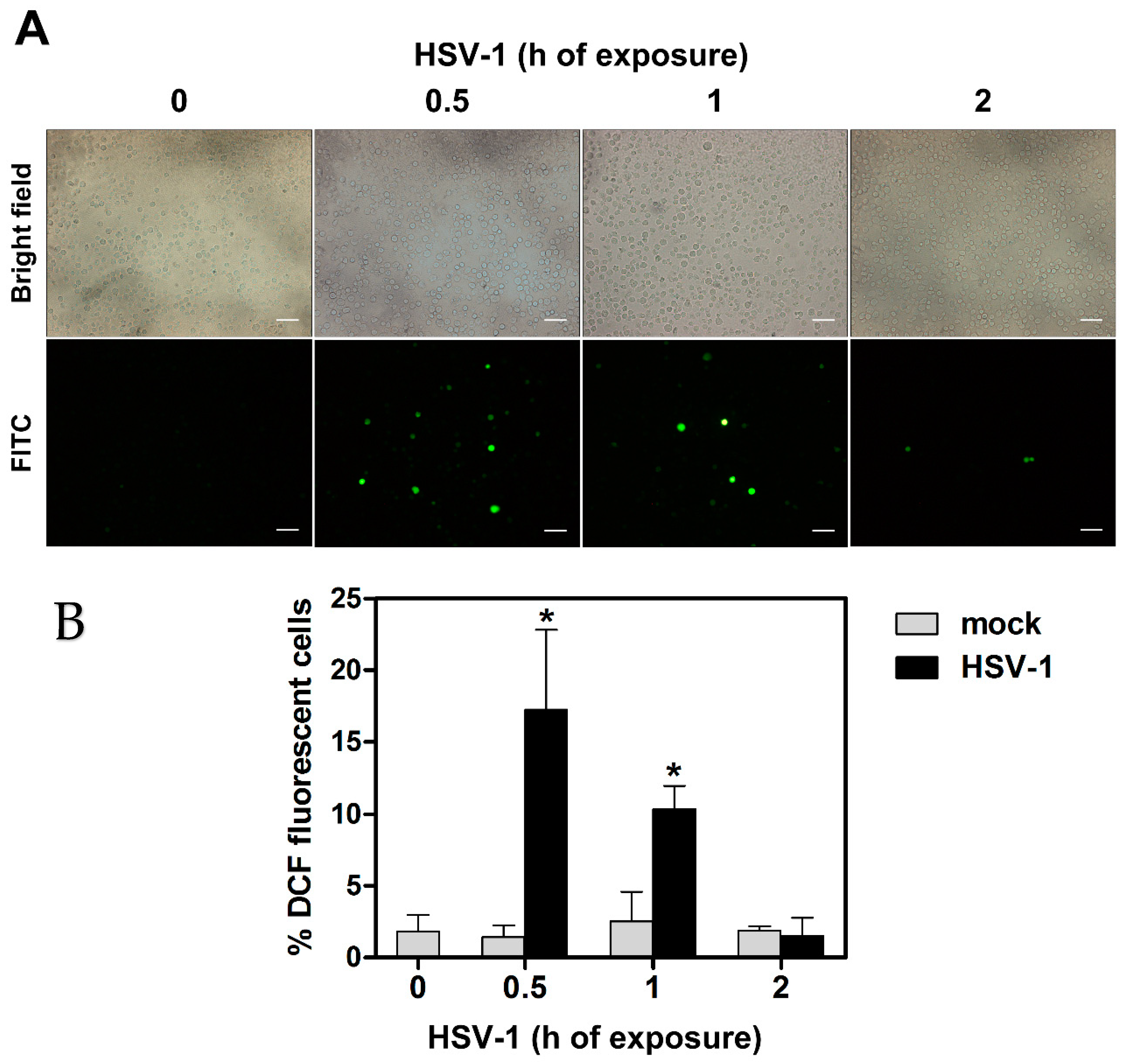
2.4. ROS Detection
2.5. Immunofluorescence Microscopy Analysis
2.6. Virus Titer (Plaque Formation) Assay
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. NF-kB Binding Assay
2.9. Isolation of Total RNA and Real-Time qPCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HSV-1 Infection Induces an Early ROS Production in Monocytic Cells
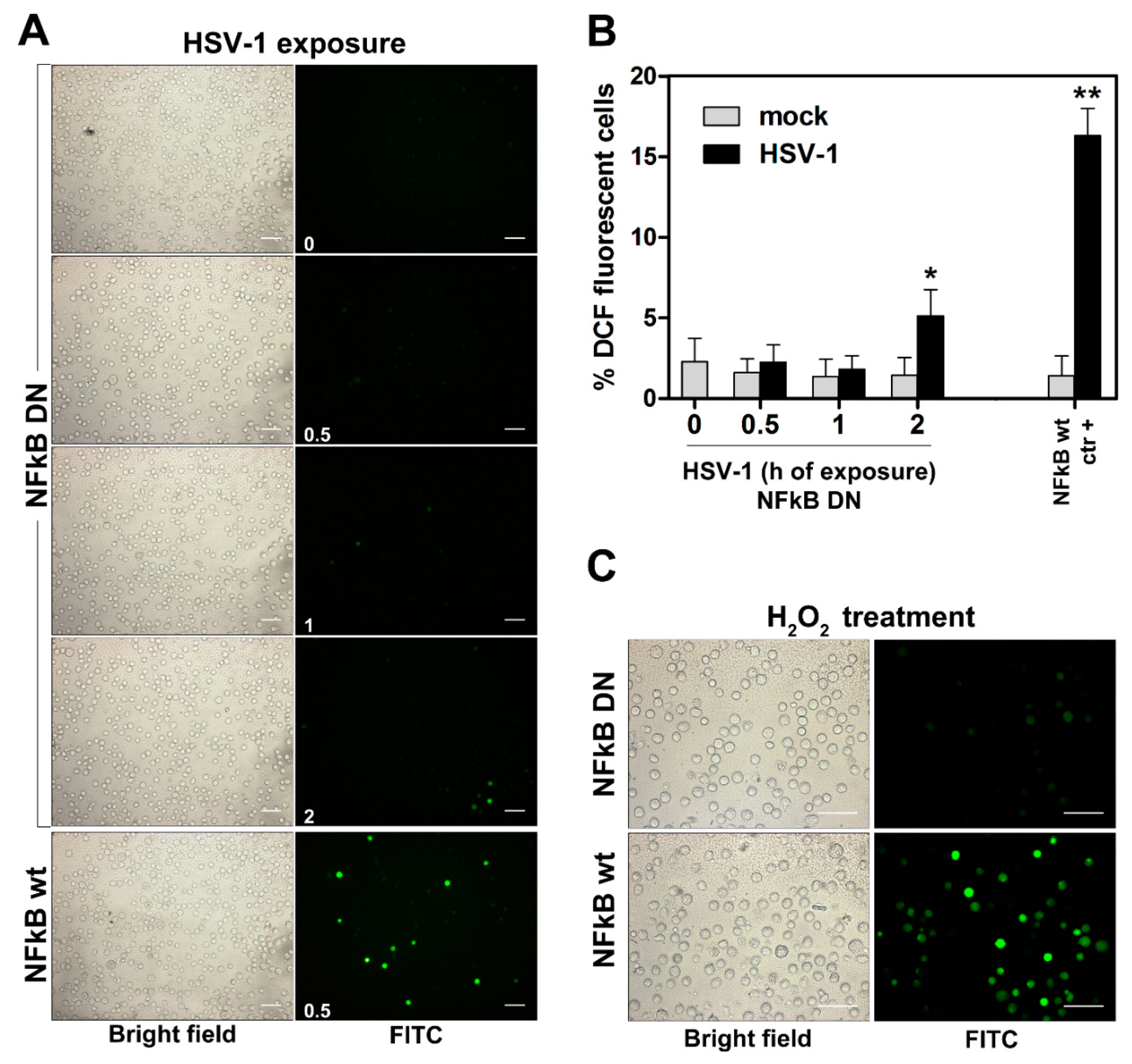
3.2. HSV-1-Induced ROS Production and Expression of Oxidant Genes Are Dependent on NF-kB Activation in Monocytic Cells
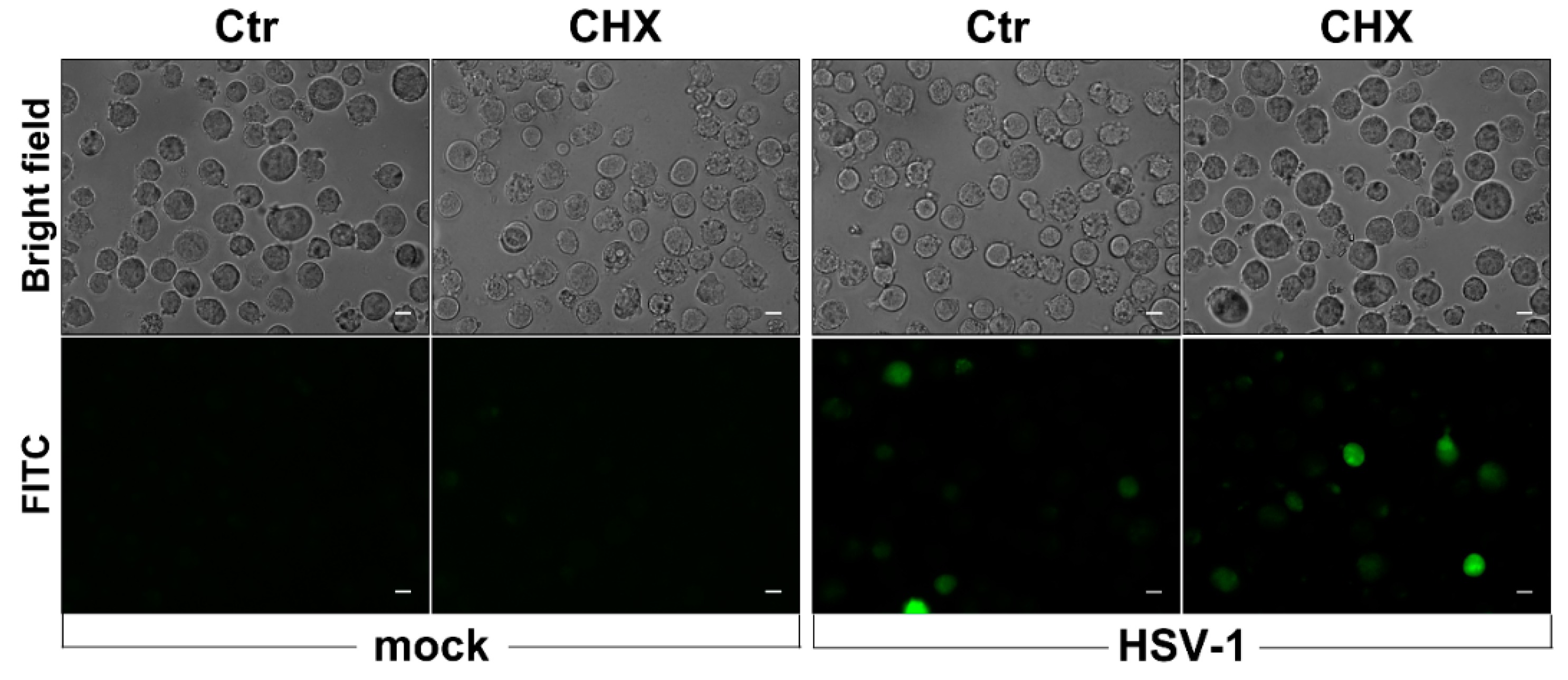
3.3. HSV-1-Induced ROS Production in Monocytic Cells Is Not Cell-Line Specific and Does Not Depend on Protein Neo-Synthesis
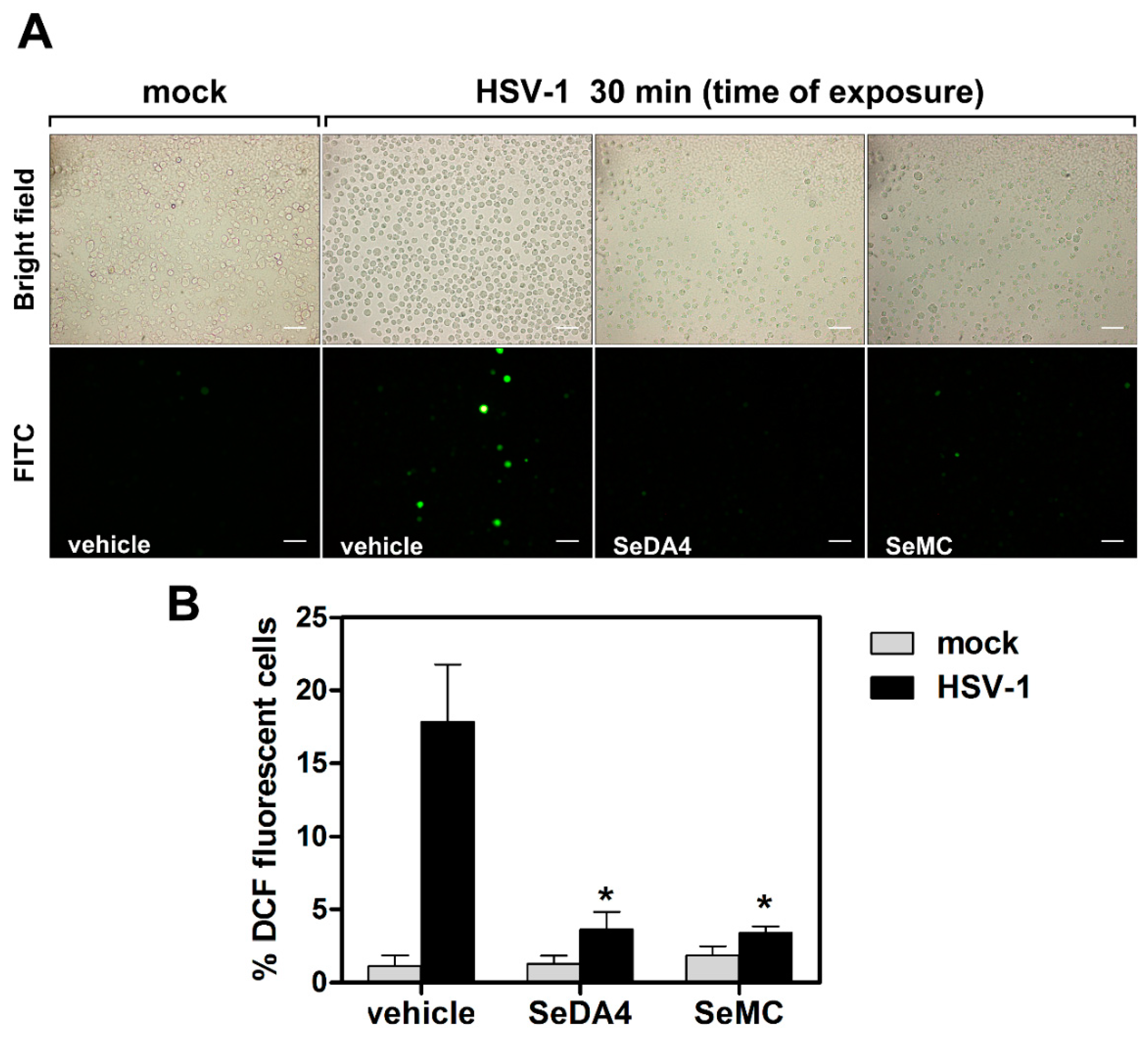
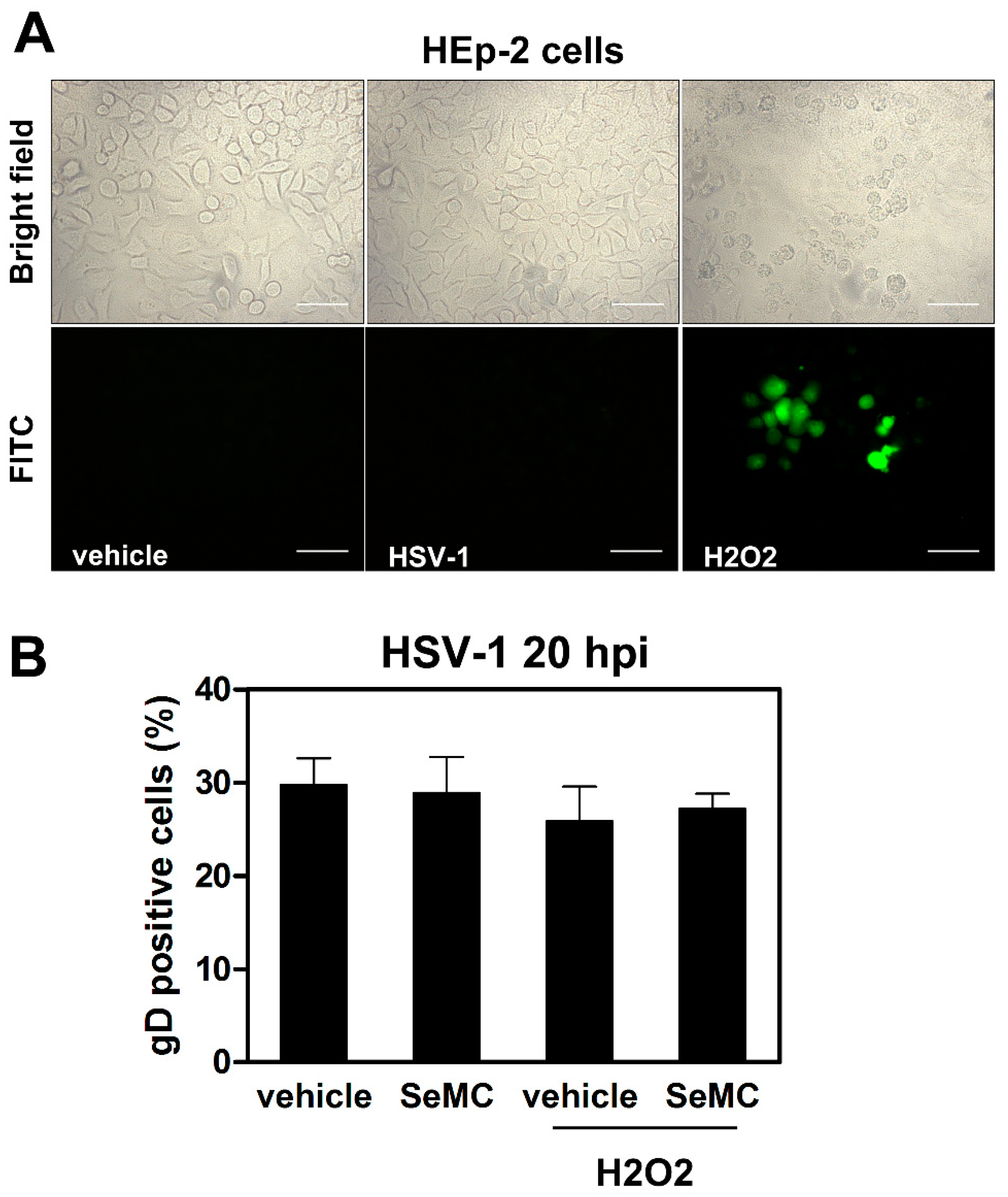
3.4. Selenium-Based Compounds Inhibit ROS Production in Monocytic Cells Infected by HSV-1
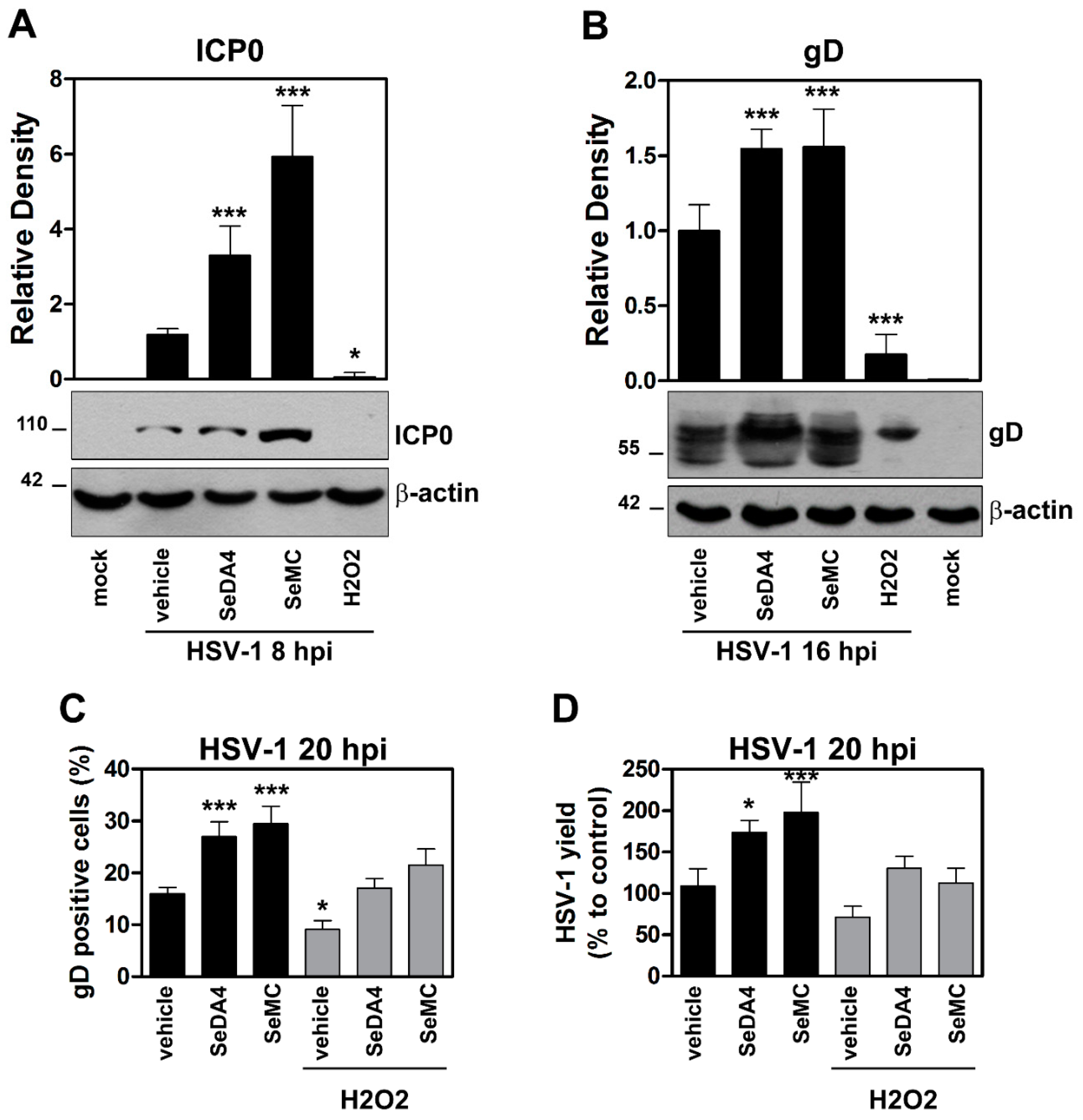
3.5. Inhibition of ROS Production Promotes Viral Replication in HSV-1 Infected Monocytic Cells in a NF-κB-Dependent Manner
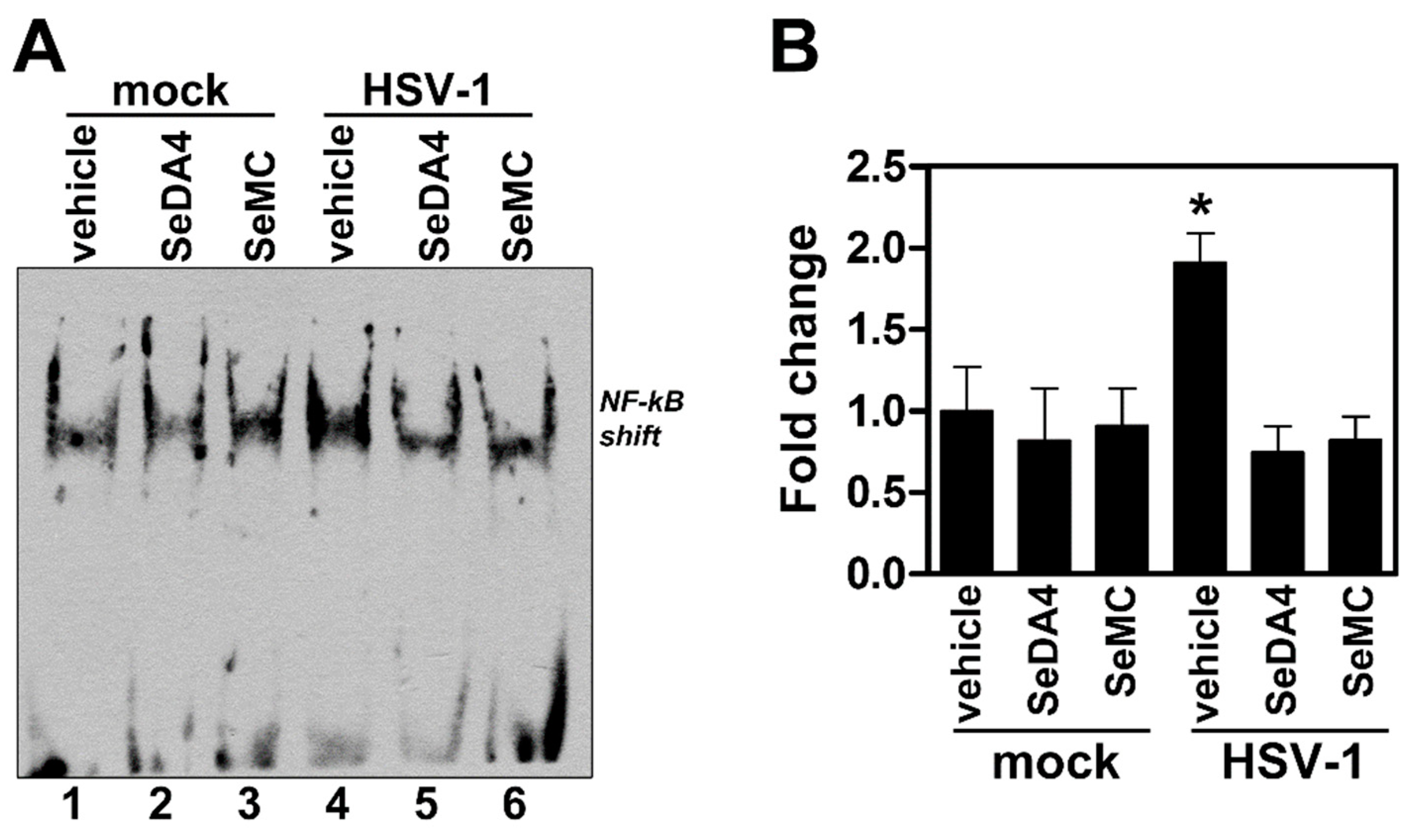
3.6. Pre-Treatment with Selenium-Based Antioxidants Inhibits NF-κB Activation in Monocytic Cells Infected by HSV-1
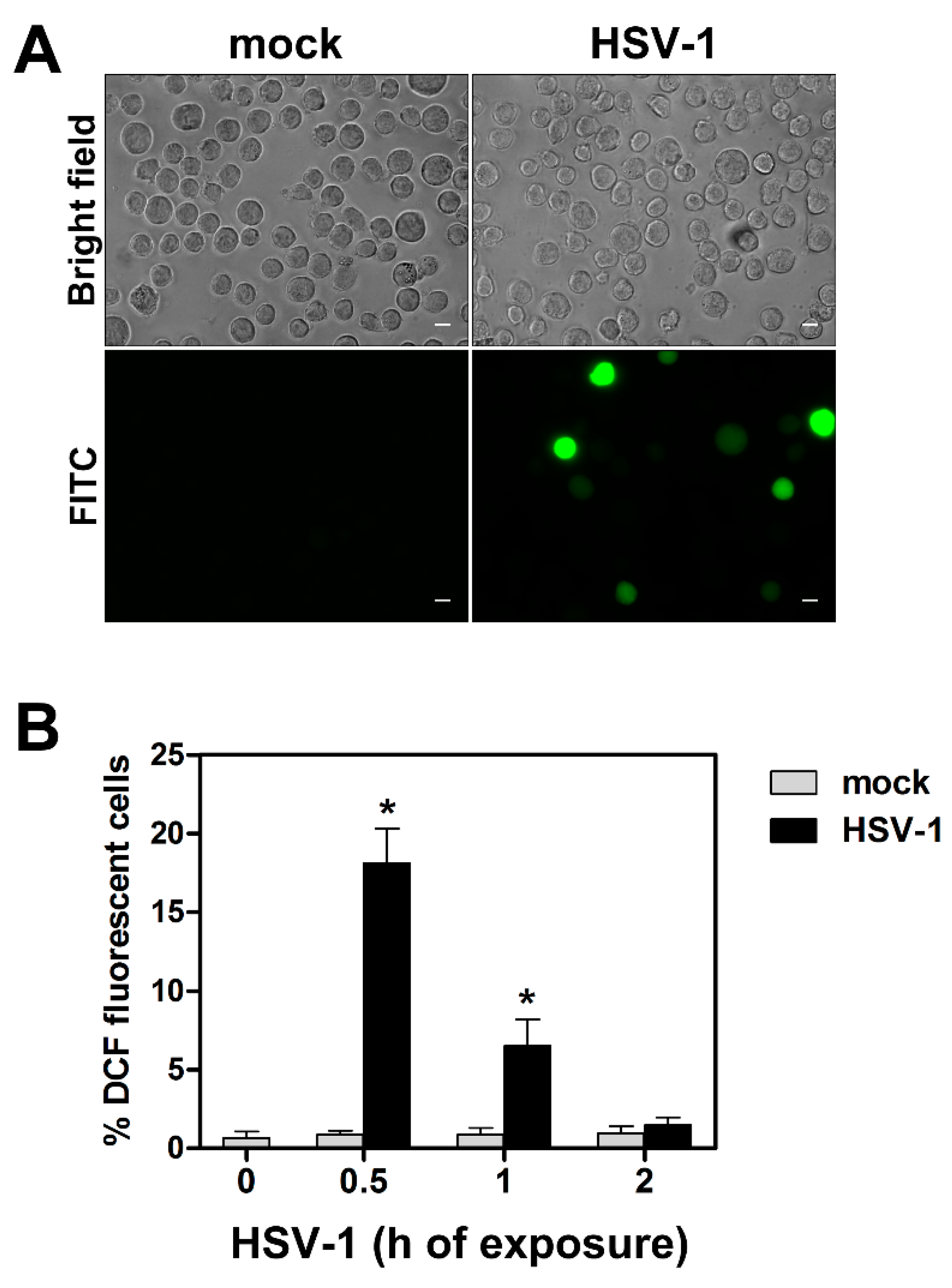
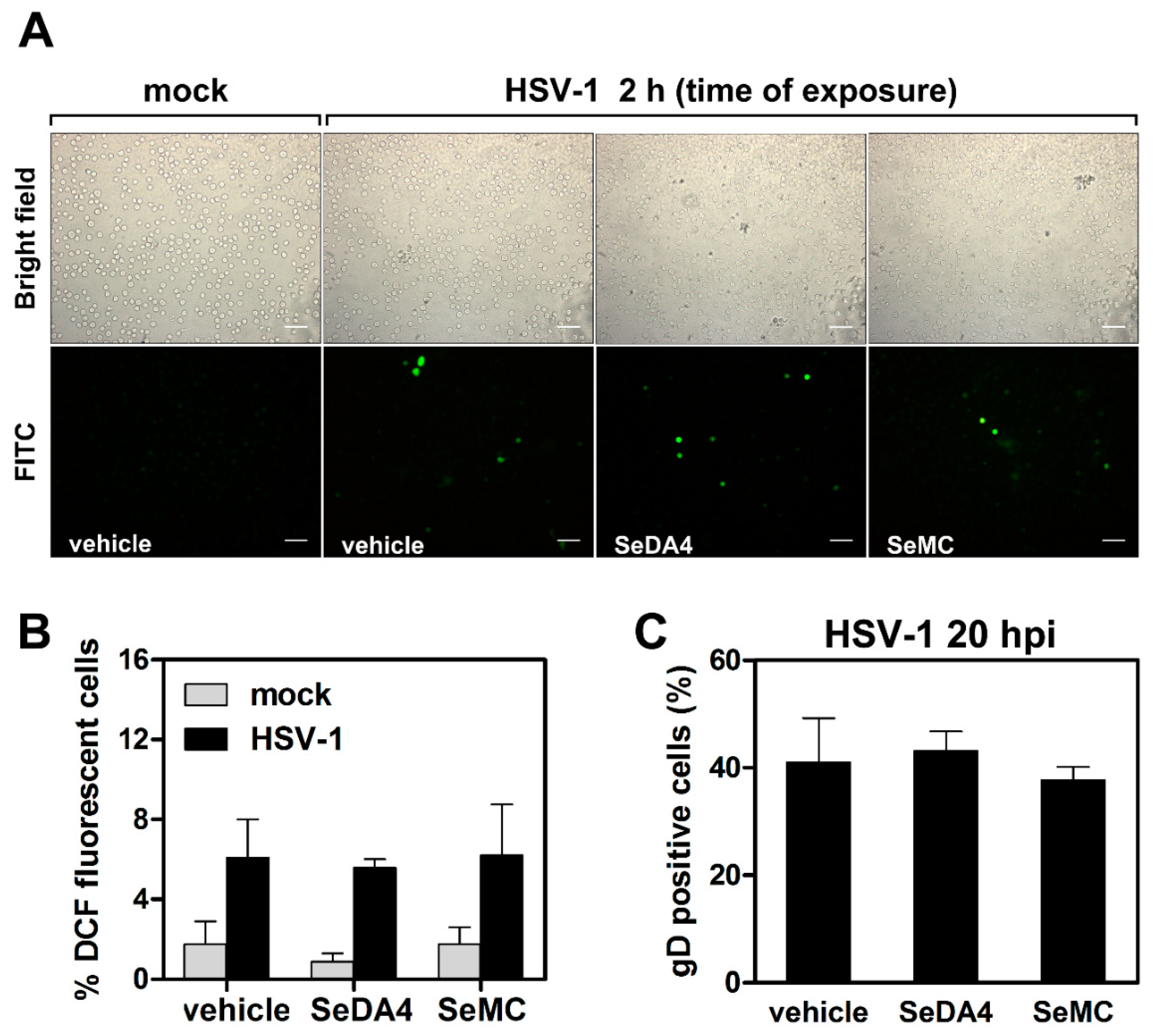
3.7. HSV-1-Induced ROS Production and Related Effects Are Monocytic Cell Type-Dependent
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wertheim, J.O.; Smith, M.D.; Smith, D.M.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Evolutionary origins of human herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizman, B.; Whitley, R.J. An inquiry into the molecular basis of HSV latency and reactivation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnann, J.W., Jr.; Whitley, R.J. Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: An Update. Curr. Infect Dis. Rep. 2017, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Vidal, S.M. Insights into the pathogenesis of herpes simplex encephalitis from mouse models. Mamm Genome 2018, 29, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amici, C.; Belardo, G.; Rossi, A.; Santoro, M.G. Activation of I kappa b kinase by herpes simplex virus type 1. A novel target for anti-herpetic therapy. J. Boil. Chem. 2001, 276, 28759–28766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amici, C.; Rossi, A.; Costanzo, A.; Ciafre, S.; Marinari, B.; Balsamo, M.; Levrero, M.; Santoro, M.G. Herpes simplex virus disrupts NF-kappaB regulation by blocking its recruitment on the IkappaBalpha promoter and directing the factor on viral genes. J. Boil. Chem. 2006, 281, 7110–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, T.; Leoni, V.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. Type I interferon and NF-kappaB activation elicited by herpes simplex virus gH/gL via alphavbeta3 integrin in epithelial and neuronal cell lines. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13911–13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goodkin, M.L.; Ting, A.T.; Blaho, J.A. NF-kappaB is required for apoptosis prevention during herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7261–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, D.; Hargett, D.; Holmes, D.; Money, E.; Bachenheimer, S.L. Efficient replication by herpes simplex virus type 1 involves activation of the IkappaB kinase-IkappaB-p65 pathway. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13582–13590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastino, A.; Sciortino, M.T.; Medici, M.A.; Perri, D.; Ammendolia, M.G.; Grelli, S.; Amici, C.; Pernice, A.; Guglielmino, S. Herpes simplex virus 2 causes apoptotic infection in monocytoid cells. Cell Death Differ. 1997, 4, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Hanson, J.; McLean, T.I.; Olgiate, J.; Hilton, M.; Miller, W.E.; Bachenheimer, S.L. Herpes simplex type 1 induction of persistent NF-kappa B nuclear translocation increases the efficiency of virus replication. Virology 1998, 247, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, M.T.; Medici, M.A.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Zaccaria, D.; Giuffre, M.; Venuti, A.; Grelli, S.; Mastino, A. Signaling pathway used by HSV-1 to induce NF-kappaB activation: Possible role of herpes virus entry receptor D. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2007, 1096, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, M.T.; Medici, M.A.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Zaccaria, D.; Giuffre-Cuculletto, M.; Venuti, A.; Grelli, S.; Bramanti, P.; Mastino, A. Involvement of gD/HVEM interaction in NF-kB-dependent inhibition of apoptosis by HSV-1 gD. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedowitz, J.C.; Blaho, J.A. Herpes simplex virus 2 modulates apoptosis and stimulates NF-kappaB nuclear translocation during infection in human epithelial HEp-2 cells. Virology 2005, 342, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fitzgerald, K.; Kurt-Jones, E.; Finberg, R.; Knipe, D.M. Herpesvirus tegument protein activates NF-kappaB signaling through the TRAF6 adaptor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11335–11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, B.K.; Imrie, R.C.; Denman, A.M. Susceptibility of human lymphocyte populations to infection by herpes simplex virus. Immunology 1977, 32, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, C.A.; Kleinerman, E.S.; Snyderman, R. Abortive and productive infections of human mononuclear phagocytes by type I herpes simplex virus. Am. J. Pathol. 1978, 91, 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Linnavuori, K.; Hovi, T. Herpes simplex virus infection in human monocyte cultures: Dose-dependent inhibition of monocyte differentiation resulting in abortive infection. J. Gen. Virol. 1981, 52, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino-Merlo, F.; Papaianni, E.; Medici, M.A.; Macchi, B.; Grelli, S.; Mosca, C.; Borner, C.; Mastino, A. HSV-1-induced activation of NF-kappaB protects U937 monocytic cells against both virus replication and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2354. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Bazhin, A.V.; Werner, J.; Karakhanova, S. Reactive oxygen species in the immune system. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 32, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, A.; Saegusa, K.; Noguchi, T.; Sadamitsu, C.; Nishitoh, H.; Nagai, S.; Koyasu, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Takeda, K.; Ichijo, H. ROS-dependent activation of the TRAF6-ASK1-p38 pathway is selectively required for TLR4-mediated innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, M.C.; Sasai, M.; Lee, H.K.; Yordy, B.; Shadel, G.S.; Iwasaki, A. Absence of autophagy results in reactive oxygen species-dependent amplification of RLR signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2770–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dosal, R.; Horan, K.A.; Rahbek, S.H.; Ichijo, H.; Chen, Z.J.; Mieyal, J.J.; Hartmann, R.; Paludan, S.R. HSV infection induces production of ROS, which potentiate signaling from pattern recognition receptors: Role for S-glutathionylation of TRAF3 and 6. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dosal, R.; Horan, K.A.; Paludan, S.R. Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species negatively regulates immune innate signaling pathways triggered by a DNA virus, but not by an RNA virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavouras, J.H.; Prandovszky, E.; Valyi-Nagy, K.; Kovacs, S.K.; Tiwari, V.; Kovacs, M.; Shukla, D.; Valyi-Nagy, T. Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection induces oxidative stress and the release of bioactive lipid peroxidation by-products in mouse P19N neural cell cultures. J. Neurovirol. 2007, 13, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiao, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Ge, H.M.; Tan, R.X.; Li, E. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus infection by oligomeric stilbenoids through ROS generation. Antivir. Res. 2012, 95, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucci, A.; Marino-Merlo, F.; De Nisco, M.; Pedatella, S.; Rossi, F.; Jacob, C.; Caputo, R.; Mastino, A. Se-(2-aminoalkyl)selenocysteines as biochemical redox agents. A tool to contrast cell injury induced by aflatoxin B1 in HepG2 cells. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, M.A.; Sciortino, M.T.; Perri, D.; Amici, C.; Avitabile, E.; Ciotti, M.; Balestrieri, E.; De Smaele, E.; Franzoso, G.; Mastino, A. Protection by herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D against Fas-mediated apoptosis: Role of nuclear factor kappaB. J. Boil. Chem. 2003, 278, 36059–36067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino-Merlo, F.; Papaianni, E.; Maugeri, T.L.; Zammuto, V.; Spano, A.; Nicolaus, B.; Poli, A.; Di Donato, P.; Mosca, C.; Mastino, A.; et al. Anti-herpes simplex virus 1 and immunomodulatory activities of a poly-gamma- glutamic acid from Bacillus horneckiae strain APA of shallow vent origin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7487–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, C.; Minutolo, A.; Balestrieri, E.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Bramanti, P.; Garaci, E.; Macchi, B.; Mastino, A. Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation sensitizes U937 cells to 3’-azido-3’-deoxythymidine induced apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e81. [Google Scholar]
- Sciortino, M.T.; Medici, M.A.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Zaccaria, D.; Giuffre-Cuculletto, M.; Venuti, A.; Grelli, S.; Mastino, A. Involvement of HVEM receptor in activation of nuclear factor kappaB by herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein D. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H.; Melchjorsen, J.; Hollsberg, P.; Paludan, S.R. Activation of NF-kappa B in virus-infected macrophages is dependent on mitochondrial oxidative stress and intracellular calcium: Downstream involvement of the kinases TGF-beta-activated kinase 1, mitogen-activated kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1, and I kappa B kinase. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 6224–6233. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, S.; Kitamura, M. Bidirectional regulation of NF-kappaB by reactive oxygen species: A role of unfolded protein response. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buelna-Chontal, M.; Zazueta, C. Redox activation of Nrf2 & NF-kappaB: A double end sword? Cell Signal 2013, 25, 2548–2557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.T.; White, T.E.; Brandariz-Nunez, A.; Diaz-Griffero, F.; Weitzman, M.D. SAMHD1 restricts herpes simplex virus 1 in macrophages by limiting DNA replication. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12949–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciortino, M.T.; Perri, D.; Medici, M.A.; Grelli, S.; Serafino, A.; Borner, C.; Mastino, A. Role of Bcl-2 expression for productive herpes simplex virus 2 replication. Virology 2006, 356, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Su, A.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lv, X.; Xu, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Harmine blocks herpes simplex virus infection through downregulating cellular NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways induced by oxidative stress. Antivir. Res. 2015, 123, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, S.A.; Sweet, T.J.; Bailey, E.; Booth, T.; Docherty, J.J. Resveratrol suppresses nuclear factor-kappaB in herpes simplex virus infected cells. Antivir. Res. 2006, 72, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lint, A.L.; Murawski, M.R.; Goodbody, R.E.; Severa, M.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Finberg, R.W.; Knipe, D.M.; Kurt-Jones, E.A. Herpes simplex virus immediate-early ICP0 protein inhibits Toll-like receptor 2-dependent inflammatory responses and NF-kappaB signaling. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10802–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nox Family Component | Gene Name | GeneBank Number | Sequence (5’→3’) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nox2/gp91phox | CYBB | NM_000397 | F | CTTCCTCAGGGGTTCCAGTG |
| R | GTGAATCGCAGAGTGAAGTGC | |||
| Nox4 | NOX4 | NM_001143837 | F | TCCAGCCTCCAGAACTTACTTC |
| R | ACCTCTTCTTTGCGTCCACT | |||
| p47phox | NCF1 | NM_000265 | F | GAGAGCGGTTGGTGGTTCTG |
| R | CACCTGCATAGTTGGGCTCA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marino-Merlo, F.; Papaianni, E.; Frezza, C.; Pedatella, S.; De Nisco, M.; Macchi, B.; Grelli, S.; Mastino, A. NF-κB-Dependent Production of ROS and Restriction of HSV-1 Infection in U937 Monocytic Cells. Viruses 2019, 11, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050428
Marino-Merlo F, Papaianni E, Frezza C, Pedatella S, De Nisco M, Macchi B, Grelli S, Mastino A. NF-κB-Dependent Production of ROS and Restriction of HSV-1 Infection in U937 Monocytic Cells. Viruses. 2019; 11(5):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050428
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarino-Merlo, Francesca, Emanuela Papaianni, Caterina Frezza, Silvana Pedatella, Mauro De Nisco, Beatrice Macchi, Sandro Grelli, and Antonio Mastino. 2019. "NF-κB-Dependent Production of ROS and Restriction of HSV-1 Infection in U937 Monocytic Cells" Viruses 11, no. 5: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050428
APA StyleMarino-Merlo, F., Papaianni, E., Frezza, C., Pedatella, S., De Nisco, M., Macchi, B., Grelli, S., & Mastino, A. (2019). NF-κB-Dependent Production of ROS and Restriction of HSV-1 Infection in U937 Monocytic Cells. Viruses, 11(5), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050428







