Inactivation and Removal of Chikungunya Virus and Mayaro Virus from Plasma-derived Medicinal Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and Cells
2.2. Virus Titration
2.3. CHIKV RNA Detection
2.4. Heat Inactivation in Cell Culture Medium and Human Serum Albumin Solution
2.5. Solvent/Detergent Treatment
2.6. Nanofiltration
2.7. Electron Microscopy
3. Results
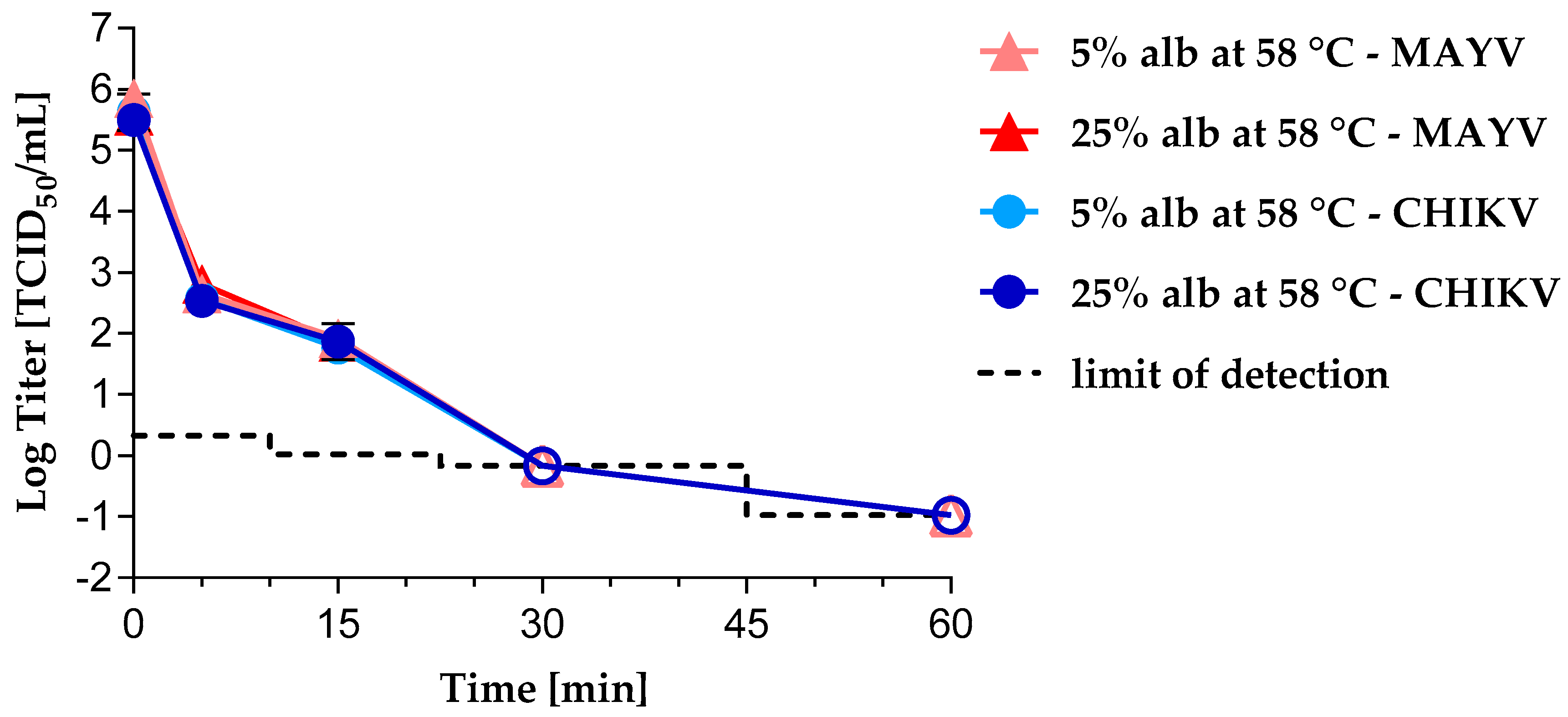
3.1. Virus Inactivation by Heat Treatment
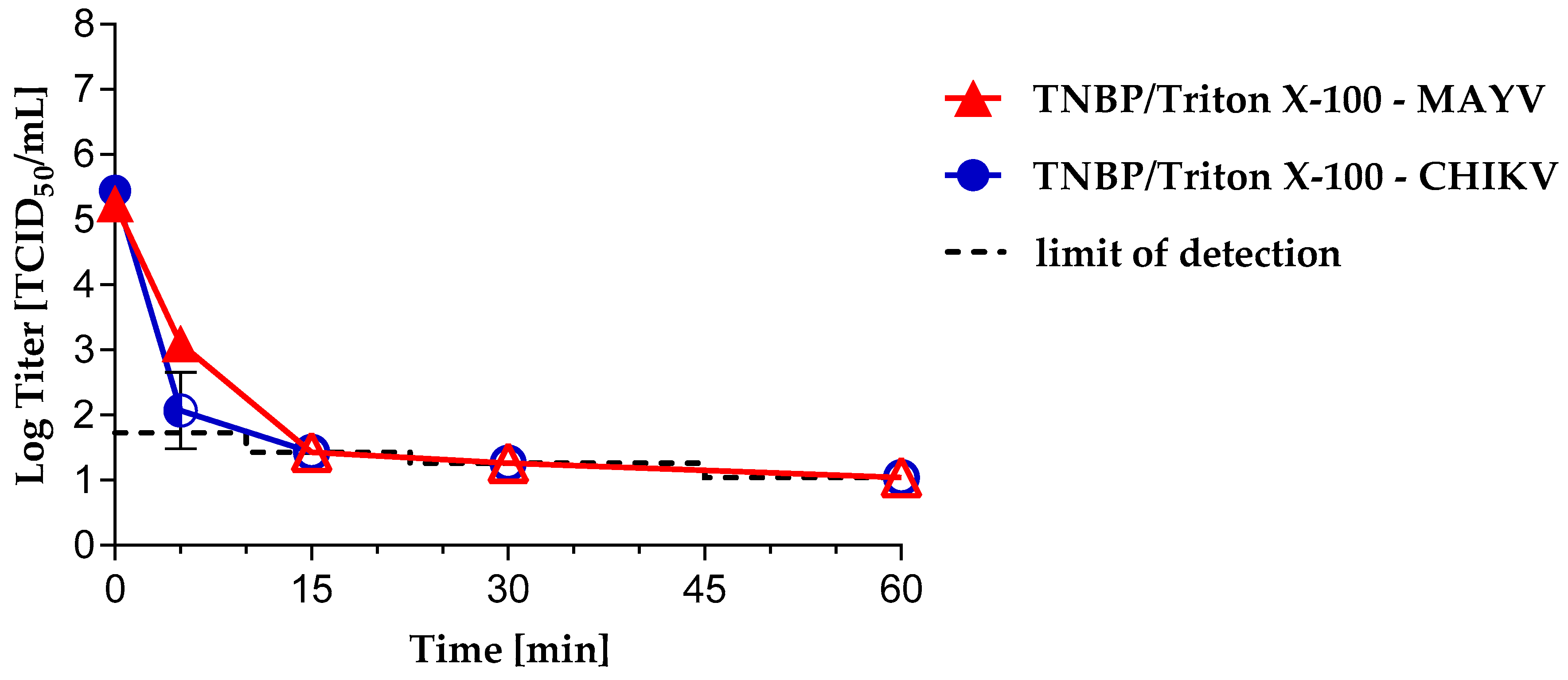
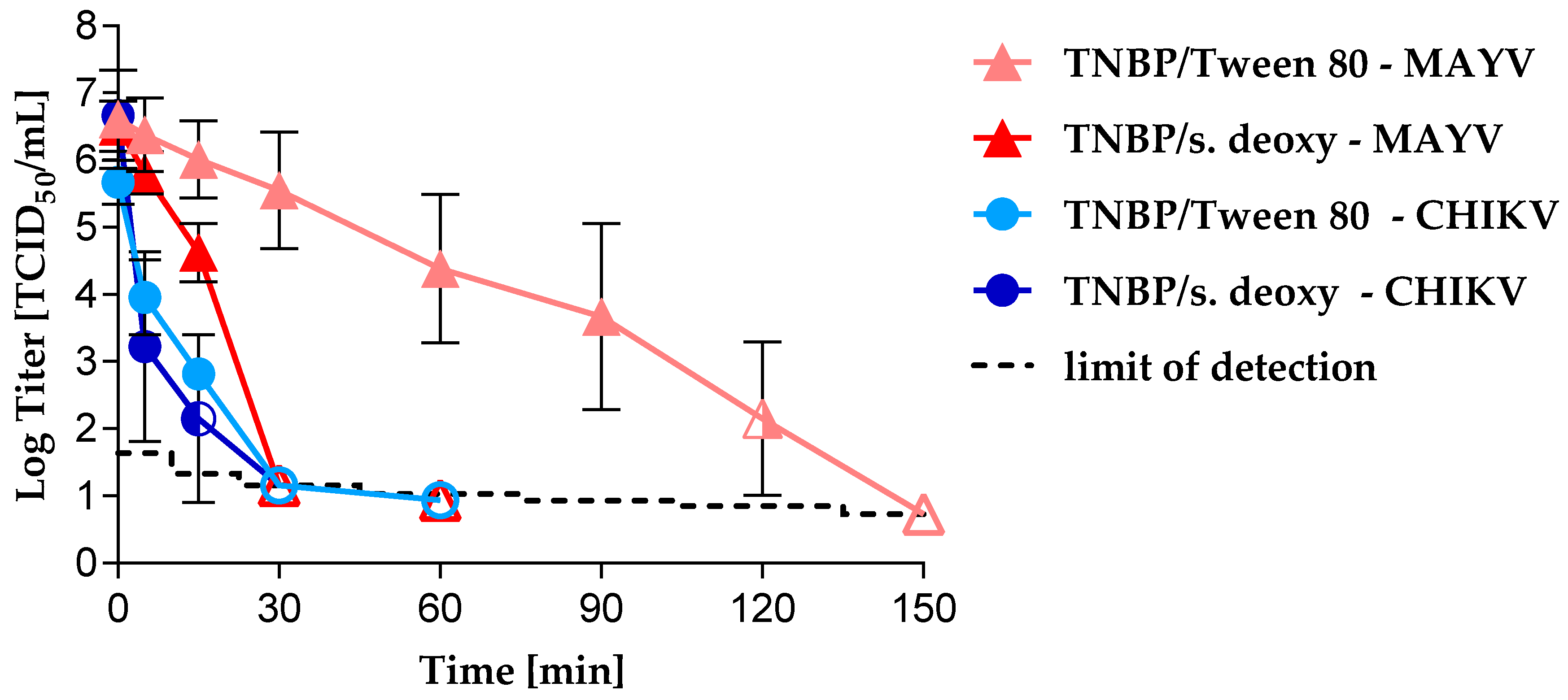
3.2. Virus Inactivation byS/D Treatment
3.3. Virus Removal by Nanofiltration
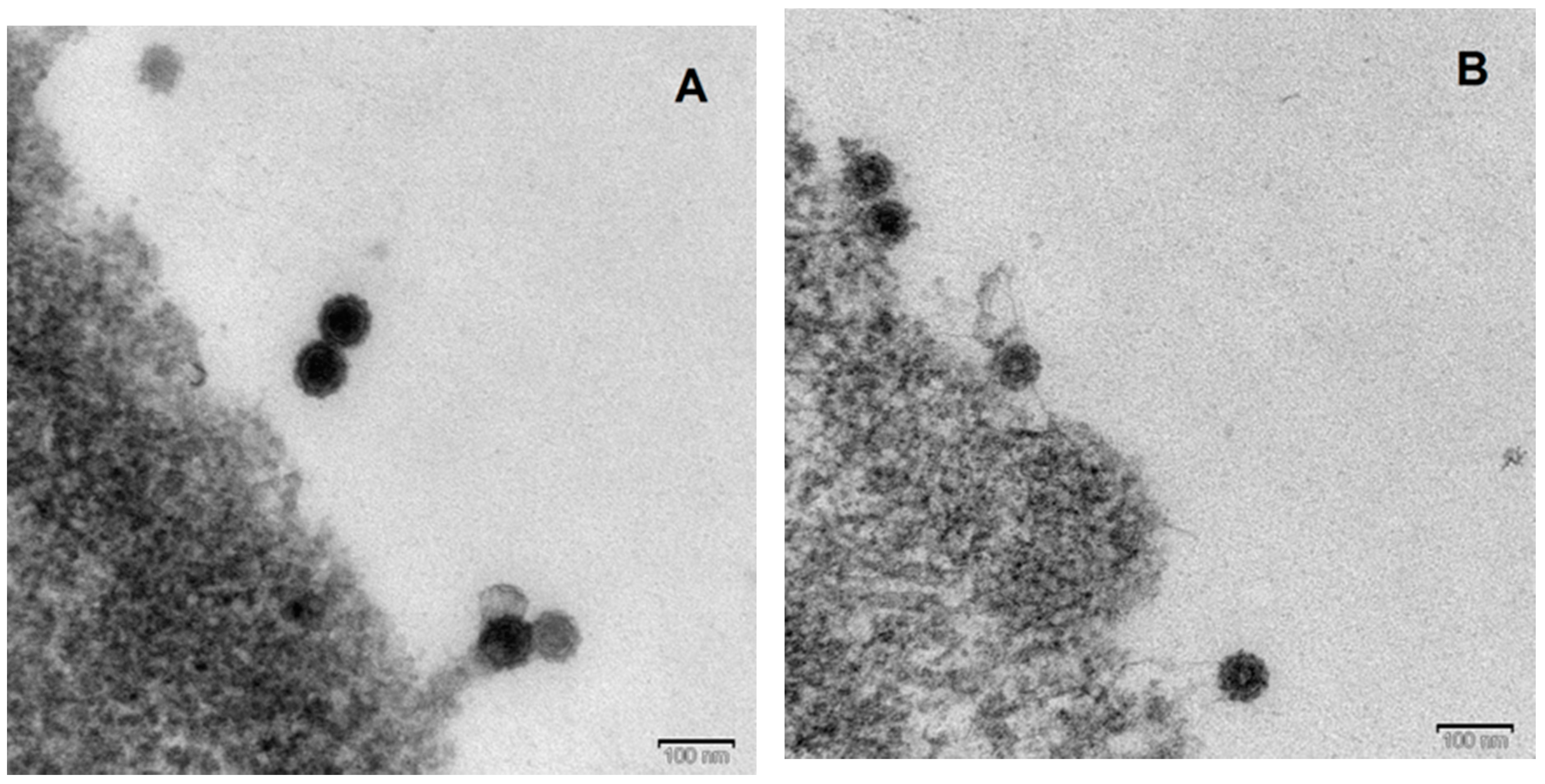
3.4. Electron Microscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. The alphaviruses: Gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 491–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paredes, A.M.; Brown, D.T.; Rothnagel, R.; Chiu, W.; Schoepp, R.J.; Johnston, R.E.; Prasad, B.V. Three-dimensional structure of a membrane-containing virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9095–9099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.C.; David, A.; Jummblatt, J.; Darnell, J.E. Lipid and protein organization in Sindbis virus. J. Mol. Biol. 1971, 60, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E. Mayaro virus: A forest virus primed for a trip to the city? Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Diease Control and Prevention. Geographic Distribution|Chikungunya Virus|CDC. 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/chikungunya/geo/index.html (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Tesh, R.B.; Watts, D.M.; Russell, K.L.; Damodaran, C.; Calampa, C.; Cabezas, C.; Ramirez, G.; Vasquez, B.; Hayes, C.G.; Rossi, C.A.; et al. Mayaro virus disease: An emerging mosquito-borne zoonosis in tropical South America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.C.; Ziegler, S.A.; Thangamani, S.; Hausser, N.L.; Kochel, T.J.; Higgs, S.; Tesh, R.B. Experimental transmission of Mayaro virus by Aedes aegypti. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cella, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Milano, T.; Fogolari, M.; Garilli, F.; Alexiev, I.; Bazzardi, R.; Salemi, M.; Junior Alcantara, L.; Angeletti, S.; et al. Mayaro virus infection, the next epidemic wave after Zika? Evolutionary and structural analysis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 11, 194. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, M.; Logue, C.H.; Oderinde, B.; Abdulmaleek, H.; Williams, J.; Lewis, J.; Laws, T.R.; Hewson, R.; Marcello, A.; Agaro, P. Evidence of arbovirus co-infection in suspected febrile malaria and typhoid patients in Nigeria. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2013, 7, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.W.; Goodman, C.H.; Holloway, K.; de Salazar, P.M.; Valadere, A.M.; Drebot, M.A. Evaluation of Commercially Available Chikungunya Virus Immunoglobulin M Detection Assays. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henss, L.; Yue, C.; Kandler, J.; Faddy, H.M.; Simmons, G.; Panning, M.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Baylis, S.A.; Schnierle, B.S. Establishment of an Alphavirus-Specific Neutralization Assay to Distinguish Infections with Different Members of the Semliki Forest complex. Viruses 2019, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassing, R.J.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Tolou, H.; van Doornum, G.; van Genderen, P.J. Cross-reactivity of antibodies to viruses belonging to the Semliki forest serocomplex. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2010, 15, 19588. [Google Scholar]
- Musso, D.; Stramer, S.L.; Busch, M.P. Zika virus: A new challenge for blood transfusion. Lancet 2016, 387, 1993–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, R.Y.; Foster, G.A.; Stramer, S.L. Keeping Blood Transfusion Safe from West Nile Virus: American Red Cross Experience, 2003 to 2012. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appassakij, H.; Khuntikij, P.; Kemapunmanus, M.; Wutthanarungsan, R.; Silpapojakul, K. Viremic profiles in asymptomatic and symptomatic chikungunya fever: A blood transfusion threat? Transfusion 2013, 53, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouard, C.; Bernillon, P.; Quatresous, I.; Pillonel, J.; Assal, A.; de Valk, H.; Desenclos, J.-C. Estimated risk of Chikungunya viremic blood donation during an epidemic on Reunion Island in the Indian Ocean, 2005 to 2007. Transfusion 2008, 48, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturi, G.; Di Luca, M.; Fortuna, C.; Remoli, M.E.; Riccardo, F.; Severini, F.; Toma, L.; Del Manso, M.; Benedetti, E.; Caporali, M.G.; et al. Detection of a chikungunya outbreak in Central Italy, August to September 2017. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liumbruno, G.M.; Calteri, D.; Petropulacos, K.; Mattivi, A.; Po, C.; Macini, P.; Tomasini, I.; Zucchelli, P.; Silvestri, A.R.; Sambri, V.; et al. The Chikungunya epidemic in Italy and its repercussion on the blood system. Blood Transfus. 2008, 6, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cadar, D.; Maier, P.; Müller, S.; Kress, J.; Chudy, M.; Bialonski, A.; Schlaphof, A.; Jansen, S.; Jöst, H.; Tannich, E.; et al. Blood donor screening for West Nile virus (WNV) revealed acute Usutu virus (USUV) infection, Germany, September 2016. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, G.; Cristiano, K.; Pupella, S.; Liumbruno, G.M. West Nile Virus in Europe and Safety of Blood Transfusion. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2016, 43, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P. Effect of sample storage conditions on virus inactivation by solvent/detergent. Biologicals 2002, 30, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.; Sims, G. Use of vegetable-derived tween 80 for virus inactivation by solvent/detergent treatment. Biologicals 1999, 27, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, B.; Bonomo, R.; Prince, A.M.; Chin, S.N.; Brotman, B.; Shulman, R.W. Solvent/detergent-treated plasma: A virus-inactivated substitute for fresh frozen plasma. Blood 1992, 79, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seitz, H.; Blümel, J.; Schmidt, I.; Willkommen, H.; Löwer, J. Comparable virus inactivation by bovine or vegetable derived Tween 80 during solvent/detergent treatment. Biologicals 2002, 30, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espindola, O.M.; Belluci, M.S.P.; Oliveira, B.C.E.P.D.; Liberto, M.I.M.; Cabral, M.C. Sindbis virus as a tool for quality control of viral inactivation of heated and chemically treated plasma-derived products. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 134, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leydold, S.M.; Farcet, M.R.; Kindermann, J.; Modrof, J.; Pölsler, G.; Berting, A.; Howard, M.K.; Barrett, P.N.; Kreil, T.R. Chikungunya virus and the safety of plasma products. Transfusion 2012, 52, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huangfu, C.; Ma, Y.; Jia, J.; Lv, M.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Inactivation of viruses by pasteurization at 60 °C for 10 h with and without 40% glucose as stabilizer during a new manufacturing process of α2-Macroglobulin from Cohn Fraction IV. Biologicals 2017, 46, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knevelman, A.; Wit, H.J.C.; Potstra, P.; Does, J.V.D.A. Development and Small-Scale Production of a Severely Heated Factor VIII Concentrate. Vox Sang. 1994, 66, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Heldebrant, C.M.; Takechi, K.; Yokoyama, K. Inactivation and elimination of viruses during preparation of human intravenous immunoglobulin. Vox Sang. 1994, 67, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spearman, C. The Method of ‘Right and Wrong Cases’ (‘Constant Stimuli’) without Gauss’s Formulae. Br. J. Psychol. 1908, 2, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärber, G. Beitrag zur kollektiven Behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv für Experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie 1931, 162, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppach, H. Log10 Reduction Factors in Viral Clearance Studies. BioProcess. J. Trends Dev. BioProcess Technol. 2014, 12, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenau, H.F.; Schwebke, I.; Blümel, J.; Eggers, M.; Rapp, I.; Steinmann, J.; Willkommen, H. 2. Mitteilung des DVV/GfV-Fachausschusses Virusdesinfektion zur DVV/RKI-Leitlinie in der Fassung vom 01.12.2014: Erläuterung zur Bedeutung, Anwendung und Berechnung des “Large-Volume-Platings” (LVP). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2016, 59, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümel, J.; Musso, D.; Teitz, S.; Miyabayashi, T.; Boller, K.; Schnierle, B.S.; Baylis, S.A. Inactivation and removal of Zika virus during manufacture of plasma-derived medicinal products. Transfusion 2017, 57, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreß, J.A.; Hanschmann, K.-M.O.; Chudy, M.; Collaborative Study Group. Collaborative Study to Evaluate a Candidate World Health Organization International Standard for Chikungunya Virus for Nucleic Acid Amplification Technique (NAT)-Based Assays; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rezvan, H.; Motallebi, Z.; Jalili, M.A.; Mousavi Hosseini, K.; Pourfathollah, A.A. Safety of Blood and Plasma derivatives: Pathogen Reducing Technologies. Med. J. Islamic Repub. Iran 2006, 20, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-J.S.; Hsu, W.-W.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Temperature Tolerance and Inactivation of Chikungunya Virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.L.; Huang, Y.-J.S.; Hsu, W.-W.; Hettenbach, S.M.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Virus-specific thermostability and heat inactivation profiles of alphaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 234, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Brault, A.C.; Reisen, W.K. Comparative thermostability of West Nile, St. Louis encephalitis, and western equine encephalomyelitis viruses during heat inactivation for serologic diagnostics. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remington, K.M.; Trejo, S.R.; Buczynski, G.; Li, H.; Osheroff, W.P.; Brown, J.P.; Renfrow, H.; Reynolds, R.; Pifat, D.Y. Inactivation of West Nile virus, vaccinia virus and viral surrogates for relevant and emergent viral pathogens in plasma-derived products. Vox Sang. 2004, 87, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farcet, M.R.; Kreil, T.R. Zika virus is not thermostable: Very effective virus inactivation during heat treatment (pasteurization) of human serum albumin. Transfusion 2017, 57, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichtelmüller, H.O.; Biesert, L.; Fabbrizzi, F.; Gajardo, R.; Gröner, A.; von Hoegen, I.; Jorquera, J.I.; Kempf, C.; Kreil, T.R.; Pifat, D.; et al. Robustness of solvent/detergent treatment of plasma derivatives: A data collection from Plasma Protein Therapeutics Association member companies. Transfusion 2009, 49, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2017/999 of 13 June 2017 amending Annex XIV to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). 2017. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32017R0999&qid=1551777234794&from=DE (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Roberts, P. Resistance of vaccinia virus to inactivation by solvent/detergent treatment of blood products. Biologicals 2000, 28, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardone, F.; Simoneau, S.; Arzel, A.; Puopolo, M.; Berardi, V.A.; Abdel-Haq, H.; Galeno, R.; de Pascalis, A.; Sbriccoli, M.; Graziano, S.; et al. Comparison of nanofiltration efficacy in reducing infectivity of centrifuged versus ultracentrifuged 263K scrapie-infected brain homogenates in “spiked” albumin solutions. Transfusion 2012, 52, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnouf, T.; Radosevich, M.; Goubran, H.; Willkommen, H. Place of Nanofiltration for Assuring Viral Safety of Biologicals. CNANO 2005, 1, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, M.; Sall, A.A.; Manuguerra, J.-C.; Koivogui, L.; Adjami, A.; Traoré, F.F.; Hedlund, K.-O.; Lindegren, G.; Mirazimi, A. Quantitative analysis of particles, genomes and infectious particles in supernatants of haemorrhagic fever virus cell cultures. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Run | Sample Description | MAYV Infectivity [log TCID50/mL ± 95% CI] | CHIKV Infectivity [log TCID50/mL ± 95% CI] | CHIKV RNA [log IU/mL] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1) 20 nm filter | Spiked load | 5.99 ± 0.30 | 5.45 ± 0.24 | n.d. |
| 0.1 µm pre-filtrate | 5.79 ± 0.30 | 5.28 ± 0.24 | 8.62 | |
| 20 nm filtrate | ≤−0.41 | ≤−0.41 | - | |
| 2) 35 nm filter | Spiked load | 5.79 ± 0.30 | 5.55 ± 0.24 | n.d. |
| 0.1 µm pre-filtrate | 5.61 ± 0.30 | 5.34 ± 0.24 | 8.62 | |
| 35 nm filtrate | ≤0.41 | ≤−0.41 | 2.29 | |
| 3) 75 nm filter | Spiked load | 6.51 ± 0.33 | 5.65 ± 0.35 | 8.87 |
| 0.1 µm pre-filtrate | 6.29 ± 0.33 | 5.43 ± 0.35 | n.d. | |
| 75 nm filtrate | 1.01 ± 0.49 | 1.09 ± 0.47 | 3.49 | |
| 4) 75, 40, 35, 20 nm filter | Spiked load | 6.31 ± 0.30 | 5.37 ± 0.24 | 8.72 |
| 75 nm filtrate | ≤1.03 | ≤1.03 | 3.73 | |
| 40 nm filtrate | ≤−0.4 | ≤−0.4 | 2.53 | |
| 35 nm filtrate | ≤−0.72 | ≤−0.72 | 2.27 | |
| 20 nm filtrate | ≤−0.73 | ≤−0.73 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, C.; Teitz, S.; Miyabashi, T.; Boller, K.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Baylis, S.A.; Blümel, J. Inactivation and Removal of Chikungunya Virus and Mayaro Virus from Plasma-derived Medicinal Products. Viruses 2019, 11, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030234
Yue C, Teitz S, Miyabashi T, Boller K, Lewis-Ximenez LL, Baylis SA, Blümel J. Inactivation and Removal of Chikungunya Virus and Mayaro Virus from Plasma-derived Medicinal Products. Viruses. 2019; 11(3):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030234
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Constanze, Sebastian Teitz, Tomoyuki Miyabashi, Klaus Boller, Lia Laura Lewis-Ximenez, Sally A. Baylis, and Johannes Blümel. 2019. "Inactivation and Removal of Chikungunya Virus and Mayaro Virus from Plasma-derived Medicinal Products" Viruses 11, no. 3: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030234
APA StyleYue, C., Teitz, S., Miyabashi, T., Boller, K., Lewis-Ximenez, L. L., Baylis, S. A., & Blümel, J. (2019). Inactivation and Removal of Chikungunya Virus and Mayaro Virus from Plasma-derived Medicinal Products. Viruses, 11(3), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030234




