Clinical and Serological Evaluation of LINDA Virus Infections in Post-Weaning Piglets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Virus Infection and Titration
2.3. RT-PCR Detection
2.4. Calibration-Curve-Estimated Copy Number of LINDA Genome Equivalents
2.5. Virus Neutralization Assay
2.6. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay and Antibodies
2.7. Animal Experiment
2.8. Pathological Examinations
3. Results
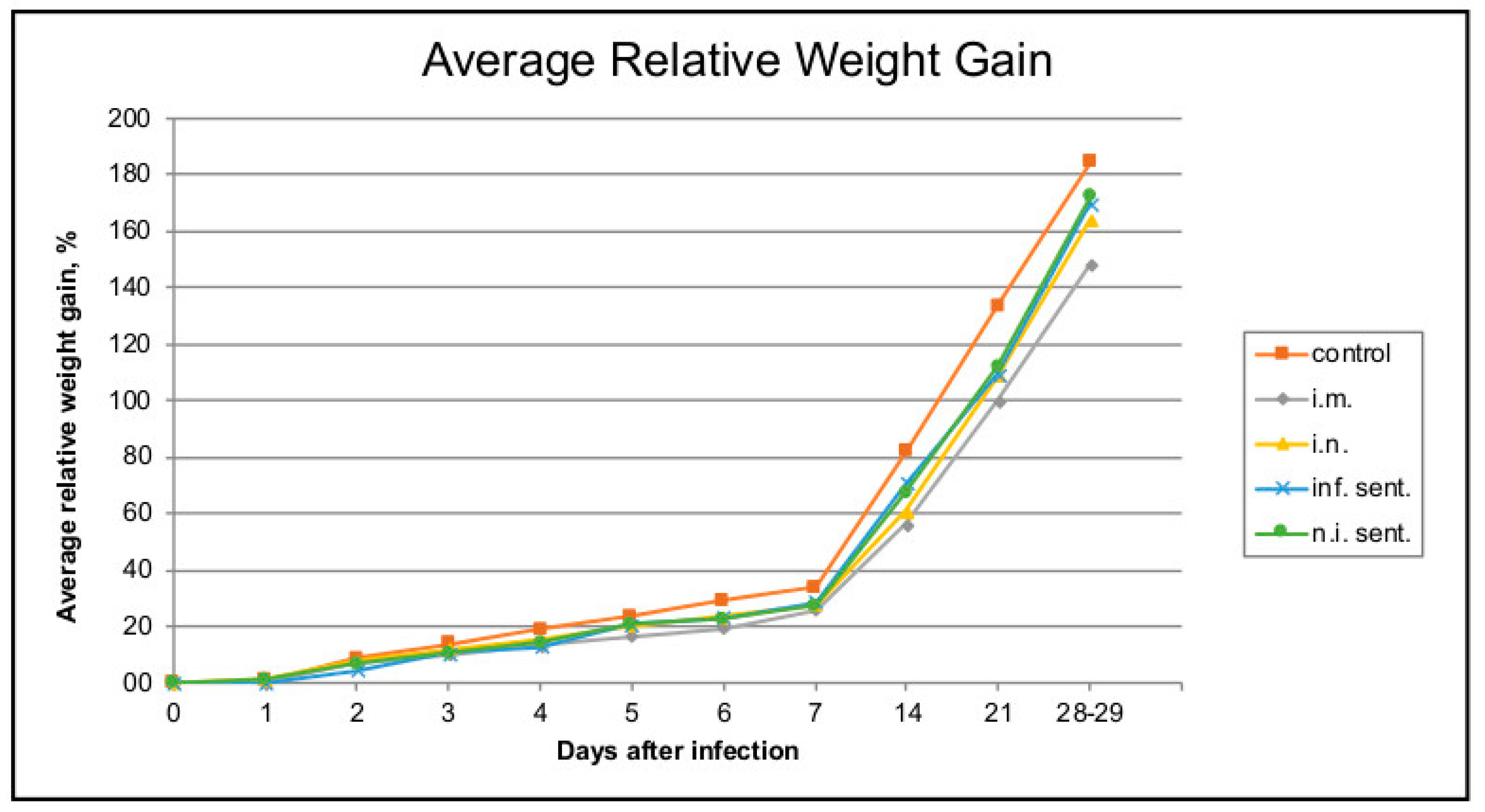
3.1. Pathogenicity and Virulence of LINDA in Weaned Piglets
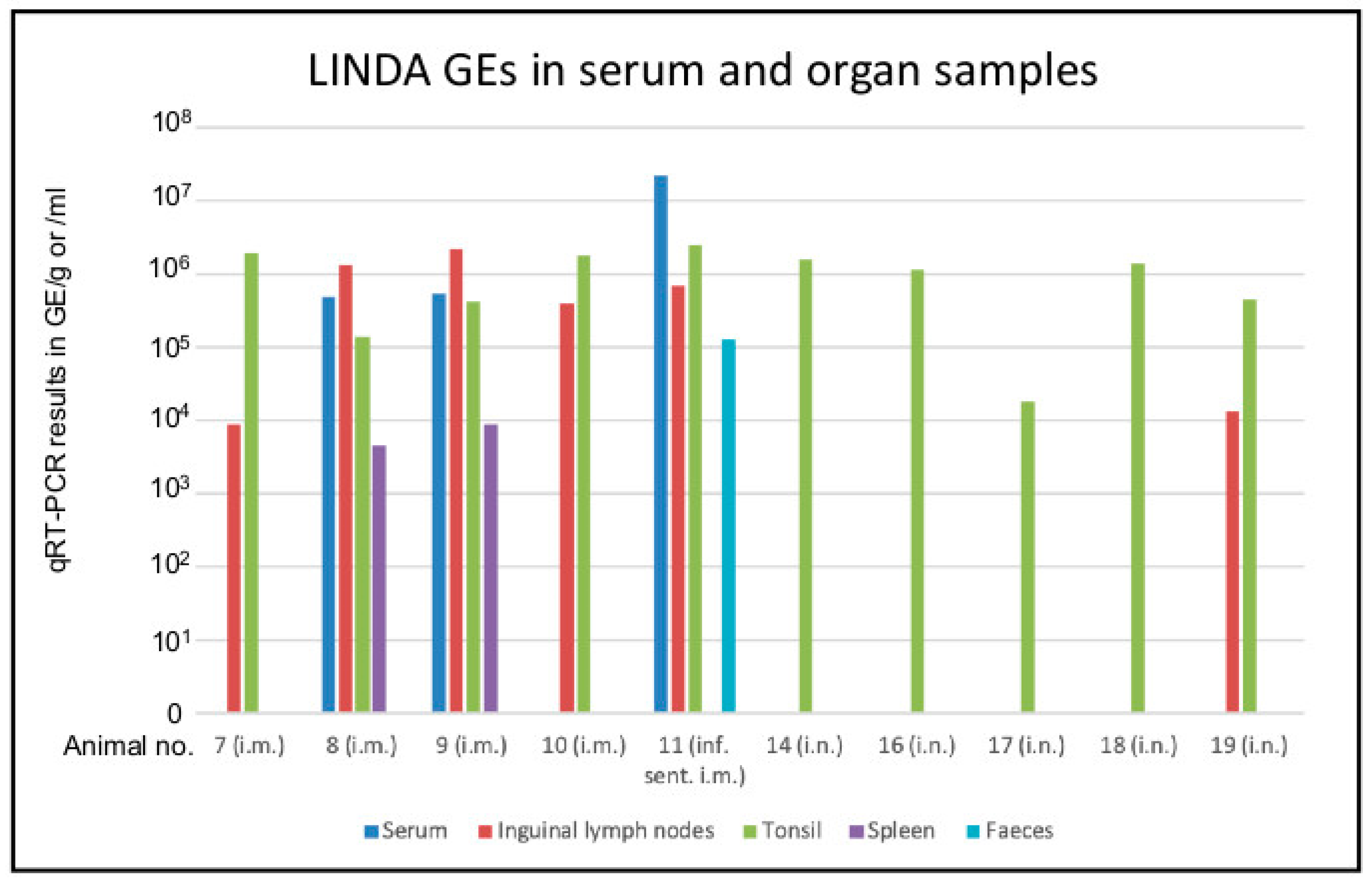
3.2. Replication of LINDA in the Immunocompetent Porcine Host
3.3. Humoral Immune Response against LINDA
3.4. Cross Neutralization of LINDA-Immune Sera with Other Pestivirus Species
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, D.B.; Meyers, G.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Monath, T.; Scott Muerhoff, A.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P.; et al. Proposed revision to the taxonomy of the genus Pestivirus, family Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol 2017, 98, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkland, P.D.; Frost, M.J.; Finlaison, D.S.; King, K.R.; Ridpath, J.F.; Gu, X. Identification of a novel virus in pigs–Bungowannah virus: A possible new species of pestivirus. Virus Res. 2007, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.; Aoki, H.; Sakoda, Y.; Kozasa, T.; Tominaga-Teshima, K.; Mine, J.; Abe, Y.; Tamura, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishine, K.; et al. Molecular, biological, and antigenic characterization of a Border disease virus isolated from a pig during classical swine fever surveillance in Japan. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2014, 26, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hause, B.M.; Collin, E.A.; Peddireddi, L.; Yuan, F.; Chen, Z.; Hesse, R.A.; Gauger, P.C.; Clement, T.; Fang, Y.; Anderson, G. Discovery of a novel putative atypical porcine pestivirus in pigs in the USA. J. Gen. Virol 2015, 96, 2994–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Sun, C.Q.; Cao, S.J.; Lin, T.; Yuan, S.S.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhai, S.L.; Huang, L.; Shan, T.L.; Zheng, H.; et al. High prevalence of bovine viral diarrhea virus 1 in Chinese swine herds. Vet. Microbiol 2012, 159, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamp, B.; Schwarz, L.; Hogler, S.; Riedel, C.; Sinn, L.; Rebel-Bauder, B.; Weissenbock, H.; Ladinig, A.; Rumenapf, T. Novel Pestivirus Species in Pigs, Austria, 2015. Emerg Infect. Dis 2017, 23, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamp, B.; Riedel, C.; Roman-Sosa, G.; Heimann, M.; Jacobi, S.; Becher, P.; Thiel, H.J.; Rumenapf, T. Biosynthesis of classical swine fever virus nonstructural proteins. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3607–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rümenapf, T.; Unger, G.; Strauss, J.H.; Thiel, H.J. Processing of the envelope glycoproteins of pestiviruses. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Stark, R.; Meyers, G.; Rümenapf, T.; Thiel, H.J. Processing of pestivirus polyprotein: Cleavage site between autoprotease and nucleocapsid protein of classical swine fever virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7088–7095. [Google Scholar]
- Lamp, B.; Riedel, C.; Wentz, E.; Tortorici, M.A.; Rumenapf, T. Autocatalytic cleavage within classical swine fever virus NS3 leads to a functional separation of protease and helicase. J. Virol. 2013, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackner, T.; Muller, A.; Pankraz, A.; Becher, P.; Thiel, H.J.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Tautz, N. Temporal modulation of an autoprotease is crucial for replication and pathogenicity of an RNA virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10765–10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tautz, N.; Elbers, K.; Stoll, D.; Meyers, G.; Thiel, H.J. Serine protease of pestiviruses: Determination of cleavage sites. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5415–5422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inch, C. World Animal Health. Can. Vet. J. 2006, 47, 790–791. [Google Scholar]
- Lohse, L.; Nielsen, J.; Uttenthal, A. Early pathogenesis of classical swine fever virus (CSFV) strains in Danish pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, P.D.; Read, A.J.; Frost, M.J.; Finlaison, D.S. Bungowannah virus--a probable new species of pestivirus--what have we found in the last 10 years? Anim. Health. Res. Rev. 2015, 16, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlaison, D.S.; King, K.R.; Gabor, M.; Kirkland, P.D. An experimental study of Bungowannah virus infection in weaner aged pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlaison, D.S.; Cook, R.W.; Srivastava, M.; Frost, M.J.; King, K.R.; Kirkland, P.D. Experimental infections of the porcine foetus with Bungowannah virus, a novel pestivirus. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, L.; Riedel, C.; Högler, S.; Sinn, L.J.; Voglmayr, T.; Wöchtl, B.; Dinhopl, N.; Rebel-Bauder, B.; Weissenböck, H.; Ladinig, A.; et al. Congenital infection with atypical porcine pestivirus (APPV) is associated with disease and viral persistence. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postel, A.; Hansmann, F.; Baechlein, C.; Fischer, N.; Alawi, M.; Grundhoff, A.; Derking, S.; Tenhundfeld, J.; Pfankuche, V.M.; Herder, V.; et al. Presence of atypical porcine pestivirus (APPV) genomes in newborn piglets correlates with congenital tremor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, S.; Yan, Y.; Shi, K.; Wang, M.; Mou, C.; Chen, Z. Molecular characterization of two novel atypical porcine pestivirus (APPV) strains from piglets with congenital tremor in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, M.; Wernike, K.; Drager, C.; Hoper, D.; Pohlmann, A.; Bergermann, C.; Schroder, C.; Klinkhammer, S.; Blome, S.; Hoffmann, B. High prevalence of highly variable atypical porcine pestiviruses found in Germany. Transboun. Emerg. Dis. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groof, A.; Deijs, M.; Guelen, L.; van Grinsven, L.; van Os-Galdos, L.; Vogels, W.; Derks, C.; Cruijsen, T.; Geurts, V.; Vrijenhoek, M.; et al. Atypical Porcine Pestivirus: A Possible Cause of Congenital Tremor Type A-II in Newborn Piglets. Viruses 2016, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, B.L.; Arruda, P.H.; Magstadt, D.R.; Schwartz, K.J.; Dohlman, T.; Schleining, J.A.; Patterson, A.R.; Visek, C.A.; Victoria, J.G. Identification of a divergent lineage porcine pestivirus in nursing piglets with congenital tremors and reproduction of disease following experimental inoculation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagatay, G.N.; Antos, A.; Meyer, D.; Maistrelli, C.; Keuling, O.; Becher, P.; Postel, A. Frequent infection of wild boar with atypical porcine pestivirus (APPV). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasza, L.; Shadduck, J.A.; Christofinis, G.J. Establishment, viral susceptibility and biological characteristics of a swine kidney cell line SK-6. Res. Vet. Sci. 1972, 13, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madin, S.H.; Darby, N.B., Jr. Established kidney cell lines of normal adult bovine and ovine origin. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1958, 98, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corapi, W.V.; Donis, R.O.; Dubovi, E.J. Monoclonal antibody analyses of cytopathic and noncytopathic viruses from fatal bovine viral diarrhea virus infections. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2823–2827. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Meyers, G.; Rumenapf, T.; Thiel, H.J. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the genome of hog cholera virus. Virology 1989, 171, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, P.; Shannon, A.D.; Tautz, N.; Thiel, H.J. Molecular characterization of border disease virus, a pestivirus from sheep. Virology 1994, 198, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridpath, J.F.; Bolin, S.R. The genomic sequence of a virulent bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) from the type 2 genotype: Detection of a large genomic insertion in a noncytopathic BVDV. Virology 1995, 212, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeiser, S.; Mast, J.; Thiel, H.J.; Konig, M. Morphogenesis of pestiviruses: New insights from ultrastructural studies of strain Giraffe-1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierholzer, J.C.; Killington, R.A. 2 - Virus isolation and quantitation. In Virology Methods Manual; Mahy, B.W.J., Kangro, H.O., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1996; Volume 1, pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, R.; Mason, D.J.; Foy, C.A.; Huggett, J.F. Considerations for accurate gene expression measurement by reverse transcription quantitative PCR when analysing clinical samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6471–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilmartin, A.A.; Lamp, B.; Rumenapf, T.; Persson, M.A.; Rey, F.A.; Krey, T. High-level secretion of recombinant monomeric murine and human single-chain Fv antibodies from Drosophila S2 cells. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2012, 25, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, E.; Ahl, R.; Stark, R.; Weiland, F.; Thiel, H.J. A second envelope glycoprotein mediates neutralization of a pestivirus, hog cholera virus. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sinn, L.J.; Zieglowski, L.; Koinig, H.; Lamp, B.; Jansko, B.; Mosslacher, G.; Riedel, C.; Hennig-Pauka, I.; Rumenapf, T. Characterization of two Austrian porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) field isolates reveals relationship to East Asian strains. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Summerfield, A.; Hofmann, M.A.; McCullough, K.C. Low density blood granulocytic cells induced during classical swine fever are targets for virus infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 63, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikalan, M.; Rajukumar, K.; Mishra, N.; Kumar, M.; Kalaiyarasu, S.; Rajesh, K.; Gavade, V.; Behera, S.P.; Dubey, S.C. Distribution pattern of bovine viral diarrhoea virus type 1 genome in lymphoid tissues of experimentally infected sheep. Vet. Res. Commun. 2016, 40, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridpath, J.F.; Falkenberg, S.M.; Bauermann, F.V.; VanderLey, B.L.; Do, Y.; Flores, E.F.; Rodman, D.M.; Neill, J.D. Comparison of acute infection of calves exposed to a high-virulence or low-virulence bovine viral diarrhea virus or a HoBi-like virus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2013, 74, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyon, S.R.; Hill, F.I.; Reichel, M.P.; Brownlie, J. Bovine viral diarrhoea: Pathogenesis and diagnosis. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, R.; La Rocca, S.A.; Paton, D.; Bensaude, E.; Sandvik, T.; Davis, L.; Turner, J.; Drew, T.; Raue, R.; Vangeel, I.; et al. Viral Dose and Immunosuppression Modulate the Progression of Acute BVDV-1 Infection in Calves: Evidence of Long Term Persistence after Intra-Nasal Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Tolnay, A.E.; Reisenhauer, C.E.; Hansen, T.R.; Smirnova, N.; Van Campen, H. Transplacental infection with non-cytopathic bovine viral diarrhoea virus types 1b and 2: Viral spread and molecular neuropathology. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarradas, J.; de la Torre, M.E.; Rosell, R.; Perez, L.J.; Pujols, J.; Munoz, M.; Munoz, I.; Munoz, S.; Abad, X.; Domingo, M.; et al. The impact of CSFV on the immune response to control infection. Virus Res. 2014, 185, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Passler, T.; Riddell, K.P.; Edmondson, M.A.; Chamorro, M.F.; Neill, J.D.; Brodersen, B.W.; Walz, H.L.; Galik, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Walz, P.H. Experimental infection of pregnant goats with bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) 1 or 2. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.E.; Heaney, J.; Thomas, C.J.; Brownlie, J. Infectivity of pestivirus following persistence of acute infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 138, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkland, P.D.; Frost, M.J.; King, K.R.; Finlaison, D.S.; Hornitzky, C.L.; Gu, X.; Richter, M.; Reimann, I.; Dauber, M.; Schirrmeier, H.; et al. Genetic and antigenic characterization of Bungowannah virus, a novel pestivirus. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiesler, A.; Seitz, K.; Schwarz, L.; Buczolich, K.; Petznek, H.; Sassu, E.; Dürlinger, S.; Högler, S.; Klang, A.; Riedel, C.; et al. Clinical and Serological Evaluation of LINDA Virus Infections in Post-Weaning Piglets. Viruses 2019, 11, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110975
Kiesler A, Seitz K, Schwarz L, Buczolich K, Petznek H, Sassu E, Dürlinger S, Högler S, Klang A, Riedel C, et al. Clinical and Serological Evaluation of LINDA Virus Infections in Post-Weaning Piglets. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110975
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiesler, Alexandra, Kerstin Seitz, Lukas Schwarz, Katharina Buczolich, Helga Petznek, Elena Sassu, Sophie Dürlinger, Sandra Högler, Andrea Klang, Christiane Riedel, and et al. 2019. "Clinical and Serological Evaluation of LINDA Virus Infections in Post-Weaning Piglets" Viruses 11, no. 11: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110975
APA StyleKiesler, A., Seitz, K., Schwarz, L., Buczolich, K., Petznek, H., Sassu, E., Dürlinger, S., Högler, S., Klang, A., Riedel, C., Chen, H.-W., Mötz, M., Kirkland, P., Weissenböck, H., Ladinig, A., Rümenapf, T., & Lamp, B. (2019). Clinical and Serological Evaluation of LINDA Virus Infections in Post-Weaning Piglets. Viruses, 11(11), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110975







