Metabolomic Analysis of Influenza A Virus A/WSN/1933 (H1N1) Infected A549 Cells during First Cycle of Viral Replication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Viral Preparation
2.2. Plaque Assay
2.3. Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.5. Sample Preparation, ELISA, and Metabolomics Analysis
2.6. Data Acquisition through LC-MS Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Differential Metabolite Analysis and Functional Pathway Analysis
3. Results
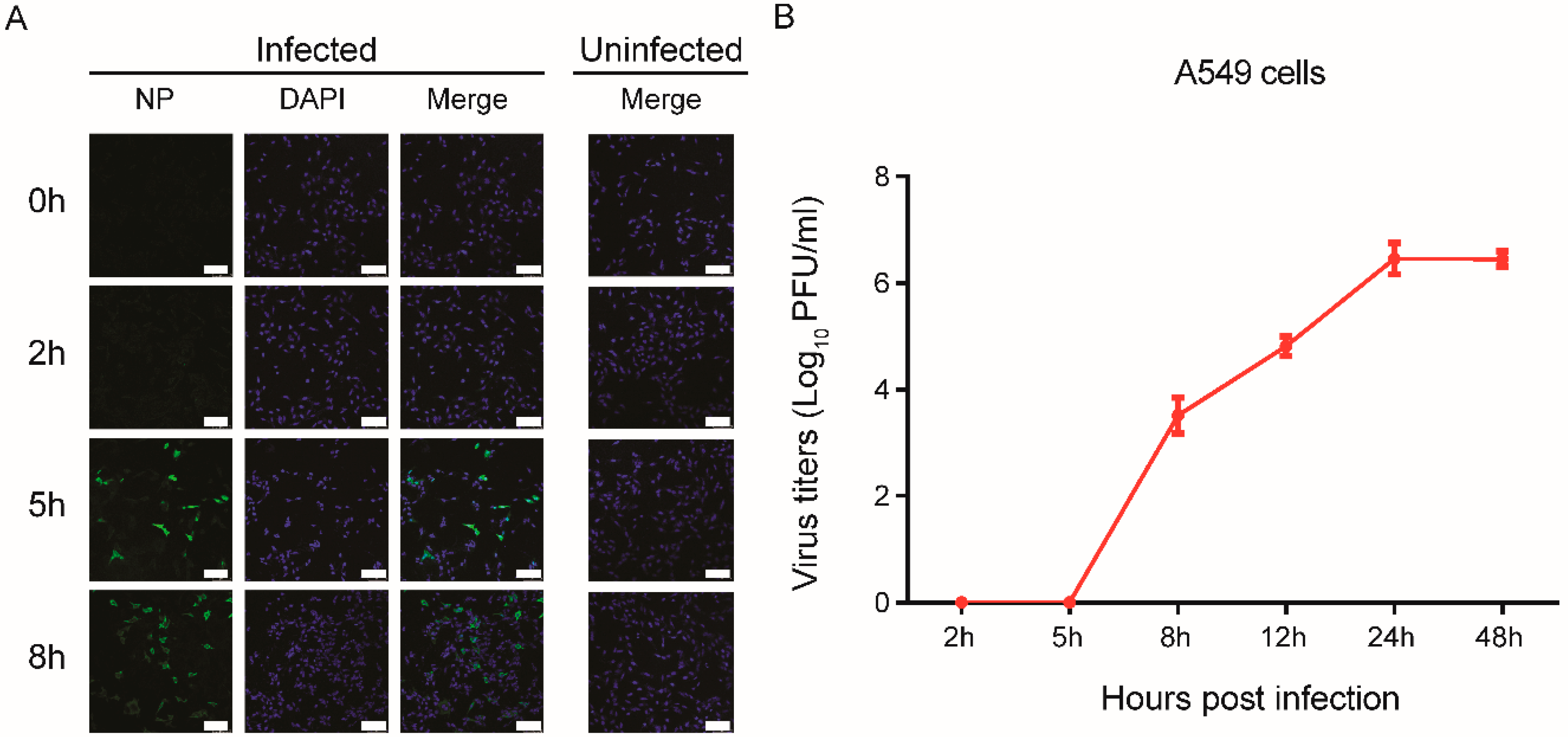
3.1. Rapid Replication of IAV in the Early Stages of Infection in Human Cells
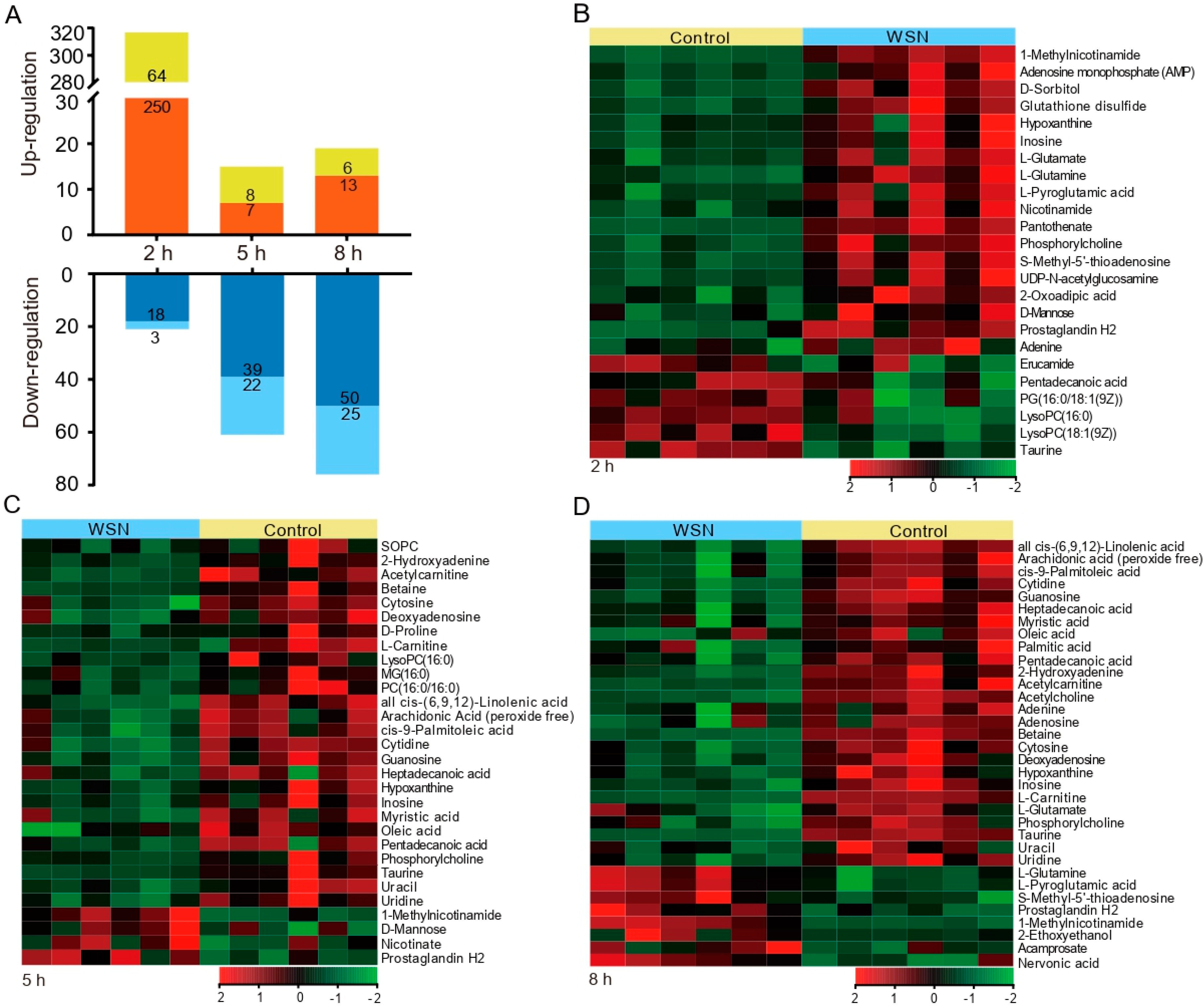
3.2. Characteristic Metabolites in Response to Virus Infection
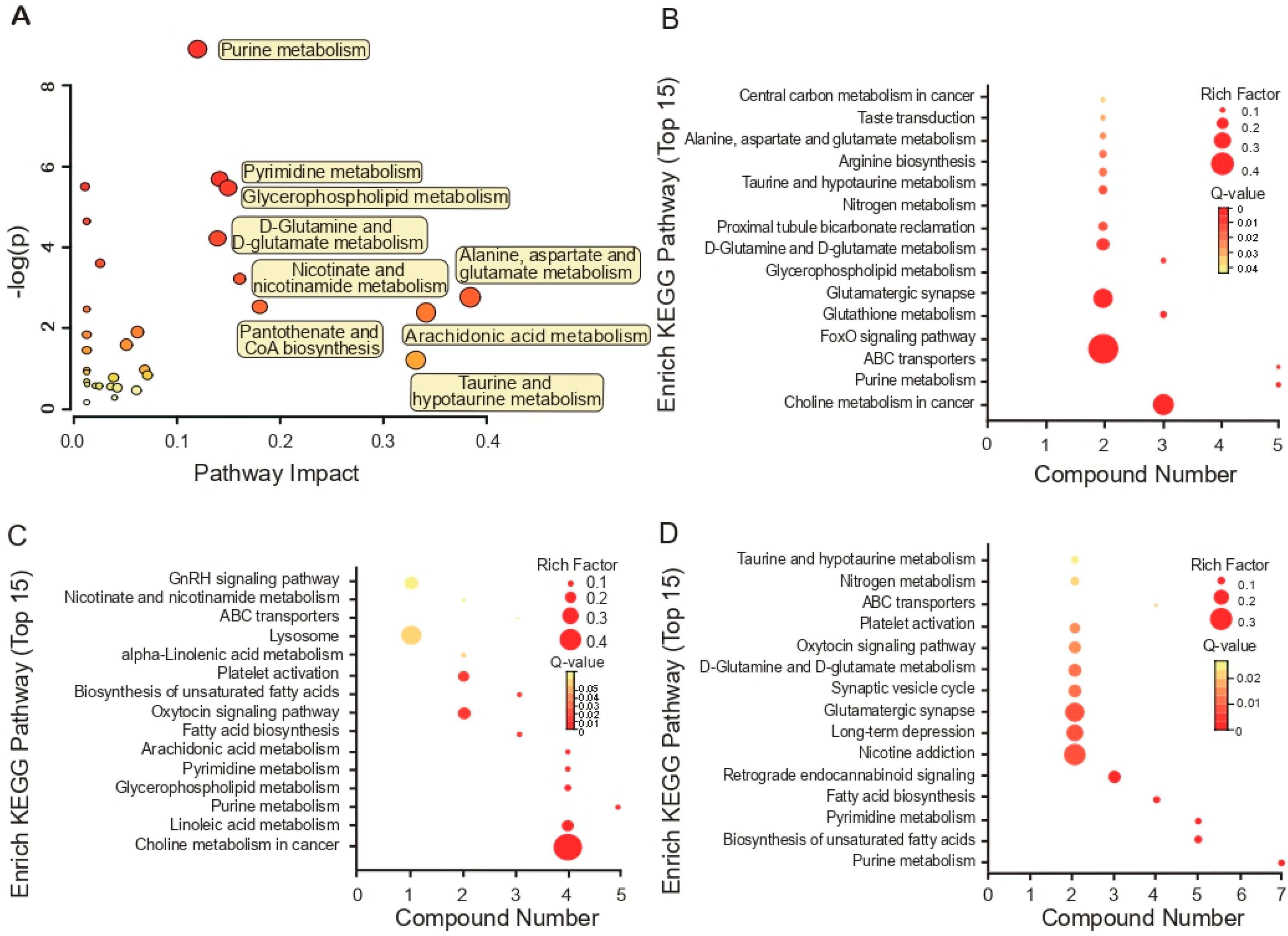
3.3. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses Based on Metabolites
3.4. Metabolite Correlation Network Diagram Analysis
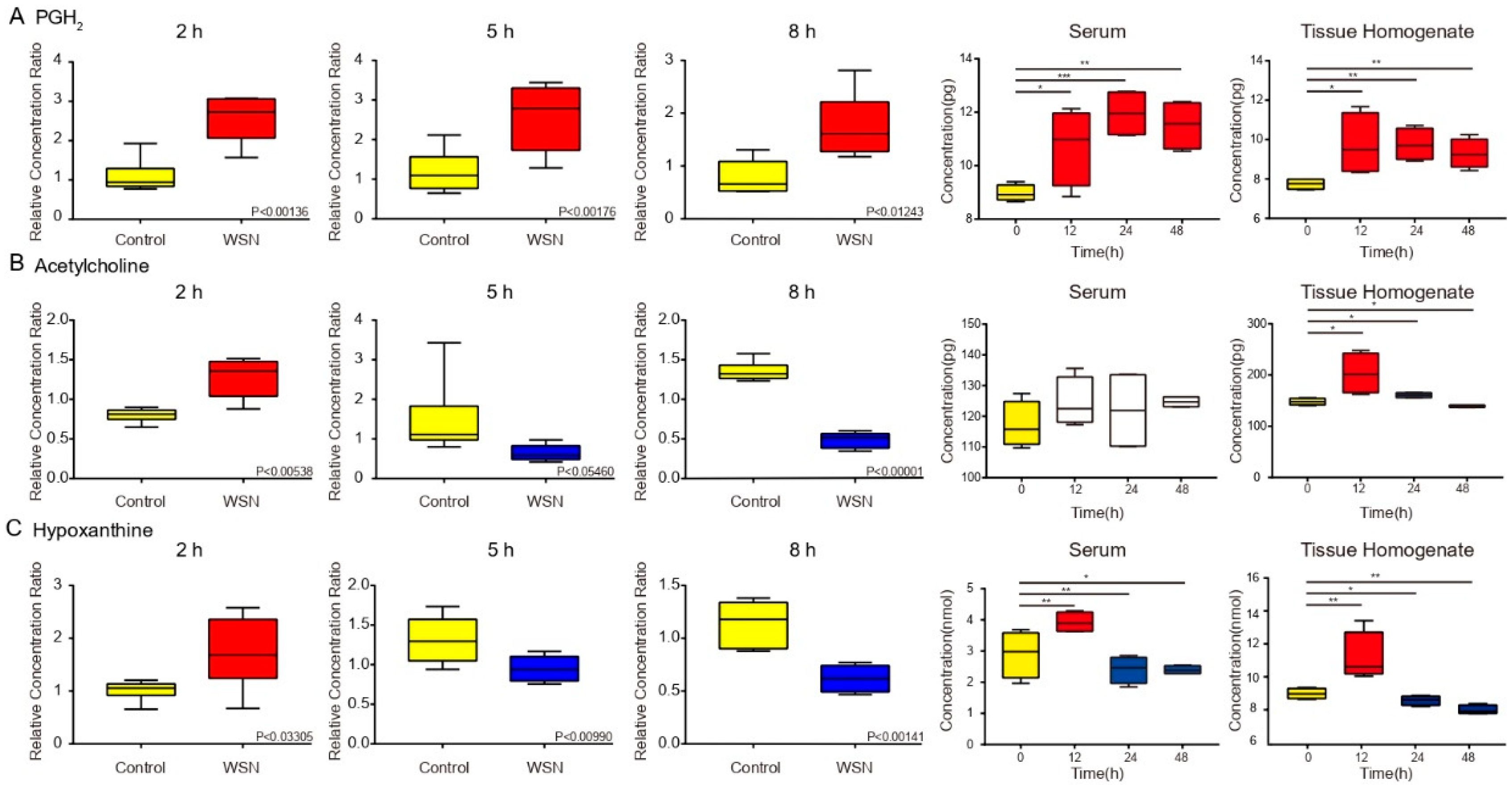
3.5. Trends in Key Metabolites by Box Plots of Different Times by Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, L.; Mahesutihan, M.; Zheng, W.; Meng, L.; Fan, W.; Li, J.; Ye, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, L. Cdc25b promotes influenza a virus replication by regulating the phosphorylation of nucleoprotein. Virology 2018, 525, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, M.; Zheng, W.; Liu, W. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of influenza a virus proteins. Viruses 2015, 7, 2668–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, B.G.; Albrecht, R.A.; Garcia-Sastre, A. Innate immune evasion strategies of influenza viruses. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cline, T.D.; Beck, D.; Bianchini, E. Influenza virus replication in macrophages: Balancing protection and pathogenesis. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Walsh, K.B.; Cahalan, S.; Fremgen, D.M.; Roberts, E.; Scott, F.; Martinborough, E.; Peach, R.; Oldstone, M.B.; Rosen, H. Endothelial cells are central orchestrators of cytokine amplification during influenza virus infection. Cell 2011, 146, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Cao, S.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, J.; Niu, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. Threonine 80 phosphorylation of non-structural protein 1 regulates the replication of influenza a virus by reducing the binding affinity with rig-i. Cell Microbiol. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Yu, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, K.; Ye, X.; Kitamura, Y.; Liu, W. Cyclophilin a interacts with influenza a virus m1 protein and impairs the early stage of the viral replication. Cell Microbiol. 2009, 11, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan-Bonnet, N. Lipid tales of viral replication and transmission. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, C.M.; Xu, S.; Munger, J. Stealing the keys to the kitchen: Viral manipulation of the host cell metabolic network. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.L.; Lagunoff, M. Viral activation of cellular metabolism. Virology 2015, 479–480, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, T.F.; Selim, A.S.M.; Lian, I.; Lee, S.M. Advancements in host-based interventions for influenza treatment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanguez, E.; Hunziker, A.; Dobay, M.P.; Yildiz, S.; Schading, S.; Elshina, E.; Karakus, U.; Gehrig, P.; Grossmann, J.; Dijkman, R.; et al. Phosphoproteomic-based kinase profiling early in influenza virus infection identifies grk2 as antiviral drug target. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Chu, H.; Chan, J.F.; Ye, Z.W.; Wen, L.; Yan, B.; Lai, P.M.; Tee, K.M.; Huang, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Srebp-dependent lipidomic reprogramming as a broad-spectrum antiviral target. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boergeling, Y.; Ludwig, S. Targeting a metabolic pathway to fight the flu. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaelings, L.; Soderholm, S.; Bugai, A.; Fu, Y.; Nandania, J.; Schepens, B.; Lorey, M.B.; Tynell, J.; Vande Ginste, L.; Le Goffic, R.; et al. Regulation of kynurenine biosynthesis during influenza virus infection. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, J.B.; Wahl, A.S.; Freund, S.; Genzel, Y.; Reichl, U. Metabolic effects of influenza virus infection in cultured animal cells: Intra- and extracellular metabolite profiling. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, R.; Genzel, Y.; Wetzel, M.; Reichl, U. Effect of influenza virus infection on key metabolic enzyme activities in mdck cells. BMC Proc. 2011, 5 (Suppl. 8), P129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.K.; Lu, Q.B.; Chen, W.W.; Xu, W.; Liu, R.; Zhang, S.F.; Du, J.; Li, H.; Yao, K.; Zhai, D.; et al. Arginine deficiency is involved in thrombocytopenia and immunosuppression in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Tang, Q.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Li, B. Serum biomarker identification by mass spectrometry in acute aortic dissection. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ma, P.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Cho, K.; Xue, S.; et al. Plasma amino acid profile in patients with aortic dissection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Kang, A.; Peng, L.; Xie, T.; Ji, J.; Zhou, W.; Shan, J.; Di, L. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry based plasma metabolomics of h1n1-induced inflammation in mice and intervention with flos lonicerae japonica-fructus forsythiae herb pair. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1092, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklund, S.; Johansson, E.; Sjostrom, L.; Mellerowicz, E.J.; Edlund, U.; Shockcor, J.P.; Gottfries, J.; Moritz, T.; Trygg, J. Visualization of gc/tof-ms-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using opls class models. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Sinelnikov, I.V.; Han, B.; Wishart, D.S. Metaboanalyst 3.0--making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W251–W257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. Kegg for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D109–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. Data, information, knowledge and principle: Back to metabolism in kegg. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D199–D205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qiu, X.; Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Meng, C.; Liao, Y.; Tan, L.; Ding, Z.; Liu, X.; Ding, C. Deep sequencing-based transcriptome profiling reveals avian interferon-stimulated genes and provides comprehensive insight into newcastle disease virus-induced host responses. Viruses 2018, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. Hmdb 3.0—The human metabolome database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, H. Influenza virus pathogenicity regulated by host cellular proteases, cytokines and metabolites, and its therapeutic options. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2015, 91, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tumpey, T.M.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Palese, P.; Swayne, D.E.; Basler, C.F. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of influenza viruses with genes from the 1918 pandemic virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3166–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, A.C.; Hilmer, K.M.; Zickovich, J.M.; Obar, J.J. Inflammatory response of mast cells during influenza a virus infection is mediated by active infection and rig-i signaling. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4676–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, J.G.; Hoek, J.B. Hexokinase ii the integration of energy metabolism and control of apoptosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 1535–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.; Cho, S.Y.; Lee, Y.S. Construction of a transcriptome-driven network at the early stage of infection with influenza a h1n1 in human lung alveolar epithelial cells. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, A.S.; Stairiker, C.J.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Monzon-Casanova, E.; Lukasiak, S.; Mueller, Y.M.; Stubbs, A.P.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Turner, M.; Katsikis, P.D. Transcriptome analysis of infected and bystander type 2 alveolar epithelial cells during influenza a virus infection reveals in vivo wnt pathway downregulation. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01325-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, K.P.; Lee, S.M.; Cheung, C.Y.; Mao, H.; Lai, A.K.; Chan, R.W.; Chan, M.C.; Tu, W.; Guan, Y.; Lau, Y.L.; et al. H5n1 influenza virus-induced mediators upregulate rig-i in uninfected cells by paracrine effects contributing to amplified cytokine cascades. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, E.A.; Swick, A.; Yin, J. Rapid induction and persistence of paracrine-induced cellular antiviral states arrest viral infection spread in a549 cells. Virology 2016, 496, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zheng, D.; Lee, Y.H.; Chan, T.K.; Kumar, Y.; Ho, W.E.; Chen, J.Z.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Ong, C.N. Metabolomics investigation reveals metabolite mediators associated with acute lung injury and repair in a murine model of influenza pneumonia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, N.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Lucio, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Chen, G.; Cai, Z. Gc/ms-based metabolomics reveals fatty acid biosynthesis and cholesterol metabolism in cell lines infected with influenza a virus. Talanta 2010, 83, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Kishton, R.J.; Rathmell, J. A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tisoncik-Go, J.; Gasper, D.J.; Kyle, J.E.; Eisfeld, A.J.; Selinger, C.; Hatta, M.; Morrison, J.; Korth, M.J.; Zink, E.M.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. Integrated omics analysis of pathogenic host responses during pandemic h1n1 influenza virus infection: The crucial role of lipid metabolism. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.C.; Quehenberger, O.; Oshansky, C.M.; Suen, R.; Armando, A.M.; Treuting, P.M.; Thomas, P.G.; Dennis, E.A.; Aderem, A. Lipidomic profiling of influenza infection identifies mediators that induce and resolve inflammation. Cell 2013, 154, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, M.L.; Wu, W.H.; Lalime, E.N.; Lorenzo, M.E.; Klein, S.L.; Pekosz, A. Palmitoylation of the influenza a virus m2 protein is not required for virus replication in vitro but contributes to virus virulence. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8655–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, M.; Kandasamy, P.; Nagashima, Y.; Posey, J.; Hartshorn, K.; Woodland, D.; Voelker, D.R. Phosphatidylglycerol suppresses influenza a virus infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metallo, C.M.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Metabolism strikes back: Metabolic flux regulates cell signaling. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2717–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.R.; Chekeni, F.B.; Trampont, P.C.; Lazarowski, E.R.; Kadl, A.; Walk, S.F.; Park, D.; Woodson, R.I.; Ostankovich, M.; Sharma, P.; et al. Nucleotides released by apoptotic cells act as a find-me signal to promote phagocytic clearance. Nature 2009, 461, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnstock, G.; Brouns, I.; Adriaensen, D.; Timmermans, J.P. Purinergic signaling in the airways. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 834–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idzko, M.; Ferrari, D.; Eltzschig, H.K. Nucleotide signalling during inflammation. Nature 2014, 509, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levine, A.J.; Puzio-Kuter, A.M. The control of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Science 2010, 330, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amie, S.M.; Noble, E.; Kim, B. Intracellular nucleotide levels and the control of retroviral infections. Virology 2013, 436, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Li, X.; Attri, K.S.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Herring, L.E.; Asara, J.M.; Lei, Y.L.; Singh, P.K.; Gao, C.; et al. O-glcnac transferase links glucose metabolism to mavs-mediated antiviral innate immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 791–803 e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, J.D.; White, E. Autophagy and metabolism. Science 2010, 330, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeffner, F.; Woods, P.S.; Davis, I.C. Activation of a1-adenosine receptors promotes leukocyte recruitment to the lung and attenuates acute lung injury in mice infected with influenza a/wsn/33 (h1n1) virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10214–10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.D.; Hu, X.; Ko, E.J.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.T.; Orr, M.; Fernandes, J.; Uppal, K.; Kang, S.M.; Jones, D.P.; et al. Metabolic pathways of lung inflammation revealed by high-resolution metabolomics (hrm) of h1n1 influenza virus infection in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R906–R916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, A.; Toy, T.; Rothenfusser, S.; Robson, N.; Vorac, J.; Dauer, M.; Stuplich, M.; Endres, S.; Cebon, J.; Maraskovsky, E.; et al. P2y receptor signaling regulates phenotype and ifn-alpha secretion of human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood 2008, 111, 3062–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuss-Duerkop, S.K.; Wang, J.; Mena, I.; White, K.; Metreveli, G.; Sakthivel, R.; Mata, M.A.; Munoz-Moreno, R.; Chen, X.; Krammer, F.; et al. Influenza virus differentially activates mtorc1 and mtorc2 signaling to maximize late stage replication. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoki, K.; Kim, J.; Guan, K.L. Ampk and mtor in cellular energy homeostasis and drug targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chi, H. Ampk helps t cells survive nutrient starvation. Immunity 2015, 42, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagih, J.; Coulombe, F.; Vincent, E.E.; Dupuy, F.; Galicia-Vazquez, G.; Yurchenko, E.; Raissi, T.C.; van der Windt, G.J.; Viollet, B.; Pearce, E.L.; et al. The energy sensor ampk regulates t cell metabolic adaptation and effector responses in vivo. Immunity 2015, 42, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayinde, D.; Casartelli, N.; Schwartz, O. Restricting hiv the samhd1 way: Through nucleotide starvation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombe, F.; Jaworska, J.; Verway, M.; Tzelepis, F.; Massoud, A.; Gillard, J.; Wong, G.; Kobinger, G.; Xing, Z.; Couture, C.; et al. Targeted prostaglandin e2 inhibition enhances antiviral immunity through induction of type i interferon and apoptosis in macrophages. Immunity 2014, 40, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Legge, K.; Perlman, S. Age-related increases in pgd(2) expression impair respiratory dc migration, resulting in diminished t cell responses upon respiratory virus infection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4921–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Time (h) | Metabolites | Formula | M/Z | Mr | HMDB | PubChem | KEGG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1-Methylnicotinamide | C7H9N2O | 137.07 | 137.1 | HMDB0000699 | 457 | C02918 |
| 2 | 2 | Pantothenate | C9H17NO5 | 218.1035 | 219.2 | HMDB0000210 | 988 | C00864 |
| 3 | 2 | Sorbitol | C6H14O6 | 181.0722 | 182.1 | HMDB0000247 | 5780 | C00794 |
| 4 | 2 | L-Glutamine | C5H10N2O3 | 147.0754 | 146.1 | HMDB0000641 | 5961 | C00064 |
| 5 | 2 | S-Methyl-5’-thioadenosine | C11H15N5O3S | 298.0959 | 297.3 | HMDB0001173 | 439176 | C00170 |
| 6 | Oxidized glutathione | C20H32N6O12S2 | 613.1575 | 612.6 | HMDB0003337 | 975 | C00127 | |
| 7 | 2 | LysoPC (18:1(9Z)) | C26H52NO7P | 522.3537 | 521.7 | HMDB0002815 | 16081932 | C04230 |
| 8 | 2 | Taurine | C2H7NO3S | 126.0208 | 125.1 | HMDB0000251 | 1123 | C00245 |
| 9 | 2 | Phosphorylcholine | C5H15NO4P | 184.0724 | 184.2 | HMDB0001565 | 1014 | C00588 |
| 10 | 2 | Uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine | C17H27N3O17P2 | 608.087 | 607.4 | HMDB0000290 | 445675 | C00043 |
| 11 | 2 | LysoPC (16:0) | C24H50NO7P | 496.3379 | 495.6 | HMDB0010382 | 460602 | C04230 |
| 12 | 2 | L-Glutamic acid | C5H9NO4 | 148.0596 | 147.1 | HMDB0000148 | 33032 | C00025 |
| 13 | 2 | Pyroglutamic acid | C5H7NO3 | 130.0488 | 129.1 | HMDB0000267 | 7405 | C01879 |
| 14 | 2 | Niacinamide (Niacinamide) | C6H6N2O | 123.0541 | 122.1 | HMDB0001406 | 936 | C00153 |
| 15 | 2 | Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) | C10H14N5O7P | 348.0695 | 347.2 | HMDB0000045 | 6083 | C00020 |
| 16 | 2 | Inosine | C10H12N4O5 | 269.0871 | 268.2 | HMDB0000195 | 6021 | C00294 |
| 17 | 2 | Hypoxanthine | C5H4N4O | 137.0446 | 136.1 | HMDB0000157 | 790 | C00262 |
| 18 | 2 | Adenine | C5H5N5 | 136.0609 | 135.1 | HMDB0000034 | 190 | C00147 |
| 19 | 2 | Erucamide | C18H19NO4 | 338.3408 | 313.3 | HMDB0029365 | 5280537 | C02717 |
| 20 | 2 | Prostaglandin H2 | C20H32O5 | 351.2177 | 352.5 | HMDB0001381 | 445049 | C00427 |
| 21 | 2 | Oxoadipic acid | C6H8O5 | 141.0171 | 160.1 | HMDB0000225 | 71 | C00322 |
| 22 | 2 | D-Mannose | C6H12O6 | 179.0562 | 180.1 | HMDB0000169 | 18950 | C00159 |
| 23 | 2 | PG (16:0/18:1(9Z)) | C40H77O10P | 747.5194 | 749.0 | HMDB0010574 | 52941750 | / |
| 24 | 2 | Pentadecanoic acid | C15H30O2 | 241.2175 | 242.4 | HMDB0000826 | 13849 | C16537 |
| 25 | 5 | Uridine | C9H12N2O6 | 245.0758 | 244.2 | HMDB0000296 | 6029 | C00299 |
| 26 | 5 | L-Carnitine | C7H15NO3 | 162.1115 | 161.2 | HMDB0000062 | 2724480 | C00318 |
| 27 | 5 | Deoxyadenosine | C10H13N5O3 | 252.1082 | 251.2 | HMDB0000101 | 13730 | C00559 |
| 28 | 5 | PC (16:0/16:0) | C40H80NO8P | 778.536 | 734.0 | HMDB0000564 | 452110 | C00157 |
| 29 | 5 | 2-Hydroxyadenine | C5H5N5O | 152.0557 | 151.1 | HMDB0000403 | 76900 | / |
| 30 | 5 | Uracil | C4H4N2O2 | 111.0198 | 112.1 | HMDB0000300 | 1174 | C00106 |
| 31 | 5 | MG (0:0/16:0/0:0) | C19H38O4 | 331.2837 | 330.5 | HMDB0011533 | 123409 | / |
| 32 | 5 | Adenosine | C10H13N5O4 | 268.1033 | 267.2 | HMDB0000050 | 60961 | C00212 |
| 33 | 5 | D-Proline | C5H9NO2 | 116.0694 | 115.1 | HMDB0003411 | 8988 | C00763 |
| 34 | 5 | Nicotinate (Nicotinic acid) | C6H5NO2 | 124.0383 | 123.1 | HMDB0001488 | 938 | C00253 |
| 35 | 5 | PC (18:0/18:1(9Z)) (SOPC) | C44H86NO8P | 832.582 | 788.1 | HMDB0008038 | 24778825 | C00157 |
| 36 | 5 | L-Acetylcarnitine | C9H17NO4 | 204.1221 | 203.2 | HMDB0000201 | 1 | C02571 |
| 37 | 5 | Cytidine | C9H13N3O5 | 244.0919 | 243.2 | HMDB0000089 | 6175 | C00475 |
| 38 | 5 | Cytosine | C4H5N3O | 112.0494 | 111.1 | HMDB0000630 | 597 | C00380 |
| 39 | 5 | Guanosine | C10H13N5O5 | 284.098 | 283.2 | HMDB0000133 | 6802 | C00387 |
| 40 | 5 | Betaine | C5H11NO2 | 118.0852 | 117.1 | HMDB0000043 | 247 | C00719 |
| 41 | 8 | Acetylcholine | C7H16NO2 | 146.1164 | 146.2 | HMDB0000895 | 187 | C01996 |
| 42 | 8 | 2-Ethoxyethanol | C4H10O2 | 151.0955 | 90.1 | HMDB0031213 | 8076 | C14687 |
| 43 | 8 | Palmitoleic acid | C16H30O2 | 253.2176 | 254.4 | HMDB0003229 | 445638 | C08362 |
| 44 | 8 | Oleic acid | C18H34O2 | 281.2488 | 282.5 | HMDB0000207 | 445639 | C00712 |
| 45 | 8 | Arachidonic acid | C20H32O2 | 303.2332 | 304.5 | HMDB0001043 | 444899 | C00219 |
| 46 | 8 | Myristic acid | C14H28O2 | 227.2022 | 228.4 | HMDB0000806 | 11005 | C06424 |
| 47 | 8 | Heptadecanoic acid | C17H34O2 | 269.2486 | 270.5 | HMDB0002259 | 10465 | / |
| 48 | 8 | Nervonic acid | C24H46O2 | 365.3424 | 366.6 | HMDB0002368 | 5281120 | C08323 |
| 49 | 8 | Palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | 255.2333 | 256.4 | HMDB0000220 | 985 | C00249 |
| 50 | 8 | Acamprosate | C5H11NO4S | 180.0335 | 181.2 | HMDB0014797 | 71158 | / |
| No. | Name of Pathway | Total | Expected | Hits | −log10 p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Purine metabolism | 92 | 1.6053 | 8 | 8.9037 |
| 2 | Pyrimidine metabolism | 60 | 1.0469 | 5 | 5.6818 |
| 3 | Nitrogen metabolism | 39 | 0.68052 | 4 | 5.4648 |
| 4 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 39 | 0.68052 | 4 | 5.4648 |
| 5 | Fatty acid biosynthesis | 49 | 0.85501 | 4 | 4.6447 |
| 6 | D-Glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism | 11 | 0.19194 | 2 | 4.2132 |
| 7 | Glutathione metabolism | 38 | 0.66307 | 3 | 3.6014 |
| 8 | Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 44 | 0.76776 | 3 | 3.2223 |
| 9 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 24 | 0.41878 | 2 | 2.7426 |
| 10 | Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 27 | 0.47113 | 2 | 2.5348 |
| 11 | beta-Alanine metabolism | 28 | 0.48857 | 2 | 2.4715 |
| 12 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | 62 | 1.0818 | 3 | 2.387 |
| 13 | Arginine and proline metabolism | 77 | 1.3436 | 3 | 1.9036 |
| 14 | Galactose metabolism | 41 | 0.71541 | 2 | 1.8366 |
| 15 | Fructose and mannose metabolism | 48 | 0.83756 | 2 | 1.5918 |
| 16 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 20 | 0.34898 | 1 | 1.2115 |
| 17 | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis | 75 | 1.3087 | 2 | 0.97063 |
| 18 | Fatty acid elongation in mitochondria | 27 | 0.47113 | 1 | 0.96782 |
| 19 | alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | 29 | 0.50602 | 1 | 0.91228 |
| 20 | Lysine biosynthesis | 32 | 0.55837 | 1 | 0.83755 |
| 21 | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 88 | 1.5355 | 2 | 0.77921 |
| 22 | Butanoate metabolism | 40 | 0.69796 | 1 | 0.67663 |
| 23 | Histidine metabolism | 44 | 0.76776 | 1 | 0.61188 |
| 24 | Primary bile acid biosynthesis | 47 | 0.82011 | 1 | 0.56861 |
| 25 | Lysine degradation | 47 | 0.82011 | 1 | 0.56861 |
| 26 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 48 | 0.83756 | 1 | 0.55507 |
| 27 | Fatty acid metabolism | 50 | 0.87246 | 1 | 0.52922 |
| 28 | Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 56 | 0.97715 | 1 | 0.46024 |
| 29 | Tryptophan metabolism | 79 | 1.3785 | 1 | 0.27865 |
| 30 | Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism | 104 | 1.8147 | 1 | 0.16712 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, X.; Zhang, K.; Min, J.; Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Ding, C.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Metabolomic Analysis of Influenza A Virus A/WSN/1933 (H1N1) Infected A549 Cells during First Cycle of Viral Replication. Viruses 2019, 11, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111007
Tian X, Zhang K, Min J, Chen C, Cao Y, Ding C, Liu W, Li J. Metabolomic Analysis of Influenza A Virus A/WSN/1933 (H1N1) Infected A549 Cells during First Cycle of Viral Replication. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111007
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Xiaodong, Kun Zhang, Jie Min, Can Chen, Ying Cao, Chan Ding, Wenjun Liu, and Jing Li. 2019. "Metabolomic Analysis of Influenza A Virus A/WSN/1933 (H1N1) Infected A549 Cells during First Cycle of Viral Replication" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111007
APA StyleTian, X., Zhang, K., Min, J., Chen, C., Cao, Y., Ding, C., Liu, W., & Li, J. (2019). Metabolomic Analysis of Influenza A Virus A/WSN/1933 (H1N1) Infected A549 Cells during First Cycle of Viral Replication. Viruses, 11(11), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111007





