The Morphology and Assembly of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Viruses and Infection
2.3. Virus Titration by Fluorescent Focal Unit (FFU) Assay
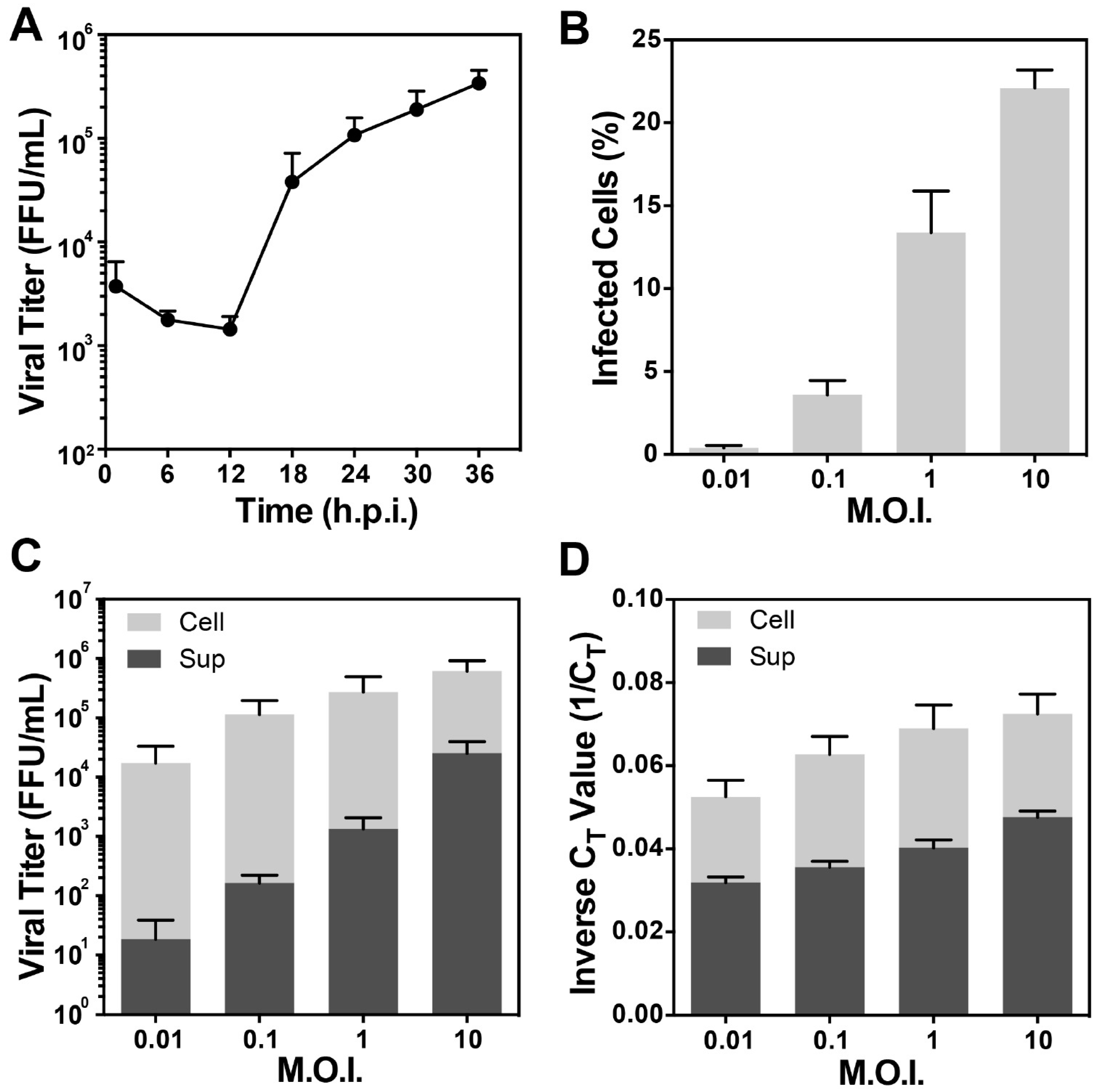
2.4. One-Step Growth Curve
2.5. Detection of RSV-Infected Cells by Flow Cytometry
2.6. RSV RNA Detection by Real Time RT-PCR Assay
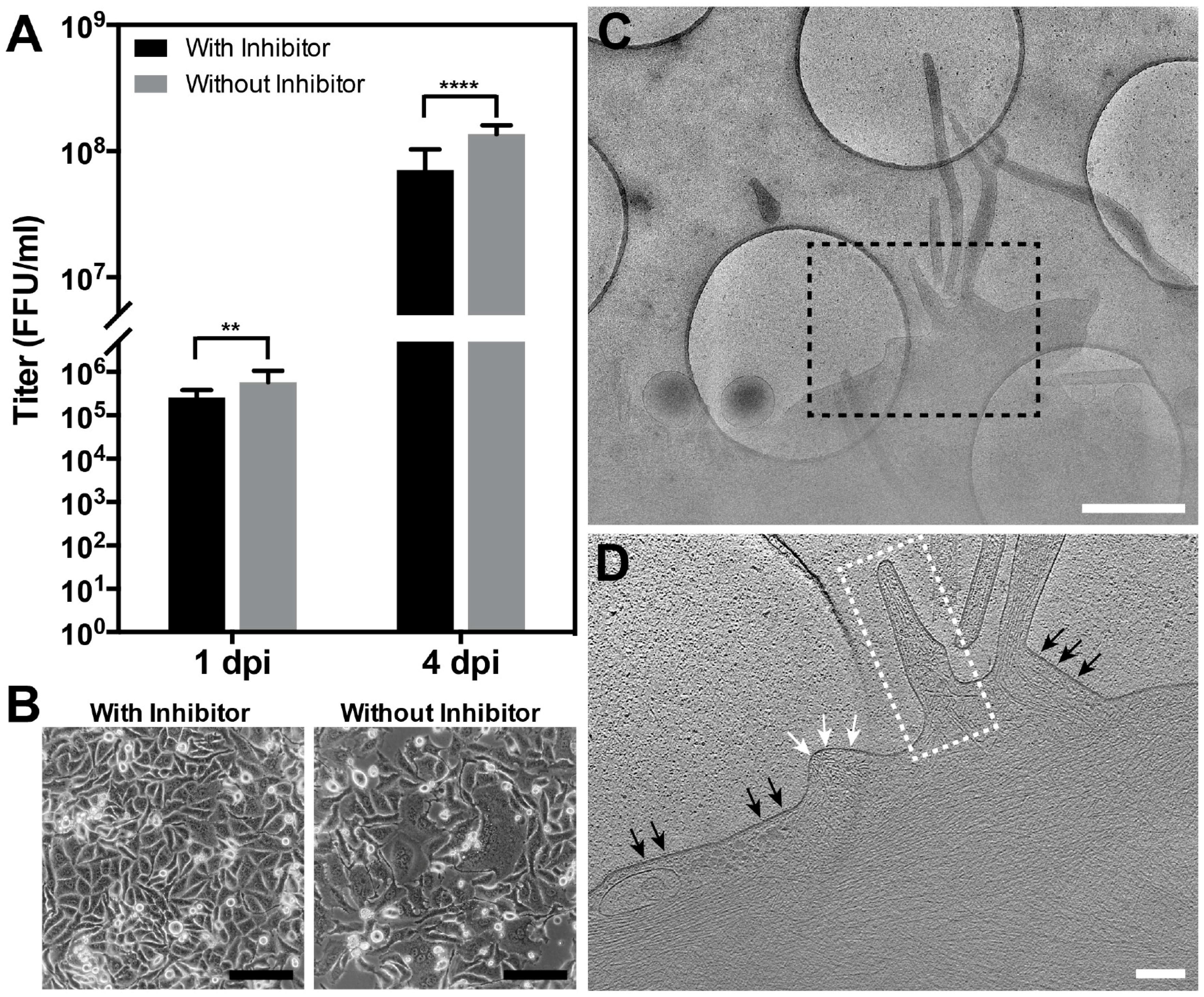
2.7. RSV Infection in the Presence of the Fusion Inhibitor BMS-433771
2.8. RSV Morphology Characterization
2.9. Thin Sectioning TEM of RSV-Infected Polarized NHBE Cells
2.10. Cryo-EM/ET Sample Preparation, Data Collection, and Image Processing
2.11. Graphs and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
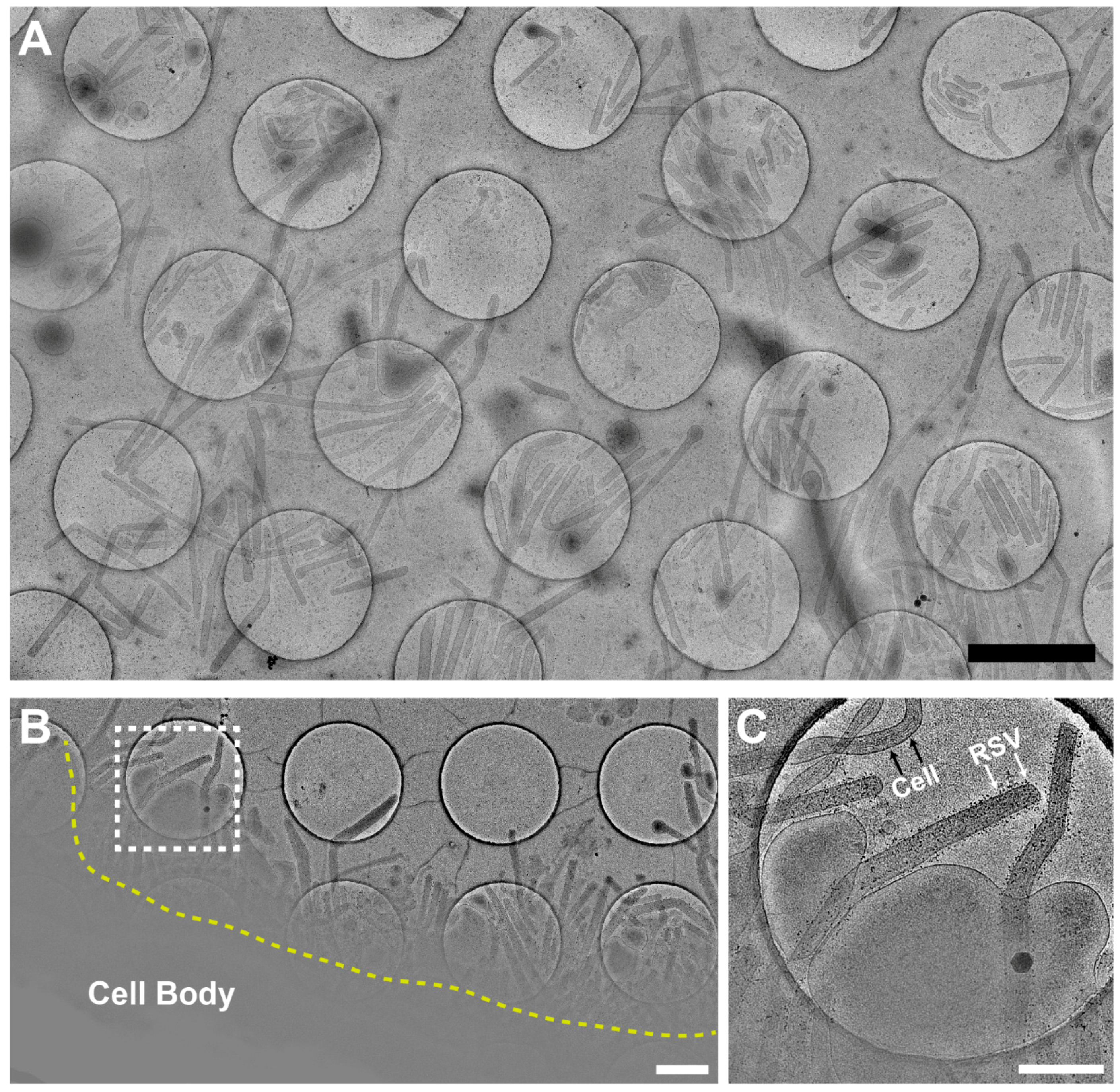
3.1. Optimization of the Conditions for Cryo-EM/ET Sample Preparation
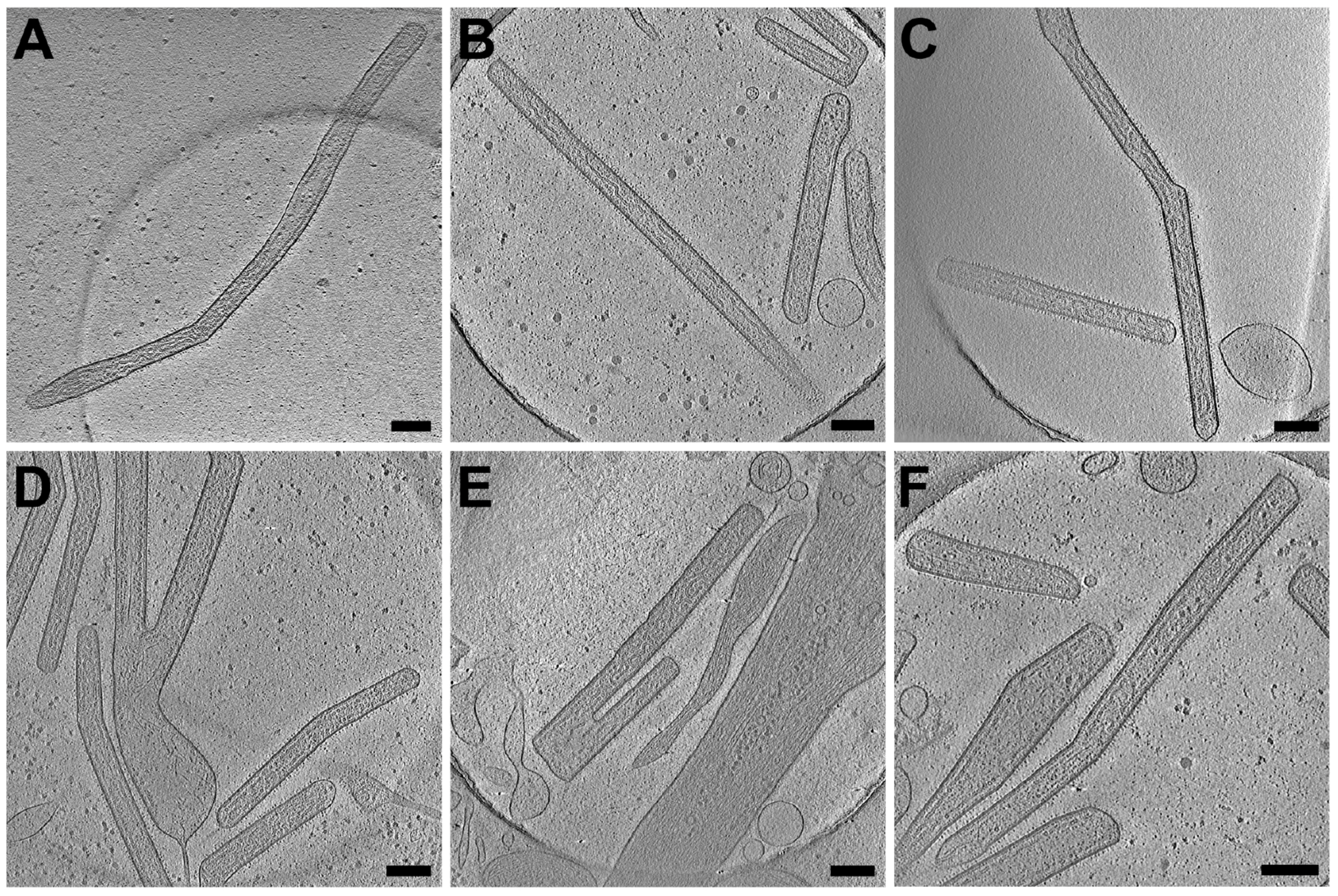
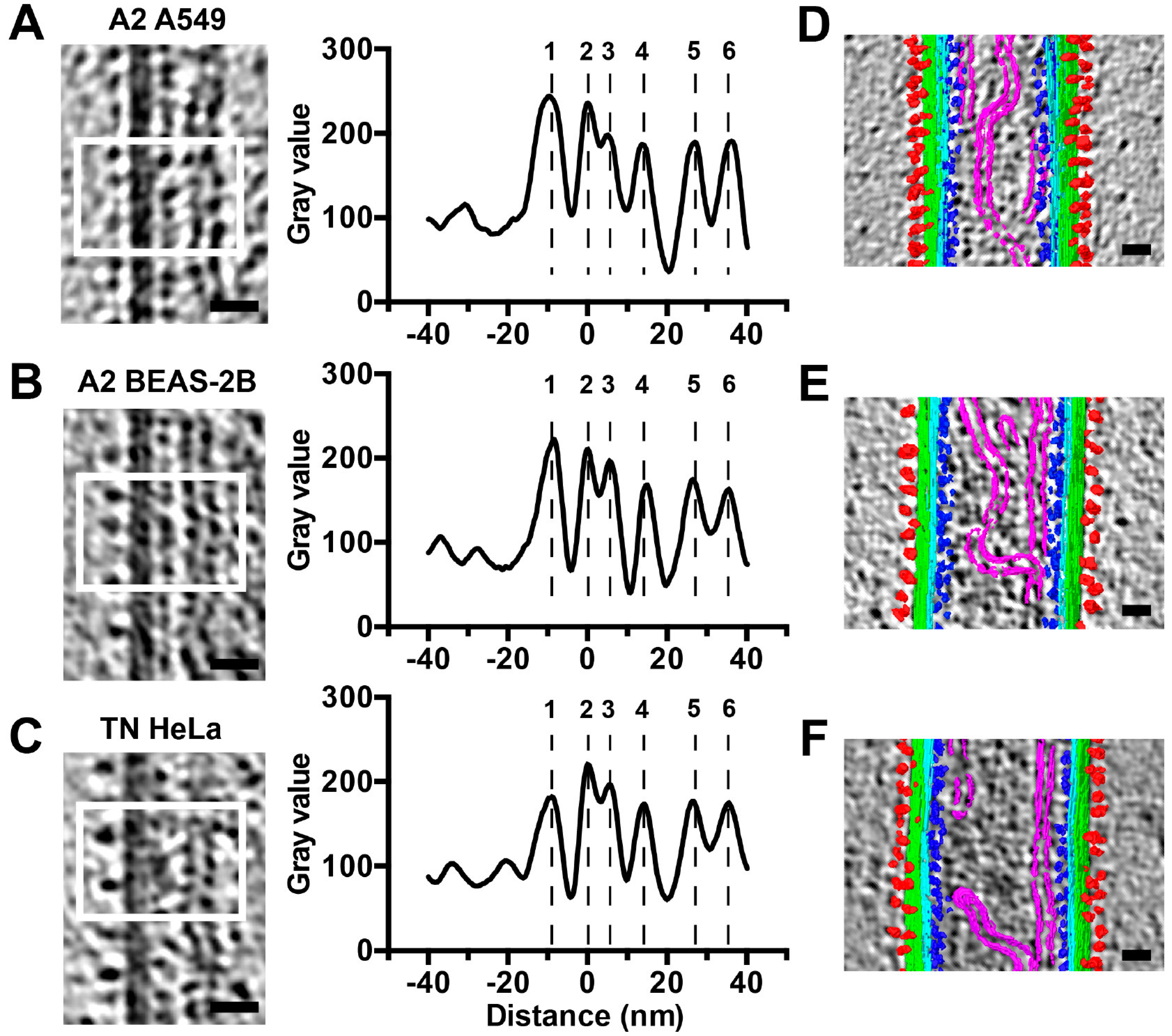
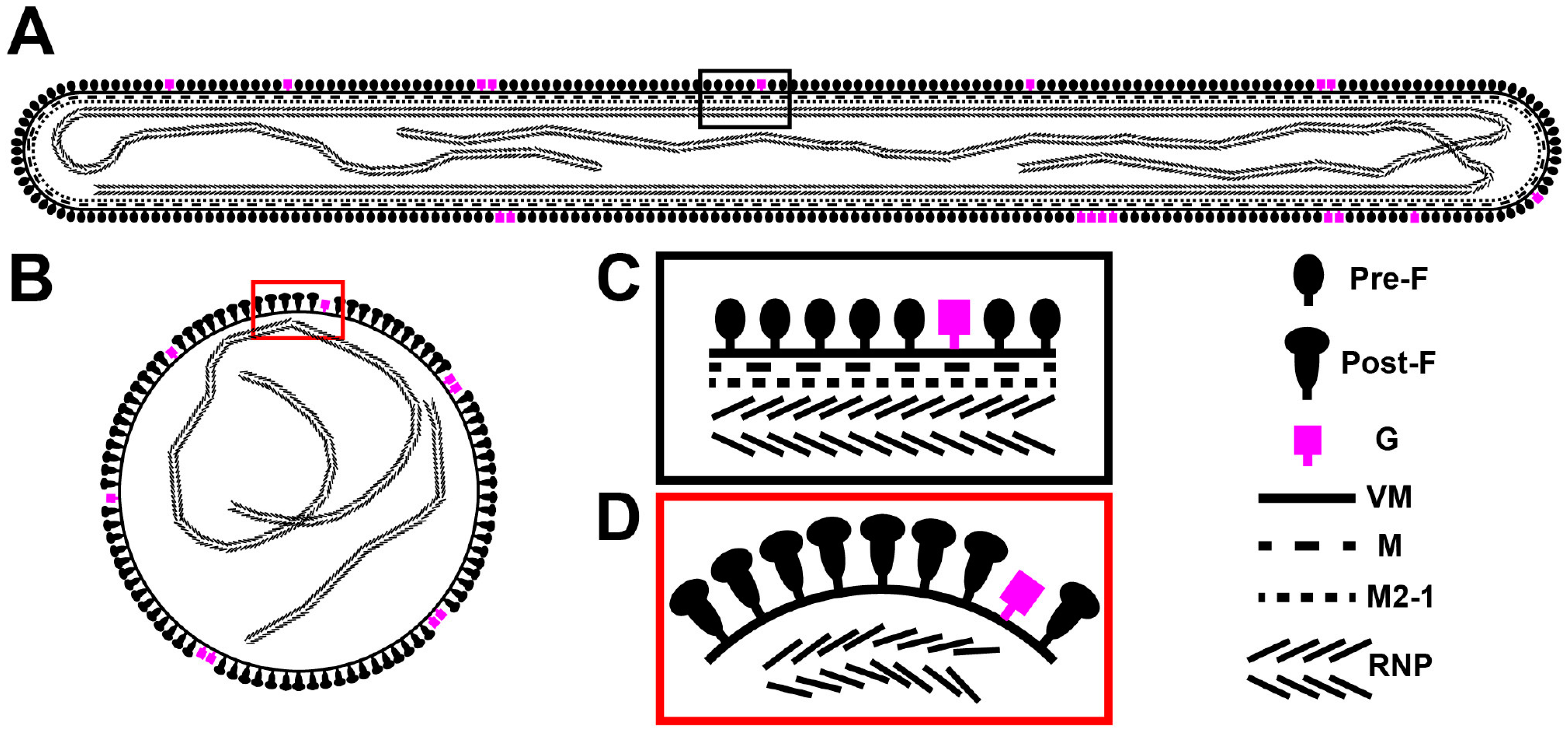
3.2. RSV Is Filamentous Independent of Cell Line
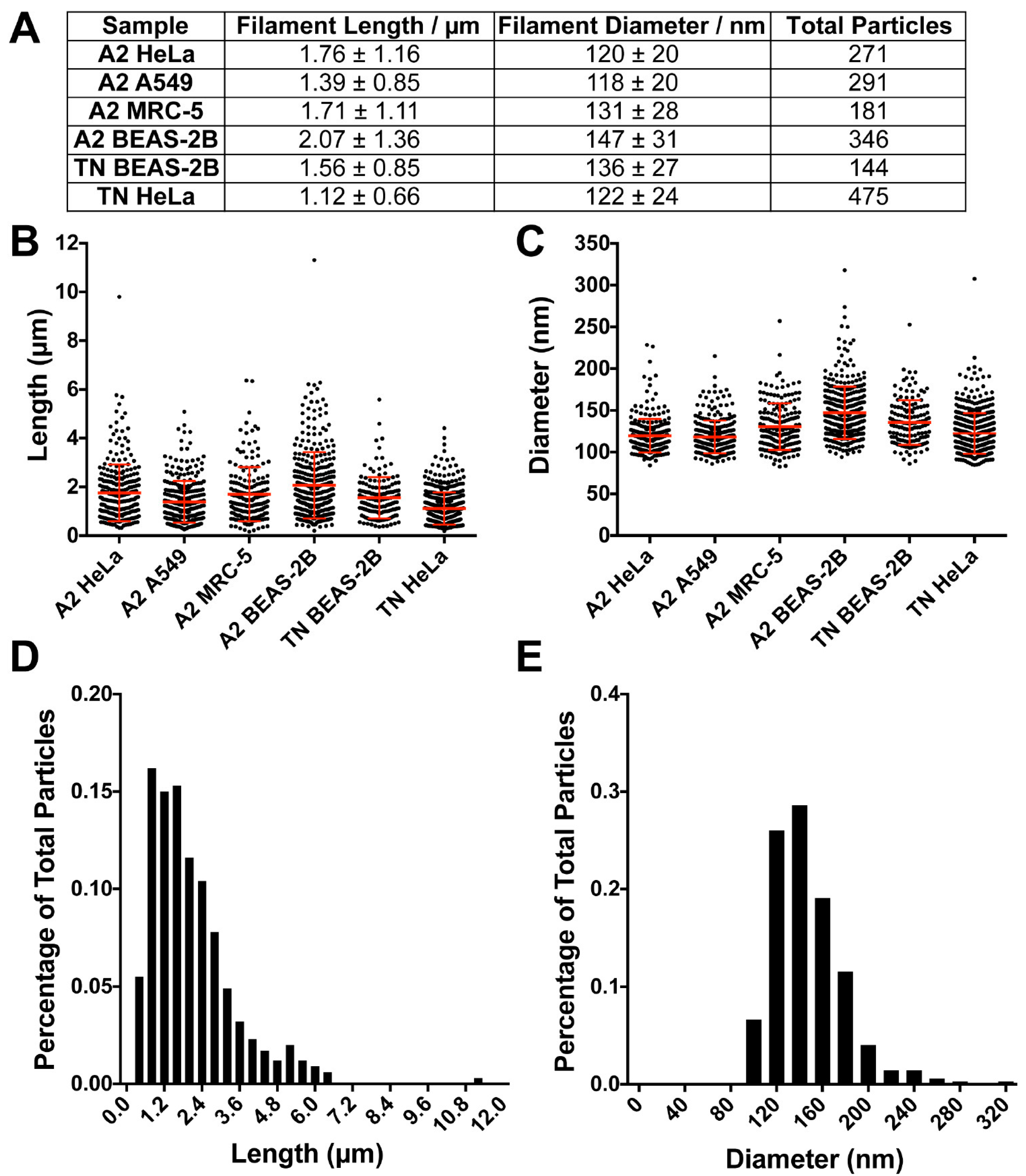
3.3. RSV Morphology Quantification
3.4. RSV Morphology Is Filamentous from RSV-Infected Polarized NHBE Cells
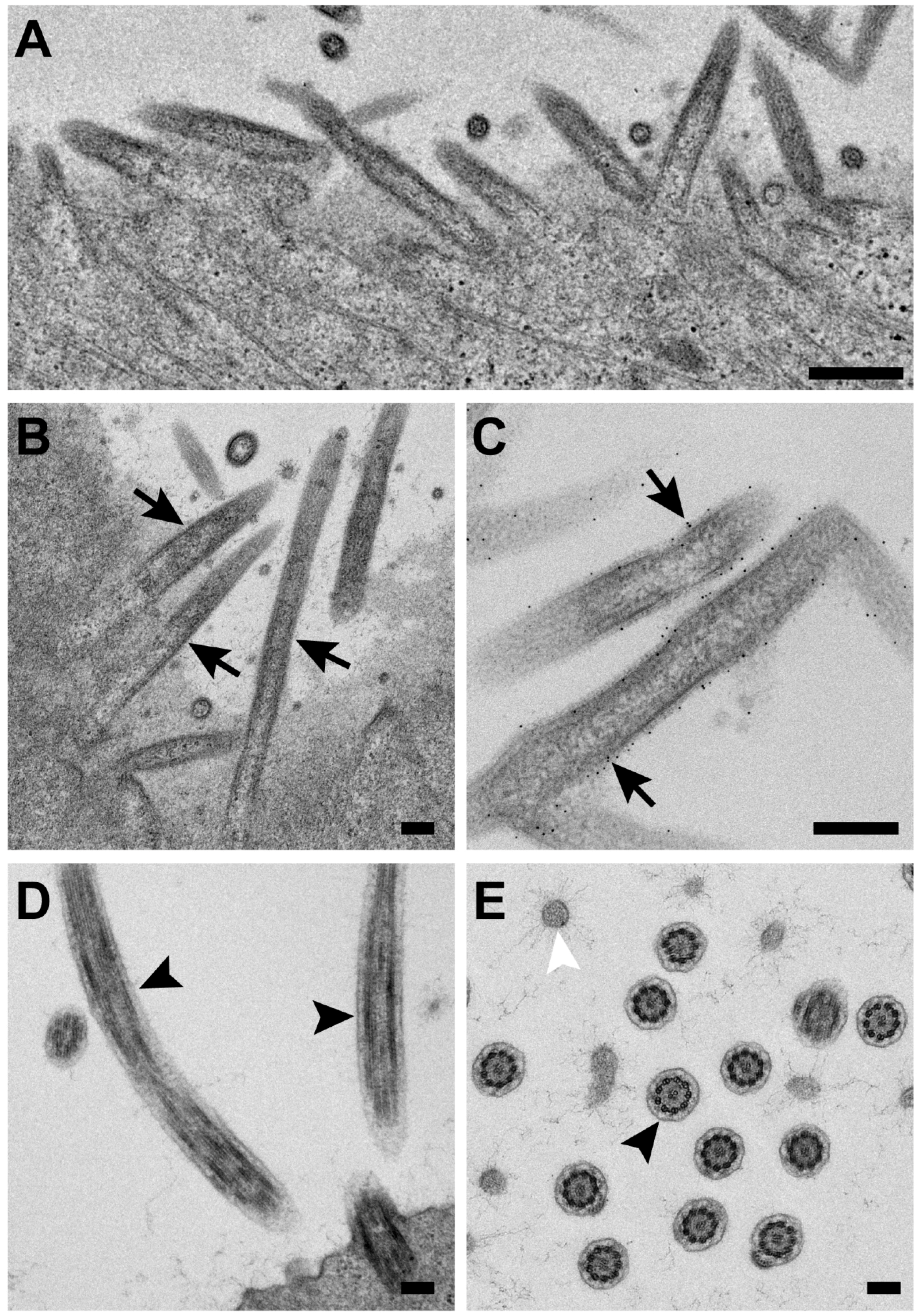
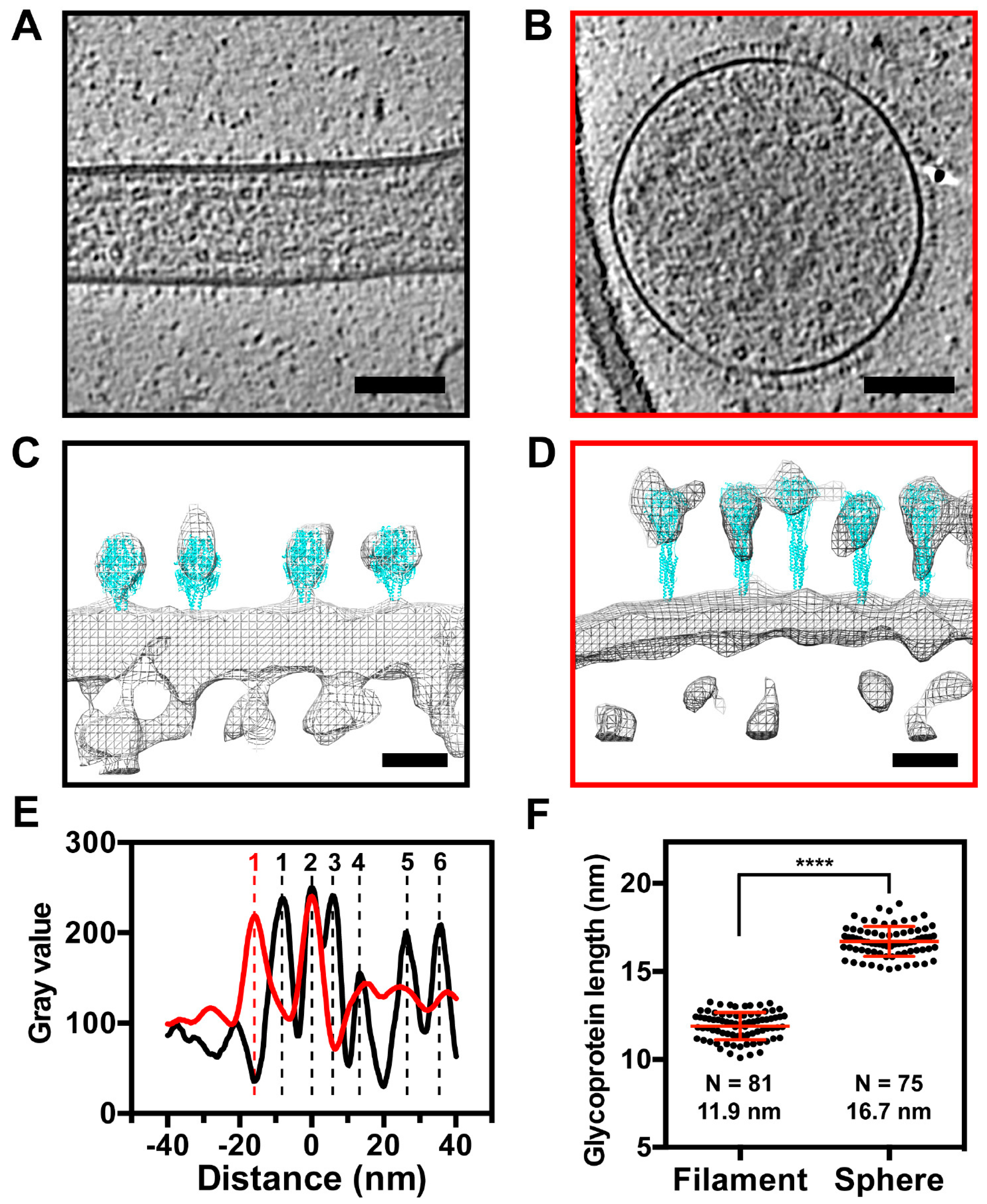
3.5. The RSV F Glycoprotein Is in Prefusion form on Filamentous Particles and in Postfusion form on Spherical Particles
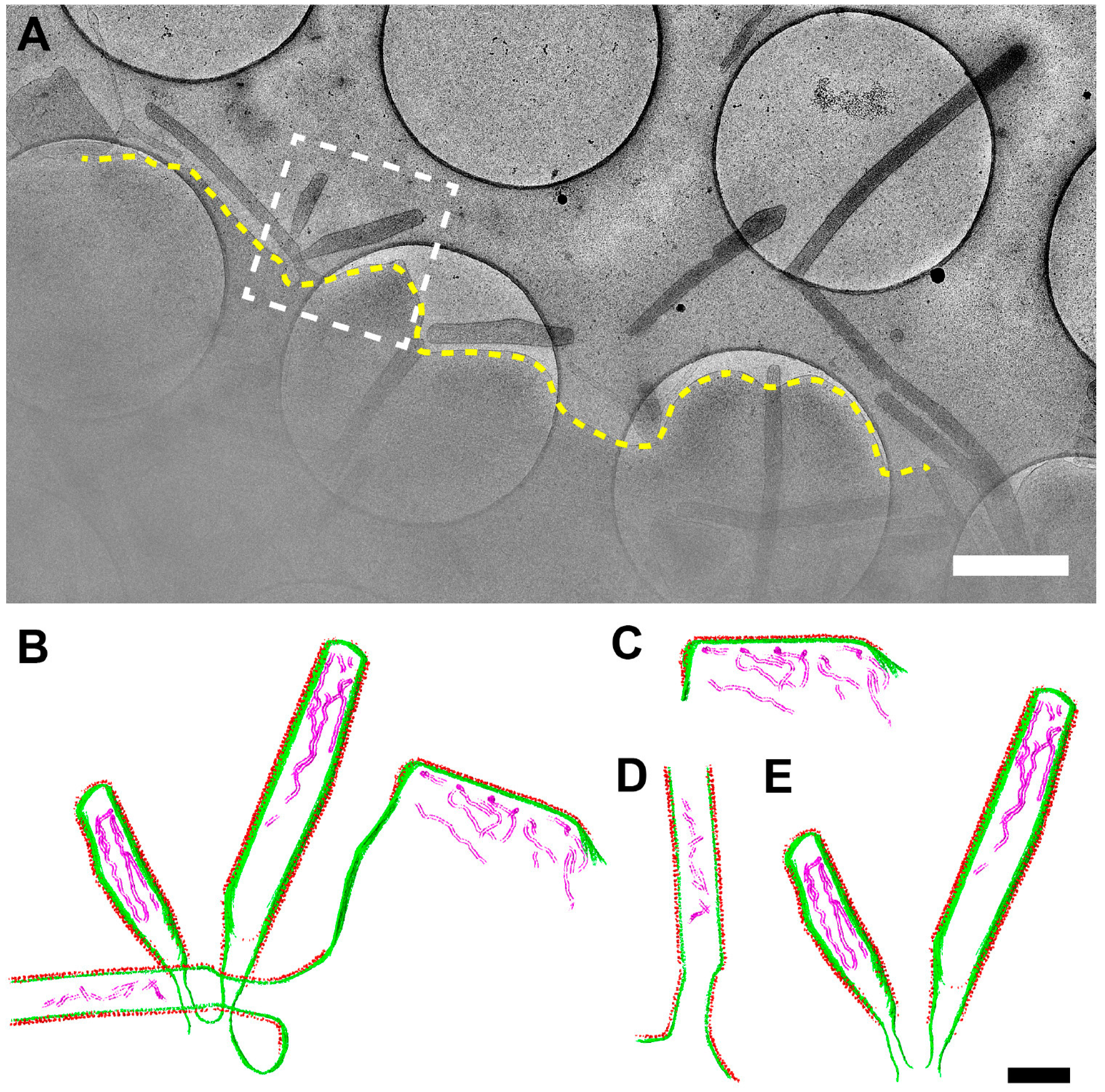
3.6. RSV Assembly Steps Revealed by Cryo-ET
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamb, R.A.; Parks, G.D. Paramyxoviridae: The viruses and their replication. In Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 1449–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.J.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Nokes, D.J.; Rappuoli, R.; Roca, A.; Graham, B.S. Strategic priorities for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine development. Vaccine 2013, 31, B209–B215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.; Drews, S.J.; Marchant, D.J. Respiratory syncytial virus: Infection, detection, and new options for prevention and treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 277–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; Bao, Y.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Beer, M.; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Bochnowski, A.; Briese, T.; Bukreyev, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the order mononegavirales: Update 2017. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawar, R.G.; Duquerroy, S.; Vonrhein, C.; Varela, P.F.; Damier-Piolle, L.; Castagne, N.; MacLellan, K.; Bedouelle, H.; Bricogne, G.; Bhella, D.; et al. Crystal structure of a nucleocapsid-like nucleoprotein-rna complex of respiratory syncytial virus. Science 2009, 326, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, S.E.; Duquerroy, S.; Galloux, M.; Loney, C.; Conner, E.; Eleouet, J.F.; Rey, F.A.; Bhella, D. The respiratory syncytial virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex forms a left-handed helical nucleocapsid. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearns, R.; Collins, P.L. Role of the M2-1 transcription antitermination protein of respiratory syncytial virus in sequential transcription. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5852–5864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Jans, D.A.; Bardin, P.G.; Meanger, J.; Mills, J.; Ghildyal, R. Association of respiratory syncytial virus m protein with viral nucleocapsids is mediated by the M2-1 protein. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8863–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, G.; Holl, J.M.; Williams, G.M.; Alonas, E.; Vanover, D.; Lifland, A.W.; Gudheti, M.; Guerrero-Ferreira, R.C.; Nair, V.; Yi, H.; et al. Structural analysis of respiratory syncytial virus reveals the position of M2-1 between the matrix protein and the ribonucleoprotein complex. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7602–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljeroos, L.; Krzyzaniak, M.A.; Helenius, A.; Butcher, S.J. Architecture of respiratory syncytial virus revealed by electron cryotomography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11133–11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.L.; Castagne, N.; Dubosclard, V.; Noinville, S.; Koch, E.; Moudjou, M.; Henry, C.; Bernard, J.; Yeo, R.P.; Eleouet, J.F. The respiratory syncytial virus m2-1 protein forms tetramers and interacts with RNA and p in a competitive manner. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6363–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, S.J.; Ariza, A.; Richard, C.A.; Kyle, H.F.; Dods, R.L.; Blondot, M.L.; Wu, W.; Trincao, J.; Trinh, C.H.; Hiscox, J.A.; et al. Crystal structure of the essential transcription antiterminator M2-1 protein of human respiratory syncytial virus and implications of its phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, M.S.; Brazas, R.M.; Holtzman, M.J. Respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural proteins NS1 and NS2 mediate inhibition of Stat2 expression and α/β interferon responsiveness. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9315–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedan, S.; Musiyenko, A.; Barik, S. Respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural proteins decrease levels of multiple members of the cellular interferon pathways. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9682–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitko, V.; Shulyayeva, O.; Mazumder, B.; Musiyenko, A.; Ramaswamy, M.; Look, D.C.; Barik, S. Nonstructural proteins of respiratory syncytial virus suppress premature apoptosis by an NF-κb-dependent, interferon-independent mechanism and facilitate virus growth. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.S.; Modjarrad, K.; McLellan, J.S. Novel antigens for RSV vaccines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Todd, S.O.; Chirkova, T.; Barnum, T.R.; Gaston, K.A.; Haynes, L.M.; Tripp, R.A.; Moore, M.L.; Anderson, L.J. An anti-G protein monoclonal antibody treats RSV disease more effectively than an anti-F monoclonal antibody in BALB/c mice. Virology 2015, 483, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirkova, T.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gaston, K.A.; Malik, F.M.; Trau, S.P.; Oomens, A.G.; Anderson, L.J. Respiratory syncytial virus G protein CX3C motif impairs human airway epithelial and immune cell responses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13466–13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.S. Vaccines against respiratory syncytial virus: The time has finally come. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3535–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwuta, J.O.; Chen, M.; Modjarrad, K.; Joyce, M.G.; Kanekiyo, M.; Kumar, A.; Yassine, H.M.; Moin, S.M.; Killikelly, A.M.; Chuang, G.Y.; et al. Prefusion f-specific antibodies determine the magnitude of RSV neutralizing activity in human sera. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 309ra162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostad, C.A.; Stobart, C.C.; Gilbert, B.E.; Pickles, R.J.; Hotard, A.L.; Meng, J.; Blanco, J.C.; Moin, S.M.; Graham, B.S.; Piedra, P.A.; et al. A recombinant respiratory syncytial virus vaccine candidate attenuated by a low-fusion f protein is immunogenic and protective against challenge in cotton rats. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7508–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobart, C.C.; Rostad, C.A.; Ke, Z.; Dillard, R.S.; Hampton, C.M.; Strauss, J.D.; Yi, H.; Hotard, A.L.; Meng, J.; Pickles, R.J.; et al. A live RSV vaccine with engineered thermostability is immunogenic in cotton rats despite high attenuation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero, J.A.; Mas, V.; McLellan, J.S. Structural, antigenic and immunogenic features of respiratory syncytial virus glycoproteins relevant for vaccine development. Vaccine 2017, 35, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, J.S.; Chen, M.; Leung, S.; Graepel, K.W.; Du, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Baxa, U.; Yasuda, E.; Beaumont, T.; et al. Structure of RSV fusion glycoprotein trimer bound to a prefusion-specific neutralizing antibody. Science 2013, 340, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, J.S.; Yang, Y.; Graham, B.S.; Kwong, P.D. Structure of respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein in the postfusion conformation reveals preservation of neutralizing epitopes. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7788–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapikian, A.Z.; Mitchell, R.H.; Chanock, R.M.; Shvedoff, R.A.; Stewart, C.E. An epidemiologic study of altered clinical reactivity to respiratory syncytial (RS) virus infection in children previously vaccinated with an inactivated RS virus vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.R.; Walsh, E.E. Formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine induces antibodies to the fusion glycoprotein that are deficient in fusion-inhibiting activity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1595–1597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Killikelly, A.M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Graham, B.S. Pre-fusion f is absent on the surface of formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 34108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krarup, A.; Truan, D.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Bogaert, L.; Bouchier, P.; Bisschop, I.J.; Widjojoatmodjo, M.N.; Zahn, R.; Schuitemaker, H.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. A highly stable prefusion RSV F vaccine derived from structural analysis of the fusion mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljeroos, L.; Butcher, S.J. Matrix proteins as centralized organizers of negative-sense RNA virions. Front. Biosci. (Landmark ed.) 2013, 18, 696–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, R.; Baviskar, P.; Duncan-Decocq, R.R.; Patel, D.; Oomens, A.G. The human respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein is required for maturation of viral filaments. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4432–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghildyal, R.; Ho, A.; Jans, D.A. Central role of the respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein in infection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhee, H.K.; Carlisle, J.L.; Beeby, A.; Money, V.A.; Watson, S.M.; Yeo, R.P.; Sanderson, J.M. Influence of lipids on the interfacial disposition of respiratory syncytical virus matrix protein. Langmuir 2011, 27, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Strauss, J.D.; Hampton, C.M.; Brindley, M.A.; Dillard, R.S.; Leon, F.; Lamb, K.M.; Plemper, R.K.; Wright, E.R. Promotion of virus assembly and organization by the measles virus matrix protein. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, A.J.; Meng, G.; Winkler, D.C.; McGinnes, L.W.; Plevka, P.; Steven, A.C.; Morrison, T.G.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure and assembly of a paramyxovirus matrix protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13996–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, A.; Maertens, G.N.; Farrell, P.J.; Bajorek, M. Dimerization of matrix protein is required for budding of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4624–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajorek, M.; Caly, L.; Tran, K.C.; Maertens, G.N.; Tripp, R.A.; Bacharach, E.; Teng, M.N.; Ghildyal, R.; Jans, D.A. The Thr205 phosphorylation site within respiratory syncytial virus matrix (M) protein modulates M oligomerization and virus production. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6380–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, F.Y.; Cox, R.G.; Lifland, A.W.; Hotard, A.L.; Williams, J.V.; Moore, M.L.; Santangelo, P.J.; Crowe, J.E., Jr. A critical phenylalanine residue in the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein cytoplasmic tail mediates assembly of internal viral proteins into viral filaments and particles. MBio 2012, 3, e00270-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslanagic, E.; Matsumoto, M.; Suzuki, K.; Nerome, K.; Tsutsumi, H.; Hung, T. Maturation of respiratory syncytial virus within HEp-2 cell cytoplasm. Acta Virol. 1996, 40, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Najjar, F.; Schmitt, A.P.; Dutch, R.E. Paramyxovirus glycoprotein incorporation, assembly and budding: A three way dance for infectious particle production. Viruses 2014, 6, 3019–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanover, D.; Smith, D.V.; Blanchard, E.L.; Alonas, E.; Kirschman, J.L.; Lifland, A.W.; Zurla, C.; Santangelo, P.J. RSV glycoprotein and genomic rna dynamics reveal filament assembly prior to the plasma membrane. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Strauss, J.D.; Ke, Z.; Alonas, E.; Dillard, R.S.; Hampton, C.M.; Lamb, K.M.; Hammonds, J.E.; Santangelo, P.J.; Spearman, P.W.; et al. Native immunogold labeling of cell surface proteins and viral glycoproteins for cryo-electron microscopy and cryo-electron tomography applications. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2015, 63, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampton, C.M.; Strauss, J.D.; Ke, Z.; Dillard, R.S.; Hammonds, J.E.; Alonas, E.; Desai, T.M.; Marin, M.; Storms, R.E.; Leon, F.; et al. Correlated fluorescence microscopy and cryo-electron tomography of virus-infected or transfected mammalian cells. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Kinter, M.; Shank, S.; Cotton, C.; Kelley, T.J.; Ziady, A.G. Dysfunction of Nrf-2 in CF epithelia leads to excess intracellular H2O2 and inflammatory cytokine production. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziady, A.G.; Sokolow, A.; Shank, S.; Corey, D.; Myers, R.; Plafker, S.; Kelley, T.J. Interaction with creb binding protein modulates the activities of nrf2 and nf-κb in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L1221–L1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Peeples, M.E.; Boucher, R.C.; Collins, P.L.; Pickles, R.J. Respiratory syncytial virus infection of human airway epithelial cells is polarized, specific to ciliated cells, and without obvious cytopathology. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5654–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotard, A.L.; Shaikh, F.Y.; Lee, S.; Yan, D.; Teng, M.N.; Plemper, R.K.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Moore, M.L. A stabilized respiratory syncytial virus reverse genetics system amenable to recombination-mediated mutagenesis. Virology 2012, 434, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodani, M.; Yang, G.; Conklin, L.M.; Travis, T.C.; Whitney, C.G.; Anderson, L.J.; Schrag, S.J.; Taylor, T.H., Jr.; Beall, B.W.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Application of taqman low-density arrays for simultaneous detection of multiple respiratory pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianci, C.; Langley, D.R.; Dischino, D.D.; Sun, Y.; Yu, K.L.; Stanley, A.; Roach, J.; Li, Z.; Dalterio, R.; Colonno, R.; et al. Targeting a binding pocket within the trimer-of-hairpins: Small-molecule inhibition of viral fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15046–15051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battles, M.B.; Langedijk, J.P.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Chaiwatpongsakorn, S.; Costello, H.M.; Kwanten, L.; Vranckx, L.; Vink, P.; Jaensch, S.; Jonckers, T.H.; et al. Molecular mechanism of respiratory syncytial virus fusion inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.R.; Mastronarde, D.N.; McIntosh, J.R. Computer visualization of three-dimensional image data using IMOD. J. Struct. Biol. 1996, 116, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastronarde, D.N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 152, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, W.J.H.; Wan, W.; Briggs, J.A.G. Implementation of a cryo-electron tomography tilt-scheme optimized for high resolution subtomogram averaging. J. Struct. Biol. 2017, 197, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. Nih image to imagej: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. Ucsf chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Peng, L.; Baldwin, P.R.; Mann, D.S.; Jiang, W.; Rees, I.; Ludtke, S.J. Eman2: An extensible image processing suite for electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 157, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Dillard, R.S.; Hampton, C.M.; Storms, R.E.; Strauss, J.D.; Wright, E.R. Native-state structural analysis of respiratory syncytial virus. Microsc. Microanal. 2016, 22, 1116–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrby, E.; Marusyk, H.; Orvell, C. Morphogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus in a green monkey kidney cell line (Vero). J. Virol. 1970, 6, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bachi, T.; Howe, C. Morphogenesis and ultrastructure of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 1973, 12, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chirkova, T.; Lin, S.; Oomens, A.G.; Gaston, K.A.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Meng, J.; Stobart, C.C.; Cotton, C.U.; Hartert, T.V.; Moore, M.L.; et al. CX3CR1 is an important surface molecule for respiratory syncytial virus infection in human airway epithelial cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, I.; McNally, B.; Willette, M.; Peeples, M.E.; Chaussabel, D.; Durbin, J.E.; Ramilo, O.; Mejias, A.; Flano, E. Plasticity and virus specificity of the airway epithelial cell immune response during respiratory virus infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5422–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.R.; Compans, R.W.; Wertz, G.W. Respiratory syncytial virus matures at the apical surfaces of polarized epithelial cells. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2667–2673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brock, S.C.; Goldenring, J.R.; Crowe, J.E., Jr. Apical recycling systems regulate directional budding of respiratory syncytial virus from polarized epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15143–15148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batonick, M.; Oomens, A.G.; Wertz, G.W. Human respiratory syncytial virus glycoproteins are not required for apical targeting and release from polarized epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8664–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianci, C.; Yu, K.L.; Combrink, K.; Sin, N.; Pearce, B.; Wang, A.; Civiello, R.; Voss, S.; Luo, G.; Kadow, K.; et al. Orally active fusion inhibitor of respiratory syncytial virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roymans, D.; Alnajjar, S.S.; Battles, M.B.; Sitthicharoenchai, P.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Rigaux, P.; Berg, J.V.D.; Kwanten, L.; Ginderen, M.V.; Verheyen, N.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of a respiratory syncytial virus fusion inhibitor. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, P.; Green, D.; Pallister, J.; Klein, R.; White, J.; Williams, C.; McMillan, P.; Tilley, L.; Lampe, M.; Hawes, P.; et al. Detailed morphological characterisation of hendra virus infection of different cell types using super-resolution and conventional imaging. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.C.; Compans, R.W. Host cell dependence of viral morphology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5746–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Najjar, F.; Cifuentes-Munoz, N.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Buchholz, U.J.; Moncman, C.L.; Dutch, R.E. Human metapneumovirus induces reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton for direct cell-to-cell spread. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, S.; Kolesnikova, L.; Krahling, V.; Riches, J.D.; Becker, S.; Briggs, J.A. Electron tomography reveals the steps in filovirus budding. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharat, T.A.; Riches, J.D.; Kolesnikova, L.; Welsch, S.; Krahling, V.; Davey, N.; Parsy, M.L.; Becker, S.; Briggs, J.A. Cryo-electron tomography of marburg virus particles and their morphogenesis within infected cells. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyzaniak, M.A.; Zumstein, M.T.; Gerez, J.A.; Picotti, P.; Helenius, A. Host cell entry of respiratory syncytial virus involves macropinocytosis followed by proteolytic activation of the F protein. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, Z.; Dillard, R.S.; Chirkova, T.; Leon, F.; Stobart, C.C.; Hampton, C.M.; Strauss, J.D.; Rajan, D.; Rostad, C.A.; Taylor, J.V.; et al. The Morphology and Assembly of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography. Viruses 2018, 10, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080446
Ke Z, Dillard RS, Chirkova T, Leon F, Stobart CC, Hampton CM, Strauss JD, Rajan D, Rostad CA, Taylor JV, et al. The Morphology and Assembly of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography. Viruses. 2018; 10(8):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080446
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Zunlong, Rebecca S. Dillard, Tatiana Chirkova, Fredrick Leon, Christopher C. Stobart, Cheri M. Hampton, Joshua D. Strauss, Devi Rajan, Christina A. Rostad, Jeannette V. Taylor, and et al. 2018. "The Morphology and Assembly of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography" Viruses 10, no. 8: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080446
APA StyleKe, Z., Dillard, R. S., Chirkova, T., Leon, F., Stobart, C. C., Hampton, C. M., Strauss, J. D., Rajan, D., Rostad, C. A., Taylor, J. V., Yi, H., Shah, R., Jin, M., Hartert, T. V., Peebles, R. S., Jr., Graham, B. S., Moore, M. L., Anderson, L. J., & Wright, E. R. (2018). The Morphology and Assembly of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography. Viruses, 10(8), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080446




